Striatal Isolated from Cyathus striatus Extracts Induces Apoptosis in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extract Production
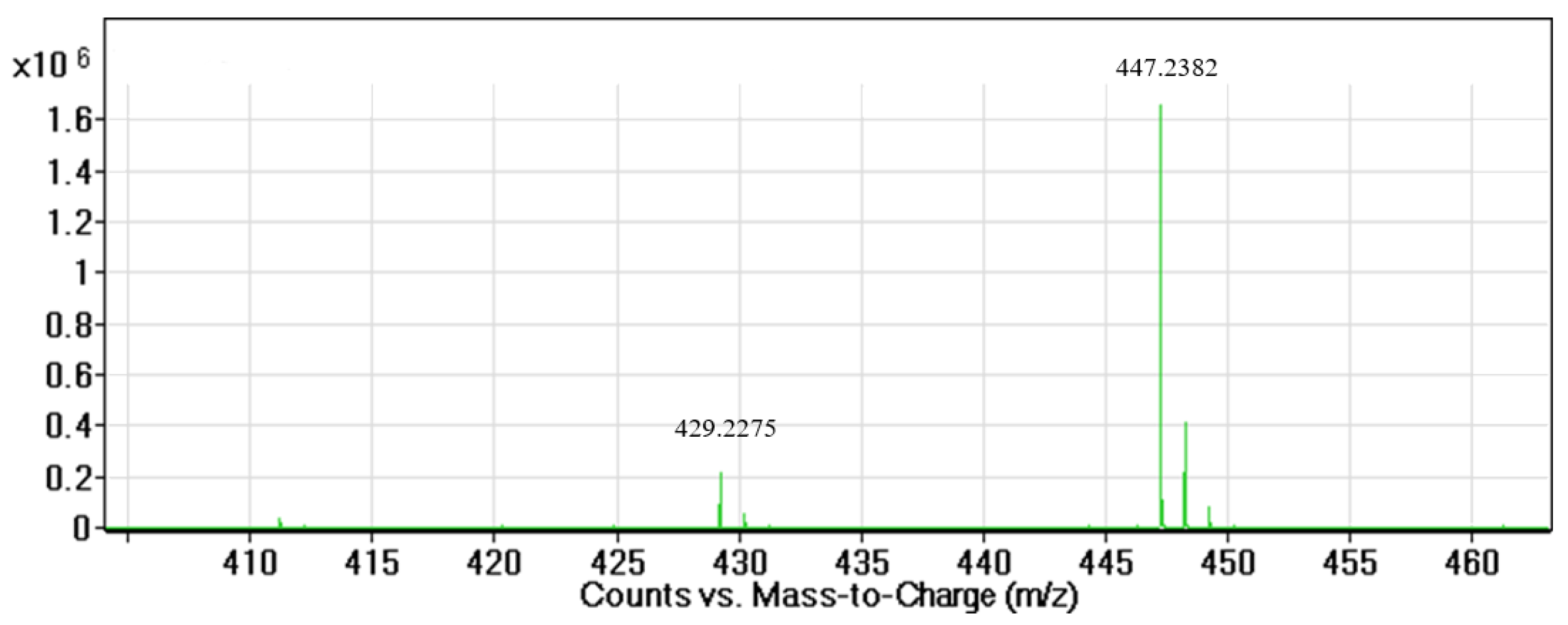
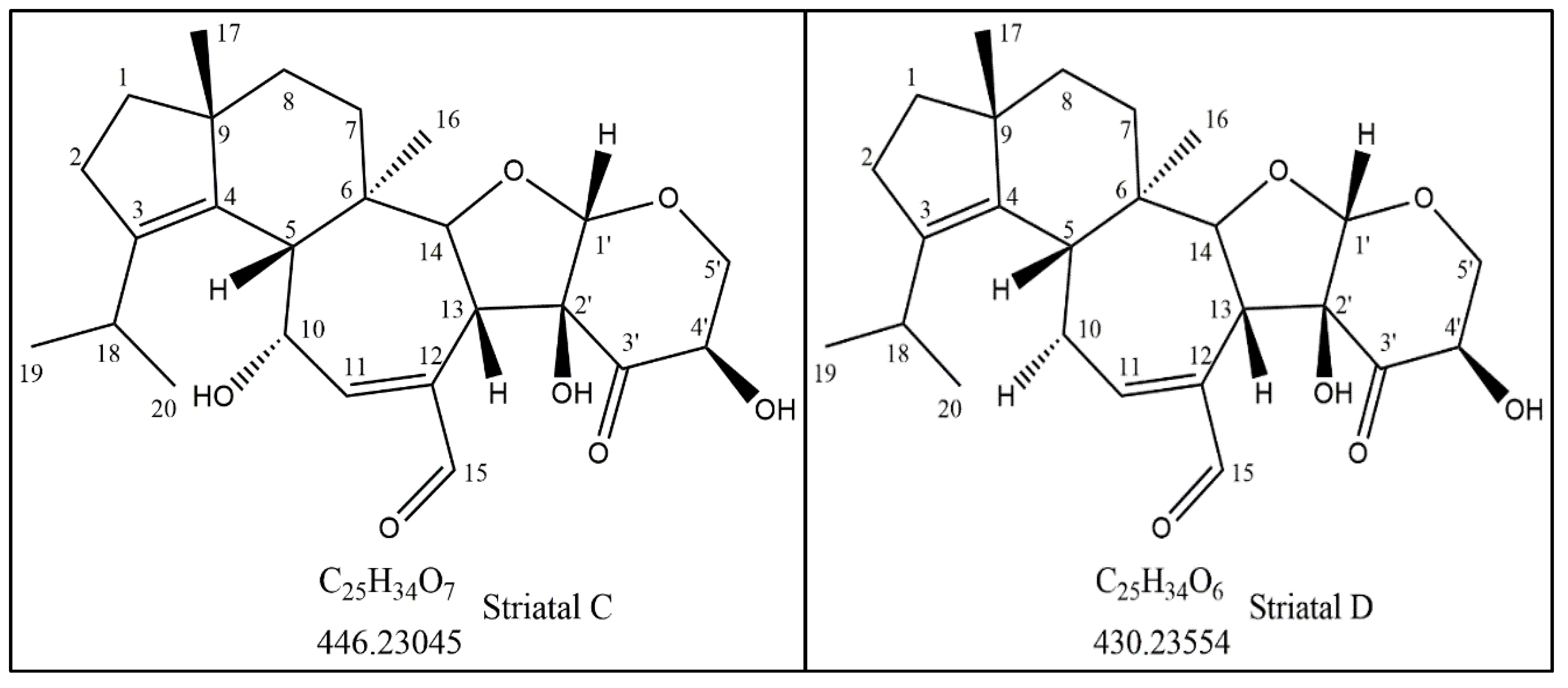
2.2. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of the Bioactive Compound
2.3. HPLC Analysis
2.4. LC–MS Analysis
2.5. NMR Analysis
2.6. Cell Culture
2.7. Cell Proliferation
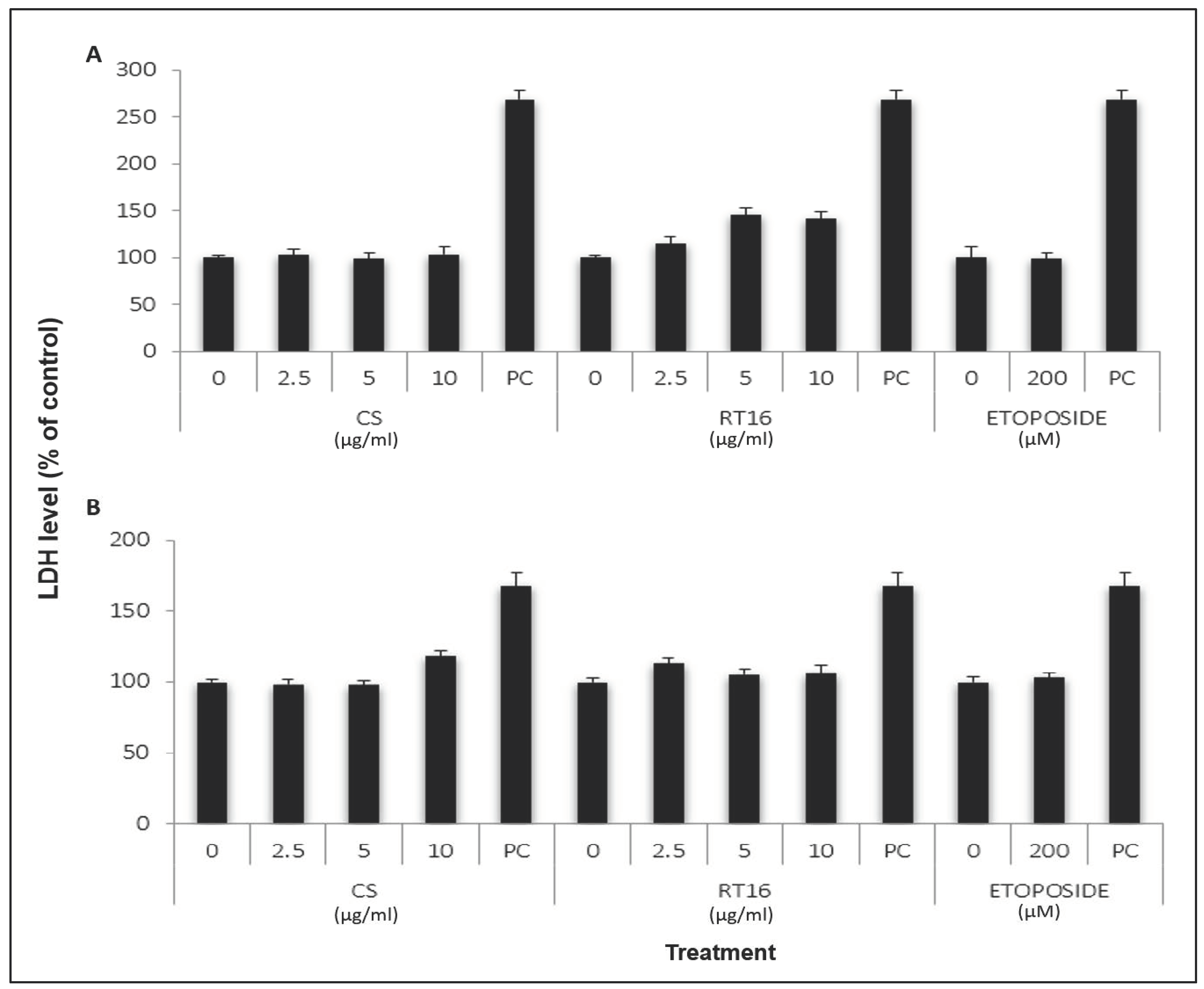
2.8. Effect of CS Extract on Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Release
2.9. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.10. Apoptosis
2.10.1. Annexin-V
2.10.2. TUNEL Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of the Active Compound Structure
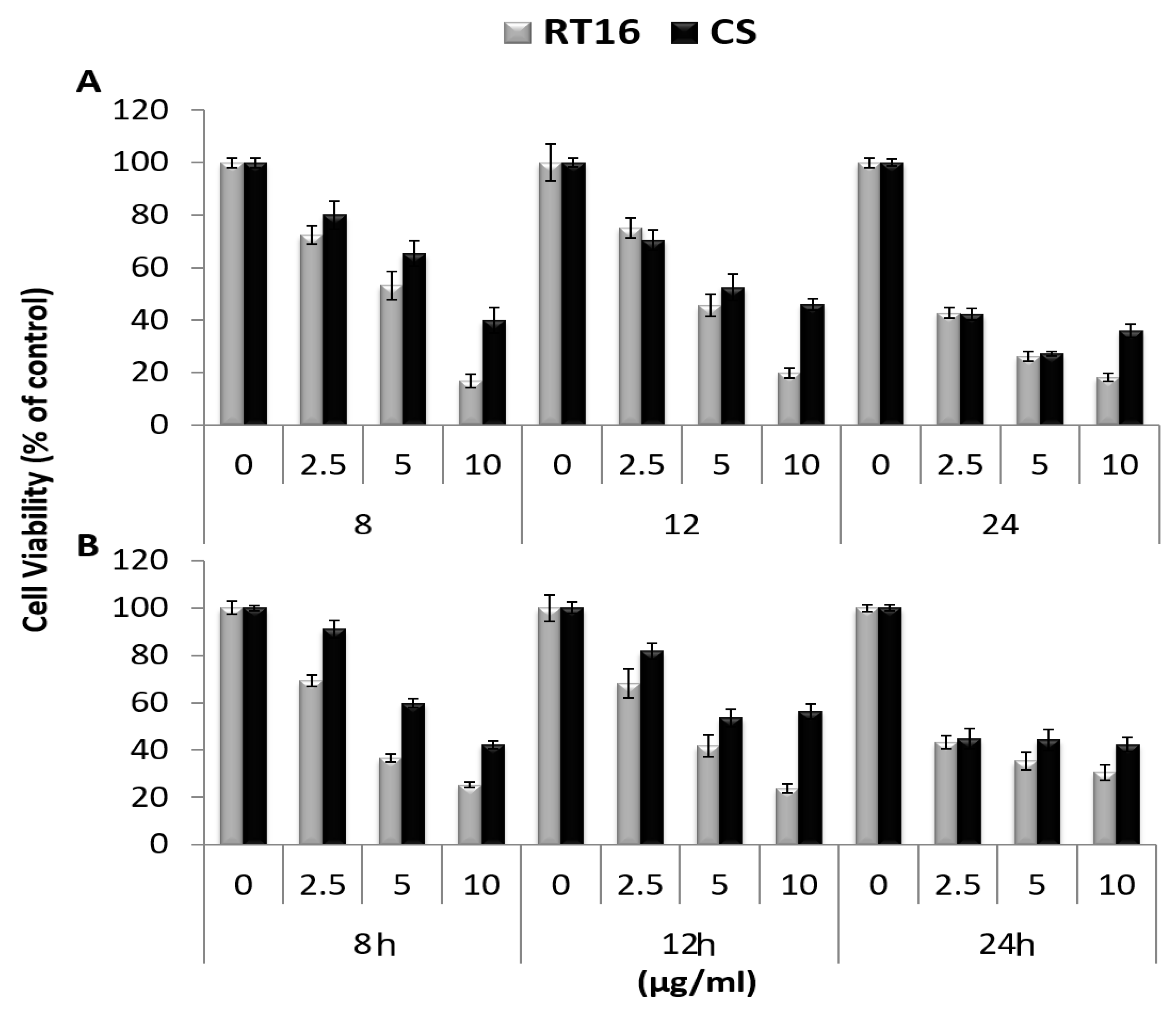
3.2. The Effect of the Isolated Active Compound on Cell Viability
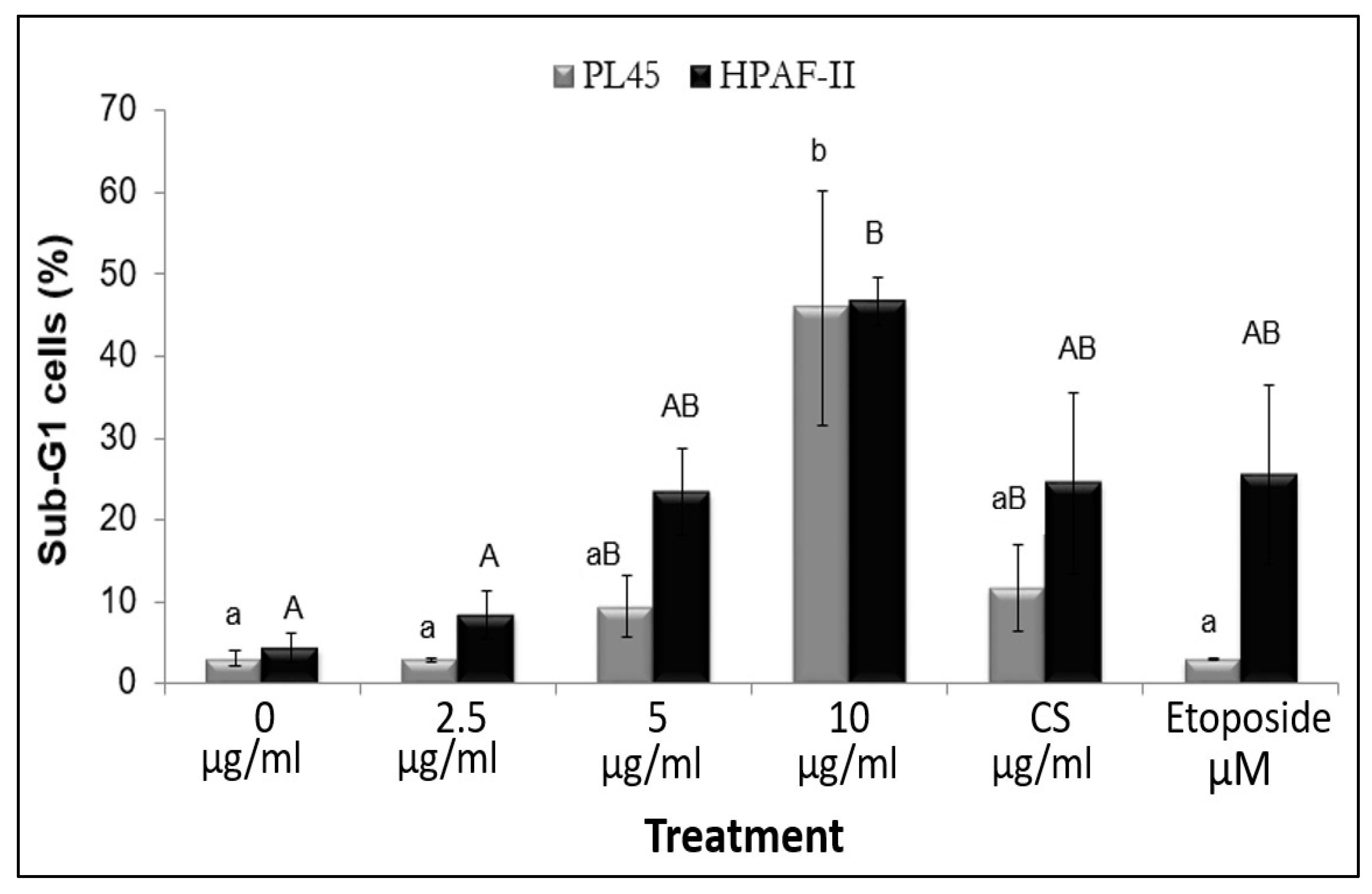
3.3. The Effect of RT16 Fraction on Cell Cycle Progression
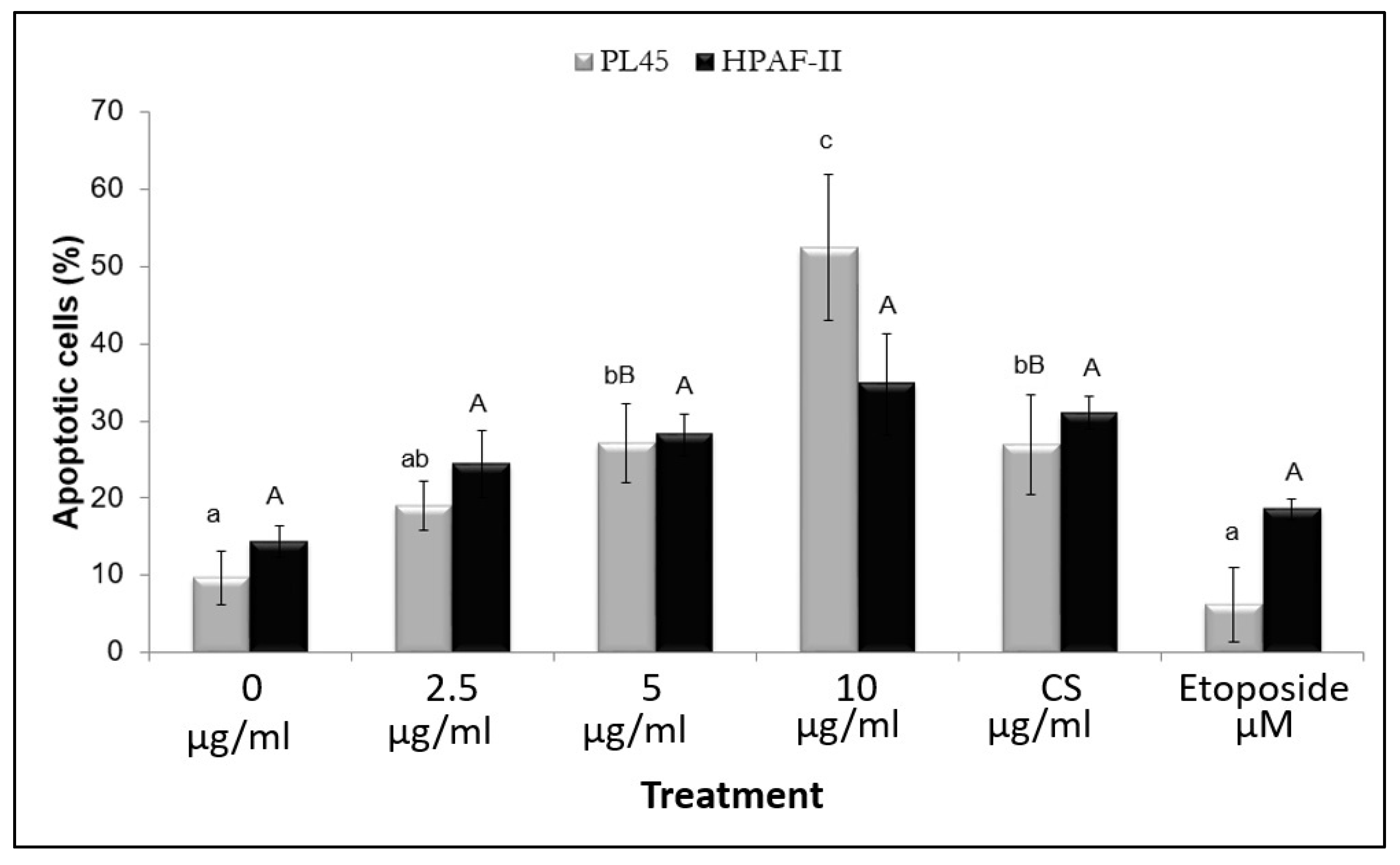
3.4. The Effect of the Isolated Active Compound on Induction of Apoptosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, G.; Gyllenhaal, C.; Soejarto, D.D. Biodiversity as a source of anticancer drugs. Curr. Drug Targets 2006, 7, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, R.; Smith, J.; Rowan, N.J. Medicinal mushrooms and cancer therapy: Translating a traditional practice into Western medicine. Perspect. Biol. Med. 2006, 49, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasser, S.P. Medicinal mushrooms as a source of antitumor and immunomodulating