Metabolite Fingerprinting Based on 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Liquid Chromatography for the Authentication of Herbal Products
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
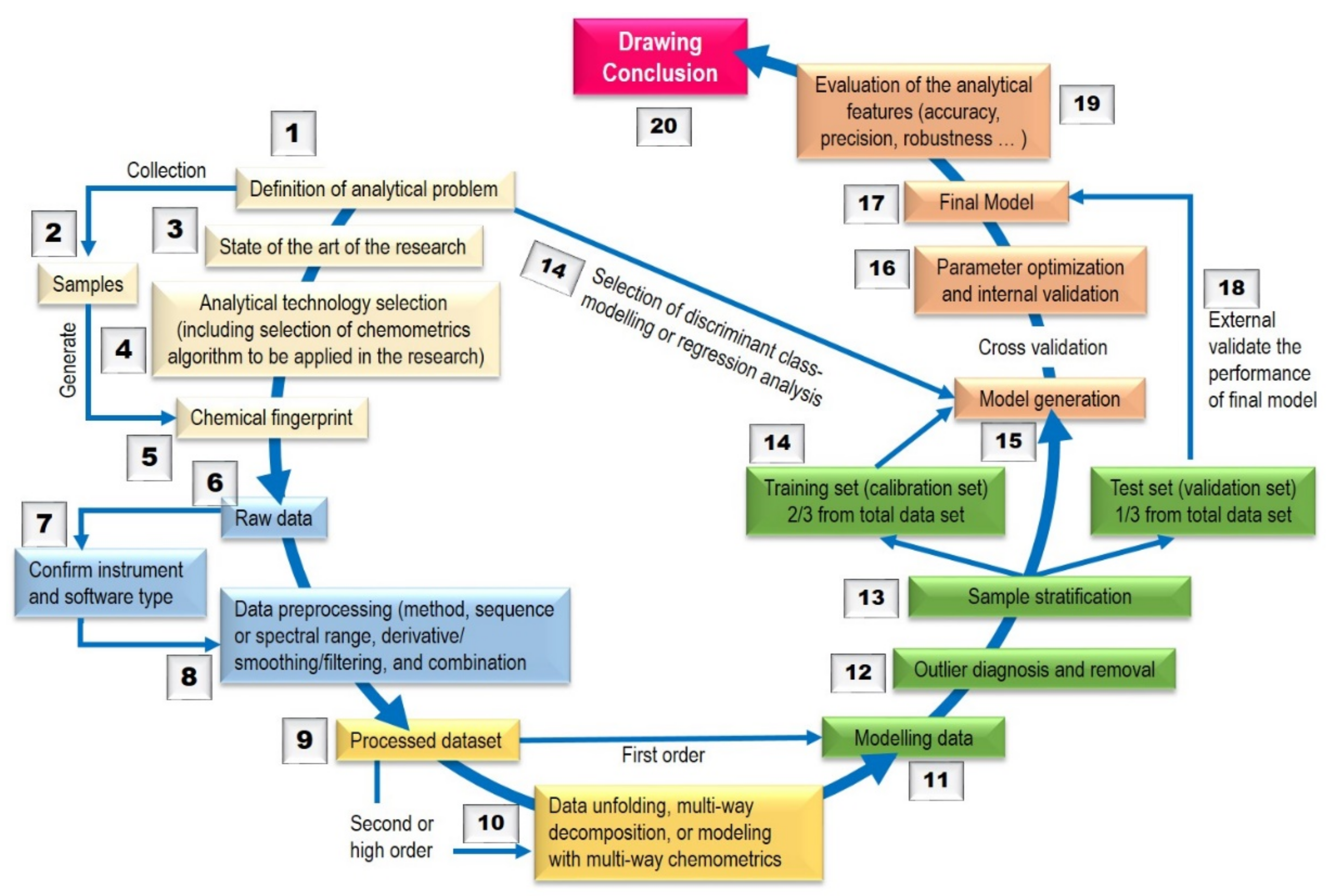
3. Chemometrics
4. Methods for Authentication of Herbal Medicines Using Metabolite Fingerprinting
4.1. Chemical Fingerprinting Using HPLC
4.2. Fingerprinting Using LC–MS/MS
4.3. Metabolite Fingerprinting Using 1H-NMR
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, P.; Yu, Z. Species authentication and geographical origin discrimination of herbal medicines by near infrared spectroscopy: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2015, 5, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indrayanto, G. Recent Development of Quality Control Methods for Herbal Derived Drug Preparations. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, A.; Rawar, E.A.; Sudevi, S.; Nurrulhidayah, A.F.; Windarsih, A. The use of chemometrics in combination with molecular spectroscopic and chromatographic methods for authentication of Curcuma species: A review. Food Res. 2020, 4, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toniolo, C.; Nicoletti, M.; Maggi, F.; Venditti, A. HPTLC determination of chemical composition variability in raw materials used in botanicals. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yao, C.-L.; Guo, D.-A. Quality assessment of herbal medicines based on chemical fingerprints combined with chemometrics approach: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 185, 113215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Puyana, M.; Pérez-Míguez, R.; Montero, L.; Herrero, M. Reprint of: Application of mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approaches for food safety, quality and traceability. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 96, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwakusumah, E.D.; Rafi, M.; Safitri, U.D.; Nurcholis, W.; Adzkiya, M.A.Z. Identification and Authentication of Jahe Merah Using Combination of FTIR Spectrocopy and Chemometrics. J. Agritech. 2014, 34, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.P.; Ketkar, P.; Nayak, S.; Roy, S. Application of DNA fingerprinting tools for authentication of ayurvedic herbal medicines-A review. J. Sci. Innov. Res. JSIR 2014, 3, 606–612. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Kuzmina, M.L.; Braukmann, T.W.A.; Borisenko, A.V.; Zakharov, E.V. Authentication of Herbal Supplements Using Next-Generation Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156426-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, M. HPTLC fingerprint: A modern approach for the analytical determination of botanicals. Rev. Bras. de Farm. 2011, 21, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, S.; Abdulla, R.; Ayupbec, A.; Aisa, H.A. Chemical Fingerprint Analysis and Quantitative Analysis of Rosa rugosa by UPLC-DAD. Molecules 2016, 21, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, C.-S.; Shin, H.-K. Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Simultaneous Quantification of Eleven Phytochemical Constituents in Traditional Korean Medicine, Sogunjung Decoction. Processes 2021, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, A.; Windarsih, A.; Hossain, M.A.M.; Johan, M.R.; Ali, M.E.; Fadzilah, N.A. Application of near- and mid-infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics for discrimination and authentication of herbal products: A review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 9, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, I.A.; Andrási, M.; Sârbu, C. Chemometric Assessment of Chromatographic Methods for Herbal Medicines Authentication and Fingerprinting. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 56, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, B.M.; Salleh, F.M.; Omar, M.S.S.; Wagiran, A. Review: DNA Barcoding and Chromatography Fingerprints for the Authentication of Botanicals in Herbal Medicinal Products. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1352948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joos, S.; Glassen, K.; Musselmann, B. Herbal Medicine in Primary Healthcare in Germany: The Patient's Perspective. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 294638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunle, O.F.; Egharevba, H.O.; Ahmadu, P.O. Standardization of herbal medicines-A review. Int. J. Biodivers. Conserv. 2012, 4, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M. Quality and safety of herbal medical products: Regulation and the need for quality assurance along the value chains. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J. Quality, efficacy and safety of complementary medicines: Fashions, facts and the future. Part I. Regulation and quality. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 55, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodeker, G.; Ong, C.-K.; Grundy, C.; Burford, G.; Shein, K. WHO Global Atlas of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicine; WHO Centre for Health Development: Kobe, Japan.
