Chronic Inflammation’s Transformation to Cancer: A Nanotherapeutic Paradigm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Inflammatory Factors Involved in Cancer Transformation
2.1. Macrophages and Denticles Cells
- By enhancing the angiogenic tumor potential factors such as IL-8, VEGF, and MIF, and by promoting lymph-angiogenesis
- Progression in the growth of tumor
- Tumor cell invasion, migration, and intravasation at primary sites JAM, and they act on endothelial cells, further promoting the tumor’s neovascularization [23].
2.2. Proinflammatory Cytokinesis
2.3. Tumor Necrosis Factor α
2.4. Interleukin
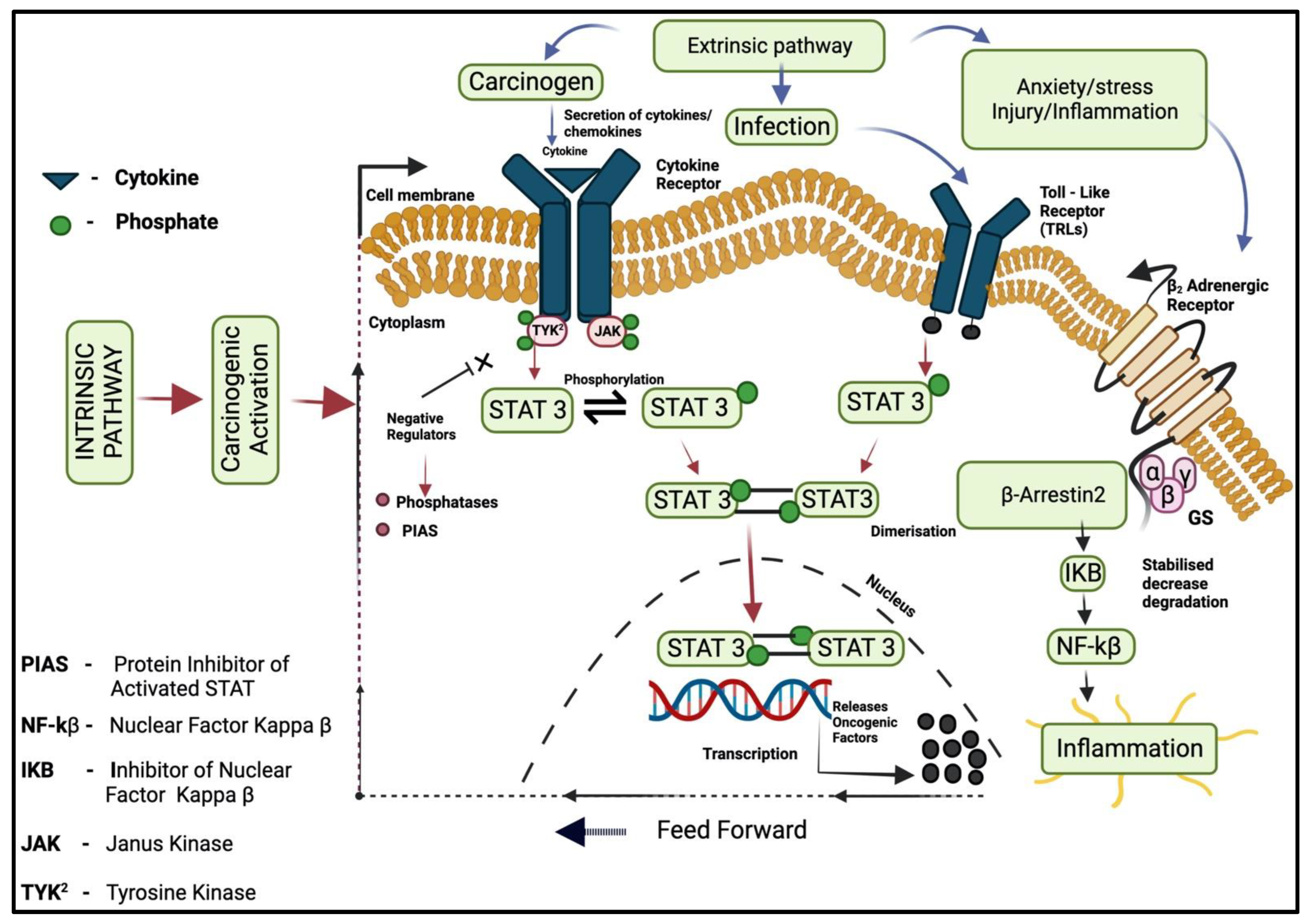
3. Inflammatory Signaling Pathways
3.1. Intrinsic Pathway
3.2. Extrinsic Pathway
3.3. Transcription Factors (NF-kB)
3.4. JAK/STAT Pathway
3.5. COX Pathway
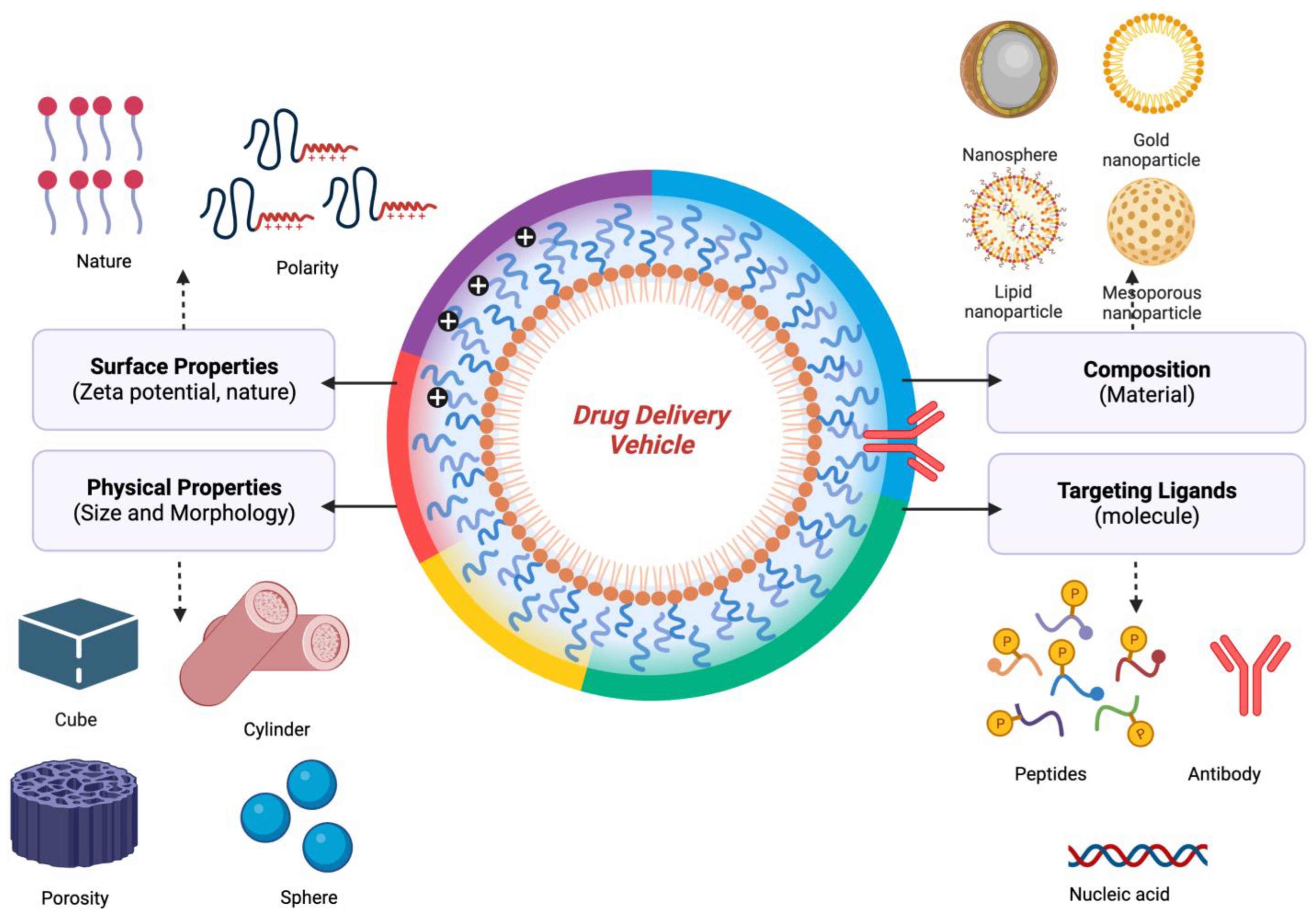
4. Cancer-Associated Inflammatory Diseases and Nanotherapy
4.1. Hepatitis
| Cancer-Linked Inflammatory Disease and Cancer | Nanoparticles | Size | Probe/Target | Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis | ZnO NPs | 5–50 nm | Zinc NPs binds to viral RNA | Promising in the inhibition of viral replication, when examined on HUH 7 cells against hepatitis C and E viruses | [81] |
| Hepatitis B | Au NPs | 50 nm | Gold NPs-antibody detect hepatitis viral antigen | They target hepatitis B antigen surface to detect the hepatitis B virus present in human serum, via antibody-antigen interaction assays | [82] |
| Hepatitis C | Amphimedon-Ag NPs | 8.22–14.30 nm | NA | They have outstanding anti-HCV, Non-structural protein S drug activity | [83] |
| Hepatitis B | Ag NPs | 10 nm | Silver NPs binds to viral RNA and halts replication | They were found to reduce the formation of extracellular HBV DNA and inhibit RNA and virions when observed on HepAD38 cells | [84] |
| Hepatic Cancer | Ag NPs | 13 ± 1 nm | NA | Inhibition of cytotoxic effects of hepatic cancer at a concentration of 10–200μg/mL on Hep-G2 cells and MCF-7 cells | [85] |
| Hepatitis | Ag/thiol graphene dots nanocomposite | NA | Riboflavin as a probe | Detection of hepatitis core antigen and use of riboflavin as a redox core probe | [86] |
| Hepatic cancer | Ag NPs | 20–50 nm | NA | They have a potent Cytotoxic effect on human hepatic cancer cells (Huh-7 cells and CHANG) at 0, 5, 20, 40, and 100μg/mL concentration | [87] |
| IBD | P@QD-MdC NPs | 150 nm | Antibody (Anti-MAd CAM-1) | Holds promising outcomes for IBD diagnosis and imagining at an early stage | [88] |
| IBD | Ginger-derived NPs | ~230 nm | Ginger NPs found to have lipids, proteins that binds to cancer cells receptor | They are prominent in the reduction of the effect of acute colitis, repair of intestinal cells, and prevention of chronic colitis-associated cancer | [89] |
| IBD | Eudragit-Mesoporous Silica nanocomposite | ~150 nm | Polymer Eudragit | At an oral dose of 0.2 mg/kg, found to prevent and improve IBD and colitis-associated cancer treatments, reduce the mRNA expression of cytokines (IL-1β, IL-10 and 17), and be effective in the therapy of IBD | [90] |
| IBD and gastrointestinal disease | Dextran-coated cerium oxide NPs | 17.5 ± 0.7 nm and 4.8 ± 1.2 nm (core) | Ceramic oxide encapsulated | For imagining IBD and as a computed tomography agent to give an image of the gastrointestinal tract affected with IBD | [91] |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Ag NPs | 2.6 and 18 nm | NA | Decreased cellular proliferation in PANC-1 cells and higher cytotoxic effect of Ag NPs on human pancreas ductal adenocarcinoma (PANC-1 cells) | [92] |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Au Nanorods | >6 nm | Polymer (bovine serum albumin) and SiO2 encapsulated | They have applications in bio-imagining and cancer therapy | [93] |
| Pancreatic Cancer | PEG-ZnO NPs | 21.8 ± 0.86 nm | Polyethylene glycol encapsulated | Observe to down-regulate the expression of anti-apoptotic BCL2 and up-regulated pro-apoptotic BAX, and found to have excellent anti-cancer activity on PANC-1 cells | [94] |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Au NPs | 20 nm | Citrate-capped Au NPs | Inhibits proliferation and tumor growth in both pancreatic cancer cells and pancreatic stellate cells | [95] |
4.2. Pancreatic Cancer