polysaccharides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 60, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasser, S.; Akavia, E. Regulatory issues of mushrooms as functional foods and dietary supplements: Safety and efficacy. In Mushrooms as Functional Foods; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wasser, S.P. Medicinal mushroom science: History, current status, future trends, and unsolved problems. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2010, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.N.; Mishra, D.; Singh, P.; Vamanu, E.; Singh, M. Therapeutic applications of mushrooms and their biomolecules along with a glimpse of in silico approach in neurodegenerative diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagodatski, A.; Yatsunskaya, M.; Mikhailova, V.; Tiasto, V.; Kagansky, A.; Katanaev, V.L. Medicinal mushrooms as an attractive new source of natural compounds for future cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 29259–29274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaturvedi, V.K.; Yadav, N.; Rai, N.K.; Bohara, R.A.; Rai, S.N.; Aleya, L.; Singh, M.P. Two birds with one stone: Oyster mushroom mediated bime Tallic Au-Pt nanoparticles for agro-waste management and anticancer activity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 13761–13775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, V.K.; Rai, S.N.; Tabassum, N.; Yadav, N.; Singh, V.; Bohara, R.A.; Singh, M.P. Rapid eco-friendly synthesis, characterization, and cytotoxic study of trimetallic stable nanomedicine: A potential material for biomedical applications. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2020, 24, 100812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.P.; Rai, S.N.; Dubey, S.K.; Pandey, A.T.; Tabassum, N.; Chaturvedi, V.K.; Singh, N.B. Biomolecules of mushroom: A recipe of human wellness. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, T. The extraction and development of antitumor-active polysaccharides from medicinal mushrooms in Japan. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 1999, 1, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomatis, L.; Melnick, R.L.; Haseman, J.; Barrett, J.C.; Huff, J. Alleged ‘misconceptions’ distort perceptions of environmental cancer risks. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Wasser, S.P. The role of culinary-medicinal mushrooms on human welfare with a pyramid model for human health. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2012, 14, 95–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasser, S.; Weis, A.L. Medicinal properties of substances occurring in higher basidiomycetes mushrooms: Current perspectives. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 1999, 1, 31–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaidman, B.-Z.; Yassin, M.; Mahajna, J.; Wasser, S.P. Medicinal mushroom modulators of molecular targets as cancer therapeutics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 67, 453–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, G.; Saur, D.; Schmid, R.M. Pancreatic cancer—Molecular alterations. Chin.-Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 6, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitra, A.; Hruban, R.H. Pancreatic Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2008, 3, 157–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsch, T.; Kleeff, J.; Friess, H. Molecular pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer: Advances and challenges. Curr. Mol. Med. 2007, 7, 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezel, A.F.; Kimmelman, A.C.; Stanger, B.Z.; Bardeesy, N.; DePinho, R.A. Genetics and biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1218–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allbutt, A.D.; Ayer, W.A.; Brodie, H.J.; Johri, B.N.; Taube, H. Cyathin, a new antibiotic complex produced by Cyathus helenae. Can. J. Microbiol. 1971, 17, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharvit, L.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Azzam, N.; Yechiel, Y.; Wasser, S.; Fares, F. Cyathus striatus Extract Induces Apoptosis in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells and Inhibits Xenograft Tumor Growth In Vivo. Cancers 2021, 13, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharvit, L.; Wasser, S.; Fares, F. The effect of culture liquid ethyl acetate mycelium extracts of medicinal mushrooms on the viability of human pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2012, 14, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassin, M.; Mahajna, J.A. Submerged cultured