Nanocarriers as Active Ingredients Enhancers in the Cosmetic Industry—The European and North America Regulation Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Nanotechnology in Cosmetology
3. Nanocarriers
3.1. Nanoemulsions
3.2. Liposomes
3.3. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles
3.4. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers
3.5. Niosomes
3.6. Nanocapsules
3.7. Nanospheres
3.8. Gold and Silver Nanoparticles
3.9. Nanocrystals
3.10. Dendrimers
3.11. Cubosomes
3.12. Hydrogels
3.13. Fullerenes/Buckyballs
3.14. Polymersomes
3.15. Carbon Nanotubes
3.16. Nanosponges
4. Active Ingredients in Cosmetic Nanocarriers
4.1. Retinoids
4.2. Antioxidants
4.3. Enzymes
4.4. Proteins and Peptides
4.5. Ceramides
4.6. Hyaluronic Acid
4.7. Organic UV Filters
| Nanocarriers | Active Ingredients | Cosmetic Use | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polymeric micelles | Curcumin | Whitening | [183] |
| Nanostructured lipid carriers | Passiflora edulis seeds oil | Whitening | [184] |
| Niosomes | Quercetin | Whitening | [109] |
| Niosomes | Arbutin | Whitening | [110] |
| Nano sponges | Azelaic acid | Whitening | [145] |
| Nanostructured lipid carriers | Orobol | Anti-ageing | [185] |
| Nanoliposomes | Carnosine Palmitoyl tripeptide-5 Acetyl hexapeptide-3 | Anti-ageing | [186] |
| Nanoemulsions | Astaxanthin | Anti-ageing | [187] |
| Dendrimers | Resveratrol | Anti-ageing | [135] |
| Solid lipid nanoparticles Nanostructured lipid carriers Nanoemulsion | Lutein | Anti-ageing | [188] |
| Nanostructured lipid carriers | Finasteride | Anti-alopecia | [189] |
| Nanoemulsions | Minoxidil | Anti-alopecia | [190] |
| Nanocapsules | Hinokitiol | Anti-alopecia | [191] |
| Lipid nanoparticles | Hinokitiol | Anti-alopecia | [192] |
| SLN-Silica particles | Octyl methoxycinnamate | Sunscreen | [193] |
| Nanostructured lipid carriers | Quercetin | Sunscreen | [104] |
| Gold nanoparticles | Snail slime | Sunscreen | [194] |
| Cellulose nanocrystals | Diethyl sinapate | Sunscreen | [195] |
| Nanoemulsions | Sunflower oil | Sunscreen | [77] |
| Nanocapsules | Octyl dimethyl para-aminobenzoic acid | Sunscreen | [119] |
| Liposomes Nanostructured lipid carriers Solid lipid nanoparticles | Avobenzone Omega-3 | UV blocking sunscreen | [196] |
| Cubosomes | Erythromycin | Anti-acne | [136] |
| Microemulsions | Curcumin | Anti-acne | [197] |
| Microemulsions | Thai basil oils | Anti-acne | [198] |
| Liposomes | Lauric acid | Anti-acne | [199] |
| Keratin: Zein nanoparticles | Fragrances (linalool and menthol) | Hair cosmetic | [200] |
5. Application and Efficacy of Active Ingredients in Cosmetic Nanocarriers
6. Limitations of Nanocarriers
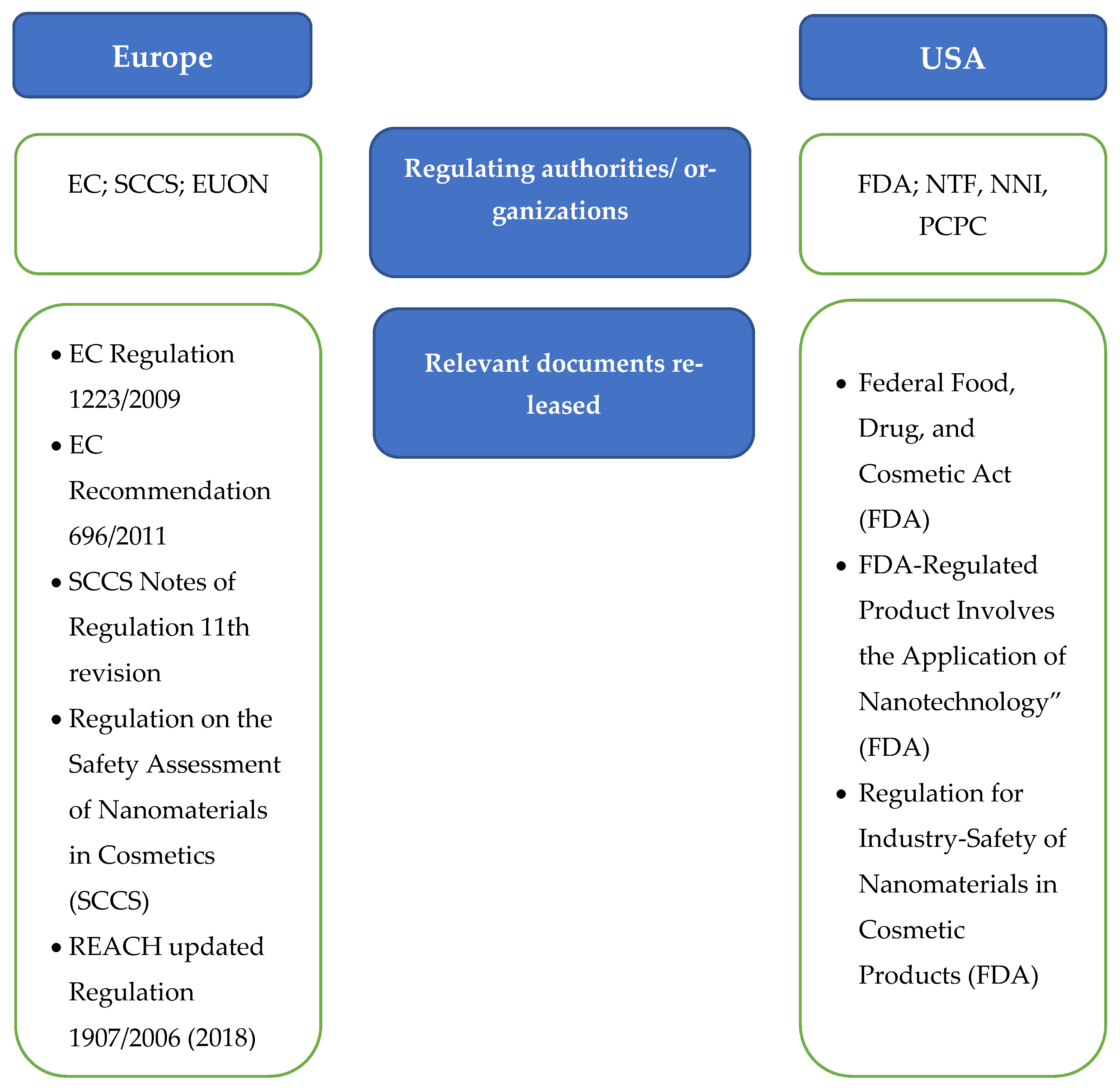
7. Cosmetics Regulation in Europe and the USA
7.1. European Regulations
7.2. USA Regulations
7.3. Other Countries
8. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, D. The Naked Ape: A Zoologist’s Study of the Human-Animal; Jonathan Cape: London, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Arda, O.; Göksügür, N.; Tüzün, Y. Basic histological structure and functions of facial skin. Clin. Dermatol. 2014, 32, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baret, M.; Bensimon, N.; Coronel, S.; Ventura, S.; Nicolas-Garcia, S.; Korichi, R.; Gazano, G. Characterization and quantification of the skin radiance through new digital image analysis. Skin. Res. Technol. 2006, 12, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.S.; Baik, S.H.; Oh, C.H. Quantitative measurement of desquamation and skin elasticity in diabetic patients. Skin. Res. Technol. 2002, 8, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Macedo, G.M.C.; Nunes, S.; Barreto, T. Skin disorders in diabetes mellitus: An epidemiology and physiopathology review. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2016, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Ko, E.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, B.G.; Shin, H.J.; Seo, D.B.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, M.N. Effects of collagen tripeptide supplement on skin properties: A prospective, randomized, controlled study. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2014, 16, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, J.E.; McDaniel, D.H.; Hickman, J.; Dispensa, L.; Le Moigne, A.; Buchner, L. A multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial assessing the effects of a multicomponent nutritional supplement for treating photoaged skin in healthy women. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2017, 16, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBaise, M.; Tarleton, S.M. Hair, Nails, and Skin: Differentiating Cutaneous Manifestations of Micronutrient Deficiency. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, S.; Manson Brown, S.; Cross, S.J.; Mehta, R. Defining Skin Quality: Clinical Relevance, Terminology, and Assessment. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etcoff, N.L. Survival of the Prettiest the Science of Beauty; Books, N.A., Ed.; Anchor Books: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Barankin, B.; DeKoven, J. Psychosocial effect of common skin diseases. Can. Fam. Physician 2002, 48, 712–716. [Google Scholar]
- Beattie, P.E.; Lewis-Jones, M.S. A comparative study of impairment of quality of life in children with skin disease and children with other chronic childhood diseases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2006, 155, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, N.; Fink, B.; Matts, P.J. Visible skin condition and perception of human facial appearance. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2010, 32, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kligman, A.M.; Graham, J.A. The psychology of appearance in the elderly. Dermatol. Clin. 1986, 4, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, S.; Rivkin, A.; Sykes, J.M.; Teller, C.F.; Weinkle, S.H.; Shumate, G.T.; Gallagher, C.J. Aesthetic Treatment Positively Impacts Social Perception: Analysis of Subjects from the HARMONY Study. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2019, 39, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayan, S.H.; Arkins, J.P.; Patel, A.B.; Gal, T.J. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled health-outcomes survey of the effect of botulinum toxin type an injection on quality of life and self-esteem. Dermatologic Surg. 2010, 36, 2088–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imadojemu, S.; Sarwer, D.B.; Percec, I.; Sonnad, S.S.; Goldsack, J.E.; Berman, M.; Sobanko, J.F. Influence of surgical and minimally invasive facial cosmetic procedures on psychosocial outcomes: A systematic review. JAMA Dermatol. 2013, 149, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinkle, S.H.; Werschler, W.P.; Teller, C.F.; Sykes, J.M.; Shamban, A.; Rivkin, A.; Narurkar, V.A.; Kaminer, M.S.; Dayan, S.; Cohen, J.L.; et al. Impact of Comprehensive, Minimally Invasive, Multimodal Aesthetic Treatment on Satisfaction with Facial Appearance: The HARMONY Study. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2018, 38, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvie, P.; Safa, M.; Chantrey, J.; Leys, C.; Cavallini, M.; Niforos, F.; Hopfinger, R.; Marx, A. Improvements in satisfaction with skin after treatment of facial fine lines with VYC-12 injectable gel: Patient-reported outcomes from a prospective study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertossi, D.; Giampaoli, G.; Lucchese, A.; Manuelli, M.; Albanese, M.; Nocini, R.; Nocini, P.F. The skin rejuvenation associated treatment-Fraxel laser, Microbotox, and low G prime hyaluronic acid: Preliminary results. Lasers Med. Sci. 2019, 34, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitakis, J. Anatomy, histology and immunohistochemistry of normal human skin. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2002, 12, 390–391. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, N.S.; Krishnaswami, V.; Vijayaraghavalu, S.; Kandasamy, R. Chapter 2—Transdermal and bioactive nanocarriers. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Nanda, A., Nanda, S., Nguyen, T.A., Rajendran, S., Slimani, Y.B.T.-N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 17–33. ISBN 978-0-12-822286-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. New insights on unique features and role of nanostructured materials in cosmetics. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, F. General aspects of cosmetics in relation to science and society. In Cosmetic Science and Technology; Sakamoto, K., Lochhead, R.Y., Maibach, H.I., Yamashita, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 3–14. ISBN 978-0-12-802005-0. [Google Scholar]
