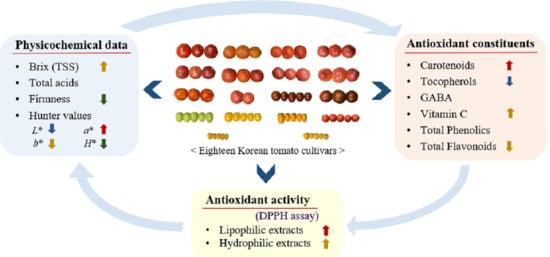
Antioxidant Constituents and Activities of the Pulp with Skin of Korean Tomato Cultivars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Physochemical Properties
2.2. Colorimetric Evaluation
2.3. Antioxidant Constituents in Tomato Pulp with Skin
2.4. Antioxidant Activity of Lipophilic and Hydrophilic Extracts
2.5. Correlations among Physicochemical Data, Antioxidant Constituent, and Antioxidant Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Total Soluble Solids (TSS), Total Acids (TA) of Pulp, and Brix Acid Ratio (BAR)
4.3. Colorimetric Evaluation
4.4. Analysis of Carotenoids and Tocopherols
4.5. Analysis of GABA and Free Amino Acids
4.6. Vitamin C Content
4.7. Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoid Contents
4.8. Antioxidant Activity Test with DPPH Radical
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Toor, R.K.; Savage, G.P. Antioxidant activity in different fractions of tomatoes. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilahun, S.; Choi, H.-R.; Baek, M.-W.; Cheol, L.-H.; Kwak, K.-W.; Park, D.-S.; Solomon, T.; Jeong, C.-S. Antioxidant properties, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) content, and physicochemical characteristics of tomato cultivars. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, A.G.; Keutgen, A.J.; Pawelzik, E. Antioxidant properties of tomato fruit (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) as affected by cultivar and processing method. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeoka, G.R.; Dao, L.; Flessa, S.; Gillespie, D.M.; Jewell, W.T.; Huebner, B.; Bertow, D.; Ebeler, S.E. Processing effects on lycopene content and antioxidant activity of tomatoes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Jia, Q.; Ji, S.; Gong, B.; Li, J.; Lü, G.; Gao, H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) alleviates salt damage in tomato by modulating Na+ uptake, the GAD gene, amino acid synthesis and reactive oxygen species metabolism. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, S.; Pék, Z.; Barna, É.; Lugasi, A.; Helyes, L. Lycopene content and colour of ripening tomatoes as affected by environmental conditions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Maguer, M.L. Lycopene in tomatoes: Chemical and physical properties affected by food processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babizhayev, M.A. Failure to withstand oxidative stress induced by phospholipid hydroperoxides as a possible cause of the lens opacities in systemic diseases and ageing. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1315, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johra, F.T.; Bepari, A.K.; Bristy, A.T.; Reza, H.M. A mechanistic review of β-carotene, lutein, and zeaxanthin in eye health and disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiola, A.; Rigano, M.M.; Calafiore, R.; Frusciante, L.; Barone, A. Enhancing the health-promoting effects of tomato fruit for biofortified food. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 139873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanfini, A.; Corbini, G.; La Rosa, C.; Dreassi, E. Antioxidant activity of tomato lipophilic extracts and interactions between carotenoids and α-tocopherol in synthetic mixtures. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, S.; Arai, C.; Takayama, M.; Matsukura, C.; Ezura, H. Efficient increase of ɣ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) content in tomato fruits by targeted mutagenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frusciante, L.; Carli, P.; Ercolano, M.R.; Pernice, R.; Di Matteo, A.; Fogliano, V.; Pellegrini, N. Antioxidant nutritional quality of tomato. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayuso-Yuste, M.C.; González-Cebrino, F.; Lozano-Ruiz, M.; Fernández-León, A.M.; Bernalte-García, M.J. Influence of ripening stage on quality parameters of five traditional tomato varieties grown under organic conditions. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Camelo, A.F.; Gómez, P.A. Comparison of color indexes for tomato ripening. Hortic. Bras. 2004, 22, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacrida, C.; Valle, E.M.; Boggio, S.B. Postharvest chilling induces oxidative stress response in the dwarf tomato cultivar Micro-Tom. Physiol. Plant. 2006, 127, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrequieta, A.; Abriata, L.A.; Boggio, S.B.; Valle, E.M. Off-the-vine ripening of tomato fruit causes alteration in the primary metabolite composition. Metabolites 2013, 3, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, K.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Cătoi, A.-F.; Vodnar, D.C. Screening of ten tomato varieties processing waste for bioactive components and their related antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batu, A. Determination of acceptable firmness and colour values of tomatoes. J. Food Eng. 2004, 61, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.A. Citrate and malate concentrations in tomato fruits: Genetic control and maturational effects. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 1972, 97, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.R.; Chae, Y.; Lee, J.G. Assessment of phytochemicals, quality attributes, and antioxidant activities in commercial tomato cultivars. Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 677–691. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.; Scott, S. Improvement of tomato flavor by genetically increasing sugar and acid contents. Euphytica 1983, 32, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabelka, E.; Yang, W.; Francis, D.M. Improved tomato fruit color within an inbred backcross line derived from Lycopersicon esculentum and L. hirsutum involves the interaction of loci. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2004, 129, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Rao, A.V. Tomato lycopene and its role in human health and chronic diseases. CMAJ 2000, 163, 739–744. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.S.; Kim, H.-J.; Li, M.; Lim, D.H.; Kim, J.; Kwak, S.-S.; Kang, C.-M.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Ahn, M.-J. Two classes of pigments, carotenoids and c-phycocyanin, in spirulina powder and their antioxidant activities. Molecules 2018, 23, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.-B. Amino acid, amino acid metabolite, and GABA content of three domestic tomato varieties. Culin. Sci. Hosp. Res. 2016, 22, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Sorrequieta, A.; Ferraro, G.; Boggio, S.B.; Valle, E.M. Free amino acid production during tomato fruit ripening: A focus on L-glutamate. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Beltrán, N.P.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Cira-Chávez, L.A.; Estrada-Alvarado, M.I.; Ornelas-Paz, J.d.J.; López-Mata, M.A.; Del-Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Total phenolic, flavonoid, tomatine, and tomatidine contents and antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of extracts of tomato plant. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 2015, 284071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Sharma, A.; Singh, B.; Nagpal, A.K. Bioactivities of phytochemicals present in tomato. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 2833–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Zamany, A.J.; Keum, Y.-S. Ripening improves the content of carotenoid, α-tocopherol, and polyunsaturated fatty acids in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) fruits. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duma, M.; Alsina, I.; Dubova, L.; Erdberga, I. Chemical composition of tomatoes depending on the stage of ripening. Chem. Technol. 2015, 66, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.; Walls, E. Ascorbic acid content and sugar-acid ratios of fresh fruit and processed juice of tomato varieties. Proc. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 1947, 50, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Tadesse, T.N.; Ibrahim, A.; Abtew, W. Degradation and formation of fruit color in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) in response to storage temperature. Am. J. Food Technol. 2015, 10, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pék, Z.; Helyes, L.; Lugasi, A. Color changes and antioxidant content of vine and postharvest-ripened tomato fruits. HortScience 2010, 45, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akihiro, T.; Koike, S.; Tani, R.; Tominaga, T.; Watanabe, S.; Iijima, Y.; Aoki, K.; Shibata, D.; Ashihara, H.; Matsukura, C. Biochemical mechanism on GABA accumulation during fruit development in tomato. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008, 49, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilahun, S.; Seo, M.H.; Hwang, I.G.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, H.R.; Jeong, C.S. Prediction of lycopene and β-carotene in tomatoes by portable chroma-meter and VIS/NIR spectra. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 136, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erge, H.S.; Karadeniz, F. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of tomato cultivars. Int. J. Food Prop. 2011, 14, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, R.; Haenen, G.R.; Van den Berg, H.; Bast, A. Applicability of an improved Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) assay for evaluation of antioxidant capacity measurements of mixtures. Food Chem. 1999, 66, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Shi, Z.; Xie, C.; Gong, W.; Hu, Z.; Peng, Y. A novel mechanism of Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) protecting human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) against H2O2-induced oxidative injury. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 217, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, V.; Puspitasari-Nienaber, N.L.