Current Sample Preparation Methodologies for Determination of Catecholamines and Their Metabolites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
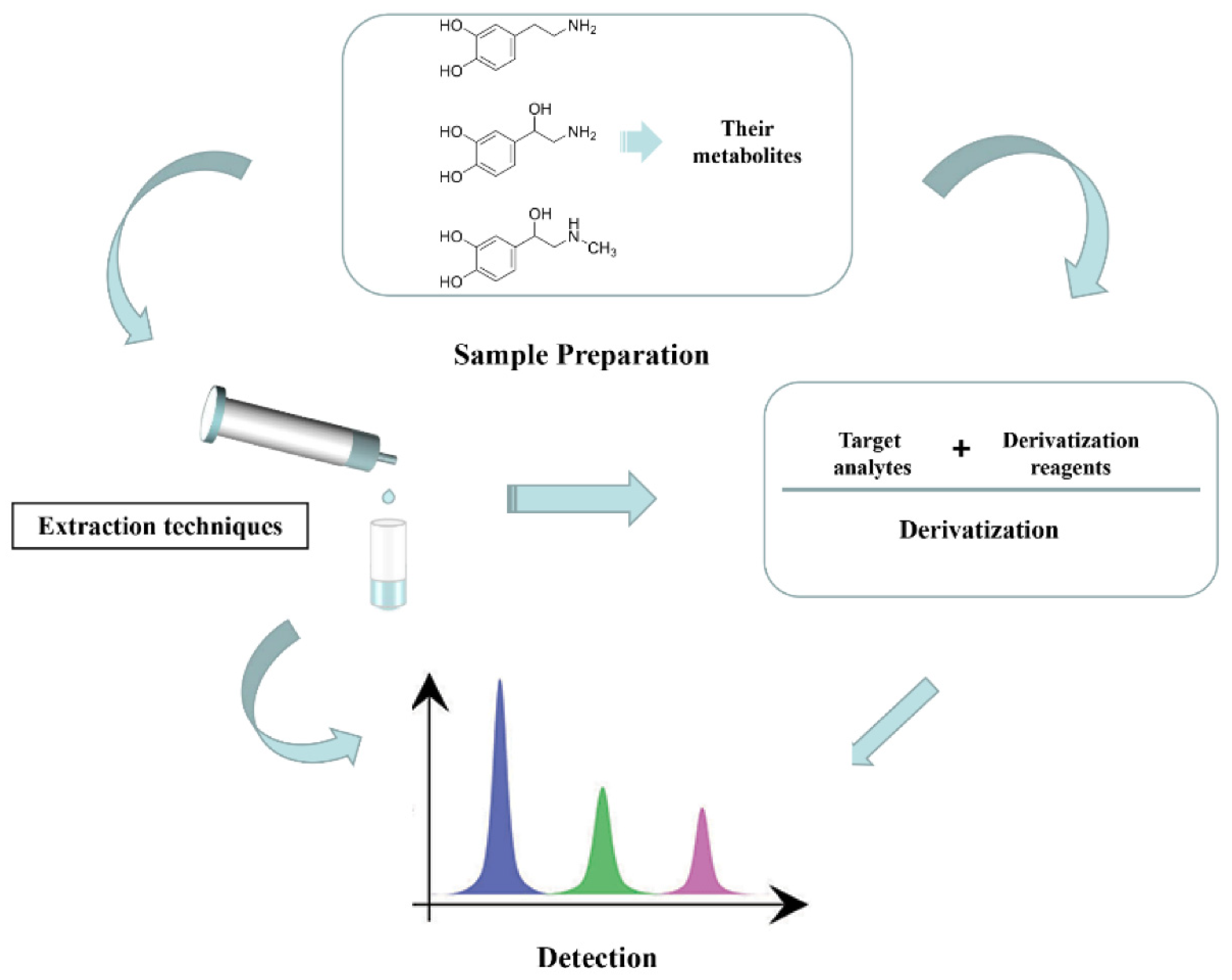
2. Sample Preparation
2.1. Liquid–Liquid Extraction-Based Approaches
2.2. Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE)
2.3. Dispersive Solid Phase Extraction/Microextraction (DSPE/DSPME)
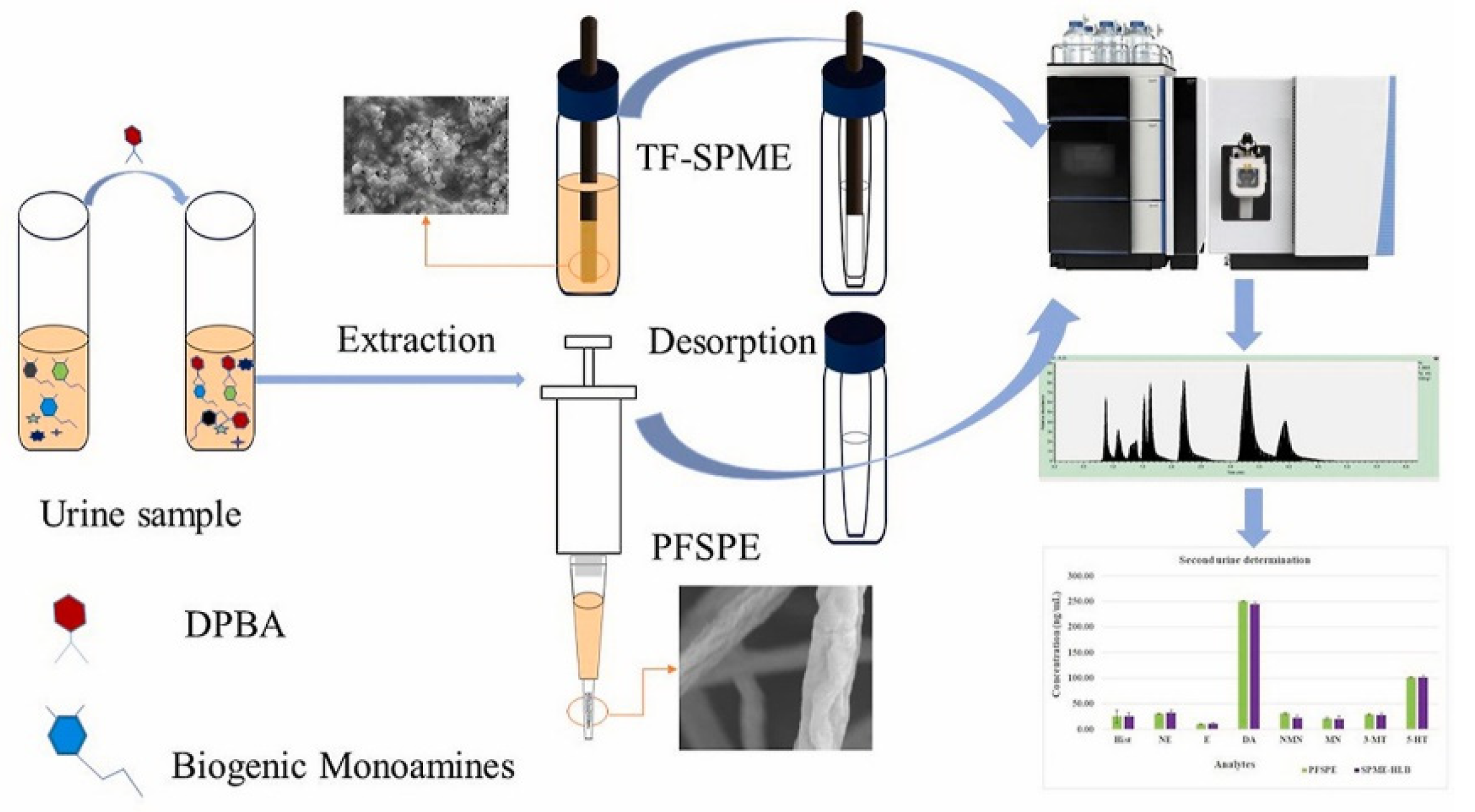
2.4. Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME)
2.5. Derivatization
3. Analytical Techniques
4. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Marcos, A.; Ambrosio, E.; Marina, M.L.; Crego, A.L. Enantioseparation of the constituents involved in the phenylalanine-tyrosine metabolic pathway by capillary electrophoresis tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1467, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercimek-Mahmutoglu, S.; Sidky, S.; Patel, J.; Kyriakopoulou, L.; Hyland, K. Retrospective review of cerebrospinal fluid catecholamine and serotonin metabolites for indications and diagnosis of neurotransmitter disorders. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014, 111, 279–280. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Carillion, A.; Na, N.; Jong, A.D.; Amour, J. Modification of the β-adrenoceptor stimulation pathway in zucker obese and obese diabetic rat myocardium. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, e241–e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.; Li, J.; Shi, H.L.; Wang, T.T.; Muhtar, W.; Du, M.; Zhang, B.B.; Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Hu, Z.B.; et al. Simultaneous quantification of seven hippocampal neurotransmitters in depression mice by LC-MS/MS. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 229, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.X.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.J.; He, B.S.; Sui, Z.Y.; Xu, H.R.; Yin, Y.D.; Liu, R.; Bi, K.S. Determination of catecholamines and their metabolites in rat urine by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the study of identifying potential markers for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 50, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeWitt, P. Recent advances in CSF biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, S49–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brichta, L.; Greengard, P.; Flajolet, M. Advances in the pharmacological treatment of Parkinson’s disease: Targeting neurotransmitter systems. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.Y.; Huang, W.; Tong, Y.K.; Tian, M.M. Hollow dummy template imprinted boronate-modified polymers for extraction of norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine prior to quantitation by HPLC. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkielstain, G.; Jha, S.; Merke, D. Chapter 9—Adrenal disorders. In Biochemical and Molecular Basis of Pediatric Disease, 5th ed.; Dietzen, D., Bennett, M., Wong, E., Haymond, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 267–296. [Google Scholar]
- Mazloum-Ardakani, M.; Khoshroo, A. High performance electrochemical sensor based on fullerene-functionalized carbon nanotubes/ionic liquid: Determination of some catecholamines. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 42, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.A.; Fernandes, P.M.V.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, F. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors for determination of catecholamine neurotransmitters: A review. Talanta 2016, 160, 653–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, B.; Song, E. Recent Advances in the Detection of Neurotransmitters. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorbunova, M.V.; Gutorova, S.V.; Berseneva, D.A.; Apyari, V.V.; Zaitsev, V.D.; Dmitrienko, S.G.; Zolotov, Y.A. Spectroscopic methods for determination of catecholamines: A mini-review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2019, 54, 631–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslehipour, A. Recent Advances in Fluorescence Detection of Catecholamines. J. Chem. Rev. 2020, 2, 130–147. [Google Scholar]
