The Biodegradation of Indigo Carmine by Bacillus safensis HL3 Spore and Toxicity Analysis of the Degradation Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
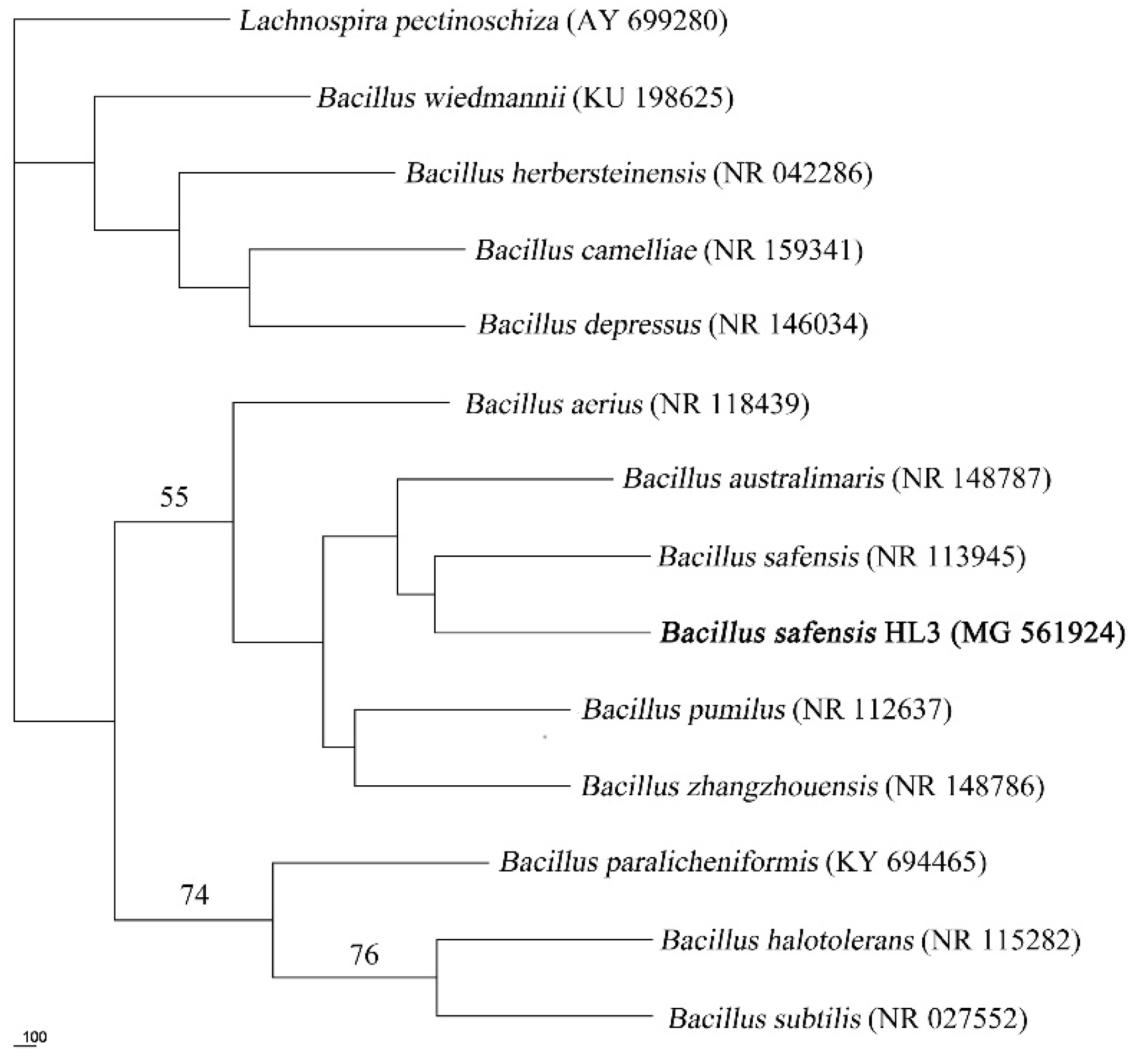
2.1. Isolation, Identification, and Biological Characteristics of the Strain
2.2. Characterization of Spore Laccase
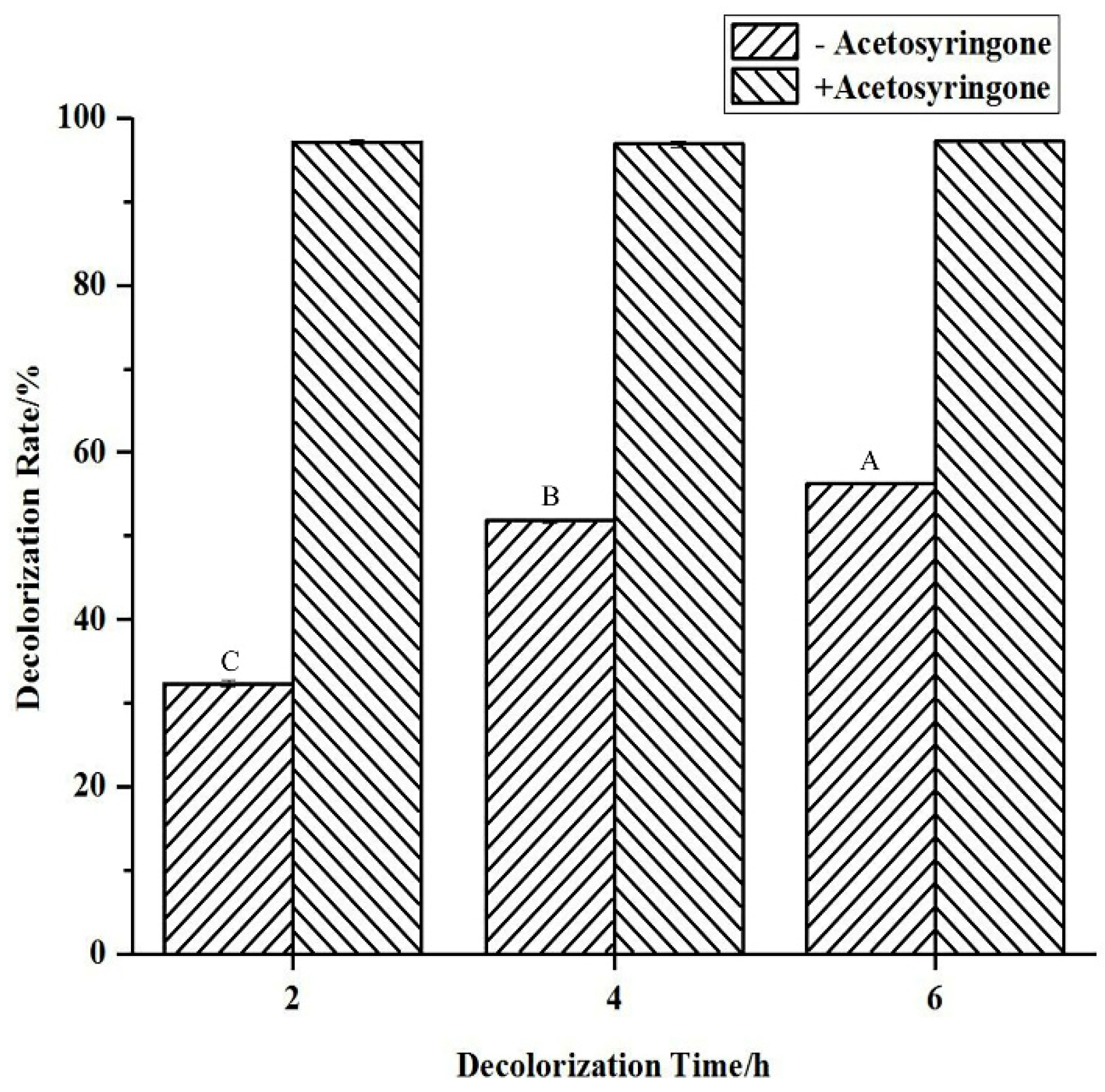
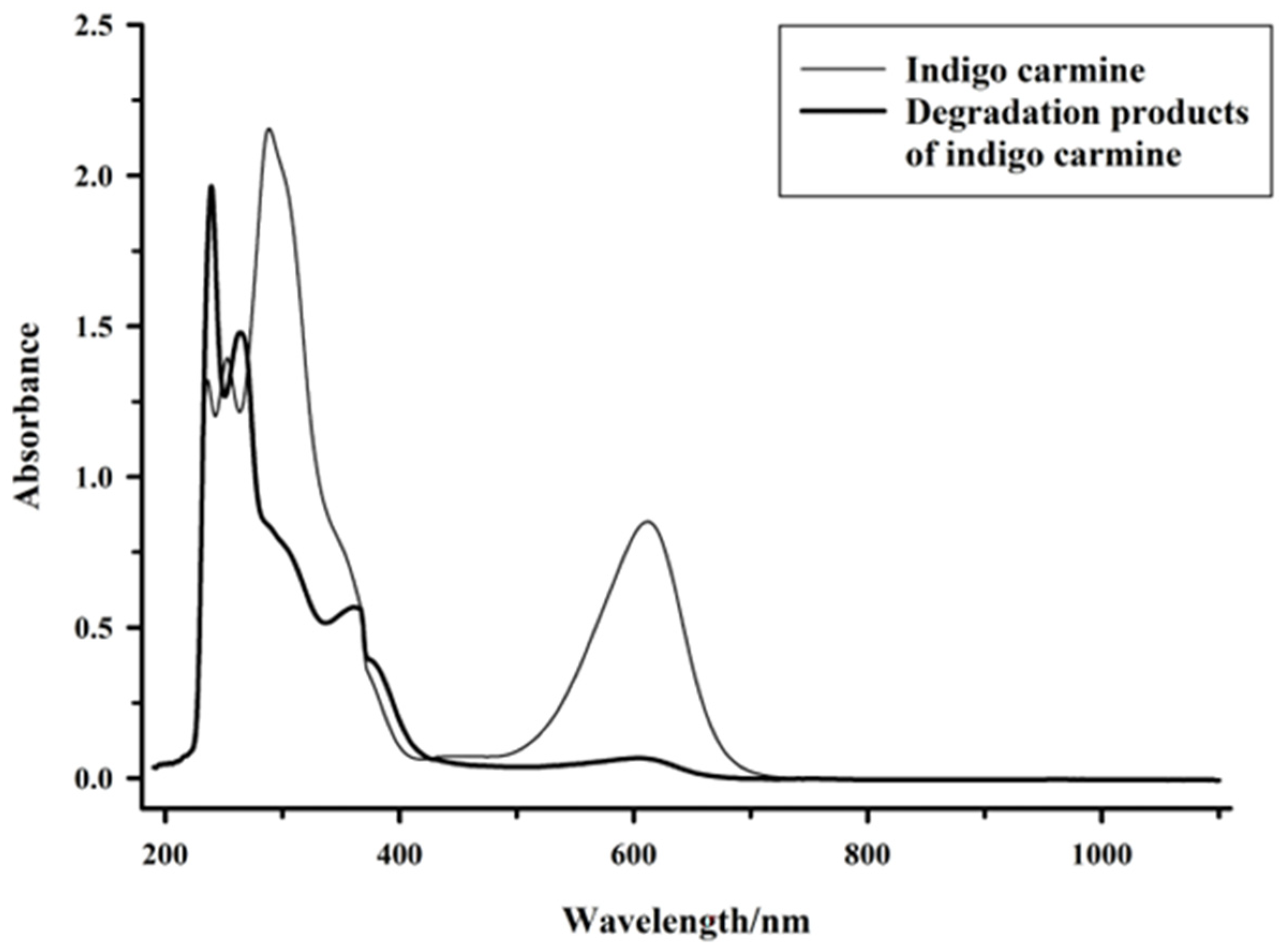
2.3. Indigo Carmine Degradation
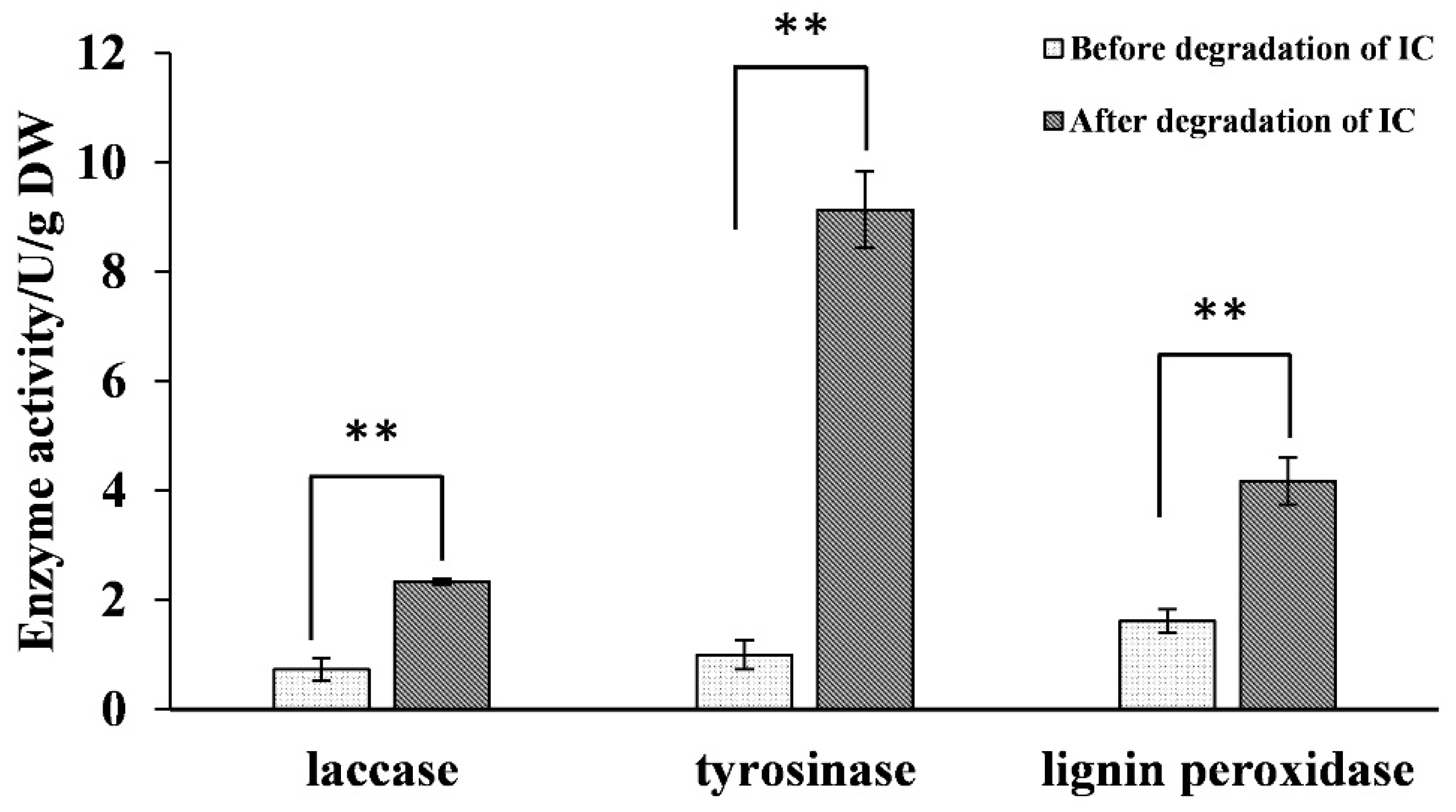
2.4. Analysis of Oxidase Activity during Biodegradation and RT-qPCR Validation
2.5. Toxicity Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General
4.2. Isolation, Identification, and Biological Characteristics of the Strain
4.3. Characterization of Spore Laccase
4.4. Indigo Carmine Degradation
4.5. Oxidase Analysis during Indigo Carmine Degradation
4.5.1. Preparation of Cell-Free Extract
4.5.2. Oxidase Detection
4.6. RT-qPCR Validation
4.7. Toxicity Analysis
4.7.1. Cytotoxicity to Human Erythrocytes
4.7.2. Phytotoxicity to Seeds of Nicotiana Tabacum
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kesraoui, A.; Selmi, T.; Seffen, M.; Brouers, F. Influence of alternating current on the adsorption of indigo carmine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9940–9950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.Z.; Guo, J.; Zeng, G.Q.; Sun, G.P. Decolorization of triphenylmethane, azo, and anthraquinone dyes by a newly isolated Aeromonas hydrophlia strain. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 1316–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaini, L.E.; Lakraimi, M.; Sebbar, E.; Meghea, A.; Bakasse, M. Removal of indigo carmine dye from water to Mg-Al-CO3-calcined layered double hydroxides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stergiopoulos, D.; Dermentzis, K.; Giannakoudakis, P.; Sotiropoulos, S. Electrochemical decolorization and removal of indigo carmine textile dye from wastewater. Glob. NEST J. 2014, 16, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rancan, E.A.; Frota, E.I.; Freitas, T.M.N.; Jordani, M.C.; Évora, P.R.B.; Castro-E-Silva, O. Evaluation of indigo carmine on hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury. Acta Cir. Bras. 2020, 35, e202000901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.S.K.; Zhong, M.Z.; Davis, R.F. Indigo