Methylene Blue Dye Adsorption on Iron Oxide-Hydrochar Composite Synthesized via a Facile Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Carbonization of Pomegranate Peels’ Waste
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
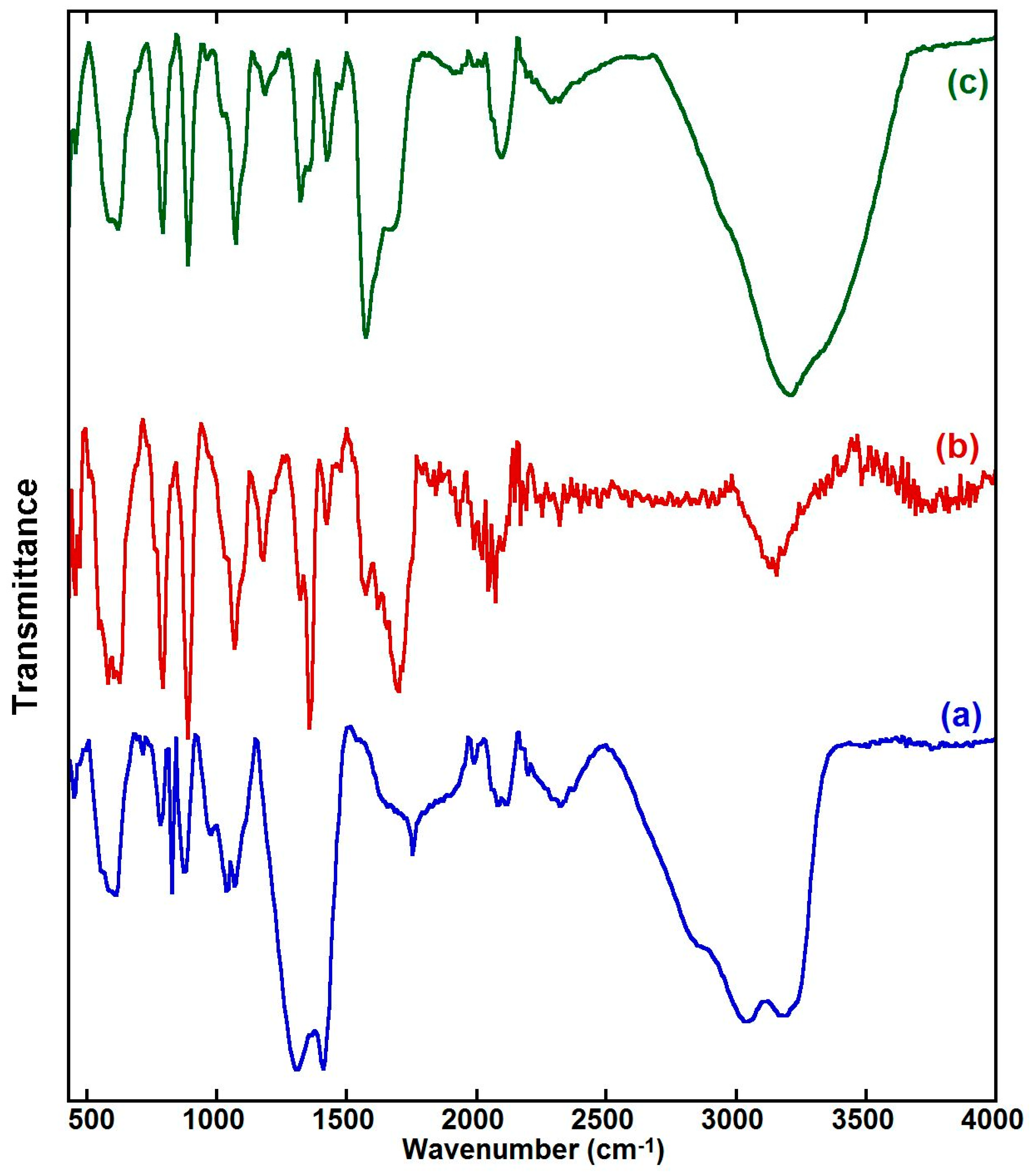
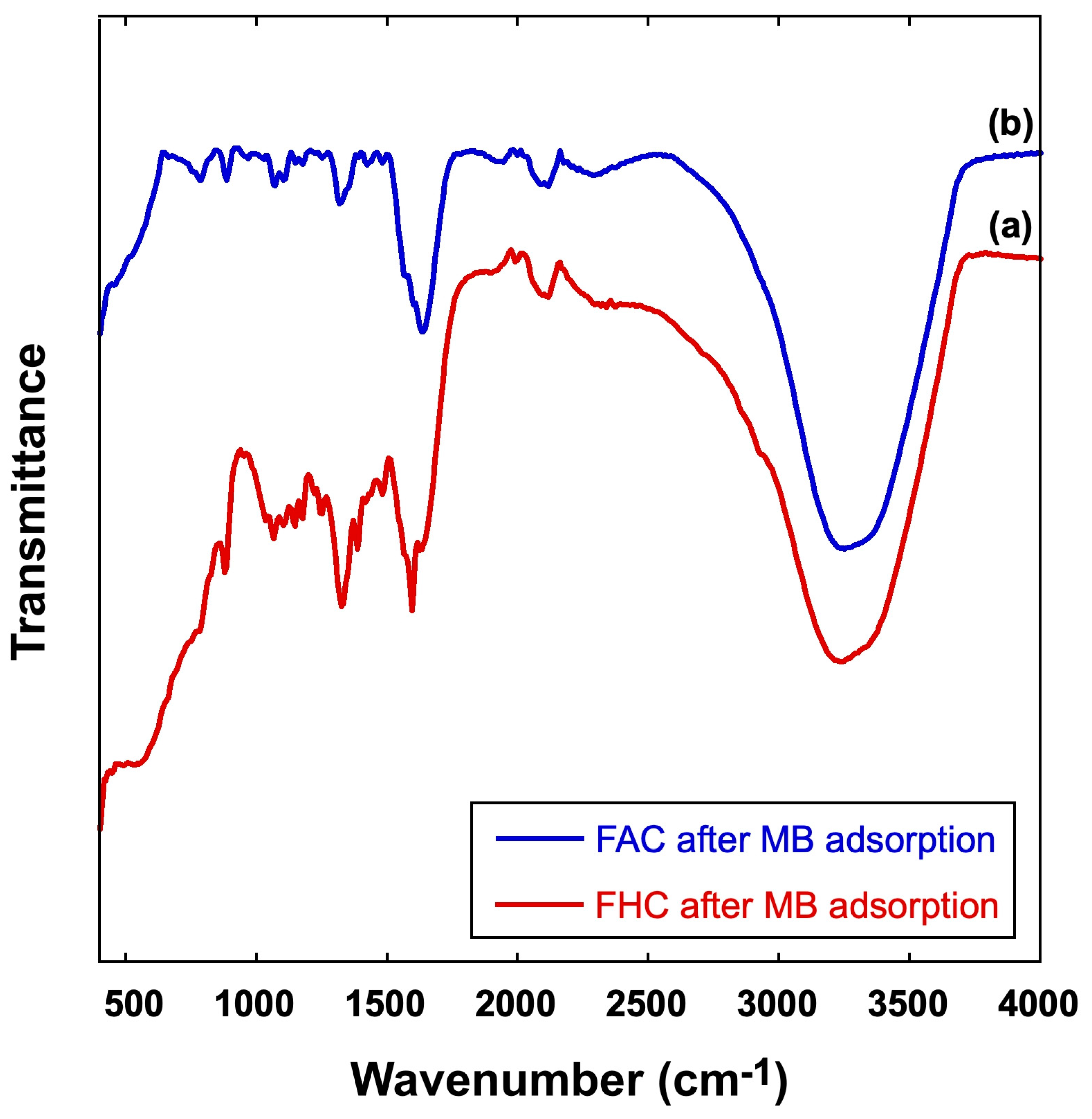
2.1. FT-IR Characterization of Prepared Samples
2.2. XRD Characterization of Prepared Samples
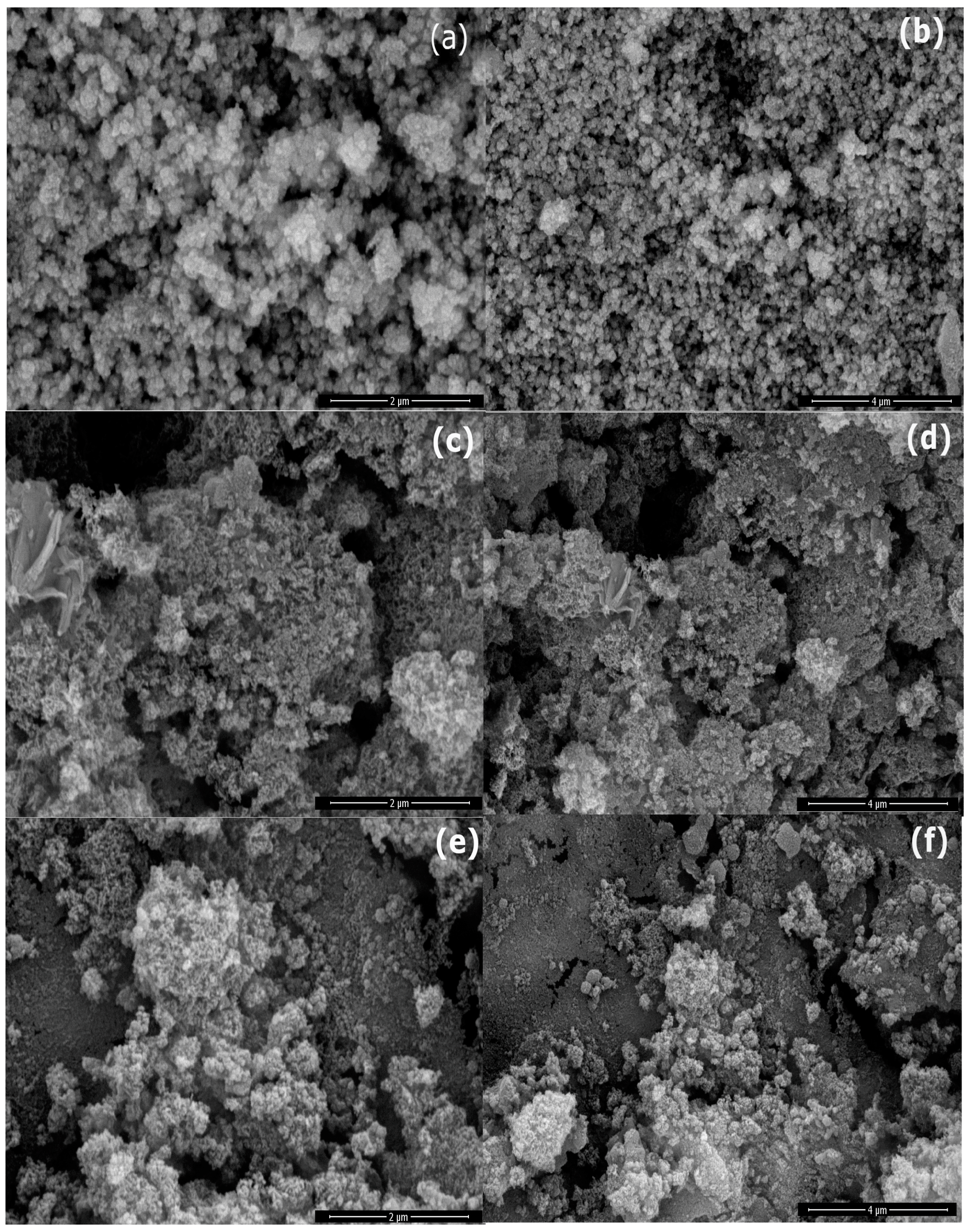
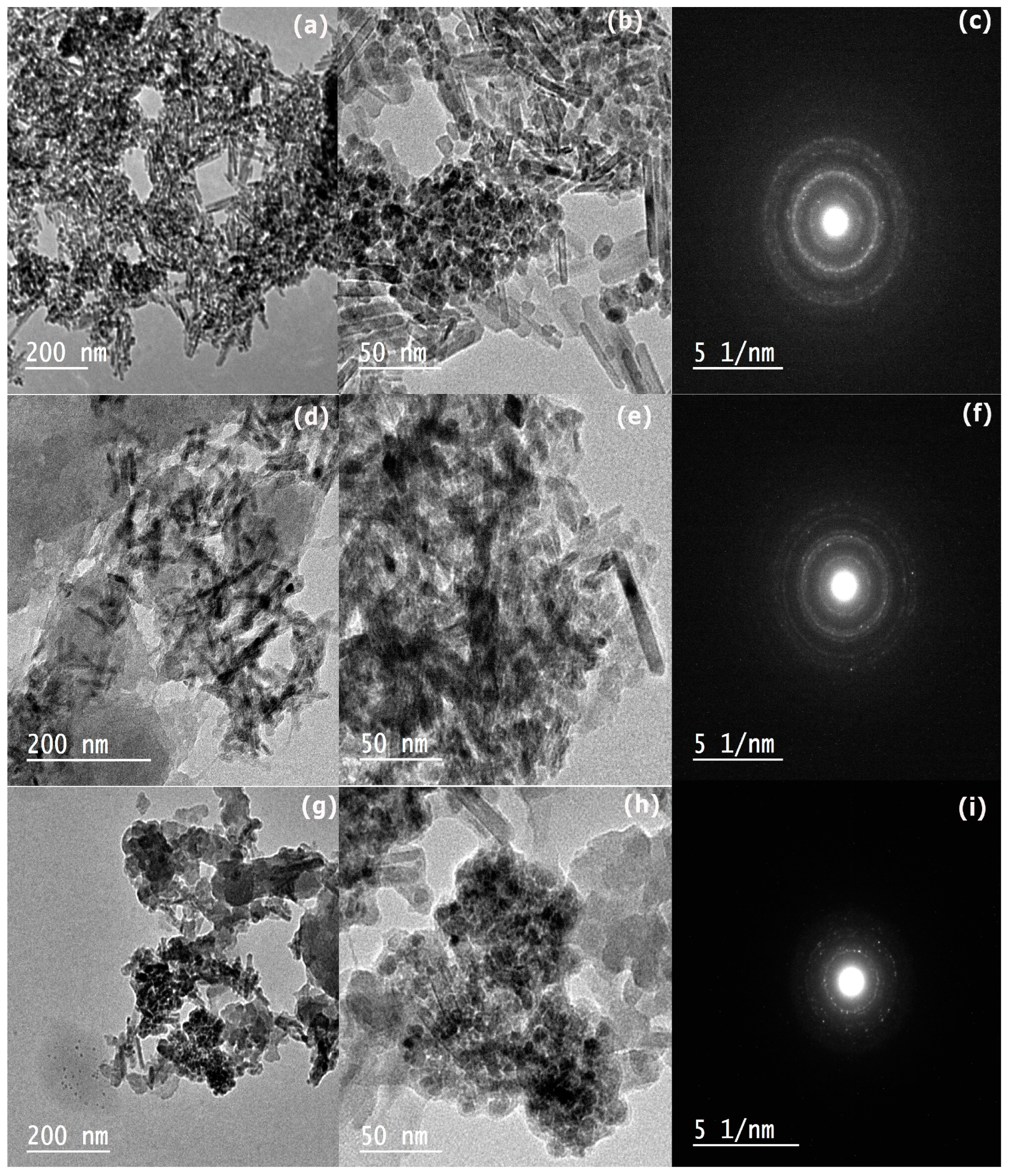
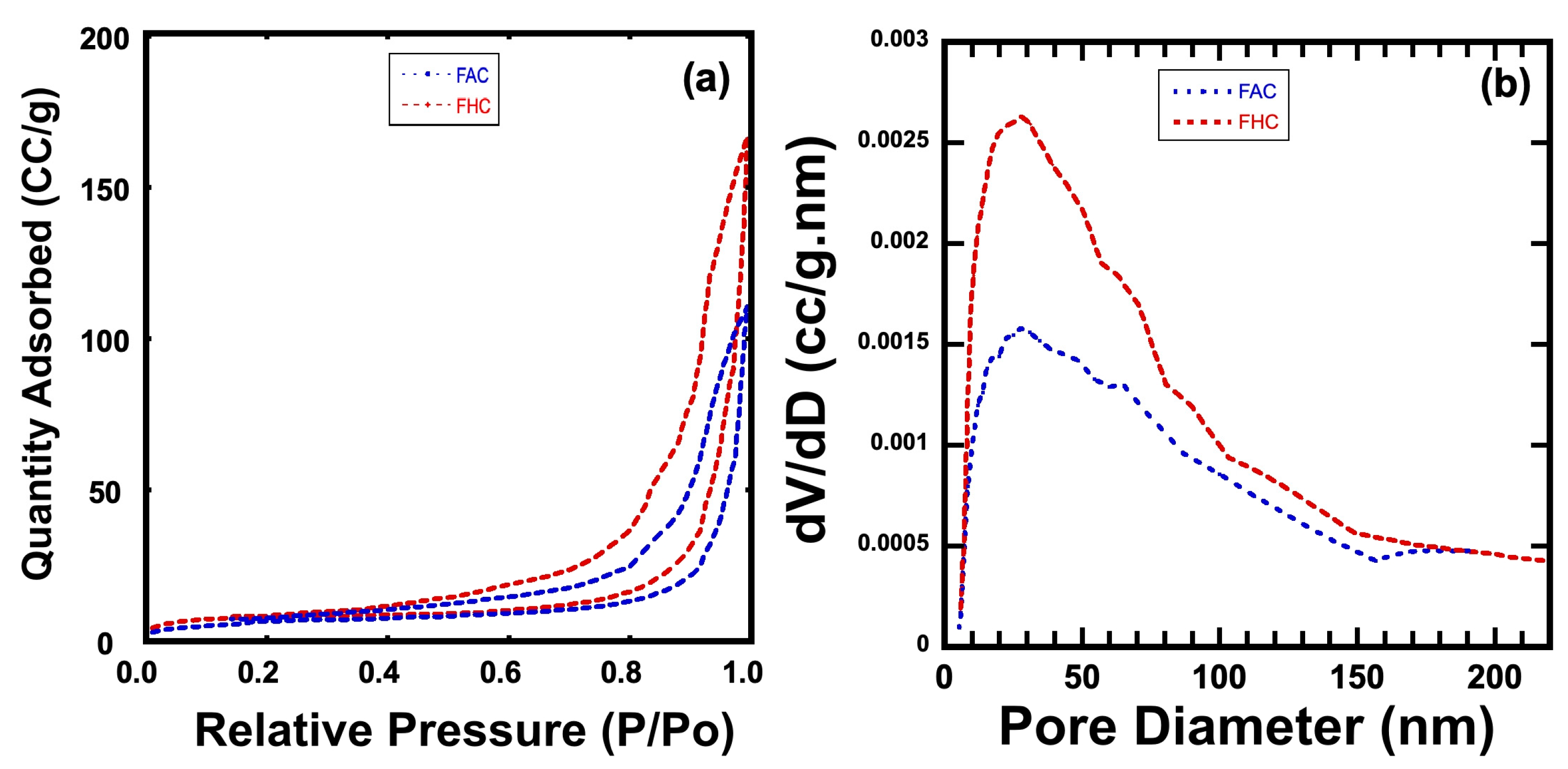
2.3. Morphology of Prepared Samples
2.4. The pH of Point of Zero Charge (pHpzc)
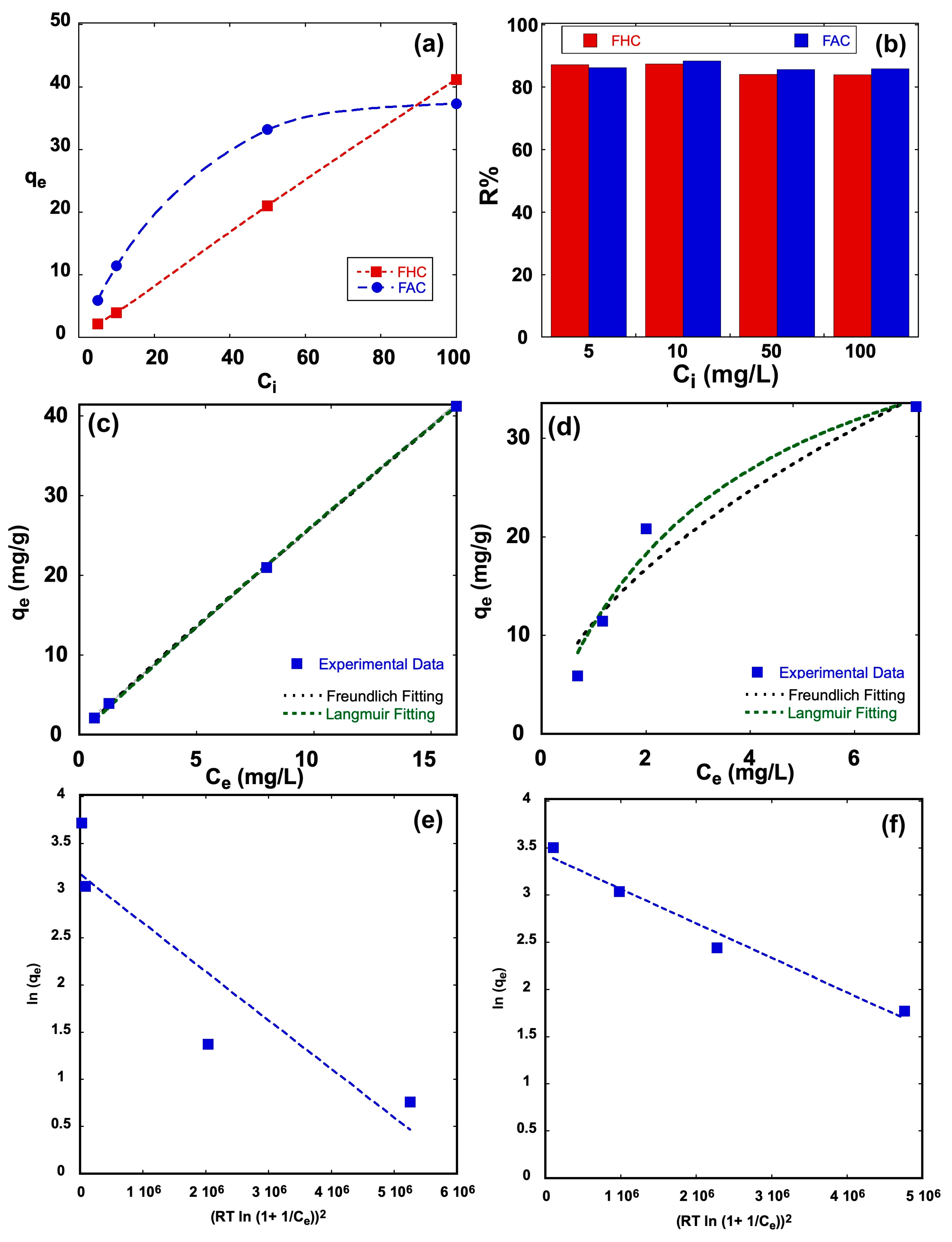
2.5. Adsorption Equilibrium of Methylene Blue Dye
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Iron Oxide (F)
3.2. Preparation of Iron Oxide-Hydrochar Composite (FHC)
3.3. Preparation of Iron Oxide-Activated Hydrochar Composite (FAC)
3.4. Determining the pH of Point of Zero Charge (pHpzc)
3.5. Adsorption Equilibrium of Methylene Blue Dye
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- HasdemİR, Z.M.; ŞİMŞEk, S. Removal of Cationic Dye in Aquatic Medium by Using a New Composite Material. Cumhur. Sci. J. 2018, 39, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalaf, M.M.; Da’na, E.; Al-Amer, K.; Hessien, M. Experimental Design Modeling of the Effect of Hexagonal Wurtzite-ZnO Synthesis Conditions on Its Characteristics and Performance as a Cationic and Anionic Adsorbent. Molecules 2019, 24, 3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Tian, F.; Zou, H.; Ye, Z.; Peng, C.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, X.; et al. ZnO/biochar nanocomposites via solvent free ball milling for enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Guo, J.; Lv, K.; Fan, J. Adsorption of methylene blue and Cd(II) onto maleylated modified hydrochar from water. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauletto, P.S.; Moreno-Perez, J.; Hernandez-Hernandez, L.E.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Dotto, G.L.; Salau, N.P.G. Novel biochar and hydrochar for the adsorption of 2-nitrophenol from aqueous solutions: An approach using the PVSDM model. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessien, M. Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Carbonization of Pomegranate Peels into Hydrochar for Environmental Applications. Energies 2022, 15, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Jadhao, P.; Kumari, K. Clay nano-adsorbent: Structures, applications and mechanism for water treatment. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prajapati, A.K.; Mondal, M.K. Novel green strategy for CuO-ZnO-C nanocomposites fabrication using marigold (Tagetes spp.) flower petals extract with and without CTAB treatment for adsorption of Cr(VI) and Congo red dye. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño, A.A.B.; Lassalle, V.L.; Horst, M.F. Magnetic hydrochar nanocomposite obtained from sunflower husk: A potential material for environmental remediation. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1239, 130509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da’na, E.; Taha, A.; Hessien, M. Application of ZnO–NiO greenly synthesized nanocomposite adsorbent on the elimination of organic dye from aqueous solutions: Kinetics and equilibrium. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 4531–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lu, B.; Xian, J.; Tsang, E.P.; Cheng, W.; Fang, J.; Fang, Z. Magnetic biochar for environmental remediation: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticle by tea extract (polyphenols) and its selective removal of cationic dyes. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 275, 111262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Zou, W.; He, F.; Hu, X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Gao, B. Biochar technology in wastewater treatment: A critical review. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomul, F.; Arslan, Y.; Kabak, B.; Trak, D.; Kenduzler, E.; Lima, E.C.; Tran, H.N. Peanut shells-derived biochars prepared from different carbonization processes: Comparison of characterization and mechanism of naproxen adsorption in water. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 726, 137828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, J.; Dey, B.; Dey, S. Sucrose-Triggered, Self-Sustained Combustive Synthesis of Magnetic Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles and Efficient Removal of Malachite Green from Water. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16510–16520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jee, S.C.; Sung, J.S.; Kadam, A.A. Supermagnetic Sugarcane Bagasse Hydrochar for Enhanced Osteoconduction in Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.; McGregor, J. