Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Edible Bird’s Nest Based on Peptide Markers by LC-QTOF-MS/MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
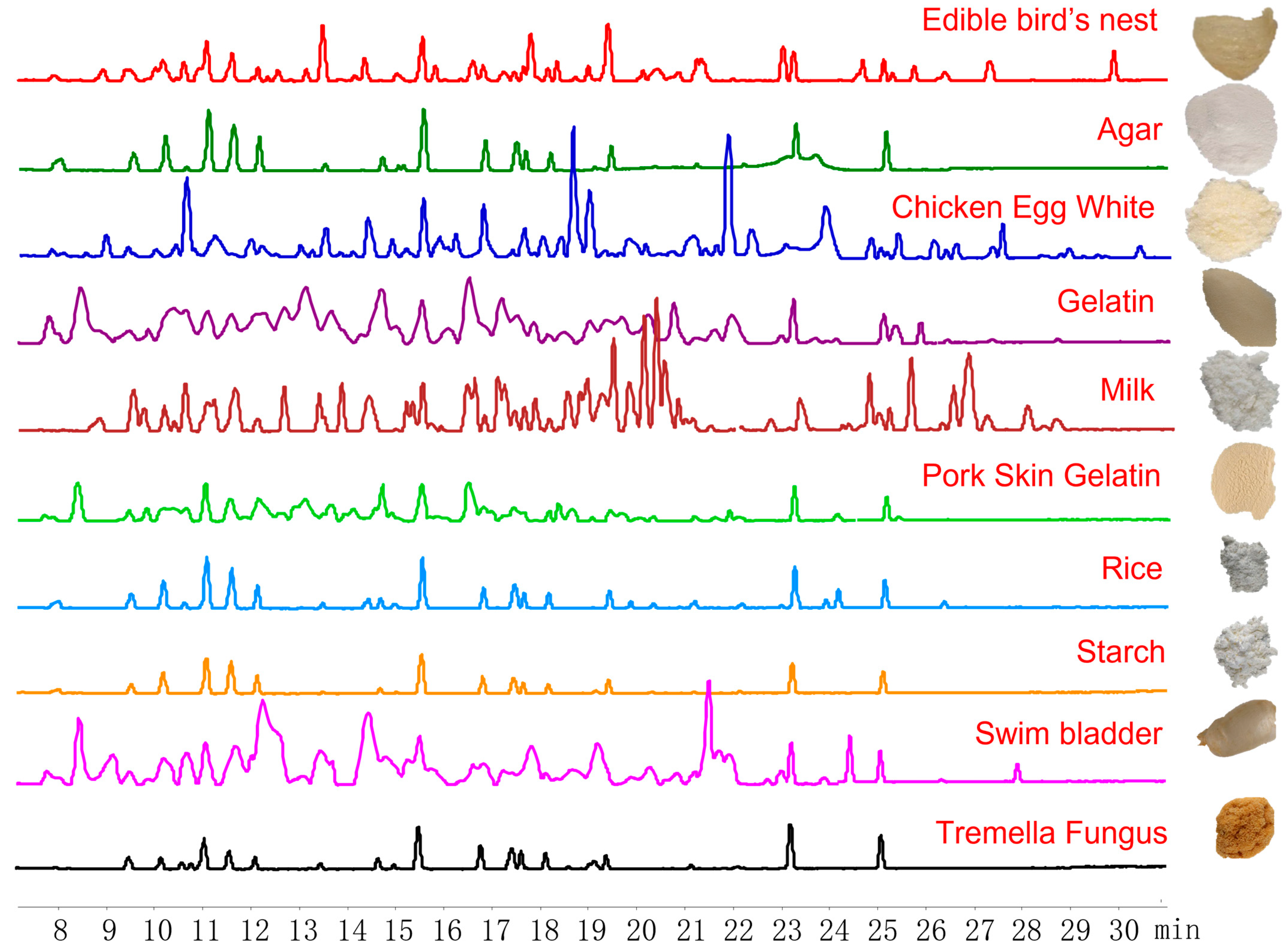
2.1. Selection of EBN-Specific Peptides
2.2. Identification of Specific Peptides
2.3. Quantitative Analysis Based on EBN-Specific Markers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. LC-QTOF-MS/MS Analysis
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Sample Availability
References
- Hun, L.T.; Wani, W.A.; Tjih, E.T.T.; Adnan, N.A.; Le Ling, Y.; Aziz, R.A.J. Investigations into the physicochemical, biochemical and antibacterial properties of edible bird’s nest. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 228–247. [Google Scholar]
- Zukefli, S.N.; Chua, L.S.; Rahmat, Z. Protein Extraction and Identification by Gel Electrophoresis and Mass Spectrometry from Edible bird’s Nest Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 10, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, N.A.; Mohamad Yusop, S.; Babji, A.S.; Lim, S.J.; Sarbini, S.R.; Hui Yan, T. Edible Bird’s Nest: Physicochemical Properties, Production, and Application of Bioactive Extracts and Glycopeptides. Food Rev. Int. 2019, 37, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, L. A comprehensive review of edible bird’s nest. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cheung, S.-H.; Li, S.C.; Cheung, H.-Y. Establishment of a holistic and scientific protocol for the authentication and quality assurance of edible bird’s nest. Food Chem. 2014, 151, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.K.L.; Wong, Z.C.F.; Lam, K.Y.C.; Cheng, L.K.W.; Zhang, L.M.; Lin, H.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W.K. Edible Bird’s Nest, an Asian Health Food Supplement, Possesses Skin Lightening Activities: Identification of N-Acetylneuraminic Acid as Active Ingredient. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 2015, 05, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalluddin, N.H.; Tukiran, N.A.; Ahmad Fadzillah, N.; Fathi, S. Overview of edible bird’s nests and their contemporary issues. Food Control 2019, 104, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Wani, W.A.; Koay, Y.S.; Kavita, S.; Tan, E.T.T.; Shreaz, S. Recent advances in the identification and authentication methods of edible bird’s nest. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.H.; Muhammad, S.A.; Aziz, F.A.; Ng, J.S.; Nasir, F.I.; Adenan, M.N.H.; Moosa, S.; Othman, Z.; Abdullah, S.N.A.; Sharif, Z.; et al. Detection of adulteration activities in edible bird’s nest using untargeted 1H-NMR metabolomics with chemometrics. Food Control 2022, 132, 108542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukiran, N.A.; Ismail, A.; Mustafa, S.; Hamid, M. Determination of porcine gelatin in edible bird’s nest by competitive indirect ELISA based on anti-peptide polyclonal antibody. Food Control 2016, 59, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Li, L.F.; Wu, W.J.; Zhang, Q.W.; Liu, M.; Wong, T.L.; Kong, H.Y.; Lai, C.H.; Bao, W.R.; Huo, C.Y.; et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of agar in edible bird’s nest and related products based on a daughter oligosaccharide-marker approach using LC-QTOF-MS. Food Control 2022, 132, 108514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui Yan, T.; Mun, S.L.; Lee, J.L.; Lim, S.J.; Daud, N.A.; Babji, A.S.; Sarbini, S.R. Bioactive sialylated-mucin (SiaMuc) glycopeptide produced from enzymatic hydrolysis of edible swiftlet’s nest (ESN): Degree of hydrolysis, nutritional bioavailability, and physicochemical characteristics. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 252–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spichtig, V.; Michaud, J.; Austin, S. Determination of sialic acids in milks and milk-based products. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 405, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, A.J.W.; Chang, L.S.; Babji, A.S.; Latip, J.; Koketsu, M.; Lim, S.J. Review of sialic acid’s biochemistry, sources, extraction and functions with special reference to edible bird’s nest. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Bai, L.; Han, W.; Ge, Y.; Yuan, F. Application of SYBRgreen PCR and 2DGE methods to authenticate edible bird’s nest food. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2020–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lai, X.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Lan, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Q.; Hong, D.; et al. Proteomic Profile of Edible Bird’s Nest Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 12477–12481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad Nasir, N.N.; Mohamad Ibrahim, R.; Abu Bakar, M.Z.; Mahmud, R.; Ab Razak, N.A. Characterization and Extraction Influence Protein Profiling of Edible Bird’s Nest. Foods 2021, 10, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hun, L.T.; Lee, C.H.; Azmi, N.A.; Liew, R.K.; Hamdan, N.; Wong, S.L.; Ong, P.Y. Amino acid determination by HPLC combined with multivariate approach for geographical classification of Malaysian Edible Bird’s Nest. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 107, 104399. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.F.; Chan, G.K.L.; Zhang, M.L.; Yao, P.; Lin, H.Q.; Dong, T.T.X.; Li, G.; Lai, X.P.; Tsim, K.W.K. Characterization of edible bird’s nest by peptide fingerprinting with principal component analysis. Food Qual. Saf. 2017, 1, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, J.; Liang, J.; Ma, X.; Xing, R.; Han, J.; Guo, L.; Chen, Y. Authentication of Edible Bird’s Nest (EBN) and its adulterants by integration of shotgun proteomics and scheduled multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) based on tandem mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2019, 125, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.R.; Lee, T.H.; Cheong, S.K.; Lim, Y.M. Untargeted metabolite profiling on the water-soluble metabolites of edible bird’s nest through liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Vet. World 2020, 13, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghassem, M.; Arihara, K.; Mohammadi, S.; Sani, N.A.; Babji, A.S. Identification of two novel antioxidant peptides from edible bird’s nest (Aerodramus fuciphagus) protein hydrolysates. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2046–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Xiong, N.