carmine inhibits endothelium-depende-nt and-independent vasodilation. Hypertension 1996, 27, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crema, A.P.S.; Borges, L.D.P.; Micke, G.A.; Debacher, N.A. Degradation of indigo carmine in water induced by non-thermal plasma, ozone and hydrogen peroxide: A comparative study and by-product identification. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, C.G.; Oliveira, A.S.; Saggioro, E.M.; Moreira, J.C. Optimization of the photocatalytic degradation of commercial azo dyes in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2014, 113, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zukawa, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Kurosawa, T.; Kamiko, N. Photolysis of indigo carmine solution by planar vacuum-ultraviolet (147 nm) light source. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, D.; Türkdemir, H. Electrochemical oxidation of textile dye indigo. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flox, C.; Ammar, S.; Arias, C.; Brillas, E.; Vargas-Zavala, A.V.; Abdelhedi, R. Electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton degradation of indigo carmine in acidic aqueous medium. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2006, 67, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, G.; Kalme, S.; Bhosale, S.; Govindwar, S.P. Biodegradation of kerosene by Asperigillus ochraceus NCIM-1146. J. Basic Microbiol. 2007, 47, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannatelli, M.D.; Ragauskas, A.J. Two decades of laccases: Advancing sustainability in the chemical industry. Chem. Rec. 2017, 17, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldrian, P. Fungal laccases occurrence and properties. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 215–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knutson, K.; Ragauskas, A. Laccase-mediator biobleaching applied to a direct yellow dyed paper. Biotechnol. Prog. 2004, 20, 1893–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutson, K.; Kirzan, S.; Ragauskas, A. Enzymatic biobleaching of two recalcitrant paper dyes with horseradish and soybean peroxidase. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, W.