- Salvioni, L.; Morelli, L.; Ochoa, E.; Labra, M.; Fiandra, L.; Palugan, L.; Prosperi, D.; Colombo, M. The emerging role of nanotechnology in skincare. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 293, 102437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council. Official Journal of the European Union. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/system/files/2016-11/cosmetic_1223_2009_regulation_en_0.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Stephan, B. Main cosmetic vehicles. In Handbook of Cosmetic Science and Technology; Barel, A., Paye, M., Maibach, H., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 128–153. ISBN 9780429135231. [Google Scholar]
- Fiume, Z. Final report on the safety assessment of Lecithin and Hydrogenated Lecithin. Int. J. Toxicol. 2001, 20, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B. Hope for nanotechnology: Anticipatory knowledge and the governance of affect. Area 2007, 39, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, A.; Mahesh, G. Public perception of nanotechnology: A contrast between developed and developing countries. Technol. Soc. 2021, 67, 101751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaz, B.; Alexiou, C.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Alves, F.; Andrews, A.M.; Ashraf, S.; Balogh, L.P.; Ballerini, L.; Bestetti, A.; Brendel, C.; et al. Diverse Applications of Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2313–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.; Lopes, I.; Magalhães, L.; Sárria, M.P.; Machado, R.; Sousa, J.C.; Botelho, C.; Teixeira, J.; Gomes, A.C. Novel concept of exosome-like liposomes for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.; Lopes, I.; Teixeira, J.; Botelho, C.; Gomes, A.C. Exosome-like Nanoparticles: A New Type of Nanocarrier. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3888–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihranyan, A.; Ferraz, N.; Strømme, M. Current status and future prospects of nanotechnology in cosmetics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 875–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Nanda, A.; Lohan, S.; Kaur, R.; Singh, B. Chapter 3—Nanocosmetics: Performance Enhancement and Safety Assurance; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 47–67. ISBN 978-0-323-42868-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.-H.; Zhang, L.; Wei, H.; Chen, H.-D. Efficacy and safety of innovative cosmeceuticals. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Chauhan, C. Emerging trends of nanotechnology in beauty solutions: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrana, H.; Avila, A.; Tsai, C.S.J. Nanomaterials in Cosmetic Products: The Challenges with regard to Current Legal Frameworks and Consumer Exposure. Nanoethics 2018, 12, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrouel, F.; Viennot, S.; Ottolenghi, L.; Gaillard, C.; Bourgeois, D. Nanoparticles as Anti-Microbial, Anti-Inflammatory, and Remineralizing Agents in Oral Care Cosmetics: A Review of the Current Situation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revia, R.A.; Wagner, B.A.; Zhang, M. A Portable Electrospinner for Nanofiber Synthesis and Its Application for Cosmetic Treatment of Alopecia. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L. Nanoencapsulation of anthocyanin by an amphiphilic peptide for stability enhancement. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, H.G. Chitosan/poly-γ-glutamic acid nanoparticles improve the solubility of lutein. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 85, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, J. Improved chemical stability and cellular antioxidant activity of resveratrol in zein nanoparticle with bovine serum albumin-caffeic acid conjugate. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Garcia, C.V.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Development of nanostructured lipid carriers for the encapsulation and controlled release of vitamin D3. Food Chem. 2017, 225, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, S.; Contri, R.V.; Guterres, S.S.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guerreiro, I.C.K. Simultaneous nanoencapsulation of lipoic acid and resveratrol with improved antioxidant properties for the skin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 192, 111023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Pandey, S.K.; Vishwakarma, N. Chapter 22—Functional nanomaterials for the cosmetics industry. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Mustansar Hussain, C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 717–730. ISBN 978-0-12-816787-8. [Google Scholar]
- Chaki Borrás, M.; Sluyter, R.; Barker, P.J.; Konstantinov, K.; Bakand, S. Y2O3 decorated TiO2 nanoparticles: Enhanced UV attenuation and suppressed photocatalytic activity with promise for cosmetic and sunscreen applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 207, 111883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.I.; Barbosa, A.I.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Costa, P.; Torres, T.; Reis, S. Freeze-Dried Softisan® 649-Based Lipid Nanoparticles for Enhanced Skin Delivery of Cyclosporine A. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaiee, S.; Assadpour, E.; Faridi Esfanjani, A.; Silva, A.S.; Jafari, S.M. Application of nano/microencapsulated phenolic compounds against cancer. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 279, 102153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maya-Cano, D.A.; Arango-Varela, S.; Santa-Gonzalez, G.A. Phenolic compounds of blueberries (Vaccinium spp.) as a protective strategy against skin cell damage induced by ROS: A review of antioxidant potential and antiproliferative capacity. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Raphaelli, C.O.; Azevedo, J.G.; dos Pereira, E.S.; Vinholes, J.R.; Camargo, T.M.; Hoffmann, J.F.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Vizzotto, M.; Rombaldi, C.V.; Wink, M.R.; et al. Phenolic-rich apple extracts have photoprotective and anti-cancer effect in dermal cells. Phytomed. Plus 2021, 1, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Dumont, M.-J.; Orsat, V. Encapsulation of phenolic compounds present in plants using protein matrices. Food Biosci. 2016, 15, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonechi, C.; Martini, S.; Ciani, L.; Lamponi, S.; Rebmann, H.; Rossi, C.; Ristori, S. Using Liposomes as Carriers for Polyphenolic Compounds: The Case of Trans-Resveratrol. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalouta, K.; Eleni, P.; Boukouvalas, C.; Vassilatou, K.; Krokida, M. Dynamic mechanical analysis of novel cosmeceutical facial creams containing nano-encapsulated natural plant and fruit extracts. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.C.; Hudson, P.L.; Burk, K.; Marangoni, A.G. Encapsulation of cycloastragenol in phospholipid vesicles enhances transport and delivery across the skin barrier. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 608, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytianos, G.; Rahdar, A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Nanomaterials in cosmetics: Recent updates. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Nanda, A. Nanotechnology in cosmetics: A boon or bane? Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2012, 94, 1467–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomeh, M.A.; Hadianamrei, R.; Sun, W.; Xu, D.; Brown, S.; Zhao, X. Stiffness-tuneable nanocarriers for controlled delivery of ASC-J9 into colorectal cancer cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 594, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jounaki, K.; Makhmalzadeh, B.S.; Feghhi, M.; Heidarian, A. Topical ocular delivery of vancomycin loaded cationic lipid nanocarriers as a promising and non-invasive alternative approach to intravitreal injection for enhanced bacterial endophthalmitis management. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 167, 105991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Zhu, C.; Wang, X.; Kong, Q.; Guo, T.; He, Z.; He, Y.; Ruan, S.; Ruan, H.; Pei, L.; et al. Cholesterol and phospholipid-free multilamellar niosomes regulate transdermal permeation of a hydrophobic agent potentially administrated for treating diseases in deep hair follicles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, S.; Awasthi, R.; Singhare, D.; Kulkarni, G.T. Topical delivery of Tacrolimus using liposome containing gel: An emerging and synergistic approach in management of psoriasis. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 142, 109838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Luo, D.; Chen, D.; Tan, X.; Bai, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, W. Current Advances of Nanocarrier Technology-Based Active Cosmetic Ingredients for Beauty Applications. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 867–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Aftab, S.; Nisar, J.; Ashiq, M.N.; Iftikhar, F.J. Nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 62, 102426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.H.; Fazal, H.; Ahmad, N.; Ali, M.; Giglioli-Guivarch, N.; Hano, C. Chapter 5—Nanomaterials for cosmeceuticals: Nanomaterials-induced advancement in cosmetics, challenges, and opportunities. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Nanda, A., Nanda, S., Nguyen, T.A., Rajendran, S., Slimani, Y.B.T.-N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 79–108. ISBN 978-0-12-822286-7. [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan, S.; Sharma, P.; Nanda, S. Chapter 8—Cosmetic nanoformulations and their intended use. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Nanda, A., Nanda, S., Nguyen, T.A., Rajendran, S., Slimani, Y.B.T.-N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 141–169. ISBN 978-0-12-822286-7. [Google Scholar]
- Do Prado, A.H.; Araújo, V.H.S.; Eloy, J.O.; Fonseca-Santos, B.; Pereira-da-Silva, M.A.; Peccinini, R.G.; Chorilli, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanostructured Lipid Nanocarriers for Enhanced Sun Protection Factor of Octyl p-methoxycinnamate. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, C.; Vaidya, F.U.; Pandey, S.M. Chapter 3—Mechanism for development of nano based drug delivery system. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Mohapatra, S., Ranjan, S., Dasgupta, N., Mishra, R., Thomas, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 35–67. ISBN 978-0-12-814029-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chavda, V.P. Chapter 4—Nano based Nano Drug Delivery: A Comprehensive Review. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Mohapatra, S., Ranjan, S., Dasgupta, N., Mishra, R., Thomas, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 69–92. ISBN 978-0-12-814029-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tilekar, K.; Khade, P.; Kakade, S.; Kotwal, S.; Patil, R. Cubosomes—A Drug Delivery System. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Biol. Sci. 2014, 4, 812–824. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Mooney, D.J. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Howard, J.B.; Vander Sande, J.B. Size analysis of single fullerene molecules by electron microscopy. Carbon N. Y. 2004, 42, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baalousha, M.; Lead, J.R.; Ju-Nam, Y. 3.05—Natural Colloids and Manufactured Nanoparticles in Aquatic and Terrestrial Systems; Wilderer, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 89–129. ISBN 978-0-444-53199-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bartenstein, J.E.; Robertson, J.; Battaglia, G.; Briscoe, W.H. Stability of polymersomes prepared by size exclusion chromatography and extrusion. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 506, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Purohit, D.; Dureja, H. Nanosponges-A Promising Novel Drug Delivery System. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 12, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Kweon, D.K.; Park, H.J. Investigations on skin permeation of hyaluronic acid-based nanoemulsion as transdermal carrier. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabri, T.-H.; Arab-Tehrany, E.; Belhaj, N.; Linder, M. Physico-chemical characterization of nano-emulsions in cosmetic matrix enriched on omega-3. J. Nanobiotechnology 2011, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arianto, A.; Cindy, C. Preparation and Evaluation of Sunflower Oil Nanoemulsion as a Sunscreen. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 3757–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Mohammadifar, M.; Aghadavoud, E.; Vakili, Z.; Aarabi, M.H.; Talaei, S.A. Deep skin wound healing potential of lavender essential oil and liquorice extract in a nanoemulsion form: Biochemical, histopathological and gene expression evidences. J. Tissue Viability 2020, 29, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singpanna, K.; Dechsri, K.; Patrojanasophon, P.; Limpachayaporn, P.; Opanasopit, P.; Nuntharatanapong, N. Transdermal delivery, cytotoxicity and anti-melanogenic activity of p-chlorophenyl benzyl ether loaded-liposomes. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 65, 102746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinato, M.; Trucillo, P.; Campardelli, R.; Perego, P.; Reverchon, E. Bioactives extraction from spent coffee grounds and liposome encapsulation by a combination of green technologies. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2020, 151, 107911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-B.; Won, B.; Yang, S.; Kim, D.-H. Asterias pectinifera derived collagen peptide-encapsulating elastic nanoliposomes for the cosmetic application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, M.J.; Kitson, C.N. Liposomes: A Perspective for Dermatologists. Dermatol. Clin. 1993, 11, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, B.; Burfeindt, J. Nanotechnology in Cosmetics BT—Nanocosmetics: From Ideas to Products; Cornier, J., Keck, C.M., Van de Voorde, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 17–25. ISBN 978-3-030-16573-4. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa-Robles, A.; Antunes-Ricardo, M.; Guajardo-Flores, D. Encapsulation of phenolic compounds with liposomal improvement in the cosmetic industry. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 593, 120125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Hu, H.; Lin, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, S.; Shi, X. Quercetin deformable liposome: Preparation and efficacy against ultraviolet B induced skin damages in vitro and in vivo. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 127, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Kale, D.P.; Swami, R.; Katiyar, S.S. Codelivery of benzoyl peroxide & adapalene using modified liposomal gel for improved acne therapy. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.B.; Misra, A.N.; Marfatia, Y.S. Preparation and comparative clinical evaluation of liposomal gel of benzoyl peroxide for acne. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2001, 27, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, M.S.; D’Souza, A.; Aibani, N.; Nair, S.S.; Sandbhor, P.; Kumari, D.; Banerjee, R. Stable Liposome in Cosmetic Platforms for Transdermal Folic acid delivery for fortification and treatment of micronutrient deficiencies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Y.; Xia, H.; Li, L.; Lee, R.J.; Xie, J.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Teng, L. Liposomal Vitamin D3 as an Anti-aging Agent for the Skin. Pharmaceutisc 2019, 11, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, S.; Gulati, N.; Verma, D.; Mukherjee, S.; Nagaich, U. Role of nanotechnology in cosmeceuticals: A review of recent advances. J. Pharm. 2018, 2018, 3420204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, D.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Nogueira, E. Design of liposomes as drug delivery system for therapeutic applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangale, M.S.; Mitkare, S.; Gattani, S.G.; Sakarkar, D.M. Recent nanotechnological aspects in cosmetics and dermatological preparations. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 88–97. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, N.; Agarwal, S.; Rayasa, M. Latest Technology Advances in Cosmaceuticals. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug Res. 2012, 4, 168–182. [Google Scholar]
