Discovery of Hepatotoxic Equivalent Markers and Mechanism of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. by Metabolomics Coupled with Molecular Docking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
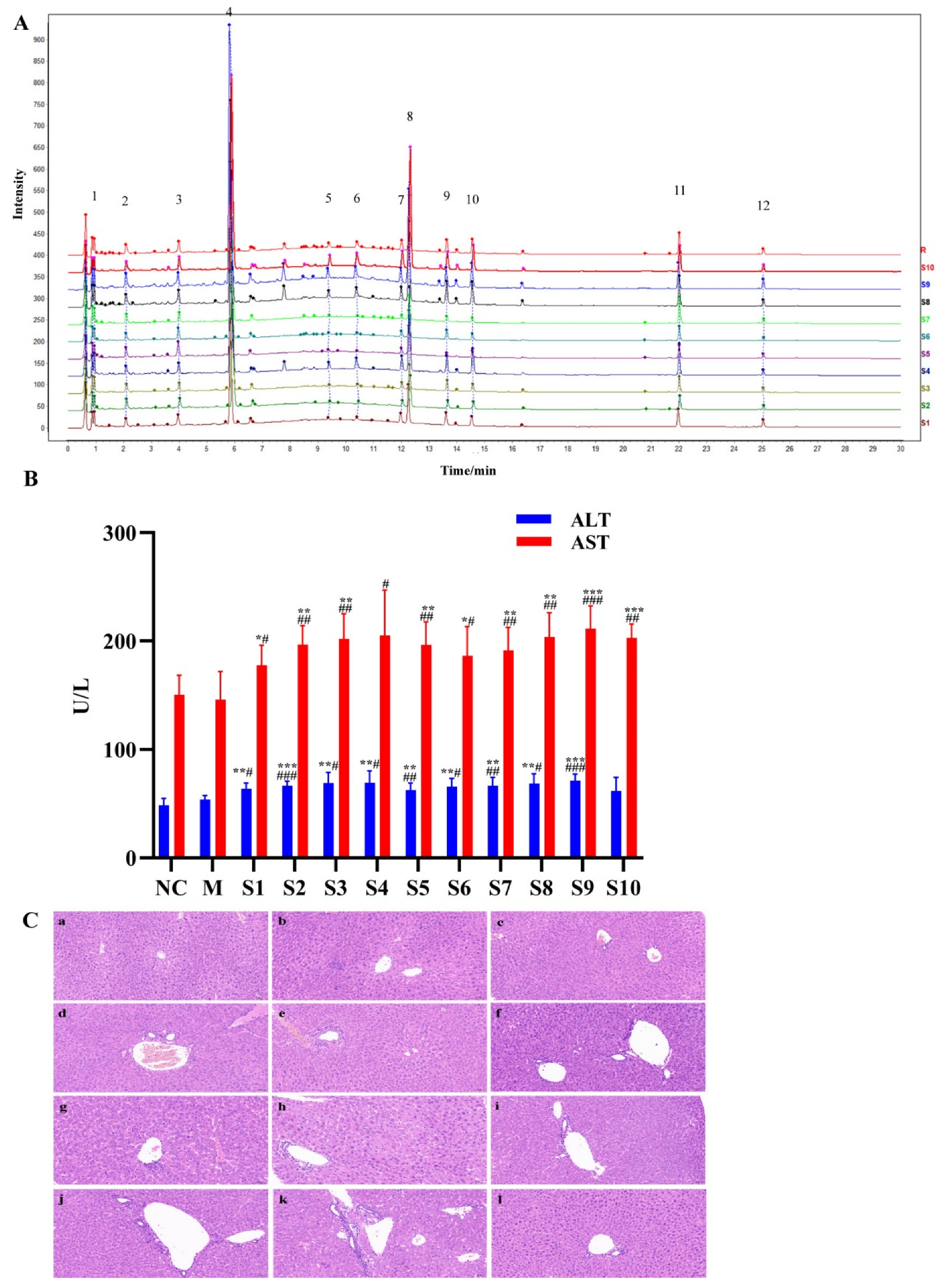
2.1. Fingerprint Analysis of PMT Extracts
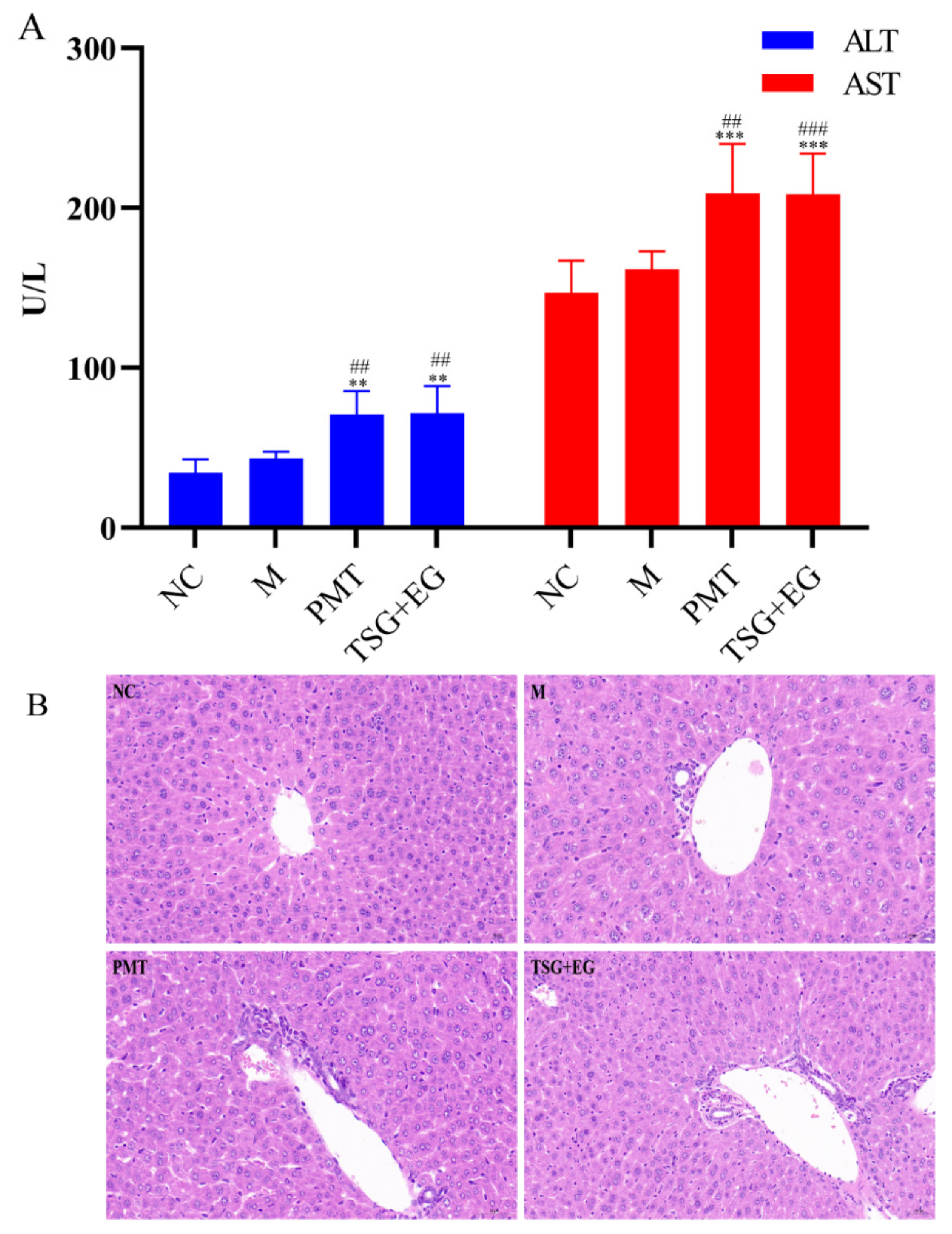
2.2. Hepatotoxicity of PMT Extracts
2.3. Discovery of Hepatotoxic Markers
2.4. Assessment of Hepatotoxic Equivalence between Candidate HEMs and Original PMT Extracts
2.5. Liver Metabolomics Analysis
2.5.1. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
2.5.2. Identification of Potential Metabolite of PMT
2.5.3. Pathway Analysis
2.6. “Metabolite−Target−Pathway” Interactive Network Analysis
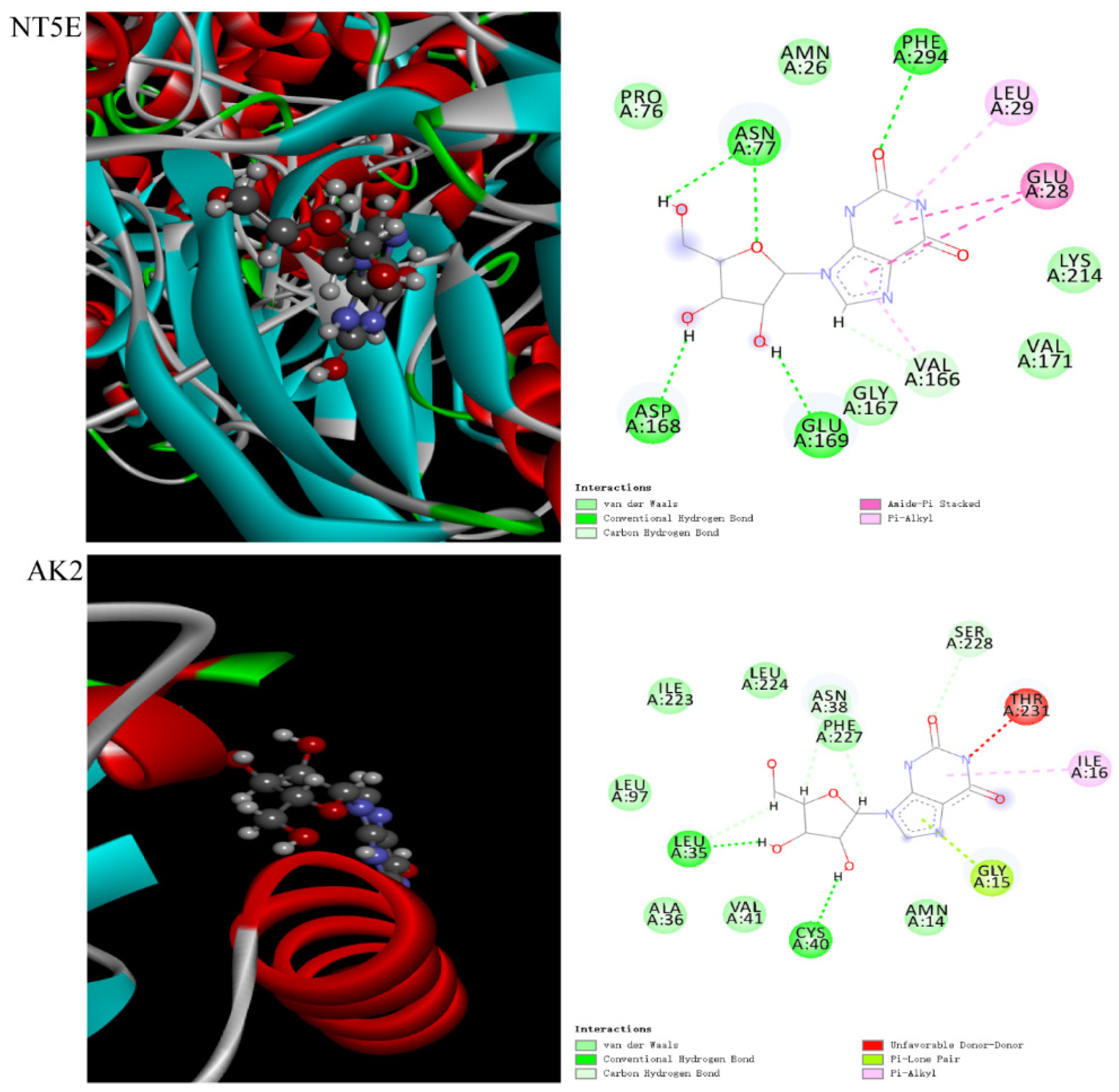
2.7. Molecular Docking
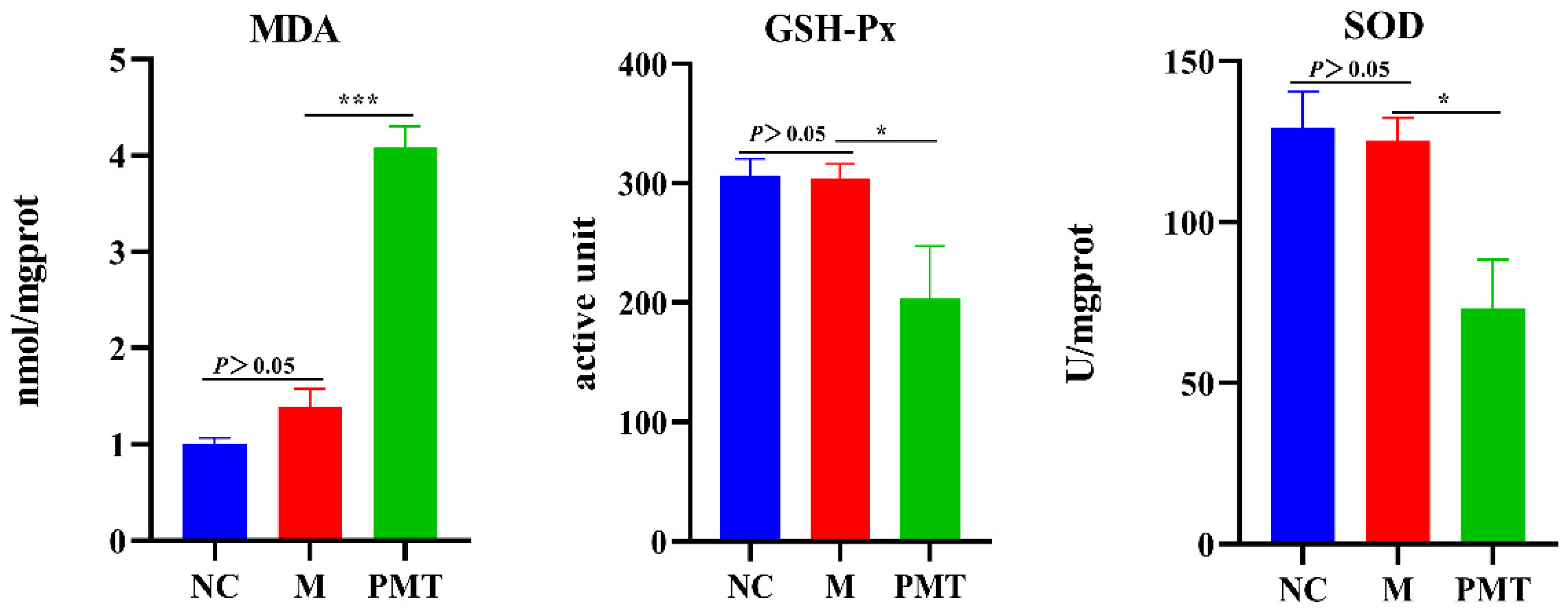
2.8. PMT Induced Oxidation Damage
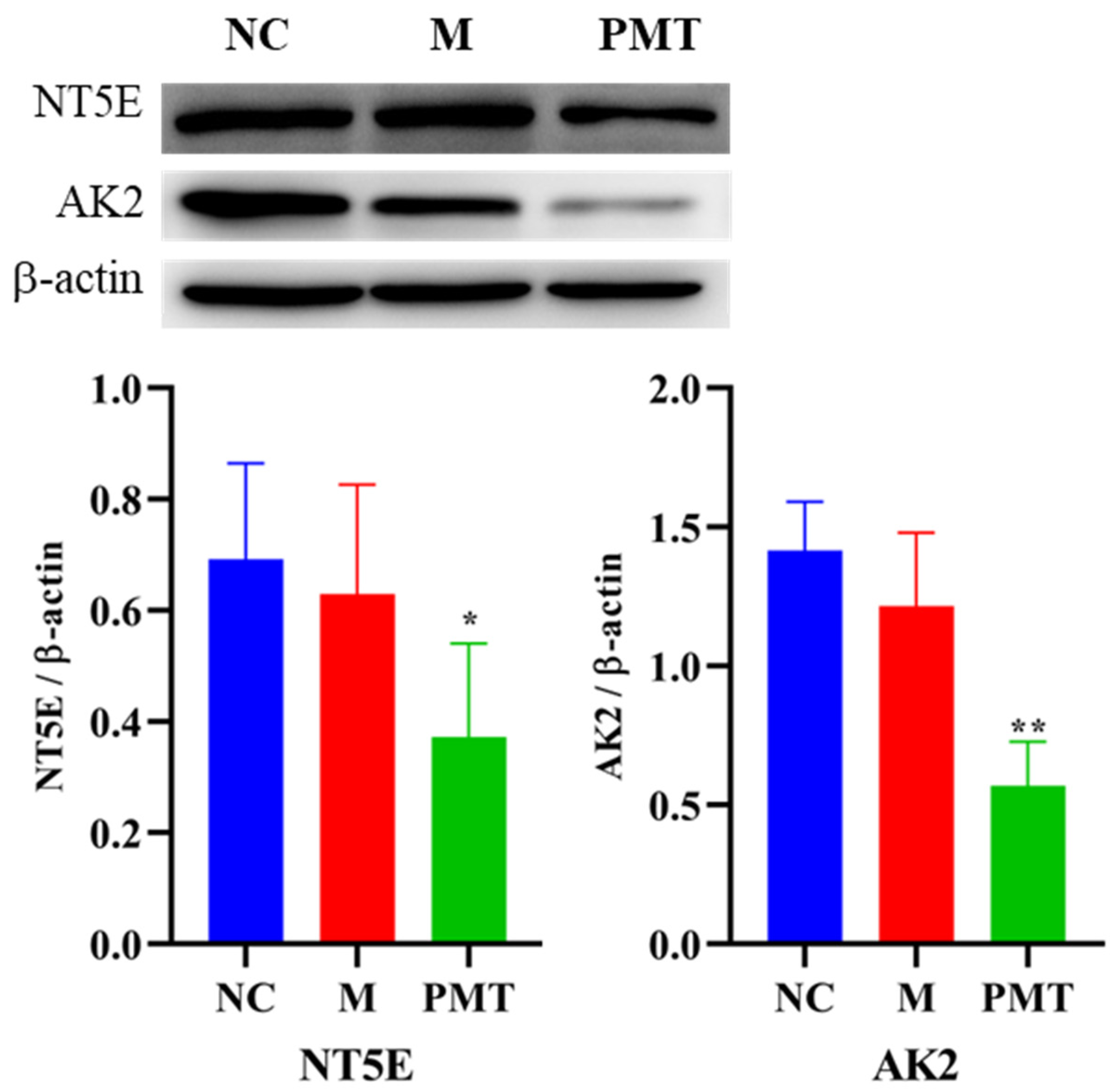
2.9. Western Blot Validation
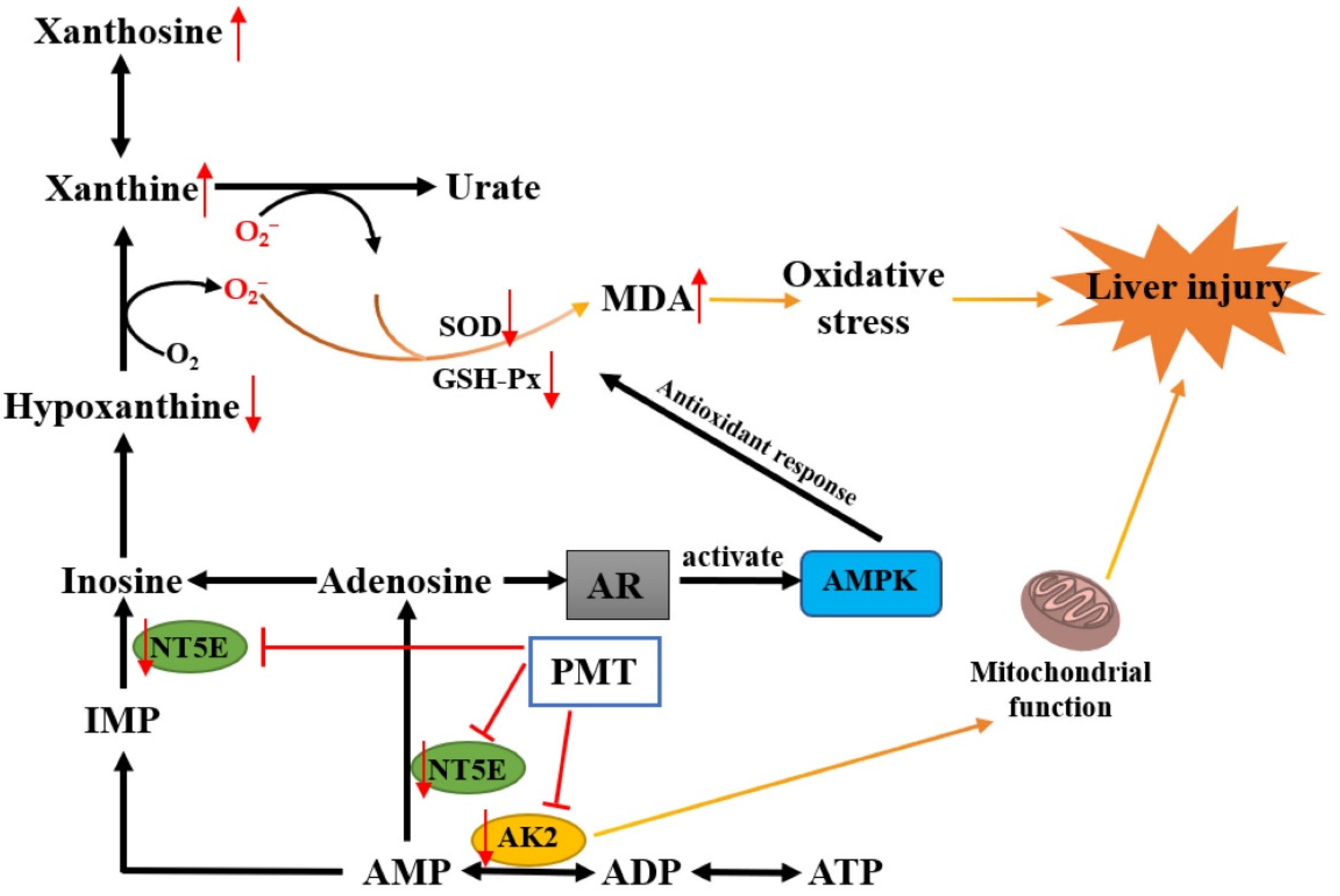
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Preparation of PMT Extracts
4.3. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Conditions
4.4. Animal Experiments
4.5. Hepatotoxicity Analysis of PMT Extracts
4.6. Establishing of UPLC Fingerprint
4.7. Quantitative Analysis of the Major Biomarkers
4.8. Hepatotoxicity Evaluation between Candidate HEMs and PMT Extracts
4.9. Hepatotoxic Mechanism of PMT Based on Liver Metabolomics
4.9.1. Preparation of Liver Samples for Metabolomics Analysis
4.9.2. Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry
4.9.3. Data Extraction and Analysis
4.10. Construction of an Integrated Network
4.11. Molecular Docking
4.12. Detection of Oxidative Stress
4.13. Western Blot
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, W.; Ma, S.; Li, S. Polygonum multiflorum Thunb.: A Review on Chemical Analysis, Processing Mechanism, Quality Evaluation, and Hepatotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, S.H.; Wang, J.B.; Song, H.B.; Li, Y.G.; He, T.T.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.X.; Wang, L.P.; Zhou, K.; et al. Clinical Analysis of Drug-induced Liver Injury Caused by Polygonum multiflorum and its Preparations. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2015, 35, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Saxena, R.; Wee, A.; Yang, R.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Jia, J. Clinicopathological features of He Shou Wu-induced liver injury: This ancient anti-aging therapy is not liver-friendly. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Chen, J.; Ren, J.; Li, Y.; Zhai, J.; Mu, W.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, W.; Tian, G.; Shang, H. Liver Damage Associated with Polygonum multiflorum Thunb.: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 459749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Z.; Niu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Song, J.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; et al. Evidence chain-based causality identification in herb-induced liver injury: Exemplification of a well-known liver-restorative herb Polygonum multiflorum. Front. Med. 2015, 9, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.K.; Li, C.Y.; Li, R.Y.; He, L.Z.; Cui, H.R.; Yin, P.; Zhang, C.E.; Li, P.Y.; Sang, X.X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Cis-stilbene glucoside in Polygonum multiflorum induces immunological idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity in LPS-treated rats by suppressing PPAR-γ. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Li, X.F.; Tu, C.; Li, N.; Ma, Z.J.; Pang, J.Y.; Jia, G.L.; Cui, H.R.; You, Y.; Song, H.B.; et al. The idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity of Polygonum multiflorum based on endotoxin model. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2015, 50, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Niu, M.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, R.; Tu, C.; Li, H.; Jing, J.; Meng, Y.; et al. Screening for main components associated with the idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity of a tonic herb, Polygonum multiflorum. Front. Med. 2017, 11, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xiao, R.; Xia, B.H.; Zhang, Z.M.; Li, C.; Wu, P.; Liao, D.F.; Lin, L.M. Investigation of the idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. through metabolomics using GC-MS. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.H.; Yuan, Y.Y.; Liu, M. The assessment of the chronic hepatotoxicity induced by Polygoni Multiflori Radix in rats: A pilot study by using untargeted metabolomics method. