Eutectic Thin-Layer Chromatography as a New Possibility for Quantification of Plant Extracts—A Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. DES Selection and Preparation
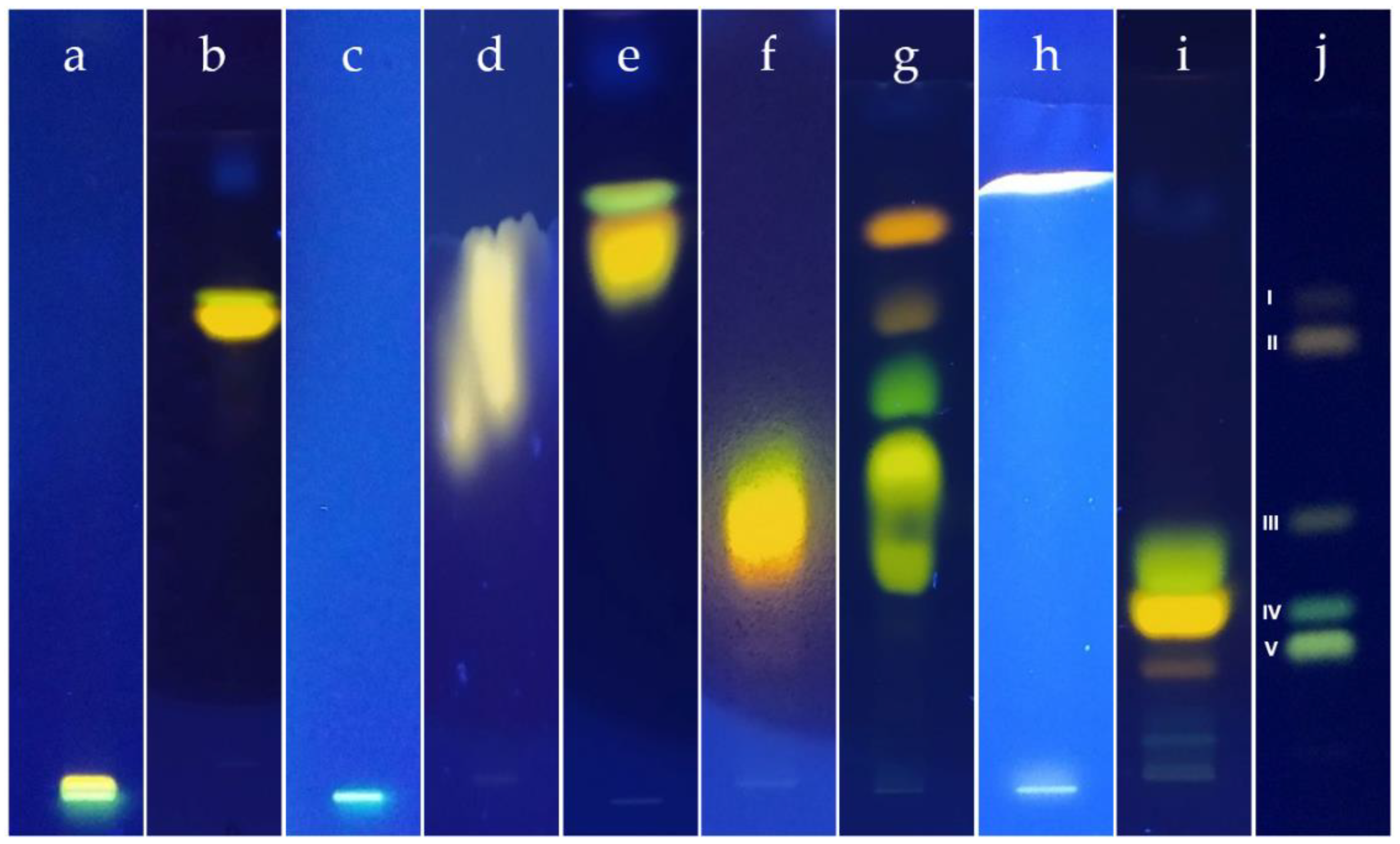
2.2. Chromatographic Analysis with Pure DES
2.3. Chromatographic Analysis of Diluted DES
2.4. Chromatographic Analysis of DES’s Mixtures
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Standards and Sample
3.3. Mobile Phases Preparation
3.4. Equipment and Chromatographic Conditions
3.5. Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Raj, D. Czy w dzisiejszych czasach proste obserwacje mogą jeszcze znacząco zmieniać postrzeganie podstawowych zjawisk? Przypadek cieczy eutektycznych. Kwart. Hist. Nauk. I Tech. 2021, 2, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, W.B. The origin of the name “onion’s fusible alloy”. J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 1050–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, V.I.B.; Craveiro, R.; Silva, J.M.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural deep eutectic systems as alternative nontoxic cryoprotective agents. Cryobiology 2018, 83, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.-N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties, Applications and Perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Varypataki, E.M.; Golovina, E.A.; Jiskoot, W.; Witkamp, G.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Natural deep eutectic solvents in plants and plant cells: In vitro evidence for their possible functions. In Advances in Botanical Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 97, pp. 159–184. ISBN 9780128216910. [Google Scholar]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Rutkowska, M.; de la Guardia, M. Are deep eutectic solvents useful in chromatography? A short review. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1639, 461918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishov, A.; Pochivalov, A.; Nugbienyo, L.; Andruch, V.; Bulatov, A. Deep eutectic solvents are not only effective extractants. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 129, 115956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.Q.; Abbasi, N.M.; Anderson, J.L. Deep eutectic solvents in separations: Methods of preparation, polarity, and applications in extractions and capillary electrochromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1633, 461613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.C.; Fernandes, J.O. Extraction techniques with deep eutectic solvents. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; van Spronsen, J.; Dai, Y.; Verberne, M.; Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R. Are Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents the Missing Link in Understanding Cellular Metabolism and Physiology? Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momotko, M.; Łuczak, J.; Przyjazny, A.; Boczkaj, G. First deep eutectic solvent-based (DES) stationary phase for gas chromatography and future perspectives for DES application in separation techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1635, 461701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, D. Thin-layer chromatography with eutectic mobile phases—Preliminary results. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1621, 461044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, Q.; Khan, S.A.; Mohammad, A. Applications of green solvents in thin-layer chromatography (TLC)—An overview. J. Planar Chromatogr.—Mod. TLC 2021, 34, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ahlgren, S.; Korthout, H.A.A.J.; Salomé-Abarca, L.F.; Bayona, L.M.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Broad range chemical profiling of natural deep eutectic solvent extracts using a high performance thin layer chromatography–based method. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1532, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fandiño, R.; Gill, I.; Vulfson, E.N. Protease-catalyzed synthesis of oligopeptides in heterogenous substrate mixtures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1994, 43, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, K.; Roghair, I.; Gallucci, F.; van Sint Annaland, M. Total vapor pressure of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: Experiments and modelling. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 115227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Gorbunov, A.; Moskvin, L.; Bulatov, A. Decomposition of deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride and phenol in aqueous phase. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 301, 112380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumandpassand, A.; Javadi, A.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. Solution decomposition of deep eutectic solvents in pH-induced solidification of floating organic droplet homogeneous liquid-liquid microextraction for the extraction of pyrethroid pesticides from milk. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abranches, D.O.; Martins, M.A.R.; Silva, L.P.; Schaeffer, N.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Phenolic hydrogen bond donors in the formation of non-ionic deep eutectic solvents: The quest for type v des. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 10253–10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Laaksonen, A.; Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Ji, X. The peculiar effect of water on ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8685–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Li, P.; Yang, H. A hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents-based integrated method for efficient and green extraction and recovery of natural products from Rosmarinus officinalis leaves, Ginkgo biloba leaves and Salvia miltiorrhiza roots. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Tong, L.; Guo, H.; Ma, C.; Qin, F.; Xiong, Z. Tailor-made deep eutectic solvents extraction combined with UPLC-MS/MS determination of icarrin and icarisid II in rat plasma and its comparative pharmacokinetic application. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 199, 114054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, L.; Karve, T.; Jain, R.; Dandekar, P. Menthol based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for extraction and purification of ergosterol using response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dortmund Data Bank. Available online: http://www.ddbst.com/ (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Santana, A.P.R.; Mora-Vargas, J.A.; Guimarães, T.G.S.; Amaral, C.D.B.; Oliveira, A.; Gonzalez, M.H. Sustainable synthesis of natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) by different methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Dietz, C.H.J.T.; Warrag, S.E.E.; Kroon, M.C. The Curious Case of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Story on the Discovery, Design, and Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 10591–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajkacz, S.; Adamek, J.; Sobska, A. Application of deep eutectic solvents and ionic liquids in the extraction of catechins from tea. Molecules 2020, 25, 3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekharan, T.R.; Chandira, R.M.; Tamilvanan, S.; Rajesh, S.C.; Venkateswarlu, B.