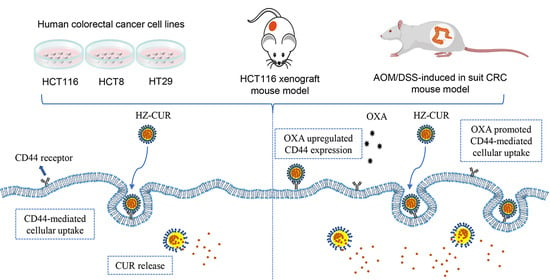
Hyaluronic Acid–Zein Core-Shell Nanoparticles Improve the Anticancer Effect of Curcumin Alone or in Combination with Oxaliplatin against Colorectal Cancer via CD44-Mediated Cellular Uptake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
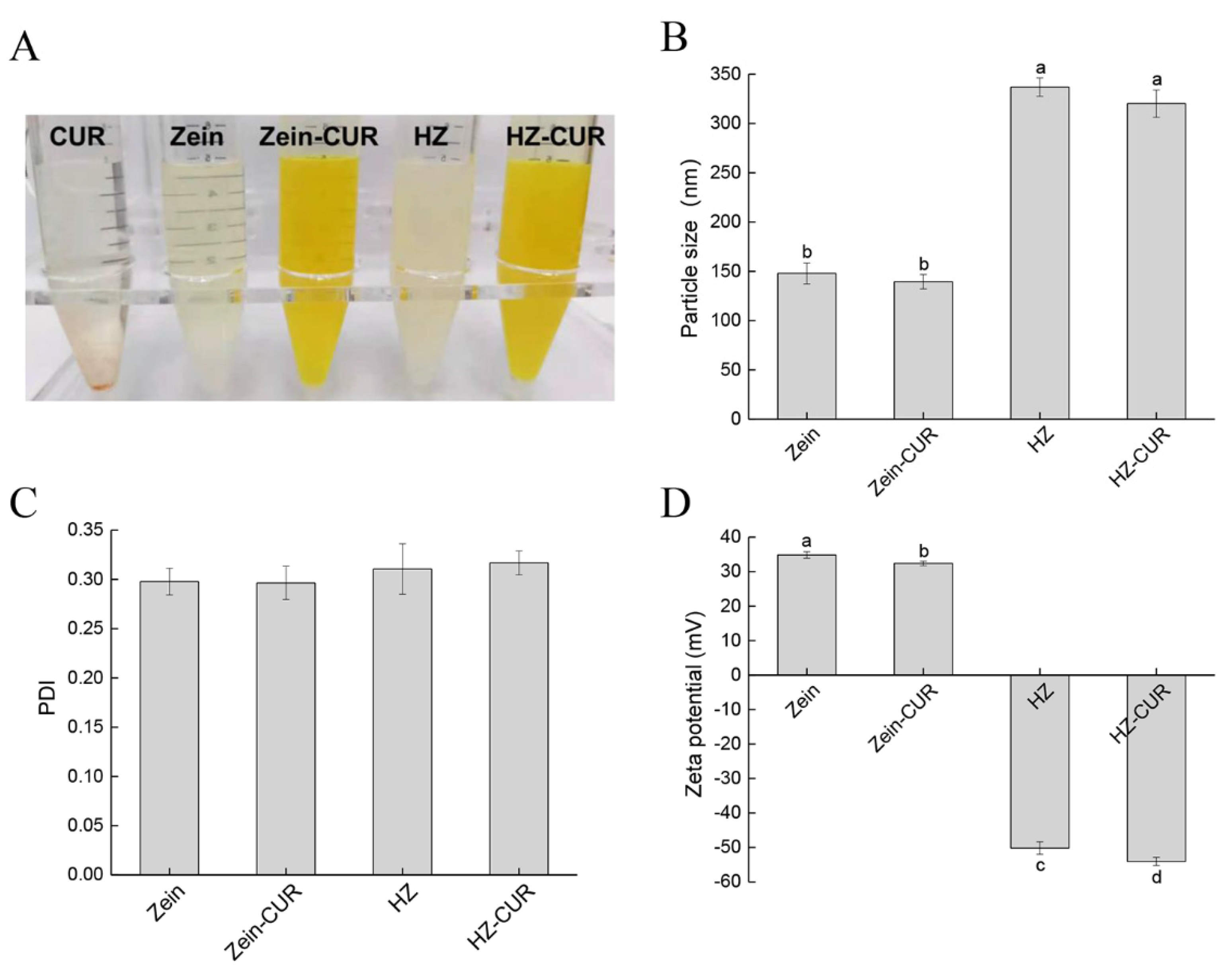
2.1. Characterization of Blank and CUR-Loaded Nanoparticles
2.2. Synergistic Effect of HZ-CUR in Combination with OXA in CRC Cells
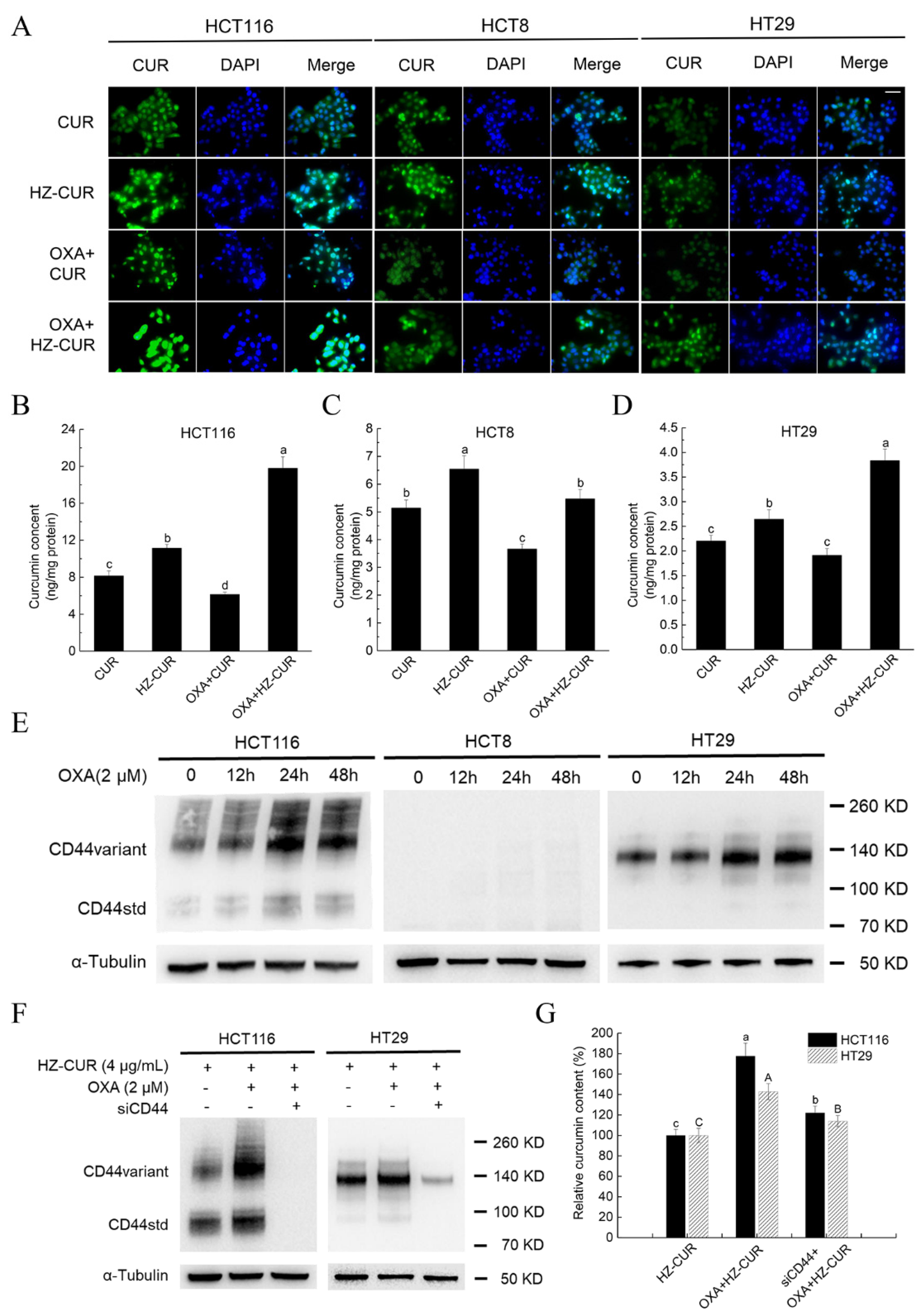
2.3. OXA Promotes Cellular Uptake of HZ-CUR via Upregulation of CD44
2.4. Anti-Tumor Effect of Plain CUR and HZ-CUR Alone and in Combination with OXA in a Subcutaneous CRC Xenograft Model in Mice
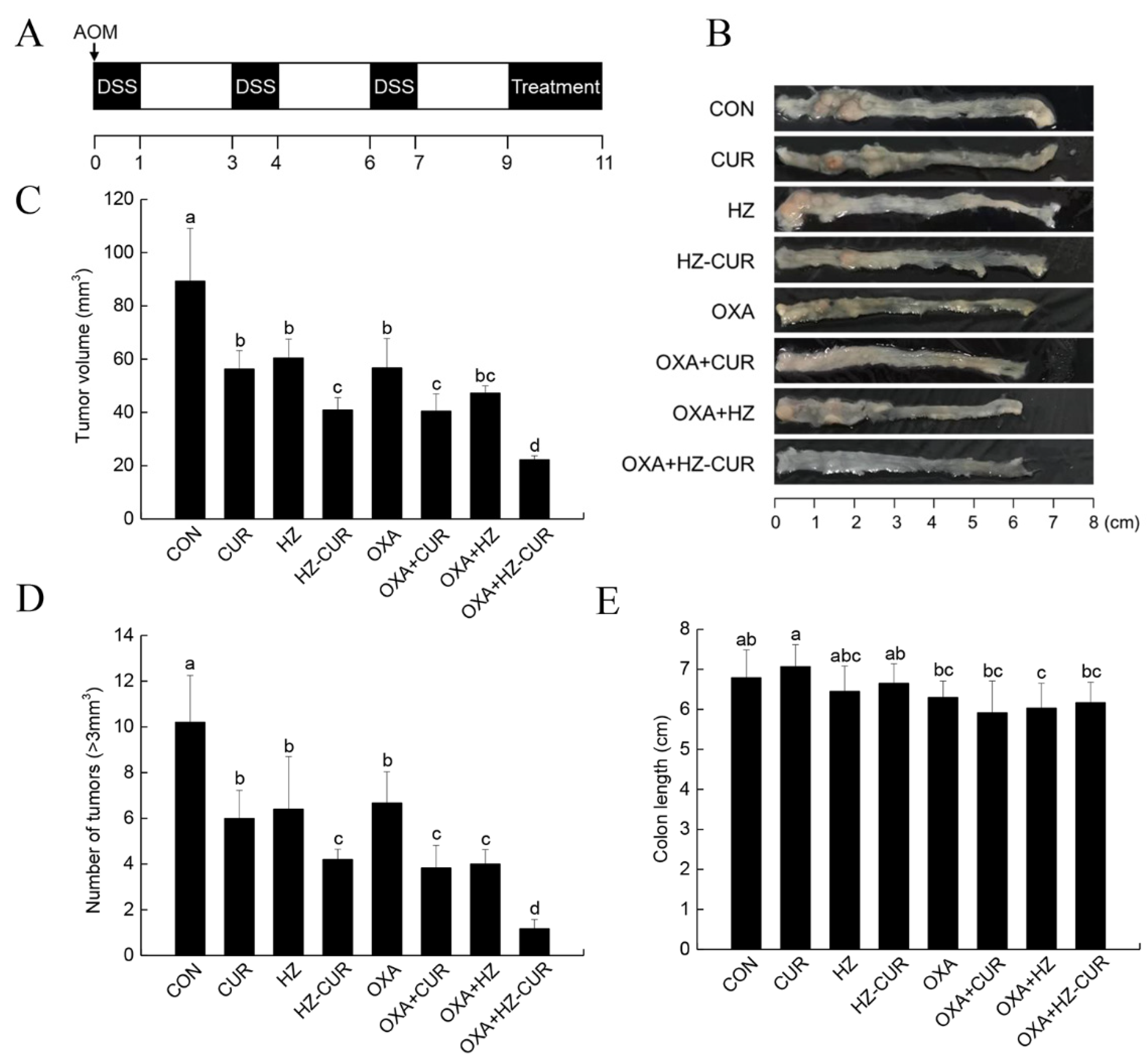
2.5. CRC Model Anti-Tumor Effect of Plain CUR and HZ-CUR Alone and in Combination with OXA in an AOM/DSS-Induced CRC Model in Mice
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Composite Nanoparticles
3.3. Characterization of Composite Nanoparticles
3.4. Cell Viability Assay
3.5. Colony-Formation Assay
3.6. Fluorescence Imaging Assay
3.7. UPLC-MS Analysis of CUR
3.8. Quantitative Cellular Uptake Analysis
3.9. Western Blot Analysis
3.10. RNA Interference Assay
3.11. Animal Studies
3.12. Immunohistochemical (IHC) and Histopathological Analysis
3.13. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mauri, G.; Gori, V.; Bonazzina, E.; Amatu, A.; Tosi, F.; Bencardino, K.; Ruggieri, L.; Patelli, G.; Arena, S.; Bardelli, A.; et al. Oxaliplatin retreatment in metastatic colorectal cancer: Systematic review and future research opportunities. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 91, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besora, S.; Santos, C.; Izquierdo, C.; Martinez-Villacampa, M.M.; Bruna, J.; Velasco, R. Rechallenge with oxaliplatin and peripheral neuropathy in colorectal cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, K.A.; Zhu, S.; Johantgen, M.; Kessler, M.D.; Renn, C.; Beutler, A.S.; Kanwar, R.; Ambulos, N.; Cavaletti, G.; Bruna, J.; et al. Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy and Identification of Unique Severity Groups in Colorectal Cancer. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2017, 54, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, L.D.; Shen, Y.Q.; Zhao, X.H.; Guo, L.J.; Yu, Z.J.; Wang, D.; Liu, L.M.; Liu, J.Z. Curcumin combined with oxaliplatin effectively suppress colorectal carcinoma in vivo through inducing apoptosis. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ruiz Porras, V.; Bystrup, S.; Martínez-Cardús, A.; Pluvinet, R.; Sumoy, L.; Howells, L.; James, M.I.; Iwuji, C.; Manzano, J.L.; Layos, L.; et al. Curcumin mediates oxaliplatin-acquired resistance reversion in colorectal cancer cell lines through modulation of CXC-Chemokine/NF-κB signalling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, L. Curcumin reverses oxaliplatin resistance in human colorectal cancer via regulation of TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 3893–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, S.; Xiang, B.; Li, L.; Lin, Y. Curcumin Attenuates Oxaliplatin-Induced Liver Injury and Oxidative Stress by Activating the Nrf2 Pathway. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Guan, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, D.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Pei, B.; Ye, M.; Xu, J.; Yue, X. Curcumin Alleviates Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress-Mediated Activation of NF-κB and Mitigating Inflammation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howells, L.M.; Iwuji, C.O.O.; Irving, G.R.B.; Barber, S.; Walter, H.; Sidat, Z.; Griffin-Teall, N.; Singh, R.; Foreman, N.; Patel, S.R.; et al. Curcumin Combined with FOLFOX Chemotherapy Is Safe and Tolerable in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in a Randomized Phase IIa Trial. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, S.; Tyagi, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Recent developments in delivery, bioavailability, absorption and metabolism of curcumin: The golden pigment from golden spice. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 46, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabanelli, R.; Brogi, S.; Calderone, V. Improving Curcumin Bioavailability: Current Strategies and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amekyeh, H.; Alkhader, E.; Sabra, R.; Billa, N. Prospects of Curcumin Nanoformulations in Cancer Management. Molecules 2022, 27, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Yao, J.; Wang, Y.; Jia, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, X. Polysaccharide-based delivery system for curcumin: Fabrication and characterization of carboxymethylated corn fiber gum/chitosan biopolymer particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 125, 107367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, T.G.; Day, C.M.; Petrovsky, N.; Garg, S. Review of polysaccharide particle-based functional drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 221, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaber, M.; Mabrouk, M.T.; Freag, M.S.; Khiste, S.K.; Fang, J.Y.; Elkhodairy, K.A.; Elzoghby, A.O. Protein-polysaccharide nanohybrids: Hybridization techniques and drug delivery applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 133, 42–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, A.; Bisharat, L.; Alkhatib, H.S.; Cespi, M. Zein as a Pharmaceutical Excipient in Oral Solid Dosage Forms: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2018, 19, 2009–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.H.L.; Duan, W.; Lee, B.J.; Tran, T.T.D. The use of zein in the controlled release of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Q.T.; Cheng, J.S.; Zhang, B. Preparation and characterization of zein/carboxymethyl dextrin nanoparticles to encapsulate curcumin: Physicochemical stability, antioxidant activity and controlled release properties. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Liang, X.; Peng, Y.; Mcclements, D.J.; Hu, K. Encapsulation of resveratrol in zein/pectin core-shell nanoparticles: Stability, bioaccessibility, and antioxidant capacity after simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Zhu, W.; Guan, S.; Fan, L.; Cai, D. Targeted delivery of honokiol by zein/hyaluronic acid core-shell nanoparticles to suppress breast cancer growth and metastasis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Huang, H. Application of hyaluronic acid as carriers in drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karousou, E.; Misra, S.; Ghatak, S.; Dobra, K.; Götte, M.; Vigetti, D.; Passi, A.; Karamanos, N.K.; Skandalis, S.S. Roles and targeting of the HAS/hyaluronan/CD44 molecular system in cancer. Matrix. Biol. 2017, 59, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattheolabakis, G.; Milane, L.; Singh, A.; Amiji, M.M. Hyaluronic acid targeting of CD44 for cancer therapy: From receptor biology to nanomedicine. J. Drug Target 2015, 23, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Higashi, T.; Hiyoshi, Y.; Yamao, T.; Uemura, N.; Matsumura, K.; Imai, K.; Yamashita, Y.I.; Baba, H. CD44 expression enhances chemoresistance and implies occult micrometastases after conversion hepatectomy for initially unresectable colorectal liver metastases. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 5955–5966. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Yang, S.; Fu, S.; Chen, F.; Cheng, K.-W. Polysaccharide-zein composite nanoparticles for enhancing cellular uptake and oral bioavailability of curcumin: Characterization, anticolorectal cancer effect, and pharmacokinetics. Front Nutr. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yu, M. Development of a nanoparticle delivery system based on zein/polysaccharide complexes. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 4108–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisbeck, F.; Ozimkovski, A.; Cherri, M.; Dimde, M.; Quaas, E.; Mohammadifar, E.; Achazi, K.; Haag, R. Gram Scale Synthesis of Dual-Responsive Dendritic Polyglycerol Sulfate as Drug Delivery System. Polymers 2021, 13, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, L.; Shen, A.; Yang, Y.; Tao, J.; Hu, Y. CD44-targeted hyaluronic acid–curcumin reverses chemotherapeutics resistance by inhibiting P-gp and anti-apoptotic pathways. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 40873–40882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, P.; Confeld, M.; Borowicz, P.; Wang, T.; Mallik, S.; Quadir, M. PEG-b-poly (carbonate)-derived nanocarrier platform with pH-responsive properties for pancreatic cancer combination therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 174, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.S.; Lin, M.M.; Lee, H.J.; Tae, K.S.; Kang, B.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, N.S.; Jeong, Y.G.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, D.K. Receptor-Meditated Endocytosis by Hyaluronic Acid@Superparamagnetic Nanovetor for Targeting of CD44-Overexpressing Tumor Cells. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, G.; Jia, Z.; Yu, Y.; Guo, J.; Hua, Y.; Guo, F.; Li, X.; Zou, W.; et al. Enrichment of CD44 in Exosomes From Breast Cancer Cells Treated With Doxorubicin Promotes Chemoresistance. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Wang, H.; He, L.; Zhang, J.; Ni, B.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Cahuzac, N.; Mehrpour, M.; Lu, Y.; et al. CD44 is of functional importance for colorectal cancer stem cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6751–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.S.