ACPNet: A Deep Learning Network to Identify Anticancer Peptides by Hybrid Sequence Information
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Features Construction
Sequence Features
Peptide Physicochemical Properties
Embedding Features
2.2.2. Model Structure
Overall Workflow
Prediction Model Constructed by RNN and Dense Networks
Implementation of ACPNet
2.2.3. Performance Evaluation of ACPNet
3. Results
3.1. The Effects of Feature Combination
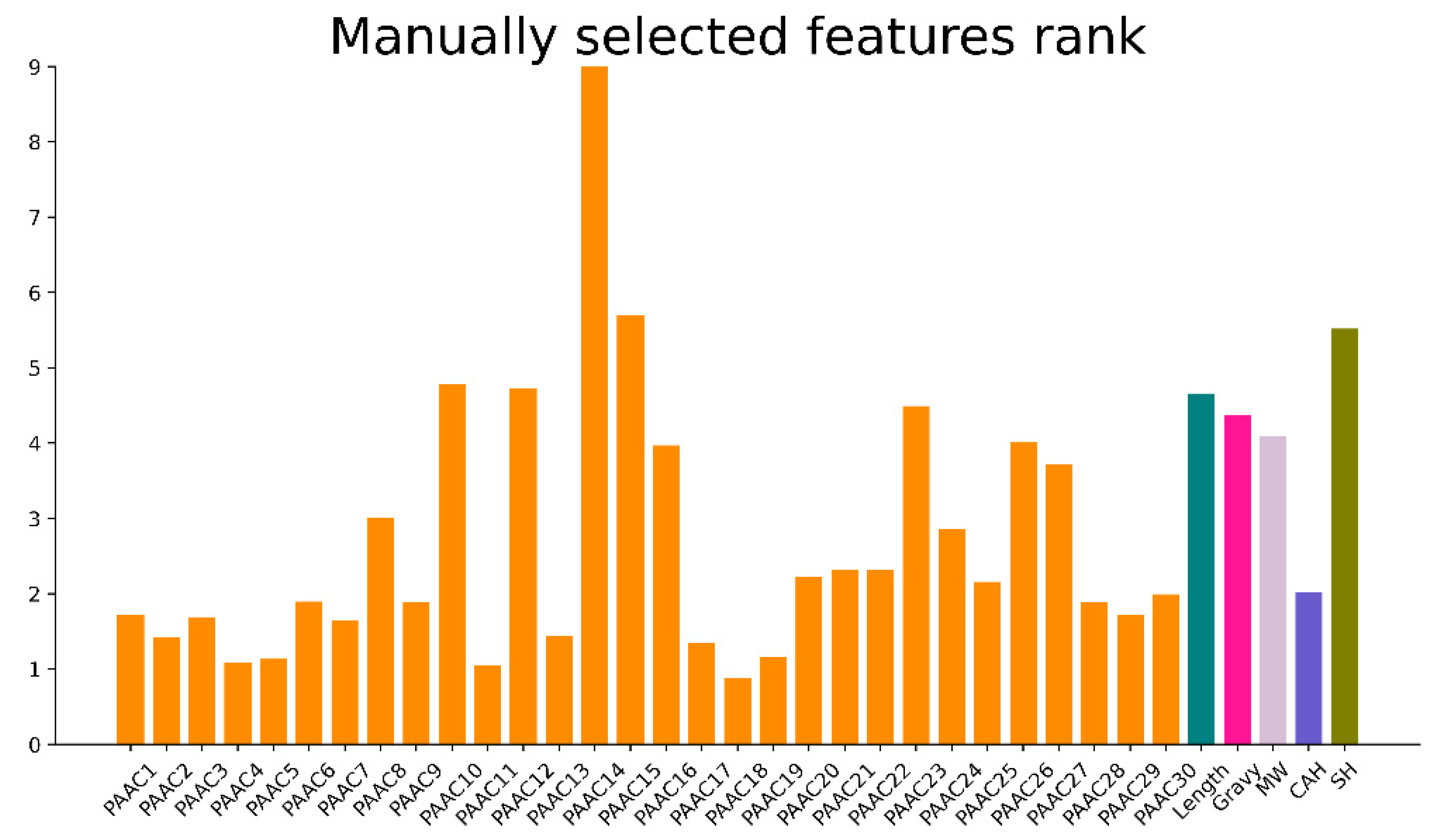
3.2. Manually Selected Features Importance Rank
3.3. Feature Visualization
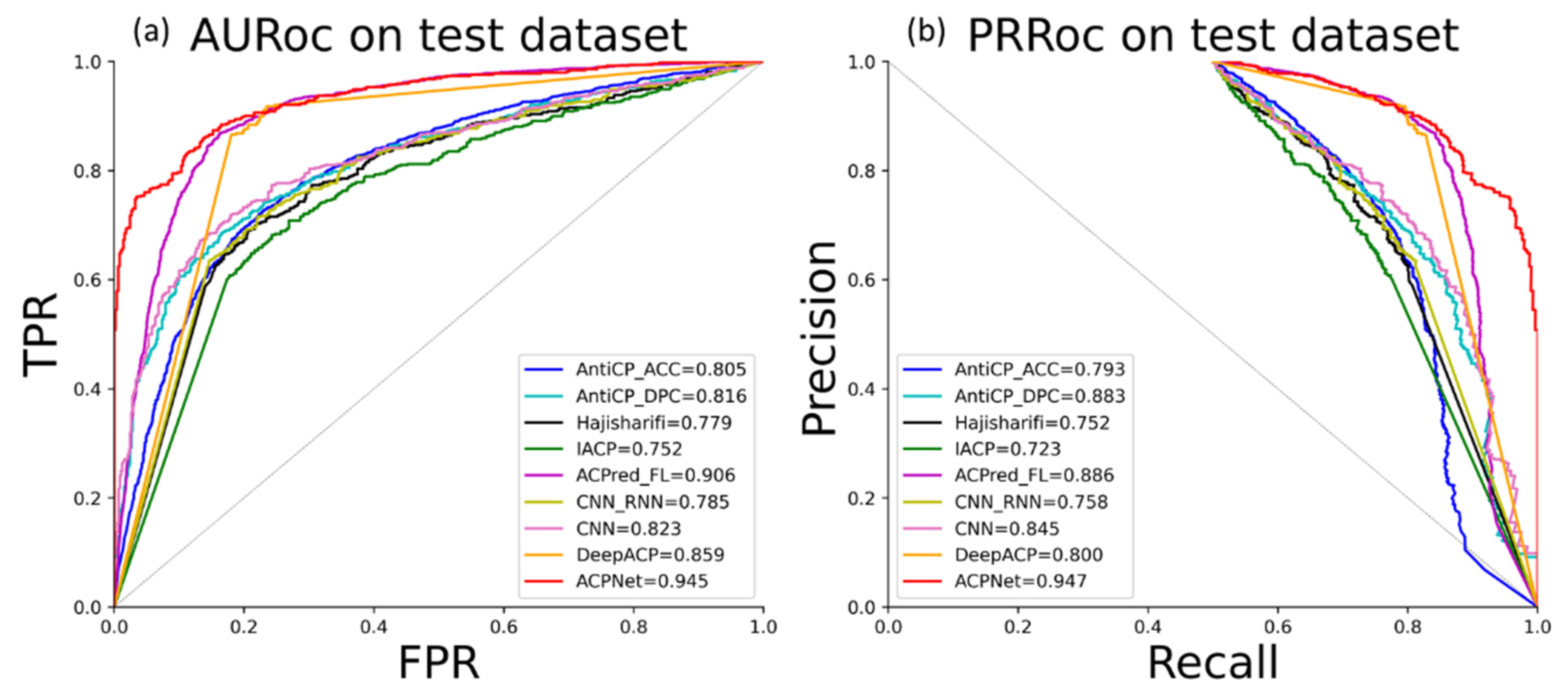
3.4. Performance Comparison of Models on Independent Datasets
3.5. Independent Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. International Agency for Research on Cancer; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chiangjong, W.; Chutipongtanate, S.; Hongeng, S. Anticancer peptide: Physicochemical property, functional aspect and trend in clinical application (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 678–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Liu, D.; Yang, Y. Anti-cancer peptides: Classification, mechanism of action, reconstruction and modification. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghoubi, A.; Khazaei, M.; Avan, A.; Hasanian, S.M.; Cho, W.C.; Soleimanpour, S. P28 Bacterial Peptide, as an Anticancer Agent. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, K.; Okumura, K.; Isogai, H.; Isogai, E. The Human Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37 and Mimics are Potential Anticancer Drugs. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyagi, A.; Kapoor, P.; Kumar, R.; Chaudhary, K.; Gautam, A.; Raghava, G.P.S. In Silico Models for Designing and Discovering Novel Anticancer Peptides. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, srep02984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathi, V.; Subramaniyam, S.; Malik, A.; Lee, G.; Manavalan, B.; Yang, D.-C. mACPpred: A Support Vector Machine-Based Meta-Predictor for Identification of Anticancer Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, Q. Prediction of Anticancer Peptides Using a Low-Dimensional Feature Model. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Feng, G.; Jing, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, P.; Wu, Q. EnACP: An Ensemble Learning Model for Identification of Anticancer Peptides. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.-C.; You, Z.-H.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, X.; Jiang, T.-H.; Chen, Z.-H. ACP-DL: A Deep Learning Long Short-Term Memory Model to Predict Anticancer Peptides Using High-Efficiency Feature Representation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.