One-Pot Hydrothermal Preparation of Hydroxyapatite/Zinc Oxide Nanorod Nanocomposites and Their Cytotoxicity Evaluation against MG-63 Osteoblast-like Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
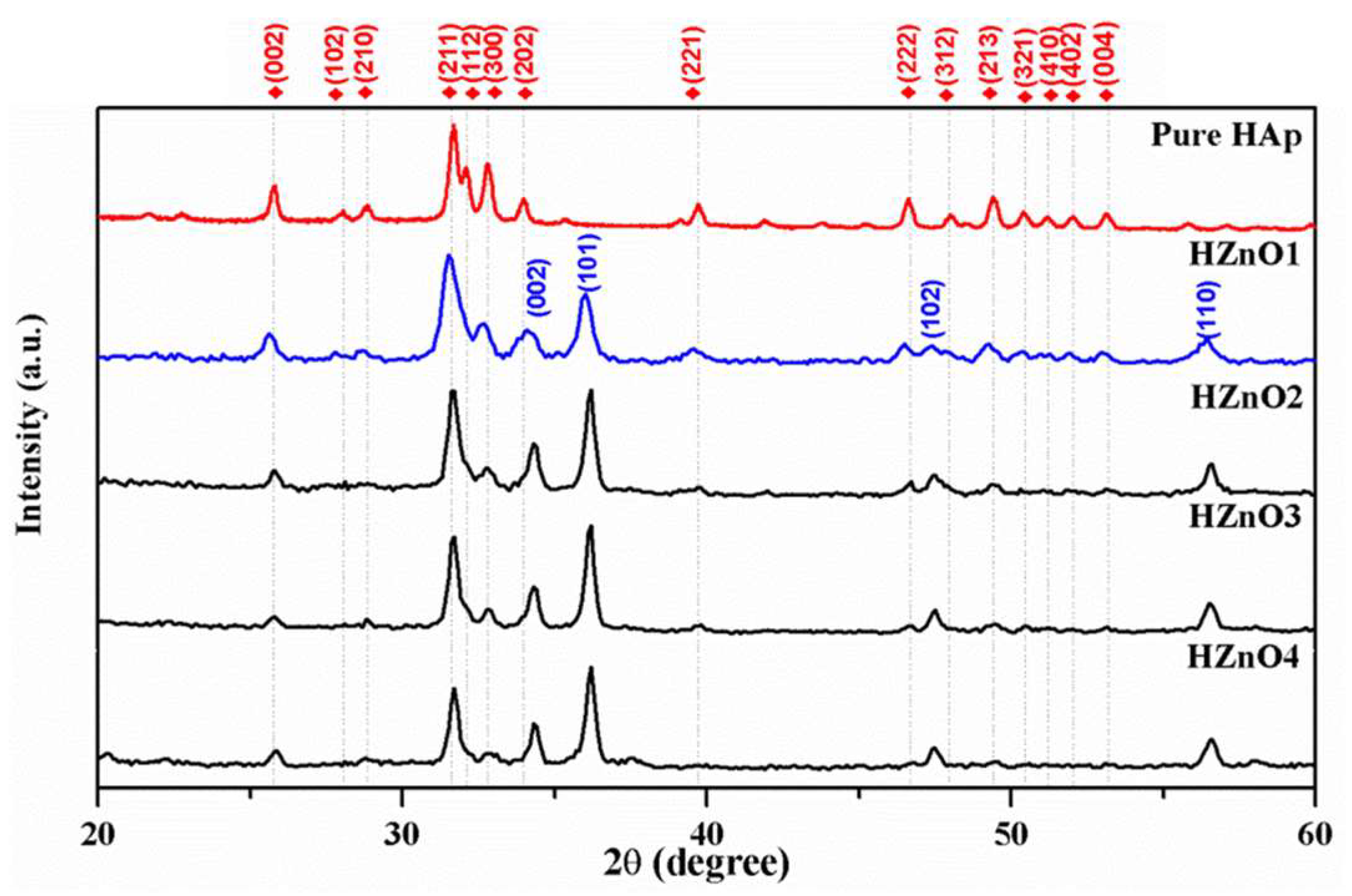
2.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
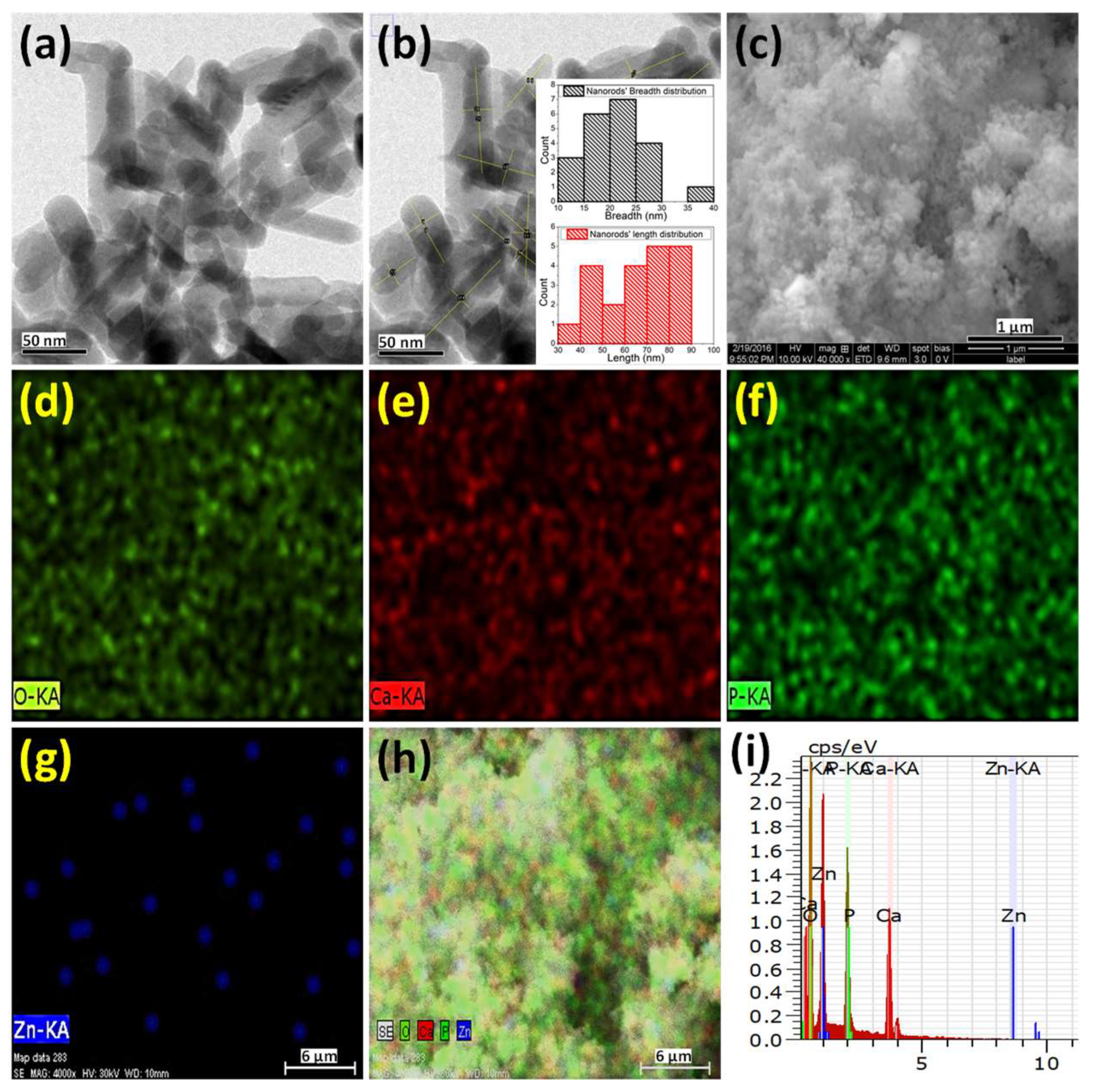
2.2. Electron Microscopy Analysis
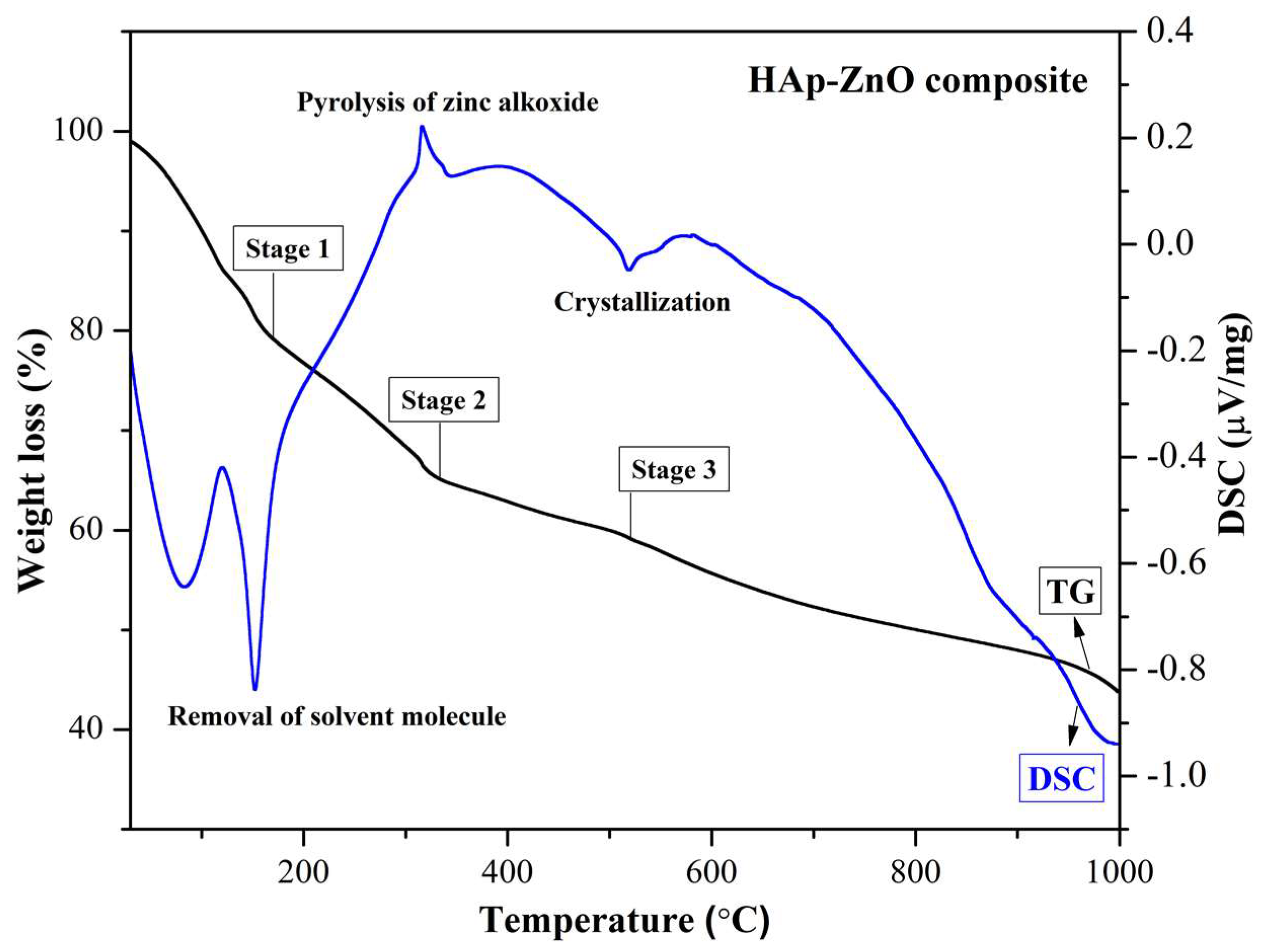
2.3. TG/DSC Analysis
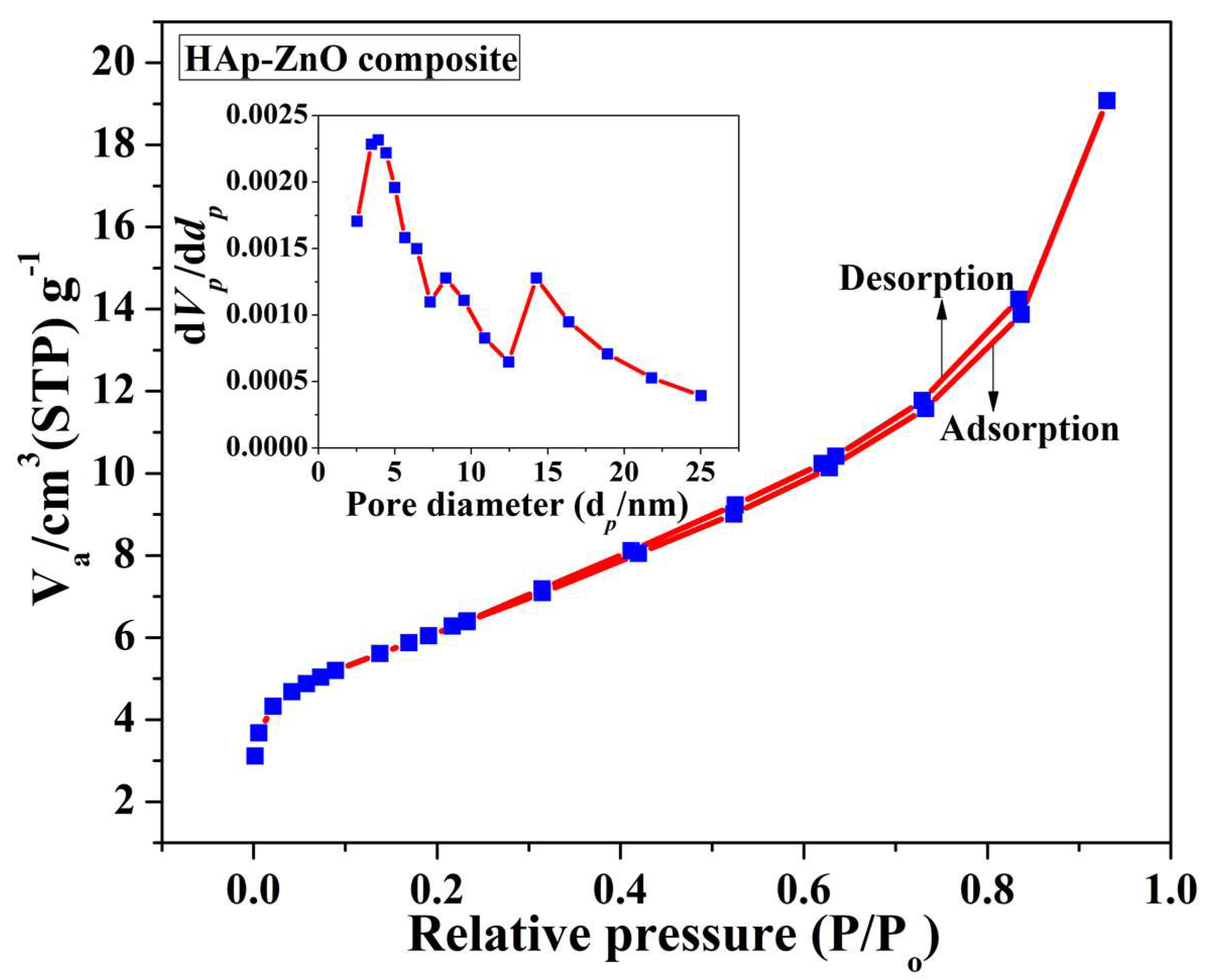
2.4. BET Analysis
2.5. Nanoindentation Study
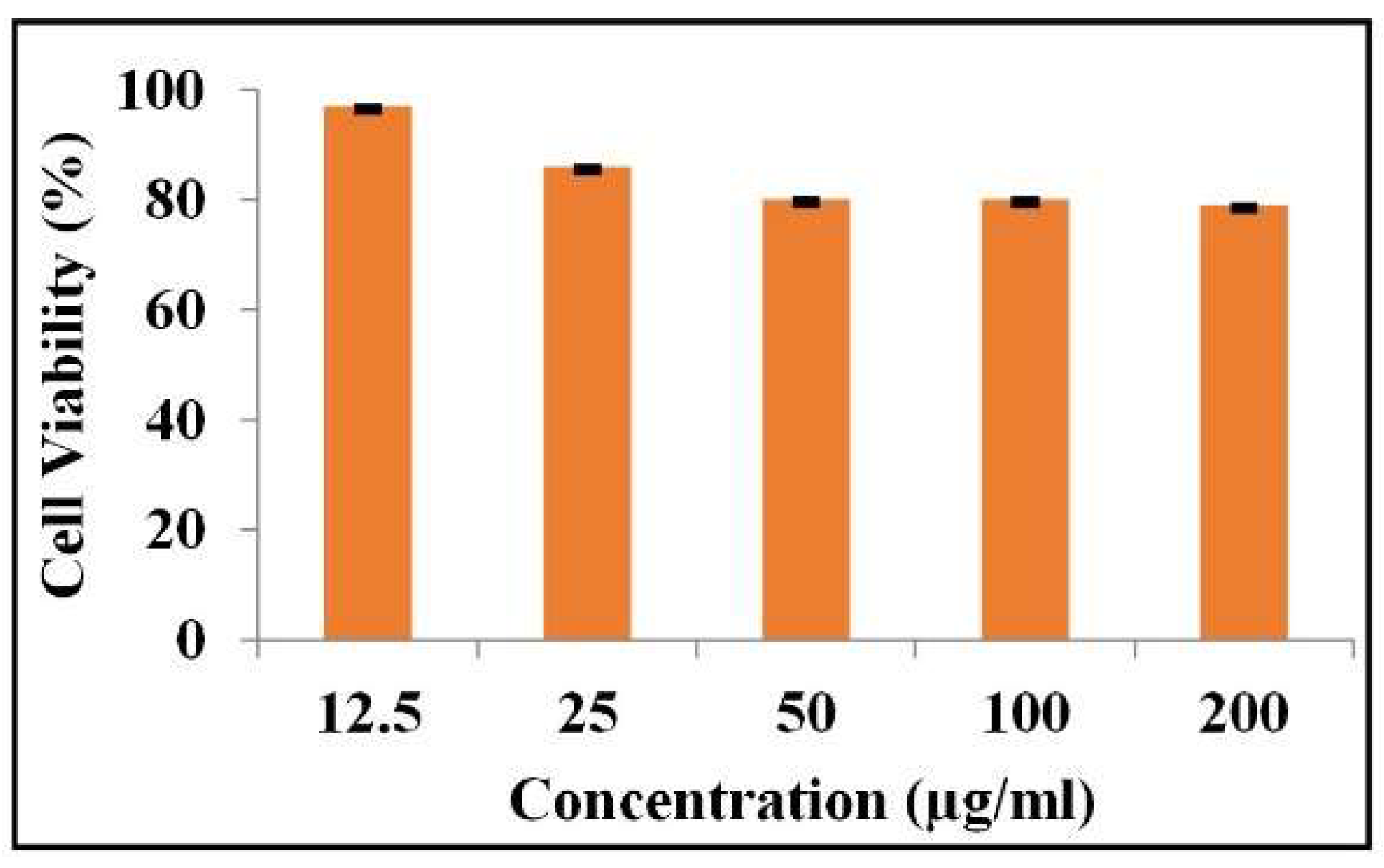
2.6. In Vitro Biocompatibility
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of HAp-ZnO Composite
3.2. Characterization of HAp-ZnO Nanocomposite
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yu, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, L.; Jin, J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, M. Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial activity and mechanism of a novel hydroxyapatite whisker/nano zinc oxide biomaterial. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 10, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.H.; Sun, L.; Weir, M.D.; Takagi, S.; Chow, L.C.; Hockey, B. Effects of incorporating nanosized calcium phosphate particles on properties of whisker-reinforced dental composites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 81, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.H.; Weir, M.D.; Sun, L. Calcium and phosphate ion releasing composite: Effect of pH on release and mechanical properties. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safronova, T.; Mukhin, E.; Putlyaev, V.; Knotko, A.; Evdokimov, P.; Shatalova, T.; Filippov, Y.; Sidorov, A.; Karpushkin, E. Amorphous calcium phosphate powder synthesized from calcium acetate and polyphosphoric acid for bioceramics application. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovani, C.B.; Gloter, A.; Azaïs, T.; Selmane, M.; Ramos, A.P.; Nassif, N. Formation of stable strontium-rich amorphous calcium phosphate: Possible effects on bone mineral. Acta Biomater. 2019, 92, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, A.A.; Robertson, S.F.; Ke, D.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bose, S. Mechanical and biological properties of ZnO, SiO2, and Ag2O doped plasma sprayed hydroxyapatite coating for orthopaedic and dental applications. Acta Biomater. 2019, 92, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, M.G.; Cai, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Roles of Hydroxyapatite Allocation and Microgroove Dimension in Promoting Preosteoblastic Cell Functions on Photocured Polymer Nanocomposites through Nuclear Distribution and Alignment. Langmuir 2015, 31, 2851–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K. Hydroxyapatite synthesis methodologies: An overview. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2010, 2, 903–907. [Google Scholar]
- Pramanik, S.; Agarwal, A.; Rai, K.; Garg, A. Development of high strength hydroxyapatite by solid-state-sintering process. Ceram. Int. 2007, 33, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currey, J. Sacrificial bonds heal bone. Nature 2001, 414, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, S.; Nayak, A.K.; Ara, T.J.; Hasnain, M.S. Hydroxyapatite composites for dentistry. Appl. Nanocomposite Mater. Dent. 2019, 1, 123–143. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, N.; Keskinbora, K.; Suvaci, E.; Basu, B. Sintering, microstructure, mechanical, and antimicrobial properties of HAp-ZnO biocomposites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 95, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.H.; Friedman, R.J. Laboratory methods for studies of bacterial adhesion. J. Microbiol. Methods 1997, 30, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Luo, L.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J. Chemical transformation of zinc oxide nanoparticles as a result of interaction with hydroxyapatite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 461, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Wei, P.; Shuai, C.; Peng, S. Characterization of Mechanical and Biological Properties of 3-D Scaffolds Reinforced with Zinc Oxide for Bone Tissue Engineering. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turlybekuly, A.; Pogrebnjak, A.D.; Sukhodub, L.F.; Sukhodub, L.B.; Kistaubayevam, A.S.; Savitskaya, I.S.; Shokatayeva, D.H.; Bondar, O.V.; Shaimardanov, Z.K.; Plotnikova, S.V.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, in vitro biocompatibility and antibacterial properties study of nanocomposite materials based on hydroxyapatite-biphasic ZnO micro-and nanoparticles embedded in Alginate matrix. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2019, 104, 109965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurenti, M.; Cauda, V. ZnO Nanostructures for Tissue Engineering Applications. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdulkareem, E.H.; Memarzadeh, K.; Allaker, R.; Huang, J.; Pratten, J.; Spratt, D. Anti-biofilm activity of zinc oxide and hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as dental implant coating materials. J. Dent. 2015, 43, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnaneshwar, P.V.; Sudakaran, S.V.; Abisegapriyan, S.; Sherine, J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Rahim, M.H.A.; Yusoff, M.M.; Jose, R.; Venugopal, J.R. Ramification of zinc oxide doped hydroxyapatite biocomposites for the mineralization of osteoblasts. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, Z.; Ghosh, R. Effect of zinc oxide addition on antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of hydroxyapatite: A potential nanocomposite for biomedical applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 21, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, F.; Bazargan-Lari, R.; Razavi, M.; Fahimipour, F.; Vashaee, D.; Tayebi, L. Nano-hydroxyapatite and nano-hydroxyapatite/zinc oxide scaffold for bone tissue engineering application. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2020, 17, 2752–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananth, K.P.; Sun, J.; Bai, J. An Innovative Approach to Manganese-Substituted Hydroxyapatite Coating on Zinc Oxide–Coated 316L SS for Implant Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenho, L.; Salgado, C.L.; Fernandez, M.H.; Monteiro, F.J.; Ferraz, M.P. Antibacterial activity and biocompatibility of three-dimensional nanostructured porous granules of hydroxyapatite and zinc oxide nanoparticles—An in vitro and in vivo study. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 315101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gezaz, M.S.; Aref, S.M.; Khatamian, M. Investigation of structural properties of hydroxyapatite/zinc oxide nanocomposites; an alternative candidate for replacement in recovery of bones in load-tolerating areas. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 226, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, M.; Muñoz-Soto, E.; Aguilera, F.S.; Osorio, E.; González-Rodríguez, M.P.; Pérez-Álvarez, M.C.; Toledano-Osorio, M.; Osorio, R. A zinc oxide-modified hydroxyapatite-based cement favored sealing ability in endodontically treated teeth. J. Dent. 2019, 88, 103162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Jiang, Z.; Li, P.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, J.; Cui, X.; Wang, Q. Novel Hydroxyapatite Whiskers Modified by Silver Ion and Nano Zinc Oxide Used for Bone Defect Repairment. Coatings 2021, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buazar, F.; Alipouryan, S.; Kroushawi, F.; Hossieni, S.A. Photodegradation of odorous 2-mercaptobenzoxazole through zinc oxide/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, C.; Xue, J.; Dong, Y. Fabrication and characterization of