- Bicker, J.; Fortuna, A.; Alves, G.; Falcão, A. Liquid chromatographic methods for the quantification of catecholamines and their metabolites in several biological samples—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 768, 12–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, C.L.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Cui, X.T. A graphene oxide/conducting polymer nanocomposite for electrochemical dopamine detection: Origin of improved sensitivity and specificity. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2014, 2, 5209–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-H.; Yu, C.-J.; Tseng, W.-L. Fluorescence assay of catecholamines based on the inhibition of peroxidase-like activity of magnetite nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 745, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, A.-M.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, G.M.; Jo, H.J.; Kim, S.H. Determination of catecholamines based on the measurement of the metal nanoparticle-enhanced fluorescence of their terbium complexes. Microchim. Acta 2012, 176, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.F.; Wang, C.Z.; Wei, Y.M. Selective enrichment and determination of monoamine neurotransmitters by CU(II) immobilized magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. Talanta 2016, 147, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, B.; Gifu, E.P.; Sandu, I.; Denoroy, L.; Parrot, S. Analysis of microdialysate monoamines, including noradrenaline, dopamine and serotonin, using capillary ultra-high performance liquid chromatography and electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 951, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schoors, J.; Lens, C.; Maes, K.; Michotte, Y.; Smolders, I.; Van Eeckhaut, A. Reassessment of the antioxidative mixture for the challenging electrochemical determination of dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin in microdialysis samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 998, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.B.; Zhu, B.J.; Liu, F.; Lyu, C.M.; Zhang, S.; Yan, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wei, H. A rapid and simple method for the simultaneous determination of four endogenous monoamine neurotransmitters in rat brain using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled with atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1002, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovac, A.; Somikova, Z.; Zilka, N.; Novak, M. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of panel of neurotransmitters in cerebrospinal fluid from the rat model for tauopathy. Talanta 2014, 119, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, J.; Sun, T.; Peng, R.; Yuan, T.-F.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Wang, S.-T.; Li, Y. LC-MS/MS determination of plasma catecholamines after selective extraction by borated zirconia. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beitollahi, H.; Safaei, M.; Tajik, S. Different Electrochemical Sensors for Determination of Dopamine as Neurotransmitter in Mixed and Clinical Samples: A Review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 2019, 6, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Därr, R.; Kuhn, M.; Bode, C.; Bornstein, S.R.; Pacak, K.; Lenders, J.W.M.; Eisenhofer, G. Accuracy of recommended sampling and assay methods for the determination of plasma-free and urinary fractionated metanephrines in the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma: A systematic review. Endocrine 2017, 56, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Kubo, T.; Hall, A.O.; Zurcher, D.M.; Phadke, S.; Wallace, R.L.; McNeil, A.J. Adapting Meaningful Learning Strategies to Teach Liquid–Liquid Extractions. J. Chem. Educ. 2019, 97, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung-Klawitter, S.; Kuseyri Hübschmann, O. Analysis of Catecholamines and Pterins in Inborn Errors of Monoamine Neurotransmitter Metabolism—From Past to Future. Cells 2019, 8, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.E.; He, Y.R.; Yan, P.; Wei, N.; Wang, R.J.; Sun, J.; Zheng, L.F.; Zhu, S.Y.; You, J.M. Sensitive and accurate determination of neurotransmitters from in vivo rat brain microdialysate of Parkinson’s disease using in situ ultrasound-assisted derivatization dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction by UHPLC-MS/MS. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 108635–108644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dasgupta, P.K. Analytical Chemistry in a Drop. Solvent Extraction in a Microdrop. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 1817–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, M.; Assadi, Y.; Hosseinia, M.R.M.; Aghaee, E.; Ahmadi, F.; Berijani, S. Determination of organic compounds in water using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1116, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lee, H.K. Liquid-phase microextraction in a single drop of organic solvent by using a conventional microsyringe. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 4634–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen-Bjergaard, S.; Rasmussen, K.E. Liquid−Liquid−Liquid Microextraction for Sample Preparation of Biological Fluids Prior to Capillary Electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2650–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Lee, H.K. Headspace liquid-phase microextraction of chlorobenzenes in soil with gas chromatography-electron capture detection. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczna, L.; Roszkowska, A.; Niedzwiecki, M.; Baczek, T. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography combined with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction as a preconcentration tool for the simultaneous determination of the panel of underivatized neurotransmitters in human urine samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1431, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.W.; Chen, Y.B.; Chen, Y.J.; Ma, M.; Tan, Y.M.; Tang, H.; Chen, B. Determination of monoamine neurotransmitters in human urine by carrier-mediated liquid-phase microextraction based on solidification of stripping phase. Talanta 2015, 144, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwir-Ferenc, A.; Biziuk, M. Solid phase extraction technique - Trends, opportunities and applications. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 677–690. [Google Scholar]
- Adaway, J.E.; Peitzsch, M.; Keevil, B.G. A novel method for the measurement of plasma metanephrines using online solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 52, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, H.I.; Yang, J.S.; Oh, H.J.; Cho, Y.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.D.; Lee, S.Y. A simple and rapid analytical method based on solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of free catecholamines and metanephrines in urine and its application to routine clinical analysis. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 49, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, H.J.; Guan, Q.; Cheng, L.M. A simple and robust liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry assay for determination of plasma free metanephrines and its application to routine clinical testing for diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.G.; Li, S.; Kellermann, G. An integrated liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry approach for the ultra-sensitive determination of catecholamines in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells to assess neural-immune communication. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1449, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, T.; Funatsu, T.; Tsunoda, M. Determination of catecholamines and related compounds in mouse urine using column-switching HPLC. Analyst 2016, 141, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Cheng, L.M.; Guan, Q.; Li, H.J.; Lu, J.; Wang, X. Development and validation of a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the measurement of urinary catecholamines in diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roiffé, R.R.; Ribeiro, W.D.; Sardela, V.F.; de la Cruz, M.N.S.; de Souza, K.R.; Pereira, H.M.G.; Aquino Neto, F.R. Development of a sensitive and fast method for detection of catecholamines and metabolites by HRMS. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Q.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Liu, J.; Shen, J.; Zhang, W.Q. High-throughput and selective solid-phase extraction of urinary catecholamines by crown ether-modified resin composite fiber. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1561, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabler, J.; Wang, S. Quantifcation of metanephrine and normetanephrine in urine using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. In Clinical Applications of Mass Spectrometry in Biomolecular Analysis: Methods and Protocols; Garg, U., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.G.; Li, S.; Kellermann, G. Simultaneous extraction and determination of monoamine neurotransmitters in human urine for clinical routine testing based on a dual functional solid phase extraction assisted by phenylboronic acid coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 2859–2871. [Google Scholar]