| Nanoparticle | Size | Role of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLGA NPs | 350–410 nm | It provides immunotolerance to cancer. It was found to induce anti-tumor therapeutic effects. CD8 T cells secreted interferons at the site of lymph nodes and spleen, and vaccinated mice were treated with PLGA NPs. | [104] |
| β-Glucan NPs (BG34-Fe3O4 conjugated carbon nanotubes) | 80–100 nm (Length) 10–20 nm (Diameter) | β-glucan from the cell wall of natural sources such as plants and fungi, have appeared to enhance anti-tumor responses through direct interaction with immune cells such as macrophages and others. It acts as an immune modulator in optimizing tumor microenvironments. | [105] |
| Anti-PD-L-1 targeted nanoplatform consists of Au-SPIO@PLGA NPs | 500 nm | It was found to achieve the promotion of polarization of TAM to M1 (classically activated macrophages) and reverse the cause of immunosuppression by TAM and block the programmed death-ligand 1/Programmed cell death pathway. | [106] |
| F Conjugated–PLGA NPs | 500 nm | The efficient and specific T-cell targeting drug delivery binding system in vitro in human cells. In vivo, it allows specific targeted delivery of an inhibitor of TGFβR1 and TLR 7/8 agonist, found to delay the growth of tumors in mice, when delivered via Programmed cell death-1 protein targeting NPs. | [107] |
| CD44TA-LIP NPs (Liposomes targeting CD44 receptor using Thioaptamers) | 204.9 | Found to exhibit a host defense mechanism against invading pathogens (TB immunopathogenesis) activate lymphocytes, and provide immunity against tuberculosis in mice. | [108] |
| Zn-pyrophosphate NPs loaded with photosensitizer pyrolipid (Zn P@Pyro) | NA | It can kill tumor cells, induces apoptosis, and tumor-specific cytotoxic T-cell responses, and disrupt tumor vasculature. It significantly prevents the metastasis of tumors to the lungs of mice. | [109] |
| PLGA NPs-based vaccine | 350–410 nm | It induces specific anti-tumor T-cell responses and activates INF-γ secretion at lymph nodes by activation of CD8+, TRP2 specific T-cells of vaccinated mice bearing melanoma B16 tumors. | [104] |
| Cytosine-phosphate-guanine coated NPs | NA | It shows rapid accumulation by Antigen-presenting cells and triggers the release of cytokines (IL-10). Induces strong anti-inflammatory responses, enhances TH1/TH2 responses, and eliminates tumor cells. | [110] |
| Nano-artificial APC iron-dextran coated NPs | 50–100 nm | It was found to enhance antigen-specific T-cell proliferation in vitro and inhibition/clearance of tumor growth | [111] |
4.3. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Gansler, T.; Ganz, P.A.; Grant, M.; Greene, F.L.; Johnstone, P.; Mahoney, M.; Newman, L.A.; Oh, W.K.; Thomas, C.R., Jr.; Thun, M.J. Sixty Years of CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and Cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory Responses and Inflammation-Associated Diseases in Organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.R.; Mantovani, A. Cancer-Related Inflammation: Common Themes and Therapeutic Opportunities; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 22, pp. 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Baby, D.; Rajguru, J.; Patil, P.; Thakkannavar, S.; Pujari, V. Inflammation and Cancer. Ann. Afr. Med. 2019, 18, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoric, J.; Antonucci, L.; Karin, M. Tannic Acid Ameliorates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity and Potentiates Its Anti-Cancer Activity: Potential Role of Tannins in Cancer Chemotherapy. Cancer Prev. Res. 2016, 9, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badic, B.; Gancel, C.H.; Thereaux, J.; Joumond, A.; Bail, J.P.; Meunier, B.; Sulpice, L. Surgical and Oncological Long Term Outcomes of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) Resection-Retrospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 53, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michielsen, P.; Ho, E. Viral Hepatitis B and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Acta Gastro-Enterol. Belg. 2011, 74, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental Regulation of Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.S.; Britton, G.J.; Hill, E.V.; Verhagen, J.; Burton, B.R.; Wraith, D.C. Regulation of Adaptive Immunity; the Role of Interleukin-10. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, M.T.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines in Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Li, S.; Hong, M.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y. The Reactive Oxygen Species in Macrophage Polarization: Reflecting Its Dual Role in Progression and Treatment of Human Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 2795090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakosta, A.; Golias, C.; Charalabopoulos, A.; Peschos, D.; Batistatou, A.; Charalabopoulos, K. Genetic Models of Human Cancer as a Multistep Process. Paradigm Models of Colorectal Cancer, Breast Cancer, and Chronic Myelogenous and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 24, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Miller, A.H. Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, L.; Mielgo, A. Macrophages and Fibroblasts, Key Players in Cancer Chemoresistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Shen, S.; Verma, I.M. NF-ΚB, an Active Player in Human Cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango Duque, G.; Descoteaux, A. Macrophage Cytokines: Involvement in Immunity and Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwawa, N.; Kobayashi, K. Macrophage in Inflammation. Curr. Drug. Targets Inflammat. Allergy 2005, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, R.; Feghali-Bostwick, C. Fibroblasts in Fibrosis: Novel Roles and Mediators. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Lan, H. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Tumor Metastasis: Biological Roles and Clinical Therapeutic Applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, Y.; Uchino, J.; Chihara, Y.; Tamiya, N.; Kaneko, Y.; Yamada, T.; Takayama, K. Tumor Neovascularization and Developments in Therapeutics. Cancers 2019, 11, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, A.; Munari, F.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, R.; Scolaro, T.; Castegna, A. The Metabolic Signature of Macrophage Responses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Nair, M.G. Macrophages in Wound Healing: Activation and Plasticity. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-D.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, Y.-M.; Ku, Y.; Seol, Y.-J. Periodontal Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration: A Narrative Review. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of Fibrosis: Therapeutic Translation for Fibrotic Disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Agrawal, S.; Gupta, S. Role of Dendritic Cells in Inflammation and Loss of Tolerance in the Elderly. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Chen, L.; Wei, X. Inflammatory Cytokines in Cancer: Comprehensive Understanding and Clinical Progress in Gene Therapy. Cells 2021, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berraondo, P.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Ochoa, M.C.; Etxeberria, I.; Aznar, M.A.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Castañón, E.; Melero, I. Cytokines in Clinical Cancer Immunotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Brand, D.D.; Zheng, S.G. Role of TNF–TNF Receptor 2 Signal in Regulatory T Cells and Its Therapeutic Implications. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masucci, M.T.; Minopoli, M.; Carriero, M.V. Tumor Associated Neutrophils. Their Role in Tumorigenesis, Metastasis, Prognosis and Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Chen, Y.; Lang, Y.; Cui, L. The Role of Cellular Prion Protein in Cancer Biology: A Potential Therapeutic Target. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 742949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasek, W.; Zagożdżon, R.; Jakobisiak, M. Interleukin 12: Still a Promising Candidate for Tumor Immunotherapy? Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014, 63, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.G.; Vrabel, M.R.; Mantooth, S.M.; Hopkins, J.J.; Wagner, E.S.; Gabaldon, T.A.; Zaharoff, D.A. Localized Interleukin-12 for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.D.; Nedjai, B.; Hurst, T.; Pennington, D.J. Cytokines and Chemokines: At the Crossroads of Cell Signalling and Inflammatory Disease. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy, R.; Pollard, J.W. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: From Mechanisms to Therapy. Immunity 2014, 41, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.; Kershaw, N.J.; Babon, J.J. The Molecular Details of Cytokine Signaling via the JAK/STAT Pathway: Cytokine Signaling via the JAK/STAT Pathway. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1984–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, K.J.; Houston, A.; Brint, E. IL-1 Family Members in Cancer; Two Sides to Every Story. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prete, A.; Allavena, P.; Santoro, G.; Fumarulo, R.; Corsi, M.M.; Mantovani, A. Molecular Pathways in Cancer-Related Inflammation. Biochem. Med. 2011, 21, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, W.A. Getting Leukocytes to the Site of Inflammation. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, R.J.; Etemadi, N.; Yeo, B.; Ernst, M. Challenging a Misnomer? The Role of Inflammatory Pathways in Inflammatory Breast Cancer. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 4754827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Shu, H.-K.G. Transcription Factor Interactions Mediate EGF-Dependent COX-2 Expression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Semenza, G.L.; Zhang, H. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and Breast Cancer Metastasis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2015, 16, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgillo, F.; Dallio, M.; Della Corte, C.M.; Gravina, A.G.; Viscardi, G.; Loguercio, C.; Ciardiello, F.; Federico, A. Carcinogenesis as a Result of Multiple Inflammatory and Oxidative Hits: A Comprehensive Review from Tumor Microenvironment to Gut Microbiota. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrad, J.E.; Lichtiger, S.; Yajnik, V. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Cancer: The Role of Inflammation, Immunosuppression, and Cancer Treatment. WJG 2016, 22, 4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofi, T.; Zaravinos, A. RNA Editing in the Forefront of Epitranscriptomics and Human Health. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, J.; Marusawa, H.; Machimoto, T.; Endo, Y.; Kinoshita, K.; Kou, T.; Haga, H.; Ikai, I.; Uemoto, S.; Chiba, T. Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase Links Bile Duct Inflammation to Human Cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2008, 47, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-ΚB Signaling in Inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orecchioni, M.; Ghosheh, Y.; Pramod, A.B.; Ley, K. Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS–) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Hong, J. Roles of NF-ΚB in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases and Their Therapeutic Approaches. Cells 2016, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicher, K.L.; Willmarth, N.E.; Garcia, J.; Boerner, J.L.; Dewey, T.G.; Ethier, S.P. Activation of a Nuclear Factor ΚB/Interleukin-1 Positive Feedback Loop by Amphiregulin in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bonito, M.; Cantile, M.; Botti, G. Pathological and Molecular Characteristics of Inflammatory Breast Cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, S449–S456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seif, F.; Khoshmirsafa, M.; Aazami, H.; Mohsenzadegan, M.; Sedighi, G.; Bahar, M. The Role of JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway and Its Regulators in the Fate of T Helper Cells. Cell Commun. Signal 2017, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, X.-F. Signaling Cross-Talk between TGF-β/BMP and Other Pathways. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolomeo, M.; Cascio, A. The Multifaced Role of STAT3 in Cancer and Its Implication for Anticancer Therapy. IJMS 2021, 22, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkenbaugh, A.; Baldwin, A. The NF-ΚB Pathway and Cancer Stem Cells. Cells 2016, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Fu, S.; Wu, J. Coordinated Regulation of Immune Contexture: Crosstalk between STAT3 and Immune Cells during Breast Cancer Progression. Cell Commun. Signal 2021, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, J.S.; Hunter, C.A. Gp130 at the Nexus of Inflammation, Autoimmunity, and Cancer. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, M.; Thiem, S.; Nguyen, P.M.; Eissmann, M.; Putoczki, T.L. Epithelial Gp130/Stat3 Functions: An Intestinal Signaling Node in Health and Disease. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, C.F.; Weigelt, B.; Sakr, R.A.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Hicks, J.; King, T.A.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Progression from Ductal Carcinoma in Situ to Invasive Breast Cancer: Revisited. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolewski, C.; Cerella, C.; Dicato, M.; Ghibelli, L.; Diederich, M. The Role of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Cell Proliferation and Cell Death in Human Malignancies. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 2010, 215158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salleh, N. Diverse Roles of Prostaglandins in Blastocyst Implantation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 968141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørregaard, R.; Kwon, T.-H.; Frøkiær, J. Physiology and Pathophysiology of Cyclooxygenase-2 and Prostaglandin E2 in the Kidney. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 34, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finetti, F.; Travelli, C.; Ercoli, J.; Colombo, G.; Buoso, E.; Trabalzini, L. Prostaglandin E2 and Cancer: Insight into Tumor Progression and Immunity. Biology 2020, 9, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.-J.; Mbonye, U.R.; DeLong, C.J.; Wada, M.; Smith, W.L. Regulation of Intracellular Cyclooxygenase Levels by Gene Transcription and Protein Degradation. Prog. Lipid Res. 2007, 46, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cabalag, C.S.; Clemons, N.J.; DuBois, R.N. Cyclooxygenases and Prostaglandins in Tumor Immunology and Microenvironment of Gastrointestinal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1813–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorente Izquierdo, C.; Mayoral, R.; Flores, J.M.; García-Palencia, P.; Cucarella, C.; Boscá, L.; Casado, M.; Martín-Sanz, P. Transgenic Mice Expressing Cyclooxygenase-2 in Hepatocytes Reveal a Minor Contribution of This Enzyme to Chemical Hepatocarcinogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farazi, P.A.; DePinho, R.A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Pathogenesis: From Genes to Environment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.-S.; Niu, X.-J.; Wang, W.-H. Genetic Alterations in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Update. WJG 2016, 22, 9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarocchi, M. Molecular Mechanism of Hepatitis B Virus-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis. WJG 2014, 20, 11630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miuma, S.; Miyamoto, J.; Taura, N.; Fukushima, M.; Sasaki, R.; Haraguchi, M.; Shibata, H.; Sato, S.; Miyaaki, H.; Nakao, K. Influence of Interferon-Free Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy on Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence: A Landmark Time Analysis and Time-Dependent Extended Cox Proportional Hazards Model Analysis. Intern. Med. 2020, 59, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guirgis, B.S.S.; Sá e Cunha, C.; Gomes, I.; Cavadas, M.; Silva, I.; Doria, G.; Blatch, G.L.; Baptista, P.V.; Pereira, E.; Azzazy, H.M.E.; et al. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Fluorescence Immunoassay for Malaria Antigen Detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpin, L.B.; Bickford, L.R.; Agollah, G.; Yu, T.-K.; Schiff, R.; Li, Y.; Drezek, R.A. Immunoconjugated Gold Nanoshell-Mediated Photothermal Ablation of Trastuzumab-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 125, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Tian, J.; Chen, X. Recent Advances in High-Performance Fluorescent and Bioluminescent RNA Imaging Probes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2824–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negahdari, B.; Darvishi, M.; Saeedi, A.A. Gold Nanoparticles and Hepatitis B Virus. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wu, X.; Li, C.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, T.; Yang, F. Targeting Selenium Nanoparticles Combined with Baicalin to Treat HBV-Infected Liver Cancer. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 8178–8185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, D.; Joshi, N.; Tao, W.; Karp, J.M.; Peer, D. Progress and Challenges towards Targeted Delivery of Cancer Therapeutics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devulapally, R.; Foygel, K.; Sekar, T.V.; Willmann, J.K.; Paulmurugan, R. Gemcitabine and Antisense-MicroRNA Co-Encapsulated PLGA–PEG Polymer Nanoparticles for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 33412–33422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Irfan, M.; Ramgir, N.; Muthe, K.P.; Debnath, A.K.; Ansari, S.; Gandhi, J.; Ranjith-Kumar, C.T.; Surjit, M. Antiviral Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Tetrapods Against the Hepatitis E and Hepatitis C Viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 881595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, M.S.; Shafiee, H. Applications of Gold Nanoparticles in Virus Detection. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1985–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shady, N.H.; Khattab, A.R.; Ahmed, S.; Liu, M.; Quinn, R.J.; Fouad, M.A.; Kamel, M.S.; Muhsinah, A.B.; Krischke, M.; Mueller, M.J.; et al. Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Protease and Helicase Inhibitors from Red Sea Sponge (Amphimedon) Species in Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Assisted by in Silico Modeling and Metabolic Profiling. IJN 2020, 15, 3377–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Sun, R.W.-Y.; Chen, R.; Hui, C.-K.; Ho, C.-M.; Luk, J.M.; Lau, G.K.; Che, C.-M. Silver Nanoparticles Inhibit Hepatitis B Virus Replication. Antivir. Ther. 2008, 13, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Wahab, R. Silver Nanoparticles: An Instantaneous Solution for Anticancer Activity against Human Liver (HepG2) and Breast (MCF-7) Cancer Cells. Metals 2022, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, A.; Roushani, M. Using Silver Nanoparticle and Thiol Graphene Quantum Dots Nanocomposite as a Substratum to Load Antibody for Detection of Hepatitis C Virus Core Antigen: Electrochemical Oxidation of Riboflavin Was Used as Redox Probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin-Jumah, M.; AL-Abdan, M.; Albasher, G.; Alarifi, S. Effects of Green Silver Nanoparticles on Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress in Normal and Cancerous Human Hepatic Cells in Vitro. IJN 2020, 15, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truffi, M.; Sevieri, M.; Morelli, L.; Monieri, M.; Mazzucchelli, S.; Sorrentino, L.; Allevi, R.; Bonizzi, A.; Zerbi, P.; Marchini, B.; et al. Anti-MAdCAM-1-Conjugated Nanocarriers Delivering Quantum Dots Enable Specific Imaging of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. IJN 2020, 15, 8537–8552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Viennois, E.; Prasad, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Han, M.K.; Xiao, B.; Xu, C.; Srinivasan, S.; et al. Edible Ginger-Derived Nanoparticles: A Novel Therapeutic Approach for the Prevention and Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colitis-Associated Cancer. Biomaterials 2016, 101, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Wong, K.Y.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Begun, J.; Santos, H.A.; Hasnain, S.Z.; Kumeria, T.; McGuckin, M.A.; Popat, A. One-Pot Synthesis of PH-Responsive Eudragit-Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposites Enable Colonic Delivery of Glucocorticoids for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Adv. Ther. 2021, 4, 2000165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naha, P.C.; Hsu, J.C.; Kim, J.; Shah, S.; Bouché, M.; Si-Mohamed, S.; Rosario-Berrios, D.N.; Douek, P.; Hajfathalian, M.; Yasini, P.; et al. Dextran-Coated Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles: A Computed Tomography Contrast Agent for Imaging the Gastrointestinal Tract and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10187–10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, E.; Zauszkiewicz-Pawlak, A.; Wojcik, M.; Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I. Silver Nanoparticles of Different Sizes Induce a Mixed Type of Programmed Cell Death in Human Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 4675–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, L.