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Biomass-Derived Magnetic Carbon Composites for Adsorption and Catalysis. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 33000–33009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Zhang, P.; Fan, M.; Xu, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Sun, H. Efficient degradation of p-nitrophenol by Fe@pomelo peel-derived biochar composites and its mechanism of simultaneous reduction and oxidation process. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Xiong, Y. Synthesis and characterization of rice husk-based magnetic porous carbon by pyrolysis of pretreated rice husk with FeCl3 and ZnCl2. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 147, 104806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faradilla, R.F.; Lucia, L.; Hakovirta, M. Remarkable Physical and Thermal Properties of Hydrothermal Carbonized Nanoscale Cellulose Observed from Citric Acid Catalysis and Acetone Rinsing. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Volpe, M.; Fiori, L.; Volpe, R.; Messineo, A.; Reza, M.T. Cationic Dye Adsorption on Hydrochars of Winery and Citrus Juice Industries Residues: Performance, Mechanism, and Thermodynamics. Energies 2020, 13, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, M.P.; Volpe, M.; Messineo, A. Hydrothermal Carbonization as a Valuable Tool for Energy and Environmental Applications: A Review. Energies 2020, 13, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Hu, X.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J.; Gao, B. One-pot synthesis and characterization of engineered hydrochar by hydrothermal carbonization of biomass with ZnCl2. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Kannan, S.; Raghavan, V. Uncatalyzed and acid-aided microwave hydrothermal carbonization of orange peel waste. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Remón, J.; Matharu, A.S. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal treatments for biomass valorisation: A critical review. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 3502–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamuddin, S.; Qureshi, S.S.; Baloch, H.A.; Siddiqui, M.T.H.; Takkalkar, P.; Mubarak, N.M.; Dumbre, D.K.; Griffin, G.J.; Madapusi, S.; Tanksale, A. Microwave Hydrothermal Carbonization of Rice Straw: Optimization of Process Parameters and Upgrading of Chemical, Fuel, Structural and Thermal Properties. Materials 2019, 12, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, L.; He, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, R.