hydroxyapatite nanomaterial dual deposited with nano silver and zinc oxide. Mater. Lett. 2018, 219, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, N.; Kakuchi, Y.; Ohtsuki, T. Antibacterial effect of zinc oxide/hydroxyapatite coatings prepared by chemical solution deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Byrappa, K. Hydrothermal processing of materials: Past, present and future. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 2085–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynyuk, O.O.; Sukhodub, L.F.; Meshkov, A.M.; Sukhodub, L.B. Structural properties of the ZnO doped hydroxyapatite nanocomposite material. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Nanomaterials: Application & Properties (NAP), Lviv, Ukraine, 14–19 September 2016; p. 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, O.S.; Sabree, I.K. The Effects of Zinc Oxide on the Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Direct Synthesis Hydroxyapatite. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2018, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of nitrogen by porous materials. J. Porous Mater. 1995, 2, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S. The use of gas adsorption for the characterization of porous solids. Colloids Surf. 1989, 38, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, C.T.; Wataha, J.C.; Sun, Z. In vitro models of biocompatibility: A review. Dent. Mater. 1996, 12, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Pati, F.; Mandal, D.; Dhara, S.; Biswas, K. In vitro evaluation of osteoconductivity and cellular response of zirconia and alumina based ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3923–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaperumal, V.R.; Mani, R.; Nachiappan, M.S.; Arumugam, K. Direct hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite/alumina nanocomposite. Mater. Charact. 2017, 134, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaperumal, V.R.; Mani, R.; Polisetti, V.; Aruchamy, K.; Oh, T. Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite (HAp)-Zirconia Nanocomposite Powder and Evaluation of Its Biocompatibility: An In Vitro Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sivaperumal, V.R.; Mani, R.; Polisetti, V.; Aruchamy, K.; Oh, T. One-Pot Hydrothermal Preparation of Hydroxyapatite/Zinc Oxide Nanorod Nanocomposites and Their Cytotoxicity Evaluation against MG-63 Osteoblast-like Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010345
Sivaperumal VR, Mani R, Polisetti V, Aruchamy K, Oh T. One-Pot Hydrothermal Preparation of Hydroxyapatite/Zinc Oxide Nanorod Nanocomposites and Their Cytotoxicity Evaluation against MG-63 Osteoblast-like Cells. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010345
Chicago/Turabian StyleSivaperumal, Vignesh Raj, Rajkumar Mani, Veerababu Polisetti, Kanakaraj Aruchamy, and Taehwan Oh. 2023. "One-Pot Hydrothermal Preparation of Hydroxyapatite/Zinc Oxide Nanorod Nanocomposites and Their Cytotoxicity Evaluation against MG-63 Osteoblast-like Cells" Molecules 28, no. 1: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010345