- Güney, G.; Kutlu, H.M.; Genç, L. Preparation and characterization of ascorbic acid loaded solid lipid nanoparticles and investigation of their apoptotic effects. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, P.P.; Polonini, H.C.; Paes, C.Q.; Restrepob, J.A.S.; Creczynksi-Pasa, T.B.; Chaves, M.G.A.M.; Brandão, M.A.F.; Pittella, F.; Raposo, N.R.B. Controlled release of resveratrol from lipid nanoparticles improves antioxidant effect. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aland, R.; Ganesan, M.; Rajeswara Rao, P. In vivo evaluation of tazarotene solid lipid nanoparticles gel for topical delivery. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug Res. 2019, 11, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Müller, R.H. Cosmetic features and applications of lipid nanoparticles (SLN®, NLC®). Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2008, 30, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, S.; Jose, S.; Sumod, U.; Sabitha, M. Nanotechnology in cosmetics: Opportunities and challenges. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Liu, S. A new healthy sunscreen system for human: Solid lipid nanoparticles as carrier for 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoylchitin and the improvement by adding Vitamin E. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2005, 36, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, L.B.; Magnussson, E.; Gunnarsson, L.; Vermehren, C.; Nielsen, H.M.; Petersson, K. Corticosteroid solubility and lipid polarity control release from solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 390, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shailesh, L.; Snehal, R.P.; Ashwini, P.; Manoj, S.; Arvind, B. Nanostructured lipid carriers in stability improvement for cosmetic nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Res. 2016, 6, 168–180. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.H.; Petersen, R.D.; Hommoss, A.; Pardeike, J. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic dermal products. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, G.Y.; Suh, J.Y.; Park, S.N. Ceramide-based nanostructured lipid carriers for transdermal delivery of isoliquiritigenin: Development, physicochemical characterization, and in vitro skin permeation studies. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felippim, E.C.; Marcato, P.D.; Maia Campos, P.M.B.G. Development of Photoprotective Formulations Containing Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Sun Protection Factor, Physical-Mechanical and Sensorial Properties. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.N.; Tolentino, S.; Pires, F.Q.; Anjos, J.L.; Alonso, A.; Gratieri, T.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gelfuso, G.M. Nanostructured lipid carriers for hair follicle-targeted delivery of clindamycin and rifampicin to hidradenitis suppurativa treatment. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoee, S.; Yaghoobian, M. Chapter 6—Niosomes: A novel approach in modern drug delivery systems. In Micro and Nano Technologies; Andronescu, E., Grumezescu, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 207–237. ISBN 978-0-323-46143-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hameed, A.; Fatima, G.R.; Malik, K.; Muqadas, A.; Fazal-ur-Rehman, M. Scope of Nanotechnology in Cosmetics: Dermatology and Skin Care Products. J. Med. Chem. Sci. 2019, 2, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, E.H.; Yapar, E.A.; Tanrıverdi, S.T.; Özer, Ö. Chapter 14—Nanocarriers in Cosmetology; Grumezescu, A., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 363–393. ISBN 978-0-323-42868-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ye, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Long, X. Niosomal Nanocarriers for Enhanced Skin Delivery of Quercetin with Functions of Anti-Tyrosinase and Antioxidant. Molecules 2019, 24, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radmard, A.; Saeedi, M.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Hashemi, S.M.H.; Nokhodchi, A. An eco-friendly and green formulation in lipid nanotechnology for delivery of a hydrophilic agent to the skin in the treatment and management of hyperpigmentation complaints: Arbutin niosome (Arbusome). Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2021, 201, 111616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malathi, S.; Balashanmugam, P.; Devasena, T.; Kalkura, S.N. Enhanced antibacterial activity and wound healing by a novel collagen blended ZnO nanoparticles embedded niosome nanocomposites. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaikul, P.; Khat-udomkiri, N.; Iangthanarat, K.; Manosroi, J.; Manosroi, A. Characteristics and in vitro anti-skin ageing activity of gallic acid loaded in cationic CTAB niosome. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 131, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manosroi, A.; Chankhampan, C.; Manosroi, W.; Manosroi, J. Transdermal absorption enhancement of papain loaded in elastic niosomes incorporated in gel for scar treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 48, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansathien, K.; Chareanputtakhun, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Opanasopit, P.; Rangsimawong, W. Hair growth-promoting effect of bioactive extract from deer antler velvet-loaded niosomes and microspicules serum. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597, 120352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.C.; Morais, F.; Simões, A.; Pereira, I.; Sequeira, J.A.D.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Veiga, F.; Ribeiro, A. Nanotechnology for the development of new cosmetic formulations. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, L.A.; Contri, R.V.; Beck, R.C.R.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. Improving drug biological effects by encapsulation into polymeric nanocapsules. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 7, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayman, M.; Kam, P.C.A. Capsaicin: A review of its pharmacology and clinical applications. Curr. Anaesth. Crit. Care 2008, 19, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contri, R.V.; Frank, L.A.; Kaiser, M.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. The use of nanoencapsulation to decrease human skin irritation caused by capsaicinoids. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- An, Q.; Ni, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y. Preparation and evaluation of polymer-encapsulated UV filter nanocapsules with miniemulsion polymerization. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushirobira, C.Y.; Afiune, L.A.F.; Pereira, M.N.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Gratieri, T. Dutasteride nanocapsules for hair follicle targeting: Effect of chitosan-coating and physical stimulus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, P.; Friedrich, M.L.; dos Santos, J.; Librelotto, D.R.N.; Maurer, L.H.; Emanuelli, T.; de da Silva, C.B.; Adams, A.I.H. Desonide nanoencapsulation with açai oil as oil core: Physicochemical characterization, photostability study and in vitro phototoxicity evaluation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 199, 111606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Tolba, E.; Schröder, H.C.; Diehl-Seifert, B.; Wang, X. Retinol encapsulated into amorphous Ca2+ polyphosphate nanospheres acts synergistically in MC3T3-E1 cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Creran, B.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles: Preparation, properties, and applications in bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakor, A.S.; Jokerst, J.; Zavaleta, C.; Massoud, T.F.; Gambhir, S.S. Gold Nanoparticles: A Revival in Precious Metal Administration to Patients. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4029–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulit-Prociak, J.; Grabowska, A.; Chwastowski, J.; Majka, T.M.; Banach, M. Safety of the application of nanosilver and nanogold in topical cosmetic preparations. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.D.; Visht, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Kumar, N. Formulation, Characterization and Application on Nanoparticle: A Review. Pharm. Sin. 2011, 2, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Abla, M.J.; Singh, N.D.; Banga, A.K. Role of Nanotechnology in Skin Delivery of Drugs BT—Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers Chemical Methods in Penetration Enhancement: Nanocarriers; Dragicevic, N., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–13. ISBN 978-3-662-47862-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kazi, K.M.; Mandal, A.S.; Biswas, N.; Guha, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Behera, M.; Kuotsu, K. Niosome: A future of targeted drug delivery systems. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.H.; Shegokar, R.; Keck, C.M. 20 years of lipid nanoparticles (SLN and NLC): Present state of development and industrial applications. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2011, 8, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, W.; Kong, S.; Ouyang, Q.; Tao, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, H. Use of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid nanocrystals to enhance anti-inflammatory activity by improving topical delivery. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2021, 205, 111791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.; Ramasamy, M.; Willis, N.C.; Kim, D.S.; Anderson, W.A.; Tam, K.C. Encapsulation and controlled release of vitamin C in modified cellulose nanocrystal/chitosan nanocapsules. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manca, M.L.; Lai, F.; Pireddu, R.; Valenti, D.; Schlich, M.; Pini, E.; Milano, G.; Fadda, A.M.; Sinico, C. Impact of nanosizing on dermal delivery and antioxidant activity of quercetin nanocrystals. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.K.; Tiwari, R.; Maurya, P.; Yadav, P. Dendrimers: A potential carrier for targeted drug delivery system. Pharm. Biol. Eval. 2016, 3, 275–287. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz del Olmo, N.; Peña González, C.E.; Rojas, J.D.; Gómez, R.; Ortega, P.; Escarpa, A.; de la Mata, F.J. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Carbosilane Dendrimers Functionalized with Polyphenolic Moieties. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentek, T.; Newenhouse, E.; O’Brien, B.; Chauhan, A.S. Development of a Topical Resveratrol Formulation for Commercial Applications Using Dendrimer Nanotechnology. Molecules 2017, 22, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Jain, P.; Jain, S.; Jain, R.; Bhargava, S.; Jain, A. Topical delivery of erythromycin through cubosomes for acne. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2018, 6, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, C.; Calarco, P.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Beccari, T.; Ricci, M.; Perioli, L. Development and Characterization of New Topical Hydrogels Based on Alpha Lipoic Acid—Hydrotalcite Hybrids. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Oberdörster, E.; Oberdörster, J. Nanotoxicology: An Emerging Discipline Evolving from Studies of Ultrafine Particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z. Liposome Formulation of Fullerene-Based Molecular Diagnostic and Therapeutic Agents. Pharmaceutics 2013, 5, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Hyodo, S. Protective effects of polyvinylpyrrolidone-wrapped fullerene against nitric oxide/peroxynitrite-induced cellular injury in human skin keratinocytes. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 21, 4579–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Discher, D.E.; Eisenberg, A. Polymer Vesicles. Science 2002, 297, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermudez, H.; Brannan, A.K.; Hammer, D.A.; Bates, F.S.; Discher, D.E. Molecular weight dependence of polymersome membrane structure, elasticity, and stability. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8203–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P. Polymersomes in Nanomedicine—A Review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 13, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.A.; Forster, C.; Feitosa, V.; Baby, A.R.; Léo, P.; Rangel-Yagui, C.O. Catalase-loaded polymersomes as a promising safe ingredient to active photoprotection. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2021, 7, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Rao, R. Enhancing efficacy and safety of azelaic acid via encapsulation in cyclodextrin nanosponges: Development, characterization and evaluation. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 5275–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tran, V.; Moon, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C. Liposomes for delivery of antioxidants in cosmeceuticals: Challenges and development strategies. J. Control. Release 2019, 300, 114–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudon, F.; Clément, Y.; Ripoll, L. Controlled Release of Retinol in Cationic Co-Polymeric Nanoparticles for Topical Application. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, K.; Saeedi, M.; Maleki Dizaj, S. Application of nanoparticles in percutaneous delivery of active ingredients in cosmetic preparations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z. Fabrication and characterization of zein/tea saponin composite nanoparticles as delivery vehicles of lutein. LWT 2020, 125, 109270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasada, M.; Budzisz, E. Retinoids: Active molecules influencing skin structure formation in cosmetic and dermatological treatments. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. Postȩpy Dermatol. Alergol. 2019, 36, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, E.B.; Fernandes, A.R.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Coutinho, T.E.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Souto, S.B.; Silva, A.M.; Santini, A. Nanomaterials for Skin Delivery of Cosmeceuticals and Pharmaceuticals. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, E.; Kaykın, M.; Şahin Bektay, H.; Güngör, S. Recent Advances on Topical Application of Ceramides to Restore Barrier Function of Skin. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snetkov, P.; Zakharova, K.; Morozkina, S.; Olekhnovich, R.; Uspenskaya, M. Hyaluronic Acid: The Influence of Molecular Weight on Structural, Physical, Physico-Chemical, and Degradable Properties of Biopolymer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisvert, A.; León-González, Z.; Tarazona, I.; Salvador, A.; Giokas, D. An overview of the analytical methods for the determination of organic ultraviolet filters in biological fluids and tissues. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 752, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, S.; Keck, C.M.; Anselmi, C.; Müller, R.H. Skin photoprotection improvement: Synergistic interaction between lipid nanoparticles and organic UV filters. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 414, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorg, O.; Antille, C.; Kaya, G.; Saurat, J.-H. Retinoids in cosmeceuticals. Dermatol. Ther. 2006, 19, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castleberry, S.A.; Quadir, M.A.; Sharkh, M.A.; Shopsowitz, K.E.; Hammond, P.T. Polymer conjugated retinoids for controlled transdermal delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 262, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limcharoen, B.; Pisetpackdeekul, P.; Toprangkobsin, P.; Thunyakitpisal, P.; Wanichwecharungruang, S.; Banlunara, W. Topical Proretinal Nanoparticles: Biological Activities, Epidermal Proliferation and Differentiation, Follicular Penetration, and Skin Tolerability. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 1510–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioele, G.; Cione, E.; Risoli, A.; Genchi, G.; Ragno, G. Accelerated photostability study of tretinoin and isotretinoin in liposome formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 293, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ourique, A.F.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Beck, R.C.R. Tretinoin-loaded nanocapsules: Preparation, physicochemical characterization, and photostability study. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 352, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenegro, L. Nanocarriers for skin delivery of cosmetic antioxidants. J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res. 2014, 2, 73–92. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Hu, J.Y.; Wang, S.Q. The role of antioxidants in photoprotection: A critical review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 67, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maretti, E.; Leo, E.; Rustichelli, C.; Truzzi, E.; Siligardi, C.; Iannuccelli, V. In vivo β-carotene skin permeation modulated by Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 597, 120322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, M.V.; Derner, R.B.; Lemos-Senna, E. Preparation and characterization of Haematococcus pluvialis carotenoid-loaded PLGA nanocapsules in a gel system with antioxidant properties for topical application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunar, K.; Kumar, U.; Deshmukh, S.K. Chapter 12—Recent Applications of Enzymes in Personal Care Products; Dhillon, G.S., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 279–298. ISBN 978-0-12-802392-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, A.C.; Bruni, N.; Meineri, G.; Corsi, D.; Cavi, N.; Gastaldi, D.; Dosio, F. Strategies to expand the therapeutic potential of superoxide dismutase by exploiting delivery approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 846–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decome, L.; De Méo, M.; Geffard, A.; Doucet, O.; Duménil, G.; Botta, A. Evaluation of photolyase (Photosome®) repair activity in human keratinocytes after a single dose of ultraviolet B irradiation using the comet assay. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2005, 79, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.N.; Pedriali Moraes, C.A. Bioactive Peptides: Applications and Relevance for Cosmeceuticals. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.F.; Martins, M.; Egipto, J.; Osório, H.; Ribeiro, A.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Changing the shape of hair with keratin peptides. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 51581–51592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Xu, H.; Xie, K.; Yang, Y. Effects of chemical structures of polycarboxylic acids on molecular and performance manipulation of hair keratin. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 58594–58603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, A.; Antón, J.M.G.; Mangues, M. A new decorin-like tetrapeptide for optimal organization of collagen fibres. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2008, 30, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, F.; Schmid, D.; Wandrey, F.; Zülli, F. Heptapeptide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for cosmetic anti-ageing applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deli, G.; Hatziantoniou, S.; Nikas, Y.; Demetzos, C. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanoemulsions containing ceramides: Preparation and physicochemical characterization. J. Liposome Res. 2009, 19, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, E.N.; Gebre-Mariam, T.; Paulos, G.; Wohlrab, J.; Neubert, R.H.H. Delivery of oat-derived phytoceramides into the stratum corneum of the skin using nanocarriers: Formulation, characterization and in vitro and ex-vivo penetration studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Tang, X.; Jia, Y.; Ho, C.-T.; Huang, Q. Applications and delivery mechanisms of hyaluronic acid used for topical/transdermal delivery—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 578, 119127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.N.A.; Roswandi, N.L.; Waqas, M.; Habib, H.; Hussain, F.; Khan, S.; Sohail, M.; Ramli, N.A.; Thu, H.E.; Hussain, Z. Hyaluronic acid, a promising skin rejuvenating biomedicine: A review of recent updates and pre-clinical and clinical investigations on cosmetic and nutricosmetic effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidekrueger, P.I.; Juran, S.; Patel, A.; Tanna, N.; Broer, P.N. Plastic Surgery Statistics in the US: Evidence and Implications. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2016, 40, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegasothy, S.M.; Zabolotniaia, V.; Bielfeldt, S. Efficacy of a New Topical Nano-hyaluronic Acid in Humans. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2014, 7, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ngoc, L.T.; Tran, V.V.; Moon, J.-Y.; Chae, M.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Recent Trends of Sunscreen Cosmetic: An Update Review. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, A. Photoprotection in the Era of Nanotechnology BT—Principles and Practice of Photoprotection; Wang, S.Q., Lim, H.W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 335–360. ISBN 978-3-319-29382-0. [Google Scholar]
- Damiani, E.; Puglia, C. Nanocarriers and Microcarriers for Enhancing the UV Protection of Sunscreens: An Overview. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 3769–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneluti, A.L.M.; Guerra, L.O.; Velasco, M.V.R.; do Rosário Matos, J.; Baby, A.R.; Kalia, Y.N. Preclinical and clinical studies to evaluate cutaneous biodistribution, safety and efficacy of UV filters encapsulated in mesoporous silica SBA-15. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 169, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z.; Chen, D. Preparation and characterization of dissolving hyaluronic acid composite microneedles loaded micelles for delivery of curcumin. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 1520–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krambeck, K.; Silva, V.; Silva, R.; Fernandes, C.; Cagide, F.; Borges, F.; Santos, D.; Otero-Espinar, F.; Lobo, J.M.S.; Amaral, M.H. Design and characterization of Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) and Nanostructured lipid carrier-based hydrogels containing Passiflora edulis seeds oil. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 600, 120444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-H.; Jeon, Y.-E.; Kang, S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, K.-T.; Kim, D.-D. Lipid Nanoparticles for Enhancing the Physicochemical Stability and Topical Skin Delivery of Orobol. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Luo, D.; Qu, W.; Chen, D.; Hong, Y.; Sheng, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, W. Nanoliposomes co-delivering bioactive peptides produce enhanced anti-ageing effect in human skin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Zhou, C.-L.; Chen, F.-P.; Han, D.; Wang, C.-Y.; Li, J.-X.; Chi, Z.; Liu, C.-G. Development of a carboxymethyl chitosan functionalized nanoemulsion formulation for increasing aqueous solubility, stability and skin permeability of astaxanthin using low-energy method. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 34, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitri, K.; Shegokar, R.; Gohla, S.; Anselmi, C.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanocarriers for dermal delivery of lutein: Preparation, characterization, stability and performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 414, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.; Pang, M.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, Y. Microneedles mediated bioinspired lipid nanocarriers for targeted treatment of alopecia. J. Control. Release 2021, 329, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, S.A.; Barradas, T.N. Developing formulations for drug follicular targeting: Nanoemulsions loaded with minoxidil and clove oil. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.L.; Kim, J.-C. In vivo hair growth promotion effects of cosmetic preparations containing hinokitiol-loaded poly(ε-caprolacton) nanocapsules. J. Microencapsul. 2008, 25, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.M.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, J.-C. Characterization and In-vitro Permeation Study of Stearic Acid Nanoparticles containing Hinokitiol. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2007, 84, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, T.; Dias-Ferreira, J.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Souza, A.L.R.; Kiill, C.P.; Gremião, M.P.D.; García, M.L.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Formulating octyl methoxycinnamate in hybrid lipid-silica nanoparticles: An innovative approach for UV skin protection. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, V.; Gubitosa, J.; Fini, P.; Nuzzo, S.; Agostiano, A.; Cosma, P. Snail slime-based gold nanoparticles: An interesting potential ingredient in cosmetics as an antioxidant, sunscreen, and tyrosinase inhibitor. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2021, 224, 112309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, D.J.; Maliha, M.; Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Browne, C.; Mouterde, L.M.M.; Simon, G.P.; Allais, F.; Garnier, G. Diethyl sinapate-grafted cellulose nanocrystals as nature-inspired UV filters in cosmetic formulations. Mater. Today Bio 2021, 12, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldas, A.R.; Faria, M.J.; Ribeiro, A.; Machado, R.; Gonçalves, H.; Gomes, A.C.; Soares, G.M.B.; Lopes, C.M.; Lúcio, M. Avobenzone-loaded and omega-3-enriched lipid formulations for production of UV blocking sunscreen gels and textiles. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 342, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Huang, H.-Y. In Vitro Anti-Propionibacterium Activity by Curcumin Containing Vesicle System. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 61, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viyoch, J.; Pisutthanan, N.; Faikreua, A.; Nupangta, K.; Wangtorpol, K.; Ngokkuen, J. Evaluation of in vitro antimicrobial activity of Thai basil oils and their micro-emulsion formulas against Propionibacterium acnes. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2006, 28, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pornpattananangkul, D.; Fu, V.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Vecchio, J.; Gao, W.; Huang, C.-M.; Zhang, L. In Vivo Treatment of Propionibacterium acnes Infection with Liposomal Lauric Acids. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinoco, A.; Gonçalves, F.; Costa, A.F.; Freitas, D.S.; Cavaco-Paulo, A.; Ribeiro, A. Keratin: Zein particles as vehicles for fragrance release on hair. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 159, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khameneh, B.; Halimi, V.; Jaafari, M.R.; Golmohammadzadeh, S. Safranal-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Evaluation of sunscreen and moisturizing potential for topical applications. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noor, N.M.; Khan, A.A.; Hasham, R.; Talib, A.; Sarmidi, M.R.; Aziz, R.; Aziz, A.A. Empty nano and micro-structured lipid carriers of virgin coconut oil for skin moisturisation. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 10, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, D.S.; Pereira, T.A.; Maciel, N.R.; Bortoloto, J.; Viera, G.S.; Oliveira, G.C.; Rocha-Filho, P.A. Formation and stability of oil-in-water nanoemulsions containing rice bran oil: In vitro and in vivo assessments. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, K.; Hariharan, K.; Qu, Z.; Rewatkar, P.; Cao, Y.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Pandey, P.; Popat, A.; Mehta, T. Tacrolimus encapsulated mesoporous silica nanoparticles embedded hydrogel for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 608, 121079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kildaci, I.; Budama-Kilinc, Y.; Kecel-Gunduz, S.; Altuntas, E. Linseed Oil Nanoemulsions for treatment of Atopic Dermatitis disease: Formulation, characterization, in vitro and in silico evaluations. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenie, L.V.; Lacatusu, I.; Oprea, O.; Bordei, N.; Bacalum, M.; Badea, N. Azelaic acid-willow bark extract-panthenol—Loaded lipid nanocarriers improve the hydration effect and antioxidant action of cosmetic formulations. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 154, 112658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereig, S.A.; El-Zaafarany, G.M.; Arafa, M.G.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.A. Self-assembled tacrolimus-loaded lecithin-chitosan hybrid nanoparticles for in vivo management of psoriasis. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 608, 121114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, S.Y.; Shin, J.-W.; Na, J.-I.; Huh, C.-H.; Youn, S.-W.; Park, K.-C. Efficacy and safety of liposome-encapsulated 4-n-butylresorcinol 0.1% cream for the treatment of melasma: A randomized controlled split-face trial. J. Dermatol. 2010, 37, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Liu, Q. ROS-responsive hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with Glabridin for anti-pigmentation properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 327, 111429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abla, M.J.; Banga, A.K. Formulation of tocopherol nanocarriers and in vitro delivery into human skin. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2014, 36, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, S.; Pirot, F.; Manconi, M.; Falson, F.; Fadda, A.M. Liposomes and niosomes as potential carriers for dermal delivery of minoxidil. J. Drug Target. 2007, 15, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourmand, A.; Abdollahi, M. Current Opinion on Nanotoxicology. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 20, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadar, H.; Maqbool, F.; Niaz, K.; Abdollahi, M. Toxicity of Nanoparticles and an Overview of Current Experimental Models. Iran. Biomed. J. 2016, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafalou, S.; Mohammadi, H.; Ramazani, A.; Abdollahi, M. Different biokinetics of nanomedicines linking to their toxicity; an overview. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.L.; Xu, Z.Z.; Fan, M.X.; Liu, H.Y.; Xie, Y.H.; Zhu, T. Study on characteristics and harm of surfactants. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2014, 6, 2233–2237. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Su, R.; Nie, S.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Application of nanotechnology in improving bioavailability and bioactivity of diet-derived phytochemicals. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, A.; Amadeu, M.S.; Lancellotti, M.; de Hollanda, L.M.; Machado, D. The role of nanomaterials in cosmetics: National and international legislative aspects. Quim. Nova 2015, 38, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union Guidance on the Safety Assessment of Nanomaterials in Cosmetics. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/system/files/2020-10/sccs_o_233_0.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Ferraris, C.; Rimicci, C.; Garelli, S.; Ugazio, E.; Battaglia, L. Nanosystems in cosmetic products: A brief overview of functional, market, regulatory and safety concerns. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission REACH—Chemicals—Environment—European Commission. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/chemicals/reach/reach_en.htm (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Report from the Commission to the European Parliament and the Council on the Use of Nanomaterials in Cosmetics and on the Review of Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009 on Cosmetic Products as Regards Nanomaterials COM/2021/403 Final. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52021DC0403 (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Safety of Nanomaterials in Cosmetic Products; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/83957/download (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- European Commission. Cooperation on Competition in Asia—Asia (China, India, Japan, Korea and ASEAN); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/fpi/calls-tenders/cooperation-competition-asia-asia-china-india-japan-korea-and-asean_en (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Marchant, G.E.; Sylvester, D.J. Transnational models for regulation of nanotechnology. J. Law Med. Ethics 2006, 34, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asia-Pacific Regulatory Guidelines—Cosmetics Bridge. Available online: https://www.cosmeticsbridge.com/asia-pacific-regulations-guidelines/ (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Environmental Protection Authority (EPA). Cosmetic Products Group Standard 2017—HSR002552; Environmental Protection Authority (EPA): Washington, DC, USA. Available online: https://www.epa.govt.nz/assets/Uploads/Documents/Hazardous-Substances/2017-Group-Standards/7f18a92020/Cosmetic-Products-Group-Standard-2017-HSR002552.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Australian Government. Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). Available online: https://www.tga.gov.au/ (accessed on 3 January 2022).