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, D.; Fan, L.; Zhao, Y. Hydrothermal pretreatment of bamboo sawdust using microwave irradiation. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semerciöz, A.S.; Göğüş, F.; Çelekli, A.; Bozkurt, H. Development of carbonaceous material from grapefruit peel with microwave implemented-low temperature hydrothermal carbonization technique for the adsorption of Cu (II). J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Li, N.; Ni, G.R.; Zhou, C.H.; Yin, X.; Huang, H.J. Recycling Pomelo Peel Waste in the Form of Hydrochar Obtained by Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Carbonization. Materials 2022, 15, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.T.H.; Chan, F.L.; Nizamuddin, S.; Baloch, H.A.; Kundu, S.; Czajka, M.; Griffin, G.J.; Tanksale, A.; Shah, K.; Srinivasan, M. Comparative study of microwave and conventional solvothermal synthesis for magnetic carbon nanocomposites and bio-oil from rice husk. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazak, O.; Tor, A. In situ preparation of magnetic hydrochar by co-hydrothermal treatment of waste vinasse with red mud and its adsorption property for Pb(II) in aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, Y.P.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Kuwano, N.; Bt Ahmad Khairudin, N.B.; Bt Mohamad, S.E.; Lee, K.X. Green Synthesis of Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles Using Seaweed (Kappaphycus alvarezii) Extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoia, M.; Istratie, R.; Păcurariu, C. Investigation of magnetite nanoparticles stability in air by thermal analysis and FTIR spectroscopy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 125, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.D.; Kynicky, J.; Ambrozova, P.; Adam, V. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Goethite Nanoparticles Used for Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution. Materials 2017, 10, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veltri, F.; Alessandro, F.; Scarcello, A.; Beneduci, A.; Arias Polanco, M.; Cid Perez, D.; Vacacela Gomez, C.; Tavolaro, A.; Giordano, G.; Caputi, L.S. Porous Carbon Materials Obtained by the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Orange Juice. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Qin, Q.; Chen, G.; Wang, W. Alkali Etching Hydrochar-Based Adsorbent Preparation Using Chinese Medicine Industry Waste and Its Application in Efficient Removal of Multiple Pollutants. Processes 2023, 11, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Ahmed, M.J.; Khanday, W.A.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H. Mesoporous activated carbon prepared from NaOH activation of rattan (Lacosperma secundiflorum) hydrochar for methylene blue removal. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 138, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Lv, J.Q.; Guo, J.Z.; Fu, S.Y.; Guo, M.; Yang, P. The polyaminocarboxylated modified hydrochar for efficient capturing methylene blue and Cu(II) from water. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haddad, M.; Mamouni, R.; Saffaj, N.; Lazar, S. Removal of a cationic dye—Basic Red 12—From aqueous solution by adsorption onto animal bone meal. J. Assoc. Arab. Univ. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 12, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngoc, D.M.; Hieu, N.C.; Trung, N.H.; Chien, H.H.; Thi, N.Q.; Hai, N.D.; Chao, H.-P. Tetracycline Removal from Water by Adsorption on Hydrochar and Hydrochar-Derived Activated Carbon: Performance, Mechanism, and Cost Calculation. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonescu, C.M.; Culita, D.C.; Tatarus, A.; Mocanu, T.; Marinescu, G.; Mitran, R.A.; Atkinson, I.; Kuncser, A.; Stanica, N. Novel Magnetic Nanocomposites Based on Carboxyl-Functionalized SBA-15 Silica for Effective Dye Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarghandi, M.R.; Hadi, M.; Moayedi, S.; Askari, F.B. Two-Parameter Isotherms Of Methyl Orange Sorption By Pinecone Derived Activated Carbon. Iran. J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng. 2009, 6, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Simsek, S.; Derin, Y.; Kaya, S.; Senol, Z.M.; Katin, K.P.; Ozer, A.; Tutar, A. High-Performance Material for the Effective Removal of Uranyl Ion from Solution: Computationally Supported Experimental Studies. Langmuir 2022, 38, 10098–10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Chapter 4—Isotherm models of adsorption processes on adsorbents and nanoadsorbents. In Interface Science and Technology; Saleh, T.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 34, pp. 99–126. [Google Scholar]
