G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR) Reconstitution and Labeling for Solution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Studies of the Structural Basis of Transmembrane Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preparation of GPCRs for NMR Studies
2.1. Solubilization of GPCRs in Detergent Micelles
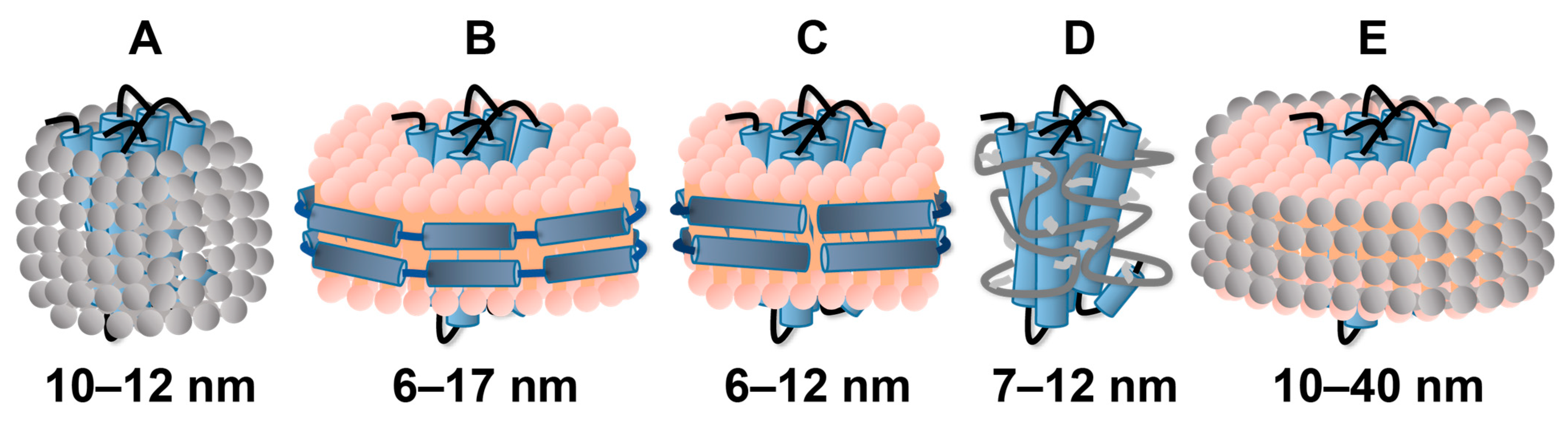
2.2. Reconstitution of GPCRs in Nanodiscs
2.3. Use of Amphipols or Bicelles for GPCR Solubilization
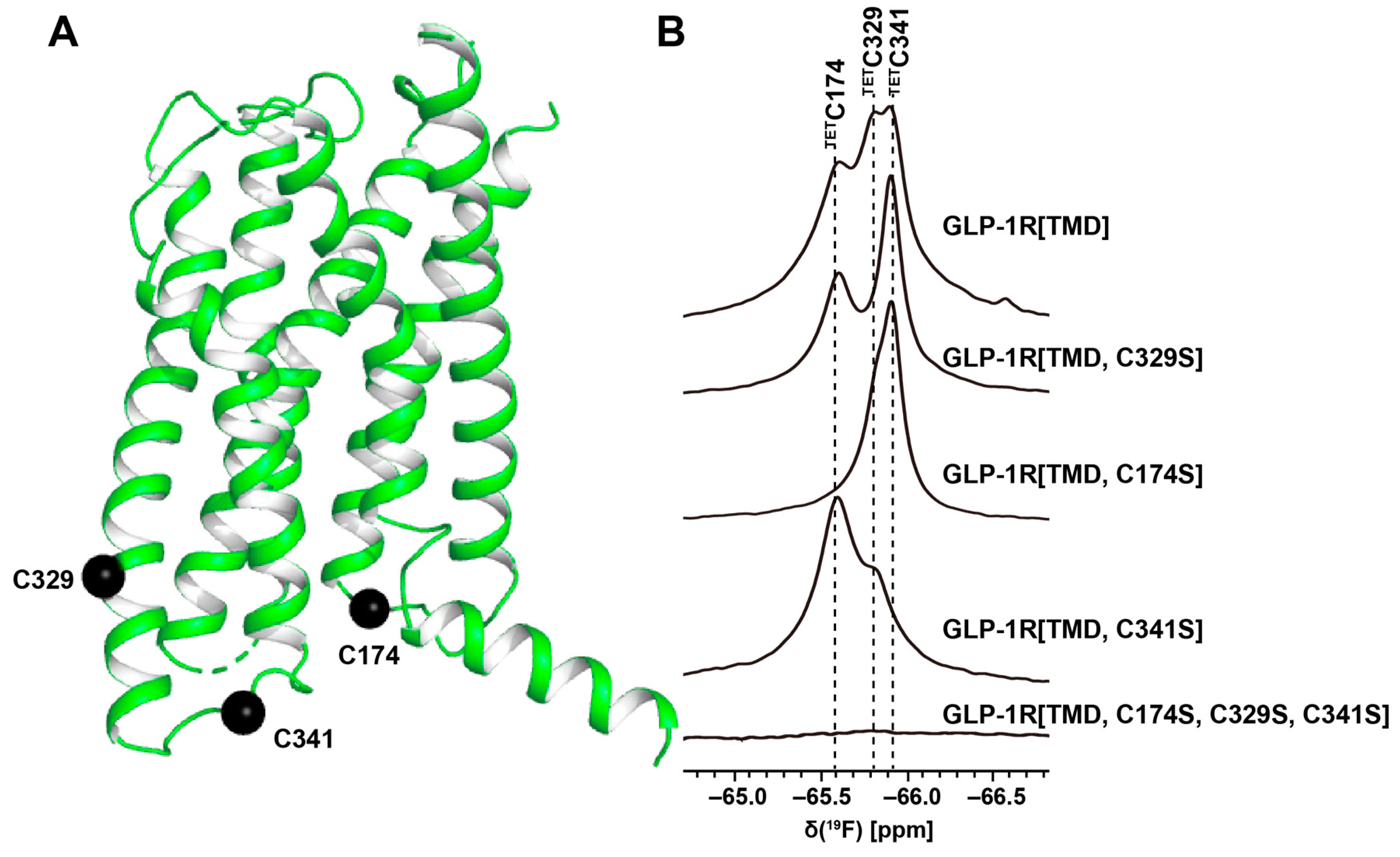
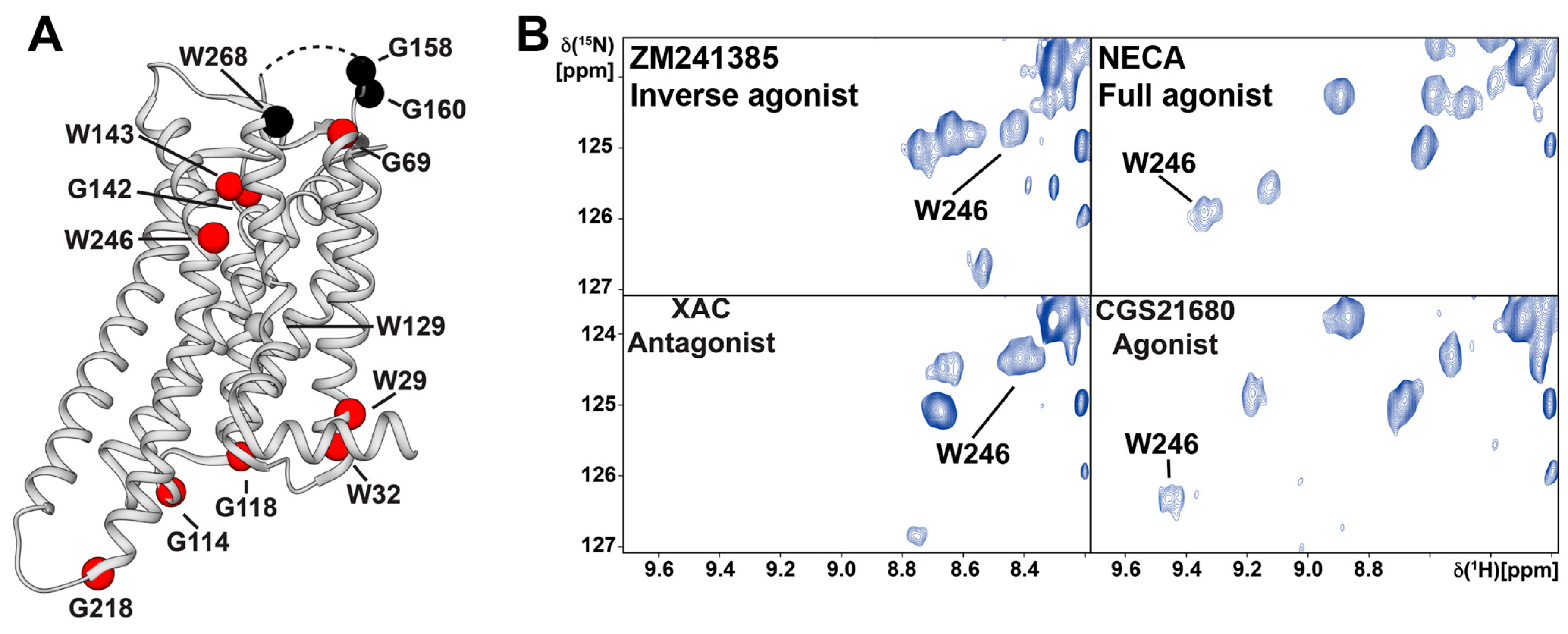
3. 19F-NMR with Observation of Extrinsic Probes Attached to GPCRs
4. NMR in Solution of GPCRs Using Stable-Isotope Labeling
5. GPCR–Ligand Interactions Studied by NMR Observation of the Ligand
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rask-Andersen, M.; Almén, M.S.; Schiöth, H.B. Trends in the exploitation of novel drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, T.I.; Bologa, C.G.; Brunak, S.; Campbell, A.; Gan, G.N.; Gaulton, A.; Gomez, S.M.; Guha, R.; Hersey, A.; Holmes, J.; et al. Unexplored therapeutic opportunities in the human genome. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A.S.; Attwood, M.M.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Schioth, H.B.; Gloriam, D.E. Trends in GPCR drug discovery: New agents, targets and indications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K. The molecular basis of G protein–coupled receptor activation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 897–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenakin, T. Inverse, protean, and ligand-selective agonism: Matters of receptor conformation. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tong, J.; Ding, K.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, S. GPCR allosteric modulator discovery. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1163, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedabadi, M.; Ghahremani, M.H.; Albert, P.R. Biased signaling of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs): Molecular determinants of GPCR/transducer selectivity and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 200, 148–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, A.; Bermudez, M. Allosteric coupling and biased agonism in G protein-coupled receptors. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 2513–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootten, D.; Christopoulos, A.; Marti-Solano, M.; Babu, M.M.; Sexton, P.M. Mechanisms of signalling and biased agonism in G protein-coupled receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 19, 638–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, D.; Stevens, R.C.; Roth, B.L. How ligands illuminate GPCR molecular pharmacology. Cell 2017, 170, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.E.; He, Y.; de Waal, P.W.; Gao, X.; Kang, Y.; Van Eps, N.; Yin, Y.; Pal, K.; Goswami, D.; White, T.A.; et al. Identification of phosphorylation codes for arrestin recruitment by G protein-coupled receptors. Cell 2017, 170, 457–469.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, Y.; McCammon, J.A. G protein-coupled receptors: Advances in simulation and drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2016, 41, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salon, J.A.; Lodowski, D.T.; Palczewski, K. The significance of G protein-coupled receptor crystallography for drug discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, R.; Ursu, O.; Gaulton, A.; Bento, A.P.; Donadi, R.S.; Bologa, C.G.; Karlsson, A.