In Vitro and In Silico Pharmacological and Cosmeceutical Potential of Ten Essential Oils from Aromatic Medicinal Plants from the Mascarene Islands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Antimicrobial
2.1.1. Antimycobacterial
2.1.2. Anti-Acne
2.1.3. Antifungal
2.2. Anti-Aging
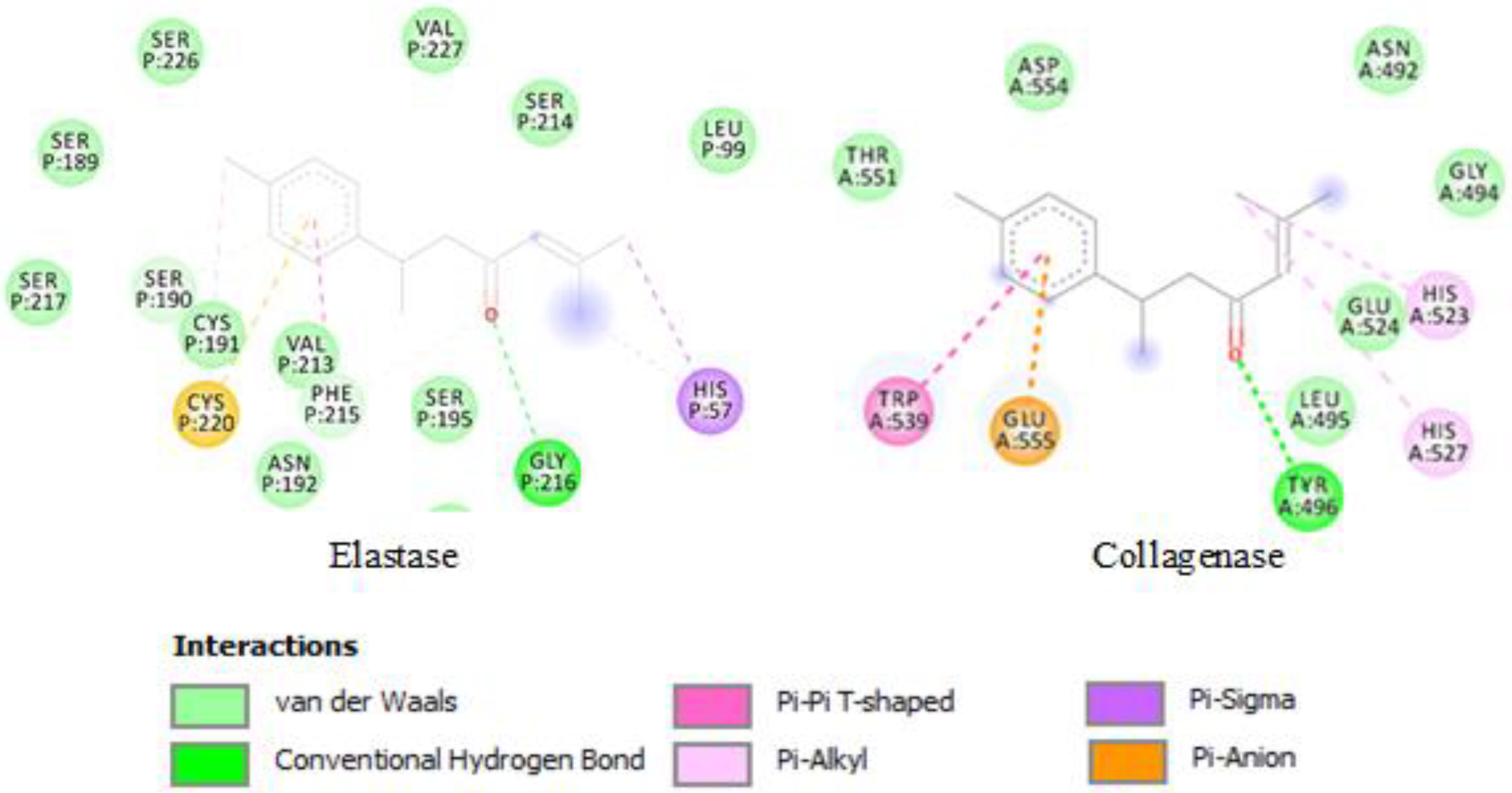
2.3. Molecular Docking
2.4. Cytotoxic/Antiproliferative Evaluation of EOs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials
3.2. Extraction of EOs
3.3. Antimicrobial Assay
3.3.1. Anti-Mycobacterium
3.3.2. Anti-Acne
3.3.3. Antifungal
Microdilution Broth Susceptibility Assay
Minimum Fungicidal Concentration
3.4. Antiaging Assay
3.4.1. Anti-Elastase
3.4.2. Anti-Collagenase
3.5. Molecular Docking
3.6. Cell Culture
In Vitro Antiproliferative Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardia, G.F.E.; de Souza Silva-Comar, F.M.; da Rocha, E.M.T.; Silva-Filho, S.E.; Zagotto, M.; Uchida, N.S.; Do Amaral, V.; Bersani-Amado, C.A.; Cuman, R.K.N. Pharmacological, medicinal and toxicological properties of lavender essential oil: A review. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e23310514933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, N.Y.; Muller, C.D.; Lobstein, A. Major bioactivities and mechanism of action of essential oils and their components. Flavour Fragr. J. 2013, 28, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.S.; Bollen, C.; Perry, E.K.; Ballard, C. Salvia for dementia therapy: Review of pharmacological activity and pilot tolerability clinical trial. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 75, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.; Sadiq, A.; Junaid, M.; Ullah, F.; Subhan, F.; Ahmed, J. Neuroprotective and anti-aging potentials of essential oils from aromatic and medicinal plants. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blowman, K.; Magalhães, M.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Cabral, C.; Pires, I.M. Anticancer properties of essential oils and other natural products. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 3149362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, S.; Sharma, K.; Guleria, S. Antimicrobial activity of some essential oils—Present status and future perspectives. Medicines 2017, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; Coppola, R.; Feo, V.D. Essential oils and antifungal activity. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campa, M.; Baron, E. Anti-aging effects of select botanicals: Scientific evidence and current trends. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziosi, P.; Manfredini, S.; Vertuani, S.; Ruscetta, V.; Radice, M.; Sacchetti, G. Evaluating essential oils in cosmetics: Antioxidant capacity and functionality. Cosmet. Toilet. 2010, 125, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jugreet, B.S.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Essential oils from 9 exotic and endemic medicinal plants from Mauritius shows in vitro antibacterial and antibiotic potentiating activities. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 132, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jugreet, B.S.; Kouadio Ibrahime, S.; Zengin, G.; Abdallah, H.H.; Mahomoodally, M.F. GC/MS profiling, in vitro and in silico pharmacological screening and principal component analysis of essential oils from three exotic and two endemic plants from Mauritius. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2000921. [Google Scholar]
- Jugreet, B.S.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Sinan, K.I.; Zengin, G.; Abdallah, H.H. Chemical variability, pharmacological potential, multivariate and molecular docking analyses of essential oils obtained from four medicinal plants. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 150, 112394. [Google Scholar]