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Schwartz, S.J. Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity of different geometrical isomers of α-carotene, β-carotene, lycopene, and zeaxanthin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenucci, M.S.; Cadinu, D.; Taurino, M.; Piro, G.; Dalessandro, G. Antioxidant composition in cherry and high-pigment tomato cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2606–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. United States Standards for Grades of Fresh Tomatoes. 1991. Available online: https://hort.purdue.edu/prod_quality/quality/tomatfrh.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- Kim, H.J.; Park, W.S.; Bae, J.-Y.; Kang, S.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.-S.; Kwak, S.-S.; Ahn, M.-J. Variations in the carotenoid and anthocyanin contents of Korean cultural varieties and home-processed sweet potatoes. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2015, 41, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Lee, J.; Ye, L.; Exler, J.; Eitenmiller, R.R. Tocopherol and tocotrienol contents of raw and processed fruits and vegetables in the United States diet. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2006, 19, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysinghe, D.; Li, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, C.; Chen, K. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacities in different edible tissues of citrus fruit of four species. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.D.; Kang, S.-N.; Bae, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Kwak, S.-S.; Jang, I.; Kim, I.-S.; Lee, C.H.; Bae, J.M.; Lee, S.W.; et al. Enhanced antioxidant and protective activities on retinal ganglion cells of carotenoids-overexpressing transgenic carrot. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
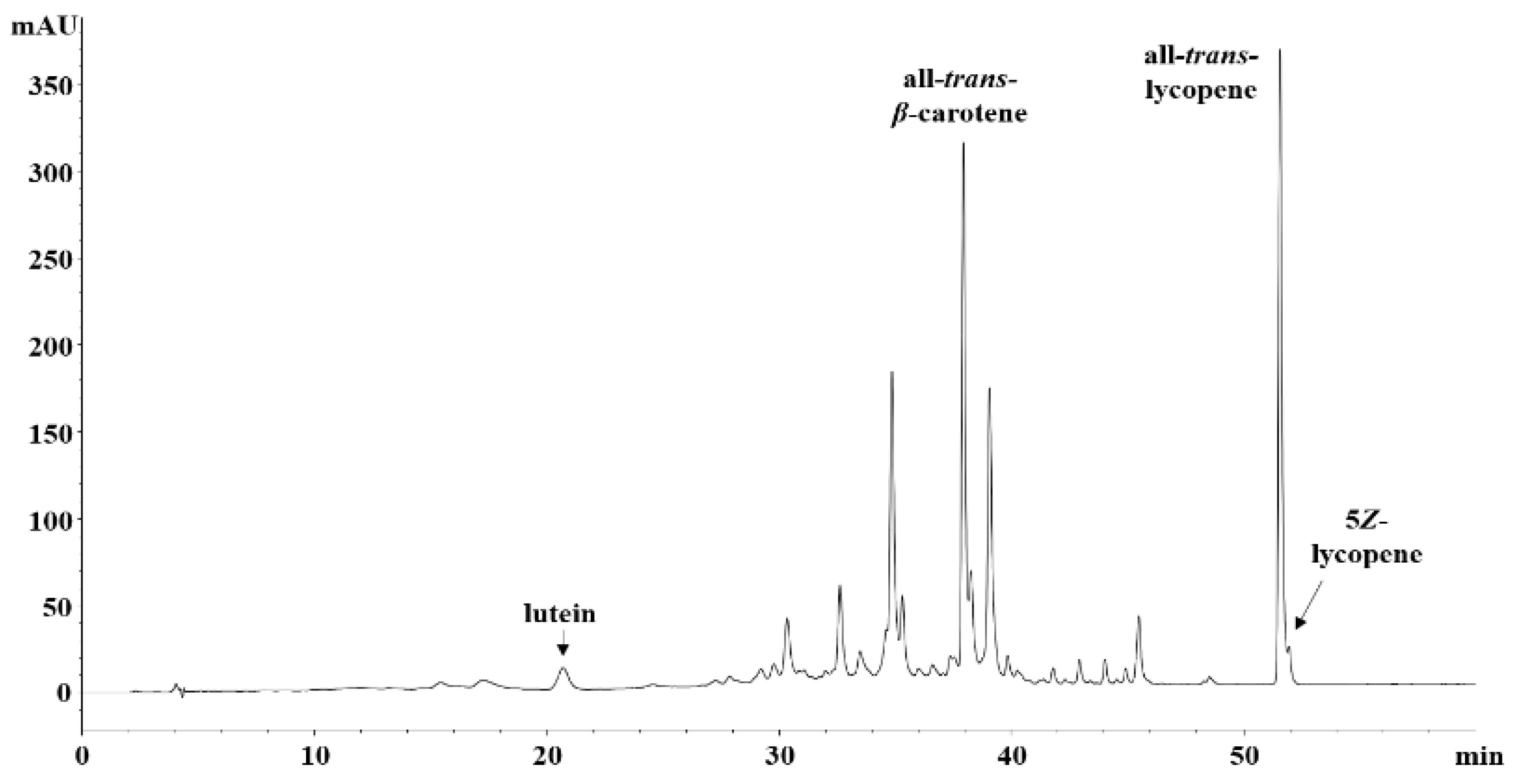
| Cultivar | Category | Firmness (N) | TSS (°Brix) | TA (mg CAE/10 g) | BAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daewang | Regular | 2.24 ± 0.46 b | 5.15 ± 0.21 e | 0.39 ± 0.01 c | 13.27 ± 0.13 e |
| Dafnis | 2.46 ± 0.46 b | 5.80 ± 0.21 e | 0.47 ± 0.05 b | 12.34 ± 0.78 ef | |
| Datlos | 2.12 ± 0.22 b | 5.56 ± 0.16 e | 0.60 ± 0.01 a | 9.26 ± 0.11 f | |
| Dongyu 250 ho | 2.00 ± 0.39 b | 5.58 ± 0.24 e | 0.41 ± 0.02 bc | 13.61 ± 0.09 e | |
| Happiness | 2.05 ± 0.51 b | 5.54 ± 0.18 e | 0.35 ± 0.01 d | 15.82 ± 0.06 d | |
| Madison | 2.17 ± 0.42 b | 6.30 ± 0.22 d | 0.45 ± 0.02 bc | 14.00 ± 0.13 e | |
| Pinktop | 2.80 ± 0.21 ab | 4.70 ± 0.19 f | 0.49 ± 0.03 b | 9.59 ± 0.19 f | |
| Super toterang | 2.80 ± 0.45 ab | 6.84 ± 0.16 d | 0.39 ± 0.04 c | 17.54 ± 1.26 d | |
| TY Altorang | 2.02 ± 0.46 b | 6.20 ± 0.16 d | 0.41 ± 0.06 bc | 15.12 ± 1.59 de | |
| Venekia 220 | 2.42 ± 0.64 b | 6.72 ± 0.29 d | 0.43 ± 0.03 bc | 15.63 ± 0.39 de | |
| Blackchoi | Medium-sized | 4.12 ± 0.27 a | 11.2 ± 0.3 b | 0.37 ± 0.03 cd | 30.27 ± 1.52 b |
| Blackchoco | 4.08 ± 0.31 a | 9.88 ± 0.17 c | 0.64 ± 0.01 a | 15.44 ± 0.02 de | |
| Greengana | 3.42 ± 0.46 ab | 9.45 ± 0.19 c | 0.41 ± 0.04 bc | 23.05 ± 1.41 c | |
| Norangdotori | 3.46 ± 0.26 ab | 10.1 ± 0.2 c | 0.37 ± 0.04 cd | 27.30 ± 2.18 b | |