- Dada, A.O.; Olalekan, A.P.; Olatunya, A.M.; Dada, O. Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich Isotherms Studies of Equilibrium Sorption of Zn2+ Unto Phosphoric Acid Modified Rice Husk. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 3, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Z. Application of Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm model at the solid/solution interface: A theoretical analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, V.P.; Huynh, T.D.; Le, H.M.; Nguyen, V.D.; Dao, V.A.; Hung, N.Q.; Tuyen, L.A.; Lee, S.; Yi, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; et al. Insight into the adsorption mechanisms of methylene blue and chromium(iii) from aqueous solution onto pomelo fruit peel. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25847–25860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Liu, G.; Liu, B.; Matsumoto, T. Preparation of reed straw hydrochar adsorbent and its environmental impact assessment. City Built Environ. 2023, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Sabar, S.; Ishak, M.A.M.; Wilson, L.D.; Ahmad Norrahma, S.S.; Talari, M.K.; Farhan, A.M. Microwave-assisted preparation of mesoporous-activated carbon from coconut (Cocos nucifera) leaf by H3PO4activation for methylene blue adsorption. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2017, 204, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Li, K.; Hang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, P.; Wei, L.; Xie, C. Efficient removal of methylene blue by activated hydrochar prepared by hydrothermal carbonization and NaOH activation of sugarcane bagasse and phosphoric acid. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 1885–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zeng, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, X.; Liu, W.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, C.; Wang, S. Iron oxide loaded biochar/attapulgite composites derived camellia oleifera shells as a novel bio-adsorbent for highly efficient removal of Cr(VI). J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Fu, L.; Yang, H.; Ouyang, J. Amino-functionalized hierarchical porous SiO2-AlOOH composite nanosheets with enhanced adsorption performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlumberger, C.; Thommes, M. Characterization of Hierarchically Ordered Porous Materials by Physisorption and Mercury Porosimetry—A Tutorial Review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2002181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phatharachindanuwong, C.; Hansupalak, N.; Chareonpanich, M.; Chisti, Y.; Limtrakul, J.; Plank, J. Morphology and adsorption capacity of sodium silicate-based hierarchical porous silica templated on natural rubber: Influence of washing–drying methods. Mater. Lett. 2014, 130, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría, E.; Maestro, A.; Porras, M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; González, C. Preparation of structured meso–macroporous silica materials: Influence of composition variables on material characteristics. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yin, W.; Zhao, T.-L.; Liu, M.; Yao, Q.-Z.; Zhou, G.-T. Efficient Removal of Congo Red, Methylene Blue and Pb(II) by Hydrochar–MgAlLDH Nanocomposite: Synthesis, Performance and Mechanism. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.H.; Le, H.H.; Pham, T.H.; Nguyen, D.T.; La, D.D.; Chang, S.W.; Lee, S.M.; Chung, W.J.; Nguyen, D.D. Comparative study on methylene blue adsorption behavior of coffee husk-derived activated carbon materials prepared using hydrothermal and soaking methods. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, D.I.; Yuliansyah, A.T.; Budiman, A. Adsorption studies of KOH-modified hydrochar derived from sugarcane bagasse for dye removal: Kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic study. Commun. Sci. Technol. 2022, 7, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrik, A.; Matik, M.; Lovás, M.; Štefušová, K.; Danková, Z.; Hredzák, S.; Václavíková, M.; Bendek, F.; Briančin, J.; Machala, L.; et al. One-step microwave synthesis of magnetic biochars with sorption properties. Carbon Lett. 2018, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Ahmed, M.J.; Khanday, W.A.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H. Mesoporous activated coconut shell-derived hydrochar prepared via hydrothermal carbonization-NaOH activation for methylene blue adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessien, M.; Leone, P.; Suchaud, M.; LeBeau, B.; Nouali, H.; Guari, Y.; Prouzet, E. Nanocrystalline iron oxide synthesised within Hierarchical Porous Silica prepared by nanoemulsion templating. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10022–10024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Langmuir | Freundlich | Dubnin–Radushkevich | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qL | KL | R2 | Kf | nfr | R2 | Qm | E | R2 | |
