Application of HPLC-QQQ-MS/MS and New RP-HPLC-DAD System Utilizing the Chaotropic Effect for Determination of Nicotine and Its Major Metabolites Cotinine, and trans-3′-Hydroxycotinine in Human Plasma Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
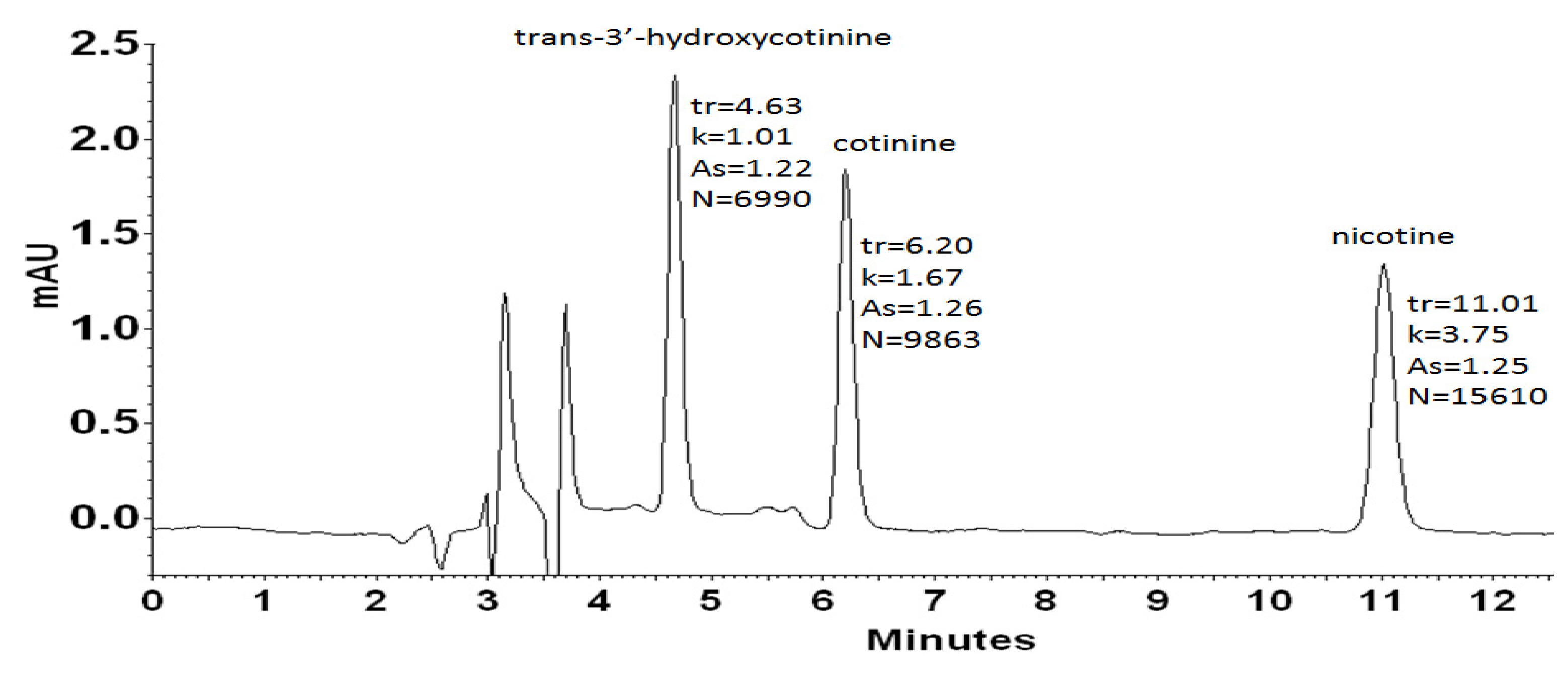
2.1. HPLC-DAD of trans-3′-Hydroxycotinine, Cotinine, Nicotine
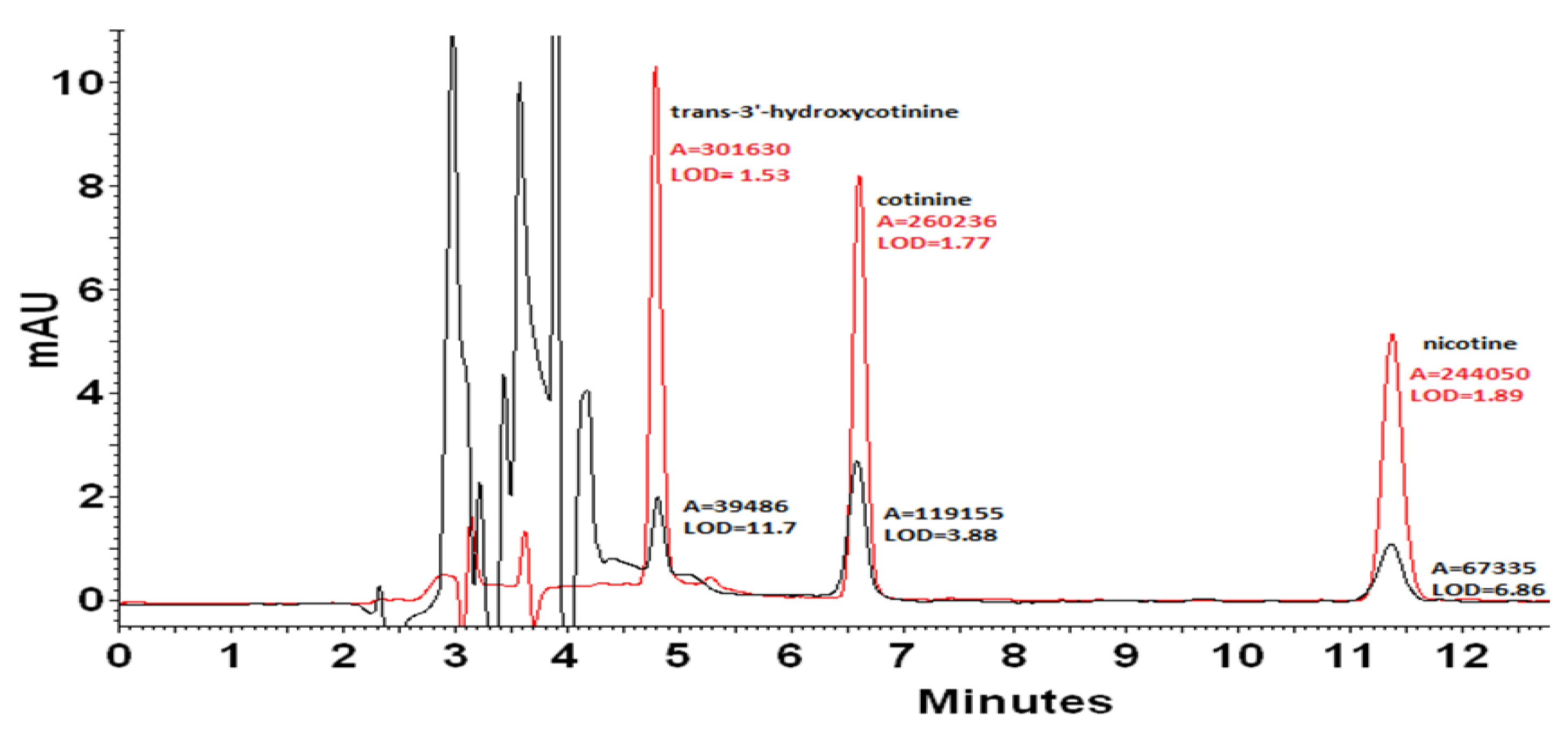
2.1.1. HPLC-DAD Method Validation
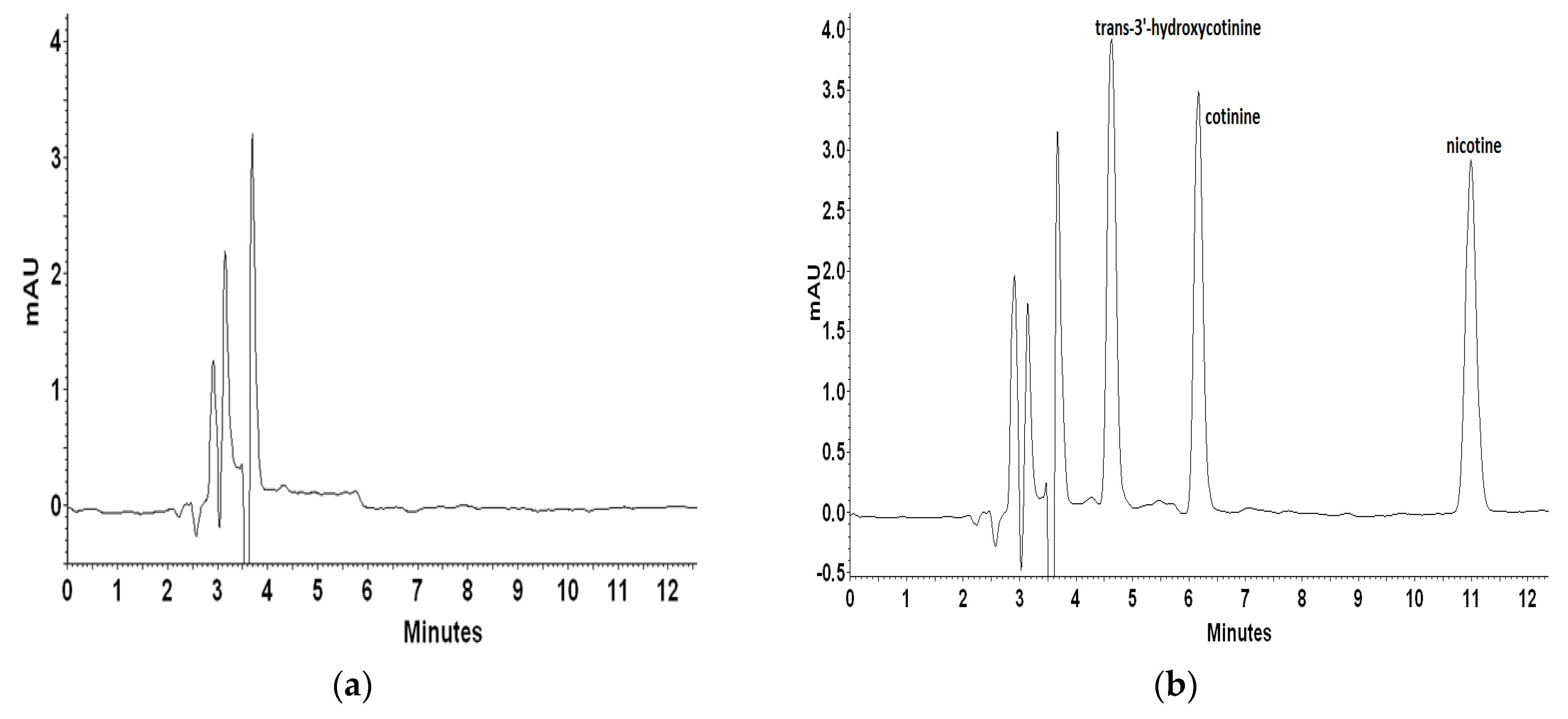
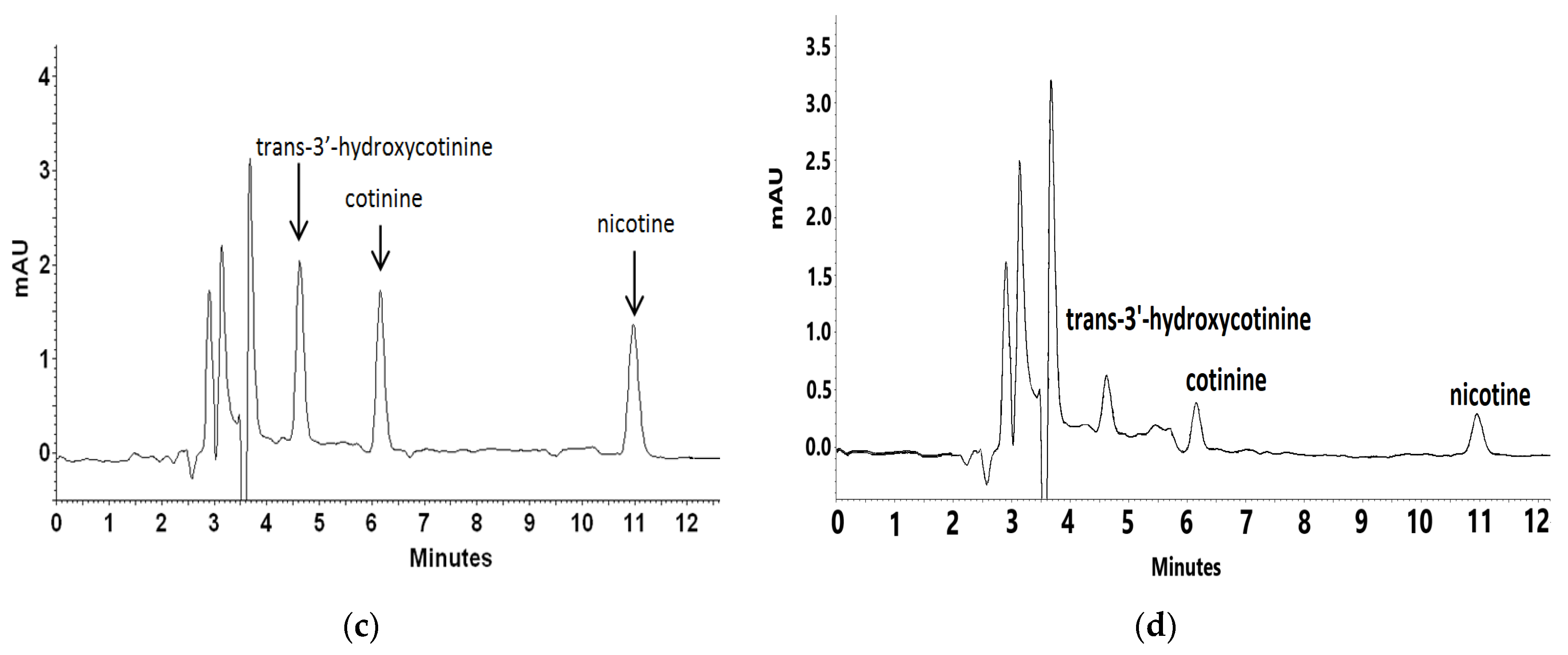
2.1.2. Analysis of Real Plasma Sample from a Tobacco-Smoking Patient
2.2. HPLC-QQQ-MS/MS of trans-3′-Hydroxycotinine, Cotinine, Nicotine
Validation of HPLC-QQQ-MS/MS
2.3. Comparison of the Results Obtained by RP-HPLC-DAD with HPLC-QQQ-MS/MS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Standards and Reagents
4.2. RP-HPLC-DAD Enriched with Chaotropic Salt
4.2.1. Preparation of Stocks and Working Standard Solutions
4.2.2. The Recovery Study
4.2.3. Preparation of the Plasma Samples from the Smoker
4.3. HPLC-QQQ-MS/MS
4.3.1. Apparatus and Detection Conditions
4.3.2. The Calibration Curve Preparation for the MS/MS Method
4.3.3. Method Validation
4.3.4. Sample Preparation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrea, S.; Winterer, G. Neuroprotective and neurotoxic effects of nicotine. Pharmacopsychiatry 2009, 42, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B. How much nicotine kills a human? Tracing back the generally accepted lethal dose to dubious self-experiments in the nineteenth century. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: https://www.rch.org.au/clinicalguide/guideline_index/Nicotine_Poisoning/ (accessed on 31 January 2019).