| Orange | 3.80 ± 0.56 a | 11.3 ± 0.3 b | 0.38 ± 0.03 cd | 29.74 ± 1.45 b | |
| Tamina | 3.00 ± 0.89 ab | 10.3 ± 0.2 c | 0.30 ± 0.02 d | 34.33 ± 1.52 a | |
| GC-9 | Small Yellow cherry | 3.17 ± 0.72 ab | 11.2 ± 0.4 b | 0.29 ± 0.02 d | 38.62 ± 1.20 a |
| GC-19 | 3.80 ± 0.32 a | 12.3 ± 0.2 a | 0.34 ± 0.02 d | 36.18 ± 1.46 a |
| Items | Cultivars | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daewang | Dafnis | Datlos | Dongyu 250 ho | Happiness | Madison | Pinktop | Super Toterang | TY Altorang | Venekia 220 | |
| L* | 57.0 ± 0.8 bc | 64.9 ± 0.7 b | 46.0 ± 1.3 de | 62.6 ± 2.4 b | 48.9 ± 0.9 d | 43.2 ± 2.7 e | 53.0 ± 0.9 c | 56.3 ± 2.0 bc | 54.3 ± 0.6 c | 60.9 ± 0.1 b |
| a* | 27.0 ± 1.2 c | 17.4 ± 1.5 d | 25.1 ± 0.3 c | 21.2 ± 1.1 c | 34.1 ± 1.1 a | 30.3 ± 0.5 b | 31.0 ± 0.7 b | 23.2 ± 0.3 c | 26.6 ± 0.3 c | 22.3 ± 0.1 c |
| b* | 30.3 ± 1.4 c | 28.9 ± 3.6 c | 21.9 ± 0.9 d | 24.8 ± 1.0 d | 33.4 ± 0.5 bc | 29.2 ± 0.8 c | 28.4 ± 0.7 cd | 30.0 ± 0.4 c | 38.6 ± 1.6 b | 24.7 ±1.1 d |
| Hue angle (°) | 17.6 ± 0.4 g | 23.9 ±0.7 e | 13.1 ± 0.9 h | 18.4 ± 0.3 g | 14.6 ± 0.6 h | 14.0 ± 0.6 h | 13.4 ± 0.7 h | 20.5 ± 0.2 f | 22.6 ± 0.3 e | 17.1 ± 0.8 g |
| Lutein (µg/g) | 8.4 ± 0.2 b | 5.4 ± 0.2 b | 6.4 ± 0.2 b | 7.3 ± 1.9 b | 5.3 ± 0.1 b | 5.1 ± 0.2 b | 6.6 ± 1.2 b | 8.1 ± 2.1 b | 8.5 ± 0.9 b | 4.9 ± 0.7 b |
| β-Carotene (µg/g) | 39.3 ± 1.0 b | 49.6 ± 3.7 a | 28.0 ± 2.5 c | 18.1 ± 2.9 d | 31.9 ± 0.4 bc | 23.3 ± 2.6 cd | 24.6 ± 0.9 cd | 29.4 ± 2.1 c | 26.6 ± 1.6 c | 24.0 ± 3.1 cd |
| Lycopene (µg/g) | 272.8 ± 3.4 c | 173.6 ± 7.3 e | 445.2 ± 24.3 a | 225.9 ± 25.6 d | 307.0 ± 10.3 c | 360.1 ± 16.7 b | 410.6 ± 18.4 a | 184.8 ± 17.6 e | 350.4 ± 34.1 b | 229.8 ± 14.8 d |
| Other carotenoids (µg/g) | 163.1 ± 2.1 b | 129.0 ± 3.7 c | 194.8 ± 21.3 a | 142.5 ± 11.0 bc | 181.8 ± 1.8 ab | 186.0 ± 3.8 a | 210.7 ± 10.5 a | 126.6 ± 7.4 c | 187.0 ± 9.9 a | 156.6 ± 6.9 b |
| Total carotenoids (µg/g) | 483.6 ± 6.8 bc | 357.7 ± 14.9 d | 674.4 ± 48.3 a | 393.8 ± 41.5 d | 526.1 ± 12.7 b | 574.5 ± 23.3 b | 652.4 ± 30.9 a | 348.9 ± 29.2 d | 572.5 ± 46.4 b | 415.2 ± 25.6 c |
| Chlorophyll a (µg/g) | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Chlorophyll b (µg/g) | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| α-Tocopherol (µg/g) | 21.5 ± 0.6 c | 30.2 ± 1.2 b | 16.5 ± 0.6 d | 25.6 ± 0.3 b | 14.6 ± 0.6 d | 18.5 ± 0.9 d | 20.6 ± 0.3 c | 17.2 ± 0.3 d | 21.2 ± 0.3 c | 29.5 ± 0.3 b |
| γ-Tocopherol (µg/g) | 0.48 ± 0.06 g | 3.44 ± 0.06 d | 1.23 ± 0.02 f | 1.27 ± 0.06 f | 0.93 ± 0.02 f | 0.25 ± 0.02 g | 1.26 ± 0.12 f | 2.20 ± 0.06 e | 0.78 ± 0.06 f | 3.09 ± 0.06 d |
| δ-Tocopherol (µg/g) | 0.21 ± 0.03 e | 0.35 ± 0.03 c | 0.23 ± 0.02 d | 0.23 ± 0.06 de | 0.22 ± 0.03 de | 0.25 ± 0.06 d | 0.27 ± 0.03 d | 0.11 ± 0.03 e | 0.76 ± 0.03 b | 0.19 ± 0.03 e |
| Total tocopherols(µg/g) | 22.2 ± 0.6 e | 34.0 ± 1.2 c | 18.0 ± 0.6 f | 26.2 ± 0.3 d | 15.7 ± 0.6 f | 19.0 ± 0.9 f | 22.1 ± 0.4 e | 19.5 ± 0.3 f | 22.7 ± 0.3 e | 32.8 ± 0.3 c |
| GABA (mg/g) | 3.9 ± 0.6 c | 4.7 ± 0.0 c | 11.8 ± 1.2 a | 6.1 ± 0.3 b | 6.2 ± 1.4 b | 6.4 ± 1.1 b | 12.3 ± 0.3 a | 4.0 ± 0.3 c | 3.7 ± 0.5 c | 2.8 ± 0.6 d |
| Total amino acids (mg/g) | 28.4 ± 4.3 c | 39.0 ± 1.0 ab | 41.7 ± 3.9 ab | 35.9 ± 1.2 b | 31.6 ± 7.1 c | 36.5 ± 5.3 b | 47.5 ± 3.3 a | 30.7 ± 3.0 c | 29.8 ± 3.5 c | 27.6 ± 6.4 c |
