Fabrication of Magnetic Al-Based Fe3O4@MIL-53 Metal Organic Framework for Capture of Multi-Pollutants Residue in Milk Followed by HPLC-UV
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Analysis
2.1. Characterization of Fe3O4@MIL-53(Al)
2.2. Optimization of the Experimental Parameters
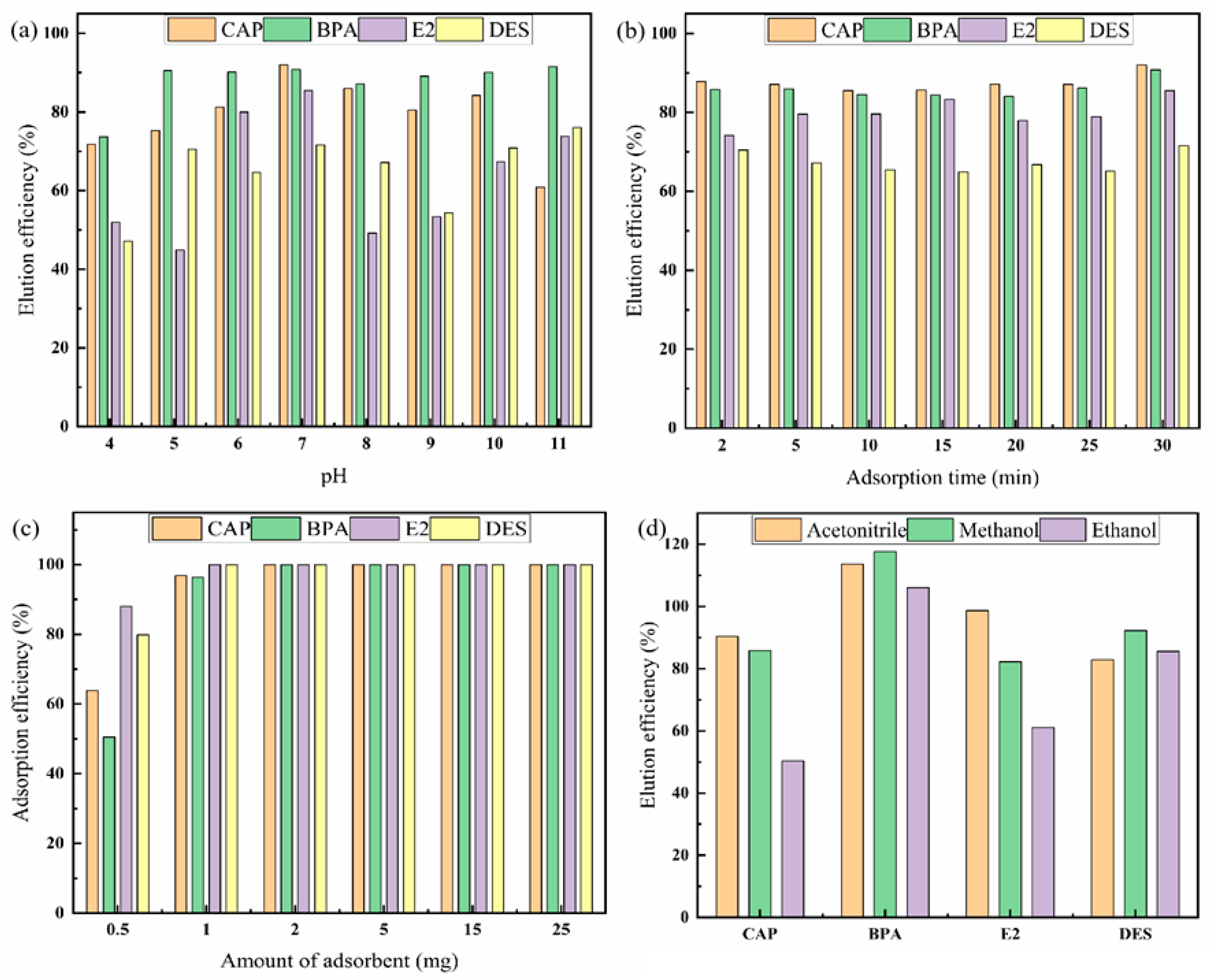
2.2.1. Effect of Adsorption Conditions
2.2.2. Optimization of Desorption Conditions
2.3. Possible Extraction Mechanisms
2.4. Reusability
2.5. Method Validation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Chemicals
3.2. Instruments and Chromatographic Conditions
3.3. Sample Preparation
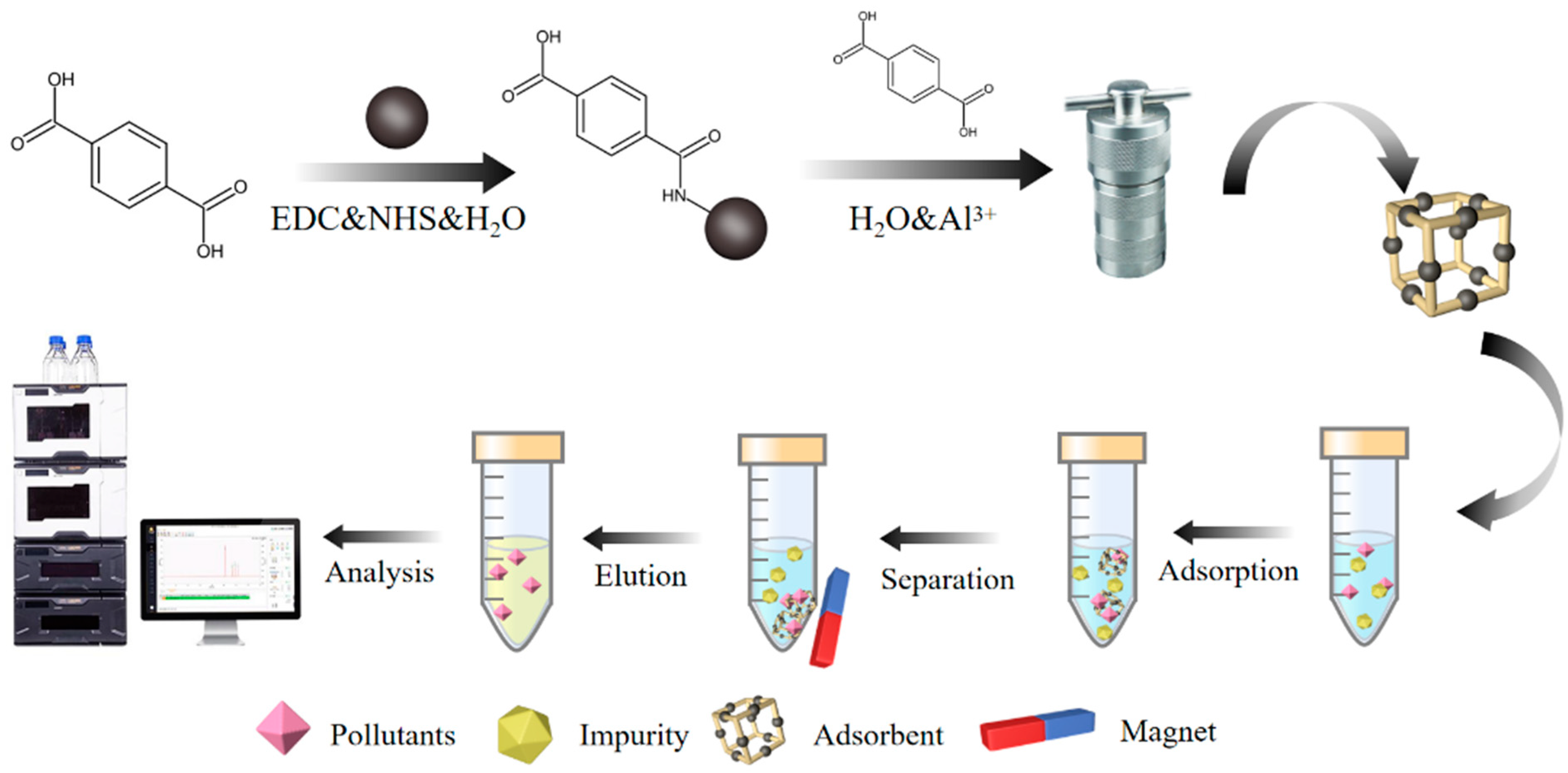
3.4. Preparation of Fe3O4@MIL-53(Al)
3.5. MSPE Procedure
3.6. Methodology Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H. Recent advances in applications of metal–organic frameworks for sample preparation in pharmaceutical analysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 411, 213235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Han, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Tuning the primary selective nanochannels of MOF thin-film nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes for efficient removal of hydrophobic endocrine disrupting compounds. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, A.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Wei, J.; Chen, D.; Peng, Y.; Luo, S. Three-dimensional petal-like graphene Co3.0Cu1.0 metal organic framework for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 884, 161144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, G.; Park, I.-H.; Medishetty, R.; Vittal, J.J. Two-dimensional metal-organic framework materials: Synthesis, structures, properties and applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 3751–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogge, S.M.J.; Bavykina, A.; Hajek, J.; Garcia, H.; Olivos-Suarez, A.I.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Vimont, A.; Clet, G.; Bazin, P.; Kapteijn, F.; et al. Metal–organic and covalent organic frameworks as single-site catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3134–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez-Serpa, A.; Jiménez-Abizanda, A.I.; Jiménez-Moreno, F.; Pasán, J.; Pino, V. Core-shell microparticles formed by the metal-organic framework CIM-80(Al) (Silica@CIM-80(Al)) as sorbent material in miniaturized dispersive solid-phase extraction. Talanta 2020, 211, 120723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Yamini, Y.; Gholami, M. Recent advances and trends in applications of solid-phase extraction techniques in food and environmental analysis. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 1207–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-H.; He, C.-Y. Advances in cellulose-based sorbents for extraction of pollutants in environmental samples. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 1151–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladole, M.R.; Pokale, P.B.; Patil, S.S.; Belokar, P.G.; Pandit, A.B. Laccase immobilized peroxidase mimicking magnetic metal organic frameworks for industrial dye degradation. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 317, 124035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, S.; Wu, G.; Arabi, M.; Tan, F.; Guan, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Preparation of magnetic metal-organic frameworks with high binding capacity for removal of two fungicides from aqueous environments. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 90, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, G.; Gao, M.; Huang, X.; Xu, D. Recent advances and applications of magnetic metal-organic frameworks in adsorption and enrichment removal of food and environmental pollutants. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 50, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Mao, H.M.; Yu, B.; Han, J.; Bhat, G. facile synthesis of the magnetic metal-organic framework fe3o4/cu-3(btc) (2) for efficient dye removal. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, G.; Wu, D.; Yu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y. Facile preparation of magnetic covalent organic framework–metal organic framework composite materials as effective adsorbents for the extraction and determination of sedatives by high-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry in meat samples. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milheiro, J.; Vilamarim, R.; Filipe-Ribeiro, L.; Cosme, F.; Nunes, F.M. An accurate single-step lle method using keeper solvent for quantification of trace amounts of sotolon in port and white table wines by HPLC-DAD. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smink, D.; Kersten, S.R.; Schuur, B. Recovery of lignin from deep eutectic solvents by liquid-liquid extraction. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z. In situ immobilization of layered double hydroxides onto cotton fiber for solid phase extraction of fluoroquinolone drugs. Talanta 2018, 186, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; He, C.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S. Dummy molecularly imprinted magnetic nanoparticles for dispersive solid-phase extraction and determination of bisphenol A in Water Samples and Orange Juice. Talanta 2017, 162, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Nazal, M.; Ihsanullah, I. Novel materials for dispersive (micro) solid-phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental water samples: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1141, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Qin, P.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, S.; Cai, Z. Facile preparation of reduced graphene oxide/ZnFe2O4 nanocomposite as magnetic sorbents for enrichment of estrogens. Talanta 2020, 208, 120440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Qin, P.; Zhang, X.; Lu, M. Magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposites as the adsorbent for extraction and pre-concentration of azo dyes in different food samples followed by high-performance liquid chromatography analysis. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2018, 35, 2099–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanourakis, S.K.; Pena-Bahamonde, J.; Bandara, P.C.; Rodrigues, D.F. Nano-based adsorbent and photocatalyst use for pharmaceutical contaminant removal during indirect potable water reuse. NPJ Clean Water 2020, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ayati, A.; Davoodi, R.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi, F.; Malekmohammadi, S.; Orooji, Y.; Fu, L.; Sillanpaa, M. Recent advances in using of chitosan-based adsorbents for removal of pharmaceutical contaminants: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hena, S.; Gutierrez, L.; Croue, J.P. Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) from wastewater using microalgae: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awfa, D.; Ateia, M.; Fujii, M.; Johnson, M.S.; Yoshimura, C. Photodegradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in water treatment using carbonaceous-TiO2 composites: A critical review of recent literature. Water Res. 2018, 142, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanekamp, J.C.; Bast, A. Antibiotics exposure and health risks: Chloramphenicol. Environ. Toxicol. Pharm. 2015, 39, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, L.R.; da Silva, L.H.M.; Fernandes, C.; Engeseth, N.J.; Gloria, M.B.A. LC-MS/MS determination of chloramphenicol in food of animal origin in Brazil. Sci. Chromatogr. 2015, 7, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Qin, M.; Liu, C.; Deng, J.; Shi, G.; Zhou, T. Ionic liquid-functionalized magnetic metal-organic framework nanocomposites for efficient extraction and sensitive detection of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in environmental water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 5357–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, E.; Rahmani, M. Al-based MIL-53 metal organic framework (MOF) as the new catalyst for friedel-crafts alkylation of benzene. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, H.; Tong, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Sheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, X. Enrichment and sensitive determination of phthalate esters in environmental water samples: A novel approach of MSPE-HPLC based on PAMAM dendrimers-functionalized magnetic-nanoparticles. Talanta 2020, 206, 120213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C. The strengthening role of the amino group in metal–organic framework MIL-53 (Al) for methylene blue and malachite green dye adsorption. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 3414–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.-W.; Choi, B.H.; Dao, C.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Choi, J.-W.; Ahn, K.-H.; Lee, S.-H. Aluminum carboxylate-based metal organic frameworks for effective adsorption of anionic azo dyes from aqueous media. