3D Neuronal Cell Culture Modeling Based on Highly Porous Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
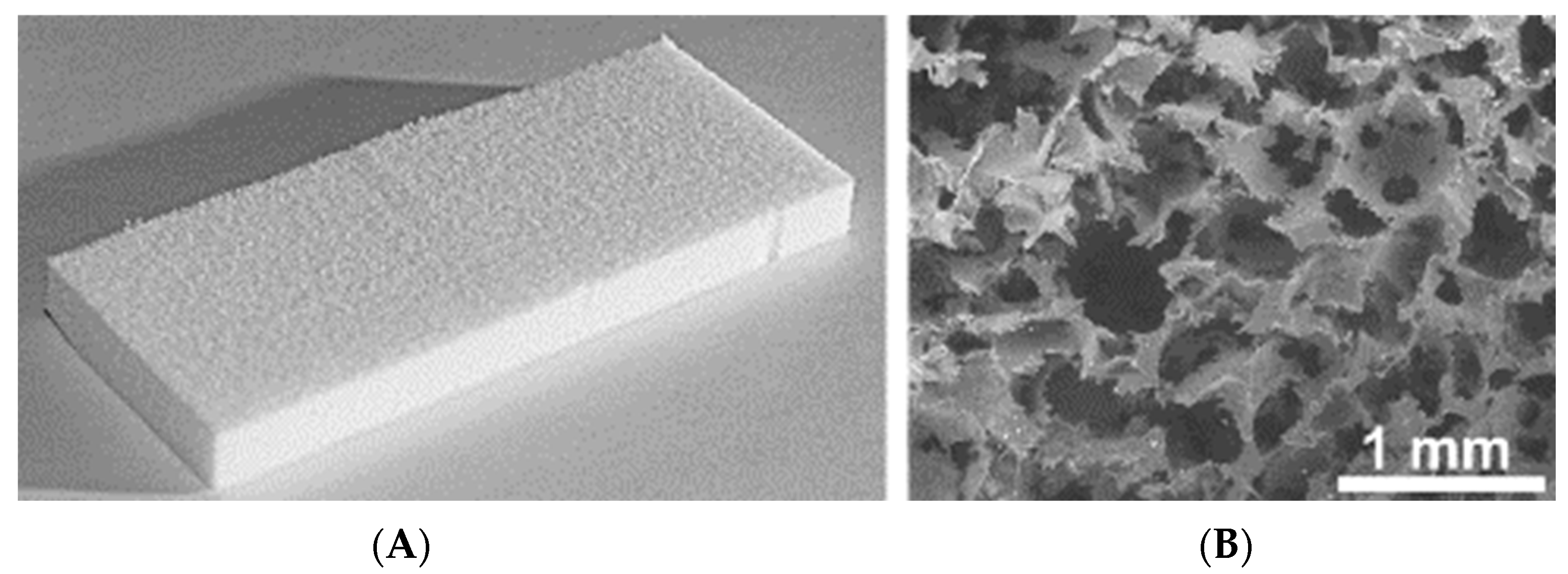
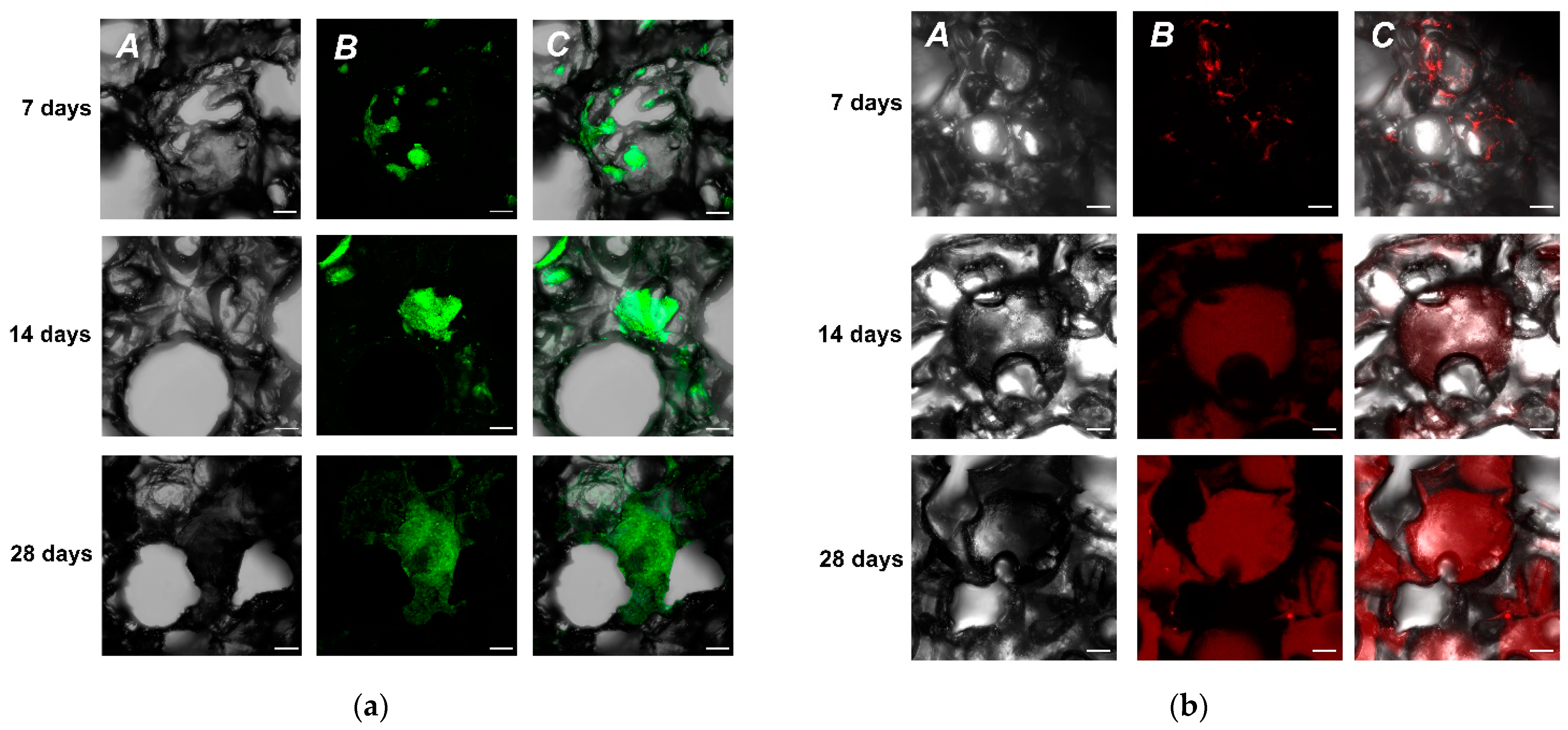
2.1. Growth of SH-SY5Y Cells and Primary Hippocampal Cell Cultures on UHMWPE Matrix
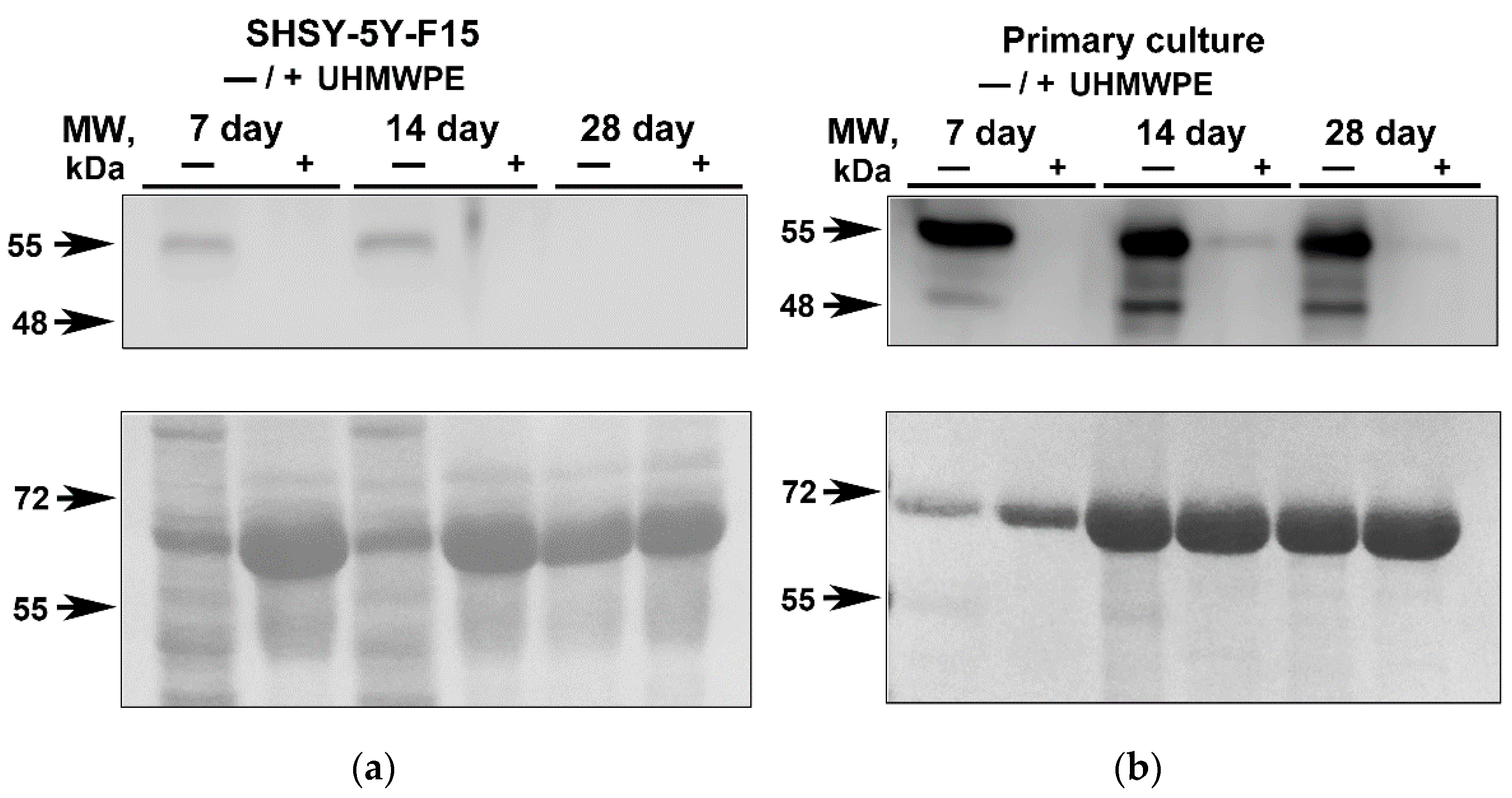
2.2. Analysis of the GFAP in Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y-F15 Cells and Primary Hippocampal Culture on UHMWPE
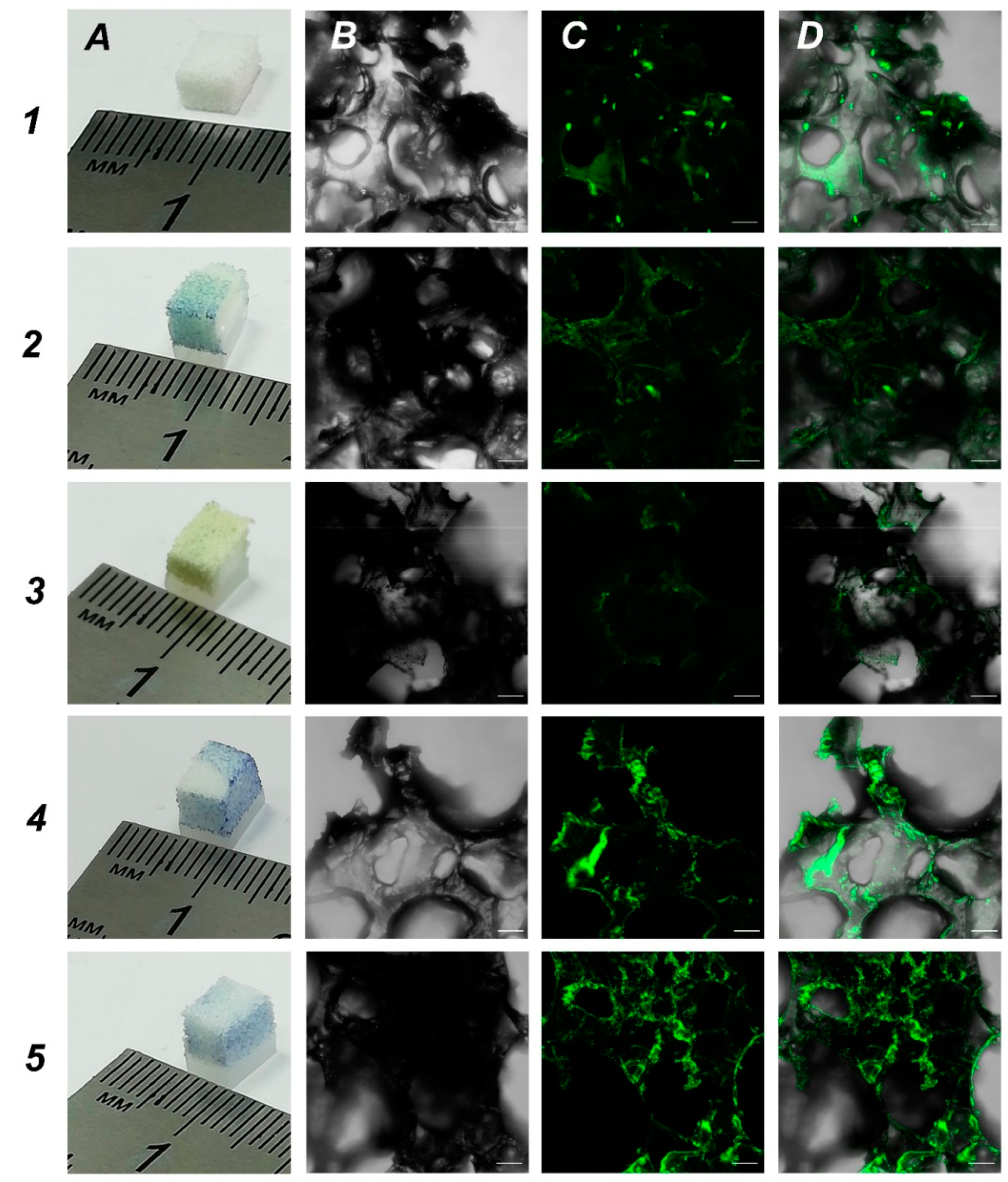
2.3. Obtaining Samples of Porous UHMWPE with Increased Surface Hydrophilicity. UHMWPE Functionalization with Biopolymers for Increased Biocompatibility
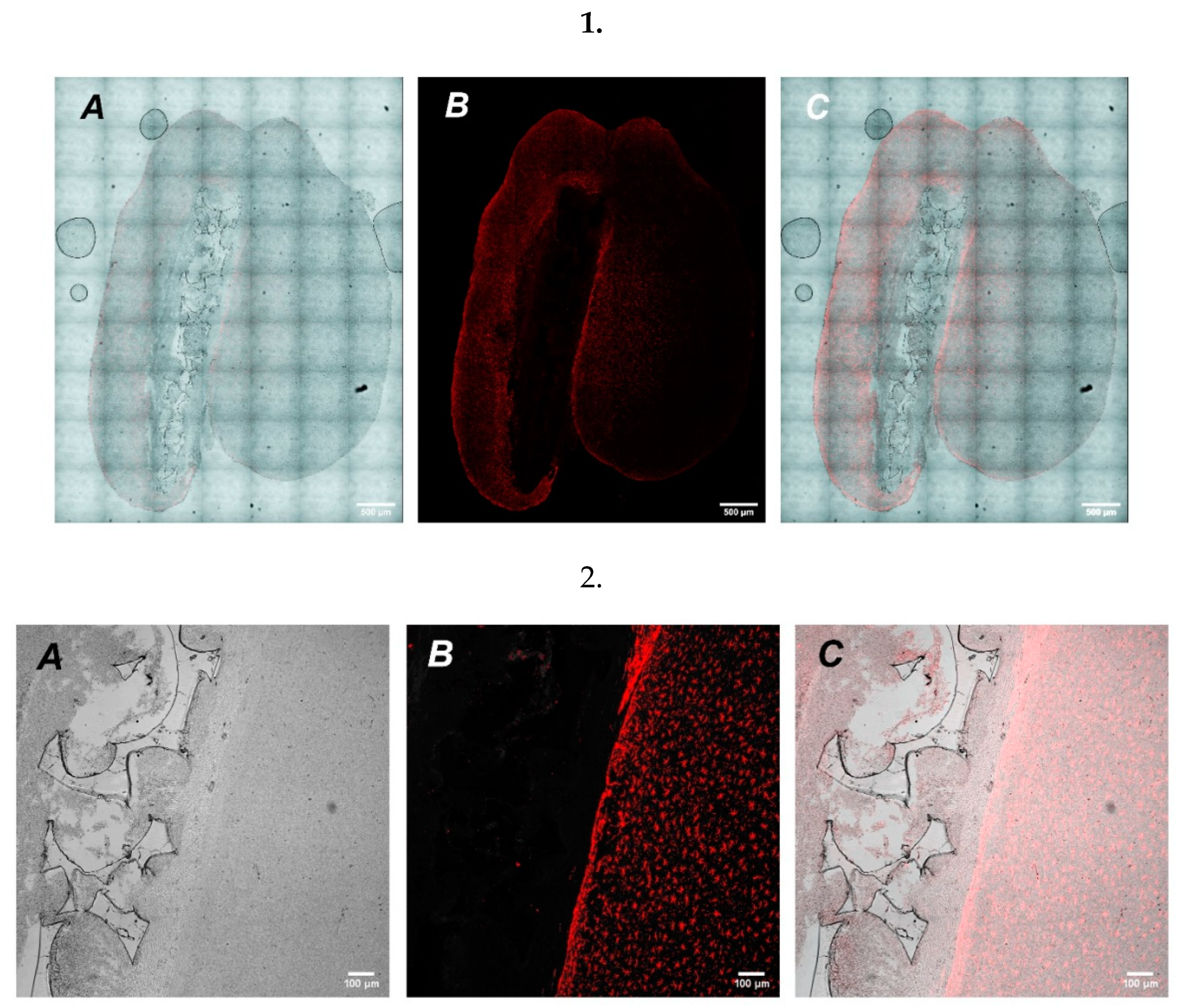
2.4. UHMWPE as a Vehicle for Cell Delivery
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture
4.2.1. Primary Culture
4.2.2. SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cell Culture
4.3. 2D and 3D Culturing of Primary Culture Cells and Human Neuroblastoma
4.4. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.5. Protein Extraction from Cells
4.6. Immunoblotting
4.7. Implantation of UHMWPE into Mouse Cortex
4.8. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
4.9. UHMWPE Functionalization
4.10. MTT Viability Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CNTs | carbon nanotubes |
| DI | deionized |
| GFAP | glial fibrillar acidic protein |
| UHMWPE | Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene |
References