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.H. Decolorization of Acid Green 25 by surface display of CotA laccase on Bacillus subtilis spores. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.A.; Seo, J.; Lee, D.W.; Pan, J.G. Decolorization of indigo carmine by laccase displayed on Bacillus subtilis spores. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2011, 49, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.L.; Jia, H.; Topiol, S.; Farinas, E.T. Engineering CotA laccase for acidic pH stability using Bacillus subtilis spore display. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, E.; Makhdoumi, A.; Asoodeh, A. Laccase mediator system obtained from a marine spore exhibits decolorization potential in harsh environmental conditions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2020, 191, 110184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Diao, H.W.; Lu, F.X.; Bie, X.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Lu, Z.X. Degradation of triphenylmethane dyes using a temperature and pH stable spore laccase from a novel strain of Bacillus vallismortis. Bioesour. Technol. 2012, 126, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siroosi, M.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Khajeh, K.; Dabirmanesh, B. Decolorization of dyes by a novel sodium azide-resistant spore laccase from a halotolerant bacterium, Bacillus safensis sp. strain S31. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 2867–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehandia, S.; Sharma, S.C.; Arya, S.K. Isolation and characterization of an alkali and thermostable laccase from a novel Alcaligenes faecalis and its application in decolorization of synthetic dyes. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 25, e00413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaouak, A.; Noomen, A.; Jelassi, H. Gamma-radiation induced decolorization and degradation on aqueous solutions of indigo carmine dye. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 317, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vautier, M.; Guillard, C.; Herrmann, J.M. Photocatalytic degradation of dyes in water: Case study of indigo and of indigo carmine. J. Catal. 