-G.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Chen, H. ACP-DA: Improving the Prediction of Anticancer Peptides Using Data Augmentation. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Jing, R.; Liu, F.; Luo, J.; Li, Y. DeepACP: A Novel Computational Approach for Accurate Identification of Anticancer Peptides by Deep Learning Algorithm. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 862–870. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.-B.; Chou, K.-C. PseAAC: A flexible web server for generating various kinds of protein pseudo amino acid composition. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 373, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strait, B.; Dewey, T. The Shannon information entropy of protein sequences. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, R.; Dill, B.D.; Chourey, K.; Shah, M.; VerBerkmoes, N.C.; Hettich, R.L. Coupling a Detergent Lysis/Cleanup Methodology with Intact Protein Fractionation for Enhanced Proteome Characterization. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 6008–6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, T.; Kodera, Y.; Oba, K.; Saito, T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Kawashima, Y.; Shichiri, M. Suprabasin-derived bioactive peptides identified by plasma peptidomics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Moreno, P.J.; Yang, J.; Gregersen, S.; Jones, N.C.; Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Sagis, L.M.; Hoffmann, S.V.; Marcatili, P.; Overgaard, M.T.; Hansen, E.B.; et al. The structure, viscoelasticity and charge of potato peptides adsorbed at the oil-water interface determine the physicochemical stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Lee, B.; Yoon, S. Deep learning in bioinformatics. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, 18, 851–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Ding, L.; Li, Z.; Pan, Y.; Gao, X. Deep learning in bioinformatics: Introduction, application, and perspective in the big data era. Methods 2019, 166, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Tian, S.; Li, Y.; Fang, Q.; Tan, R.; Pan, Y.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y.; Gao, X. Modern deep learning in bioinformatics. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 12, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherstinsky, A. Fundamentals of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Network. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2020, 404, 132306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karim, F.; Majumdar, S.; Darabi, H.; Chen, S. LSTM Fully Convolutional Networks for Time Series Classification. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Wu, L.; Ma, X.; Zhang, W.; Fan, J.; Yu, X.; Zeng, W.; Zhou, H. Evaluation of CatBoost method for prediction of reference evapotranspiration in humid regions. J. Hydrol. 2019, 574, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Melville, J. Umap: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.03426. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, P.; Bhagat, D.; Mahalwal, M.; Sharma, N.; Raghava, G.P.S. AntiCP 2.0: An updated model for predicting anticancer peptides. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 22, bbaa153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajisharifi, Z.; Piryaiee, M.; Beigi, M.M.; Behbahani, M.; Mohabatkar, H. Predicting anticancer peptides with Chou′s pseudo amino acid composition and investigating their mutagenicity via Ames test. J. Theor. Biol. 2014, 341, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Hayat, M.; Iqbal, M.; Jan, M.A. iACP-GAEnsC: Evolutionary genetic algorithm based ensemble classification of anticancer peptides by utilizing hybrid feature space. Artif. Intell. Med. 2017, 79, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACPred-FL: A Sequence-Based Predictor Using Effective Feature Representation to Improve the Prediction of Anti-Cancer Peptides|Bioinformatics|Oxford Academic. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/34/23/4007/5026665?login=true (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Lawrence, S.; Giles, C.L.; Tsoi, A.C.; Back, A.D. Face recognition: A convolutional neural-network approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1997, 8, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyd, K.; Eng, K.H.; Page, C.D. Area under the Precision-Recall Curve: Point Estimates and Confidence Intervals. In Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases; Blockeel, H., Kersting, K., Nijssen, S., Železný, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 451–466. [Google Scholar]
- Grisoni, F.; Neuhaus, C.S.; Gabernet, G.; Müller, A.T.; Hiss, J.A.; Schneider, G. Designing Anticancer Peptides by Constructive Machine Learning. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 1300–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, G.; Su, R.; Wei, L. ACPred-Fuse: Fusing multi-view information improves the prediction of anticancer peptides. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 21, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triclosan Offers Protection against Blood Stages of Malaria by Inhibiting Enoyl-ACP Reductase of Plasmodium Falciparum|Nature Medicine. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nm0201_167 (accessed on 31 October 2021).