- Kenny, P.A.; Lee, G.Y.; Myers, C.A.; Neve, R.M.; Semeiks, J.R.; Spellman, P.T.; Lorenz, K.; Lee, E.H.; Barcellos-Hoff, M.H.; Petersen, O.W.; et al. The morphologies of breast cancer cell lines in three-dimensional assays correlate with their profiles of gene expression. Mol. Oncol. 2007, 1, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Birgersdotter, A.; Sandberg, R.; Ernberg, I. Gene expression perturbation in vitro—A growing case for three-dimensional (3D) culture systems. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2005, 15, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poincloux, R.; Collin, O.; Lizarraga, F.; Romao, M.; Debray, M.; Piel, M.; Chavrier, P. Contractility of the cell rear drives invasion of breast tumor cells in 3D Matrigel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gargotti, M.; Lopez-Gonzalez, U.; Byrne, H.J.; Casey, A. Comparative studies of cellular viability levels on 2D and 3D in vitro culture matrices. Cytotechnology 2018, 70, 261–273. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadriraju, K.; Chen, C.S. Engineering cellular microenvironments to improve cell-based drug testing. Drug Discov. Today 2002, 7, 612–620. [Google Scholar]
- Tibbitt, M.W.; Anseth, K.S. Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 655–663. [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal, S. Culture and assay systems used for 3D cell culture. Corning 2014, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jakus, A.E.; Secor, E.B.; Rutz, A.L.; Jordan, S.W.; Hersam, M.C.; Shah, R.N. Three-dimensional printing of high-content graphene scaffolds for electronic and biomedical applications. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4636–4648. [Google Scholar]