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 59, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merib, J.; Spudeit, D.A.; Corazza, G.; Carasek, E.; Anderson, J.L. Magnetic ionic liquids as versatile extraction phases for the rapid determination of estrogens in human urine by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4689–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.-L.; Fu, Q.-B.; Wang, M.-L.; Lin, J.-M.; Zhao, R.-S. Determination of trace bisphenols in functional beverages through the magnetic solid-phase extraction with MOF-COF composite. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senosy, I.A.; Guo, H.-M.; Ouyang, M.-N.; Lu, Z.-H.; Yang, Z.-H.; Li, J.-H. Magnetic solid-phase extraction based on nano-zeolite imidazolate framework-8-functionalized magnetic graphene oxide for the quantification of residual fungicides in water, honey and fruit juices. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Gao, M.; Qian, F.; Gu, H.; Zhang, Z. Preconcentration/extraction of trace bisphenols in milks using a novel effervescent reaction-assisted dispersive solid-phase extraction based on magnetic nickel-based n-doped graphene tubes. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.V.; Rallapalli, P.B.S.; Dangi, G.P.; Tayade, R.J.; Somani, R.S.; Bajaj, H.C. MIL-53(AI): An efficient adsorbent for the removal of nitrobenzene from aqueous solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10516–10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, M.; Palomino, G.T.; Cabello, C.P. Metal–Organic Framework@Carbon hybrid magnetic material as an efficient adsorbent for pollutant extraction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 6419–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Li, G. A novel electrochemical sensor based on Fe3O4-doped nanoporous carbon for simultaneous determination of diethylstilbestrol and 17 beta-estradiol in toner. Talanta 2018, 188, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolmohammad-Zadeh, H.; Zamani, A.; Shamsi, Z. Extraction of four endocrine-disrupting chemicals using a Fe3O4/graphene oxide/di-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid nano-composite, and their quantification by HPLC-UV. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Xue, S.; Zhang, L. Novel functionalized magnetic ionic liquid green separation technology coupled with high performance liquid chromatography: A rapid approach for determination of estrogens in milk and cosmetics. Talanta 2020, 209, 120542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Afy, N.; Sereshti, H.; Hijazi, A.; Nodeh, H.R. Determination of three tetracyclines in bovine milk using magnetic solid phase extraction in tandem with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with HPLC. J. Chromatogr. B Analyst. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1092, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.-Z.; Wang, Y.-H.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Gao, Z.-X.; Zhou, H.-Y. Development and application of magnetic solid phase extraction in tandem with liquid-liquid extraction method for determination of four tetracyclines by HPLC with UV detection. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2884–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Whole Milk | Skimmed Milk | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analytes | Added (μg/mL) | Recovery (%) | RSD (n = 3, %) | Recovery (%) | RSD (n = 3, %) |