- Georgiev, C.; Damianov, D.; Iliev, I.; Todorov, T.; Boshnakova, T. Mutsinozni kartsinomi na g’rdata s nevroendokrinna diferentsiatsiia. Khirurgiia 1999, 55, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.-Z.; Xie, P.; Chan, K. Quality control of herbal medicines. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 812, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananto, D.; Yusditia, L.; Wahyu, L. Analysis of BKO (chemical drugs) Content (Antalgin and Dexamethasone) in Herbal Medicine Using Iodimetry Titration and HPLC Method. Elkawnie J. Islamic Sci. Technol. 2020, 6, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, S.A.; Cunningham, D.G.; Marles, R.J. Assessment of herbal medicinal products: Challenges, and opportunities to increase the knowledge base for safety assessment. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 243, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Pang, X.; Liao, B.; Yao, H.; Song, J.; Chen, S. An authenticity survey of herbal medicines from markets in China using DNA barcoding. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, K.M.; Patil, L.S.; Khanvilkar, V.V.; Kadam, V.J. Fingerprinting Techniques in Herbal Standardization. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 4, 1049–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Gad, H.A.; El-Ahmady, S.; Abou-Shoer, M.I.; Al-Azizi, M.M. Application of Chemometrics in Authentication of Herbal Medicines: A Review. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 24, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Venditti, A.; Foddai, S.; Toniolo, C.; Nicoletti, M. A new problem. Contamination of botanicals by phthalates. Rapid detection tests. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 28, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, A.; Nugroho, A.; Lukitaningsih, E. Sudjadi Application of Vibrational Spectroscopy in Combination with Chemometrics Techniques for Authentication of Herbal Medicine. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2014, 49, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikam, P.H.; Kareparamban, J.; Jadhav, A.; Kadam, V.; Jadhav, A. Future Trends in Standardization of Herbal Drugs. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 2, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yang, H.; Qi, L.-W.; Liu, E.-H.; Ren, M.-T.; Yan, Y.-T.; Chen, J.; Li, P. Unbiased metabolite profiling by liquid chromatography–quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and multivariate data analysis for herbal authentication: Classification of seven Lonicera species flower buds. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1245, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, A.; Putri, A.R. The Chemometrics Techniques in Combination with Instrumental Analytical Methods Applied in Halal Authentication Analysis. Indones. J. Chem. 2019, 19, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Su, R.; Ruan, G.; Du, F.; Li, G. Current application of chemometrics in traditional Chinese herbal medicine research. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1026, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irnawati, I.; Riswanto, F.D.O.; Riyanto, S.; Martono, S. Pemanfaatan Paket Perangkat Lunak R factoextra dan FactoMineR serta Aplikasi Analisis Komponen Utama dalam Autentikasi Beragam Jenis Minyak The use of software package of R factoextra and FactoMineR and its application in Principal componenet analysis for authentication of oils. Indones. J. Chemom. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Fan, X.; Cheng, Y.; Agarwal, R.; Moore, C.M.V.; Chen, S.T.; Tong, W. Chemometric Analysis for Identification of Botanical Raw Materials for Pharmaceutical Use: A Case Study Using Panax notoginseng. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Rutledge, D.N.; Roßmann, A.; Waiblinger, H.-U.; Mahler, M.; Ilse, M.; Kuballa, T.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Determination of rice type by1H NMR spectroscopy in combination with different chemometric tools. J. Chemom. 2014, 28, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuchote, C.; Somwong, P. Similarity analysis of the chromatographic fingerprints of Thai herbal Ya-Ha-Rak remedy using HPLC. Interprof. J. Health Sci. 2019, 17, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Berrueta, L.A.; Salces, R.M.A.; Héberger, K. Supervised pattern recognition in food analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1158, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.H.; Shao, Y.W. Classification of Chinese Herbal Medicine Based on Improved LDA Algorithm Using Machine Olfaction. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 239–240, 1532–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Tongkao-On, W.; Kimble, B.; Qiao, V.L.; Beilun, L.; Li, K.M.; Roufogalis, B.; Depo, Y.; Meicun, Y.; Li, G.Q. Multiple Chromatographic and Chemometric Methods for Quality Standardisation of Chinese Herbal Medicines. World Sci. Technol. 2010, 12, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.S.; Pereira-Filho, E.R.; Ferreira, A.G.; Boffo, E.F.; Figueira, G.M. Authenticity study of Phyllanthus species by NMR and FT-IR Techniques coupled with chemometric methods. Quim. Nova 2012, 35, 2210–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Hu, Y. Non-Negative Matrix Factorization-Based SIMCA Method to Classify Traditional Chinese Medicine by HPLC Fingerprints. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2011, 49, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Onel, H. Machine Learning Basics with the K-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm Medium. 2018. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/machine-learning-basics-with-the-k-nearest-neighbors-algorithm-6a6e71d01761 (accessed on 17 November 2021).