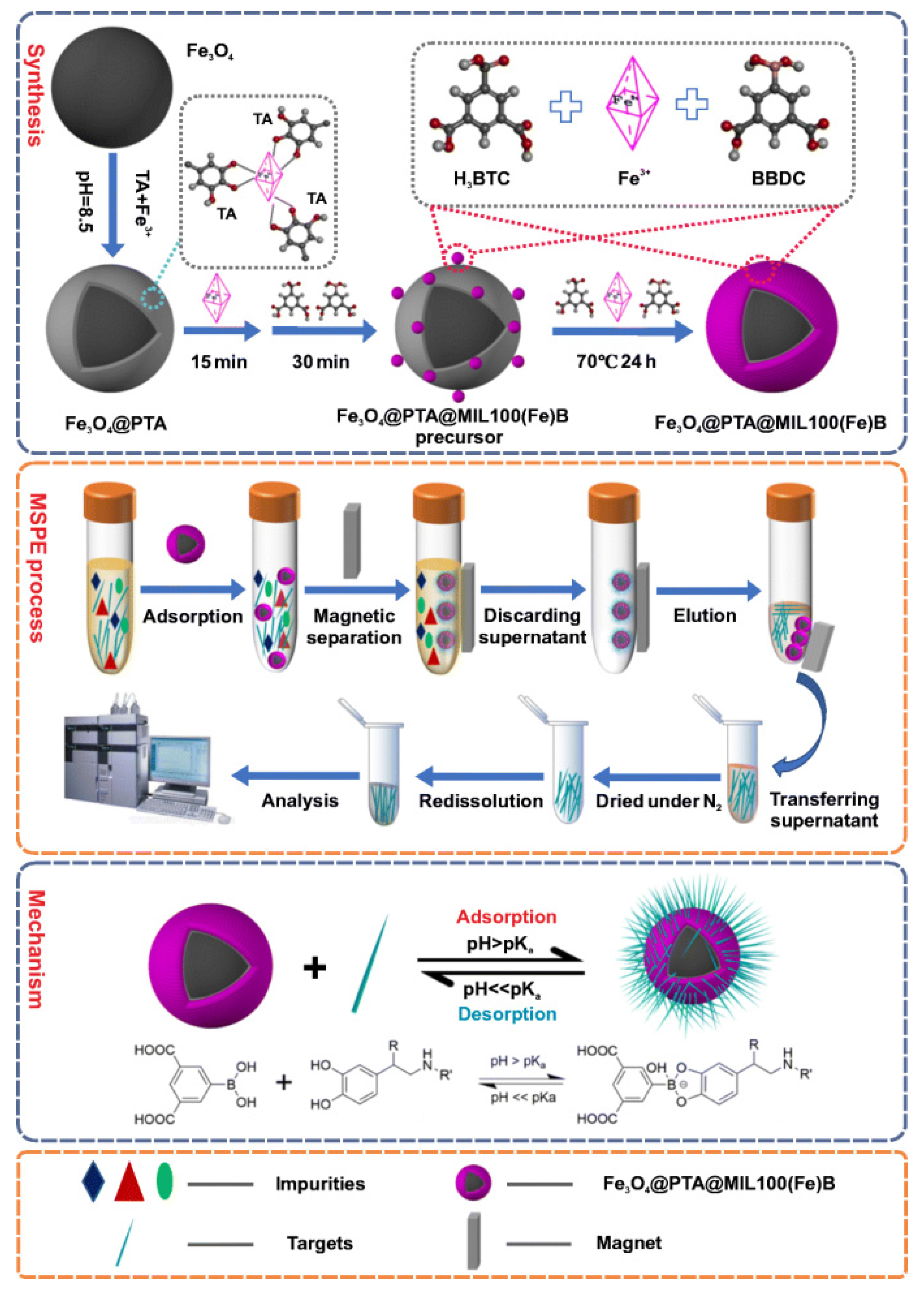
- Xing, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Hou, X. Tannic acid-directed synthesis of magnetic and boronic acid-functionalized metal-organic frameworks for selective extraction and quantification of catecholamines in human urine. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y. Boronic acid-modified polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes on polydopamine-coated magnetized graphene oxide for selective and high-capacity extraction of the catecholamines epinephrine, dopamine and isoprenaline. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tang, Y.; Xu, B.; Xu, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhang, W. Automated on-line packed fiber solid phase extraction for determination of urinary catecholamines. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1139, 121983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohyuddin, A.; Hussain, D.; Fatima, B.; Athar, M.; Ashiq, M.N.; Najam-ul-Haq, M. Gallic acid functionalized UiO-66 for the recovery of ribosylated metabolites from human urine samples. Talanta 2019, 201, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Hussain, D.; Saleem, S.; Mehdi, S.; Javeed, R.; Jabeen, F.; Najam-ul-Haq, M. Metal–organic framework-based affinity materials in proteomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiades, M.; Lehotay, S.J.; Stajnbaher, D.; Schenck, F.J. Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Malik, A.K.; Pico, Y. Sample preparation methods for the determination of pesticides in foods using CE-UV/MS. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.B.; Qiu, H.W.; Rui, Q.H.; Liao, Y.F.; Chen, Y.M.; Xu, J.; Zhan, P.P.; Zhao, Y.G. Fast determination of catecholamines in human plasma using carboxyl-functionalized magnetic-carbon nanotube molecularly imprinted polymer followed by liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1429, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.W.; Chen, Y.B.; Luo, Y.M.; Tan, Y.M.; Ma, M.; Chen, B.; Xie, Q.J.; Luo, X.B. Determination of catecholamines in urine using aminophenylboronic acid functionalized magnetic nanoparticles extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography and electrochemical detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y. Facile synthesis of boronic acid-functionalized magnetic metal-organic frameworks for selective extraction and quantification of catecholamines in rat plasma. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 41976–41985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Q.; Li, H.; Shi, X.Z.; Xu, G.W. Facile synthesis of Fe3O4@polyethyleneimine modified with 4-formylphenylboronic acid for the highly selective extraction of major catecholamines from human urine. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 2857–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtada, K.; de Andrés, F.; Galván, I.; Ríos, Á.; Zougagh, M. LC-MS determination of catecholamines and related metabolites in red deer urine and hair extracted using magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotube poly(styrene-co-divinylbenzene) composite. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1136, 121878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.B.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Dong, C.