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Hersey, A.; Oprea, T.I.; et al. A comprehensive map of molecular drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, C.J.; Koglin, M.; Olson, W.C.; Marshall, F.H. Opportunities for therapeutic antibodies directed at G protein-coupled receptors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 787–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heukers, R.; De Groof, T.W.M.; Smit, M.J. Nanobodies detecting and modulating GPCRs outside in and inside out. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2019, 57, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheloha, R.W.; Fischer, F.A.; Woodham, A.W.; Daley, E.; Suminski, N.; Gardella, T.J.; Ploegh, H.L. Improved GPCR ligands from nanobody tethering. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, P.J.; Lazar, G.A. Next generation antibody drugs: Pursuit of the ‘high-hanging fruit’. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.; Ahmad, A.B.; Sehar, U.; Georgieva, E.R. Lipid membrane mimetics in functional and structural studies of integral membrane proteins. Membranes 2021, 11, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavito, R.M.; Ferguson-Miller, S. Detergents as tools in membrane biochemistry. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32403–32406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serebryany, E.; Zhu, G.A.; Yan, E.C. Artificial membrane-like environments for in vitro studies of purified G protein-coupled receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiener, M.C. A pedestrian guide to membrane protein crystallization. Methods 2004, 34, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.J.Y.; Gabriel, F.; Tandale, A.; Nietlispach, D. Structure and dynamics of GPCRs in lipid membranes: Physical principles and experimental approaches. Molecules 2020, 25, 4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Manglik, A.; Alvares, R.; Kobilka, B.K.; Prosser, R.S. Role of detergents in conformational exchange of a G protein-coupled receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36305–36311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Ghosh, S.; Jana, S.; Robertson, N.; Tate, C.G.; Vaidehi, N. How do branched detergents stabilize GPCRs in micelles? Biochemistry 2020, 59, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisov, I.G.; Sligar, S.G. Nanodiscs in membrane biochemistry and biophysics. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 4669–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staus, D.P.; Wingler, L.M.; Pichugin, D.; Prosser, R.S.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Detergent- and phospholipid-based reconstitution systems have differential effects on constitutive activity of G protein-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 13218–13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumura, T.; Kondo, K.; Kurita, M.; Kofuku, Y.; Natsume, M.; Imai, S.; Shiraishi, Y.; Ueda, T.; Shimada, I. Activation of adenosine A2A receptor by lipids from docosahexaenoic acid revealed by NMR. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frauenfeld, J.; Löving, R.; Armache, J.P.; Sonnen, A.F.; Guettou, F.; Moberg, P.; Zhu, L.; Jegerschöld, C.; Flayhan, A.; Briggs, J.A.; et al. A saposin-lipoprotein nanoparticle system for membrane proteins. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, K.; Holyoake, J.; Pomès, R.; Privé, G.G. Structure of saposin A lipoprotein discs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2908–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flayhan, A.; Mertens, H.D.T.; Ural-Blimke, Y.; Martinez Molledo, M.; Svergun, D.I.; Löw, C. Saposin lipid nanoparticles: A highly versatile and modular tool for membrane protein research. Structure 2018, 26, 345–355.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chien, C.H.; Helfinger, L.R.; Bostock, M.J.; Solt, A.; Tan, Y.L.; Nietlispach, D. An adaptable phospholipid membrane mimetic system for solution NMR studies of membrane proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14829–14832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöpfer, K.; Hagn, F. Beyond detergent micelles: The advantages and applications of non-micellar and lipid-based membrane mimetics for solution-state NMR. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2019, 114–115, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tribet, C.; Audebert, R.; Popot, J.L. Amphipols: Polymers that keep membrane proteins soluble in aqueous solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 15047–15050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giusti, F.; Casiraghi, M.; Point, E.; Damian, M.; Rieger, J.; Bon, C.L.; Pozza, A.; Moncoq, K.; Baneres, J.L.; Catoire, L.J. Structure of the agonist 12-HHT in its BLT2 receptor-bound state. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mary, S.; Damian, M.; Rahmeh, R.; Mouillac, B.; Marie, J.; Granier, S.; Banères, J.L. Amphipols in G protein-coupled receptor pharmacology: What are they good for? J. Membr. Biol. 2014, 247, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoonens, M.; Popot, J.L. Amphipols for each season. J. Membr. Biol. 2014, 247, 759–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanders, C.R., 2nd; Landis, G.C. Reconstitution of membrane proteins into lipid-rich bilayered mixed micelles for NMR studies. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 4030–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Prytulla, S.; De Angelis, A.A.; Brown, J.M.; Kiefer, H.; Opella, S.J. High-resolution NMR spectroscopy of a GPCR in aligned bicelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7402–7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Brock, A.; Herberich, B.; Schultz, P.G. Expanding the genetic code of Escherichia coli. Science 2001, 292, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frieden, C.; Hoeltzli, S.D.; Bann, J.G. The preparation of 19F-labeled proteins for NMR studies. Methods Enzymol. 2004, 380, 400–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.J.; Horst, R.; Katritch, V.; Stevens, R.C.; Wüthrich, K. Biased signaling pathways in β2-adrenergic receptor characterized by 19F-NMR. Science 2012, 335, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitevski-LeBlanc, J.L.; Prosser, R.S. Current applications of 19F-NMR to studies of protein structure and dynamics. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2012, 62, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didenko, T.; Liu, J.J.; Horst, R.; Stevens, R.C.; Wüthrich, K. Fluorine-19 NMR of integral membrane proteins illustrated with studies of GPCRs. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, P.; Jarema, M.; Mosser, K.; Daniel, W.E. Lac repressor: 3-fluorotyrosine substitution for nuclear magnetic resonance studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 3471–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.; Hu, W.; Li, X.; Skinner, J.J.; Liu, D.; Wüthrich, K. Solvent-accessibility of discrete residue positions in the polypeptide hormone glucagon by 19F-NMR observation of 4-fluorophenylalanine. J. Biomol. NMR 2017, 68, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crowley, P.B.; Kyne, C.; Monteith, W.B. Simple and inexpensive incorporation of 19F-tryptophan for protein NMR spectroscopy. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10681–10683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinrucken, H.C.; Amrhein, N. The herbicide glyphosate is a potent inhibitor of 5-enolpyruvyl-shikimic acid-3-phosphate synthase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1980, 94, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arntson, K.E.; Pomerantz, W.C. Protein-observed fluorine NMR: A bioorthogonal approach for small molecule discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5158–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogan, A.A.; Thorn, K.S. Anatomy of hot spots in protein interfaces. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 280, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picard, L.P.; Prosser, R.S. Advances in the study of GPCRs by 19F-NMR. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2021, 69, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmich, U.A.; Pfleger, N.; Glaubitz, C. 19F-MAS NMR on proteorhodopsin: Enhanced protocol for site-specific labeling for general application to membrane proteins. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manglik, A.; Kim, T.H.; Masureel, M.; Altenbach, C.; Yang, Z.; Hilger, D.; Lerch, M.T.; Kobilka, T.S.; Thian, F.S.; Hubbell, W.L.; et al. Structural insights into the dynamic process of β2-adrenergic receptor signaling. Cell 2015, 161, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horst, R.; Liu, J.J.; Stevens, R.C.; Wüthrich, K. β2-adrenergic receptor activation by agonists studied with 19F-NMR spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 10762–10765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, L.; Larda, S.T.; Frank Li, Y.F.; Manglik, A.; Prosser, R.S. A comparison of chemical shift sensitivity of trifluoromethyl tags: Optimizing resolution in 19F-NMR studies of proteins. J. Biomol. NMR 2015, 62, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sušac, L.; O’Connor, C.; Stevens, R.C.; Wüthrich, K. In-membrane chemical modification (IMCM) for site-specific chromophore labeling of GPCRs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 15246–15249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Hu, W.; Liu, D.; Wüthrich, K. Design and preparation of the class B G protein-coupled receptors GLP-1R and GCGR for 19F-NMR studies in solution. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 4053–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orton, H.W.; Qianzhu, H.; Abdelkader, E.H.; Habel, E.I.; Tan, Y.J.; Frkic, R.L.; Jackson, C.J.; Huber, T.; Otting, G. Through-space scalar 19F–19F couplings between fluorinated noncanonical amino acids for the detection of specific contacts in proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 19587–19598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewen, M.C.; Klein-Seetharaman, J.; Getmanova, E.V.; Reeves, P.J.; Schwalbe, H.; Khorana, H.G. Solution 19F nuclear overhauser effects in structural studies of the cytoplasmic domain of mammalian rhodopsin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4888–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, J.C.; Hammill, J.T.; Mehl, R.A. Site-specific incorporation of a 19F-amino acid into proteins as an NMR probe for characterizing protein structure and reactivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellitti, S.E.; Jones, D.H.; Lagpacan, L.; Hao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, H.; Brittain, S.M.; Brinker, A.; Caldwell, J.; Bursulaya, B.; et al. In vivo incorporation of unnatural amino acids to probe structure, dynamics, and ligand binding in a large protein by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9268–9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Shen, L.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, T.; Tao, H.; Yao, D.; Wu, L.; et al. A genetically encoded F-19 NMR probe reveals the allosteric modulation mechanism of cannabinoid receptor 1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 16320–16325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnihan, E.C.; Young, D.D.; Schultz, P.G.; Stubbe, J. Incorporation of fluorotyrosines into ribonucleotide reductase using an evolved, polyspecific aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15942–15945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, T.S.; Ahmad, I.; Yin, J.A.; Schultz, P.G. An enhanced system for unnatural amino acid mutagenesis in E. coli. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 395, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokoch, M.P.; Zou, Y.; Rasmussen, S.G.; Liu, C.W.; Nygaard, R.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Fung, J.J.; Choi, H.J.; Thian, F.S.; Kobilka, T.S.; et al. Ligand-specific regulation of the extracellular surface of a G protein-coupled receptor. Nature 2010, 463, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sounier, R.; Mas, C.; Steyaert, J.; Laeremans, T.; Manglik, A.; Huang, W.; Kobilka, B.K.; Déméné, H.; Granier, S. Propagation of conformational changes during μ-opioid receptor activation. Nature 2015, 524, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cong, X.; Maurel, D.; Demene, H.; Vasiliauskaite-Brooks, I.; Hagelberger, J.; Peysson, F.; Saint-Paul, J.; Golebiowski, J.; Granier, S.; Sounier, R. Molecular insights into the biased signaling mechanism of the μ-opioid receptor. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 4165–4175.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goba, I.; Goricanec, D.; Schum, D.; Hillenbrand, M.; Pluckthun, A.; Hagn, F. Probing the conformation states of neurotensin receptor 1 variants by NMR site-directed methyl labeling. Chembiochem 2021, 22, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Seetharaman, J.; Getmanova, E.V.; Loewen, M.C.; Reeves, P.J.; Khorana, H.G. NMR spectroscopy in studies of light-induced structural changes in mammalian rhodopsin: Applicability of solution 19F-NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13744–13749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.H.; Chung, K.Y.; Manglik, A.; Hansen, A.L.; Dror, R.O.; Mildorf, T.J.; Shaw, D.E.; Kobilka, B.K.; Prosser, R.S. The role of ligands on the equilibria between functional states of a G protein-coupled receptor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9465–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prosser, R.S.; Ye, L.; Pandey, A.; Orazietti, A. Activation processes in ligand-activated G protein-coupled receptors: A case study of the adenosine A2A receptor. Bioessays 2017, 39, 1700072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frei, J.N.; Broadhurst, R.W.; Bostock, M.J.; Solt, A.; Jones, A.J.Y.; Gabriel, F.; Tandale, A.; Shrestha, B.; Nietlispach, D. Conformational plasticity of ligand-bound and ternary GPCR complexes studied by 19F-NMR of the β1-adrenergic receptor. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Hu, Y.; Batebi, H.; Heng, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Niu, X.; Li, H.; Hildebrand, P.W.; Jin, C.; et al. Analysis of β2AR-Gs and β2AR-Gi complex formation by NMR spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 23096–23105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casiraghi, M.; Damian, M.; Lescop, E.; Point, E.; Moncoq, K.; Morellet, N.; Levy, D.; Marie, J.; Guittet, E.; Baneres, J.L.; et al. Functional modulation of a G protein-coupled receptor conformational landscape in a lipid bilayer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11170–11175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, L.D.; Dikiy, I.; Chapman, K.; Rödström, K.E.; Aramini, J.; LeVine, M.V.; Khelashvili, G.; Rasmussen, S.G.; Gardner, K.H.; Rosenbaum, D.M. Ligand modulation of sidechain dynamics in a wild-type human GPCR. Elife 2017, 6, e28505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kofuku, Y.; Ueda, T.; Okude, J.; Shiraishi, Y.; Kondo, K.; Maeda, M.; Tsujishita, H.; Shimada, I. Efficacy of the β2-adrenergic receptor is determined by conformational equilibrium in the transmembrane region. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nygaard, R.; Zou, Y.; Dror, R.O.; Mildorf, T.J.; Arlow, D.H.; Manglik, A.; Pan, A.C.; Liu, C.W.; Fung, J.J.; Bokoch, M.P.; et al. The dynamic process of β2-adrenergic receptor activation. Cell 2013, 152, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kofuku, Y.; Ueda, T.; Okude, J.; Shiraishi, Y.; Kondo, K.; Mizumura, T.; Suzuki, S.; Shimada, I. Functional dynamics of deuterated β2-adrenergic receptor in lipid bilayers revealed by NMR spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 13376–13379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okude, J.; Ueda, T.; Kofuku, Y.; Sato, M.; Nobuyama, N.; Kondo, K.; Shiraishi, Y.; Mizumura, T.; Onishi, K.; Natsume, M.; et al. Identification of a conformational equilibrium that determines the efficacy and functional selectivity of the μ-opioid receptor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 15771–15776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solt, A.S.; Bostock, M.J.; Shrestha, B.; Kumar, P.; Warne, T.; Tate, C.G.; Nietlispach, D. Insight into partial agonism by observing multiple equilibria for ligand-bound and Gs-mimetic nanobody-bound β1-adrenergic receptor. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumbak, F.; Keen, A.C.; Gunn, N.J.; Gooley, P.R.; Bathgate, R.A.D.; Scott, D.J. Optimization and 13CH3 methionine labeling of a signaling competent neurotensin receptor 1 variant for NMR studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1860, 1372–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Hu, Y.; Kaindl, J.; Risel, P.; Hübner, H.; Maeda, S.; Niu, X.; Li, H.; Gmeiner, P.; Jin, C.; et al. Conformational complexity and dynamics in a muscarinic receptor revealed by NMR spectroscopy. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 53–65.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rößler, P.; Mayer, D.; Tsai, C.J.; Veprintsev, D.B.; Schertler, G.F.X.; Gossert, A.D. GPCR activation states induced by nanobodies and Mini-G proteins compared by NMR spectroscopy. Molecules 2020, 25, 5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogai, S.; Deupi, X.; Opitz, C.; Heydenreich, F.M.; Tsai, C.J.; Brueckner, F.; Schertler, G.F.; Veprintsev, D.B.; Grzesiek, S. Backbone NMR reveals allosteric signal transduction networks in the β1-adrenergic receptor. Nature 2016, 530, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grahl, A.; Abiko, L.A.; Isogai, S.; Sharpe, T.; Grzesiek, S. A high-resolution description of β1-adrenergic receptor functional dynamics and allosteric coupling from backbone NMR. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.; Yokomizo, T.; Kofuku, Y.; Shiraishi, Y.; Ueda, T.; Shimada, I. Structural equilibrium underlying ligand-dependent activation of β2-adrenoreceptor. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.L.; Baptista, D.; Strauss, M.; Sun, Z.J.; Grigoriu, S.; Huser, S.; Pluckthun, A.; Hagn, F.; Walz, T.; Hogle, J.M.; et al. Covalently circularized nanodiscs for studying membrane proteins and viral entry. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, M.T.; Lee, M.Y.; Gao, Z.G.; White, K.L.; Didenko, T.; Horst, R.; Audet, M.; Stanczak, P.; McClary, K.M.; Han, G.W.; et al. Allosteric coupling of drug binding and intracellular signaling in the A2A adenosine receptor. Cell 2018, 172, 68–80.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eddy, M.T.; Gao, Z.G.; Mannes, P.; Patel, N.; Jacobson, K.A.; Katritch, V.; Stevens, R.C.; Wüthrich, K. Extrinsic tryptophans as NMR probes of allosteric coupling in membrane proteins: Application to the A2A adenosine receptor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, M.T.; Martin, B.T.; Wüthrich, K. A2A adenosine receptor partial agonism related to structural rearrangements in an activation microswitch. Structure 2021, 29, 170–176.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulry, E.; Ray, A.P.; Eddy, M.T. Production of a human histamine receptor for NMR spectroscopy in aqueous solutions. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervushin, K.; Riek, R.; Wider, G.; Wüthrich, K. Attenuated T2 relaxation by mutual cancellation of dipole-dipole coupling and chemical shift anisotropy indicates an avenue to NMR structures of very large biological macromolecules in solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12366–12371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Opitz, C.; Isogai, S.; Grzesiek, S. An economic approach to efficient isotope labeling in insect cells using homemade 15N-, 13C- and 2H-labeled yeast extracts. J. Biomol. NMR 2015, 62, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautier, A.; Mott, H.R.; Bostock, M.J.; Kirkpatrick, J.P.; Nietlispach, D. Structure determination of the seven-helix transmembrane receptor sensory rhodopsin II by solution NMR spectroscopy. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bemis, G.W.; Murcko, M.A. The properties of known drugs. 1. Molecular frameworks. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 2887–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejzo, J.; Lepre, C.A.; Peng, J.W.; Bemis, G.W.; Ajay; Murcko, M.A.; Moore, J.M. The SHAPES strategy: An NMR-based approach for lead generation in drug discovery. Chem. Biol. 1999, 6, 755–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buratto, R.; Mammoli, D.; Chiarparin, E.; Williams, G.; Bodenhausen, G. Exploring weak ligand–protein interactions by long-lived NMR states: Improved contrast in fragment-based drug screening. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11376–11380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Millet, O.; Loria, J.P.; Kroenke, C.D.; Pons, M.; Palmer, A.G. The static magnetic field dependence of chemical exchange linebroadening defines the NMR chemical shift time scale. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 2867–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lu, M.; Liu, D.; Yang, L.; Yi, C.; Ma, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Frimurer, T.M.; Wang, M.W.; et al. Human substance P receptor binding mode of the antagonist drug aprepitant by NMR and crystallography. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Liu, D.; Yang, L.; Wüthrich, K. GPCR large-amplitude dynamics by 19F-NMR of aprepitant bound to the neurokinin 1 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2122682119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Shapiro, M.J. NOE pumping: A novel NMR technique for identification of compounds with binding affinity to macromolecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 10258–10259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Meinecke, R.; Mayer, M.; Meyer, B. Detecting binding affinity to immobilized receptor proteins in compound libraries by HR-MAS STD NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 5336–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Meyer, B. Characterization of ligand binding by saturation transfer difference NMR spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1784–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvit, C.; Pevarello, P.; Tatò, M.; Veronesi, M.; Vulpetti, A.; Sundström, M. Identification of compounds with binding affinity to proteins via magnetization transfer from bulk water. J. Biomol. NMR 2000, 18, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.; White, K.L.; Doncescu, N.; Didenko, T.; Roth, B.L.; Czaplicki, G.; Stevens, R.C.; Wüthrich, K.; Milon, A. NMR structure and dynamics of the agonist dynorphin peptide bound to the human kappa opioid receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11852–11857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimada, I.; Ueda, T.; Kofuku, Y.; Eddy, M.T.; Wüthrich, K. GPCR drug discovery: Integrating solution NMR data with crystal and cryo-EM structures. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 59–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehl, A.; Hu, H.; Maeda, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Q.; Paggi, J.M.; Latorraca, N.R.; Hilger, D.; Dawson, R.; Matile, H.; et al. Structure of the µ-opioid receptor–Gi protein complex. Nature 2018, 558, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Nafría, J.; Nehmé, R.; Edwards, P.C.; Tate, C.G. Cryo-EM structure of the serotonin 5-HT1B receptor coupled to heterotrimeric Go. Nature 2018, 558, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Kumar, K.; Shalev-Benami, M.; Robertson, M.J.; Hu, H.; Banister, S.D.; Hollingsworth, S.A.; Latorraca, N.R.; Kato, H.E.; Hilger, D.; Maeda, S.; et al. Structure of a signaling cannabinoid receptor 1-G protein complex. Cell 2019, 176, 448–458.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilger, D.; Kumar, K.K.; Hu, H.; Pedersen, M.F.; O’Brien, E.S.; Giehm, L.; Jennings, C.; Eskici, G.; Inoue, A.; Lerch, M.; et al. Structural insights into differences in G protein activation by family A and family B GPCRs. Science 2020, 369, eaba3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wu, L.; Yuan, S.; Wu, M.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, S.; Zhao, S.; Hua, T.; Liu, Z.-J. Structural basis of CXC chemokine receptor 2 activation and signalling. Nature 2020, 585, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Che, T.; Panova, O.; DiBerto, J.F.; Lyu, J.; Krumm, B.E.; Wacker, D.; Robertson, M.J.; Seven, A.B.; Nichols, D.E.; et al. Structure of a hallucinogen-activated Gq-coupled 5-HT2A serotonin receptor. Cell 2020, 182, 1574–1588.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazhahan, V.; Ma, N.; Pándy-Szekeres, G.; Kooistra, A.J.; Lee, Y.; Gloriam, D.E.; Vaidehi, N.; Tate, C.G. Structure of the class D GPCR Ste2 dimer coupled to two G proteins. Nature 2021, 589, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seven, A.B.; Barros-Álvarez, X.; de Lapeyrière, M.; Papasergi-Scott, M.M.; Robertson, M.J.; Zhang, C.; Nwokonko, R.M.; Gao, Y.; Meyerowitz, J.G.; Rocher, J.-P.; et al. G protein activation by a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature 2021, 595, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, H.; Wang, H.; Pan, B.; Feng, D.; Guo, C.; Yang, L.; Liu, D.; Wüthrich, K. G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR) Reconstitution and Labeling for Solution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Studies of the Structural Basis of Transmembrane Signaling. Molecules 2022, 27, 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092658
Ge H, Wang H, Pan B, Feng D, Guo C, Yang L, Liu D, Wüthrich K. G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR) Reconstitution and Labeling for Solution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Studies of the Structural Basis of Transmembrane Signaling. Molecules. 2022; 27(9):2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092658
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Haoyi, Huixia Wang, Benxun Pan, Dandan Feng, Canyong Guo, Lingyun Yang, Dongsheng Liu, and Kurt Wüthrich. 2022. "G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR) Reconstitution and Labeling for Solution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Studies of the Structural Basis of Transmembrane Signaling" Molecules 27, no. 9: 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092658
APA StyleGe, H., Wang, H., Pan, B., Feng, D., Guo, C., Yang, L., Liu, D., & Wüthrich, K. (2022). G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR) Reconstitution and Labeling for Solution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Studies of the Structural Basis of Transmembrane Signaling. Molecules, 27(9), 2658. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092658