- Samui, P.; Kothari, D.P. Utilization of a least square support vector machine (LSSVM) for slope stability analysis. Sci. Iran. 2011, 18, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, J.; Esslinger, S.; Fauhl-Hassek, C. Review of validation and reporting of non-targeted fingerprinting approaches for food authentication. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 885, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lestari, H.P.; Martono, S.; Wulandari, R.; Rohman, A. Simultaneous analysis of Curcumin and demethoxycurcumin in Curcuma xanthorriza using FTIR spectroscopy and chemometrics. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Esslinger, S.; Riedl, J.; Fauhl-Hassek, C. Potential and limitations of non-targeted fingerprinting for authentication of food in official control. Food Res. Int. 2014, 60, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszykowski, M.; Walczak, B. Use and abuse of chemometrics in chromatography. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2006, 25, 1081–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharyuk, P.; Nazarenko, D.; Oseledets, I.; Rodin, I.; Shpigun, O.; Tsitsilin, A.; Lavrentyev, M. Employing fingerprinting of medicinal plants by means of LC-MS and machine learning for species identification task. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.N.; Jha, Z.; Sharma, D.K. Chemometrics Evaluation of the Herbal Drug Andrographis paniculata. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1929–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, G.; Fahmi, H.; Liam, T.; Ali, M.A.; Adibah, F.; Majid, A.; Roji, M. Development of HPLC Fingerprint Analysis of Traditional Diabetes Herbal. J. Teknol. Sci. Eng. 2014, 68, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Habibie, H.; Heryanto, R.; Rafi, M.; Darusman, L.K. Development of Quality Control Method for Glucofarmaka Antidiabetic Jamu by HPLC Fingerprint Analysis. Indones. J. Chem. 2017, 17, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balekundri, A.; Mannur, V. Quality control of the traditional herbs and herbal products: A review. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, C.-S.; Shin, H.-K. Quality assessment of traditional herbal formula, Hyeonggaeyeongyo-tang through simultaneous determination of twenty marker components by HPLC–PDA and LC–MS/MS. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windarsih, A.; Rohman, A.; Swasono, R.T. Application of H-NMR metabolite fingerprinting and chemometrics for the authentication of Curcuma longa adulterated with Curcuma manga. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 8, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windarsih, A.; Rohman, A.; Swasono, R.T. Authentication of turmeric using proton-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2018, 10, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, A.; Wijayanti, T.; Windarsih, A.; Riyanto, S. The Authentication of Java Turmeric (Curcuma xanthorrhiza) Using Thin Layer Chromatography and 1H-NMR Based-Metabolite Fingerprinting Coupled with Multivariate Analysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windarsih, A.; Rohman, A.; Swasono, R.T. Application of 1H-NMR based metabolite fingerprinting and chemometrics for authentication of Curcuma longa adulterated with C. heyneana. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2019, 13, 100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, M.; Ren, X.; Jiang, M.; Deng, Y. Rapid authentication and differentiation of herbal medicine using 1H NMR fingerprints coupled with chemometrics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 160, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, E.A.; Cagliani, L.R.; Polissiou, M.G.; Consonni, R. Evaluation of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) adulteration with plant adulterants by 1H NMR metabolite fingerprinting. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Martínez, E.; Florentino-Ramos, E.; Pérez-Hernández, N.; Zepeda-Vallejo, L.G.; Villa-Ruano, N.; Velázquez-Ponce, M.; García-Mendoza, F.; Bañuelos-Hernández, A.E. 1 H NMR-based metabolomic fingerprinting to determine metabolite levels in serrano peppers (Capsicum annum L.) grown in two different regions. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, M.; Kim, B.H.; Ahn, S. Identification of the Geographical Origin of Asian Red Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Powders Using 1 H NMR Spectroscopy. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2020, 41, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Pérez, A.; Romero-González, R.; Frenich, A.G. A metabolomics approach based on 1H NMR fingerprinting and chemometrics for quality control and geographical discrimination of black pepper. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 105, 104235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.; Laserna, A.K.C.; Li, S.F.Y. 1H NMR-based metabolomics for the discrimination of celery (Apium graveolens L. var. dulce) from different geographical origins. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmi, F.; Nguyen, A.T.; Nacoulma, A.P.; Sheridan, H.; Wang, J.; Guendouze, N.; Madani, K.; Duez, P. Discrimination of Mentha species grown in different geographical areas of Algeria using 1H-NMR-based metabolomics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 189, 113430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M.A.; Labib, R.M.; Noleto, C.; Porzel, A.; Wessjohann, L.A. NMR approach for the authentication of 10 cinnamon spice accessions analyzed via chemometric tools. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 90, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviano, G.; Paris, D.; Melck, D.; Fantasma, F.; Motta, A.; Iorizzi, M. Metabolite variation in three edible Italian Allium cepa L. by NMR-based metabolomics: A comparative study in fresh and stored bulbs. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurani, L.H.; Rohman, A.; Windarsih, A.; Guntarti, A.; Riswanto, F.D.O.; Lukitaningsih, E.; Fadzillah, N.A.; Rafi, M. Metabolite Fingerprinting Using 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Chemometrics for Classification of Three Curcuma Species from Different Origins. Molecules 2021, 26, 7626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandusky, P.; Raftery, D. Use of Selective TOCSY NMR Experiments for Quantifying Minor Components in Complex Mixtures: Application to the Metabonomics of Amino Acids in Honey. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditti, A.; Frezza, C.; Maggi, F.; Lupidi, G.; Bramucci, M.; Quassinti, L.; Giuliani, C.; Cianfaglione, K.; Papa, F.; Serafini, M.; et al. Phytochemistry, micromorphology and bioactivities of Ajuga chamaepitys (L.) Schreb. (Lamiaceae, Ajugoideae): Two new harpagide derivatives and an unusual iridoid glycosides pattern. Fitoterapia 2016, 113, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditti, A.; Frezza, C.; Celona, D.; Sciubba, F.; Foddai, S.; Delfini, M.; Serafini, M.; Bianco, A. Phytochemical comparison with quantitative analysis between two flower phenotypes of Mentha aquatica L.: Pink-violet and white. AIMS Mol. Sci. 2017, 4, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, P.; Kruger, N.J.; Ratcliffe, R.G. Metabolite fingerprinting and profiling in plants using NMR. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 56, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, N.J.; Troncoso-Ponce, M.A.; Ratcliffe, R.G. 1H NMR metabolite fingerprinting and metabolomic analysis of perchloric acid extracts from plant tissues. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No. | Instruments | Chemometrics Techniques | Sample | Brief Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HPLC, UPLC, NIR, and CE | PCA and HCA | Panax notoginseng | Identification of Panax notoginseng can be performed using a combination of analytical chemistry methods and chemometrics techniques. | [33] |
| 2 | HPLC | PCA and SIMCA | Andrographis paniculata Nees | A. paniculata from different origins were successfully classified using SIMCA based on the predefined PCA model. | [51] |
| 3 | UPLC-DAD | N/A | Rosa rugosa | Authentication of Rosa rugosa was carried out and 23 characteristic fingerprint peaks were verified. | [10] |
| 4 | HPLC | N/A | Andrographis paniculata, Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Curcuma xanthorrhiza, Eugenia polyantha, and Orthosiphon stamineus | HPLC fingerprint analysis can be applied for the quality control method for glucofarmaka antidiabetic jamu. | [52,53] |
| 5 | LC–MS/MS | N/A | The Sogunjung decoction (Korean traditional medicine) | Eleven marker components in the Sogunjung decoction were detected in amounts of 0.01–51.83 mg/g. | [54] |