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 203, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wang, J.; Xiao, X. Comparative study on preparation of polygoni multiflori radix based on hapatotoxic bioassay. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2015, 40, 2325–2329. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, D.; Fei, Z.; Wnag, Z.; Zhou, M.; Li, K.; Sun, Z. Hepatotoxicity of short time oral administration of aqueous extract of polygoni multflori radix in rats. Chin. J. Pharmacovigil. 2017, 14, 321–325. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. Study on hepatotoxicity of aqueous extract of Polygonum multiflorum in rats after 28-day oral administration-analysis on correlation of cholestasis. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012, 37, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Ni, B.; Lin, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Yin, X.; Qu, C.; Ni, J. Traditional usages, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb.: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 159, 158–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-L.; Huang, X.-J.; Li, M.-M.; Ou, G.-M.; Zhao, B.-X.; Chen, M.-F.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Wang, Y.; Ye, W.-C. Polygonflavanol A, a novel flavonostilbene glycoside from the roots of Polygonum multiflorum. Phytochem. Lett. 2012, 5, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xie, J.; Mao, X.-J.; Wang, M.-J.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Zhaori, G.-T.; Zhao, R.-H. Hepatoxicity of major constituents and extractions of Radix Polygoni Multiflori and Radix Polygoni Multiflori Praeparata. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-B.; Li, L.; Dai, Z.; Wu, Y.; Geng, X.-C.; Li, B.; Ma, S.-C.; Wang, A.-G.; Su, Y.-L. Polygonumnolides C1–C4; minor dianthrone glycosides from the roots of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 18, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Song, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.L. Influence of process methods on contents of chemical component Radix Polygoni Multiflori. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2005, 30, 336–340. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wei, F.; Ma, S. A stepwise strategy integrating metabolomics and pseudotargeted spectrum-effect relationship to elucidate the potential hepatotoxic components in Polygonum multiflorum. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 935336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, F.; Dou, Z.; Yang, W.; Hu, L.; Liu, C. Rapid Discovery of the Potential Toxic Compounds in Polygonum multiflorum by UHPLC/Q-Orbitrap-MS-Based Metabolomics and Correlation Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Du, T.; Dai, S.; Wei, F.; Chen, X.; Ma, S. Identification of intrinsic hepatotoxic compounds in Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. using machine-learning methods. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Lamers, R.J.; Korthout, H.A.; van Nesselrooij, J.H.; Witkamp, R.F.; van der Heijden, R.; Voshol, P.J.; Havekes, L.M.; Verpoorte, R.; van der Greef, J. Metabolomics in the context of systems biology: Bridging traditional Chinese medicine and molecular pharmacology. Phytother. Res. 2005, 19, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Pan, M.; Liu, L.; Zhu, M.; Fang, C.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, H. Mechanism of suxiao jiuxin pills against myocardial ischemia based on metabolomics. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 4719–4729. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, M.; Xiao, H. Metabolomic Responses of Human Hepatocytes to Emodin, Aristolochic Acid, and Triptolide: Chemicals Purified from Traditional Chinese Medicines. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2015, 29, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, M.; Diao, T.; Tang, J.; Dai, M.; Chen, S.; Lin, G. Metabonomics study on Polygonum multiflorum induced liver toxicity in rats by GC-MS. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 10986–10992. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xing, Y.; Liu, E.; Gao, X.; Wang, L.; Fu, Z. Biomarkers and Mechanism Analysis for Polygoni Multiflori Radix Preparata-Induced Liver Injury by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS-Based Metabolomics. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 7677392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-Y.; Gao, H.-Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, T.-Y.; Wang, S.