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q.W.; Lei, Y.Y.; Luo, L.Q.; Feng, Y.Q. Facile synthesis of a boronate affinity sorbent from mesoporous nanomagnetic polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes composite and its application for enrichment of catecholamines in human urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 944, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.; Rickert, D.; Khaled, A.; Pawliszyn, J. High throughput determination of free biogenic monoamines and their metabolites in urine using thin-film solid phase microextraction. Talanta 2021, 232, 122438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podjava, A.; Šilaks, A. Synthesis and sorptive properties of molecularly imprinted polymer for simultaneous isolation of catecholamines and their metabolites from biological fluids. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 2021, 44, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, Y.; Qian, C.; Xiang, Z.; Ouyang, G. Physical assistive technologies of solid-phase microextraction: Recent trends and future perspectives. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 115916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, M.; Naccarato, A.; Sindona, G.; Tagarelli, A. A reliable and simple method for the assay of neuroendocrine tumor markers in human urine by solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 759, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessonova, E.; Kartsova, L.; Gallyamova, V. Ionic liquids based on imidazole for online concentration of catecholamines in capillary electrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 2304–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espina-Benitez, M.B.; Randon, J.; Demesmay, C.; Dugas, V. Development and application of a new in-line coupling of a miniaturized boronate affinity monolithic column with capillary zone electrophoresis for the selective enrichment and analysis of cis-diol-containing compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1494, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.L.; Xia, L.J.; Huang, X.; Guo, X.F.; Ding, J.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.Q. Highly Sensitive Determination for Catecholamines Using Boronate Affinity Polymer Monolith Microextraction with In-Situ Derivatization and HPLC Fluorescence Detection. Chromatographia 2018, 81, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudjoe, E.; Pawliszyn, J. Optimization of solid phase microextraction coatings for liquid chromatography mass spectrometry determination of neurotransmitters. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1341, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.G.; Zhu, A.W.; Shi, G.Y. Selective extraction and analysis of catecholamines in rat blood microdialysate by polymeric ionic liquid-diphenylboric acid-packed capillary column and fast separation in high-performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical detector. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1409, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.T.; Hu, Y.F.; Li, G.K. Online micro-solid-phase extraction based on boronate affinity monolithic column coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of monoamine neurotransmitters in human urine. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1342, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Gong, M.J. On-line preconcentration of fluorescent derivatives of catecholamines in cerebrospinal fluid using flow-gated capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1450, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracino, M.A.; Santarcangelo, L.; Raggi, M.A.; Mercolini, L. Microextraction by packed sorbent (MEPS) to analyze catecholamines in innovative biological samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2015, 104, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Zhang, Y. Simple, rapid, and cost-effective microextraction by the packed sorbent method for quantifying of urinary free catecholamines and metanephrines using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application in clinical analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2763–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
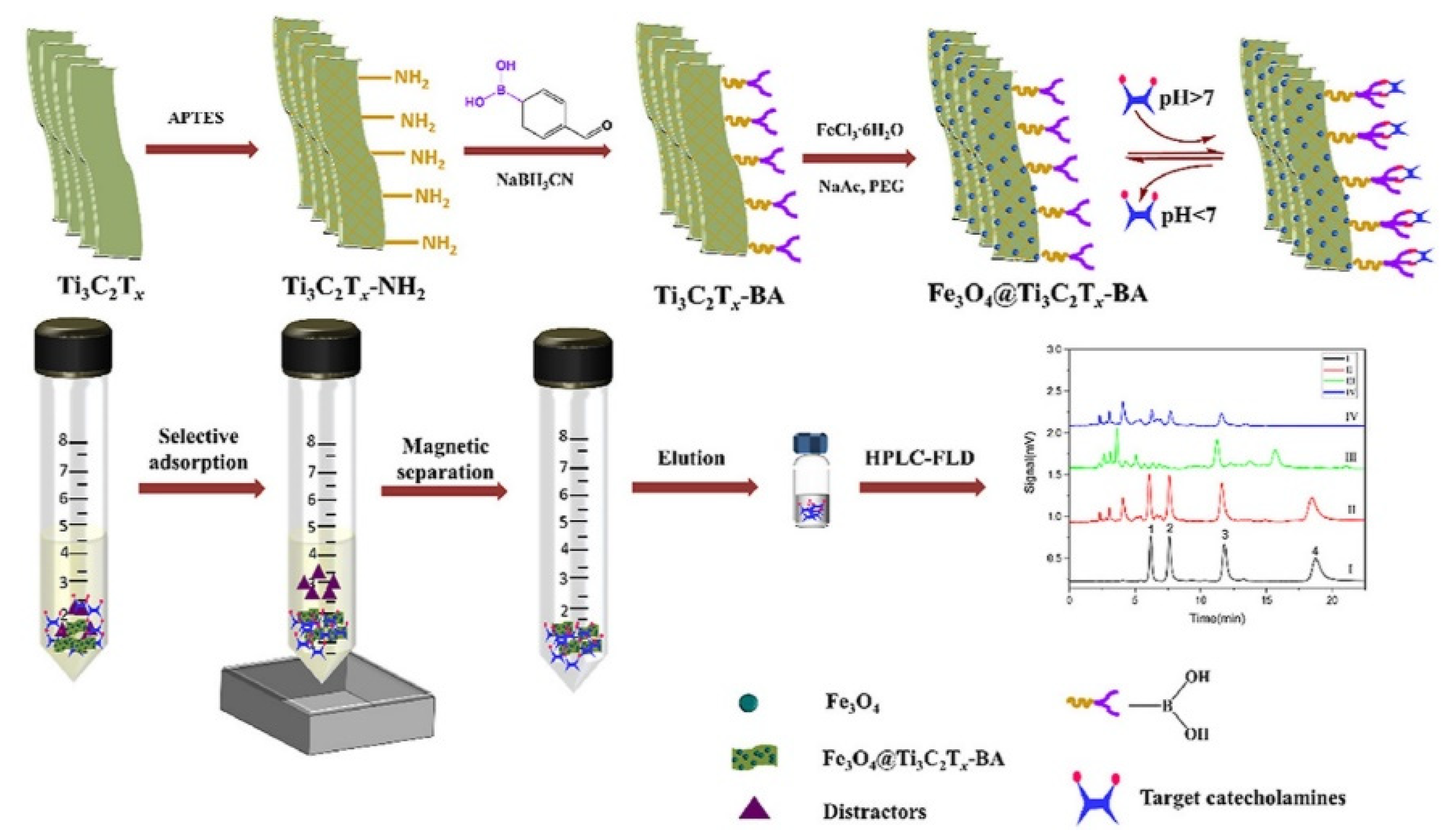