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Yang, S. Small Gold Nanorods: Recent Advances in Synthesis, Biological Imaging, and Cancer Therapy. Materials 2017, 10, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, S.; Tao, Z.; Wang, C.; Huang, M.; Zhang, X. PEGylated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Apoptosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cells through Reactive Oxygen Species. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 13, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Xiong, X.; Chakraborty, P.K.; Shameer, K.; Arvizo, R.R.; Kudgus, R.A.; Dwivedi, S.K.D.; Hossen, M.N.; Gillies, E.M.; Robertson, J.D.; et al. Gold Nanoparticle Reprograms Pancreatic Tumor Microenvironment and Inhibits Tumor Growth. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10636–10651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnam, N.M.; Peterson, J.M.; Talbert, E.E.; Ladner, K.J.; Rajasekera, P.V.; Schmidt, C.R.; Dillhoff, M.E.; Swanson, B.J.; Haverick, E.; Kladney, R.D.; et al. NF-ΚB Regulates GDF-15 to Suppress Macrophage Surveillance during Early Tumor Development. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3796–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, L.H.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.-S.; Muñoz, N.M.; Majumdar, A.; Chen, J.; Mishra, L. Targeting TGF-β Signaling in Cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, K.; Normann, L.; Sendler, M.; Käding, A.; Heidecke, C.-D.; Partecke, L.I.; von Bernstorff, W. TRAIL Promotes Tumor Growth in a Syngeneic Murine Orthotopic Pancreatic Cancer Model and Affects the Host Immune Response. Pancreas 2016, 45, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Bai, B.; Sha, S.; Yu, P.; An, Y.; Wang, S.; Kong, X.; Liu, C.; Wei, N.; Feng, Q. Interleukin-1β Induces Autophagy by Affecting Calcium Homeostasis and Trypsinogen Activation in Pancreatic Acinar Cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 3620. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Pierre-Pierre, N.; Yan, X.; Huo, Q.; Almodovar, A.J.O.; Valerio, F.; Rivera-Ramirez, I.; Griffith, E.; Decker, D.D.; Chen, S.; et al. Gold Nanoparticle-Enabled Blood Test for Early Stage Cancer Detection and Risk Assessment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6819–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobetz, M.A.; Chan, D.S.; Neesse, A.; Bapiro, T.E.; Cook, N.; Frese, K.K.; Feig, C.; Nakagawa, T.; Caldwell, M.E.; Zecchini, H.I.; et al. Hyaluronan Impairs Vascular Function and Drug Delivery in a Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Gut 2013, 62, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Crawford, A.J.; Wojtynek, N.E.; Holmes, M.B.; Souchek, J.J.; Almeida-Porada, G.; Ly, Q.P.; Cohen, S.M.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; Mohs, A.M. Indocyanine Green Loaded Hyaluronan-Derived Nanoparticles for Fluorescence-Enhanced Surgical Imaging of Pancreatic Cancer. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, C.; Yu, X.; Wu, L. Hyaluronic Acid-Mediated Multifunctional Iron Oxide-Based MRI Nanoprobes for Dynamic Monitoring of Pancreatic Cancer. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 10486–10493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdy, S.; Molavi, O.; Ma, Z.; Haddadi, A.; Alshamsan, A.; Gobti, Z.; Elhasi, S.; Samuel, J.; Lavasanifar, A. Co-Delivery of Cancer-Associated Antigen and Toll-like Receptor 4 Ligand in PLGA Nanoparticles Induces Potent CD8+ T Cell-Mediated Anti-Tumor Immunity. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5046–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Kim, J.A.; Huang, A.Y.-C. Optimizing Tumor Microenvironment for Cancer Immunotherapy: β-Glucan-Based Nanoparticles. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Jiang, J.; Wan, C.; Pan, G.; Kong, F.; Zhai, R.; Hu, C.; Ying, H. AntiPD-L1 Antibody Conjugated Au-SPIOs Nanoplatform for Enhancing Radiosensitivity and Triggering Anti-Tumor Immune Response. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, D.; Park, C.G.; Hartl, C.A.; Subedi, N.; Cartwright, A.N.; Puerto, R.B.; Zheng, Y.; Maiarana, J.; Freeman, G.J.; Wucherpfennig, K.W. T Cell-Targeting Nanoparticles Focus Delivery of Immunotherapy to Improve Antitumor Immunity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Chau, E.; Mishra, A.; DeAnda, A.; Hegde, V.L.; Sastry, J.K.; Haviland, D.; Jagannath, C.; Godin, B.; Khan, A. CD44 Receptor Targeted Nanoparticles Augment Immunity against Tuberculosis in Mice. J. Control. Release 2022, 349, 796–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Chan, C.; Guo, N.; Han, W.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Lin, W. Photodynamic Therapy Mediated by Nontoxic Core–Shell Nanoparticles Synergizes with Immune Checkpoint Blockade to Elicit Antitumor Immunity and Antimetastatic Effect on Breast Cancer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16686–16695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, F.; Yu, S.; Xu, Z.; Wang, F.; Liu, X. Enhanced Immunostimulatory Activity of a Cytosine-Phosphate-Guanosine Immunomodulator by the Assembly of Polymer DNA Wires and Spheres. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 17167–17176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perica, K.; Medero, A.D.L.; Durai, M.; Chiu, Y.L.; Bieler, J.G.; Sibener, L.; Niemöller, M.; Assenmacher, M.; Richter, A.; Edidin, M. Nanoscale Artificial Antigen Presenting Cells for T Cell Immunotherapy. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, K.; Bednarkiewicz, A.; Liu, X.; Jin, D. Advances in Highly Doped Upconversion Nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Dumlupinar, G.; Andersson-Engels, S.; Melgar, S. Emerging Applications of Upconverting Nanoparticles in Intestinal Infection and Colorectal Cancer. IJN 2019, 14, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, H.; Sepahy, A.A.; Amini, K.; Saadatmand, S. The Effect of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Synthesized by Bacillus Tequilensis on Clb Gene Expression of Colorectal Cancer-Causing Escherichia Coli. Arch. Pharm. Pract. 2020, 11, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Movagharnia, R.; Baghbani-Arani, F.; Sadat Shandiz, S.A. Cytotoxicity Effects of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles on Human Colon Cancer (HT29) Cells. KAUMS J. 2018, 22, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sadalage, P.S.; Patil, R.V.; Havaldar, D.V.; Gavade, S.S.; Santos, A.C.; Pawar, K.D. Optimally Biosynthesized, PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized with Quercetin and Camptothecin Enhance Potential Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Cancer and Anti-Angiogenic Activities. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Guo, A.; Xu, J.; You, Q.-D.; Xu, X.-L. Discovery of a Potent Grp94 Selective Inhibitor with Anti-Inflammatory Efficacy in a Mouse Model of Ulcerative Colitis. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 9513–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sohrab, S.S.; Raj, R.; Nagar, A.; Hawthorne, S.; Paiva-Santos, A.C.; Kamal, M.A.; El-Daly, M.M.; Azhar, E.I.; Sharma, A. Chronic Inflammation’s Transformation to Cancer: A Nanotherapeutic Paradigm. Molecules 2023, 28, 4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114413
Sohrab SS, Raj R, Nagar A, Hawthorne S, Paiva-Santos AC, Kamal MA, El-Daly MM, Azhar EI, Sharma A. Chronic Inflammation’s Transformation to Cancer: A Nanotherapeutic Paradigm. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114413
Chicago/Turabian StyleSohrab, Sayed Sartaj, Riya Raj, Amka Nagar, Susan Hawthorne, Ana Cláudia Paiva-Santos, Mohammad Amjad Kamal, Mai M. El-Daly, Esam I. Azhar, and Ankur Sharma. 2023. "Chronic Inflammation’s Transformation to Cancer: A Nanotherapeutic Paradigm" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114413
APA StyleSohrab, S. S., Raj, R., Nagar, A., Hawthorne, S., Paiva-Santos, A. C., Kamal, M. A., El-Daly, M. M., Azhar, E. I., & Sharma, A. (2023). Chronic Inflammation’s Transformation to Cancer: A Nanotherapeutic Paradigm. Molecules, 28(11), 4413. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114413