- Rodgman, A.; Perfetti, T.A. The Chemical Components of Tobacco and Tobacco Smoke, 2nd ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jemal, A.; Thun, M.J.; Ries, L.A.; Howe, H.L.; Weir, H.K.; Center, M.M.; Ward, E.; Wu, X.C.; Eheman, C.; Anderson, R.; et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2005, featuring trends in lung cancer, tobacco use, and tobacco control. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 1672–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic 2009: Implementing Smoke-Free Environments; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic 2021: Addressing New and Emerging Products; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Benowitz, N.L. Pharmacology of nicotine: Addiction, smoking-induced disease, and therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 49, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benowitz, N.L.; Hukkanen, J.; Jacob, P., III. Nicotine chemistry, metabolism, kinetics and biomarkers. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2009, 192, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hukkanen, J.; Jacob, P., III; Benowitz, N.L. Metabolism and disposition kinetics of nicotine. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 79–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yildiz, D. Nicotine, its metabolism and an overview of its biological effects. Toxicon 2004, 43, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, J.A.; Chenoweth, M.J.; Tyndale, R.F. Pharmacogenetics of nicotine and associated smoking behaviors. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 23, 37–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benowitz, N.L. Cotinine as a biomarker of environmental tobacco smoke exposure. Epidemiol. Rev. 1996, 18, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seccareccia, F.; Zuccaro, P.; Pacifici, R.; Meli, P.; Pannozzo, F.; Freeman, K.M.; Santaquilani, A.; Giampaoli, S. Serum cotinine as a marker of environmental tobacco smoke exposure in epidemiological studies: The experience of the MATISS project. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 18, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.E.; Johnson, L.M.; Pullo, D.A. Characterization of multiple products of cytochrome P450 2A6-catalyzed cotinine metabolism. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1999, 12, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Kawka, J.; Tatarczak-Michalewska, M. Levels of the Thiocyanate in the Saliva of Tobacco Smokers in Comparison to e-Cigarette Smokers and Nonsmokers Measured by HPLC on a Phosphatidylcholine Column. Molecules 2019, 24, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haley, N.J.; Hoffmann, D. Analysis for nicotine and cotinine in hair to determine cigarette smoker status. Clin. Chem. 1985, 31, 1598–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machacek, D.A.; Jiang, N.S. Quantification of cotinine in plasma and saliva by liquid chromatography. Clin. Chem. 1986, 32, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, M.A.; Johnson, J.; Jacob, P.; Benowitz, N.L. Cotinine in the serum, saliva, and urine of nonsmokers, passive smokers, and active smokers. Am. J. Public Health 1988, 78, 699–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Lee, D.H.; Park, J.G.; Lee, Y.T.; Chung, J. A sensitive enzyme immunoassay for measuring cotinine in passive smokers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccaro, P.; Altieri, I.; Rosa, M.; Passa, A.R.; Pichini, S.; Ricciarello, G.; Pacifici, R. Determination of nicotine and four metabolites in the serum of smokers by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J. Chromatogr. 1993, 621, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, M.; Ota, T.; Morikawa, A.; Mawatari, K.; Fukuuchi, T.; Yamaoka, N.; Kaneko, K.; Nakagomi, K. Simultaneous determination of nicotine and cotinine in serum using high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorometric detection and postcolumn UV-photoirradiation system. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2013, 934, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avagyan, R.; Spasova, M.; Lindholm, J. Determination of Nicotine-Related Impurities in Nicotine Pouches and Tobacco-Containing Products by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Separations 2021, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Awwad, A.; Arafat, T.; Schmitz, O.J. Simultaneous determination of nicotine, cotinine, and nicotine N-oxide in human plasma, semen, and sperm by LC-Orbitrap MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6473–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, F.; Regenthal, R.; Burgos-Guerrero, I.L.; Hegerl, U.; Preiss, R. Determination of nicotine and cotinine in human serum by means of LC/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, P., III; Yu, L.; Duan, M.; Ramos, L.; Yturralde, O.; Benowitz, N.L. Determination of the nicotine metabolites cotinine and trans-3′-hydroxycotinine in biologic fluids of smokers and non-smokers using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Biomarkers for tobacco smoke exposure and for phenotyping cytochrome P450 2A6 activity. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabr, R.Q.; Elsherbiny, M.E.; Somayaji, V.; Pollak, P.T.; Brocks, D.R. A liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for nicotine and cotinine; utility in screening tobacco exposure in patients taking amiodarone. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2011, 25, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakleya, D.M.; Huestis, M.A. Optimization and validation of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous quantification of nicotine, cotinine, trans-3′-hydroxycotinine and norcotinine in human oral fluid. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2349–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dobrinas, M.; Choong, E.; Noetzli, M.; Cornuz, J.; Ansermot, N.; Eap, C.B. Quantification of nicotine, cotinine, trans-3′-hydroxycotinine and varenicline in human plasma by a sensitive and specific UPLC-tandem mass-spectrometry procedure for a clinical study on smoking cessation. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 3574–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheidweiler, K.B.; Shakleya, D.M.; Huestis, M.A. Simultaneous quantification of nicotine, cotinine, trans-3′-hydroxycotinine, norcotinine and mecamylamine in human urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chazeron, I.; Daval, S.; Ughetto, S.; Richard, D.; Nicolay, A.; Lemery, D.; Llorca, P.M.; Coudoré, F. GC-MS determined cotinine in an epidemiological study on smoking status at delivery. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 21, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Man, C.N.; Gam, L.-H.; Ismail, S.; Lajis, R.; Awang, R. Simple, rapid and sensitive assay method for simultaneous quantification of urinary nicotine and cotinine using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2006, 844, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.; Kushnir, M.M.; Urry, F.M.; Rockwood, A.L. Quantitation of nicotine, its metabolites, and other related alkaloids in urine, serum, and plasma using LC-MS-MS. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 603, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Iba, M.M.; Weisel, C.P. Simultaneous and sensitive measurement of anabasine, nicotine, and nicotine metabolites in human urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- von Weymarn, L.B.; Thomson, N.M.; Donny, E.C.; Hatsukami, D.K.; Murphy, S.E. Quantitation of the Minor Tobacco Alkaloids Nornicotine, Anatabine, and Anabasine in Smokers’ Urine by High Throughput Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghavi, T.; Novalen, M.; Lerman, C.; George, T.P.; Tyndale, R.F. A Comparison of Direct and Indirect Analytical Approaches to Measuring Total Nicotine Equivalents in Urine. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaik, F.B.; Nagajothi, G.; Swarnalatha, K.; Kumar, C.S.; Maddu, N. Quantification of Nicotine and Cotinine in Plasma, Saliva, and Urine by HPLC Method in Chewing Tobacco Users. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2019, 20, 3617–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, E.I.; Norris, H.R.; Rollins, D.E.; Tiffany, S.T.; Wilkins, D.G. A novel validated procedure for the determination of nicotine, eight nicotine metabolites and two minor tobacco alkaloids in human plasma or urine by solid-phase extraction coupled with liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meger, M.; Meger-Kossien, I.; Schuler-Metz, A.; Janket, D.; Scherer, G. Simultaneous determination of nicotine and eight nicotine metabolites in urine of smokers using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 778, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuffey, J.E.; Wei, B.; Bernert, J.T.; Morrow, J.C.; Xia, B.; Wang, L.; Blount, B.C. Validation of a LC-MS/MS method for quantifying urinary nicotine, six nicotine metabolites and the minor tobacco alkaloids—Anatabine and anabasine—In smokers’ urine. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marclay, F.; Saugy, M. Determination of nicotine and nicotine metabolites in urine by hydrophilic interaction chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Potential use of smokeless tobacco products by ice hockey players. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7528–7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Inoue, R.; Yagi, K.; Saito, K. Determination of nicotine, cotinine, and related alkaloids in human urine and saliva by automated in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heavner, D.L.; Richardson, J.D.; Morgan, W.T.; Ogden, M.W. Validation and application of a method for the determination of nicotine and five major metabolites in smokers’ urine by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2005, 19, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Feng, J.; Rehmani, I.J.; Miller, S.; McGuffey, J.E.; Blount, B.C.; Wang, L. A high-throughput robotic sample preparation system and HPLC-MS/MS for measuring urinary anatabine, anabasine, nicotine and major nicotine metabolites. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 436, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, C.; Kosewick, J.; Wang, S. A simple, fast, and sensitive method for the measurement of serum nicotine, cotinine, and nornicotine by LC-MS/MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2394–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, I.; Wang, P. Simultaneous serum nicotine, cotinine, and trans-3′-hydroxycotinine quantitation with minimal sample volume for tobacco exposure status of solid organ transplant patients. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 928, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, G.D.; Davis, R.A.; Ogden, M.W. A rapid LC-MS-MS method for the determination of nicotine and cotinine in serum and saliva samples from smokers: Validation and comparison with a radioimmunoassay method. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2005, 43, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdallah, I.A.; Hammell, D.C.; Stinchcomb, A.L.; Hassan, H.E. A fully validated LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of nicotine and its metabolite cotinine in human serum and its application to a pharmacokinetic study after using nicotine transdermal delivery systems with standard heat application in adult smokers. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1020, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Vardavas, C.I.; Terzi, I.; Kavalakis, M.; Kokkinakis, M.; Liesivuori, J.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Hair nicotine/cotinine concentrations as a method of monitoring exposure to tobacco smoke among infants and adults. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.I.; Murray, G.J.; Rollins, D.E.; Tiffany, S.T.; Wilkins, D.G. Validation of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the detection of nicotine biomarkers in hair and an evaluation of wash procedures for removal of environmental nicotine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2011, 35, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Cho, H.D.; Suh, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, E.; Jin, C.H.; Wang, Y.; Cha, S.; Im, H.; Han, S.B. Analysis of Nicotine Metabolites in Hair and Nails Using QuEChERS Method Followed by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inukai, T.; Kaji, S.; Kataoka, H. Analysis of nicotine and cotinine in hair by on-line in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry as biomarkers of exposure to tobacco smoke. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 156, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetiyanukornkul, T.; Toriba, A.; Kizu, R.; Kimura, K.; Hayakawa, K. Hair analysis of nicotine and cotinine for evaluating tobacco smoke exposure by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2004, 18, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; McGuffey, J.; Xia, Y.; Guillot, T.; McGahee, E.; Wang, L.; Blount, B. Sensitive, Rapid and High Throughput Measurement of Nicotine in Human Serum by Automation and Liquid Chromatography-Atmospheric Pressure Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, B.; Blount, B.C.; Wang, L. Sensitive Quantification of Nicotine in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid by Acetone Precipitation Combined with Isotope-Dilution Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 13962–13969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flieger, J. The effect of chaotropic mobile phase additives on the separation of selected alkaloids in reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1113, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flieger, J.; Czajkowska-Żelazko, A. Comparison of chaotropic salt and ionic liquid as mobile phase additives in reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of biogenic amines. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flieger, J.; Siwek, A.; Pizoń, M. Usefulness of chaotropic salt additive in RP-HPLC of organic nonionized compounds. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, P.; Vas, C.; Bui, T.; Drake, A.; Mcadam, K. Spectroscopic investigations into the acid–base properties of nicotine at different temperatures. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattes, W.; Yang, X.; Orr, M.S.; Richter, P.; Mendrick, D.L. Biomarkers of Tobacco Smoke Exposure. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2014, 67, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, S.; DeStefano, A. Key elements of bioanalytical method validation for small molecules. AAPS J. 2007, 9, E109–E114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, C.T.; Bansal, S.; Booth, B.; DeStefano, A.J.; Rose, M.J.; Sailstad, J.; Shah, V.P.; Skelly, J.P.; Swann, P.G.; Weiner, R. Quantitative bioanalytical methods validation and implementation: Best practices for chromatographic and ligand binding assays. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1962–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Overview of Cotinine Cutoff Values for Smoking Status Classification. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

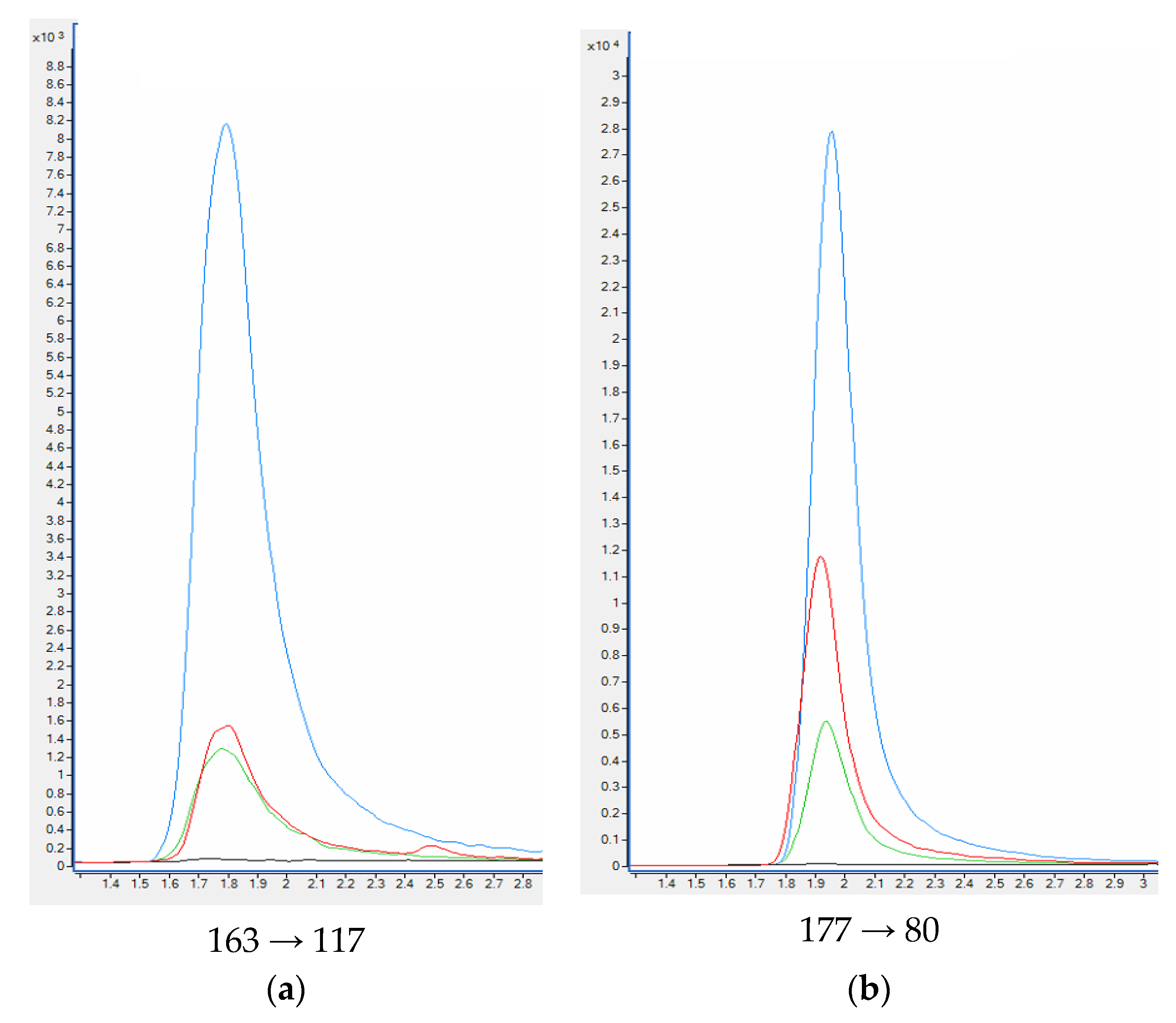
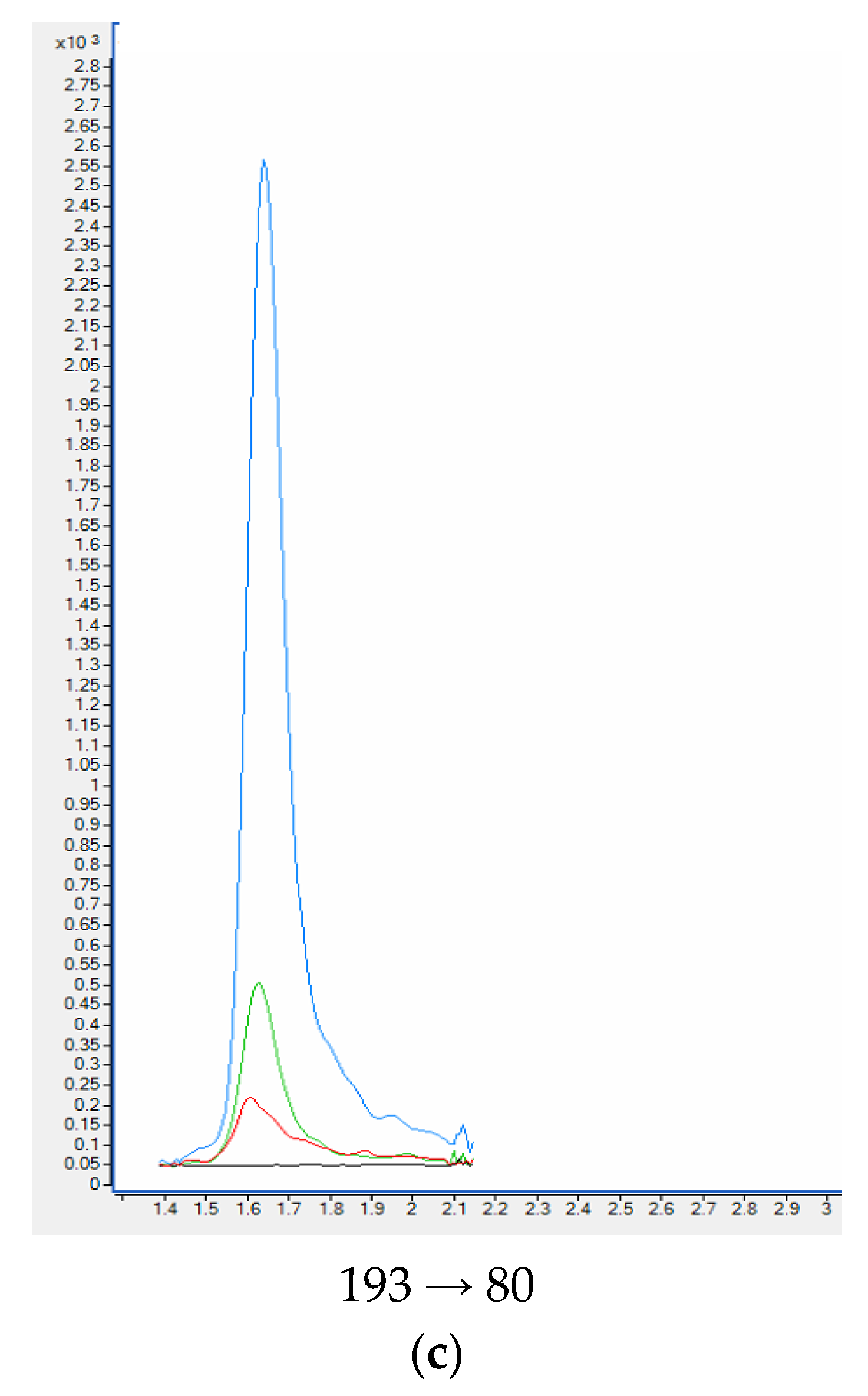
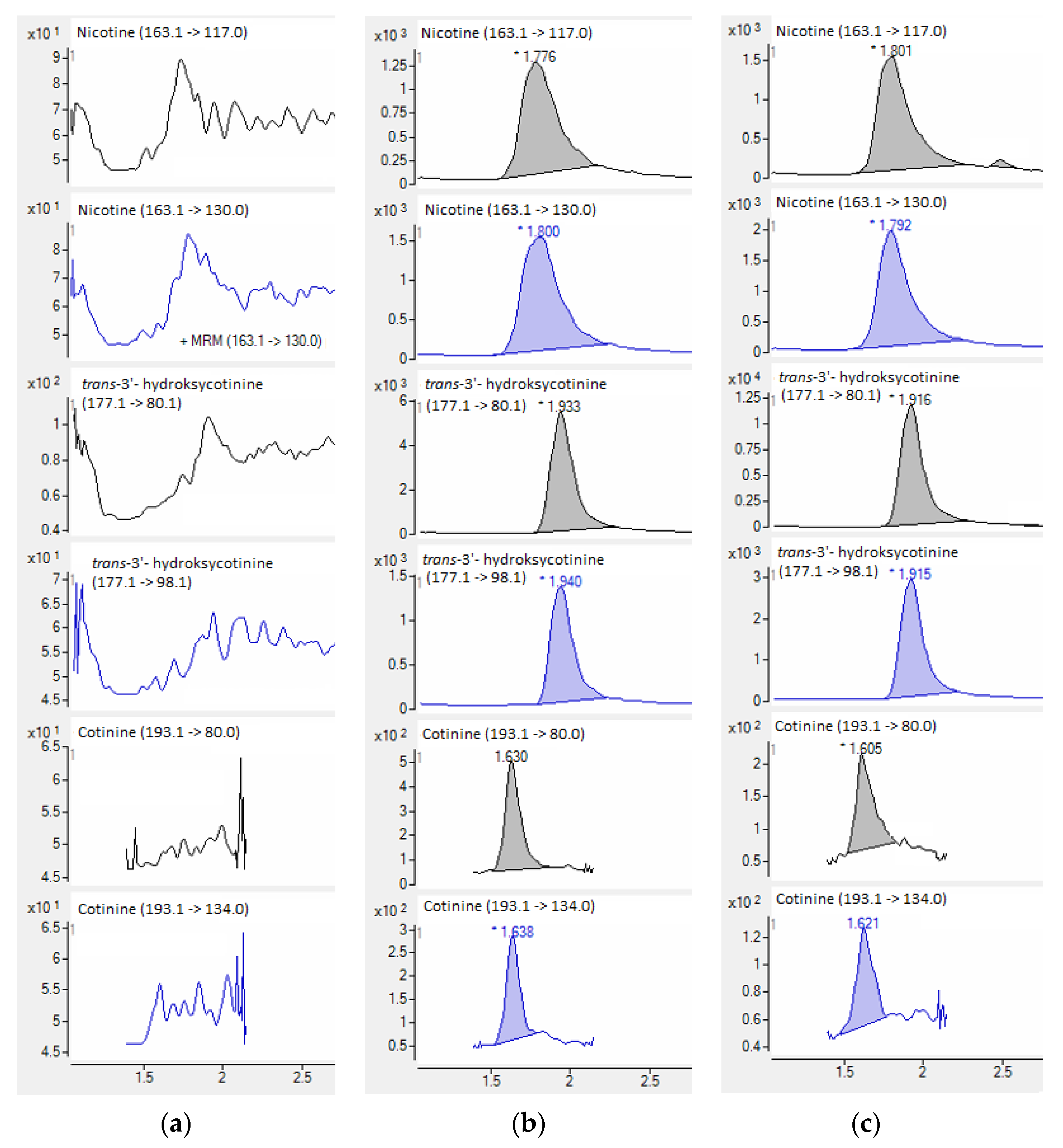
| Compound | Slope (a) ± sa | Intercept (b) ± sb | R2 | se 1 | F 2 | LOD [ng ml−1] | LLOQ [ng ml−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trans-3′-hydroksycotinine | 159.47 ± 3.54 | 2143.35 ± 1962.59 | 0.9980 | 2975.1 | 2024.92 | 1.47 | 4.42 |
| cotinine | 146.14 ± 2.46 | 1238.95 ± 1364.26 | 0.9989 | 2068.1 | 3519.14 | 1.59 | 4.78 |
| nicotine | 153.49 ± 3.44 | 2491.18 ± 1902.49 | 0.9980 | 2884.0 | 1996.34 | 1.50 | 4.51 |
| Compound | Analyte Concentration [ng ml−1] | Intra Day Precision | Inter Day Precision | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extraction Yield [% ± SD] | Repeatability [CV] | Extraction Yield [% ± SD] | Repeatability [CV] | ||