mycelium extracts of higher Basidiomycetes mushrooms selectively inhibit proliferation and induce differentiation of K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2003, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.A.; Alam, S.S.; Jabbar, A. Standardization of Medium. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Khan+IA%2C+Alam+SS%2C+Jabbar+A.+Standardization+of+medium+for+the+production+of+maximum+phytotoxic+activity+by+Fusarium+oxysporum+f.+sp.+ciceris.+Pak+J+Biol+Sci.+2001%3B4%2811%29%3A1374-1376.&btnG= (accessed on 6 March 2022).
- Moran, J.; Schnellmann, R.G. A Rapid β-NADH-Linked Fluorescence Assay for Lactate Dehydrogenase in Cellular Death. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 1996, 36, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johri, B.N.; Brodie, H.J. Extracellular Production of Indolics by the Fungus Cyathus. Mycologia 1971, 63, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayer, W.A.; Reffstrup, T. Metabolites of bird’s nest fungi. Part 18. new oxygenated cadinane derivatives from Cyathus striatus. Tetrahedron 1982, 38, 1409–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayer, W.A.; Flanagan, R.J.; Reffstrup, T. Metabolites of bird’s nest fungi-19. New triterpenoid carboxylic acids from Cyathus striatus and Cyathus pygmaeus. Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 2069–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, N.K.; Kaushik, N.; Attri, P.; Kumar, N.; Kim, C.H.; Verma, A.K.; Choi, E.H. Biomedical Importance of Indoles. Molecules 2013, 18, 6620–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon-Kedmi, M.; Yannai, S.; Fares, F.A. Induction of apoptosis in human prostate cancer cell line, PC3, by 3,3′-diindolylmethane through the mitochondrial pathway. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 91, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fares, F.A.; Ge, X.; Yannai, S.; Rennert, G. Dietary indole derivatives induce apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998, 451, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, F.; Azzam, N.; Appel, B.; Fares, B.; Stein, A. The potential efficacy of 3,3′-diindolylmethane in prevention of prostate cancer development. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2010, 19, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon-Kedmi, M.; Fares, F.A.; Yannai, S. Therapeutic Activity of 3,3′-Diindolylmethane on Prostate Cancer in an in vivo Model. Prostate 2004, 61, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, N.F.; El-Hussieny, M.; Ewies, E.F.; El Shehry, M.F.; Awad, H.M.; Fouad, M.A. Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking of New Benzofuran and Indole Derivatives as Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors. Drug Dev. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.E. Indoles Derived From Glucobrassicin: Cancer Chemoprevention by Indole-3-Carbinol and 3,3′-Diindolylmethane. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudzik, M.; Korzonek-Szlacheta, I.; Król, W. Triterpenes as Potentially Cytotoxic Compounds. Molecules 2015, 20, 1610–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilic, M.; Ilic, I. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9694–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, H.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, B.; You, L.; Zhao, Y. Advances in the epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: Trends, risk factors, screening, and prognosis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 520, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Carbon Number | 13C-NMR (ppm) | a HSQC 1H NMR Shifts (ppm) and Multiplicity | b Number of Protons | 13C-NMR DEPT135 | Adjacent 1H-COSY (ppm) | HMBC Correlations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 39.22 | 1.72t | 2 | CH2 | 2.3 | |
| C2 | 28.85 | 2.31t | 2 | CH2 | 1.72 | C3, C4 |
| C3 | 140.16 | - | - | - | - | |
| C4 | 134.94 | - | - | - | - | |
| C5 | 46.02 | 2.17 | 1 | CH | - | C3, C4, C6, C7, C11, C16 |
| C6 | 42.15 | - | - | - | - | |
| C7 | 28.78 | 1.58 | 2 | CH2 | C6, C9 | |
| C8 | 36.60 | 1.57 | 2 | CH2 | C4, C6, C9 | |
| C9 | 49.17 | - | - | - | - | |
| C10 | 68.77 | 4.96d | 1 | CH | 6.90 | C4, C5, C6, C11, C12, |
| C11 | 154.64 | 6.90dd | 1 | CH | 4.96 | C15, C5 |
| C12 | 143.12 | - | - | - | - | |
| C13 | 45.88 | 3.27, 3.28d | 1 | CH | 4.5 | C6, C11, C12, C14, C2′, C3′ |
| C14 | 86.57 | 4.52, 4.54d | 1 | CH | 3.27 | C5, C7, C12, C16 |
| C15 | 197.01 | 9.3s | 1 | CH | - | C12, C13 |
| C16 | 21.11 | 1.22s | 3 | CH3 | - | C5, C6, C7, C14 |
| C17 | 23.88 | 0.96s | 3 | CH3 | - | C1, C4, C8, C9, |