-T.; Yang, J.-B.; Hao, R.-R.; Pang, F.; Wei, F.; Liu, Z.-G.; et al. Integrated spatially resolved metabolomics and network toxicology to investigate the hepatotoxicity mechanisms of component D of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.E.; Niu, M.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.L.; Ma, Z.J.; Xiong, Y.; Dong, X.P.; Li, R.Y.; Feng, W.W.; Dong, Q.; et al. Urine metabolomics study on the liver injury in rats induced by raw and processed Polygonum multiflorum integrated with pattern recognition and pathways analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Shi, N.; Han, X.; Li, G.; Wen, B.; Gao, J. UPLC/MS/MS-Based Metabolomics Study of the Hepatotoxicity and Nephrotoxicity in Rats Induced by Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 10489–10500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Li, N.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.E.; Feng, W.W.; Li, G.Q.; Li, R.Y.; Tu, C.; Han, X.; Bai, Z.F.; et al. Screening for biomarkers of liver injury induced by Polygonum multiflorum: A targeted metabolomic study. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Fang, C.; Pan, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Xian, Z.; Xiao, H. Assessing potential liver injury induced by Polygonum multiflorum using potential biomarkers via targeted sphingolipidomics. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1578–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Tu, C.; Gao, D.; Wang, R.L.; Zhang, H.Z.; Niu, M.; Li, R.Y.; Zhang, C.E.; Li, R.S.; Xiao, X.H.; et al. Metabolomic Study on Idiosyncratic Liver Injury Induced by Different Extracts of Polygonum multiflorum in Rats Integrated with Pattern Recognition and Enriched Pathways Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, W.; Müller-Hill, B. Isolation of the lac repressor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1966, 56, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, D.; Schlegel, H.G. Regulation of the pyruvate kinase from Alcaligenes eutrophus H 16 in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Microbiol. 1975, 105, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.X.; Li, X.; Snyder, M. Investigating metabolite-protein interactions: An overview of available techniques. Methods 2012, 57, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Scott, D.O. Structure-based drug metabolism predictions for drug design. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2010, 75, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, V.; Sethumadhavan, R. Drug resistance mechanism of PncA in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Biomol. Struct Dyn. 2014, 32, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, V. Structural analysis of oncogenic mutation of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 2276–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, B.; Al-Subaie, A.M.; Ahmad, F.; Surapaneni, K.M.; Alsamman, K. Effect of novel leukemia mutations (K75E & E222K) on interferon regulatory factor 1 and its interaction with DNA: Insights from molecular dynamics simulations and docking studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 5235–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Subaie, A.M.; Kamaraj, B. The Structural Effect of FLT3 Mutations at 835th Position and Their Interaction with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Inhibitors: In Silico Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.K.; Oakley, A.; Purohit, R. Mechanistic behavior and subtle key events during DNA clamp opening and closing in T4 bacteriophage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Bhardwaj, V.K.; Das, P.; Purohit, R. Identification of 11β-HSD1 inhibitors through enhanced sampling methods. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 5005–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, D.B.; Decornez, H.; Furr, J.R.; Bajorath, J. Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: Methods and applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.F.; Fernandes, P.A.; Ramos, M.J. Protein-ligand docking: Current status and future challenges. Proteins 2006, 65, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, D.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; Li, H. Discovery of Hepatotoxic Equivalent Combinatorial Markers from Dioscorea bulbifera tuber by Fingerprint-Toxicity Relationship Modeling. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurin, J.; Lindor, K.D.; Crippin, J.S.; Gossard, A.; Gores, G.J.; Ludwig, J.; Rakela, J.; McGill, D.B. Ursodeoxycholic acid or clofibrate in the treatment of non-alcohol-induced steatohepatitis: A pilot study. Hepatology 1996, 23, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbert-Bismut, F.; Ratziu, V.; Pieroni, L.; Charlotte, F.; Benhamou, Y.; Poynard, T. Biochemical markers of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C virus infection: A prospective study. Lancet 2001, 357, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Cao, H.; Guo, S.; Gu, L.; Hu, W.; Cheng, M.; Bai, D.; Chen, J.; Mao, C.; Li, L.; et al. UPLC fingerprint and muli-components content determination of different processed products of anglica sinensis. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2019, 44, 2499–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Lin, Y.; Lei, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Xia, B.; Li, C.; Liao, D.; Wu, P.; Lin, L. Analyzing crude/processed root of Polygonum multiflorum from different habitats by UPLC fingerprint and mode identification methods. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2017, 42, 2305–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, Y. Comparative study on differences of gardeniae fructus and its stir-baked prepared slices based on whole and partial fingerprint and multivariate statistical analysis. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2020, 51, 2460–2466. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Psychogios, N.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Lin, G.; Yu, Q.; Li, Q.; Mai, L.; Cheng, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, Y. Anti-Hyperuricemic and Nephroprotective Effects of Dihydroberberine in Potassium Oxonate- and Hypoxanthine-Induced Hyperuricemic Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 645879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Nakagome, I.; Hirono, S.; Itoh, T.; Fujiwara, R. Inhibition of adenosine deaminase (ADA)-mediated metabolism of cordycepin by natural substances. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharafshah, A.; Keshavarz, P.; Rezaei, S.; Farhadian, N. Association and in silico studies of ENPP1 gene variants with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Northern Iranian population. Gene 2018, 675, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; El-Gamal, M.I.; Zaib, S.; Anbar, H.S.; Zaraei, S.-O.; Sbenati, R.M.; Pelletier, J.; Sévigny, J.; Oh, C.-H.; Iqbal, J. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and docking studies of new pyrazole-based thiourea and sulfonamide derivatives as inhibitors of nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausekle, E.; Ejaz, S.A.; Khan, S.U.; Ehlers, P.; Villinger, A.; Lecka, J.; Sévigny, J.; Iqbal, J.; Langer, P. New one-pot synthesis of N-fused isoquinoline derivatives by palladium-catalyzed C-H arylation: Potent inhibitors of nucleotide pyrophosphatase-1 and -3. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 11402–11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, B.; Yelibayeva, N.; Ospanov, M.; Ejaz, S.A.; Afzal, S.; Khan, S.U.; Abilov, Z.A.; Turmukhanova, M.Z.; Kalugin, S.N.; Safarov, S.; et al. Synthesis of 2-arylated thiadiazolopyrimidones by Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling: A new class of nucleotide pyrophosphatase (NPPs) inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 107556–107571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snášel, J.; Nauš, P.; Dostál, J.; Hnízda, A.; Fanfrlík, J.; Brynda, J.; Bourderioux, A.; Dušek, M.; Dvořáková, H.; Stolaříková, J.; et al. Structural basis for inhibition of mycobacterial and human adenosine kinase by 7-substituted 7-(Het)aryl-7-deazaadenine ribonucleosides. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8268–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toti, K.S.; Osborne, D.; Ciancetta, A.; Boison, D.; Jacobson, K.A. South (S)- and North (N)-Methanocarba-7-Deazaadenosine Analogues as Inhibitors of Human Adenosine Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 6860–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, C.; Mozziconacci, O.; Zhu, R.; Xu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Chen, R.; Huang, Y.; Holzbeierlein, J.M.; Schöneich, C.; et al. Xanthine oxidase-mediated oxidative stress promotes cancer cell-specific apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 139, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marton, Z.; Guillon, R.; Krimm, I.; Preeti; Rahimova, R.; Egron, D.; Jordheim, L.P.; Aghajari, N.; Dumontet, C.; Périgaud, C.; et al. Identification of Noncompetitive Inhibitors of Cytosolic 5′-Nucleotidase II Using a Fragment-Based Approach. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9680–9696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, M.I. Molecular docking investigation of the amantadine binding to the enzymes upregulated or downregulated in Parkinson’s disease. Admet Dmpk 2020, 8, 149–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seffernick, J.L.; Dodge, A.G.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Bumpus, J.A.; Wackett, L.P. Bacterial ammeline metabolism via guanine deaminase. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Duan, L.; Guo, L.; Liu, K.; Liu, E.H.; Li, P. Characterization and classification of seven citrus herbs by liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and genetic algorithm optimized support vector machines. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1339, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Q.; Song, D.F.; Li, R.Q.; Yang, H.; Qi, L.W.; Xin, G.Z.; Wang, D.Q.; Song, H.P.; Chen, J.; Hao, H.; et al. Identification of effective combinatorial markers for quality standardization of herbal medicines. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1345, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y. Hepatotoxicity evaluation of eighteen components in polygoni multiflori radix with zebrafish(Danio rerio)model. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2018, 30, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Li, X.; Yin, P.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Li, F.; Xiao, X. Preliminary study on hepatotoxic components in polygoni multiflorum radix based on processing and toxicity-decreasing. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2017, 48, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, F.; Ye, R. New approach on similarity analysis of chromatographic fingerprint of herbal medicine. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1104, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Li, P.; Yang, H.; Gao, W.; Li, H.J. From chemical consistency to effective consistency in precise quality discrimination of Sophora flower-bud and Sophora flower: Discovering efficacy-associated markers by fingerprint-activity relationship modeling. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 132, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudthavorasit, S.; Wongravee, K.; Leepipatpiboon, N. Characteristic fingerprint based on gingerol derivative analysis for discrimination of ginger (Zingiber officinale) according to geographical origin using HPLC-DAD combined with chemometrics. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.J.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wu, M.Q.; Chen, P.; Wu, X.R.; Ma, X.P.; Guo, W.Y.; Yang, M.H. Combination of chemical fingerprint and bioactivity evaluation to explore the antibacterial components of Salvia miltiorrhizae. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.L.; Xie, M.; Yang, X.Y.; Song, Y.; Yan, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.Z.; Tian, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Spectrum-effect relationships as a systematic approach to traditional chinese medicine research: Current status and future perspectives. Molecules 2014, 19, 17897–17925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, X.; Ni, H.; Li, P.; Li, H.J. Discovery of quality control markers from traditional Chinese medicines by fingerprint-efficacy modeling: Current status and future perspectives. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 159, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lin, H.; Yin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Han, J.; Qu, C.; Ni, J. Characterization of the constituents in rat plasma after oral administration of radix polygoni multiflori extracts by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Jia, Z.; Chen, K.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Duan, F.; Xian, Z.; Wei, Z.; Chen, L.; Xiao, H. Studies on constituents of Polygonum multiflorum extract in vivo and in votro based on UPLC-1-TOF-MS. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2018, 43, 2796–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalis, V.; Symillides, M.; Macheras, P. Bioequivalence of highly variable drugs: A comparison of the newly proposed regulatory approaches by FDA and EMA. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantu-Medellin, N.; Kelley, E.E. Xanthine oxidoreductase-catalyzed reactive species generation: A process in critical need of reevaluation. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Fu, S.; Qu, C.; Li, H.; Ni, J. Inhibition of Mitochondrial Complex Function-The Hepatotoxicity Mechanism of Emodin Based on Quantitative Proteomic Analyses. Cells 2019, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yin, P.