- El Omari, K.; Hamze, M.; Alwan, S.; Osman, M.; Jama, C.; Chihib, N.E. In-vitro evaluation of the antibacterial activity of the essential oils of Micromeria barbata, Eucalyptus globulus and Juniperus excelsa against strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (including MDR), Mycobacterium kansasii and Mycobacterium gordonae. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankute, M.; Nataraj, V.; Lee, O.Y.C.; Wu, H.H.; Ridell, M.; Garton, N.J.; Barer, M.R.; Minnikin, D.E.; Bhatt, A.; Besra, G.S. The role of hydrophobicity in tuberculosis evolution and pathogenicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1315. [Google Scholar]
- Polyudova, T.V.; Eroshenko, D.V.; Pimenova, E.V. The biofilm formation of nontuberculous mycobacteria and its inhibition by essential oils. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2021, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lelovic, N.; Mitachi, K.; Yang, J.; Lemieux, M.R.; Ji, Y.; Kurosu, M. Application of Mycobacterium smegmatis as a surrogate to evaluate drug leads against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Antibiot. 2020, 73, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, M. Biohazard levels and biosafety protection for Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains with different virulence. Biosaf. Health 2020, 2, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.; Escobar, P.; Martínez, J.R.; Leal, S.M.; Stashenko, E.E. Composition of three essential oils, and their mammalian cell toxicity and antimycobacterial activity against drug resistant-tuberculosis and nontuberculous mycobacteria strains. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1934578X1100601143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chraibi, M.; Farah, A.; Lebrazi, S.; El Amine, O.; Houssaini, M.I.; Fikri-Benbrahim, K. Antimycobacterial natural products from Moroccan medicinal plants: Chemical composition, bacteriostatic and bactericidal profile of Thymus satureioides and Mentha pulegium essential oils. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 836–840. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Yuan, R.; Xin, K.Z.; Lu, Z.; Ma, Y. Antimicrobial susceptibility, biotypes and phylotypes of clinical Cutibacterium (formerly Propionibacterium) acnes strains isolated from acne patients: An observational study. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 9, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juliano, C.; Marchetti, M.; Pisu, M.L.; Usai, M. In vitro antimicrobial activity of essential oils from Sardinian flora against Cutibacterium (Formerly Propionibacterium) acnes and its enhancement by chitosan. Sci. Pharm. 2018, 86, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Humphrey, S. Antibiotic resistance in acne treatment. Skin Ther. Lett. 2012, 17, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Sardana, K.; Gupta, T.; Garg, V.K.; Ghunawat, S. Antibiotic resistance to Propionobacterium acnes: Worldwide scenario, diagnosis and management. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavero, R.Y.; Akerreta, S.; Calvo, M.I. Medicinal plants used for dermatological affections in Navarra and their pharmacological validation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.; Lyles, J.T.; Li, T.; Saitta, A.; Addie-Noye, E.; Tyler, P.; Quave, C.L. Anti-acne activity of Italian medicinal plants used for skin infection. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orafidiya, L.O.; Agabani, E.O.; Oyedele, A.O. Preliminary clinical tests on topical preparations of Ocimum gratissimum Linn leaf essential oil for the treatment of acne vulgaris. Clin. Drug Investig. 2002, 22, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viyoch, J.; Pisutthanan, N.; Faikreua, A.; Nupangta, K.; Wangtorpol, K.; Ngokkuen, J. Evaluation of in vitro antimicrobial activity of Thai basil oils and their micro-emulsion formulas against Propionibacterium acnes. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2006, 28, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.; Sachan, A.K.; Jain, S.; Barik, R. Studies on inhibitory effect of Eucalyptus oil on sebaceous glands for the management of acne. Indian J. Nat. Prod. Resour. 2011, 2, 345–349. [Google Scholar]