- Sentiment Analysis of Comment Texts Based on BiLSTM|IEEE Journals & Magazine|IEEE Xplore. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8684825 (accessed on 31 October 2021).
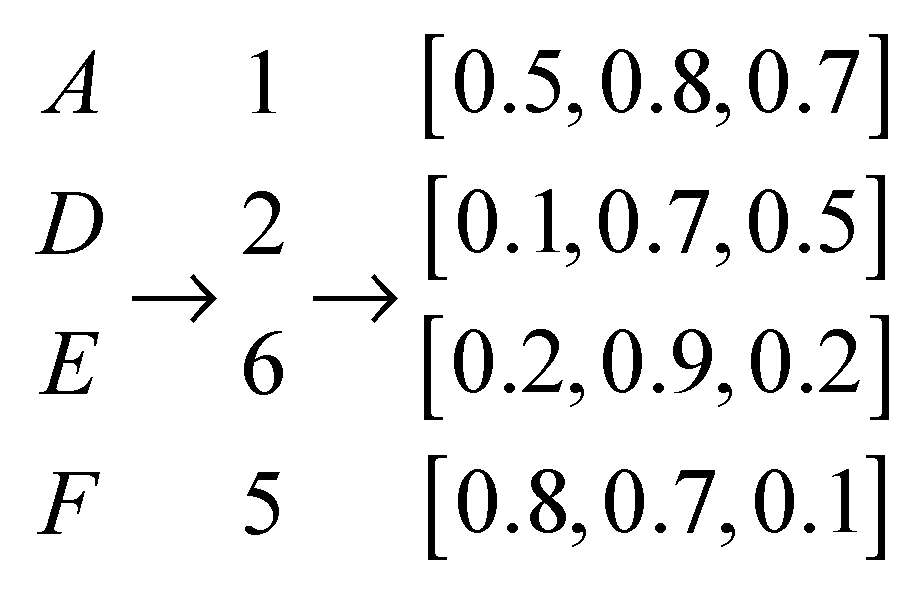


| ACPs Number | Non-ACPs Number | Average Length | Max Length | Min Length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACPs250 | 250 | 250 | 27 | 97 | 11 |
| ACPs82 | 82 | 82 | 27 | 207 | 11 |
| ACPs20 | 10 | 10 | 24 | 47 | 13 |
| Feature Types | Feature Name | Dimensions |
|---|---|---|
| Sequence features | PAAC | 30 |
| Length | 1 | |
| Shannon entropy | 1 | |
| Peptide physicochemical properties | Gravy | 1 |
| Molecular_weight | 1 | |
| Charge_at_pH(10) | 1 | |
| Embedding features | Position embedding | 50 |
| TP | TN | FP | FN | Accuracy | F1-Score | Recall | Precise | MCC | AUC | PRAUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 65 | 68 | 14 | 17 | 81.0 | 80.7 | 79.2 | 82.2 | 0.622 | 0.841 | 0.832 |
| AE | 67 | 73 | 9 | 15 | 85.3 | 84.8 | 81.7 | 88.1 | 0.709 | 0.867 | 0.878 |
| MS + AE | 72 | 75 | 7 | 10 | 89.6 | 89.4 | 87.8 | 90.1 | 0.793 | 0.945 | 0.947 |
| TP | TN | FP | FN | Accuracy | F1-Score | Recall | Precision | MCC | AUC | PRAUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 60 | 63 | 22 | 19 | 75.0 | 75.5 | 73.1 | 75.9 | 0.500 | 0.775 | 0.763 |
| RF | 81 | 28 | 1 | 54 | 66.4 | 74.6 | 98.7 | 60.0 | 0.431 | 0.704 | 0.697 |
| CatBoost | 64 | 77 | 18 | 5 | 85.9 | 84.7 | 78.0 | 92.7 | 0.728 | 0.883 | 0.891 |
| ACPNet | 72 | 75 | 7 | 10 | 89.6 | 89.4 | 87.8 | 91.1 | 0.793 | 0.945 | 0.947 |
| TP | TN | FP | FN | Accuracy | F1-Score | Recall | Precision | MCC | AUC | PRAUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AntiCP_ACC | 56 | 71 | 26 | 11 | 77.4 | 75.2 | 68.3 | 83.6 | 0.558 | 0.805 | 0.793 |
| Anticp_DPC | 61 | 69 | 21 | 13 | 79.3 | 78.2 | 74.4 | 82.4 | 0.588 | 0.816 | 0.883 |
| Hajisharifi | 55 | 71 | 27 | 11 | 76.8 | 74.3 | 67.1 | 83.3 | 0.547 | 0.779 | 0.752 |
| IACP | 56 | 66 | 26 | 16 | 74.4 | 72.7 | 68.3 | 78.8 | 0.491 | 0.752 | 0.723 |
| ACPred-FL | 66 | 79 | 16 | 3 | 88.4 | 87.4 | 80.5 | 95.7 | 0.778 | 0.906 | 0.886 |
| CNN-RNN | 59 | 67 | 23 | 15 | 76.8 | 75.6 | 72.0 | 79.7 | 0.539 | 0.785 | 0.758 |
| CNN | 64 | 65 | 18 | 17 | 78.6 | 78.5 | 78.0 | 79.0 | 0.573 | 0.823 | 0.845 |