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Cui, H.; Ni, H.; Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Bo, Z. Study on the mechanism of PPAR-γ dependent immunological idiosyncrasy liver injury induced by Polygonum multiflorum. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2017, 52, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, K.; Zebisch, M.; Pippel, J.; El-Tayeb, A.; Müller, C.E.; Sträter, N. Crystal structure of the human ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73): Insights into the regulation of purinergic signaling. Structure 2012, 20, 2161–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, S.C.; Sévigny, J.; Zimmermann, H. The E-NTPDase family of ectonucleotidases: Structure function relationships and pathophysiological significance. Purinergic Signal. 2006, 2, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, V.; Lu, B.; Rajakumar, S.; Cowan, P.J.; Dwyer, K.M. The CD39-adenosinergic axis in the pathogenesis of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Purinergic Signal. 2013, 9, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Pacher, P.; Vizi, E.S.; Haskó, G. CD39 and CD73 in immunity and inflammation. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavis, P.A.; Stagg, J.; Darcy, P.K.; Smyth, M.J. CD73: A potent suppressor of antitumor immune responses. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcedo, K.P.; Rouse, M.A.; Jung, G.S.; Fu, D.; Minor, M.; Willcockson, H.H.; Greene, K.G.; Snider, N.T. CD73 Maintains Hepatocyte Metabolic Integrity and Mouse Liver Homeostasis in a Sex-Dependent Manner. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, S. Hepatocyte levels of CD73 contribute to Mallory-Denk body formation. Hepatology 2014, 60, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, N.T.; Griggs, N.W.; Singla, A.; Moons, D.S.; Weerasinghe, S.V.; Lok, A.S.; Ruan, C.; Burant, C.F.; Conjeevaram, H.S.; Omary, M.B. CD73 (ecto-5′-nucleotidase) hepatocyte levels differ across mouse strains and contribute to mallory-denk body formation. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1790–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredholm, B.B. Adenosine, an endogenous distress signal, modulates tissue damage and repair. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltzschig, H.K. Adenosine: An old drug newly discovered. Anesthesiology 2009, 111, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borea, P.A.; Gessi, S.; Merighi, S.; Vincenzi, F.; Varani, K. Pharmacology of Adenosine Receptors: The State of the Art. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1591–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinovitch, R.C.; Samborska, B.; Faubert, B.; Ma, E.H.; Gravel, S.-P.; Andrzejewski, S.; Raissi, T.C.; Pause, A.; St.-Pierre, J.; Jones, R.G. AMPK Maintains Cellular Metabolic Homeostasis through Regulation of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzeja, P.; Terzic, A. Adenylate kinase and AMP signaling networks: Metabolic monitoring, signal communication and body energy sensing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 1729–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzeja, P.P.; Terzic, A. Phosphotransfer networks and cellular energetics. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzeja, P.P.; Chung, S.; Faustino, R.S.; Behfar, A.; Terzic, A. Developmental enhancement of adenylate kinase-AMPK metabolic signaling axis supports stem cell cardiac differentiation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 19300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, E.; Lagresle-Peyrou, C.; Susini, S.; De Chappedelaine, C.; Sigrist, N.; Sadek, H.; Chouteau, M.; Cagnard, N.; Fontenay, M.; Hermine, O.; et al. AK2 deficiency compromises the mitochondrial energy metabolism required for differentiation of human neutrophil and lymphoid lineages. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaloul-Gonzalez, L.; Mohsen, A.W.; Karunanidhi, A.; Seminotti, B.; Chong, H.; Madan-Khetarpal, S.; Sebastian, J.; Vockley, C.W.; Reyes-Múgica, M.; Vander Lugt, M.T.; et al. Reticular Dysgenesis and Mitochondriopathy Induced by Adenylate Kinase 2 Deficiency with Atypical Presentation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Wyder, S.; Forslund, K.; Heller, D.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Santos, A.; Tsafou, K.P.; et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.; Morris, J.H.; Demchak, B.; Bader, G.D. Biological network exploration with Cytoscape 3. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 47, 8.13.1–8.13.24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Olson, A.J. Using AutoDock for ligand-receptor docking. Curr. Protoc Bioinform. 2008, 24, 8.14.1–8.14.40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | S9 | S10 | Reference Fingerprint | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1.000 | 0.995 | 0.993 | 0.983 | 0.99 | 0.992 | 0.985 | 0.986 | 0.975 | 0.967 | 0.992 |