- Briganti, S.; Picardo, M. Antioxidant activity, lipid peroxidation and skin diseases. What’s new. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2003, 17, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayslich, C.; Grange, P.A.; Dupin, N. Cutibacterium acnes as an opportunistic pathogen: An update of its virulence-associated factors. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, K.; Miskei, M.; Farkas, I.; Dombrádi, V. The phosphatome of opportunistic pathogen Candida species. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2021, 35, 40–51. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, R.; Pradhan, D.; Hasan, Z.; Singh, H.; Jain, A.K.; Khan, L.A. A systematic review on distribution and antifungal resistance pattern of Candida species in the Indian population. Med. Mycol. 2021, 59, 1145–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asong, J.A.; Amoo, S.O.; McGaw, L.J.; Nkadimeng, S.M.; Aremu, A.O.; Otang-Mbeng, W. Antimicrobial activity, antioxidant potential, cytotoxicity and phytochemical profiling of four plants locally used against skin diseases. Plants 2019, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedroso, R.D.S.; Balbino, B.L.; Andrade, G.; Dias, M.C.P.S.; Alvarenga, T.A.; Pedroso, R.C.N.; Pimenta, L.P.; Lucarini, R.; Pauletti, P.M.; Januário, A.H.; et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-Candida spp. activity of plant-derived products. Plants 2019, 8, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holanda, L.; Bezerra, G.B.; Ramos, C.S. Potent antifungal activity of essential oil from Morinda citrifolia fruits rich in short-chain fatty acids. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2020, 20, S448–S454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İşcan, G. Antibacterial and anticandidal activities of common essential oil constituents. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2017, 11, 374–388. [Google Scholar]
- Osorio, E.; Bravo, K.; Cardona, W.; Yepes, A.; Osorio, E.H.; Coa, J.C. Antiaging activity, molecular docking, and prediction of percutaneous absorption parameters of quinoline–hydrazone hybrids. Med. Chem. Res. 2019, 28, 1959–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Era, B.; Floris, S.; Sogos, V.; Porcedda, C.; Piras, A.; Medda, R.; Fais, A.; Pintus, F. Anti-aging potential of extracts from Washingtonia filifera seeds. Plants 2021, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binic, I.; Lazarevic, V.; Ljubenovic, M.; Mojsa, J.; Sokolovic, D. Skin ageing: Natural weapons and strategies. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 827248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, M.; Ikeda, N.; Kato, Y.; Minamino, M.; Watabe, K. Inhibition of elastase activity by essential oils in vitro. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2002, 1, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, P.T.B.; Tawata, S. Anti-oxidant, anti-aging, and anti-melanogenic properties of the essential oils from two varieties of Alpinia zerumbet. Molecules 2015, 20, 16723–16740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aumeeruddy-Elalfi, Z.; Lall, N.; Fibrich, B.; Van Staden, A.B.; Hosenally, M.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Selected essential oils inhibit key physiological enzymes and possess intracellular and extracellular antimelanogenic properties in vitro. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Pan, C.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, W.; Liang, X.; Shi, Y.; Liang, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, Z. Antiaging effect of Curcuma longa L. essential oil on ultraviolet-irradiated skin. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohani, A.; Verma, A.; Hema, G.; Pathak, K. Topical delivery of geranium/calendula essential oil-entrapped ethanolic lipid vesicular cream to combat skin aging. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 4593759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhu, W. Molecular docking for drug discovery and development: A widely used approach but far from perfect. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 1707–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sethi, A.; Joshi, K.; Sasikala, K.; Alvala, M. Molecular docking in modern drug discovery: Principles and recent applications. In Drug Discovery and Development—New Advances; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, J.N.; Toloue, M. Biological studies of turmeric oil, Part 1: Selective in vitro anticancer activity of turmeric oil (TO) and TO-paclitaxel combination. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1934578X1300800632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-González, C.; Pérez-Ramos, J.; Méndez-Cuesta, C.A.; Serrano-Vega, R.; Martell-Mendoza, M.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, S. Cytotoxic activity of essential oils of some species from Lamiaceae family. In Cytotoxicity-Definition, Identification, and Cytotoxic Compounds; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; p. 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabral, C.; Efferth, T.; Pires, I.M.; Severino, P.; Lemos, M.F. Natural products as a source for new leads in cancer research and treatment. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 8243680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legault, J.; Pichette, A. Potentiating effect of β-caryophyllene on anticancer activity of α-humulene, isocaryophyllene and paclitaxel. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 1643–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabi, T.; Bishayee, A. D-Limonene sensitizes docetaxel-induced cytotoxicity in human prostate cancer cells: Generation of reactive oxygen species and induction of apoptosis. J. Carcinog. 2009, 8, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Lall, N.; Chrysargyris, A.; Lambrechts, I.; Fibrich, B.; Blom Van Staden, A.; Twilley, D.; De Canha, M.N.; Ooshuizen, C.B.; Bodiba, D.; Tzortzakis, N. Sideritis perfoliata (subsp. perfoliata) nutritive value and its potential medicinal properties. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 521. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Sureda, A.; Tenore, G.C.; Daglia, M.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Valussi, M.; Tundis, R.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Ademiluyi, A.O.; et al. Biological activities of essential oils: From plant chemoecology to traditional healing systems. Molecules 2017, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashar, A.; Locke, I.C.; Evans, C.S. Cytotoxicity of lavender oil and its major components to human skin cells. Cell Prolif. 2004, 37, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayala, B.; Bassole, I.H.; Scifo, R.; Gnoula, C.; Morel, L.; Lobaccaro, J.M.A.; Simpore, J. Anticancer activity of essential oils and their chemical components—A review. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 4, 591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, Y.; Gupta, V.K.; Jaitak, V. Anticancer activity of essential oils: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 3643–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiki, L.M.; Barbieri, A.M.E.; Araujo, R.C.; Veríssimo, C.J.; Louvandini, H.; Ferreira, J.F.S. Synergistic interaction of ten essential oils against Haemonchus contortus in vitro. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 243, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Grewal, K.; Jandrotia, R.; Batish, D.R.; Singh, H.P.; Kohli, R.K. Essential oils as anticancer agents: Potential role in malignancies, drug delivery mechanisms, and immune system enhancement. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Corasaniti, M.T.; Bagetta, G.; Morrone, L.A. Exploitation of cytotoxicity of some essential oils for translation in cancer therapy. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 397821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liju, V.B.; Jeena, K.; Kuttan, R. Article details cytotoxicity, antitumour and anticarcinogenic activity of Curcuma longa essential oil. Indian Drugs 2014, 51, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaru, S.P.; Mahmud, R.; Abdul Majid, A.M.S.; Ismail, S.; Man, C.N. Chemical composition, antioxidant and cytotoxicity activities of the essential oils of Myristica fragrans and Morinda citrifolia. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjamalai, A.; Grace, V.B. The chemotherapeutic effect of essential oil of Plectranthus amboinicus (Lour) on lung metastasis developed by B16F-10 cell line in C57BL/6 mice. Cancer Investig. 2013, 31, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moayedi, Y.; Greenberg, S.A.; Jenkins, B.A.; Marshall, K.L.; Dimitrov, L.V.; Nelson, A.M.; Owens, D.M.; Lumpkin, E.A. Camphor white oil induces tumor regression through cytotoxic T cell-dependent mechanisms. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumeeruddy-Elalfi, Z.; Gurib-Fakim, A.; Mahomoodally, F. Antimicrobial, antibiotic potentiating activity and phytochemical profile of essential oils from exotic and endemic medicinal plants of Mauritius. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 71, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, N.; Henley-Smith, C.J.; De Canha, M.N.; Oosthuizen, C.B.; Berrington, D. Viability reagent, PrestoBlue, in comparison with other available reagents, utilized in cytotoxicity and antimicrobial assays. Int. J. Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 420601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamatou, G.P.P. Indigenous Salvia Species: An Investigation of Their Pharmacological Activities and Phytochemistry. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Seebaluck-Sandoram, R.; Lall, N.; Fibrich, B.; Van Staden, A.B.; Mahomoodally, F. Antibiotic-potentiating activity, phytochemical profile, and cytotoxicity of Acalypha integrifolia Willd.(Euphorbiaceae). J. Herb. Med. 2018, 11, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lall, N.; Kishore, N.; Fibrich, B.; Lambrechts, I.A. In vitro and in vivo activity of Myrsine africana on elastase inhibition and anti-wrinkle activity. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pientaweeratch, S.; Panapisal, V.; Tansirikongkol, A. Antioxidant, anti-collagenase and anti-elastase activities of Phyllanthus emblica, Manilkara zapota and silymarin: An in vitro comparative study for anti-aging applications. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irwin, J.J.; Sterling, T.; Mysinger, M.M.; Bolstad, E.S.; Coleman, R.G. ZINC: A free tool to discover chemistry for biology. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09 Revision D. 01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009; p. 106. [Google Scholar]
| MIC (mg/mL) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria Tested | Essential Oils | Antibiotics | ||||||||||
| CAF | CAL | CC | CL | MC | PA | PC | PS | SC | SS | CIP | TRC | |
| M. smegmatis (ATCC MC2 155) | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.125 | NI1 b | 3.13 × 10−4 | - |
| C. acnes (ATCC 6919) | NI2 c | NI2 c | NI2 c | NI2 c | 2 | 0.50 | NI2 c | NI2 c | 0.50 | NI2 c | - | 7.8 × 10−4 |
| MIC/MFC (mg/mL) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungi Tested | Essential Oils | Antifungals | ||||||||||
| CAF | CAL | CC | CL | MC | PA | PC | PS | SC | SS | Nystatin | Amphotericin B | |