| FHC | 556.33 | 0.005 | 0.999 | 2.988 | 1.059 | 0.999 | 24.05 | 10.31 | 0.833 |
| FAC | 50.418 | 0.281 | 0.968 | 11.273 | 1.781 | 0.93 | 30.88 | 12.27 | 0.973 |
| Ci (ppm) | 5 | 10 | 50 | 100 | Average RL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FHC | 0.9758 | 0.9527 | 0.8011 | 0.6681 | 0.8615 |
| FAC | 0.4155 | 0.2622 | 0.0664 | 0.03432 | 0.1858 |
| Adsorbents | Synthesis Method | Adsorption | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrochar | Hydrothermal carbonization | R% = 60–80 | [36] |
| Hydrochar-MgAl double hydroxide | Hydrothermal route | qL = 157 mg/g | [56] |
| Activated hydrochar | Hydrothermal carbonization | qL = 357 mg/g | [50] |
| Hydrochar | Hydrothermal carbonization | qL = 5.12 mg/g | [58] |
| Magnetic biochar | Microwave pyrolysis | qL = 144.9 mg/g | [59] |
| Activated Hydrochar | Hydrothermal carbonization | qL = 200.01 mg/g | [60] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hessien, M. Methylene Blue Dye Adsorption on Iron Oxide-Hydrochar Composite Synthesized via a Facile Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Carbonization of Pomegranate Peels’ Waste. Molecules 2023, 28, 4526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114526
Hessien M. Methylene Blue Dye Adsorption on Iron Oxide-Hydrochar Composite Synthesized via a Facile Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Carbonization of Pomegranate Peels’ Waste. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114526
Chicago/Turabian StyleHessien, Manal. 2023. "Methylene Blue Dye Adsorption on Iron Oxide-Hydrochar Composite Synthesized via a Facile Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Carbonization of Pomegranate Peels’ Waste" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114526
APA StyleHessien, M. (2023). Methylene Blue Dye Adsorption on Iron Oxide-Hydrochar Composite Synthesized via a Facile Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Carbonization of Pomegranate Peels’ Waste. Molecules, 28(11), 4526. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114526






