Analysis of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics: A Challenge in Food Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
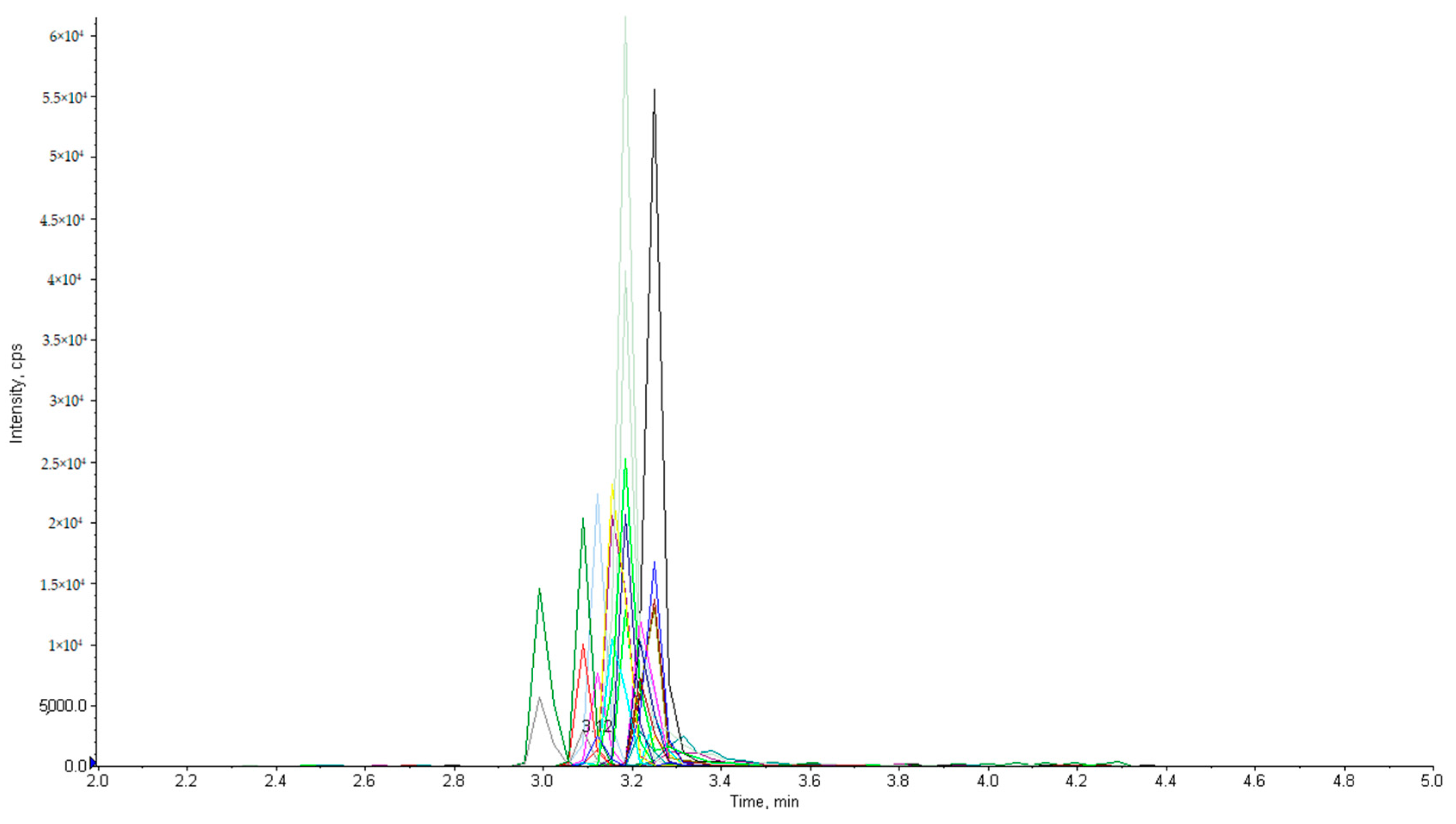
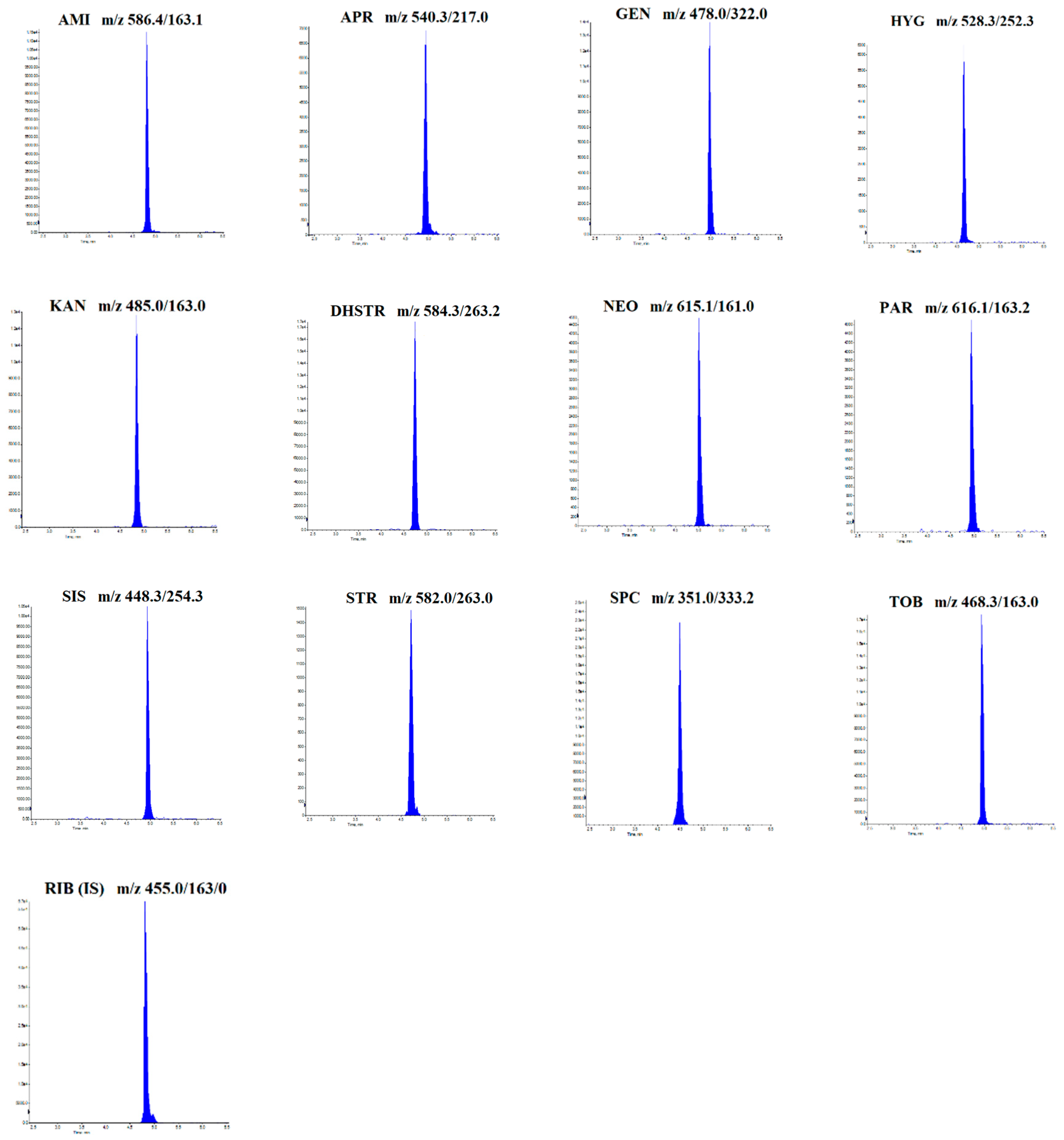
2.1. Optimization of LC-MS/MS Conditions
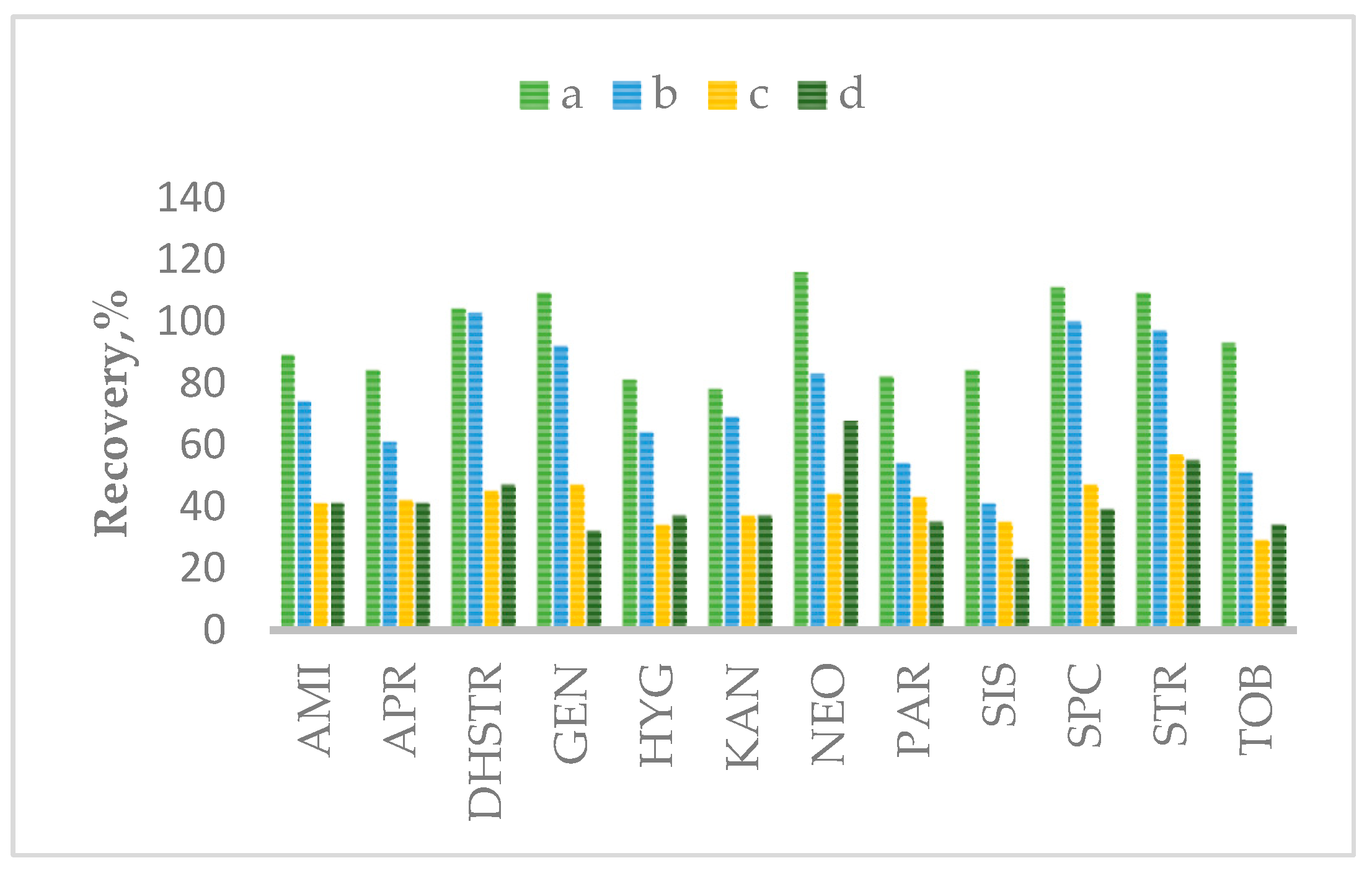
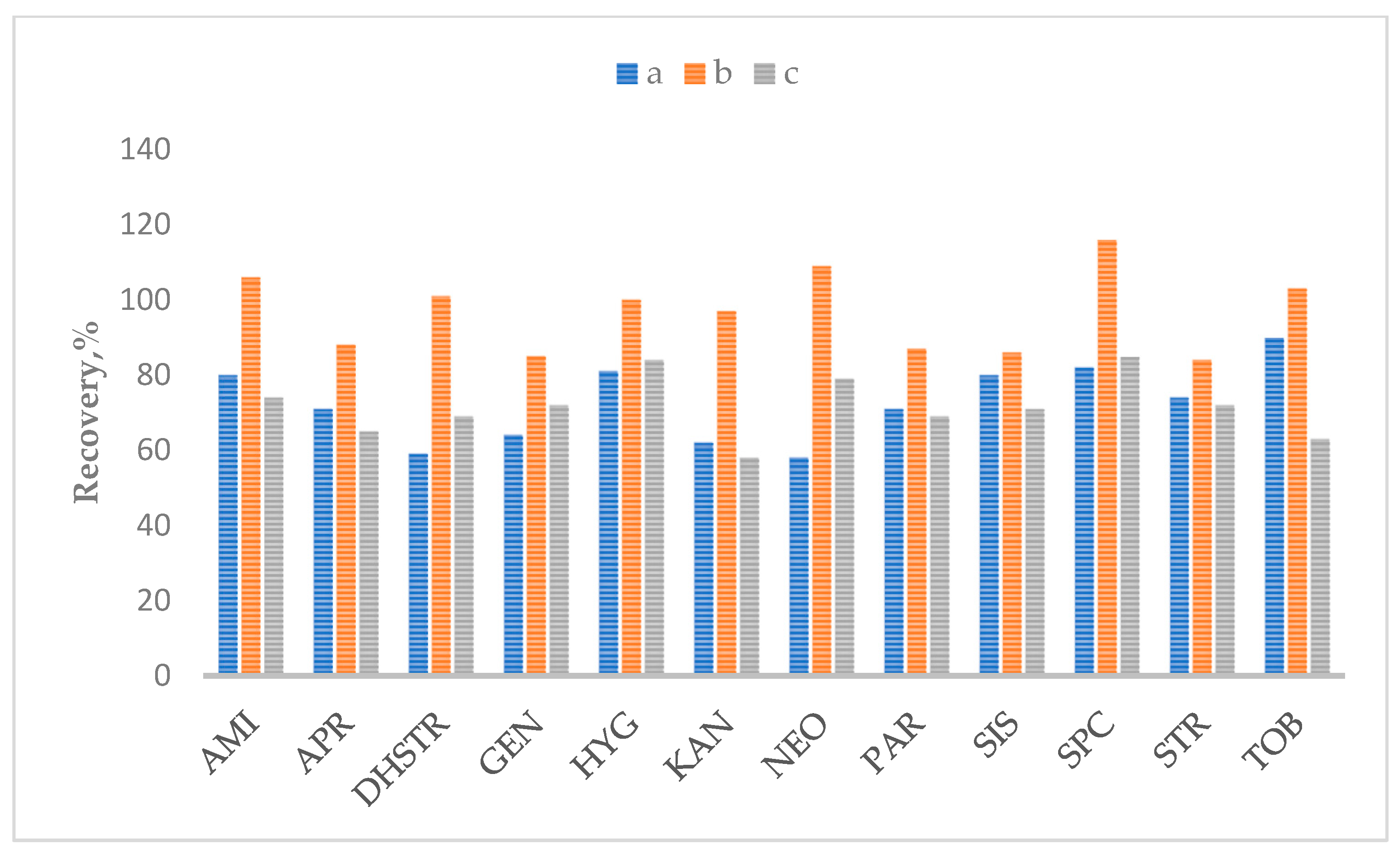
2.2. Optimization of Sample Preparation
2.3. Method Validation
2.4. Aminoglycosides in Real Samples
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of the Standard Stock Solution and Working Solutions
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.4. UHPLC-MS/MS Analysis
3.5. Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Macneil, J.D.; Kay, J.F. Chemical Analysis of Antibiotic Residues in Food. In Chemical Analysis of Antibiotic Residues in Food; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K.M.; Serio, A.W.; Kane, T.R.; Connolly, L.E. Aminoglycosides: An Overview. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a027029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaufmann, A.; Butcher, P.; Maden, K. Determination of aminoglycoside residues by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry in a variety of matrices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 711, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farouk, F.; Azzazy, H.M.E.; Niessen, W.M.A. Challenges in the determination of aminoglycoside antibiotics, a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 890, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Commission Regulation (EU) No 37/2010; Official Journal of the European Union, (L 15/1); EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Rúbies, A.; Companyõ, R.; Centrich, F. Determination of aminoglycoside residues in kidney and honey samples by hydrophilic interaction chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 2710–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, J. Optimization and application of parallel solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of 11 aminoglycoside residues in honey and royal jelly. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1542, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. Report for 2012 on the Results from the Monitoring of Veterinary Medicinal Product Residues and Other Substances in Live Animals and Animal Products; EFSA supporting publication 2014:EN-540; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2014; 65p. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Report for 2013 on the Results from the Monitoring of Veterinary Medicinal Product Residues and Other Substances in Live Animals and Animal Products; EFSA supporting publication 2015:EN-723; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2015; 69p. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Report for 2014 on the Results from the Monitoring of Veterinary Medicinal Product Residues and Other Substances in Live Animals and Animal Products; EFSA Supporting publication 2016:EN-923; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2016; 70p. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Report for 2015 on the Results from the Monitoring of Veterinary Medicinal Product Residues and Other Substances in Live Animals and Animal Products; EFSA Supporting publication 2017:14(11):EN-1150; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2017; 69p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Report for 2016 on the Results from the Monitoring of Veterinary Medicinal Product Residues and Other Substances in Live Animals and Animal Products; EFSA supporting publication 2018:EN-1358; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2018; 75p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Report for 2017 on the Results from the Monitoring of Veterinary Medicinal Product Residues and Other Substances in Live Animals and Animal Products; EFSA supporting publication 2019:EN-1578; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2019; 88p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Report for 2018 on the Results from the Monitoring of Veterinary Medicinal Product Residues and Other Substances in Live Animals and Animal Products; EFSA supporting publication 2020:EN-1775; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2020; 74p, ISSN 2397-8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Report for 2019 on the Results from the Monitoring of Veterinary Medicinal Product Residues and Other Substances in Live Animals and Animal Products; EFSA supporting publication 2021:EN-1997; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2021; 