| C. albicans (ATCC 10,231) | (32) | (4) | (16) | (8) | (0.25) | (2) | (4) | - | (8) | (8) | (1.56 × 10−3) | (3.13 × 10−3) |
| FS | FC | FS | FS | FC | FC | FS | FC | FS | FS | FS | ||
| [ND] | [32] | [16] | [16] | (16) | [3.13 × 10−3] | [ND] | ||||||
| C. tropicalis (ATCC 750) | (8) | (0.016) | (8) | (1) | (0.25) | (2) | (2) | (32) | (1) | (1) | (1.56 × 10−3) | (1.25 × 10−2) |
| FS | FS | FC | FC | FS | FS | FC | FS | FS | FC | FS | FS | |
| [16] | [0.0625] | [1] | [4] | [ND] | [2] | [ND] | [ND] | |||||
| EO | Elastase Inhibition | Collagenase Inhibition |
|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µg/mL) | IC50 (mg/mL) | |
| CAF | NI1000 | 1.46 ± 0.19 |
| CAL | 275.95 ± 13.86 | 1.54 ± 0.40 |
| CC | NI1000 | 1.34 ± 0.09 |
| CL | 89.22 ± 23.72 | 0.17 ± 0.01 |
| MC | NI1000 | 0.62 ± 0.04 |
| PA | NI1000 | 0.33 ± 0.02 |
| PC | 354.65 ± 21.43 | 0.37 ± 0.02 |
| PS | 233.47 ± 21.45 | 0.77 ± 0.17 |
| SC | 767.2 ± 27.99 | 0.84 ± 0.13 |
| SS | 459.2 ± 21.24 | 0.18 ± 0.04 |
| Positive control | ||
| Ursolic acid | 10.10 ± 15.27 | - |
| 1,1 Phenanthroline | - | 4.20 × 10−3 ± 0.00 |
| EOs | Major Compounds | Collagenase | PP Elastase |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAF | Limonene | −3.87 a (1.5 mM) b | −5.61 (77.7 µM) |
| CAL | Sabinene | −3.87 (1.5 mM) | −5.36 (118.8 µM) |
| CC | 1,8-Cineole | −4.07 (1.0 mM) | −5.30 (130.8 µM) |
| CL | Turmerone | −5.11 (179.0 µM) | −6.64 (13.6 µM) |
| MC | Octanoic acid | −3.67 (2.1 mM) | −4.91 (249.7 µM) |
| PA | Carvacrol | −4.55 (459.4 µM) | −5.45 (100.9 µM) |
| PC | Myristicin | −3.56 (2.4 mM) | −5.73 (63.0 µM) |
| PS | Myrcene | −3.32 (3.7 mM) | −4.68 (374.3 µM) |
| SC | (E)-β-Ocimene | −3.29 (3.9 mM) | −4.63 (401.0 µM) |
| SS | β-Pinene | −4.13 (938.4 µM) | −5.47 (97.0 µM) |
| EOs | IC50 ± SD (µg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| HaCat | UCT-MEL1 | |
| CAF | 182.70 ± 3.54 | NI400 |
| CAL | 33.73 ± 7.06 | 277.25 ± 1.48 |
| CC | 250.90 ± 0.57 | NI400 |
| CL | 56.1 ± 1.90 | 88.91 ± 5.83 |
| MC | NI400 | NI400 |
| PA | 49.12 ± 2.58 | 189.50 ± 1.41 |
| PC | 104.50 ± 4.24 | NI400 |
| PS | 50.33 ± 1.43 | 95.52 ± 0.77 |
| SC | 34.17 ± 5.32 | 95.37 ± 4.34 |
| SS | 54.70 ± 3.59 | 94.09 ± 1.85 |
| ActinomycinD | 2.85 × 10−2 ± 8.49 × 10−4 | 8.65 × 10−3 ± 1.13 × 10−4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jugreet, B.S.; Lall, N.; Anina Lambrechts, I.; Reid, A.-M.; Maphutha, J.; Nel, M.; Hassan, A.H.; Khalid, A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Van, B.L.; et al. In Vitro and In Silico Pharmacological and Cosmeceutical Potential of Ten Essential Oils from Aromatic Medicinal Plants from the Mascarene Islands. Molecules 2022, 27, 8705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248705
Jugreet BS, Lall N, Anina Lambrechts I, Reid A-M, Maphutha J, Nel M, Hassan AH, Khalid A, Abdalla AN, Van BL, et al. In Vitro and In Silico Pharmacological and Cosmeceutical Potential of Ten Essential Oils from Aromatic Medicinal Plants from the Mascarene Islands. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248705
Chicago/Turabian StyleJugreet, Bibi Sharmeen, Namrita Lall, Isa Anina Lambrechts, Anna-Mari Reid, Jacqueline Maphutha, Marizé Nel, Abdallah H. Hassan, Asaad Khalid, Ashraf N. Abdalla, Bao Le Van, and et al. 2022. "In Vitro and In Silico Pharmacological and Cosmeceutical Potential of Ten Essential Oils from Aromatic Medicinal Plants from the Mascarene Islands" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248705
APA StyleJugreet, B. S., Lall, N., Anina Lambrechts, I., Reid, A.-M., Maphutha, J., Nel, M., Hassan, A. H., Khalid, A., Abdalla, A. N., Van, B. L., & Mahomoodally, M. F. (2022). In Vitro and In Silico Pharmacological and Cosmeceutical Potential of Ten Essential Oils from Aromatic Medicinal Plants from the Mascarene Islands. Molecules, 27(24), 8705. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248705