| 6 | HPLC-PDA and LC–MS/MS | N/A | Hyeonggaeyeongyo-tang (Korean traditional medicine) | The amounts of 20 marker components using HPLC–PDA and LC–MS/MS were determined to be 0.18–14.60 and 0.01–1.76 mg/freeze-dried g, respectively. | [55] |
| 7 | RRLC–ESI/QTOF MS | PCA and SVM | Lonicera species | Seven Lonicera species flower buds were classified with six marker compounds. | [31] |
| 8 | 1H-NMR | PLSA–DA, OPLSA–DA, and PLS | Curcuma longa, Curcuma heyneana, and Curcuma manga | The authentic C. longa samples were successfully separated from the adulterated samples with the good and accurate calibration chemometrics models. | [56,57] |
| 9 | 1H-NMR | PCA and OPLSA–DA | Curcuma xanthorrhiza and Curcuma aeruginosa | The acceptable discrimination parameters were achieved with a high value of R2X, R2Y and Q2(cum). | [58,59] |
| 10 | 1H-NMR | PCA, PLSA–DA, and N-nearest neighbors (N3) | Polygoni multiflori Radix, and Cynanchi auriculati Radix | In total, 70.99% data contributions were involved in the PCA model. PLSA–DA and N3 were effective to employ the authentication stage. | [60] |
| 11 | 1H-NMR | PCA and O2PLSA–DA | Crocus sativus (Saffron) | Metabolites of pirocrocin (1.12, 1.16, 2.08, 4.28, and 10.04 ppm) and crocins (1.96, 4.16, 5.40, 6.52, 6.64, 6.84, and 7.32 ppm) were found higher in authentic Saffron samples. | [61] |
| 12 | 1H-NMR | PCA and OPLSA–DA | Capsicum annum L. (serrano pepper) | Metabolites of citrate, lactate, aspartate, leucine, and sucrose in serrano peppers were successfully identified and classified. | [62] |
| 13 | 1H-NMR | CDA | Capsicum annuum L. | Korean, Chinese, and Vietnamese red pepper powders were successfully differentiated. | [63] |
| 14 | 1H-NMR | OPLSA–DA | Pepper nigrum L. (black pepper) | PCA was used to differentiate piperine samples from Srilanka, Brazil, and Vietnam. OPLSA–DA model using CD3OD resulted in the value of R2X (0.977), R2Y (0.962), and Q2 (0.928). | [64] |
| 15 | 1H-NMR | PCA and PLSA–DA | Apium graveolens L. var. dulce | All samples were correctly classified without misclassification, indicating a good performance of the OPLSA–DA model. | [65] |
| 16 | 1H-NMR | PCA and OPLSA–DA | Mentha species | Three species of Mentha were classified with good predictive ability (Q2 = 0.978). | [66] |
| 17 | 1H-NMR | PCA and OPLSA–DA | Cinanmomum verum and Cinnamomum cassia | Eugenol was found to be a potential biomarker of Cinnamomum verum, whereas the presence of fatty acids was found as a potential biomarker of Cinnamomum cassia. | [67] |
| 18 | 1H-NMR | PCA and OPLSA–DA | Allium cepa L. | White onion was characterized by the presence of glucose, sucrose, FOS, and sterols, whereas the red onion contained sterols and glucose. Important metabolites in yellow onion were methiin, free isoalliin, γ-glutamyl-isoalliin, glutamine, malate, and choline. | [68] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riswanto, F.D.O.; Windarsih, A.; Lukitaningsih, E.; Rafi, M.; Fadzilah, N.A.; Rohman, A. Metabolite Fingerprinting Based on 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Liquid Chromatography for the Authentication of Herbal Products. Molecules 2022, 27, 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041198
Riswanto FDO, Windarsih A, Lukitaningsih E, Rafi M, Fadzilah NA, Rohman A. Metabolite Fingerprinting Based on 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Liquid Chromatography for the Authentication of Herbal Products. Molecules. 2022; 27(4):1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041198
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiswanto, Florentinus Dika Octa, Anjar Windarsih, Endang Lukitaningsih, Mohamad Rafi, Nurrulhidayah A. Fadzilah, and Abdul Rohman. 2022. "Metabolite Fingerprinting Based on 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Liquid Chromatography for the Authentication of Herbal Products" Molecules 27, no. 4: 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041198
APA StyleRiswanto, F. D. O., Windarsih, A., Lukitaningsih, E., Rafi, M., Fadzilah, N. A., & Rohman, A. (2022). Metabolite Fingerprinting Based on 1H-NMR Spectroscopy and Liquid Chromatography for the Authentication of Herbal Products. Molecules, 27(4), 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27041198









