Porous Organic Cage-Embedded C10-Modified Silica as HPLC Stationary Phase and Its Multiple Separation Functions
Abstract
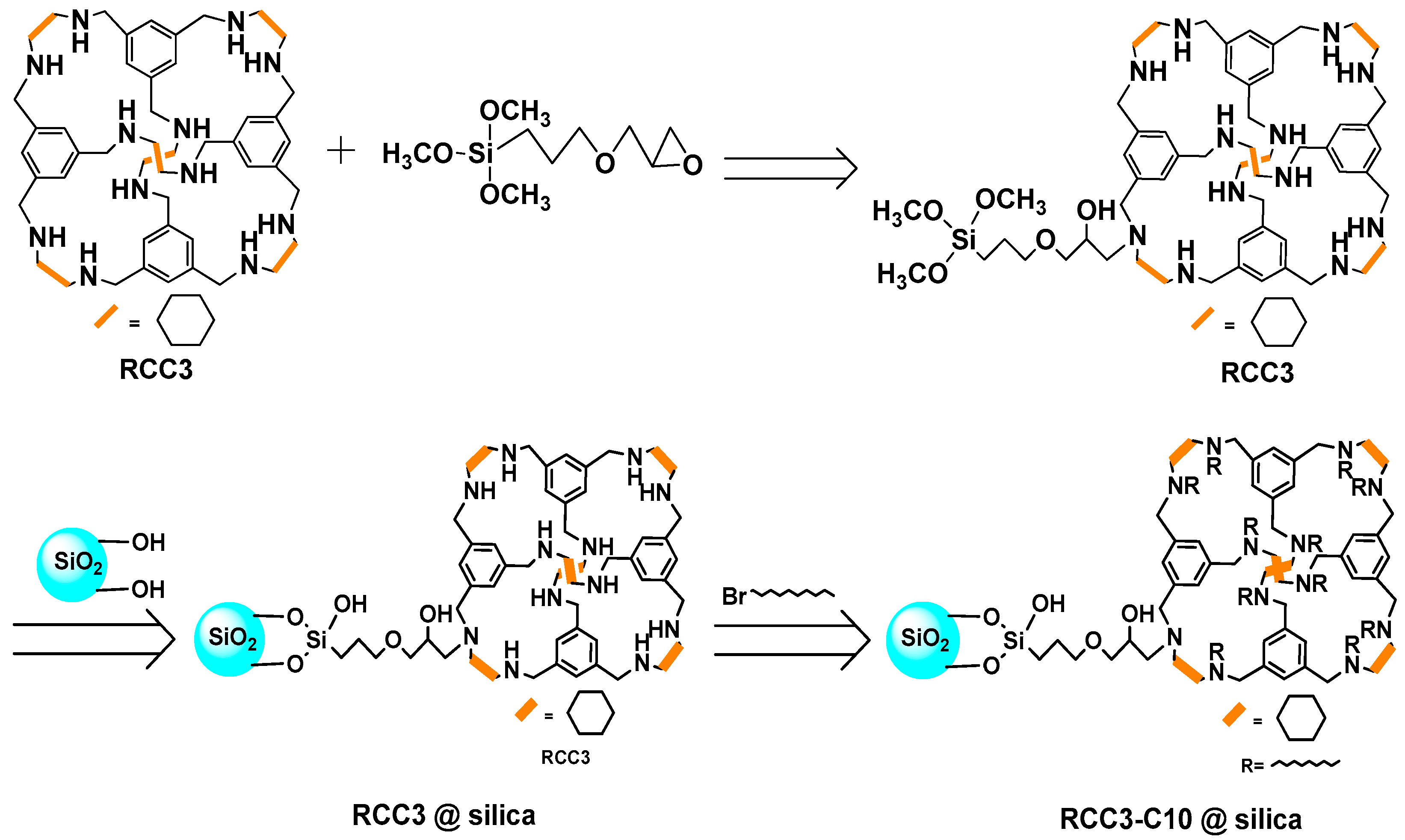
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of RCC3-C10@silica
2.2. The Evaluation of Chromatographic Separation Performance
2.2.1. The Resolution of Chiral Alcohols
2.2.2. Tanaka Test Analysis
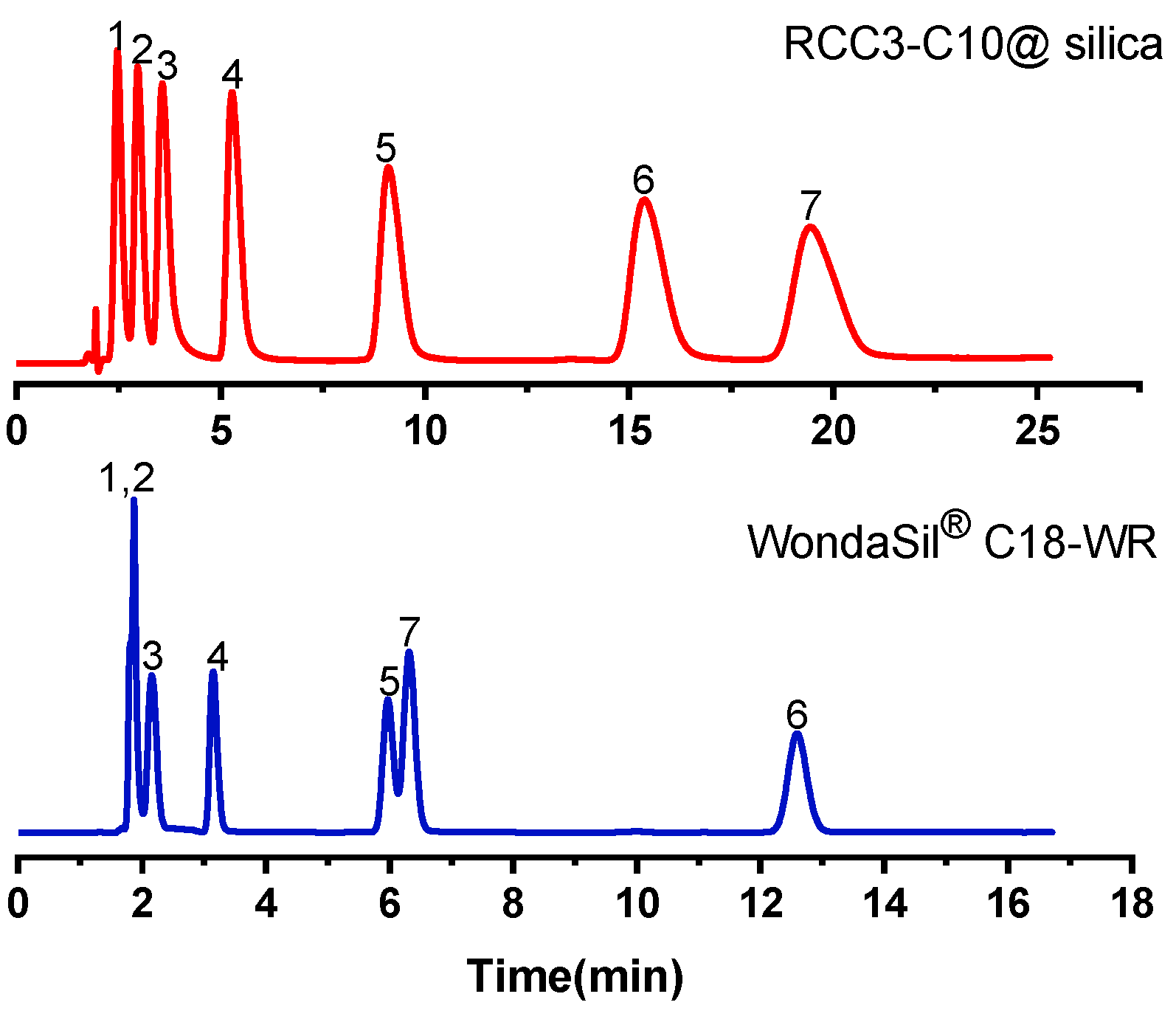
2.2.3. Separation of Alkyl Benzenes
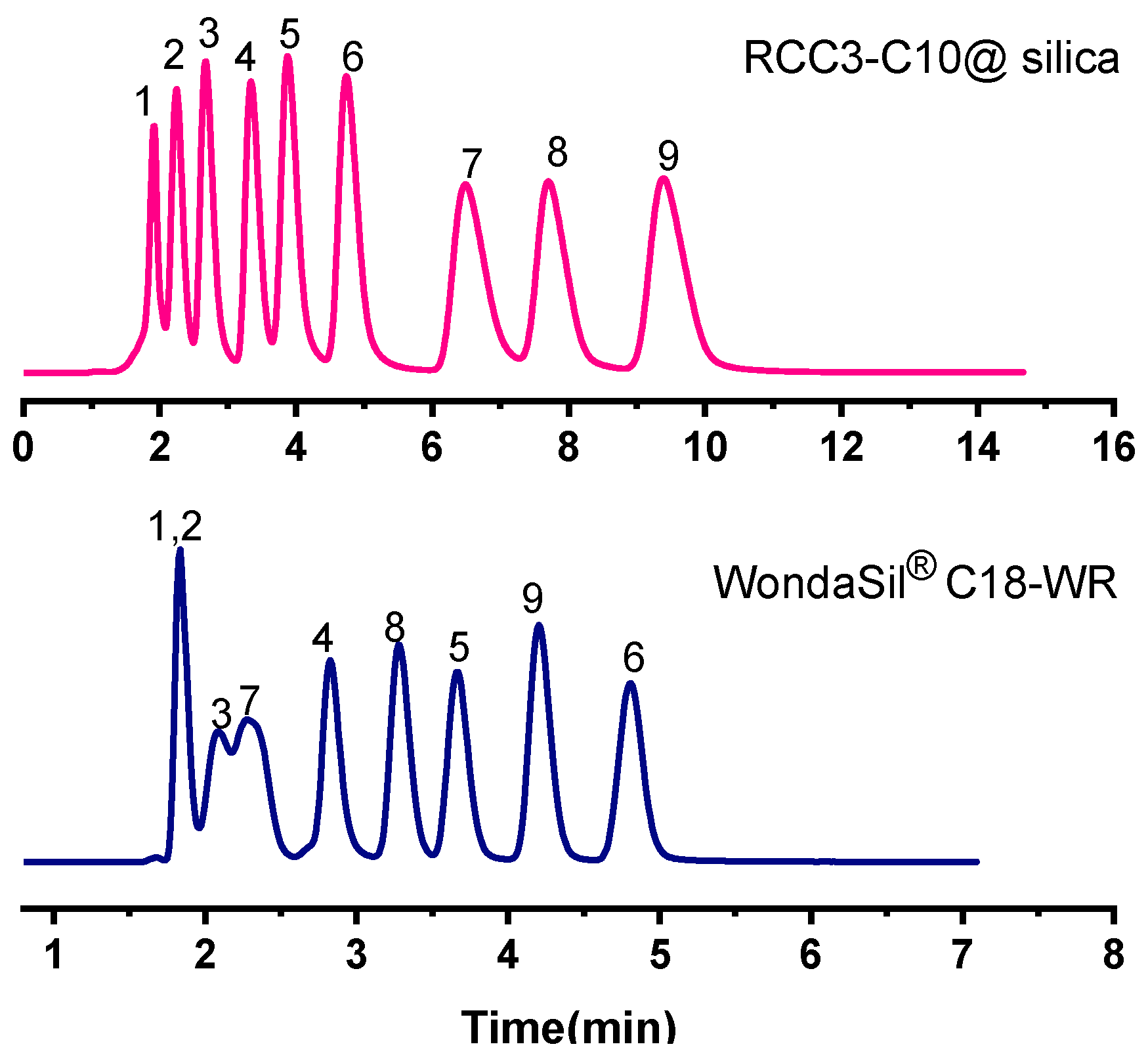
2.2.4. Separation of PAHs
2.2.5. Separation of Polar Aromatic Analytes
2.2.6. Separation of Nucleosides and Sulfonamides
2.2.7. Separation of Flavonoids
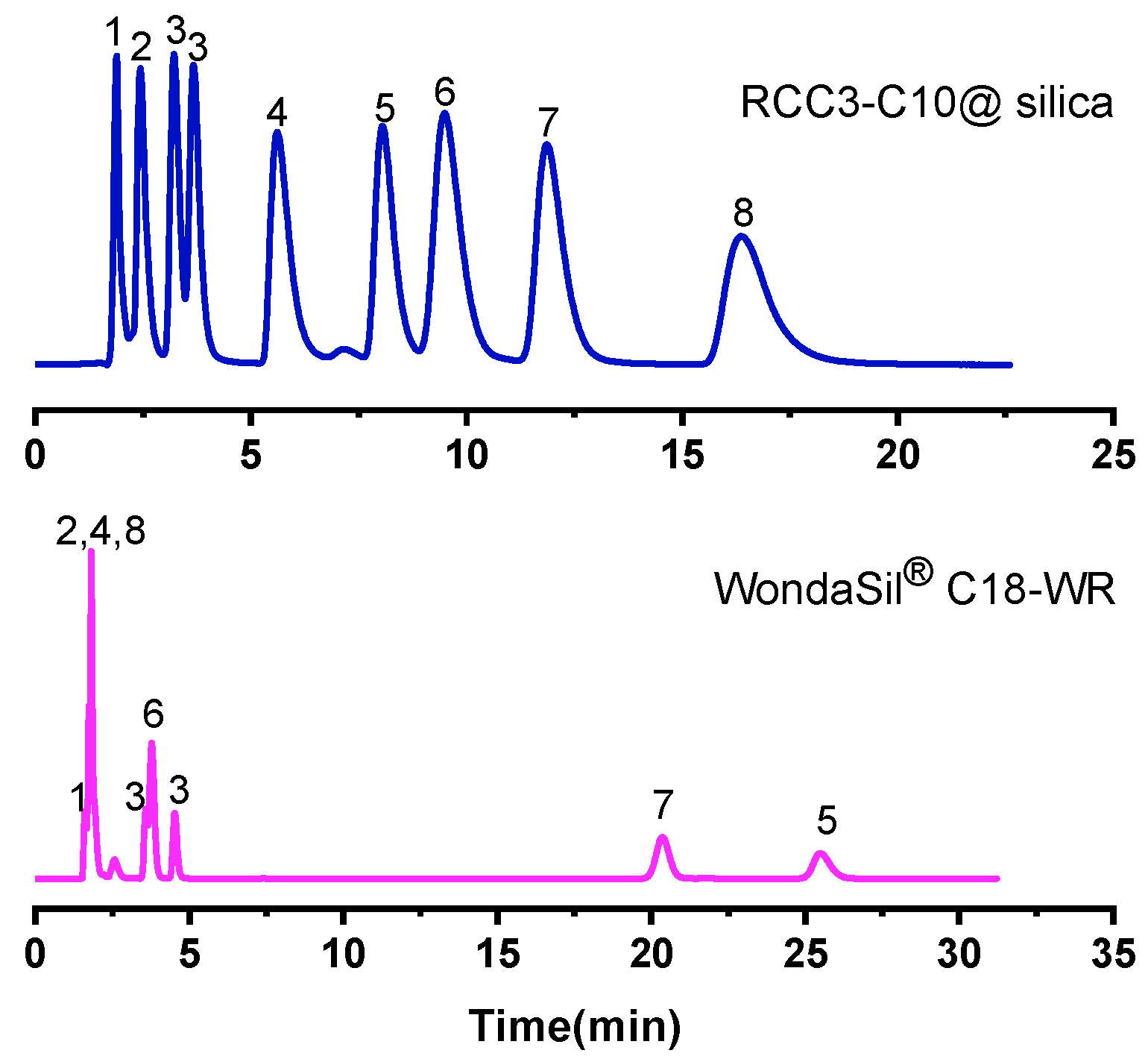
2.2.8. Separation of Complex Mixture
2.3. The Efficiency and Repeatability of RCC3-C10@silica Column
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Preparation of RCC3-C10@silica
3.4. Column Packing
3.5. Sample Preparation and Chromatographic Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jouyban, A.; Sorouraddin, M.H.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Somi, M.H.; Fazeli-Bakhtiyari, R. Determination of five antiarrhythmic drugs in human plasma by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2015, 134, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraji, M. Determination of some red dyes in food samples using