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Jiang, L. Using RSM for Optimum of Optimum Production of Peptides from Edible Bird’s Nest By-Product and Characterization of Its Antioxidant’s Properties. Foods 2022, 11, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.-K.; Wong, K.-H.; Lo, S.C.-L. Identification of peptides released from hot water insoluble fraction of edible bird’s nest under simulated gastro-intestinal conditions. Food Res. Int. 2016, 85, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| - | Observed m/z | RT (min) | White EBN b | Grass EBN b | Adulterants a | Peptide | Common Peaks b | EBN Peptide Marker |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 375.2250 | 7.96 | + c | − c | + | − | /c | / |
| 2 | 280.6746 | 7.97 | + | + | − | + | + | E1 d |
| 3 | 237.1235 | 9.04 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 4 | 272.1722 | 9.51 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 5 | 381.7042 | 9.61 | + | + | − | + | + | E2 |
| 6 | 447.6996 | 9.81 | − | + | − | + | + | G1 d |
| 7 | 373.8247 | 9.82 | + | + | − | + | + | E3 |
| 8 | 292.1648 | 10.05 | + | − | − | + | + | W1 d |
| 9 | 548.2486 | 10.07 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 10 | 258.1691 | 10.24 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 11 | 402.2467 | 10.24 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 12 | 454.7018 | 10.24 | + | − | − | + | + | W2 |
| 13 | 467.2138 | 10.38 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 14 | 231.1710 | 10.67 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 15 | 305.1666 | 10.99 | + | − | − | + | + | W3 |
| 16 | 339.1850 | 10.99 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 17 | 582.2528 | 11.01 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 18 | 389.2400 | 11.09 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 19 | 277.6512 | 11.49 | + | − | − | + | + | W4 |
| 20 | 347.6992 | 11.63 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 21 | 382.1620 | 12.01 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 22 | 629.3627 | 12.56 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 23 | 258.6615 | 12.59 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 24 | 288.2036 | 12.59 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 25 | 280.1954 | 12.86 | + | − | − | + | + | W5 |
| 26 | 265.1557 | 13.54 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 27 | 494.2616 | 14.44 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 28 | 350.1712 | 15.09 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 29 | 820.3634 | 15.13 | + | + | − | + | + | E4 |
| 30 | 335.2230 | 15.39 | − | + | − | + | + | G2 |
| 31 | 509.2615 | 15.79 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 32 | 417.7010 | 16.15 | − | + | − | + | + | G3 |
| 33 | 804.3734 | 16.24 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 34 | 404.1986 | 16.65 | + | + | − | + | + | E5 |
| 35 | 366.2030 | 16.66 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 36 | 300.1459 | 17.25 | + | + | − | + | + | E6 |
| 37 | 498.7967 | 17.87 | + | + | − | + | + | E7 |
| 38 | 507.2456 | 18.39 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 39 | 346.2350 | 19.48 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 40 | 364.2235 | 19.48 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 41 | 321.7031 | 20.45 | + | − | − | + | + | W6 |
| 42 | 844.3728 | 20.63 | + | + | − | + | + | E8 |