| S2 | 0.995 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 0.981 | 0.995 | 0.992 | 0.992 | 0.984 | 0.977 | 0.958 | 0.992 |
| S3 | 0.993 | 0.998 | 1.000 | 0.98 | 0.993 | 0.992 | 0.995 | 0.982 | 0.975 | 0.95 | 0.99 |
| S4 | 0.983 | 0.981 | 0.98 | 1.000 | 0.979 | 0.976 | 0.971 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.987 | 0.998 |
| S5 | 0.99 | 0.995 | 0.993 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.992 | 0.991 | 0.982 | 0.976 | 0.95 | 0.989 |
| S6 | 0.992 | 0.992 | 0.992 | 0.976 | 0.992 | 1.000 | 0.988 | 0.979 | 0.971 | 0.951 | 0.987 |
| S7 | 0.985 | 0.992 | 0.995 | 0.971 | 0.991 | 0.988 | 1.000 | 0.974 | 0.965 | 0.937 | 0.982 |
| S8 | 0.986 | 0.984 | 0.982 | 0.997 | 0.982 | 0.979 | 0.974 | 1.000 | 0.995 | 0.984 | 0.998 |
| S9 | 0.975 | 0.977 | 0.975 | 0.997 | 0.976 | 0.971 | 0.965 | 0.995 | 1.000 | 0.979 | 0.994 |
| S10 | 0.967 | 0.958 | 0.95 | 0.987 | 0.95 | 0.951 | 0.937 | 0.984 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.982 |
| Reference fingerprint | 0.992 | 0.992 | 0.99 | 0.998 | 0.989 | 0.987 | 0.982 | 0.998 | 0.994 | 0.982 | 1.000 |
| Group | Spearman r | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSG | 0.3043 | 0.3926 | |
| ALT | EG | 0.2467 | 0.492 |
| TSG + EG | 0.2973 | 0.4041 | |
| TSG | 0.7552 | 0.0115 | |
| AST | EG | 0.6868 | 0.0283 |
| TSG + EG | 0.7482 | 0.0128 |
| No | Retention Time (min) | m/z | Ionization Mode | Formula | Metabolites | HMDB ID | PMT/ M | KEGG Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.1 | 134.0230 | M − H | C4H6O5 | D-Malic acid | HMDB0031518 | up | Butanoate metabolism |
| 2 | 1.2 | 220.0492 | M − H | C6H9N2O5P | 3-(Imidazol-4-yl)-2-oxopropyl phosphate | HMDB0012236 | up | Histidine metabolism |
| 3 | 1.2 | 284.0787 | M − H | C10H12N4O6 | Xanthosine | HMDB0000299 | up | Purine metabolism |
| 4 | 1.6 | 136.0372 | M + H | C5H4N4O | Hypoxanthine | HMDB0000157 | down | Purine metabolism |
| 5 | 1.9 | 152.0348 | M − H | C5H4N4O2 | Xanthine | HMDB0000292 | up | Purine metabolism |
| 6 | 2.6 | 217.1327 | M + H | C10H19NO4 | Propionylcarnitine | HMDB0000824 | down | / |
| 7 | 3.7 | 165.0793 | M + H | C9H11NO2 | Benzocaine | HMDB0004992 | down | / |
| 8 | 6.6 | 495.3236 | M + H | C24H50NO7P | LysoPC(0:0/16:0) | HMDB0240262 | down | / |
| 9 | 6.8 | 186.1358 | M + H | C9H18N2O2 | 3-[(3-Methylbutyl)nitrosoamino]-2-butanone | HMDB0033553 | down | / |
| 10 | 6.8 | 501.2864 | M + H | C32H39NO4 | Fexofenadine | HMDB0005030 | down | / |
| 11 | 6.8 | 111.0432 | M + H | C4H5N3O | Cytosine | HMDB0000630 | down | Pyrimidine metabolism |
| 12 | 8.0 | 147.0764 | M − H | C6H13NOS | 5-Methylthiopentanaldoxime | METPA1772 | down | Glucosinolate biosynthesis |
| 13 | 8.4 | 188.0184 | M − H | C7H8O4S | p-Cresol sulfate | HMDB0011635 | up | Toluene degradation |
| 14 | 8.5 | 193.0755 | M − H | C10H11NO3 | 3-Carbamoyl-2-phenylpropionaldehyde | HMDB0060366 | up | Drug metabolism—cytochrome P450 |
| 15 | 9.2 | 501.2844 | M − H | C25H44NO7P | LysoPE(0:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) | HMDB0011487 | down | / |
| 16 | 15.2 | 501.294 | M − H | C25H35D5N2O6S | Leukotriene D4 | HMDB0003080 | down | Arachidonic acid metabolism |
| 17 | 15.6 | 553.3491 | M − H | C29H48NO7P | LysoPE(0:0/24:6(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z,18Z,21Z)) | HMDB0011499 | up | / |
| Pathway Name | Match Status | p | −log(p) | FDR | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purine metabolism | 3/66 | 0.013319 | 1.8755 | 1 | 0.05133 |
| Drug metabolism–cytochrome P450 | 1/27 | 0.19579 | 0.70821 | 1 | 0.07692 |
| Arachidonic acid metabolism | 1/36 | 0.25279 | 0.59723 | 1 | 0 |
| Metabolite | Protein | Total Score | Crash | Polar | D Score | PMF Score | G Score | Chem Score | Global CScore | Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypoxanthine | NT5E | 3.62 | −0.46 | 1.99 | −35.96 | −24.68 | −109.77 | −13.56 | 2 | 0.44 |
| XDH | 3.68 | −0.40 | 4.81 | −21.21 | −29.74 | −54.39 | −15.96 | 2 | 0.11 | |
| PDE3A | 4.58 | −0.06 | 3.91 | −41.96 | −18.26 | −79.18 | −6.62 | 1 | 0.44 | |
| PDE5A | 4.79 | −0.47 | 3.54 | −61.71 | −28.38 | −119.14 | −7.23 | 2 | 0.45 | |