| Vitamin C (mg AAE/g) | 2.06 ± 0.18 bc | 1.86 ± 0.04 c | 1.89 ± 0.04 c | 2.90 ± 0.05 a | 2.26 ± 0.12 bc | 2.48 ± 0.05 b | 1.94 ± 0.05 c | 1.70 ± 0.04 c | 2.44 ± 0.05 b | 1.98 ± 0.05 c |
| Antioxidant Activity of Lipophilic Extracts | ||||||||||
| Total phenolics (μmol GAE/g) | 17.2 ± 0.1 b | 18.4 ± 1.0 a | 13.3 ± 0.3 d | 13.4 ± 0.3 d | 18.8 ± 0.1 a | 18.3 ± 0.1 a | 12.8 ± 0.2 d | 18.8 ± 0.5 a | 17.7 ± 0.6 b | 18.5 ± 0.1 a |
| Total flavonoids (μmol QE/g) | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| DPPH (μmol TE/g) | 29.7 ± 3.7 a | 17.6 ± 1.8 b | 26.4 ± 1.5 a | 11.4 ± 0.8 c | 27.3 ± 3.5 a | 25.2 ± 2.3 a | 19.0 ± 1.0 b | 19.8 ± 1.7 b | 28.7 ± 2.0 a | 21.6 ± 1.9 b |
| Antioxidant Activity of Hydrophilic Extracts | ||||||||||
| Total phenolics (μmol GAE/g) | 16.3 ± 1.6 c | 17.8 ± 0.4 c | 18.3 ± 0.1 bc | 15.6 ± 0.7 d | 14.1 ± 2.2 d | 18.3 ± 0.6 bc | 13.0 ± 0.3 d | 15.4 ± 0.8 d | 27.2 ± 1.3 a | 16.6 ± 0.4 c |
| Total flavonoids (μmol QE/g) | 6.1 ± 0.2 d | 7.1 ± 0.5 c | 6.1 ± 0.4 d | 5.5 ± 0.3 d | 5.6 ± 0.3 d | 6.5 ± 0.4 c | 6.0 ± 0.3 d | 6.6 ± 0.5 c | 7.7 ± 0.6 b | 7.2 ± 0.6 c |
| DPPH (μmol TE/g) | 34.3 ± 2.4 c | 33.2 ± 2.8 c | 32.7 ± 2.5 c | 36.9 ± 0.7 b | 27.4 ± 1.8 d | 38.9 ± 4.9 b | 37.2 ± 5.5 b | 28.2 ± 2.3 d | 37.3 ± 2.0 b | 34.5 ± 2.7 c |
| Items | Cultivars | |||||||||
| Blackchoi | Blackchoco | Greengana | Norangdotori | Orange | Tamina | GC-9 | GC-19 | |||
| L* | 50.1 ± 0.3 d | 59.0 ± 0.3 b | 70.3 ± 0.6 a | 77.1 ± 2.5 a | 55.1 ± 0.4 c | 46.8 ± 0.6 de | 74.2 ± 1.0 a | 72.6 ± 1.0 a | ||
| a* | 18.8 ± 0.1 d | 3.8 ± 0.1 e | −11.7 ± 0.7 g | −3.3 ± 0.5 f | 11.6 ± 0.5 d | 33.9 ± 0.7 a | 1.0 ± 0.5 e | 0.8 ± 0.3 e | ||
| b* | 26.1 ± 0.2 d | 27.4 ± 0.3 cd | 31.1 ± 2.4 c | 35.8 ± 0.5 b | 47.0 ± 0.9 a | 33.2 ± 2.1 bc | 41.8 ± 1.0 b | 38.1 ± 2.7 b | ||
| Hue angle (°) | 20.9 ± 0.1 f | 37.8 ± 0.1 d | 65.1 ± 1.1 a | 48.1 ± 1.0 b | 36.5 ± 0.5 d | 14.7 ± 0.8 h | 43.2 ± 0.3 c | 42.4 ± 0.5 c | ||
| Lutein (µg/g) | 8.9 ± 0.9 b | 26.2 ± 2.6 a | 5.7 ± 1.5 b | 5.6 ± 1.0 b | 4.4 ± 0.4 b | 2.9 ± 0.1 b | 5.5 ± 0.2 b | 4.2 ± 0.3 b | ||
| β-Carotene (µg/g) | 49.1 ± 3.8 a | 55.0 ± 1.4 a | 0.9 ± 0.3 e | 0.9 ± 0.3 e | 41.0 ± 5.5 b | 36.5 ± 1.8 b | 2.6 ± 0.3 e | 1.6 ± 0.2 e | ||
| Lycopene (µg/g) | 294.5 ± 15.8 c | 190.0 ± 24.9 e | ND | ND | ND | 246.4 ± 19.1 d | ND | ND | ||
| Other carotenoids (µg/g) | 172.3 ± 26.6 ab | 137.9 ± 9.9 bc | 0.8 ± 0.1 d | 0.9 ± 0.0 d | 25.8 ± 0.8 d | 155.3 ± 4.1 b | 1.8 ± 0.3 d | 0.8 ± 0.3 d | ||
| Total carotenoids (µg/g) | 524.8 ± 47.1 b | 409.1 ± 38.8 c | 7.4 ± 1.8 f | 7.3 ± 1.3 f | 71.2 ± 6.8 e | 441.1 ± 25.1 c | 9.9 ± 0.8 f | 6.6 ± 0.7 f | ||
| Chlorophyll a (µg/g) | 65.6 ± 3.7 ab | 79.8 ± 18.9 a | 50.5 ± 4.8 b | ND | 23.8 ± 0.0 c | ND | 8.3 ± 2.5 c | 6.4 ± 2.7 c | ||
| Chlorophyll b (µg/g) | 16.6 ± 1.1 c | 56.1 ± 1.6 a | 27.5 ± 3.8 b | 9.8 ± 1.3 d | 10.8 ± 0.2 d | ND | 6.4 ± 0.8 d | 5.9 ± 1.1 d | ||
| α-Tocopherol (µg/g) | 27.1 ± 0.6 b | 29.5 ± 0.6 b | 20.9 ± 0.3 c | 28.6 ± 0.3 b | 23.3 ± 0.3 c | 5.5 ± 0.3 e | 61.8 ± 0.3 a | 58.3 ± 0.9 a | ||
| γ-Tocopherol (µg/g) | 9.36 ± 0.12 a | 10.1 ± 0.1 a | 3.00 ± 0.06 d | 3.67 ± 0.12 d | 6.67 ± 0.06 b | 4.21 ± 0.27 c | 3.45 ± 0.02 d | 4.18 ± 0.02 c | ||
| δ-Tocopherol (µg/g) | 1.58 ± 0.02 a | 1.65 ± 0.02 a | 0.91 ± 0.02 b | 0.87 ± 0.03 b | 1.25 ± 0.03 a | 0.42 ± 0.03 c | 0.62 ± 0.02 b | 0.75 ± 0.03 b | ||