| DeepACP | 64 | 72 | 18 | 10 | 82.9 | 82.0 | 78.0 | 86.5 | 0.662 | 0.859 | 0.800 |
| ACPNet | 72 | 75 | 7 | 10 | 89.6 | 89.4 | 87.8 | 91.13 | 0.793 | 0.945 | 0.947 |
| Id | Sequence | Score | Label |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KLWKKIEKLIKKLLTSIR | 0.9999 | ACP |
| 2 | YIWARAERVWLWWGKFLSL | 0.9994 | ACP |
| 3 | DLFKQLQRLFLGILYCLYKIW | 0.8732 | ACP |
| 4 | AIKKFGPLAKIVAKV | 0.7043 | ACP |
| 5 | RWNGRIIKGFYNLVKIWKDLKG | 0.9620 | ACP |
| 6 | KVWKIKKNIRRLLHGIKRGWKG | 0.9993 | ACP |
| 7 | GFWARIGKVFAAVKNL | 0.9988 | ACP |
| 8 | AFLYRLTRQIRPWWRWLYKW | 0.4979 | Non-ACP |
| 9 | RIWGKHSRYIKIVKRLIQ | 0.9993 | ACP |
| 10 | QIWHKIRKLWQIIKDGF | 0.9997 | ACP |
| 11 | CGESCVWIPCVTSIFNCKCKENKVCYHDKIP | 0.0001 | Non-ACP |
| 12 | SDEKASPDKHHRFSLSRYAKLANRLANPKLLETFLSKWIGDRGNRSV | 0.2383 | Non-ACP |
| 13 | DVKGMKKAIKGILDCVIEKGYDKLAAKLKKVIQQLWE | 0.4986 | Non-ACP |
| 14 | AGWGSIFKHIFKAGKFIHGAIQAHND | 0.011 | Non-ACP |
| 15 | ATCDLASGFGVGSSLCAAHCIARRYRGGYCNSKAVCVCRN | 0.0032 | Non-ACP |
| 16 | GWKIGKKLEHHGQNIRDGLISAGPAVFAVGQAATIYAAAK | 0.0015 | Non-ACP |
| 17 | FLGALIKGAIHGGRFIHGMIQNHH | 0.4750 | Non-ACP |
| 18 | FLPAIAGILSQLF | 0.1818 | Non-ACP |
| 19 | ALWMTLLKKVLKAAAKALNAVLVGANA | 0.0052 | Non-ACP |
| 20 | EGGGPQWAVGHFM | 0.1243 | Non-ACP |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Yang, S.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Y. ACPNet: A Deep Learning Network to Identify Anticancer Peptides by Hybrid Sequence Information. Molecules 2022, 27, 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051544
Sun M, Yang S, Hu X, Zhou Y. ACPNet: A Deep Learning Network to Identify Anticancer Peptides by Hybrid Sequence Information. Molecules. 2022; 27(5):1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051544
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Mingwei, Sen Yang, Xuemei Hu, and You Zhou. 2022. "ACPNet: A Deep Learning Network to Identify Anticancer Peptides by Hybrid Sequence Information" Molecules 27, no. 5: 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051544
APA StyleSun, M., Yang, S., Hu, X., & Zhou, Y. (2022). ACPNet: A Deep Learning Network to Identify Anticancer Peptides by Hybrid Sequence Information. Molecules, 27(5), 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051544






