Rapid, Simultaneous, and Automatic Determination of Lead and Cadmium in Cereals with a New High Performance Composite Hollow Cathode Lamp Coupled to Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
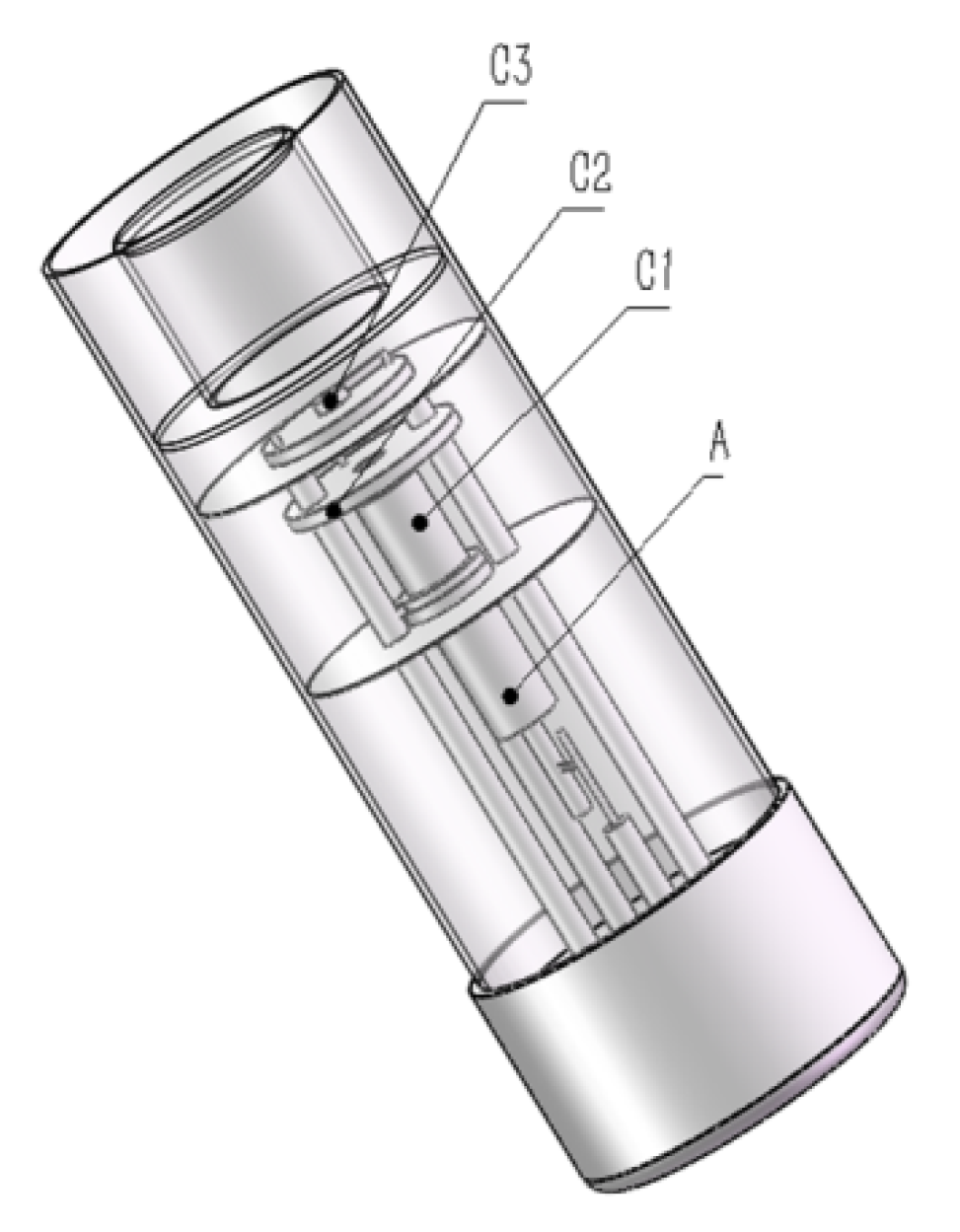
2.1. LCC-HCL Development and Evaluation
2.2. Optimization of the Method
2.2.1. Optimization of the Heating Program
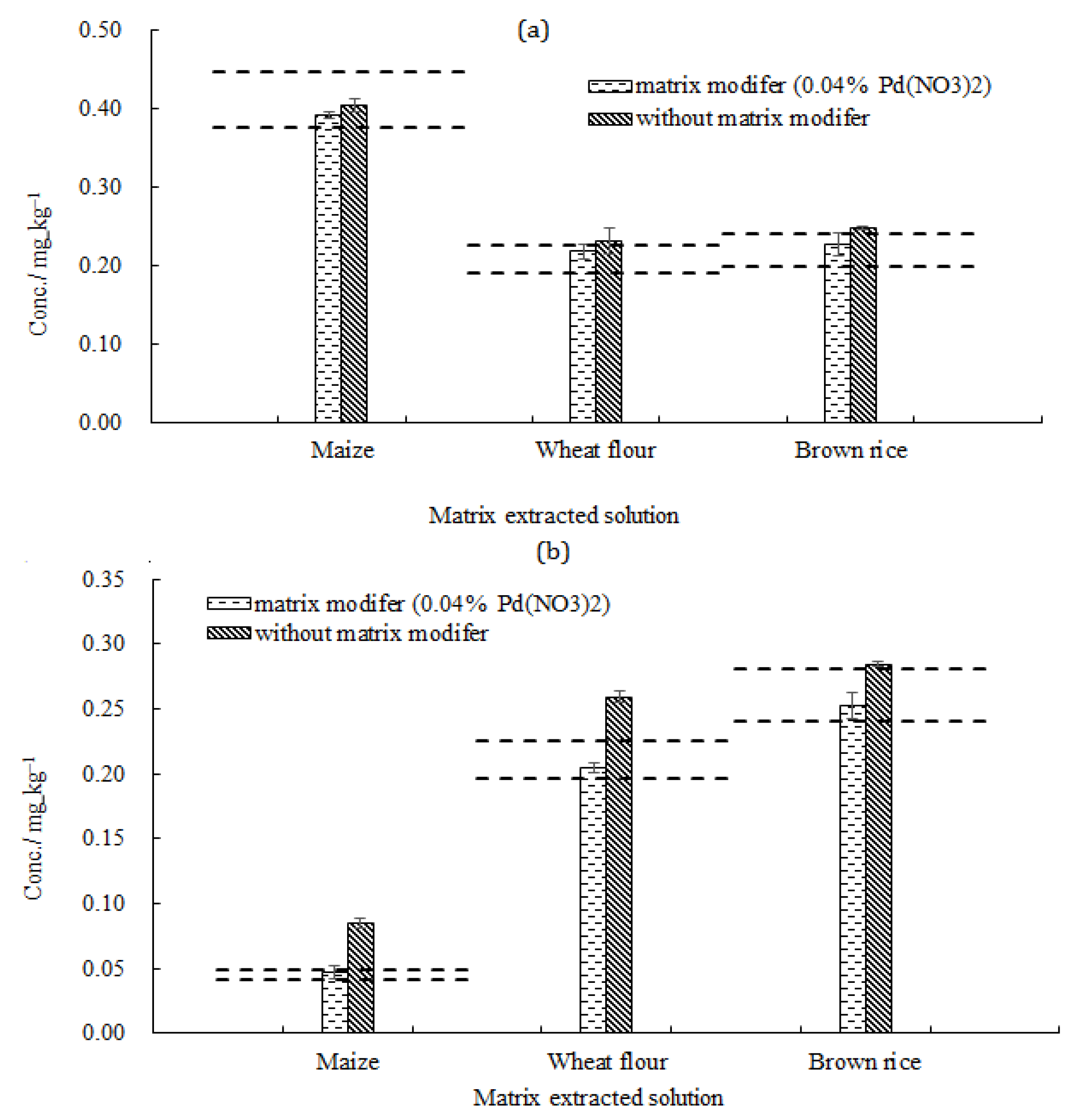
2.2.2. Extraction of Pb and Cd from Cereals
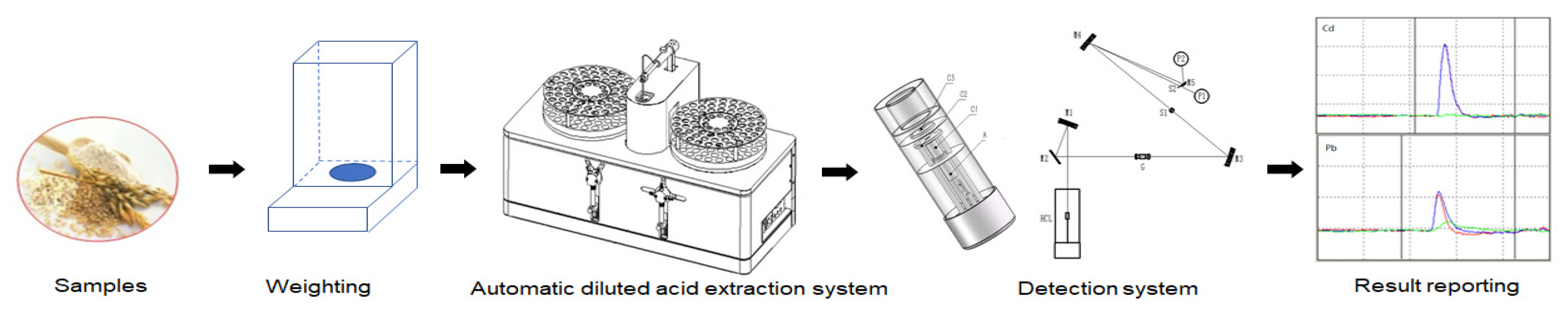
2.3. Automation Diluted Acid Extraction System
2.4. Interferences
2.4.1. Inorganic Interference
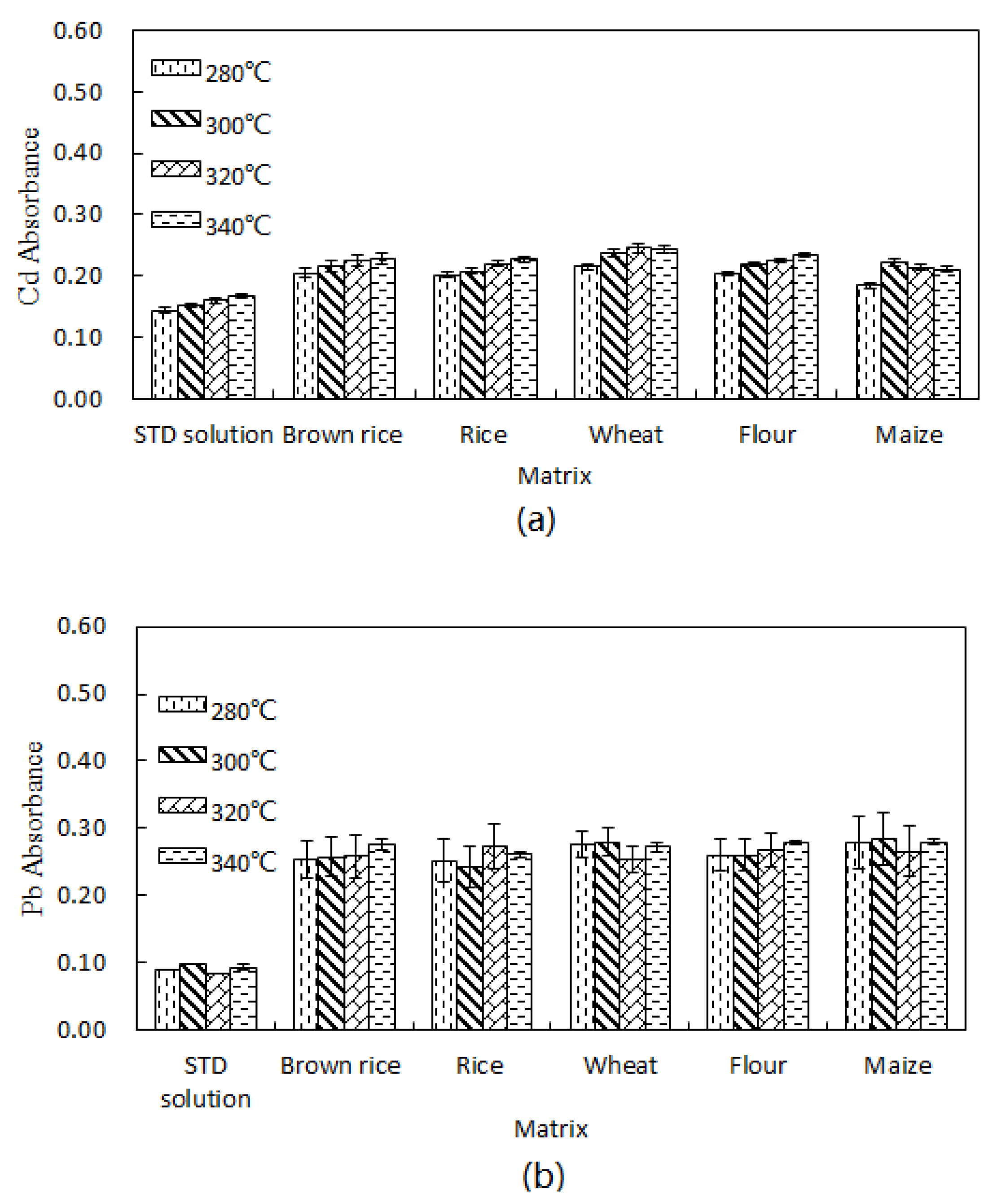
2.4.2. Matrix Effect
2.5. Performance of the Method
2.5.1. Trueness
2.5.2. Precision
2.5.3. Calibration Curves, Linearity, and Limit of Detection and Quantification
2.6. Naturally Contaminated Sample Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Testing Samples
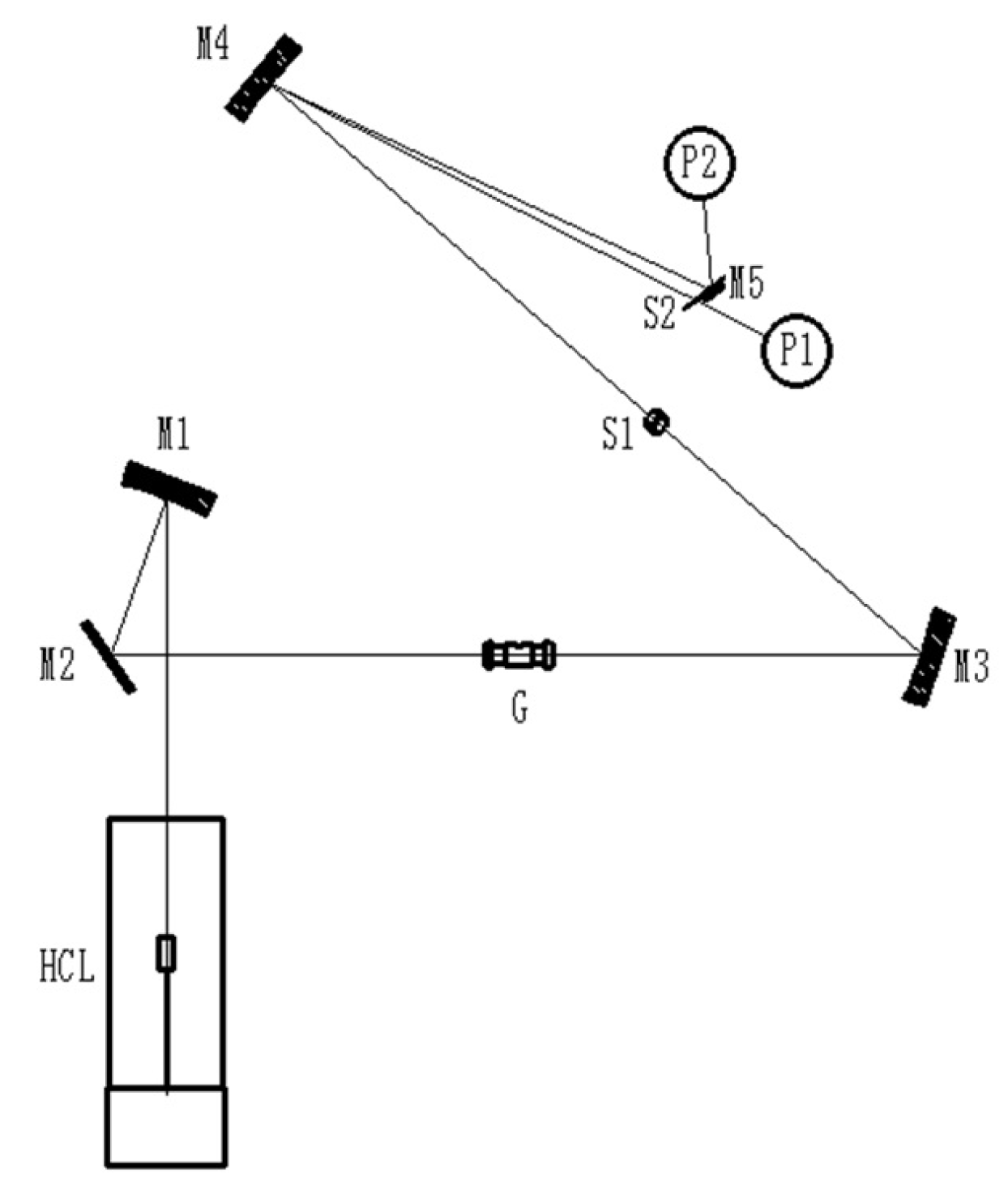
3.2. Instruments and Conditions
3.3. Sample Preparation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ma, C.; Iwaishimada, M.; Tatsuta, N.; Nakai, K.; Isobe, T.; Takagi, M.; Nishihama, Y.; Nakayama, S.F. Health Risk Assessment and Source Apportionment of Mercury, Lead, Cadmium, Selenium, and Manganese in Japanese Women: An Adjunct Study to the Japan Environment and Children’s Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrini, R.; Ghezzi, L.; Arrighi, S.; Genovesi, L.; Frassi, C.; Pandolfi, L. Trace Elements in Soil and Urban Groundwater in an Area Impacted by Metallurgical Activity: Health Risk Assessment in the Historical Barga Municipality (Tuscany, Italy). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Islam, M.A.; Khan, R.A. Characterization of chemical elements in common spices of Bangladesh for dietary intake and possible health risk assessment by INAA and AAS techniques. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 318, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, S.; Ashraf, K.; Sultan, K.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Ali, H.M.; Chen, Y.; Zaman, Q.U. Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Metals and Metalloids in Soil, Water and Plant Continuum of Fragrant Rice. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerasundara, L.; Magana-Arachchi, D.N.; Ziyath, A.M.; Goonetilleke, A.; Vithanage, M. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in a congested city environment in a developing country: Kandy City, Sri Lanka. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 220, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.B.; Fu, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Qi, F.Y.; Shao, Z.L.; Jing, M. Heavy Metal Contamination and Health Risk Assessment in the Soil Surrounding a Secondary Lead Plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 41, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Pacer, E.J.; Palmer, C.D.; Parsons, P.J. Determination of lead in blood by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry with Zeeman background correction: Improving a well-established method to support a lower blood lead reference value for children. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2022, 190, 106524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataee, M.; Ahmadi-Jouibari, T.; Fattahi, N. Application of microwave-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for ultra-trace determination of lead and cadmium in cereals and agricultural products. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2016, 96, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, R.M.; Antunes, A.C.N.; Vieira, M.A.; Medina, A.L.; Ribeiro, A.S. Evaluation of sample preparation methods for the determination of As, Cd, Pb, and Se in rice samples by GF AAS. Microchem. J. 2016, 124, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyele, I.O.; Shokunbi, O.S. Comparative analysis of dry ashing and wet digestion methods for the determination of trace and heavy metals in food samples. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, D.M.; Nomura, C.S. Direct Determination of Potentially Toxic Elements in Rice by SS-GF AAS: Development of Methods and Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6299–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Qi, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, T. Uncertainty evaluation of determination of cadmium in rice by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Food Safety Qual. 2019, 9, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Ke, S.; Yan, Q.; Li, W. The Comparison of Three Methods for the Detection of Cadmium in the Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 38, 320–323. (In Chinese). Available online: https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS2015S1067.htm (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Welz, B.; Vale, M.G.R.; Pereira, É.R.; Castilho, I.N.B.; Dessuy, M.B. Continuum source atomic absorption spectrometry: Past, present and future aspects-a critical review. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2014, 25, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, C.C.; de Jesus, A.; Potes, M.L.; Vieira, M.A.; Samios, D.; Silva, M.M. Direct Determination of Cd, Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Na, Ni, Pb, and Zn in Ethanol Fuel by High-Resolution Continuum Source Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 7358–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welz, B.; Becker-Ross, H.; Florek, S.; Heitmann, U. High-Resolution Continuum Source AAS: The Better Way to Do Atomic Absorption Spectrometry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; Bezerra, M.A.; Santos, A.S.; Santos, W.N.L.d.; Novaes, C.G.; de Oliveira, O.M.C.; Oliveira, M.L.; Garcia, R.L. Atomic absorption spectrometry—A multi element technique. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 100, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleluia, A.C.M.; de Santana, F.A.; Brandao, G.C.; Ferreira, S.L.C. Sequential determination of cadmium and lead in organic pharmaceutical formulations using high-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2017, 130, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.V.; Walsh, A. High intensity hollow-cathode lamps. Spectrochim. Acta 1965, 21, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensburg, H.C.V.; Zeeman, P.B. The determination of gold, platinum, palladium and rhodium by atomic absorption spectrophotometry with an ultrasonic nebulizer and a multi-element high-intensity hollow-cathode lamp with selective modulation. Anal. Chim. Acta 1968, 42, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myöhänen, T.; Mäntylahti, V.; Koivunen, K.; Matilainen, R. Simultaneous determination of As, Cd, Cr and Pb in aqua regia digests of soils and sediments using electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry and fast furnace programs. Spectrochim. Acta B At. Spectrosc. 