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Lin, Q.L.; Fu, D. Targeting Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells as an Effective Treatment for Colorectal Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat 2020, 19, 1533033819892261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, F.; Ye, L.; Jiang, W.; Hargest, R. Targeting Hyaluronic Acid and Peritoneal Dissemination in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2021, S1533-0028, 00130–00134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, G.; Song, J.; Teng, G.J.; Niu, G.; Chen, X. Mapping Sentinel Lymph Node Metastasis by Dual-probe Optical Imaging. Theranostics 2017, 7, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turley, E.A.; Naor, D. RHAMM and CD44 peptides-analytic tools and potential drugs. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 1775–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Paton, J.C.; Herdman, B.P.; Rogers, T.J.; Beddoe, T.; Paton, A.W. The B subunit of an AB5 toxin produced by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi up-regulates chemokines, cytokines, and adhesion molecules in human macrophage, colonic epithelial, and brain microvascular endothelial cell lines. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Deng, W.; Xie, R.; Zeng, X. Effect of Tiam1 gene silencing on the LYVE-1 expression in rectal cancer. Chin. J. Clin. 2013, 7, 8649–8652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatin, S.; Yari Khosroushahi, A. Overviews on the cellular uptake mechanism of polysaccharide colloidal nanoparticles. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 1668–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seok, H.-Y.; Rejinold, N.S.; Lekshmi, K.M.; Cherukula, K.; Park, I.-K.; Kim, Y.-C. CD44 targeting biocompatible and biodegradable hyaluronic acid cross-linked zein nanogels for curcumin delivery to cancer cells: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Control Release 2018, 280, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhu, M.; Qiu, F.; Li, W.; Wang, M.; Guo, Y.; Xi, X.; Du, B. Curcumin may be a potential adjuvant treatment drug for colon cancer by targeting CD44. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 88, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghobi, Z.; Movassaghpour, A.; Talebi, M.; Abdoli Shadbad, M.; Hajiasgharzadeh, K.; Pourvahdani, S.; Baradaran, B. The role of CD44 in cancer chemoresistance: A concise review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 903, 174147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Dong, L.; Chang, P. CD44v6 engages in colorectal cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Xie, L.; Huang, A.; Xue, C.; Gu, Z.; Wang, K.; Zong, S. The Prognostic and Clinical Value of CD44 in Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Sun, C.; Dai, L.; Yang, S.; Wei, Y.; Mao, L.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Effect of molecular weight of hyaluronan on zein-based nanoparticles: Fabrication, structural characterization and delivery of curcumin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.-C. Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amararathna, M.; Hoskin, D.W.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside-Rich Haskap Berry Administration Suppresses Carcinogen-Induced Lung Tumorigenesis in A/JCr Mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Yang, S.; Chen, F.; Cheng, K.-W. Hyaluronic Acid–Zein Core-Shell Nanoparticles Improve the Anticancer Effect of Curcumin Alone or in Combination with Oxaliplatin against Colorectal Cancer via CD44-Mediated Cellular Uptake. Molecules 2022, 27, 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051498
Liu L, Yang S, Chen F, Cheng K-W. Hyaluronic Acid–Zein Core-Shell Nanoparticles Improve the Anticancer Effect of Curcumin Alone or in Combination with Oxaliplatin against Colorectal Cancer via CD44-Mediated Cellular Uptake. Molecules. 2022; 27(5):1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051498
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lu, Shufang Yang, Feng Chen, and Ka-Wing Cheng. 2022. "Hyaluronic Acid–Zein Core-Shell Nanoparticles Improve the Anticancer Effect of Curcumin Alone or in Combination with Oxaliplatin against Colorectal Cancer via CD44-Mediated Cellular Uptake" Molecules 27, no. 5: 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051498
APA StyleLiu, L., Yang, S., Chen, F., & Cheng, K.-W. (2022). Hyaluronic Acid–Zein Core-Shell Nanoparticles Improve the Anticancer Effect of Curcumin Alone or in Combination with Oxaliplatin against Colorectal Cancer via CD44-Mediated Cellular Uptake. Molecules, 27(5), 1498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051498