a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent-based vortex assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 2019, 1591, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaria, J.; Anupama, K.V.; Nidheesh, P.V. Tetracyclines in the environment: An overview on the occurrence, fate, toxicity, detection, removal methods, and sludge management. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 145291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessens, H.A.; van Straten, M.A. Review on the chemical and thermal stability of stationary phases for reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 2004, 1060, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanganyado, E.; Lu, Z.J.; Fu, Q.G.; Schlenk, D.; Gan, J. Chiral pharmaceuticals: A review on their environmental occurrence and fate processes. Water Res. 2017, 124, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.M.; Yuan, L.M. Recent development trends for chiral stationary phases based on chitosan derivatives, cyclofructan derivatives and chiral porous materials in high performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varfaj, I.; Carotti, A.; Mangiapelo, L.; Cossignani, L.; Taticchi, A.; Macchiarulo, A.; Ianni, F.; Sardella, R. Environmentally Sustainable Achiral and Chiral Chromatographic Analysis of Amino Acids in Food Supplements. Molecules 2022, 27, 7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozawa, T.; Jones, J.T.A.; Swamy, S.I.; Jiang, S.; Adams, D.J.; Shakespeare, S.; Clowes, R.; Bradshaw, D.; Hasell, T.; Chong, S.Y.; et al. Porous organic cages. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasell, T.; Cooper, A.I. Porous organic cages: Soluble, modular and molecular pores. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.I. Porous Molecular Solids and Liquids. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.C.; Sun, J.K.; Kitta, M.; Pang, H.; Xu, Q. Encapsulating highly catalytically active metal nanoclusters inside porous organic cages. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.L.; Jiang, S.; Hasell, T.; Liu, M.; Sun, S.J.; Cheetham, A.K.; Sivaniah, E.; Cooper, A.I. Porous Organic Cage Thin Films and Molecular-Sieving Membranes. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2629–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, J.; Liao, T.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X. Porous organic cage for enantiomeric fluorescence recognition of amino acid and hydroxy acid. Luminescence 2021, 36, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wei, Q.; An, N.; Meng, C.; Hu, Z. Organic Small-Molecule Electrodes: Emerging Organic Composite Materials in Supercapacitors for Efficient Energy Storage. Molecules 2022, 27, 7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.M.; Zhang, J.H.; Yuan, L.M. Enantioseparations by Gas Chromatography Using Porous Organic Cages as Stationary Phase. In Chiral Separations: Methods and Protocols, 3rd ed.; Scriba, G.K.E., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1985, pp. 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.H.; Xie, S.M.; Chen, L.; Wang, B.J.; He, P.G.; Yuan, L.M. Homochiral Porous Organic Cage with High Selectivity for the Separation of Racemates in Gas Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 7817–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Xie, S.M.; Wang, B.J.; He, P.G.; Yuan, L.M. A homochiral porous organic cage with large cavity and pore windows for the efficient gas chromatography separation of enantiomers and positional isomers. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.M.; Zhang, J.H.; Fu, N.; Wang, B.J.; Chen, L.; Yuan, L.M. A chiral porous organic cage for molecular recognition using gas chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 903, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H.; Xie, S.M.; Wang, B.J.; He, P.G.; Yuan, L.M. Highly selective separation of enantiomers using a chiral porous organic cage. J. Chromatogr. 