2002, 57, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, H.S.; Santos, A.C.; Portugal, L.A.; Costa, A.C.; Miró, M.; Ferreira, S.L. Pre-concentration procedure for determination of copper and zinc in food samples by sequential multi-element flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2008, 77, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zheng, Y. High Performance Hollow Cathode Lamp. Mod. Sci. Instrum. 1991, 4, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, M.H.D.; Droushiotis, N.; Wu, Z.; Kelsall, G.; Li, K. High-Performance, Anode-Supported, Microtubular SOFC Prepared from Single-Step-Fabricated, Dual-Layer Hollow Fibers. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2480–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.; Gao, Y. Determination of Lead in Water by Microflame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Chin. Anal. Lab. 1994, 6, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Bakırdere, S.; Yaroğlu, T.; Tırık, N.; Demiröz, M.; Fidan, A.K.; Maruldalı, O.; Karaca, A. Determination of As, Cd, and Pb in Tap Water and Bottled Water Samples by Using Optimized GFAAS System with Pd-Mg and Ni as Matrix Modifiers. J. Spectrosc. 2012, 2013, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kas, R.; Hummadi, K.K.; Kortlever, R.; De Wit, P.; Milbrat, A.; Luiten-Olieman, M.W.; Benes, N.E.; Koper, M.T.M.; Mul, G. Three-dimensional porous hollow fibre copper electrodes for efficient and high-rate electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 14082:2003; Foodstuffs Determination of Trace Elements Determination of Lead, Cadmium, Zinc, Copper, Iron and Chromium by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS) after Dry Ashing. British Standards Institution BSI EN: London, UK, 2003.