- Pasca, A.M.; Sloan, S.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Tian, Y.; Makinson, C.D.; Huber, N.; Kim, C.H.; Park, J.Y.; O’Rourke, N.A.; Nguyen, K.D.; et al. Functional cortical neurons and astrocytes from human pluripotent stem cells in 3D culture. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- Worthington, P.; Drake, K.M.; Li, Z.; Napper, A.D.; Pochan, D.J.; Langhans, S.A. Beta-hairpin hydrogels as scaffolds for high-throughput drug discovery in three-dimensional cell culture. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 535, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J.; Zhu, W.; Nowicki, M.; Lee, G.; Heo, D.N.; Kim, J.; Zuo, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.G. 3D printing nano conductive multi-walled carbon nanotube scaffolds for nerve regeneration. J. Neural. Eng. 2018, 15, 016018. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Duan, B.; Lu, A.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, L. Biocompatible chitin/carbon nanotubes composite hydrogels as neuronal growth substrates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Choi, E.J.; Cho, J.H.; Cho, A.N.; Jin, Y.; Yang, K.; Song, C.; Cho, S.W. Three-Dimensional Electroconductive Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels Incorporated with Carbon Nanotubes and Polypyrrole by Catechol-Mediated Dispersion Enhance Neurogenesis of Human Neural Stem Cells. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3060–3072. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.; Merino, S.; Gonzalez-Dominguez, J.M.; Rauti, R.; Ballerini, L.; Prato, M.; Vazquez, E. Graphene Improves the Biocompatibility of Polyacrylamide Hydrogels: 3D Polymeric Scaffolds for Neuronal Growth. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 10942. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Struzyna, L.A.; Adewole, D.O.; Gordian-Velez, W.J.; Grovola, M.R.; Burrell, J.C.; Katiyar, K.S.; Petrov, D.; Harris, J.P.; Cullen, D.K. Anatomically Inspired Three-dimensional Micro-tissue Engineered Neural Networks for Nervous System Reconstruction, Modulation, and Modeling. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 123, e55609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimkin, A.V.; Senatov, F.S.; Anisimova, N.Y.; Kiselevskiy, M.V.; Zalepugin, D.Y.; Chernyshova, I.V.; Tilkunova, N.A.; Kaloshkin, S.D. Multilayer porous UHMWPE scaffolds for bone defects replacement. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 73, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maksimkin, A.V.; Senatov, F.S.; Niaza, K.; Dayyoub, T.; Kaloshkin, S.D. Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene/Titanium-Hybrid Implant for Bone-Defect Replacement. Materials 2020, 13, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossovsky, N. Biological Consequences of Polymeric Materials: Silicones, PMMA, UHMWPE. In Advances in Materials Science and Implant Orthopedic Surgery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 25–46. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, N.A.; Njuguna, J.; Kandasubramanian, B. UHMWPE for biomedical applications: Performance and functionalization. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 125, 109529. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, S.M. UHMWPE Biomaterials Handbook: Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene in Total Joint Replacement and Medical Devices; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Senatov, F.; Amanbek, G.; Orlova, P.; Bartov, M.; Grunina, T.; Kolesnikov, E.; Maksimkin, A.; Kaloshkin, S.; Poponova, M.; Nikitin, K.; et al. Biomimetic UHMWPE/HA scaffolds with rhBMP-2 and erythropoietin for reconstructive surgery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol Appl. 2020, 111, 110750. [Google Scholar]
- Smelt, H.; Cheng, W.; Tyler, S.; Virmani, R. TCT-125 Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene Membrane for Use in Vascular Stent Graft Applications—Preliminary Evidence from an Ovine Peripheral Implantation Model. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70 (Suppl. 18), B56. [Google Scholar]
- Maksimkin, A.V.; Kaloshkin, S.D.; Tcherdyntsev, V.V.; Chukov, D.I.; Stepashkin, A.A. Technologies for manufacturing ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene-based porous structures for bone implants. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 47, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, M.; Nonaka, T.; Arai, T.; Kametani, F.; Buchman, V.L.; Ninkina, N.; Bachurin, S.O.; Akiyama, H.; Goedert, M.; Hasegawa, M. Methylene blue and dimebon inhibit aggregation of TDP-43 in cellular models. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 2419–2424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, W.; Fu, X.; Li, Z.; Ou, J.; Yang, Z.; Xiang, M.; Qin, Z. Porous Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene/Functionalized Activated Nanocarbon Composites with Improved Biocompatibility. Materials 2021, 14, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Arzhakova, O.V.; Nazarov, A.I.; Solovei, A.R.; Dolgova, A.A.; Kopnov, A.Y.; Chaplygin, D.K.; Tyubaeva, P.M.; Yarysheva, A.Y. Mesoporous Membrane Materials Based on Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene: From Synthesis to Applied Aspects. Membranes 2021, 11, 834. [Google Scholar]
- Lermontov, S.A.; Maksimkin, A.V.; Sipyagina, N.A.; Malkova, A.N.; Kolesnikov, E.A.; Zadorozhnyy, M.Y.; Straumal, E.A.; Dayyoub, T. Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene with hybrid porous structure. Polymer 2020, 202, 122744. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, K.; Paxinos, G. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; p. 246. [Google Scholar]
- Connor-Robson, N.; Peters, O.M.; Millership, S.; Ninkina, N.; Buchman, V.L. Combinational losses of synucleins reveal their differential requirements for compensating age-dependent alterations in motor behavior and dopamine metabolism. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 46, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, D.C.; Schmidt, O.; Ninkina, N.; Jones, P.A.; Sharkey, J.; Buchman, V.L. Developmental loss and resistance to MPTP toxicity of dopaminergic neurones in substantia nigra pars compacta of gamma-synuclein, alpha-synuclein and double alpha/gamma-synuclein null mutant mice. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Ninkina, N.; Papachroni, K.; Robertson, D.C.; Schmidt, O.; Delaney, L.; O’Neill, F.; Court, F.; Rosenthal, A.; Fleetwood-Walker, S.M.; Davies, A.M.; et al. Neurons expressing the highest levels of gamma-synuclein are unaffected by targeted inactivation of the gene. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 8233–8245. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ustyugov, A.A.; Sipyagina, N.A.; Malkova, A.N.; Straumal, E.A.; Yurkova, L.L.; Globa, A.A.; Lapshina, M.A.; Chicheva, M.M.; Chaprov, K.D.; Maksimkin, A.V.; et al. 3D Neuronal Cell Culture Modeling Based on Highly Porous Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene. Molecules 2022, 27, 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072087
Ustyugov AA, Sipyagina NA, Malkova AN, Straumal EA, Yurkova LL, Globa AA, Lapshina MA, Chicheva MM, Chaprov KD, Maksimkin AV, et al. 3D Neuronal Cell Culture Modeling Based on Highly Porous Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene. Molecules. 2022; 27(7):2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072087
Chicago/Turabian StyleUstyugov, Aleksey A., Nataliya A. Sipyagina, Alena N. Malkova, Elena A. Straumal, Lyudmila L. Yurkova, Anastasiya A. Globa, Maria A. Lapshina, Maria M. Chicheva, Kirill D. Chaprov, Aleksey V. Maksimkin, and et al. 2022. "3D Neuronal Cell Culture Modeling Based on Highly Porous Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene" Molecules 27, no. 7: 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072087
APA StyleUstyugov, A. A., Sipyagina, N. A., Malkova, A. N., Straumal, E. A., Yurkova, L. L., Globa, A. A., Lapshina, M. A., Chicheva, M. M., Chaprov, K. D., Maksimkin, A. V., & Lermontov, S. A. (2022). 3D Neuronal Cell Culture Modeling Based on Highly Porous Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene. Molecules, 27(7), 2087. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072087