2015, 1426, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zhang, J.; Fu, N.; Wang, B.; Hu, C.; Yuan, L. Application of Homochiral Alkylated Organic Cages as Chiral Stationary Phases for Molecular Separations by Capillary Gas Chromatography. Molecules 2016, 21, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Kong, F.Y.; Fan, D.H.; Wang, W. Porous Organic Cage Embedded C18 Amide Silica Stationary Phase for High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasell, T.; Zhang, H.F.; Cooper, A.I. Solution-Processable Molecular Cage Micropores for Hierarchically Porous Materials. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5732–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.Q.; Zhou, Y.F.; Zhang, F.W.; Cui, Y. A Highly Fluorescent Metallosalalen-Based Chiral Cage for Enantioselective Recognition and Sensing. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 6455–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.Q.; Tan, C.X.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Low, P.J.; Jiang, J.W.; Cui, Y. Chiral NH-Controlled Supramolecular Metallacycles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Ahumada, E.; He, D.L.; Berryman, V.; Lopez-Olvera, A.; Hernandez, M.; Jancik, V.; Martis, V.; Vera, M.A.; Lima, E.; Parker, D.J.; et al. SO2 Capture Using Porous Organic Cages. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 17556–17563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Zhu, P.J.; Xie, S.M.; Zi, M.; Yuan, L.M. Homochiral porous organic cage used as stationary phase for open tubular capillary electrochromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 999, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, R. Carbon dot-decorated porous organic cage as fluorescent sensor for rapid discrimination of nitrophenol isomers and chiral alcohols. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1050, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHale, C.; Soliven, A.; Schuster, S. A simple approach for reversed phase column comparisons via the Tanaka test. Microchem. J. 2021, 162, 105793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Little, M.A.; Jelfs, K.E.; Jones, J.T.A.; Schmidtmann, M.; Chong, S.Y.; Hasell, T.; Cooper, A.I. Acid- and Base-Stable Porous Organic Cages: Shape Persistence and pH Stability via Post-synthetic “Tying” of a Flexible Amine Cage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7583–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
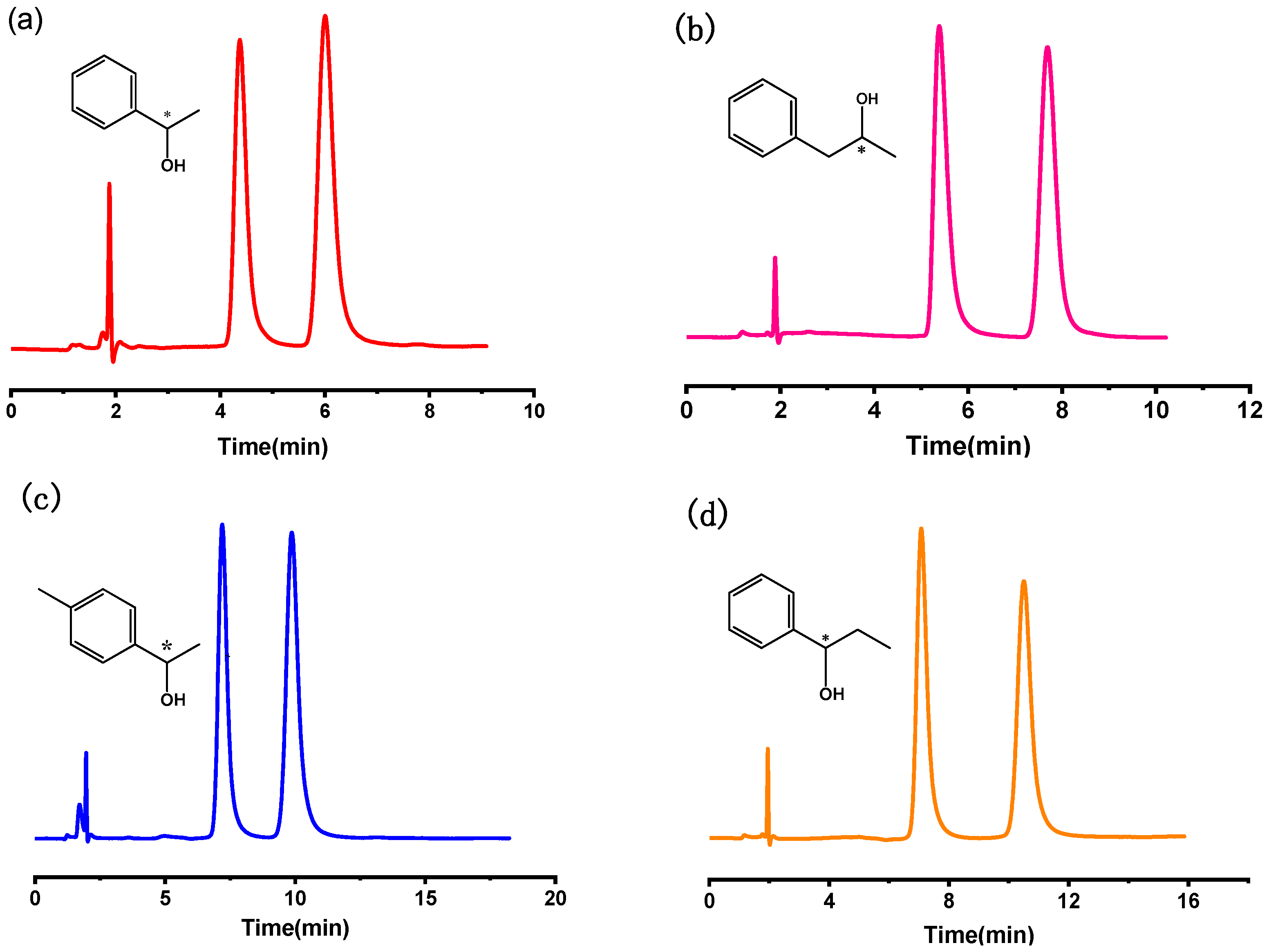

| Solute | k1 | k2 | α | Rs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| phenyl ethanol | 1.32 | 2.19 | 1.66 | 2.95 |
| 1-phenyl-2-propanol | 1.85 | 3.07 | 1.66 | 3.73 |
| p-methyl phenyl-ethanol | 2.34 | 3.58 | 1.53 | 3.27 |