| Total tocopherols (µg/g) | 38.0 ± 0.7 b | 41.3 ± 0.6 b | 24.8 ± 0.3 d | 33.1 ± 0.4 c | 31.2 ± 0.3 c | 10.2 ± 0.6 g | 65.9 ± 0.3 a | 63.3 ± 0.9 a | ||
| GABA (mg/g) | 2.6 ± 0.5 d | 8.2 ± 0.4 b | 7.5 ± 0.4 b | 2.1 ± 0.2 d | 2.5 ± 0.2 d | 3.3 ± 0.0 c | 3.5 ± 0.0 c | 3.7 ± 0.2 c | ||
| Total amino acids (mg/g) | 29.6 ± 6.8 c | 38.0 ± 3.7 ab | 38.0 ± 0.4 ab | 24.9 ± 3.2 c | 29.5 ± 1.1 c | 36.2 ± 0.4 b | 31.5 ± 1.1 c | 35.8 ± 3.1 b | ||
| Vitamin C (mg AAE/g) | 1.98 ± 0.04 c | 2.19 ± 0.10 bc | 0.23 ± 0.04 e | 0.43 ± 0.03 e | 0.23 ± 0.03 e | 2.60 ± 0.05 b | 1.10 ± 0.04 d | 1.06 ± 0.04 d | ||
| Antioxidant Activity of Lipophilic Extracts | ||||||||||
| Total phenolics (μmol GAE/g) | 18.9 ± 1.2 a | 17.9 ± 0.1 ab | 15.8 ± 0.4 c | 17.2 ± 0.3 b | 19.1 ± 0.3 a | 13.1 ± 0.2 d | 15.0 ± 0.2 c | 18.1 ± 0.1 ab | ||
| Total flavonoids (μmol QE/g) | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||
| DPPH (μmol TE/g) | 18.8 ± 1.4 b | 11.4 ± 2.2 c | 10.8 ± 0.7 c | 9.9 ± 1.2 c | 9.0 ± 1.7 c | 25.1 ± 0.7 a | 10.2 ± 0.2 c | 8.8 ± 0.6 c | ||
| Antioxidant Activity of Hydrophilic Extracts | ||||||||||
| Total phenolics (μmol GAE/g) | 14.6 ± 0.7 d | 19.1 ± 0.1 b | 13.4 ± 0.1 d | 18.2 ± 0.9 bc | 16.8 ± 0.2 c | 20.3 ± 0.2 b | 18.1 ± 0.2 c | 21.4 ± 0.2 b | ||
| Total flavonoids (μmol QE/g) | 6.7 ± 0.6 c | 6.9 ± 0.5 c | 7.2 ± 0.3 c | 10.8 ± 0.8 a | 10.8 ± 1.3 a | 8.6 ± 0.6 b | 10.7 ± 0.8 a | 10.6 ± 0.8 a | ||
| DPPH (μmol TE/g) | 31.2 ± 1.0 d | 35.3 ± 3.9 c | 15.7 ± 2.3 f | 22.8 ± 0.9 e | 20.5 ± 0.9 e | 41.9 ± 5.0 a | 26.4 ± 1.0 e | 23.9 ± 1.0 e | ||
| Traits | TA | L* | a* | b* | h° | Lut | β-Car | Lyc | TCar | TToco | GABA | TAA | AAC | TPhe-L | DPPH-L | TPhe-H | TFla-H | DPPH-H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brix | −0.23 | 0.08 | −0.35 | 0.08 | 0.39 | −0.11 | −0.15 | −0.45 | −0.49 | 0.19 | −0.64 * | −0.58 | −0.08 | 0.65 * | −0.01 | 0.34 | 0.60 | −0.18 |
| TA | −0.28 | −0.17 | −0.59 | −0.34 | −0.22 | −0.03 | 0.58 | 0.55 | 0.03 | 0.72 * | 0.71 * | −0.31 | −0.60 | −0.04 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.26 | |
| L* | −0.77 ** | −0.08 | 0.71 * | 0.17 | 0.32 | −0.79 ** | −0.78 ** | 0.83 ** | −0.50 | −0.23 | −0.04 | 0.08 | −0.59 | −0.07 | 0.24 | −0.02 | ||
| a* | 0.38 | −0.67 * | −0.08 | −0.29 | 0.64 * | 0.67 * | −0.77 ** | 0.36 | 0.09 | 0.14 | −0.02 | 0.56 | −0.15 | −0.38 | −0.03 | |||
| b* | 0.42 | 0.37 | 0.20 | −0.02 | 0.03 | −0.24 | −0.41 | −0.38 | 0.15 | 0.51 | 0.46 | 0.50 | 0.37 | −0.05 | ||||
| h° | 0.37 | 0.47 | −0.69 * | −0.68 * | 0.56 | −0.68 * | −0.39 | −0.04 | 0.44 | −0.21 | 0.49 | 0.62 | −0.06 |
| Traits | TA | L* | a* | b* | h° | Lut | β-Car | Lyc | TCar | TToco | GABA | TAA | AAC | TPhe-L | DPPH-L | TPhe-H | TFla-H | DPPH-H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brix | −0.36 | −0.59 | 0.57 | 0.40 | −0.62 | −0.27 | 0.54 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.18 | −0.73 | −0.06 | 0.07 | 0.52 | 0.17 | −0.04 | 0.29 | 0.11 |
| TA | 0.16 | −0.41 | −0.35 | 0.27 | 0.96 ** | 0.36 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.66 | 0.76 | −0.45 | 0.15 | 0.37 | −0.46 | 0.10 | −0.42 | 0.07 | |
| L* | −0.89 * | 0.07 | 0.87 * | −0.01 | −0.82 * | −0.76 | −0.79 | 0.25 | 0.19 | −0.54 | −0.70 | 0.09 | −0.71 | −0.24 | 0.29 | −0.69 | ||
| a* | 0.01 | −0.96 ** | −0.20 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.73 | −0.44 | −0.47 | 0.74 | 0.72 | −0.30 | 0.84 * | 0.49 | −0.01 | 0.79 | |||