- Raj, R.K.; Chandrul, K.K. Regulatory Requirements for Cosmetics in Relation with Regulatory Authorities in India against US, Europe, Australia and Asian Countries. Int. J. Pharma Res. Health Sci. 2016, 4, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Carriers | Composition | Size Range | References |
|---|---|---|---|
Nanoemulsions | Nanoscale droplets comped by oil, surfactant, water cosurfactant | 50–200 nm | [22,64] |
Liposomes | Vesicular structures with an aqueous core enclosed by one or more bilayer membranes composed of natural or synthetic phospholipids. Liposomes also have cholesterol in their composition | 20 nm–2 µm | [64,65] |
Solid lipid nanoparticles | Composed by a shell of a single layer with a lipoic core made from complex glyceride mixtures, purified triglycerides, and waxes; They are stabilized by polymers or surfactants | 50–1000 nm | [22,65] |
Nanostructured lipid carriers | Structures that present an aqueous and oily phase | 10–1000 nm | [66] |
Niosomes | Vesicles with a bilayer structure synthesized from nonionic surfactants possessing hydrophilic and hydrophobic terminals; are conjugated with cholesterol and polyethene glycol | 100 nm–2 µm | [22,65] |
Nanocapsules | They have a solid and liquid core, where the active ingredients are protected and entrapped by a polymeric membrane which can be natural or synthetic | 100–500 nm | [65,67] |
Nanospheres | Crystalline or amorphous spherical nanoparticles having a core-shelled structure | 10–200 nm | [64] |
Nanogold | Nanoparticles of gold | 5–400 nm | [64] |
Nanosilver | Nanoparticles of silver | 1–100 nm | [64] |
Nanocrystals | Aggregates of atoms that combine into a “cluster” (Chavda) | 10–400 nm | [65,68] |
Dendrimers | Three-dimensional synthetic polymers are micellar, globular, radially symmetric and monodisperse. | 2–200 nm | [64] |
Cubosomes | They are prepared by self-assembly of liquid crystalline particles of some surfactants when combined with water and a microstructure at a specific ratio; Microstructure of cubosomes is obtained by the ratio of water, surfactant system and aqueous lipids | 10–500 nm | [64,69] |
Hydrogels | Polymeric networks with physical and chemical cross-links, expanding without dissolving in water or other biological fluids. | 10–100 nm | [65,70] |
Fullerenes/Buckyballs | They are composed by 60 atoms of carbon | 0.4–1.6 nm | [71,72] |
Polymersomes | They are formed by self-assemble copolymer amphiphiles blocks, consisting in artificial vesicles which have an aqueous cavity in the center | 100 nm–few µm | [65,73] |
Carbon nanotubes | Empty cylindrical fibers formed by graphene walls that are rolled “chiral” angles | 0.7–50 nm | [65] |
Nanosponges | These are free-flowing particles and have a 3D network of degradable polyester | <1 µm | [64,74] |
| Active Ingredient | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|
| Retinoids | Chemical structure exposes the retinoids to photopolymerization, photodegradation, photooxidation and photoisomerization; Some of them cause sensitization and skin irritation | [150] |
| Antioxidants | Limited stability in topical preparations | [151] |
| Enzymes | The native structure is destabilized by many common ingredients, which strongly affects enzymatic activity; their high molecular weight limit enzymes skin penetration | [25] |
| Peptides | Susceptible to degradation and low permeability | [25] |
| Ceramides | Low solubility | [152] |
| Hyaluronic acid | Hyaluronic acid with high molecular weight and hydrophilicity reveals poor penetration | [153] |
| Organic UV filters | May cause many adverse effects due to the production of toxic metabolites and ROS, which can be triggered by percutaneous accumulation and absorption | [154,155] |
| Country | Definition | Rules | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | Product that are not a cosmetic or a drug, is a “quasi-drugs” | Ingredients need to be pre-approved before including them into the “quasi-drugs” classification and require pre-approval before introduced them into the market | [223] |
| Korea | Korea Food and Drug Administration (KFDA) classifies them as “functional cosmetics” | KFDA is responsible for improving the safety and evaluation of functional cosmetics | [224] |
| Thailand | According to the used ingredients in cosmeceuticals, they are classified as “controlled cosmetics” | the notification from the FDA for the use of this products is mandatory | [225] |
| New Zealand | The category in which cosmeceuticals are accommodated is called “related products” | The regulation applied in New Zealand is similar to the EU legislation. The specifics of claims regulation and nanomaterials are the same and must be notified to Environmental Protection Authority (EPA) | [226] |
| Australia | In Australia, goods can be categorized based on claims about the product and product composition; the borderline products are classified as “therapeutic goods” | Only approved ingredients are used for the manufacture of these products. The Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods is the organization that registers "therapeutic goods". | [227] |
| USA | In the U.S., there are three categories: cosmetics, drugs, and over-the-counter medications. There is not a legal definition of cosmeceuticals according to FDA. | Classification by the U.S. FDA depends on the claims of the products. | [222] |
| European Union | The EU does not have a category to be called cosmeceuticals, but it has stringent law in which any claims made by the company are required to be submitted as a proof | The European regulation requires that cosmetic manufacturers declare all the nanoparticles/nanomaterials present in their products. They are required to add the word nano to the ingredient list. Regulation (EC) No.1223/2009. | [26] |
| China | “cosmetics for special use” | Similar to the FDA, but more rigorous, the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) requires that all foreign cosmetic products, before their release into the Chinese market, perform a safety evaluation comprising of several tests such as microbiology, toxicity, long-term toxicity, and carcinogenic. The manufacturers are also required to conduct trials to ensure their safety for humans. The cosmetics (imported) are divided into two main categories: special use cosmetics and ordinary ones. As a result, each category needs a distinct type of permit from the State Food and Drug Administration (SFDA). Finally, the Health Administration Department of the State Council—SFDA—must issue hygiene or record-keeping permit for the marketing of cosmetics. | [228] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, C.; Coelho, C.; Teixeira, J.A.; Ferreira-Santos, P.; Botelho, C.M. Nanocarriers as Active Ingredients Enhancers in the Cosmetic Industry—The European and North America Regulation Challenges. Molecules 2022, 27, 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051669
Oliveira C, Coelho C, Teixeira JA, Ferreira-Santos P, Botelho CM. Nanocarriers as Active Ingredients Enhancers in the Cosmetic Industry—The European and North America Regulation Challenges. Molecules. 2022; 27(5):1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051669
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Cristiana, Cristina Coelho, José A. Teixeira, Pedro Ferreira-Santos, and Claudia M. Botelho. 2022. "Nanocarriers as Active Ingredients Enhancers in the Cosmetic Industry—The European and North America Regulation Challenges" Molecules 27, no. 5: 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051669
APA StyleOliveira, C., Coelho, C., Teixeira, J. A., Ferreira-Santos, P., & Botelho, C. M. (2022). Nanocarriers as Active Ingredients Enhancers in the Cosmetic Industry—The European and North America Regulation Challenges. Molecules, 27(5), 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051669