- EN 14083:2003; Foodstuffs Determination of Trace Elements Determination of Lead, Cadmium, Chromium and Molybdenum by Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (GFAAS) after Pressure Digestion. British Standards Institution BSI EN: London, UK, 2003.
- EN 14084:2003; Foodstuffs Determination of Trace Elements Determination of Lead, Cadmium, Zinc, Copper and Iron by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS) after Microwave Digestion. British Standards Institution BSI EN: London, UK, 2003.
- AOAC Official Method 999.10. Lead, Cadmium, Zinc, Copper, Andiron in Foods Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry after Microwave Digestion; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- EN ISO 15774-2017; Animal and Vegetable Fats and Oils. Determination of Cadmium Content by Direct Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. British Standards Institution BSI EN: London, UK, 2017.
- Zhou, M.H.; Wang, S.X.; Wu, Y.X. Rapid Direct Sampling Detection of Pb in Grain Using Diluted Acid Extraction Coupled with Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 3, 459–460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.H.; Wu, Y.X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, J.; Wang, S.X. Development and Collaborative Study of a Diluted Acid Mild Extraction Method for Determination of Cadmium in Grain by Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Anal. Sci. 2019, 35, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Zhou, M.H.; Tian, W.; Wu, Y.X.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.X. In situ fast analysis of cadmium in rice by diluted acid extraction-anodic stripping voltammetry. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19965–19972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.M.; Tian, W.; Zhang, Q.J.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.Y.; Wang, X.S. A rapid on-site analysis method for the simultaneous extraction and determination of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in cereals. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32839–32847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitmann, U.; Welz, B.; Borges, D.L.; Lepri, F.G. Feasibility of peak volume, side pixel and multiple peak registration in high-resolution continuum source atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta B At. Spectrosc. 2007, 62, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resano, M.; Aramendia, M.; Belarra, M.A. High-resolution continuum source graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry for direct analysis of solid samples and complex materials: A tutorial review. J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 2014, 29, 2229–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljerf, L.; Mashlah, A. Characterization and validation of candidate reference methods for the determination of calcium and magnesium in biological fluids. Microchem. J. 2017, 132, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 11843-5: 2008; Capability of Detection—Part 5: Methodology in the Linear and Non-Linear Calibration Cases. International Organization for Standardization/Technical Committee ISO/TC 69: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.