| b* | 0.10 | −0.50 | −0.16 | −0.65 | −0.60 | −0.21 | −0.46 | −0.03 | −0.60 | 0.16 | −0.38 | 0.13 | 0.87 | −0.42 | ||||
| h° | 0.03 | −0.72 | −0.81 * | −0.82 * | 0.21 | 0.48 | −0.59 | −0.78 | 0.12 | −0.79 | −0.50 | 0.08 | −0.83 * |
| Traits | L* | a* | b* | h° | Lut | β-Car | Lyc | TCar | TToco | GABA | TAA | AAC | TPhe-L | DPPH-L | TPhe-H | TFla-H | DPPH-H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TA | −0.27 | 0.05 | −0.57 * | −0.15 | 0.65 ** | 0.40 | 0.44 | 0.46 | −0.19 | 0.71 ** | −0.28 | 0.21 | −0.09 | 0.10 | −0.02 | −0.48 * | 0.27 |
| L* | −0.83 ** | 0.33 | 0.78 ** | −0.03 | −0.60 ** | −0.82 ** | −0.83 ** | 0.69 ** | −0.32 | −0.30 | −0.61 ** | 0.05 | −0.74 ** | 0.03 | 0.57 * | −0.59 * | |
| a* | −0.33 | −0.96 ** | −0.18 | 0.48 * | 0.84 ** | 0.85 ** | −0.66 ** | 0.18 | 0.31 | 0.78 ** | −0.13 | 0.83 ** | 0.01 | −0.59 * | 0.75 ** | ||
| b* | 0.46 | −0.26 | −0.27 | −0.61 ** | −0.62 ** | 0.37 | −0.50 * | 0.03 | −0.55 * | 0.25 | −0.35 | 0.35 | 0.80 ** | −0.48 * | |||
| h° | 0.10 | −0.51 * | −0.85 ** | −0.87 ** | 0.54 * | −0.20 | −0.21 | −0.81 ** | 0.13 | −0.76 ** | 0.01 | 0.61 ** | −0.79 ** | ||||
| Lut | 0.46 | 0.10 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.25 | −0.20 | 0.22 | 0.15 | −0.11 | 0.09 | −0.25 | 0.19 | |||||
| β-Car | 0.45 | 0.56 * | −0.32 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.39 | −0.03 | −0.42 | 0.46 | ||||||
| Lyc | 0.99 ** | −0.61 ** | 0.52 * | 0.10 | 0.78 ** | −0.25 | 0.81 ** | 0.01 | −0.77 ** | 0.76 ** | |||||||
| TCar | −0.62 ** | 0.48 * | 0.11 | 0.81 ** | −0.18 | 0.81 ** | 0.00 | −0.79 ** | 0.79 ** | ||||||||
| TToco | −0.29 | −0.34 | −0.40 | 0.19 | −0.69 ** | 0.17 | 0.61 ** | −0.38 | |||||||||
| GABA | −0.10 | 0.21 | −0.55 * | 0.15 | −0.28 | −0.55 * | 0.21 | ||||||||||
| TAA | 0.28 | −0.45 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.40 | |||||||||||
| AAC | −0.20 | 0.64 ** | 0.17 | −0.68 ** | 0.91 ** | ||||||||||||
| TPhe-L | −0.03 | 0.09 | 0.14 | −0.31 | |||||||||||||
| DPPH-L | 0.13 | −0.60 ** | 0.60 ** | ||||||||||||||
| TPhe-H | 0.38 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||
| TFla-H | −0.50 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, D.-M.; Kwon, J.-M.; Jeong, W.-J.; Jung, Y.J.; Kang, K.K.; Ahn, M.-J. Antioxidant Constituents and Activities of the Pulp with Skin of Korean Tomato Cultivars. Molecules 2022, 27, 8741. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248741
Kang D-M, Kwon J-M, Jeong W-J, Jung YJ, Kang KK, Ahn M-J. Antioxidant Constituents and Activities of the Pulp with Skin of Korean Tomato Cultivars. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8741. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248741
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Dong-Min, Ji-Min Kwon, Woo-Jin Jeong, Yu Jin Jung, Kwon Kyoo Kang, and Mi-Jeong Ahn. 2022. "Antioxidant Constituents and Activities of the Pulp with Skin of Korean Tomato Cultivars" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8741. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248741
APA StyleKang, D.-M., Kwon, J.-M., Jeong, W.-J., Jung, Y. J., Kang, K. K., & Ahn, M.-J. (2022). Antioxidant Constituents and Activities of the Pulp with Skin of Korean Tomato Cultivars. Molecules, 27(24), 8741. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248741