2001, 201, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.F.B.; Martins, A.R.; Krambrock, K.; Rosmaninho, M.G.; Binatti, I.; Moura, F.C.C. Understanding photocatalytic activity and mechanism of nickel-modified niobium mesoporous nanomaterials. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2020, 388, 112168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, D.; Sultana, P.; Gupta, G.S.D. Oxidative damage and changes in the glutathione redox system in erythrocytes from rats treated with hexachlorocyclohexane. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1991, 29, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epolito, W.J.; Yang, H.; Bottomley, L.A.; Pavlostathis, S.G. Kinetics of zero-valent iron reductive transformation of the anthraquinone dye reactive blue 4. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydili, M.I.; Matthews, R.D.; Pavlostathis, S.G. Decolorization of a reactive copper-phthalocyanine dye under methanogenic conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junnarkar, N.; Murty, D.S.; Bhatt, N.S.; Madamwar, D. Decolourization of diazo dye direct red 81 by a novel bacterial consortium. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 22, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.S.D.; Madeira, L.M.; Boaventura, R.A.R. Treatment of textile effluent by chemical (fenton’s reagent) and biological (sequencing batch reactor) oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumova, E.T.; Stoitsova, S.R.; Paunova-Krasteva, T.S.; Pashova, S.B.; Angelova, M.B. Copper stress and filamentous fungus Humicola lutea 103-ultrastructural changes and activities of key metabolic enzymes. Can. J. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Singh, S.; Kaur, K.; Arya, S.K.; Sharma, P. Thermo and halo tolerant laccase from Bacillus sp. SS4, evaluation for its industrial usefulness. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Pei, Z.J.; Wang, D.H. Organic solvent pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuels and biochemicals: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Sun, C.; Liang, J.; Han, Y.; Yu, J.; Liang, Z. Improvement of laccase production and its characterization by mutagenesis. J. Food Biochem. 2015, 39, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, K.; Verma, P. Laccase: Addressing the ambivalence associated with the calculation of enzyme activity. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourbonnais, R.; Paice, M.G. Oxidation of non-phenolic substrates. An expanded role for laccase in lignin biodegradation. FEBS Lett. 1990, 267, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.X.; Geng, Y.Y.; Yan, M.Y.; Huang, J. Stable ABTS immobilized in the MIL-100(Fe) metal-organic framework as an efficient mediator for laccase-catalyzed decolorization. Molecules 2017, 22, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jadhav, U.U.; Dawkar, V.V.; Ghodake, G.S.; Govindwar, S.P. Biodegradation of Direct Red 5B, a textile dye by newly isolated Comamonas sp. UVS. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, A.H.D.S.; Candeias, F.S.; Silva, S.C.D.; Vicentini, F.C.; Assumpcao, M.H.M.T.; Brown, A.; Souza, G.L.C. Photoinduced degradation of indigo carmine: Insights from a computational investigation. J. Mol. Model. 2020, 26, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, F.V.D.; Lima, G.M.D.; Augusti, R.; Coelho, M.G.; Ardisson, J.D.; Romero, O.B. A versatile approach to treat aqueous residues of textile industry: The photocatalytic degradation of indigo carmine dye employing the autoclaved cellular concrete/Fe2O3 system. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 180, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Gordillo, A.; Rodríguez-González, V.; Oros-Ruiz, S.; Gómez, R. Photodegradation of indigo carmine dye by CdS nanostructures under blue-light irradiation emitted by LEDs. Catal. Today 2016, 266, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Răducan, A.; Puiu, M.; Oancea, P.; Colbea, C.; Velea, A.; Dinu, B.; Mihăilescu, A.M.; Galaon, T. Fast decolourization of indigo carmine and crystal violet in aqueous environments through micellar catalysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 210, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandelbauer, A.; Kessler, W.; Kessler, R.W. Online UV-visible spectroscopy and multivariate curve resolution as powerful tool for model-free investigation of laccase-catalysed oxidation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labhane, P.K.; Sonawane, S.H.; Sonawane, G.H.; Patil, S.P.; Huse, V.R. Influence of Mg doping on ZnO nanoparticles decorated on graphene oxide (GO) crumpled paper like sheet and its high photo catalytic performance under sunlight. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 114, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Goyes, R.E.; Silva-Agredo, J.; Vazquez-Arenas, J.; Romero-Ibarra, I.; Torres-Palma, R.A. The effect of different operational parameters on the electrooxidation of indigo carmine on Ti/IrO2-SnO2-Sb2O3. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3010–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanavel, M.; Bankole, P.O.; Selvam, R.; Govindwar, S.P.; Sadasivam, S.K. Synergistic effect of biological and advanced oxidation process treatment in the biodegradation of remazol yellow RR dye. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorell, M.M.; Pajot, H.F.; Rovati, J.I.; Figueroa, L.I.C. Optimization of culture medium composition for manganese peroxidase and tyrosinase production during reactive black 5 decolourization by the yeast Trichosporon akiyoshidainum. Yeast 2012, 29, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surwase, S.V.; Deshpande, K.K.; Phugare, S.S.; Jadhav, J.P. Biotransformation studies of textile dye remazol orange 3R. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalme, S.D.; Jadhav, S.U.; Parshetti, G.K.; Govindwar, S.P. Biodegradation of green HE4B: Co-substrate effect, biotransformation enzymes and metabolite toxicity analysis. Indian J. Microbiol. 2010, 50, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawkar, V.V.; Jadhav, U.U.; Jadhav, S.U.; Govindwar, S.P. Biodegradation of disperse textile dye brown 3REL by newly isolated Bacillus sp. VUS. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Batish, M.; Sharma, P.; Capalash, N. Xenobiotics enhance laccase activity in alkali-tolerant γ-proteobacterium JB. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2009, 40, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alimi, H.; Hfaeidh, N.; Bouoni, Z.; Sakly, M.; Rhouma, K.B. Protective effect of Opuntia ficus indica f. inermis prickly pear juice upon ethanol-induced damages in rat erythrocytes. Alcohol 2012, 46, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, S.B.; Dallali, C.; Ellafi, A.; Bouslama, L.; Feriani, A.; Sayadi, S. Extracellular enzymatic activities of bacterial strains isolated from tunisian biotopes: Decolorization and detoxification of indigo carmine. Catal. Lett. 2021, 151, 1248–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmode, T.R.; Kurade, M.B.; Sapkal, R.T.; Bhosale, C.H.; Jeon, B.H.; Govindwar, S.P. Sequential photocatalysis and biological treatment for the enhanced degradation of the persistent azo dye methyl red. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Zhao, M.; Li, D.B.; Cui, D.Z.; Lu, L.; Wei, X.D. Isolation and characterization of a novel Bacillus subtilis WD23 exhibiting laccase activity from forest soil. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 5496–5502. Available online: https://academicjournals.org/journal/AJB/article-full-text-pdf/1BC7C4432522 (accessed on 23 August 2010). [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhao, M.; Wang, T.N.; Zhao, L.Y.; Du, M.H.; Li, T.L. Characterization and dye decolorization ability of an alkaline resistant and organic solvents tolerant laccase from Bacillus licheniformis LS04. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 115, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Cui, D.Z.; Lu, L.; Zhang, N.; Yang, H.Y.; Zhao, M.; Dai, S.J. Cloning and characterization of CotA laccase from Bacillus subtilis WD23 decoloring dyes. Ann. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taqieddin, E.; Amiji, M. Enzyme immobilization in novel alginate-chitosan core-shell microcapsules. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, M.; Kirk, K. Lignin peroxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Method Enzymol. 1988, 161, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamboli, D.P.; Kurade, M.B.; Waghmode, T.R.; Joshi, S.M.; Govindwar, S.P. Exploring the ability of Sphingobacterium sp. ATM to degrade textile dye Direct Blue GLL, mixture of dyes and textile effluent and production of polyhydroxyhexadecanoic acid using waste biomass generated after dye degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrathall, J.R.; Oliver, C.; Silagi, S.; Essner, E. Suppression of pigmentation in mouse melanoma cells by 5-bromodeoxyuridine: Effects of tyrosinase activity and melanosome formation. J. Cell Biol. 1973, 57, 406–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Serial Number | Retention Time (min) | Adduct of the Substance | Experimental m/z of the Adduct | Theoretical m/z of the Adduct | Chemical Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indigo carmine sample | |||||
