Beyond Pristine Metal–Organic Frameworks: Preparation of Hollow MOFs and Their Composites for Catalysis, Sensing, and Adsorption Removal Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
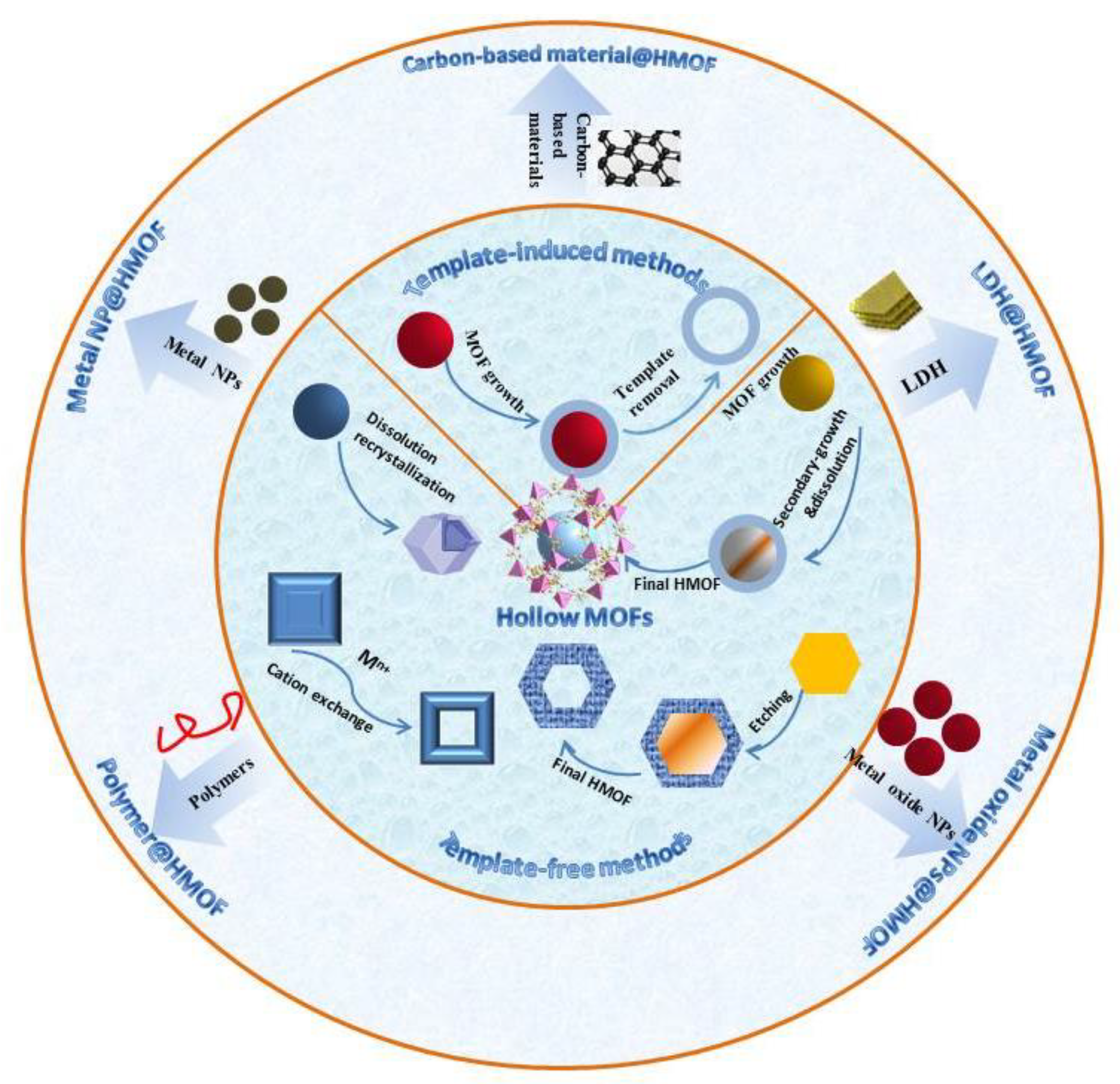
2. Synthetic Strategies of Hollow MOFs and Their Composites
2.1. Template-Induced Methods
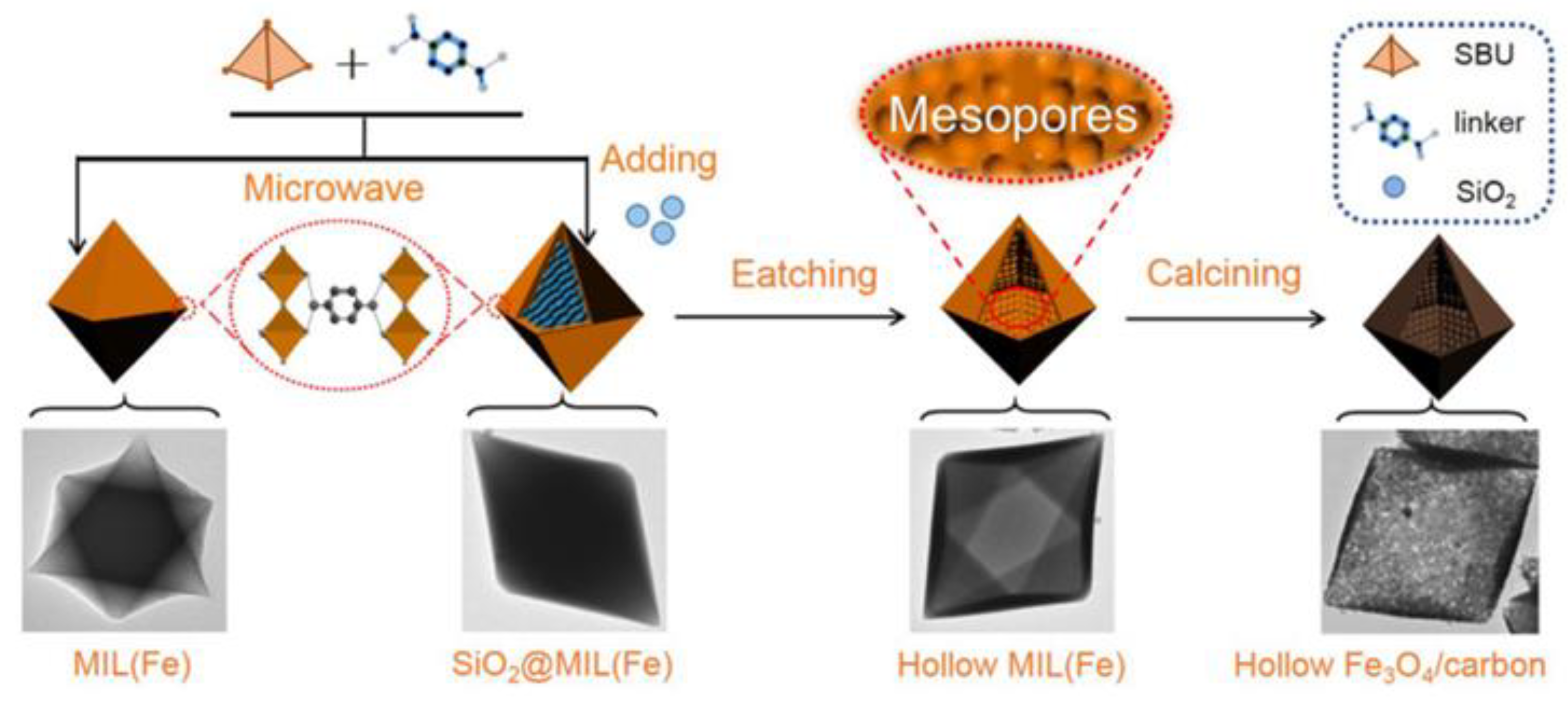
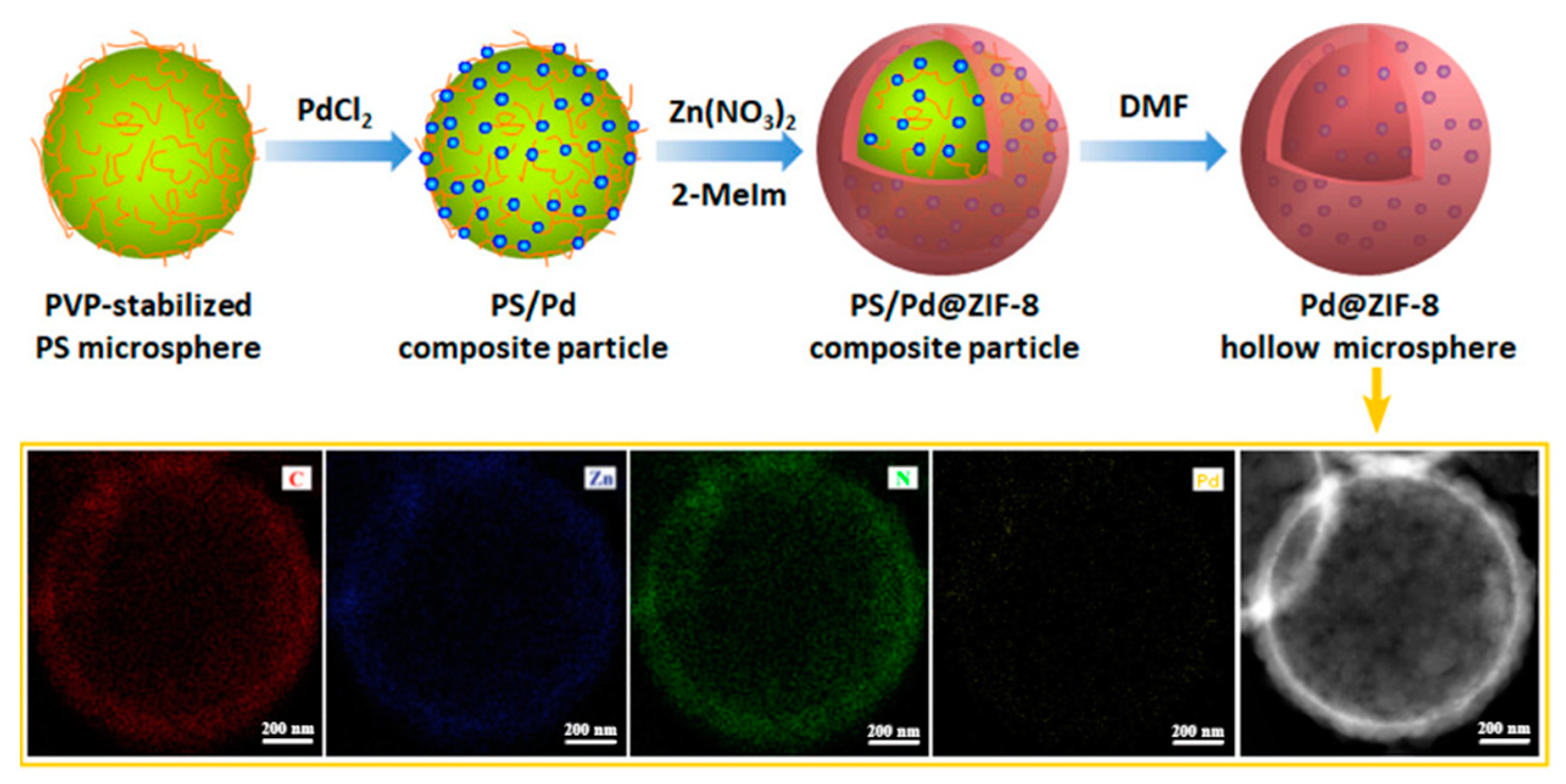
2.1.1. Hard-Template-Induced Methods
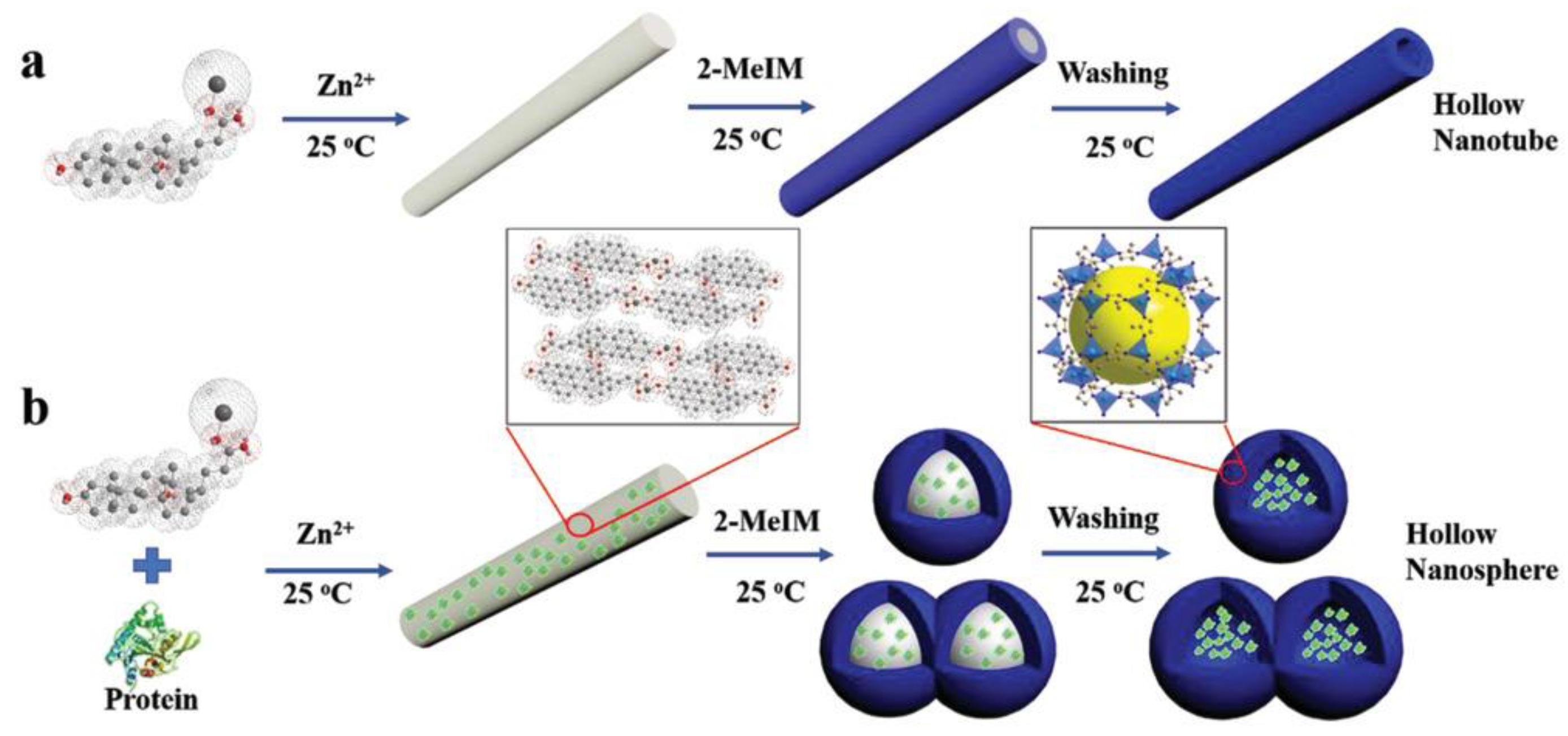
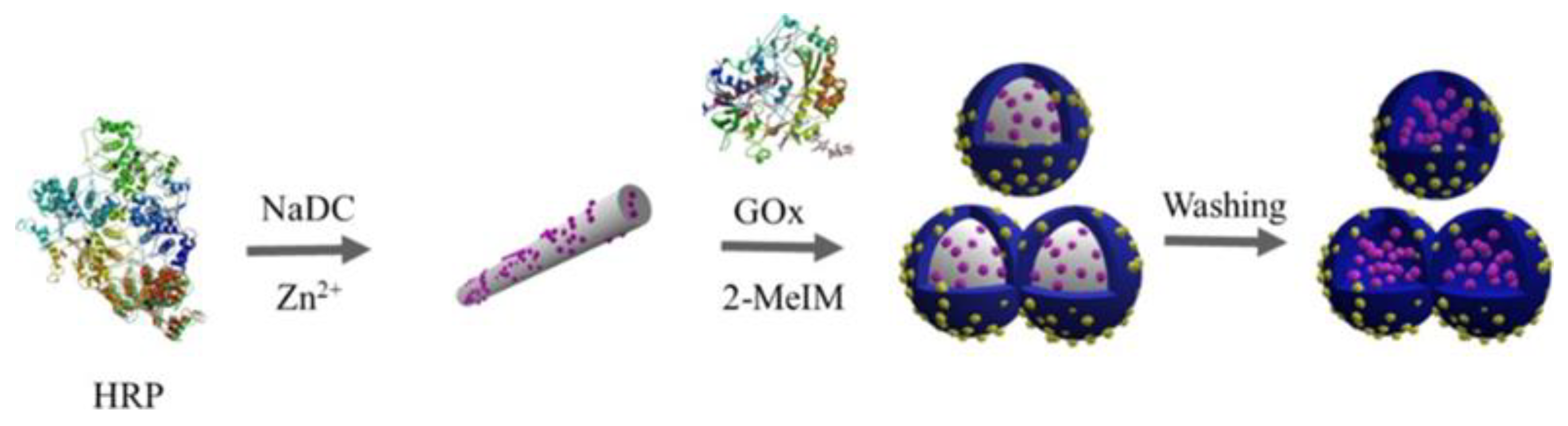
2.1.2. Soft-Template-Induced Methods
2.2. Template-Free Methods
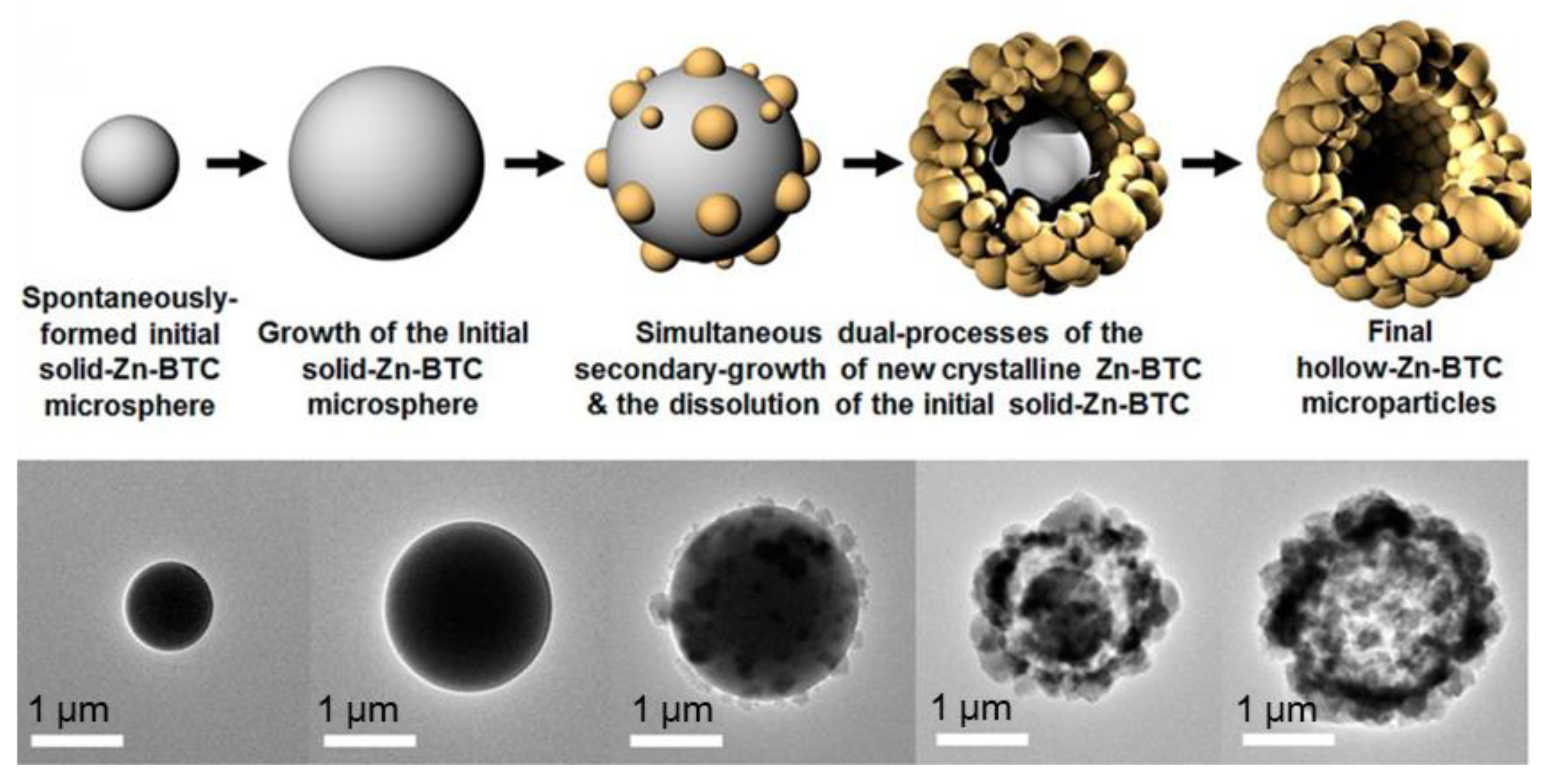
2.2.1. Ostwald Ripening Principle
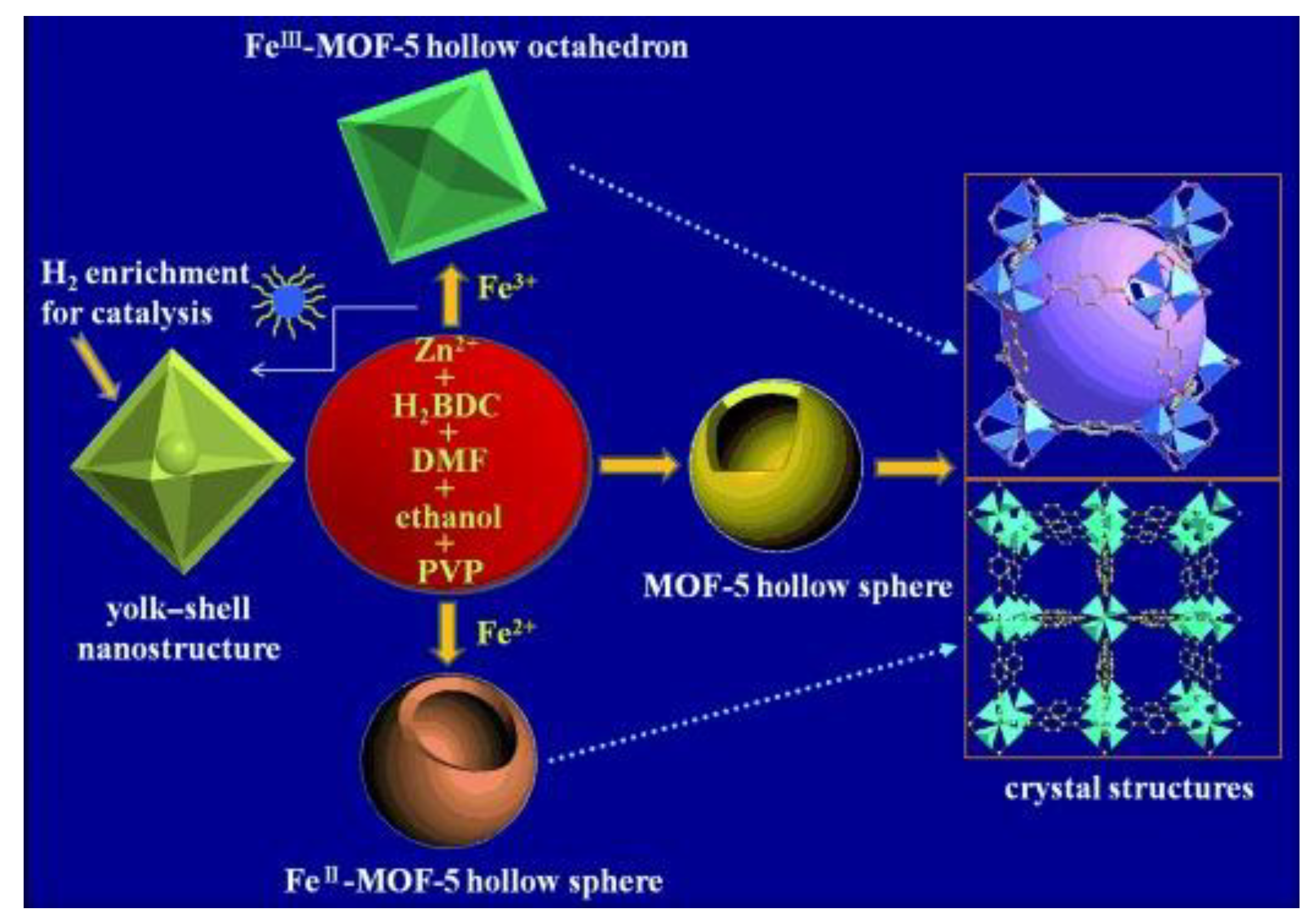
2.2.2. The Kirkendall Effect
2.2.3. Surface-Energy-Driven Mechanism
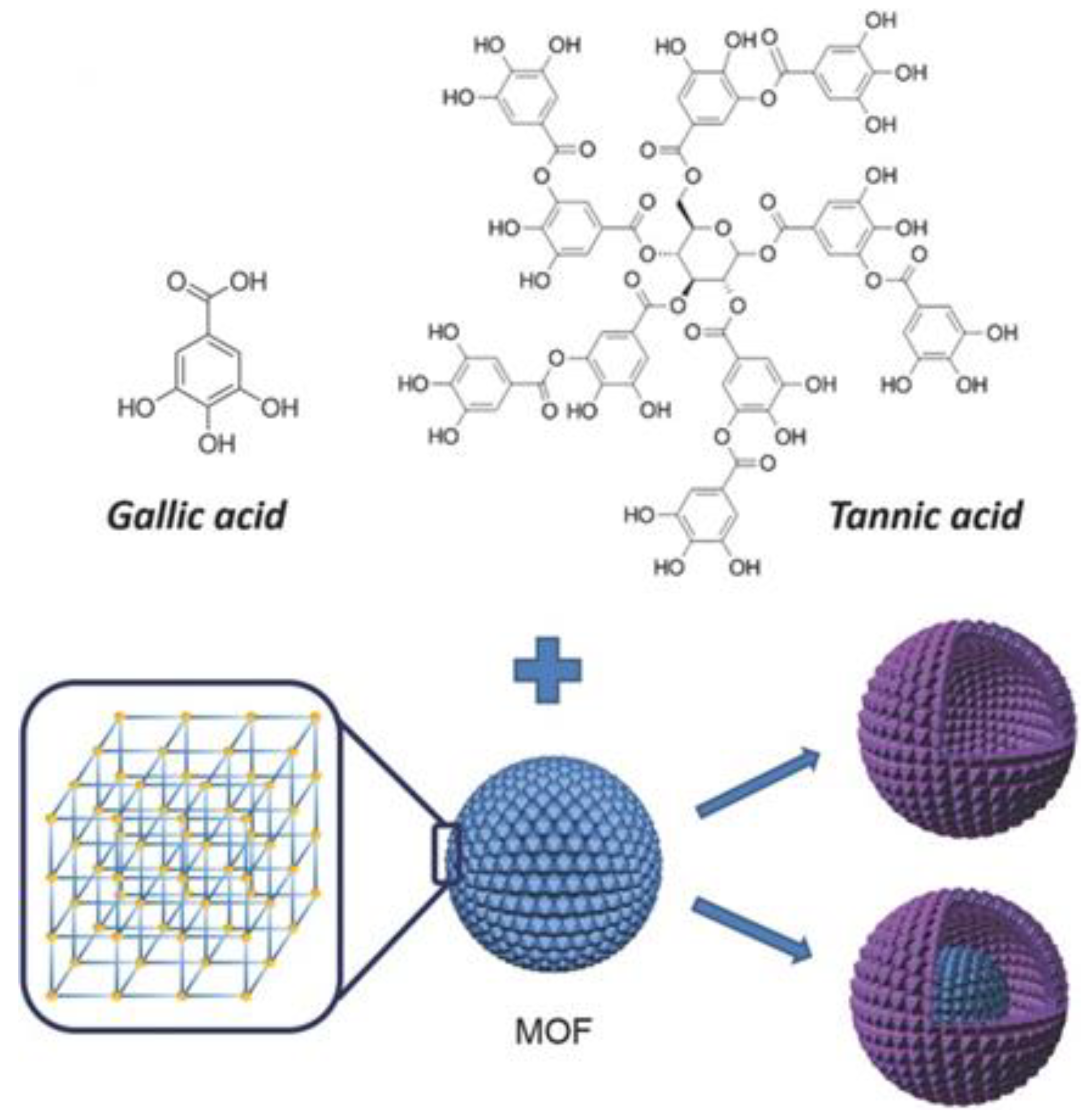
2.2.4. Partial-Etching Method
3. Applications
3.1. Electrochemical Sensing
3.2. Catalysis
3.3. Adsorption and Removal
3.4. Other Applications
4. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.L.; Eddaoudi, M.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Design and Synthesis of an Exceptionally Stable and Highly Porous Metal-Organic Framework. Nature 1999, 402, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Teo, W.L.; Binte Ariff, S.K.; Zhou, W.Q.; Jana, D.; Fiona Phua, S.Z. Solvent-and HF-Free Synthesis of Flexible Chromium-Based MIL-53 and MIL-88B. ChemNanoMat 2020, 6, 204–207. [Google Scholar]
- Celeste, A.; Paolone, A.; Itie, J.P.; Borondics, F.; Joseph, B.; Grad, O.; Blanita, G.; Zlotea, C.; Capitani, F. Mesoporous Metal-Organic Framework MIL-101 at High Pressure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15012–15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Santiago-Portillo, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Garcia, H. Engineering UiO-66 Metal Organic Framework for Heterogeneous Catalysis. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 899–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Cui, X.; Du, X.; Lu, X. UiO Series of Metal-Organic Frameworks Composites as Advanced Sorbents for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions: Synthesis, Applications and Adsorption Mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneff, J.I.; Butler, K.S.; Kotula, P.G.; Rue, B.E.; Sava Gallis, D.F. Expanding the ZIFs Repertoire for Biological Applications with the Targeted Synthesis of ZIF-20 Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 27295–27304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Yan, Z.; Mo, X.; Peng, X.; Chen, L. Morphology Control Synthesis of ZIF-8 as Highly Efficient Catalyst for the Cycloaddition of CO2 to Cyclic Carbonate. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 3212–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Huang, Y.; Huang, G.; Guan, Q.; Dong, Y.; Lu, J.; Yu, S.H.; Jiang, H.L. Integration of Pd Nanoparticles with Engineered Pore Walls in MOFs for Enhanced Catalysis. Chem 2021, 7, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, H.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Song, Y. Cu-Hemin Metal-Organic-Frameworks/Chitosan-Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites with Peroxidase-Like Bioactivity for Electrochemical Sensing. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ge, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Xuan, H.; Li, X. Adsorption of Cr(VI) on Nano Uio-66-NH2 MOFs in Water. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1937–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro, I.A.; Wells, C.J.R.; Forgan, R.S. Multivariate Modulation of the Zr MOF UiO-66 for Defect-Controlled Combination Anticancer Drug Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5211–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, X. Secondary-Component Incorporated Hollow MOFs and Derivatives for Catalytic and Energy-Related Applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1800743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Xu, J.; Low, Z.X.; Chen, C.; Jiang, H.; Chen, R. A Simple and Versatile Synthesis Strategy of Hollow MOFs for CO2 Separation and Catalysis. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 7944–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Zeng, H.C. A Shell-by-Shell Approach for Synthesis of Mesoporous Multi-Shelled Hollow MOFs for Catalytic Applications. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2020, 37, 2000101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.X.; Huang, J.J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, S.J.; Sun, X.M.; Zhang, W.N.; Liu, J.F.; Huo, F.W. Multi-Shelled Hollow Metal–Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5512–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosler, C.; Aijaz, A.; Turner, S.; Filippousi, M.; Shahabi, A.; Xia, W.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Muhler, M.; Fischer, R.A. Hollow Zn/Co Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework (ZIF) and Yolk-Shell Metal@Zn/Co ZIF Nanostructures. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 3304–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Mao, Y.; Shi, S.; Wan, M.; Ma, C.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, N. Fabrication of Magnetic Pd/MOF Hollow Nanospheres with Double-Shell Structure: Toward Highly Efficient and Recyclable Nanocatalysts for Hydrogenation Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 32251–32260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Liang, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Wang, C. Tailored Synthesis of Hollow MOF/Polydopamine Janus Nanoparticles for Synergistic Multi-Drug Chemo-Photothermal Therapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Zeng, Y.J. Ferrocenyl Metal-Organic Framework Hollow Microspheres for In Situ Loading Palladium Nanoparticles as A Heterogeneous Catalyst. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 8995–9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, P.; Cao, S.; Guo, X.; Ding, J.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, M.; Pang, H. Polypyrrole Coated Hollow Metal–Organic Framework Composites for Lithium–Sulfur Batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 19465–19470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Lo, W.S.; Huang, Y.D.; Si, X.; Liao, F.S.; Lin, S.W.; Williams, B.P.; Sun, T.Q.; Lin, H.W.; An, Y.; et al. Probing Interactions between Metal-Organic Frameworks and Freestanding Enzymes in a Hollow Structure. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 6630–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.J.; Wiese, M.; Schonberger, A.A.; Wessling, M. Catalytically Active Hollow Fiber Membranes with Enzyme-Embedded Metal-Organic Framework Coating. Angew. Chem. 2020, 59, 16047–16053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, W.; Xia, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, G. Hydrothermally Reduced Graphene Oxide Interfaces for Synthesizing High-Performance Metal-Organic Framework Hollow Fiber Membranes. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1800032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Wan, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, S.; Fan, S.; Dong, M.; Ye, Z.; Peng, X. Carbon Nanotubes Decorated Hollow Metal–Organic Frameworks for Efficient Solar-Driven Atmospheric Water Harvesting. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.; Du, M.; Shen, B.; Ji, J.; Dong, C.; Xing, M.; Zhang, J. Hollow Fe3O4/Carbon with Surface Mesopores Derived from MOFs for Enhanced Lithium Storage Performance. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Qi, S.; Chen, Y.; Yin, M.; Zhang, L.; Ge, K.; Wei, X.; Tian, X.; Wang, P.; Li, M.; et al. Hierarchical Mesoporous Hollow Ce-MOF Nanosphere as Oxidase Mimic for Highly Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of Ascorbic Acid. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 777, 138749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Lv, N.; Li, D.; Li, H.; Xue, X.; Jiang, W.; Xu, Z.; Che, G. Construction of MOF-Shell Porous Materials and Performance Studies in the Selective Adsorption and Separation of Benzene Pollutants. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 9076–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ni, X.; Ye, S.; Gu, Z.G.; Li, Y.; Ngai, T. A Smart Route for Encapsulating Pd Nanoparticles into a ZIF-8 Hollow Microsphere and their Superior Catalytic Properties. Langmuir 2020, 36, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasapriyan, V. Nanoparticles Sandwiched in Hollow Amorphous Metal–Organic Frameworks with Enhanced Diffusion for Highly selective Benzene Oxidation. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.H.; Tang, Y.; Chou, L.Y.; Sneed, B.T.; Brodsky, C.N.; Zhao, Z.; Tsung, C.K. Yolk-Shell Nanocrystal@ZIF-8 Nanostructures for Gas-Phase Heterogeneous Catalysis with Selectivity Control. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14345–14348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, G.; Fan, L.; Zhou, S.; Yang, X. Fabrication of Integrated Cu2O@HKUST-1@Au Nanocatalysts via Galvanic Replacements toward Alcohols Oxidation Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 35234–35243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.L.; Huang, Z.Q.; Mao, J.; Chen, W.J.; Wang, B.; Yang, F.W.; Liu, S.H.; Zhang, H.J.; Qiu, L.P.; Chen, J.H. A Facile Synthesis of Uniform Hollow MIL-125 Titanium-Based Nanoplatform for Endosomal Esacpe and Intracellular Drug Delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhou, L.; Ma, L.; He, Y.; Zheng, X.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, Y. MOF-Based Nanotubes to Hollow Nanospheres through Protein-Induced Soft-Templating Pathways. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.C.; Zeng, H.C. Self-Templating Synthesis of Hollow Spheres of MOFs and their Derived Nanostructures. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11591–11594. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Dai, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Lei, J. A Surfactant Template-Assisted Strategy for Synthesis of ZIF-8 Hollow Nanospheres. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhou, L.; He, Y.; Ma, L.; Liu, G.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, Y. Compartmentalization of Biocatalysts by Immobilizing Bienzyme in Hollow ZIF-8 for Colorimetric Detection of Glucose and Phenol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 59, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Choi, S.; Lee, H.J.; Oh, M. Hollow Metal–Organic Framework Microparticles Assembled via a Self-Templated Formation Mechanism. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 5169–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chu, D.; Yan, L.; Lai, H.; Chu, X.Q.; Ge, D.; Chen, X. Enhanced Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing Based on Porous ZIF-67 Hollow Nanoprisms. N. J. Chem. 2021, 45, 10031–10039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Lan, M.; Wang, Z.; Wan, H.; Li, G.; Zhu, J.; Tang, B.; Liu, H. Effectively Facilitating the Proton Conduction of Proton Exchange Membrane by Polydopamine Modified Hollow Metal−Organic Framework. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 644, 120098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Wang, L.; Irran, E.; Yu, H.; Gao, J.; Fan, D.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Ding, W.; Amin, A.M.; et al. Hollow Ferrocenyl Coordination Polymer Microspheres with Micropores in Shells Prepared by Ostwald Ripening. Angew. Chem. 2010, 49, 9237–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Heterobimetallic Metal–Organic Framework Nanocages as Highly Efficient Catalysts for CO2 Conversion under Mild Conditions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 2964–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
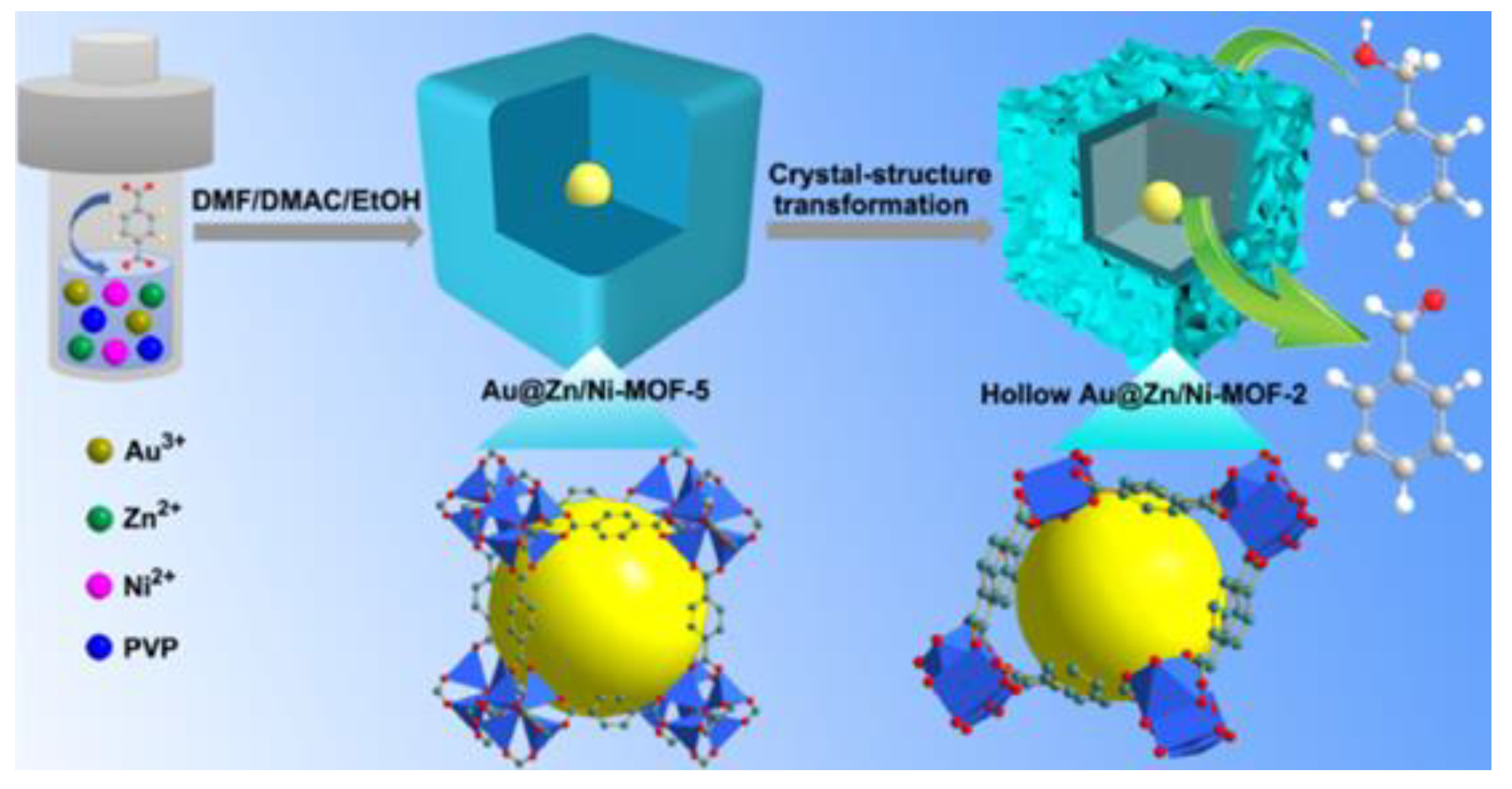
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Nosheen, F.; Saleem, F.; He, W.; Wang, X. Hierarchical Zn/Ni-MOF-2 Nanosheet-Assembled Hollow Nanocubes for Multicomponent Catalytic Reactions. Angew. Chem. 2014, 53, 12517–12521. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, G.; He, W.; Wang, X. Well-Defined Metal-Organic Framework Hollow Nanocages. Angew. Chem. 2014, 53, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Han, A.; Liu, W.; Xu, H.; Liu, J. Hollow Mesoporous Metal–Organic Frameworks with Enhanced Diffusion for Highly Efficient Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 5973–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Ju, Y.; Liang, K.; Suma, T.; Cui, J.; Caruso, F. Void Engineering in Metal–Organic Frameworks via Synergistic Etching and Surface Functionalization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 5827–5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, H.; Yang, Y.; Feng, S.; Zeng, M.; Li, Q.; Xu, D. Shape-Defined Hollow Structural Co-MOF-74 and Metal Nanoparticles@Co-MOF-74 Composite through a Transformation Strategy for Enhanced Photocatalysis Performance. Small 2019, 15, 1902287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Han, B.