| Element | Test Item | Result | Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead | Drif (Abs/15 min) | 0.000 ± 0.004 | ≤±0.008 |
| Noise (Abs) | 0.0010 | ≤0.006 | |
| Sensitivity (Abs) | 0.137 ± 0.007 | ≤10 | |
| Cadmium | Drif (Abs/15 min) | 0.002 ± 0.004 | ≤±0.008 |
| Noise (Abs) | 0.0026 | ≤0.006 | |
| Sensitivity (Abs) | 0.333 ± 0.030 | ≤10 |
| Spectrometer Conditions | Heating Program | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Pb | Step | Temperature (°C) | Ramp (s) | Hold (s) | Argon | |
| Wavelength (nm) | 228.8 | 217.0 | Drying 1 | 75 | 5 | 2 | ON |
| Bandpass (nm) | 2.0 | 0.7 | Drying 2 | 90 | 5 | 2 | ON |
| Sample volume (μL) | 12 | 12 | Drying 3 | 110 | 10 | 2 | ON |
| Modifier Volume (μL) | 3 | 3 | Drying 4 | 120 | 5 | 2 | ON |
| Lamp current (mA) | 4 | 4 | Pyrolysis | 320 | 5 | 5 | ON |
| Atomization | 1700 | 2 | 1 | OFF | |||
| Cleaning | 2450 | 1 | 1 | ON | |||
| Added Element | Item | Cd | Pb | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical Value (μg·L−1) | 2 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 16 | |
| Comparison without addition of other elements | Measured value (μg·L−1) | 2.13 | 3.93 | 7.99 | 4.19 | 8.18 | 15.94 |
| Relative difference (%) | 6.4 | −1.8 | −0.1 | 4.8 | 2.3 | −0.4 | |
| Zn | Measured value (μg·L−1) | 1.91 | 4.18 | 7.95 | 4.08 | 7.84 | 15.93 |
| Relative difference (%) | −4.3 | 4.5 | −0.6 | 2 | −2 | −0.4 | |
| Cu | Measured value (μg·L−1) | 2.01 | 4.11 | 8.17 | 4.01 | 8.16 | 15.72 |
| Relative difference (%) | 0.6 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 0.3 | 2 | −1.8 | |
| Fe | Measured value (μg·L−1) | 2.09 | 4.19 | 8.04 | -- | -- | -- |
| Relative difference (%) | 4.7 | 4.7 | 0.5 | -- | -- | -- | |
| Sn | Measured value (μg·L−1) | 2.12 | 3.87 | 7.85 | -- | -- | -- |
| Relative difference (%) | 5.8 | −3.3 | −1.9 | -- | -- | -- | |
| Item | Matrix for Matching Standard Curve | Certified Value | Uncertainty | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Wheat | Wheat Flour | Maize | Brown Rice | Rice | ||||
| Cd (mg·kg−1) | Brown Rice | 0.262 ± 0.018 | 0.266 ± 0.016 | 0.256 ± 0.012 | 0.262 ± 0.014 | 0.252 ± 0.014 | 0.261 | 0.020 |
| Wheat | 0.162 ± 0.013 | 0.165 ± 0.010 | 0.159 ± 0.012 | 0.165 ± 0.008 | 0.162 ± 0.009 | 0.155 | 0.013 | |
| Maize | 0.043 ± 0.007 | 0.041 ± 0.002 | 0.042 ± 0.002 | 0.043 ± 0.006 | 0.042 ± 0.004 | 0.045 | 0.004 | |
| Pb (mg·kg−1) | Brown Rice | 0.224 ± 0.012 | 0.228 ± 0.012 | 0.222 ± 0.008 | 0.223 ± 0.016 | 0.226 ± 0.016 | 0.220 | 0.020 |
| Wheat | 0.234 ± 0.013 | 0.238 ± 0.014 | 0.227 ± 0.010 | 0.226 ± 0.016 | 0.234 ± 0.015 | 0.220 | 0.018 | |
| Maize | 0.399 ± 0.016 | 0.408 ± 0.017 | 0.385 ± 0.008 | 0.387 ± 0.010 | 0.399 ± 0.016 | 0.417 | 0.030 | |
| Matrix | Certified No. | Analysis of Reference Materials | Comparison of Two Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detected Value | Certified Value Range | T Value (p > 0.05, t = 4.30) | |||||
| (values ± SD, mg·kg−1) | (mg·kg−1) | ||||||
| Pb | Cd | Pb | Cd | Pb | Cd | ||
| Wheat | GBW(E)100379 | 0.207 ± 0.003 | 0.154 ± 0.006 | 0.202~0.238 | 0.142~0.168 | 0.32 | 1.02 |
| Rice | GBW(E)080684a | 0.208 ± 0.005 | 0.482 ± 0.009 | 0.205~0.245 | 0.454~0.510 | 1.78 | 2.89 |
| Brown rice | GBW(E)100377 | 0.207 ± 0.007 | 0.257 ± 0.005 | 0.200~0.240 | 0.241~0.281 | 0.29 | 2.79 |
| Maize | GBW(E)100380 | 0.401 ± 0.005 | 0.042 ± 0.002 | 0.387~0.447 | 0.041~0.049 | 1.24 | 2.67 |
| Item | Cd | Pb |
|---|---|---|
| Calibration curve equation | Abs = −0.00055 × [Conc.]2 + 0.0528 × [Conc.] + 0.0032 | Abs = 0.0111 × Conc. + 0.0022 |
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| LOD | 0.0013 mg·kg−1 (0.051 μg·L−1) | 0.012 mg·kg−1 (0.49 μg·L−1) |