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents as an Alternate to Other Harmful Solvents. Review 2022, 12, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) Guidelines, Q2 (R1) Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology. In ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guideline; ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Zalewski, D. Qualitative and quantitative determination of main alkaloids of Chelidonium majus L. using thin-layer chromatographic-densitometric method. Acta Chromatogr. 2017, 29, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, S.; Wójciak-Kosior, M.; Płachno, B.J.; Sowa, I.; Włodarczyk, M.; Matkowski, A. Quaternary alkaloids in Chelidonium majus in vitro cultures. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 123, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, D.; Kielisz, P. High-performance thin-layer chromatographic–densitometric determination of the major triterpene saponins and their aglycones from centella asiatica. J. Planar. Chromatogr.–Mod. TLC 2019, 32, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Bladt, S. Plant Drug Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; ISBN 978-3-540-58676-0. [Google Scholar]


| Components | Molar Ratio | No | Obtaining Procedure |
|---|---|---|---|
| borneol + phenol | 1:1 | E1 | P2 |
| camphor + formic acid | 1:1 | E2 | P1 |
| camphor + phenol | 1:1 | E3 | P1 |
| camphor + phenyl salicylate | 1:1 | E4 | P1 |
| menthol + acetic acid | 1:1 | E5 | P1 |
| menthol + borneol | 8:2 | E6 | P2 |
| menthol + lactic acid | 1:2 | E7 | P1 |
| menthol + limonene | 1:1 | E8 | P1 |
| menthol + phenol | 1:1 | E9 | P1 |
| menthol + thymol | 1:1 | E10 | P1 |
| thymol + acetic acid | 1:1 | E11 | P2 |
| thymol + linalool | 1:1 | E12 | P1 |
| thymol + phenol | 1:1 | E13 | P1 |
| choline chloride + malic acid 1 | 1:1 | E14 | P3 |
| choline chloride + oxalic acid 1 | 1:1 | E15 | P2 |
| choline chloride + phenol 1 | 1:2 | E16 | P1 |
| choline chloride + lactic acid 1 | 1:1 | E17 | P3 |
| E1 | E2 | E3 | E4 | E5 | E6 | E7 | E8 | E9 | E10 | E11 | E12 | E13 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E14 | − | * | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| E15 | * | * | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| E16 | * | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + |
| E17 | − | − | * | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | + |
| DES Mix Name | Component 1 | Component 2 | Component 1 to 2 Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| EM1 | E3 | E11 | 1:1 |
| EM2 | E3 | E8 | 1:1 |
| EM3 | E3 | E8 | 2:1 |
| EM4 | E3 | E8 | 3:1 |
| EM5 | E3 | E8 | 3:2 |
| EM6 | E9 | E11 | 1:1 |
| EM7 | E17 | E11 | 1:1 |
| EM8 | E17 | E13 | 1:1 |
| EM9 | E16 | E2 | 1:1 |
| EM9 | E16 | E11 | 1:1 |
| EM10 | E16 | E13 | 1:1 |
| Compound | Concentration (mg g−1 Dry Weight) |
|---|---|
| Berberine | 0.636 ± 0.052 |
| Chelerythrine | 0.789 ± 0.067 |
| Chelidonine | 0.216 ± 0.035 |
| Coptisine | 0.992 ± 0.013 |
| Sanguinarine | 1.410 ± 0.009 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raj, D. Eutectic Thin-Layer Chromatography as a New Possibility for Quantification of Plant Extracts—A Case Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092960
Raj D. Eutectic Thin-Layer Chromatography as a New Possibility for Quantification of Plant Extracts—A Case Study. Molecules. 2022; 27(9):2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092960
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaj, Danuta. 2022. "Eutectic Thin-Layer Chromatography as a New Possibility for Quantification of Plant Extracts—A Case Study" Molecules 27, no. 9: 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092960
APA StyleRaj, D. (2022). Eutectic Thin-Layer Chromatography as a New Possibility for Quantification of Plant Extracts—A Case Study. Molecules, 27(9), 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092960






