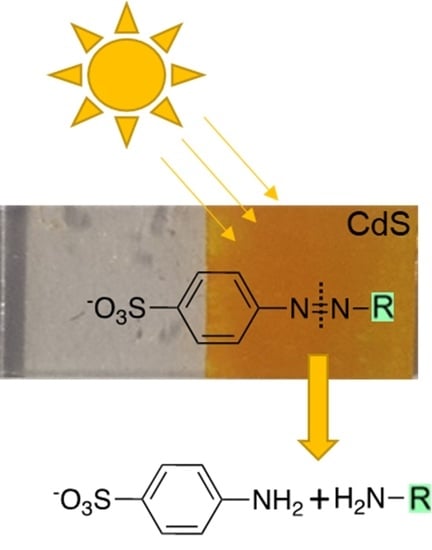
Visible Light Reductive Photocatalysis of Azo-Dyes with n–n Junctions Based on Chemically Deposited CdS
Abstract
Share and Cite
Mazzanti, M.; Milani, M.; Cristino, V.; Boaretto, R.; Molinari, A.; Caramori, S. Visible Light Reductive Photocatalysis of Azo-Dyes with n–n Junctions Based on Chemically Deposited CdS. Molecules 2022, 27, 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092924
Mazzanti M, Milani M, Cristino V, Boaretto R, Molinari A, Caramori S. Visible Light Reductive Photocatalysis of Azo-Dyes with n–n Junctions Based on Chemically Deposited CdS. Molecules. 2022; 27(9):2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092924
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazzanti, Michele, Martina Milani, Vito Cristino, Rita Boaretto, Alessandra Molinari, and Stefano Caramori. 2022. "Visible Light Reductive Photocatalysis of Azo-Dyes with n–n Junctions Based on Chemically Deposited CdS" Molecules 27, no. 9: 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092924
APA StyleMazzanti, M., Milani, M., Cristino, V., Boaretto, R., Molinari, A., & Caramori, S. (2022). Visible Light Reductive Photocatalysis of Azo-Dyes with n–n Junctions Based on Chemically Deposited CdS. Molecules, 27(9), 2924. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092924