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, B.; Shi, J.; Yang, G. Hollow Metal-Organic Framework Polyhedra Synthesized by A CO2-Ionic Liquid Interfacial Templating Route. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 416, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carne-Sanchez, A.; Imaz, I.; Cano-Sarabia, M.; Maspoch, D. A Spray-Drying Strategy for Synthesis of Nanoscale Metal-Organic Frameworks and their Assembly into Hollow Superstructures. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carson, C.G.; Hardcastle, K.; Schwartz, J.; Liu, X.; Hoffmann, C.; Gerhardt, R.A.; Tannenbaum, R. Synthesis and Structure Characterization of Copper Terephthalate Metal–Organic Frameworks. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 2338–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.Y.; Ricco, R.; Liang, K.; Ludwig, J.; Kim, J.O.; Falcaro, P.; Kim, D.P. Bioactive MIL-88A Framework Hollow Spheres via Interfacial Reaction In-Droplet Microfluidics for Enzyme and Nanoparticle Encapsulation. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 7903–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surble, S.; Serre, C.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Millange, F.; Ferey, G. A New Isoreticular Class of Metal-Organic-Frameworks with the MIL-88 Topology. Chem. Commun. 2006, 3, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.L.; Eddaoudi, M.; Hyde, S.T.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Interwoven Metal-Organic Framework on a Periodic Minimal Surface with Extra-Large Pores. Science 2001, 291, 1021–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nathaniel, J.K.; Rosi, L.; Eddaoudi, M.; Chen, B.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Rod Packings and Metal-Organic Frameworks Constructed from Rod-Shaped Secondary Building Units. J. Am Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1504–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Cavka, J.H.; Jakobsen, S.; Olsbye, U.; Guillou, N.; Lamberti, C.; Bordiga, S.; Lillerud, K.P. A New Zirconium Inorganic Building Brick Forming Metal Organic Frameworks with Exceptional Stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13850–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Yan, H.; Chen, Y.Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Lu, J.; Jiang, H.L.; et al. Hollow Metal-Organic Framework Nanospheres via Emulsion-Based Interfacial Synthesis and their Application in Size-Selective Catalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18163–18171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Kong, R.M.; Xia, L.; Qu, F. Metal-Organic Framework as A Multi-Component Sensor for Detection of Fe3+ Ascorbic Acid and Acid Phosphatase. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wen, D. Sensing Nanomaterials of Wearable Glucose Sensors. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.K.; Ye, H.L.; Zhao, X.X.; Sun, L.X.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Han, Z.Y.; Yuan, R.; He, H. Artful Union of a Zirconium-Porphyrin MOF/GO Composite for Fabricating an Aptamer-based Electrochemical Sensor with Superb Detecting Performance. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2851–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Yao, Y.; Liu, Y. Construction of a Voltammetric Sensor Based on MIL-101 Hollow Cages for Electrocatalytic Oxidation and Sensitive Determination of Nitrofurazone. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 848, 113287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
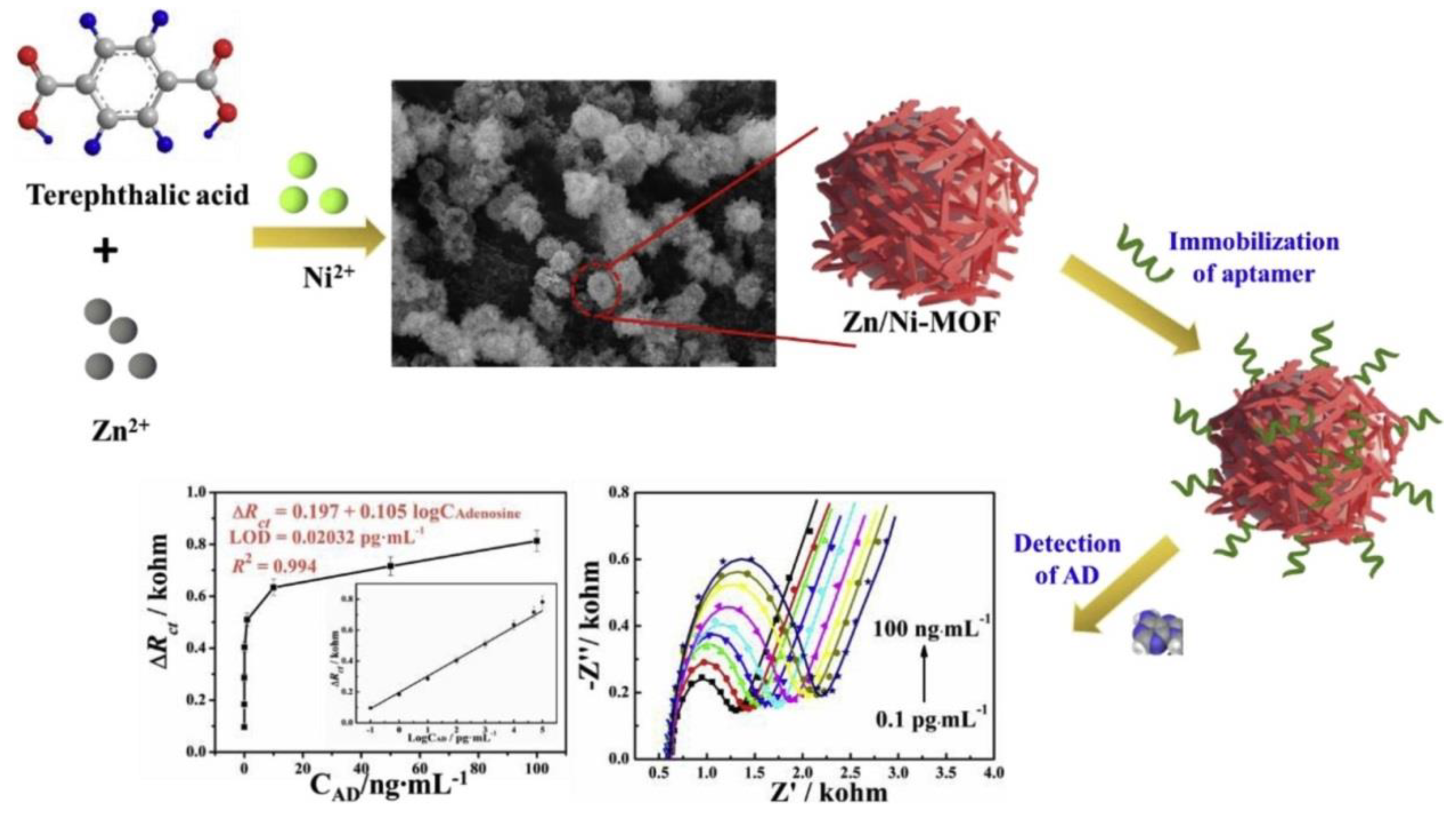
- Tian, K.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, C.; He, L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Du, M. Hierarchically Structured Hollow Bimetallic ZnNi MOF Microspheres as A Sensing Platform for Adenosine Detection. Sens. Actuators B 2020, 303, 127199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
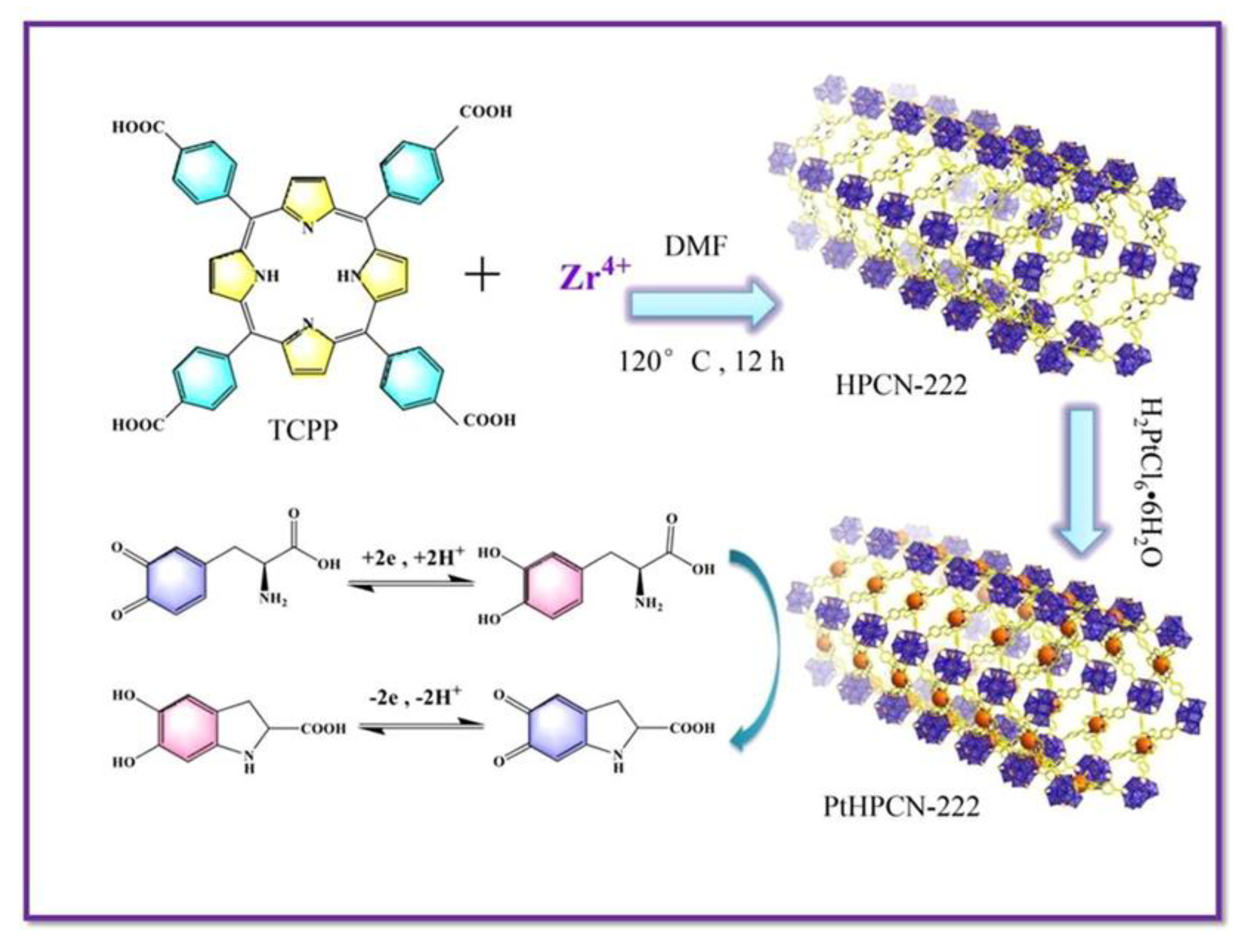
- Liu, L.; Li, F.; Liu, T.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M. Porphyrin Zirconium-Based MOF Dispersed Single Pt Atom for Electrocatalytic Sensing Levodopa. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 921, 116701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, Y.; Wu, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Hollow Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Nanospheres as Highly Efficient Cooperative Catalysts for [3+3] Cycloaddition Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13963–13966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, X.; Wan, Q.; Han, B.; Zhang, J. Improved Catalytic Performance of Co-MOF-74 by Nanostructure Construction. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5995–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Ding, S.; Chen, C. Step by Step Construction of Multifunctional Hollow Double Shell MNPs@MOF as a Powerful Tandem/Cascade Catalyst. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 738736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Wang, P.; Lu, R.; Feng, S.; Yuan, G.; Wang, C. Design and Synthesis of Hollow Ce/Zr-UiO-66 Nanoreactors for Synergistic and Efficient Catalysis. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 312, 123306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Pan, A.; Yuan, J.; Ke, F.; Wu, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J. One-Step Construction of a Hollow Au@Bimetal-Organic Framework Core-Shell Catalytic Nanoreactor for Selective Alcohol Oxidation Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 12463–12471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.C.M. Well-Arranged and Confined Incorporation of PdCo Nanoparticles within a Hollow and Porous Metal-Organic Framework for Superior Catalytic Activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 58, 866–871. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Qin, P.; Han, L.; Zhu, W.; Duan, S.; Lu, M.; Cai, Z. Facile Preparation of Nano-g-C3N4/UiO-66-NH2 Composite as Sorbent for High-efficient Extraction and Preconcentration of Food Colorants Prior to HPLC Analysis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Song, D.; Li, R.; Liu, P.; Wang, J. Diaminomaleonitrile Functionalized Double-Shelled Hollow MIL-101 (Cr) for Selective Removal of Uranium from Simulated Seawater. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Q.T.N.; Cho, K. Caesium Adsorption on a Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework (ZIF-8) Functionalized by Ferrocyanide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 581, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