82p, ISSN 2397-8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); Brocca, D.; Salvatore, S. Report for 2020 on the Results from the Monitoring of Veterinary Medicinal Product Residues and Other Substances in Live Animals and Animal Products; EFSA supporting publication 2022:EN-7143; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2022; 91p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); Brocca, D.; Salvatore, S. Report for 2021 on the Results from the Monitoring of Veterinary Medicinal Product Residues and Other Substances in Live Animals and Animal Product; EFSA supporting publication 2023:EN7886; EFSA: Parma, Italy, 2023; 111p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plozza, T.; Trenerry, V.C.; Zeglinski, P.; Nguyen, H.; Johnstone, P. The confirmation and quantification of selected aminoglycoside residues in animal tissue and bovine milk by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Dasenaki, M.E.; Michali, C.S.; Thomaidis, N.S. Analysis of 76 veterinary pharmaceuticals from 13 classes including aminoglycosides in bovine muscle by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1452, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajda, A.; Nowacka-Kozak, E.; Gbylik-Sikorska, M.; Posyniak, A. Multi-residues UHPLC–MS/MS analysis of 53 antibacterial compounds in poultry feathers as an analytical tool in food safety assurance. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1104, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinka, M.; Wojnowski, W.; Wasik, A. Determination of aminoglycoside antibiotics: Current status and future trends. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 116034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Niu, H.; Li, F.; Gao, H.; Yu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, Y.; et al. Affinity-Based Analysis Methods for the Detection of Aminoglycoside Antibiotic Residues in Animal-Derived Foods: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R.; Kang, H.S. Multi-residue determination of twenty aminoglycoside antibiotics in various food matrices by dispersive solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 2021, 130, 108374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehotay, S.J.; Lightfield, A.R. Simultaneous analysis of aminoglycosides with many other classes of drug residues in bovine tissues by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry using an ion-pairing reagent added to final extracts. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, F.; Sasanya, J.J.; Cannavan, A. Development of a Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometric Method for Simultaneous Determination of 15 Aminoglycoside Residues in Porcine Tissues. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2587–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Mei, M.; Huang, X. Development of multiple monolithic fiber solid-phase microextraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the sensitive monitoring of aminoglycosides in honey and milk samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4203–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Wang, L.; Luo, C.; Wang, X.; Sun, C. Simultaneous Determination of 11 Aminoglycoside Residues in Honey, Milk, and Pork by Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Solid Phase Extraction. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guironnet, A.; Sanchez-Cid, C.; Vogel, T.M.; Wiest, L.; Vulliet, E. Aminoglycosides analysis optimization using ion pairing liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry and application on wastewater samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1651, 462133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saluti, G.; Diamanti, I.; Giusepponi, D.; Pucciarini, L.; Rossi, R.; Moretti, S.; Sardella, R.; Galarini, R. Simultaneous determination of aminoglycosides and colistins in food. Food Chem. 2018, 266, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, F.; Yang, B.; Liang, X. A polyvinyl alcohol-functionalized sorbent for extraction and determination of aminoglycoside antibiotics in honey. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1403, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tölgyesi, Á.; Barta, E.; Sohn, M.; Sharma, V.K. Determination of Antimicrobial Residues in Honey by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 2043–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsand, J.B.; Jank, L.; Martins, M.T.; Hoff, R.B.; Barreto, F.; Pizzolato, T.M.; Sirtori, C. Determination of aminoglycoside