| 1 | 5.42 | [M-2Na]2− | 209.9862 | 209.9867 | indigo carmine |
| 2 | 5.32 | [M-H]− | 225.9812 | 225.9816 | isatin 5-sulfonic acid |
| Degradation products of indigo carmine | |||||
| 1 | 17.56 | [M+H]+ | 200.0326 | 200.0376 | indoline-5-sulfonic acid |
| 2 | 12.34 | [M+H]+ | 148.0391 | 148.0393 | isatin |
| 3 | 11.68 | [M+H]+ | 130.1227 | 130.1226 | (2-aminocyclohexyl) methanol |
| 4 | 9.35 | [M-H]− | 150.0549 | 150.0561 | 2-aminophenylacetic acid |
| 5 | 9.63 | [M+H]+ | 152.0359 | 152.0342 | 2-nitrobenzaldehyde |
| 6 | 5.19 | [M+H]+ | 122.0602 | 122.0600 | 2-aminobenzaldehyde |
| Sample | 2−ΔΔCt †† |
|---|---|
| Control group | 1.00 ± 0 |
| Treatment group | 2.60 ± 0.40 ** |
| Normal Erythrocytes (×107 mL−1) †† | Germination Rate of N. tabacum (%) †† | |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 5.15 ± 0.23 A | 53 ± 3 a |
| IC | 3.58 ± 0.08 C | 20 ± 5 b |
| DP | 4.43 ± 0.13 B | 52 ± 2 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, S.; Cui, D.; Sun, H.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Zhao, M. The Biodegradation of Indigo Carmine by Bacillus safensis HL3 Spore and Toxicity Analysis of the Degradation Products. Molecules 2022, 27, 8539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238539
Wang C, Wang S, Zhang J, Jiang S, Cui D, Sun H, Liu C, Li L, Zhao M. The Biodegradation of Indigo Carmine by Bacillus safensis HL3 Spore and Toxicity Analysis of the Degradation Products. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238539
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chunlei, Sijia Wang, Jieru Zhang, Shumin Jiang, Daizong Cui, Haiqiong Sun, Chengwei Liu, Lili Li, and Min Zhao. 2022. "The Biodegradation of Indigo Carmine by Bacillus safensis HL3 Spore and Toxicity Analysis of the Degradation Products" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238539
APA StyleWang, C., Wang, S., Zhang, J., Jiang, S., Cui, D., Sun, H., Liu, C., Li, L., & Zhao, M. (2022). The Biodegradation of Indigo Carmine by Bacillus safensis HL3 Spore and Toxicity Analysis of the Degradation Products. Molecules, 27(23), 8539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238539