- Hu, K.; Pang, T.; Shi, Y.; Han, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z. Magnetic borate-modified Mxene: A highly affinity material for the extraction of catecholamines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1176, 338769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Li, S.; Zhu, Q.F.; Wang, Q.; Hussain, D.; Feng, Y.Q. Derivatization for liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry analysis of small-molecular weight compounds. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.S.; Zheng, S.N.; Su, G.Y.; Lu, X.M.; Yang, J.Y.; Xiong, Z.L.; Wu, C.F. In vivo study on the neurotransmitters and their metabolites change in depressive disorder rat plasma by ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 988, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.F.; Zhao, X.E.; Zhu, S.Y.; Tao, Y.D.; Ji, W.H.; Geng, Y.L.; Wang, X.A.; Chen, G.A.; You, J.M. A new combined method of stable isotope-labeling derivatization-ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of neurotransmitters in rat brain microdialysates by ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1054, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, A.G.; Zeglinski, P.T.; Coleman, K.E.; Whiting, M.J. Dilute, derivatise and shoot: Measurement of urinary free metanephrines and catecholamines as ethyl derivatives by LC-MSMS. Clin. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaryan, A.; Ligor, T.; Buszewski, B.; Temerdashev, A.; Dmitrieva, E.; Gashimova, E. LC-MS/MS Determination of Catecholamines in Urine Using FMOC-Cl Derivatization on Solid-Phase Extraction Cartridge. Chromatographia 2018, 81, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Yin, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. High electrochemical performance of RuO2–Fe2O3 nanoparticles embedded ordered mesoporous carbon as a supercapacitor electrode material. Energy 2016, 106, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Guo, X.F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.S. Analysis of catecholamines and related compounds in one whole metabolic pathway with high performance liquid chromatography based on derivatization. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.E.; Zhu, S.Y.; Yang, H.M.; You, J.M.; Song, F.R.; Liu, Z.Q.; Liu, S.Y. Simultaneous determination of amino acid and monoamine neurotransmitters in PC12 cells and rats models of Parkinson’s disease using a sensitizing derivatization reagent by UHPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 995, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, J.X.; Cui, W.Q.; Zhang, J.W.; Wu, D.Q.; Yu, X.R.; Luo, Y.B.; Jiang, X.Y.; Zhu, F.P.; Hussain, D.; et al. A simultaneous extraction/derivatization strategy coupled with liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of free catecholamines in biological fluids. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1654, 462474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Park, N.H.; Ahn, T.B.; Chung, B.C.; Hong, J. Profiling of a wide range of neurochemicals in human urine by very-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry combined with in situ selective derivatization. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1526, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.S.; Chen, J.N.; Ma, Y.F. Simultaneous determination of catecholamines and polyamines in PC-12 cell extracts by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography with ultraviolet absorbance detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 805, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.H.; Lu, C.Y.; Tseng, W.L. Selective enrichment of catecholamines using iron oxide nanoparticles followed by CE with UV detection. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.G.; Li, S.; Kellermann, G. Pre-analytical and analytical validations and clinical applications of a miniaturized, simple and cost-effective solid phase extraction combined with LC-MS/MS for the simultaneous determination of catecholamines and metanephrines in spot urine samples. Talanta 2016, 159, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peaston, R.T.; Graham, K.S.; Chambers, E.; van der Molen, J.C.; Ball, S. Performance of plasma free metanephrines measured by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heideloff, C.; Payto, D.; Wang, S. Quantitation of Free Metanephrines in Plasma by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1378, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Naccarato, A.; Gionfriddo, E.; Sindona, G.; Tagarelli, A. Development of a simple and rapid solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry method for the analysis of dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine in human urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 810, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerstedt, S.A.; O’Kane, D.J.; Singh, R.J. Measurement of Plasma Free Metanephrine and Normetanephrine by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Diagnosis of Pheochromocytoma. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jian, M.; Huang, H.; Li, K.; Chuan, L.; Li, L.; Jiang, L. A 3-min UPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of plasma catecholamines and their metabolites: Method verification and diagnostic efficiency. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 87, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, P.; Liu, M.; Shi, H.; Kang, W. Determination of monoamine neurotransmitters and metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography based on Ag(III) complex chemiluminescence detection. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 593, 113594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, M.L.; Schmedes, A. Highly sensitive LC-MS/MS analysis of catecholamines in plasma. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 82, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polikarpova, D.; Makeeva, D.; Kolotilina, N.; Dolgonosov, A.; Peshkova, M.; Kartsova, L. Nanosized cation exchanger for the electrophoretic separation and preconcentration of catecholamines and amino acids. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
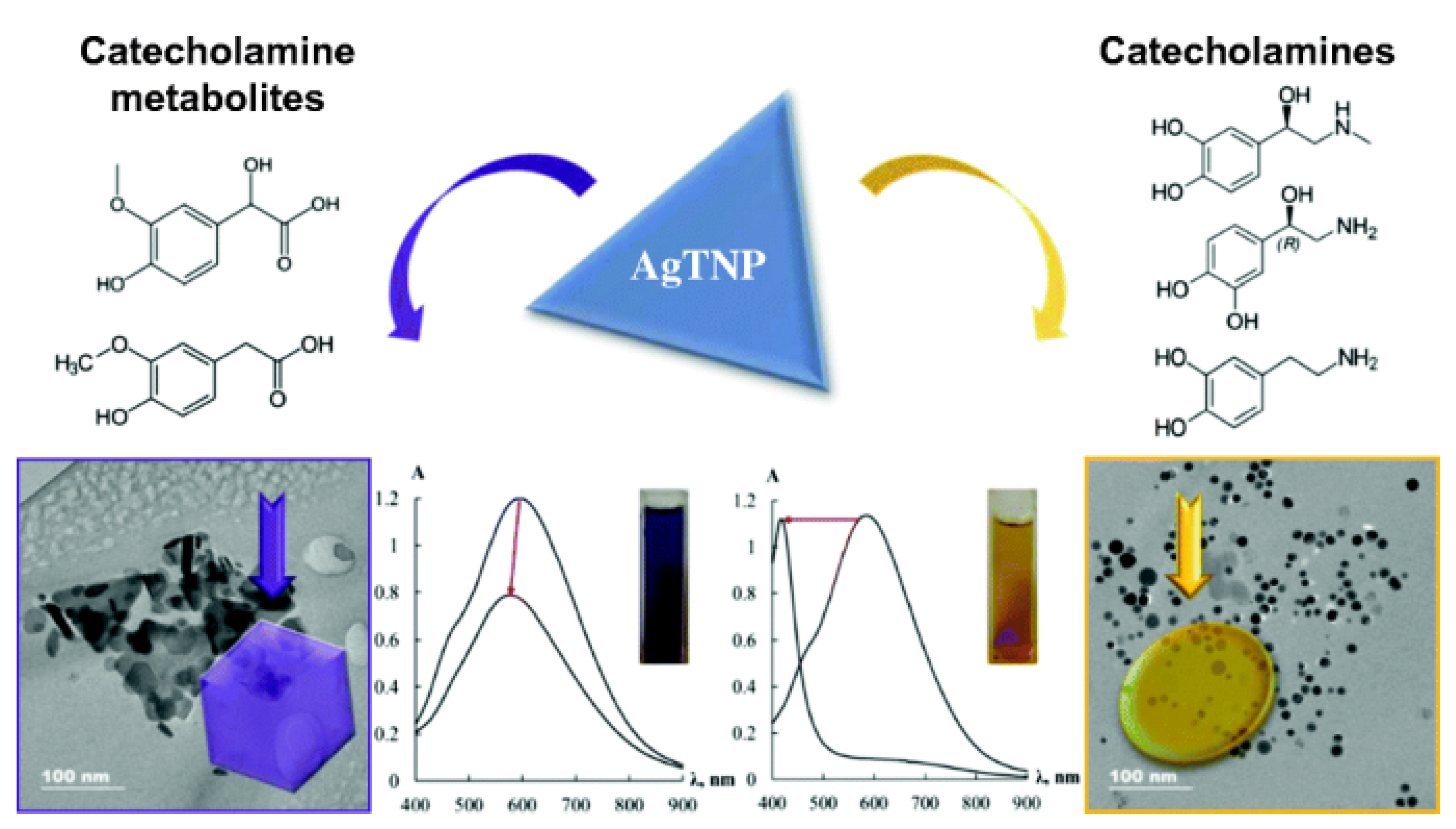
- Zaytsev, V.D.; Furletov, A.A.; Apyari, V.V.; Garshev, A.V.; Dmitrienko, S.G.; Zolotov, Y.A. Label-free silver triangular nanoplates for spectrophotometric determination of catecholamines and their metabolites. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

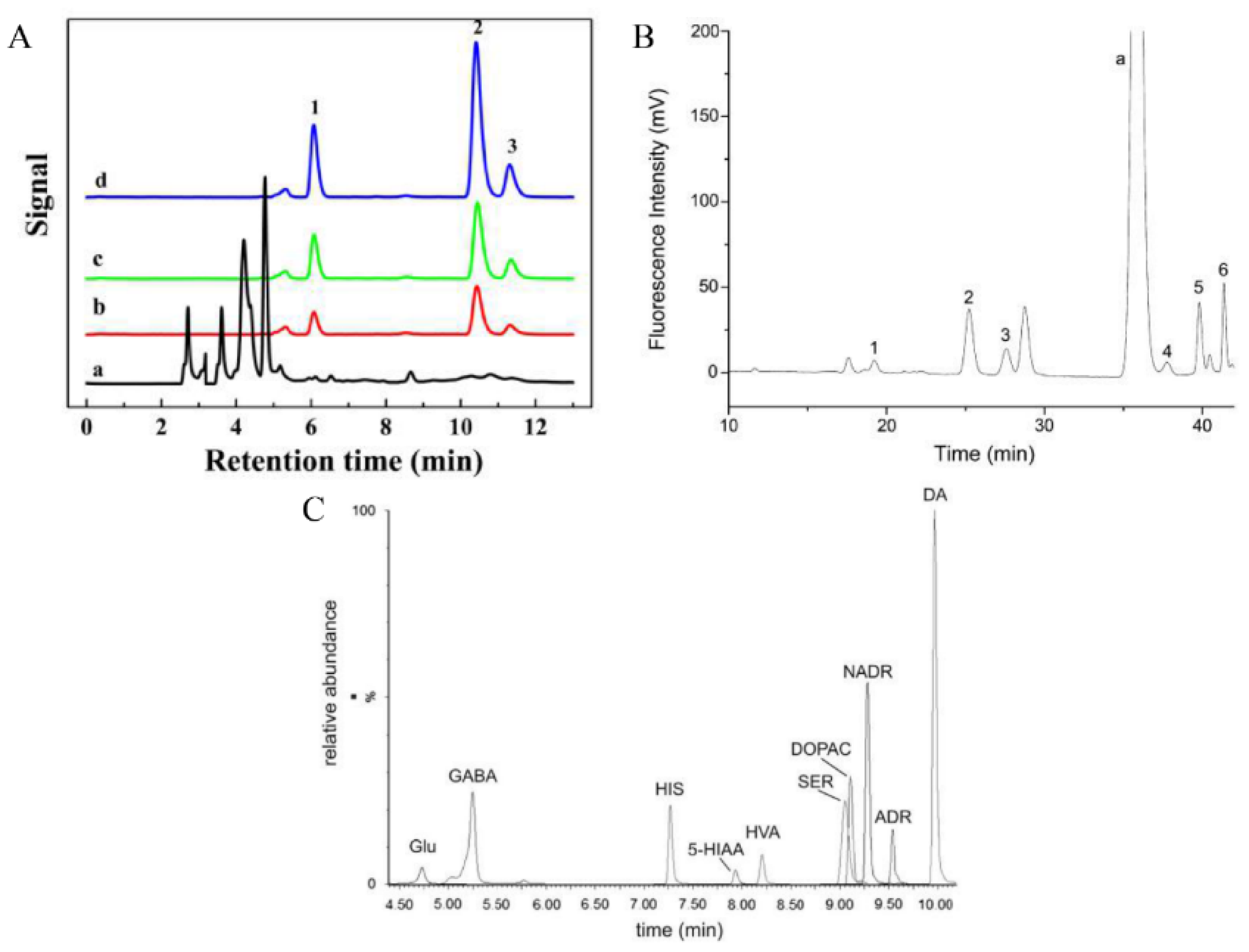
| Sorbents | Analytes | Matrix | LOQs | Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oasis weak cation exchange (WCX) | normetanephrine (NMN), 3-methoxytyramine (3-MT), metanephrine (MN) | human plasma | NMN: 75.0 pmol/L 3-MT: 37.5 pmol/L MN: 37.5 pmol/L | LC-MS/MS | [38] |
| Strata-X-CW | norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA), epinephrine (E) | human plasma | NE: 7.4 ng/mL DA: 5.4 ng/mL E: 3.8 ng/mL | LC-MS/MS | [39] |
| Evolute® WCX | MN, NMN | human plasma | MN: 0.07 nmol/L NMN: 0.06 nmol/L | LC-MS/MS | [40] |
| 96-well hydrophilic-lipophilic-balanced (HLB) Elution plate | E, NE, DA | human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) | E: 1 pg/mL NE: 5 pg/mL DA: 5 pg/mL | LC-MS/MS | [41] |
| precolumn modified with phenylboronic acid | E, NE, DA | mouse urine | NE: 163 fmol/L DA: 127 fmol/L E: 196 fmol/L | LC-FLD | [42] |
| HLB solid-phase cartridges | E, NE, DA | human urine | NE: 0.4 ng/mL DA: 0.3 ng/mL E: 0.2 ng/mL | LC-MS/MS | [43] |
| Strata-X-CW | E, NE, DA, MN, NMN | urine | NE: 5.0 ng/mL DA: 5.0 ng/mL E: 5.0 ng/mL MN: 5.0 ng/mL NMN: 5.0 ng/mL | LC-MS/MS | [44] |
| electrospun composite fibers | E, NE, DA | human urine | NE: 0.2 ng/mL DA: 0.5 ng/mL E: 0.2 ng/mL | LC-FLD | [45] |
| boronate-modified hollow dummy template imprinted polymers (B-hDIPs) | E, NE, DA | human urine | NE: 157.0 ng/mL DA: 141.0 ng/mL E: 51.0 ng/mL | LC-UV | [8] |
| Bond-Elut Plexa | MN, NMN | urine | MN: 0.2 μmol/L NMN: 0.3 μmol/L | LC-MS/MS | [46] |
| 96-well HLB microplate | E, NE, DA, serotonine (5-HT) | human urine | NE: 2.0 ng/mL DA: 4.0 ng/mL E: 1.0 ng/mL 5-HT: 4.0 ng/mL | LC-MS/MS | [47] |
| Fe3O4@PTA@MIL-100(Fe)-B | norepinephrine, epinephrine, and dopamine | Human Urine | NE: 0.050 ng/mL E: 0.11 ng/mL DA: 0.20 ng/mL | LC-FLD | [48] |
| magGO@POSS-BA | epinephrine, dopamine, and isoprenaline | Human urine | 0.54–2.3 ng·mL−1 | LC-FLD | [49] |
| Polycrown ether composite nanofiber | Catecholamines | Human urine | 1 ng/mL | LC-FLD | [50] |
| Sorbents | Analytes | Matrix | LOQs | Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aminophenylboronic acid functionalized magnetic nanoparticles | NE, DA, E | human urine | NE: 26.0 ng/mL DA: 23.6 ng/mL E: 6.7 ng/mL | HPLC-ECD | [56] |
| MG@MIL-100-B composites (boronic acid functionalized MIL-100) | NE, DA, E | rat plasma | NE: 0.10 ng/mL DA: 0.01 ng/mL E: 0.01 ng/mL | HPLC-MS/MS | [57] |
| Fe3O4@PEI-FPBA | NE, DA, E | human urine | NE: 0.20 ng/mL DA: 0.03 ng/mL E: 0.08 ng/mL | LC-MS | [58] |