| LOQ | 0.0043 mg·kg−1 (0.17 μg·L−1) | 0.040 mg·kg−1 (1.61 μg·L−1) |
| Sample | Matrix | Recovery of Pb in Different Labs (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| 1# | wheat | 102.7 | 104.9 | 102.7 | 107.7 | 104.6 | 113.4 | 104.6 | 99.2 |
| 2# | wheat | 102.8 | 101.8 | 97.3 | 101.8 | 108.7 | 101.3 | 108.7 | 92.9 |
| 3# | wheat | 94.5 | 90.0 | 92.0 | 92.0 | 89.4 | 95.2 | 88.1 | 89.4 |
| 4# | maize | 102.2 | 98.6 | 95.1 | 106.0 | 107.9 | 101.1 | 107.9 | 91.0 |
| 5# | maize | 108.7 | 108.7 | 107.1 | 107.1 | 109.2 | 104.5 | 109.7 | 105.6 |
| 6# | maize | 96.7 | 98.9 | 110.9 | 110.9 | 94.6 | 103.3 | 102.2 | 97.8 |
| 7# | brown rice | 88.1 | 87.3 | 88.6 | 89.4 | 85.8 | 87.3 | 85.8 | 85.5 |
| 8# | brown rice | 87.7 | 86.8 | 90.4 | 93.2 | 94.5 | 91.8 | 96.4 | 80.4 |
| 9# | brown rice | 93.0 | 95.8 | 91.2 | 94.0 | 91.2 | 99.5 | 91.2 | 82.9 |
| Sample | Matrix | Recovery of Cd in Different Labs (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ||
| 1# | wheat | 95.5 | 98.7 | 93.9 | 98.4 | 95.8 | 95.5 | 102.2 | 88.2 |
| 2# | wheat | 94.8 | 104.6 | 105.5 | 97.2 | 101.3 | 95.6 | 103.8 | 93.5 |
| 3# | wheat | 84.0 | 104.8 | 103.5 | 100.1 | 112.9 | 102.2 | 116.9 | 104.8 |
| 4# | maize | 97.1 | 102.5 | 102.1 | 101.1 | 102.5 | 95.3 | 102.6 | 100.0 |
| 5# | maize | 100.4 | 88.4 | 100.4 | 102.7 | 93.2 | 90.8 | 102.7 | 95.6 |
| 6# | maize | 88.0 | 104.0 | 100.0 | 112.0 | 96.0 | 88.0 | 100.0 | 104.0 |
| 7# | brown rice | 96.6 | 101.4 | 99.7 | 102.7 | 102.2 | 97.9 | 96.3 | 99.4 |
| 8# | brown rice | 105.0 | 105.0 | 111.1 | 106.5 | 113.6 | 104.5 | 116.7 | 100.9 |
| 9# | brown rice | 99.2 | 97.1 | 112.4 | 104.8 | 114.5 | 98.5 | 111.7 | 107.5 |
| Item | Parameters | Item | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analyzed mass | 111Cd and 208Pb | Sampling depth | 8.0 mm |
| RF power | 1500 W | Torch-H | 0.3 mm |
| Carrier gas flow rate | 0.76 L min−1 | Torch-V | 0.4 mm |
| Makeup gas flow rate | 0.45 L min−1 | Integration time | 0.3 s·point−1 |
| Nebulizer pump flow rate | 0.10 rps | Interference equation | [208Pb] = [206] + [207] + [208] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Cui, W.; Tian, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, M. Rapid, Simultaneous, and Automatic Determination of Lead and Cadmium in Cereals with a New High Performance Composite Hollow Cathode Lamp Coupled to Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Molecules 2022, 27, 8571. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238571
Wu Y, Wang S, Cui W, Tian W, Zhang J, Chen X, Zhou M. Rapid, Simultaneous, and Automatic Determination of Lead and Cadmium in Cereals with a New High Performance Composite Hollow Cathode Lamp Coupled to Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8571. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238571
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yanxiang, Songxue Wang, Weibing Cui, Wei Tian, Jieqiong Zhang, Xi Chen, and Minghui Zhou. 2022. "Rapid, Simultaneous, and Automatic Determination of Lead and Cadmium in Cereals with a New High Performance Composite Hollow Cathode Lamp Coupled to Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8571. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238571
APA StyleWu, Y., Wang, S., Cui, W., Tian, W., Zhang, J., Chen, X., & Zhou, M. (2022). Rapid, Simultaneous, and Automatic Determination of Lead and Cadmium in Cereals with a New High Performance Composite Hollow Cathode Lamp Coupled to Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Molecules, 27(23), 8571. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238571