| trans-3′-hydroxcotinine | 100 | 96.02 ± 2.57 | 2.67 | 87.96 ± 3.06 | 3.47 |
| 500 | 102.22 ± 0.53 | 0.52 | 104.61 ± 2.14 | 2.04 | |
| 1000 | 100.04 ± 2.35 | 2.35 | 101.02 ± 1.98 | 1.98 | |
| cotinine | 100 | 93.49 ± 0.32 | 0.34 | 97.40 ± 1.63 | 1.67 |
| 500 | 100.03 ± 1.60 | 1.59 | 102.93 ± 2.00 | 1.95 | |
| 1000 | 98.02 ± 2.71 | 2.76 | 100.37 ± 2.03 | 2.02 | |
| nicotine | 100 | 100.27 ± 3.88 | 3.87 | 112.35 ± 6.31 | 5.61 |
| 500 | 100.68 ± 2.34 | 2.32 | 100.60 ± 0.85 | 0.85 | |
| 1000 | 97.94 ± 2.71 | 2.77 | 94.66 ± 3.10 | 3.28 | |
| Compound | The Calibration Curve | The Plasma Sample [ng mL−1] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Linear Equation | R2 | Conc. in Sample | Conc. in Plasma | SD | |
| Nicotine | y = 267.70 x + 81,194 | 0.9882 | 51.02 | 20.92 | 0.61 |
| Cotinine | y = 132.58 x + 17,314.44 | 0.9999 | 130.62 | 53.55 | 1.48 |
| trans-3′-hydroksycotinine | y = 191.96 x + 3427.33 | 0.9817 | 17.85 | 7.39 | 0.08 |
| Compound | Slope (a) | Intercept (b) | R2 | LOD [ng mL−1] | LOQ [ng mL−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trans-3′-hydroksycotinine | 0.004926 | −0.003564 | 0.9990 | 0.07 | 0.15 |
| cotinine | 0.082795 | 0.017080 | 0.9990 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| nicotine | 0.035986 | −0.061937 | 0.9989 | 0.04 | 0.10 |
| Analyte | Analyte Concentration [ng mL−1] | Recovery % | Intra Day Precision CV% | Inter Day Precision CV% | Smoker’s Plasma Sample | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conc. [ng mL−1] | SD | |||||
| trans-3′-hydroxycotinine | 20 | 81.9% | 2.9% | 4.6% | 7.544 | 0.714 |
| 200 | 96.4% | 1.4% | 5.6% | |||
| cotinine | 20 | 83.2% | 1.3% | 5.1% | 50.180 | 0.551 |
| 200 | 94.8% | 1.3% | 4.5% | |||
| nicotine | 20 | 76.8% | 2.1% | 5.7% | 19.588 | 0.001 |
| 200 | 93.1% | 1.8% | 6.6% | |||
| Compounds | Precursor Ion [m/z] | Product Ion [m/z] | Fragmentor [V] | Collision Energy [V] | Polarity | Retention Time [min.] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trans-3′-hydroxcotinine | 193 | 134 | 144 | 20 | Positive | 1.77 |
| 80 | 28 | |||||
| cotinine | 177 | 98 | 144 | 20 | Positive | 2.13 |
| 80 | 28 | |||||
| cotinine-d3 | 180 | 101 | 116 | 24 | Positive | 2.13 |
| 80 | 28 | |||||
| nicotine | 163 | 130 | 116 | 20 | Positive | 1.79 |
| 117 | 28 | |||||
| nicotine-d4 | 167 | 136 | 116 | 16 | Positive | 1.80 |
| 134 | 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baj, J.; Flieger, W.; Przygodzka, D.; Buszewicz, G.; Teresiński, G.; Pizoń, M.; Maciejewski, R.; Flieger, J. Application of HPLC-QQQ-MS/MS and New RP-HPLC-DAD System Utilizing the Chaotropic Effect for Determination of Nicotine and Its Major Metabolites Cotinine, and trans-3′-Hydroxycotinine in Human Plasma Samples. Molecules 2022, 27, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030682
Baj J, Flieger W, Przygodzka D, Buszewicz G, Teresiński G, Pizoń M, Maciejewski R, Flieger J. Application of HPLC-QQQ-MS/MS and New RP-HPLC-DAD System Utilizing the Chaotropic Effect for Determination of Nicotine and Its Major Metabolites Cotinine, and trans-3′-Hydroxycotinine in Human Plasma Samples. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030682
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaj, Jacek, Wojciech Flieger, Dominika Przygodzka, Grzegorz Buszewicz, Grzegorz Teresiński, Magdalena Pizoń, Ryszard Maciejewski, and Jolanta Flieger. 2022. "Application of HPLC-QQQ-MS/MS and New RP-HPLC-DAD System Utilizing the Chaotropic Effect for Determination of Nicotine and Its Major Metabolites Cotinine, and trans-3′-Hydroxycotinine in Human Plasma Samples" Molecules 27, no. 3: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030682
APA StyleBaj, J., Flieger, W., Przygodzka, D., Buszewicz, G., Teresiński, G., Pizoń, M., Maciejewski, R., & Flieger, J. (2022). Application of HPLC-QQQ-MS/MS and New RP-HPLC-DAD System Utilizing the Chaotropic Effect for Determination of Nicotine and Its Major Metabolites Cotinine, and trans-3′-Hydroxycotinine in Human Plasma Samples. Molecules, 27(3), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030682