| C18 | 26.35 | 3.0q | 1 | CH | 0.98, 1.04 | C3, C2, C19, C20 |
| C19 | 21.87 | 0.98d | 3 | CH3 | 3.0 | C3, C18, C20 |
| C20 | 21.62 | 1. 04d | 3 | CH3 | 3.0 | C3, C18, C19 |
| C1′ | 108.02 | 5.29s | 1 | CH | - | C14, C5′, C3′ |
| C2′ | 83.50 | - | 0 | - | - | |
| C3′ | 204.30 | - | 0 | - | - | |
| C4′ | 75.00 | 4.03 | 1 | CH | 3.7 | |
| C5′ | 68.62 | 4.30, 4.28, 3.80, 3.78dd | 2 | CH2 | 4.03 | C4′, C3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fares, F.; Khatib, S.; Vaya, J.; Sharvit, L.; Eizenberg, E.; Wasser, S. Striatal Isolated from Cyathus striatus Extracts Induces Apoptosis in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092746
Fares F, Khatib S, Vaya J, Sharvit L, Eizenberg E, Wasser S. Striatal Isolated from Cyathus striatus Extracts Induces Apoptosis in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2022; 27(9):2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092746
Chicago/Turabian StyleFares, Fuad, Soliman Khatib, Jacob Vaya, Lital Sharvit, Einav Eizenberg, and Solomon Wasser. 2022. "Striatal Isolated from Cyathus striatus Extracts Induces Apoptosis in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells" Molecules 27, no. 9: 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092746
APA StyleFares, F., Khatib, S., Vaya, J., Sharvit, L., Eizenberg, E., & Wasser, S. (2022). Striatal Isolated from Cyathus striatus Extracts Induces Apoptosis in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Molecules, 27(9), 2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092746