| 43 | 441.7166 | 20.65 | + | − | − | + | + | W7 |
| 44 | 294.8142 | 20.7 | + | − | − | + | + | W8 |
| 45 | 468.7439 | 20.78 | + | − | − | + | + | W9 |
| 46 | 350.2074 | 21.07 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 47 | 344.255 | 21.32 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 48 | 336.1926 | 21.4 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 49 | 525.7603 | 22.46 | + | − | − | − | / | / |
| 50 | 477.7330 | 23.14 | + | + | − | + | + | E9 |
| 51 | 630.8100 | 24.56 | + | + | − | + | + | E10 |
| 52 | 479.2879 | 24.73 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| 53 | 472.3140 | 25.78 | + | − | + | + | − | / |
| 54 | 711.4410 | 26.43 | + | − | + | + | + | W10 |
| 55 | 391.7429 | 27.35 | + | − | − | + | + | W11 |
| 56 | 410.7169 | 27.35 | + | − | − | + | + | W12 |
| 57 | 433.7006 | 28.04 | + | − | − | + | + | W13 |
| 58 | 491.3200 | 29.94 | + | − | + | − | / | / |
| Peptide Marker | Observed m/z | Retention Time (min) | Charge State | Sequence | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E7 | 498.8056 | 17.91 | 2 | VSAPGPVLTR | De novo |
| W2 | 454.6704 | 10.37 | 2 | AMESINSR | Database |
| G1 | 447.6998 | 9.88 | 2 | SDDSLWR | De novo |
| Marker No. | Linear Regression a | Range | R2 | LOD b | LOQ b | Repeatability | Recovery % (RSD, n = 3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg) | (mg) | (mg) | Intra-Day (n = 6) | Inter-Day (n = 3) | Low c (Spiking 80%) | Middle c (Spiking 100%) | High c (Spiking 120%) | |||
| W2 | y = 169511x − 106601 | 0.5–40 | 0.9962 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 1.1% | 1.3% | 113.6 (4.3%) | 111.7 (5.1%) | 111.4 (3.8%) |
| E7 | y = 180636x + 14740 | 0.5–40 | 0.9980 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 1.8% | 4.7% | 117.7 (2.6%) | 116.1 (4.5%) | 100.6 (5.3%) |
| G1 | y = 34915x + 10205 | 0.5–40 | 0.9953 | 0.13 | 0.42 | 1.1% | 3.0% | 111.6 (3.3%) | 111.1 (6.2%) | 105.0 (1.9%) |
| Sample Code | W2 a (mg/mL) | E7 a (mg/mL) | G1 a (mg/mL) | Type | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD-01 | 12.72 ± 0.60 | 14.16 ± 0.84 | 4.60 ± 0.36 | Instant product | China |
| PD-02 | 3.21 ± 0.04 | 3.52 ± 0.24 | 3.40 ± 0.28 | Instant product | China |
| PD-03 | 7.64 ± 0.12 | 7.32 ± 0.32 | 7.52 ± 0.24 | Instant product | China |
| PD-04 | 12.24 ± 0.48 | 13.12 ± 0.64 | ND b | Instant product | China |
| PD-05 | 15.52 ± 0.61 | 15.60 ± 0.72 | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-06 | 5.92 ± 0.28 | 6.04 ± 0.36 | 5.41 ± 0.20 | Instant product | China |
| PD-07 | 52.72 ± 0.92 | 55.32 ± 2.24 | 8.96 ± 0.44 | Instant product | China |
| PD-08 | 61.08 ± 1.56 | 61.56 ± 2.56 | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-09 | 74.80 ± 1.81 | 75.84 ± 2.96 | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-10 | 41.84 ± 1.28 | 42.68 ± 1.24 | 5.41 ± 0.36 | Instant product | China |
| PD-11 | 18.32 ± 0.76 | 21.88 ± 0.88 | 10.52 ± 0.48 | Instant product | China |
| PD-12 | ND b | ND b | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-13 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-14 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-15 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-16 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-17 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-18 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-19 | 3.20 ± 0.08 | 3.56 ± 0.09 | ND | Beverage | China |