| CF@m-CNTs-MIP | NE, DA, E | human plasma | NE: 0.076 ng/mL DA: 0.010 ng/mL E: 0.018 ng/mL | UFLC-MS/MS | [55] |
| magnetic MWCNT poly(STY-DVB) composite | NE, DA, E, DL-3,4-dihydroxymandelic acid (DHMA), DL-3,4-dihydroxyphenyl glycol (DOPEG) | red deer urine | NE: 248 ng/mL DA: 205 ng/mL E: 188 ng/mL DHMA: 146 ng/mL DOPEG: 232 ng/mL | LC-MS | [59] |
| IDA-Cu(II) functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 (Fe3O4@SiO2 @IDA-Cu) magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) | NE, DA, E, 5-HT, isoprenaline(IP), tyramine (TA) | rabbit plasma | NE: 0.43 ng/mL DA: 0.20 ng/mL E: 0.33 ng/mL 5-HT: 0.16 ng/mL IP: 0.31 ng/mL TA: 0.27 ng/mL | HPLC-FLD | [19] |
| Fe3O4@POSS-AAPBA | NE, isoprenaline hydrochloride (IE), E | human urine | NE: 2.70 ng/mL IE: 4.40 ng/mL E: 2.96 ng/mL | HPLC-UV | [60] |
| Polycrown ether (PCE) composite nanofiber | biogenic monoamines | Human urine | 0.25–500 ng/mL | UPLC-MS/MS | [61] |
| Borated zirconia | epinephrine (E), norepinephrine (NE), and dopamine (DA), | Plasma | E: 0.008 ng/mL NE: 0.020 ng/mL DA 0.004 ng/mL | LC-MS/MS | [24] |
| Derivatization Reagents | Analytes | Matrix | Derivatization Conditions | LOQs | LODs | Detection | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | pH | Time (min) | |||||||
| 10-methyl-acridone-2-sulfonyl chloride | L-DOPA, DA, NE, E, Trp, 5-HTP, 5-HT | rat brain microdialysates | 37 | 10.5 | 3 | 0.015–0.040 nmol/L | 0.002–0.010 nmol/L | UHPLC-MS/MS | [77] |
| TMBB-Su | Tyr, L-DOPA, DA, NE, E, and MN | mice liver and brain | 25 | 7.6 | 40 | -- | 0.10–0.40 nmol/L | HPLC-FLD | [81] |
| acetaldehyde | NE, DA, E, NMN, MN, 3-MT | human urine | 36 | 5 | 30 | 1–14 nmol/L | -- | LC-MS/MS | [78] |
| Benzoyl chloride | NE, DA, E, 5-HT, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), homovanilic acid (HVA), glutamic acid (Glu), γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) | rat cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) | 25 | 7.4 | -- | 0.15–5.00 ng/mL | 0.02–2.00 ng/mL | UHPLC-MS | [23] |
| FMOC-Cl | E, DA, octopamine | human urine | 25 | 9.5 | 20 | 5–50 ng/mL | 2.5–25 ng/mL | HPLC-MS/MS | [79] |
| methanol | 20 neurochemicals | human urine | 90 | <4 | 90 | 0.3–12.0 ng/mL | 0.1–3.6 ng/mL | UPLC-MS/MS | [84] |
| 4-carbonyl chloride rosamine (CCR) | 21 neurotransmitters (NTs) | rat brain and blood | 25 | 9.5 | 1 | -- | 1 × 10−4–3 × 10−3 nmol/L | UPLC-MS/MS | [29] |
| 10-ethyl-acridone-3-sulfonyl chloride (EASC) | Glu, Asp, Gly, GABA, taurine (Tau), DA, 5-HT | PC12 cells | 37 | 10.5 | 3 | 0.004–3.8 nmol/L | 0.014–13.1 nmol/L | UPLC-MS/MS | [82] |
| Lissamine rhodamine B sulfonylchloride (LRSC) | DA, 5-HT and their biosynthesis precursors and metabolites | rat brain microdialysates | 37 | 10.5 | 3 | 0.002–0.008 nmol/L | 0.015–0.040 nmol/L | UHPLC-MS/MS | [80] |
| dansyl chloride | NE, DA, 5-HT, HVA, HIAA, GABA, Glu | rat plasma | 65 | 11.0 | 20 | -- | 0.991–5030 fmol/L | HPLC-MS/MS | [76] |
| ZrO2/phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) | norepinephrine (NE), epinephrine (E) and dopamine (DA) | Human Urine | 25 | 10 | 10 | 0.035 ng/mL | 0.100 ng/mL | UHPLC-MS/MS | [83] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, N.; Bu, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, B.; Xu, X.; Shi, X.; Hussain, D.; Xu, X.; Chen, D. Current Sample Preparation Methodologies for Determination of Catecholamines and Their Metabolites. Molecules 2022, 27, 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092702
Shi N, Bu X, Zhang M, Wang B, Xu X, Shi X, Hussain D, Xu X, Chen D. Current Sample Preparation Methodologies for Determination of Catecholamines and Their Metabolites. Molecules. 2022; 27(9):2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092702
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Nian, Xinmiao Bu, Manyu Zhang, Bin Wang, Xinli Xu, Xuezhong Shi, Dilshad Hussain, Xia Xu, and Di Chen. 2022. "Current Sample Preparation Methodologies for Determination of Catecholamines and Their Metabolites" Molecules 27, no. 9: 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092702
APA StyleShi, N., Bu, X., Zhang, M., Wang, B., Xu, X., Shi, X., Hussain, D., Xu, X., & Chen, D. (2022). Current Sample Preparation Methodologies for Determination of Catecholamines and Their Metabolites. Molecules, 27(9), 2702. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092702