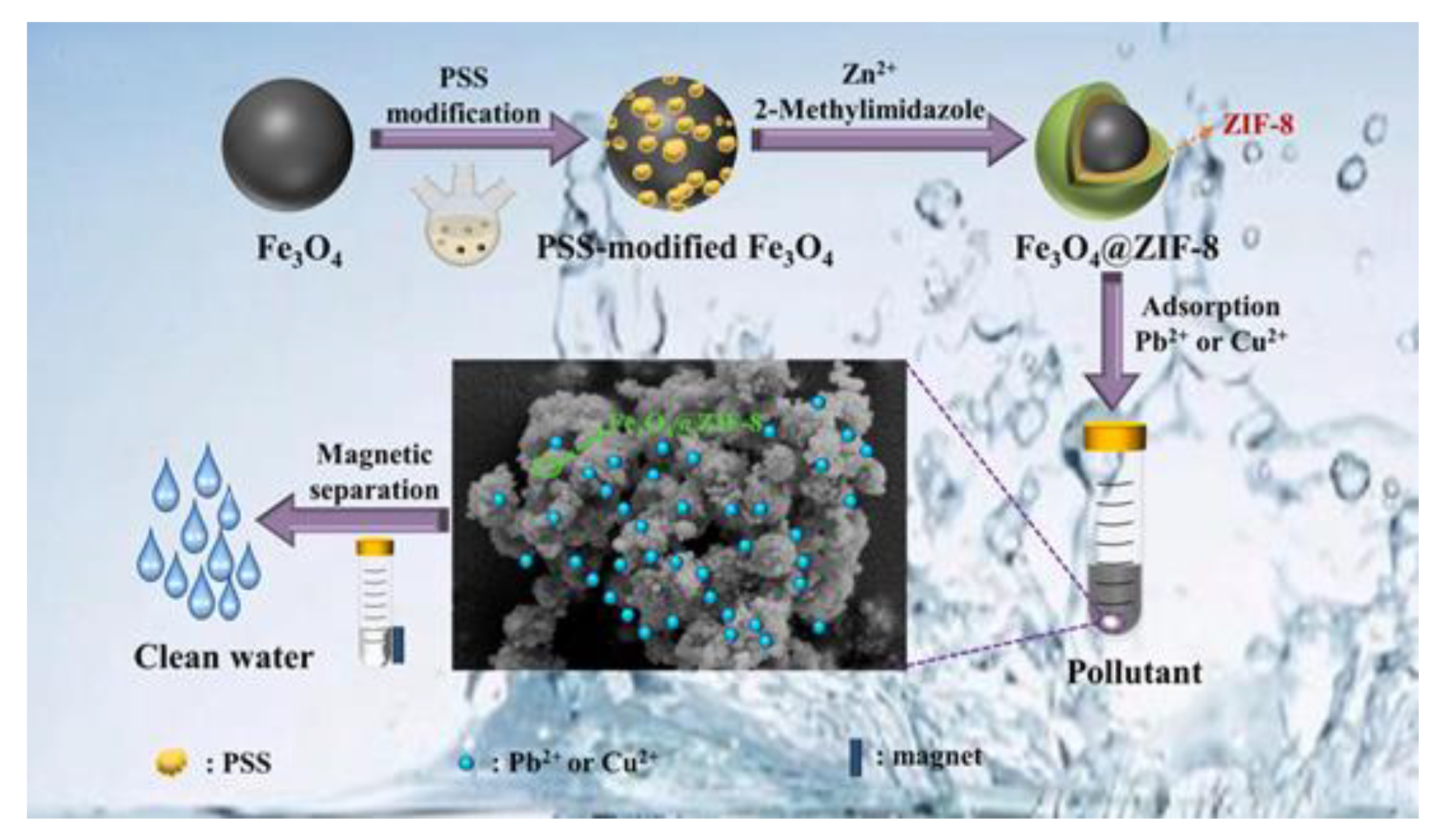
- Jiang, X.; Su, S.; Rao, J.; Li, S.; Lei, T.; Bai, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, X. Magnetic Metal-Organic Framework (Fe3O4@ZIF-8) Core-Shell Composite for the Efficient Removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II) from Water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, A.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, G.; Mao, J.; Meng, Q. Polyphenol Etched ZIF-8 Modified Graphene Oxide Nanofiltration Membrane for Efficient Removal of Salts and Organic Molecules. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetya, N.; Li, K. MOF-808 and its Hollow Fibre Adsorbents for Efficient Diclofenac Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Du, X.; Lu, X. Hollow Co-MOF-74 Incorporated Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes with Hierarchical Structures for Enhanced Removal of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Drain-Type Adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 449, 137759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Cai, Y.; Cao, S.; Li, S.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, S.; Feng, X.; Cao, A.; et al. Facile Fabrication of Multifunctional Metal-Organic Framework Hollow Tubes To Trap Pollutants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16482–16485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.C.; Cui, R.X.; Song, L.J.; Liu, Z.L. Hollow Structural Metal–Organic Frameworks Exhibit High Drug Loading Capacity, Targeted Delivery and Magnetic Resonance/Optical Multimodal Imaging. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 17291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Dong, R.; Zhang, J.; Tang, H.; Li, Q.; Shao, H.; Jiang, X. Nanoscale Metal-Organic Frameworks That are Both Fluorescent and Hollow for Self-Indicating Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 18554–18562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.J.; He, B.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Peng, C.; Wang, Y.; Su, Z.; Hao, Q. Hollow Porous Nanocuboids Cobalt-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks with Coordination Defects as Anode for Enhanced Lithium Storage. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 17178–17190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Tao, K.; Liu, R.; Han, L. Hollow and Hierarchical Cobalt–Metal Organic Framework@CoCr2O4Microplate Array as a Battery-Type Electrode for High-Performance Hybrid Supercapacitors. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhou, C.; Liu, H.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, X.; Han, X.; Zhu, F.; Lu, Y.; Cao, X.; Gu, H. In Situ Simultaneous Cavitation-Doping Approach for Constructing Bimetallic Metal-Organic Framework Hollow Nanospheres with Enhanced Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 61, 5977–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhong, L.; Wang, X.; Chai, L.; Li, Q.; Li, T.T.; Hu, Y.; Qian, J.; Huang, S. Thermal Conversion of Hollow Nickel-Organic Framework into Bimetallic FeNi3 Alloy Embedded in Carbon Materials as Efficient or Electrocatalyst. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 354, 136716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chai, L.; Ding, J.; Zhong, L.; Du, Y.; Li, T.T.; Hu, Y.; Qian, J.; Huang, S. Chemical and Norphological Transformation of MOF-Derived Bimetallic Phosphide for Efficient Oxygen Evolution. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Huang, Q.; Xue, J.; Yang, Y.; Mao, L.; Huang, S.; Qian, J. Morphologically Controlled Metal-Organic Framework-Derived FeNi Oxides for Efficient Water Oxidation. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 61, 8909–8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Ding, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, T.T.; Hu, Y.; Qian, J.; Huang, S. Differentiated Oxygen Evolution Behavior in MOF-Derived Oxide Nanomaterials Induced by Phase Transition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 55454–55462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Abbreviation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| AD | Adenosine |
| ARS | Alizarin red S |
| CMC | Critical micelle concentration |
| CNT | Carbon nanotube |
| CnTAB | Alkyltrimethylammonium bromide |
| DAMN | Diaminomaleonitrile |
| DMAC | Dimethylacetamide |
| DMF | N,N–Dimethylformamide |
| GA | Gallic acid |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| LDH | Layered double hydroxide |
| MIL | Materials of Institute Lavoisier |
| MO | Methyl orange |
| MOFs | Metal–organic frameworks |
| NaDC | Metal–sodium deoxycholate |
| NFZ | Nitrofuranone |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| PAHs | Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| TA | Tannic acid |
| TOF | Turn over frequency |
| UIO | University of Oslo |
| ZIF | Zeolitic imidazolate framework |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zha, X.; Zhao, X.; Webb, E.; Khan, S.U.; Wang, Y. Beyond Pristine Metal–Organic Frameworks: Preparation of Hollow MOFs and Their Composites for Catalysis, Sensing, and Adsorption Removal Applications. Molecules 2023, 28, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010144
Zha X, Zhao X, Webb E, Khan SU, Wang Y. Beyond Pristine Metal–Organic Frameworks: Preparation of Hollow MOFs and Their Composites for Catalysis, Sensing, and Adsorption Removal Applications. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010144
Chicago/Turabian StyleZha, Xiaoqian, Xianhui Zhao, Erin Webb, Shifa Ullah Khan, and Yang Wang. 2023. "Beyond Pristine Metal–Organic Frameworks: Preparation of Hollow MOFs and Their Composites for Catalysis, Sensing, and Adsorption Removal Applications" Molecules 28, no. 1: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010144
APA StyleZha, X., Zhao, X., Webb, E., Khan, S. U., & Wang, Y. (2023). Beyond Pristine Metal–Organic Frameworks: Preparation of Hollow MOFs and Their Composites for Catalysis, Sensing, and Adsorption Removal Applications. Molecules, 28(1), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010144