| ADK | 3.43 | −0.32 | 0.44 | −61.35 | −21.57 | −127.56 | −7.29 | 2 | 0.46 | |
| ENPP1 | 3.21 | −0.28 | 3.32 | −50.70 | −27.29 | −83.53 | −6.55 | 1 | 0.32 | |
| ADA | 3.45 | −0.22 | 1.79 | −49.32 | −28.60 | −94.28 | −9.73 | L | 0.19 | |
| PNP | 3.59 | −0.21 | 0.92 | −60.20 | −18.68 | −106.95 | −8.91 | 2 | 0.43 | |
| NT5C2 | 3.42 | −0.79 | 2.00 | −71.08 | −55.92 | −113.60 | −14.40 | 2 | 0.40 | |
| AK2 | 4.99 | −0.14 | 4.08 | −49.17 | −19.32 | −84.25 | −6.68 | 2 | 0.46 | |
| IMPDH2 | 2.70 | −1.29 | 1.77 | −54.66 | −21.21 | −118.69 | −13.58 | 2 | 0.40 | |
| CANT1 | 4.17 | −0.37 | 3.51 | −54.69 | −33.65 | −83.43 | −12.94 | 1 | 0.29 | |
| HPRT1 | 3.68 | −0.05 | 2.68 | −31.02 | −50.60 | −74.85 | −13.58 | 1 | 0.21 | |
| GDA | 3.12 | −0.09 | 4.08 | −11.87 | −14.64 | −42.34 | −6.16 | 2 | 0.37 | |
| Xanthosine | NT5E | 6.54 | −0.60 | 5.39 | −107.22 | −44.53 | −204.37 | −5.17 | 4 | 0.51 |
| XDH | 1.77 | −1.01 | 2.57 | −44.63 | −5.37 | −77.36 | −6.51 | 2 | 0.18 | |
| PDE3A | 4.77 | −1.48 | 3.59 | −125.93 | −1.01 | −140.46 | −7.95 | 2 | 0.29 | |
| PDE5A | −4.43 | −11.72 | 2.45 | −156.64 | 26.82 | −255.74 | −13.94 | 2 | 0.52 | |
| ADK | −4.09 | −12.85 | 1.40 | −183.09 | 39.70 | −258.38 | −5.82 | 2 | 0.39 | |
| ENPP1 | 4.89 | −0.53 | 3.71 | −97.29 | −52.72 | −126.75 | −6.24 | 2 | 0.42 | |
| ADA | 3.31 | −4.25 | 1.67 | −135.84 | −34.69 | −225.05 | −9.18 | 2 | 0.42 | |
| PNP | −1.60 | −8.85 | 2.78 | −135.42 | 28.43 | −233.08 | −11.94 | 2 | 0.36 | |
| NT5C2 | 4.27 | −5.60 | 6.40 | −170.44 | −129.21 | −200.58 | −15.48 | 2 | 0.51 | |
| AK2 | 5.62 | −0.98 | 4.25 | −94.40 | −9.20 | −141.24 | −5.76 | 3 | 0.50 | |
| IMPDH2 | 0.21 | −5.93 | 2.14 | −155.75 | 15.64 | −217.59 | −12.97 | 2 | 0.51 | |
| CANT1 | 4.00 | −1.91 | 2.30 | −140.67 | −57.79 | −165.05 | −3.05 | 2 | 0.32 | |
| HPRT1 | 4.40 | −0.98 | 4.69 | −100.57 | −36.89 | −146.16 | −14.66 | 1 | 0.43 | |
| GDA | 3.43 | −0.84 | 2.98 | −88.25 | −17.53 | −155.70 | −4.31 | 3 | 0.49 | |
| Xanthine | NT5E | 3.42 | −0.31 | 2.17 | −48.57 | −17.36 | −111.29 | −12.89 | 2 | 0.40 |
| XDH | 1.82 | −0.16 | 2.68 | −32.42 | −35.69 | −46.75 | −12.65 | 2 | 0.14 | |
| PDE3A | 4.12 | −0.18 | 3.56 | −55.08 | −16.02 | −95.64 | −9.92 | 1 | 0.44 | |
| PDE5A | 4.42 | −1.06 | 3.14 | −79.06 | −12.36 | −129.64 | −7.10 | 2 | 0.42 | |
| ADK | 3.63 | −0.10 | 0.02 | −76.60 | −25.27 | −131.98 | −9.44 | 2 | 0.48 | |
| ENPP1 | 4.70 | −0.09 | 4.57 | −50.32 | −29.71 | −65.72 | −12.92 | 3 | 0.28 | |
| ADA | 3.36 | −0.53 | 1.41 | −77.80 | −62.12 | −127.63 | −13.13 | 2 | 0.47 | |
| PNP | 4.34 | −0.22 | 1.98 | −71.61 | −3.81 | −118.35 | −6.92 | 2 | 0.58 | |
| NT5C2 | 3.08 | −1.69 | 2.80 | −76.81 | −63.86 | −117.95 | −12.74 | 2 | 0.48 | |
| AK2 | 3.08 | −0.11 | 2.13 | −50.38 | −16.15 | −83.59 | −6.73 | 1 | 0.37 | |
| IMPDH2 | 2.50 | −2.45 | 2.21 | −74.40 | 1.40 | −134.67 | −11.39 | 2 | 0.47 | |
| CANT1 | 4.37 | −0.48 | 4.41 | −62.35 | −28.46 | −94.41 | −12.13 | 1 | 0.29 | |
| HPRT1 | 3.47 | −0.71 | 3.28 | −52.21 | −32.82 | −81.77 | −9.90 | 1 | 0.46 | |
| GDA | 2.12 | −0.06 | 2.49 | −32.17 | −16.37 | −55.93 | −9.41 | 1 | 0.17 |
| Metabolite | Protein | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Xanthosine | NT5E | −6.95 |
| AK2 | −6.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Feng, M.; Wu, H.; Dai, Y.; Jia, Z.; Fang, C.; Liu, M.; Yan, X.; Zhu, M.; et al. Discovery of Hepatotoxic Equivalent Markers and Mechanism of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. by Metabolomics Coupled with Molecular Docking. Molecules 2023, 28, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010025
Zhang Y, Liu L, Feng M, Wu H, Dai Y, Jia Z, Fang C, Liu M, Yan X, Zhu M, et al. Discovery of Hepatotoxic Equivalent Markers and Mechanism of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. by Metabolomics Coupled with Molecular Docking. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yinhuan, Lirong Liu, Menghan Feng, Hao Wu, Yihang Dai, Zhixin Jia, Cong Fang, Mingyan Liu, Xiaoning Yan, Meixia Zhu, and et al. 2023. "Discovery of Hepatotoxic Equivalent Markers and Mechanism of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. by Metabolomics Coupled with Molecular Docking" Molecules 28, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010025
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, L., Feng, M., Wu, H., Dai, Y., Jia, Z., Fang, C., Liu, M., Yan, X., Zhu, M., Huang, B., Qu, B., & Xiao, H. (2023). Discovery of Hepatotoxic Equivalent Markers and Mechanism of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. by Metabolomics Coupled with Molecular Docking. Molecules, 28(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010025