| 1-phenyl-1-propanol | 2.64 | 4.45 | 1.69 | 4.09 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Han, S.; Yu, H.; Yu, Q.; Pei, D.; Lv, W.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Ding, R.; Wang, Q.; et al. Porous Organic Cage-Embedded C10-Modified Silica as HPLC Stationary Phase and Its Multiple Separation Functions. Molecules 2022, 27, 8895. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248895
Wang L, Han S, Yu H, Yu Q, Pei D, Lv W, Wang J, Li X, Ding R, Wang Q, et al. Porous Organic Cage-Embedded C10-Modified Silica as HPLC Stationary Phase and Its Multiple Separation Functions. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8895. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248895
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Litao, Siqi Han, Haiyang Yu, Qinghua Yu, Dong Pei, Wenjing Lv, Jiasheng Wang, Xingyu Li, Ruifang Ding, Qibao Wang, and et al. 2022. "Porous Organic Cage-Embedded C10-Modified Silica as HPLC Stationary Phase and Its Multiple Separation Functions" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8895. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248895
APA StyleWang, L., Han, S., Yu, H., Yu, Q., Pei, D., Lv, W., Wang, J., Li, X., Ding, R., Wang, Q., & Lv, M. (2022). Porous Organic Cage-Embedded C10-Modified Silica as HPLC Stationary Phase and Its Multiple Separation Functions. Molecules, 27(24), 8895. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248895