| CAP | 0 | ND | ND | ||
| 0.10 | 101.49 | 0.025 | 92.45 | 0.054 | |
| 0.15 | 93.43 | 1.951 | 97.43 | 0.053 | |
| 0.20 | 94.78 | 0.076 | 88.17 | 0.011 | |
| BPA | 0 | ND | ND | ||
| 0.10 | 99.66 | 0.048 | 96.52 | 0.033 | |
| 0.15 | 104.30 | 0.173 | 103.88 | 0.149 | |
| 0.20 | 111.64 | 0.046 | 91.94 | 0.041 | |
| E2 | 0 | ND | ND | ||
| 0.10 | 91.32 | 0.067 | 91.93 | 0.052 | |
| 0.15 | 98.73 | 0.022 | 96.90 | 0.036 | |
| 0.20 | 91.40 | 0.073 | 100.41 | 0.108 | |
| DES | 0 | ND | ND | ||
| 0.10 | 113.46 | 0.019 | 107.58 | 0.021 | |
| 0.15 | 99.86 | 1.404 | 97.63 | 0.043 | |
| 0.20 | 102.19 | 0.002 | 99.40 | 0.027 | |
| Adsorbent | Method of Extraction | Analysis | Target | Linear Range (ng mL−1) | LODs (μg L−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4-NC | / | sensor | DES a, E2 b | 0.01–20 μmol/L | 4.6–4.9 nmol/L | [38] |
| Fe3O4/GO/DEHPA NC | MSPE | HPLC-UV | ph c, MP d, PP e, BPA f | 0.05–5 | 2.5–14.3 | [39] |
| MILs | DLLME | HPLC | E1 g, E2, HP h, CMA i, MGA j, MPA k | 20–1000 | 5–15 | [40] |
| MI-MNP | d-SPE | HPLC-UV | BPA | 50–1000 | 0.3 | [17] |
| Fe3O4@MIL-53(Al) | MSPE | HPLC-UV | CAP l, BPA, E2, DES | 50–5000 | 4–108 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-H.; Ren, S.-Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Han, D.-P.; Qin, K.; Peng, Y.; Han, T.; Gao, Z.-X.; et al. Fabrication of Magnetic Al-Based Fe3O4@MIL-53 Metal Organic Framework for Capture of Multi-Pollutants Residue in Milk Followed by HPLC-UV. Molecules 2022, 27, 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072088
Liu X-L, Wang Y-H, Ren S-Y, Li S, Wang Y, Han D-P, Qin K, Peng Y, Han T, Gao Z-X, et al. Fabrication of Magnetic Al-Based Fe3O4@MIL-53 Metal Organic Framework for Capture of Multi-Pollutants Residue in Milk Followed by HPLC-UV. Molecules. 2022; 27(7):2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xue-Li, Yong-Hui Wang, Shu-Yue Ren, Shuang Li, Yu Wang, Dian-Peng Han, Kang Qin, Yuan Peng, Tie Han, Zhi-Xian Gao, and et al. 2022. "Fabrication of Magnetic Al-Based Fe3O4@MIL-53 Metal Organic Framework for Capture of Multi-Pollutants Residue in Milk Followed by HPLC-UV" Molecules 27, no. 7: 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072088
APA StyleLiu, X.-L., Wang, Y.-H., Ren, S.-Y., Li, S., Wang, Y., Han, D.-P., Qin, K., Peng, Y., Han, T., Gao, Z.-X., Cui, J.-Z., & Zhou, H.-Y. (2022). Fabrication of Magnetic Al-Based Fe3O4@MIL-53 Metal Organic Framework for Capture of Multi-Pollutants Residue in Milk Followed by HPLC-UV. Molecules, 27(7), 2088. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072088