| PD-20 | ND | ND | ND | Beverage | China |
| PD-21 | ND | ND | ND | Beverage | China |
| PD-22 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-23 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-24 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-25 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-26 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-27 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-28 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-29 | ND | ND | ND | Beverage | China |
| PD-30 | ND | ND | ND | Beverage | China |
| PD-31 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-32 | 4.81 ± 0.27 | 5.52 ± 0.33 | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-33 | ND | ND | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-34 | 22.24 ± 1.12 | 24.60 ± 1.32 | 6.64 ± 0.24 | Instant product | China |
| PD-35 | 18.40 ± 1.16 | 20.12 ± 1.18 | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-36 | 23.92 ± 1.20 | 24.64 ± 1.39 | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-37 | 4.04 ± 0.12 | 7.01 ± 0.24 | 12.08 ± 0.44 | Instant product | China |
| PD-38 | 16.96 ± 0.52 | 20.68 ± 0.64 | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-39 | 8.04 ± 0.24 | 10.01 ± 0.42 | 3.32 ± 0.13 | Instant product | China |
| PD-40 | 71.80 ± 1.88 | 73.56 ± 2.52 | 12.44 ± 0.68 | Instant product | China |
| PD-41 | 14.92 ± 0.64 | 15.16 ± 0.81 | ND | Instant product | China |
| PD-42 | ND | ND | ND | Beverage | Vietnam |
| PD-43 | 4.04 ± 0.12 | 4.24 ± 0.21 | ND | Beverage | Vietnam |
| PD-44 | 15.44 ± 0.60 | 15.52 ± 0.68 | ND | Beverage | Vietnam |
| PD-45 | 13.12 ± 0.44 | 13.20 ± 0.65 | ND | Beverage | Vietnam |
| PD-46 | 3.48 ± 0.13 | 3.52 ± 0.14 | ND | Beverage | Vietnam |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.-J.; Li, L.-F.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Fung, H.-Y.; Kong, H.-Y.; Wong, T.-L.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Liu, M.; Bao, W.-R.; Huo, C.-Y.; et al. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Edible Bird’s Nest Based on Peptide Markers by LC-QTOF-MS/MS. Molecules 2022, 27, 2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092945
Wu W-J, Li L-F, Cheng H-Y, Fung H-Y, Kong H-Y, Wong T-L, Zhang Q-W, Liu M, Bao W-R, Huo C-Y, et al. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Edible Bird’s Nest Based on Peptide Markers by LC-QTOF-MS/MS. Molecules. 2022; 27(9):2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092945
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wen-Jie, Li-Feng Li, Hui-Yuan Cheng, Hau-Yee Fung, Hau-Yee Kong, Tin-Long Wong, Quan-Wei Zhang, Man Liu, Wan-Rong Bao, Chu-Ying Huo, and et al. 2022. "Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Edible Bird’s Nest Based on Peptide Markers by LC-QTOF-MS/MS" Molecules 27, no. 9: 2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092945
APA StyleWu, W.-J., Li, L.-F., Cheng, H.-Y., Fung, H.-Y., Kong, H.-Y., Wong, T.-L., Zhang, Q.-W., Liu, M., Bao, W.-R., Huo, C.-Y., & Han, Q.-B. (2022). Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Edible Bird’s Nest Based on Peptide Markers by LC-QTOF-MS/MS. Molecules, 27(9), 2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092945