residues in milk and muscle based on a simple and fast extraction procedure followed by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry and time of flight mass spectrometry. Talanta 2016, 154, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, D.; Uemura, M.; Sakiyama, T.; Yamano, T. Sensitivity enhancement of aminoglycosides in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry by post-column addition of trace sodium acetate in methanol. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2018, 35, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrada, H.; Moltó, J.C.; Mañes, J.; Font, G. Determination of aminoglycoside and macrolide antibiotics in meat by pressurized liquid extraction and LC-ESI-MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, B.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H. Novel Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry for the Analysis of Twenty Antibiotics Residues in Dairy Products. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Rainville, P. Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Aminoglycosides in Foods Using an Ethylene-Bridged Hybrid Zwitterionic Stationary Phase and Hydrophilic–Lipophilic-Balanced Solid-Phase Extraction Cartridges. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 7593–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, C.; Guillarme, D.; Staub Spörri, A.; Cognard, E.; Ortelli, D.; Edder, P.; Rudaz, S. Aminoglycoside analysis in food of animal origin with a zwitterionic stationary phase and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 882, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bładek, T.; Posyniak, A.; Gajda, A.; Gbylik, M.; Zmudzki, J. Multi-class procedure for analysis of antibacterial compounds in eggs by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2012, 56, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajda, A.; Bładek, T.; Gbylik-Sikorska, M.; Nowacka-Kozak, E.; Angastiniotis, K.; Simitopoulou, M.; Kefalas, G.; Ferrari, P.; Levallois, P.; Fourichon, C.; et al. Analysis of Antimicrobials in Muscle and Drinking Water in Terms of Reducing the Need of Antimicrobial Use by Increasing the Health and Welfare of Pig and Broiler. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbylik, M.; Posyniak, A.; Mitrowska, K.; Bladek, T.; Zmudzki, J. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part A Multi-residue determination of antibiotics in fish by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherlet, M.; De Baere, S.; De Backer, P. Determination of gentamicin in swine and calf tissues by high-performance liquid chromatography combined with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 35, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoy, M.C.; Woo, P.M.; Ulrich, P.; Tarres, A.; Mottier, P.; Desmarchelier, A. Determination of 14 aminoglycosides by LC-MS/MS using molecularly imprinted polymer solid phase extraction for clean-up. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2018, 35, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Shang, D.; Xing, J.; Zhai, Y. Determination of gentamicin C components in fish tissues through SPE-Hypercarb-HPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1093–1094, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING REGULATION (EU) 2021/808 of 22 March 2021 on the Performance of Analytical Methods for Residues of Pharmacologically Active Substances Used in Food-Producing Animals and on the Interpretation of Results as Well as on the Methods to Be Used for Sampling and Repealing Decisions 2002/657/EC and 98/179/EC; Official Journal of the European Union, 21 May 2021. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2021/808/oj (accessed on 6 May 2023).

| Aminoglycoside | Food Origin (Animal Species) | MRL (µg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Apramycin | Bovine | 1000 (muscle, fat) 10,000 (liver) 20,000 (kidney) |
| Dihydrostreptomycin | All ruminants, porcine, rabbit | 500 (muscle, fat, liver) 1000 (kidney) 200 (ruminants’ milk) |
| Gentamicin | All mammalian food producing species and fin fish | 50 (muscle, fat) 200 (liver) 750 (kidney) 100 (milk) |
| Kanamycin | All food-producing species except fin fish | 100 (muscle, fat) 600 (liver) 2500 (kidney) 150 (milk) |
| Neomycin | All food-producing species | 500 (muscle, fat, except fish) 5500 (liver, except fish) 9000 (kidney, except fish) 1500 (milk) 500 (eggs) |
| Paromomycin | All food-producing species | 500 (muscle) 1500 (liver, kidney; except fish) 200 (eggs) |
| Spectinomycin | Ovine | 300 (muscle) 500 (fat) 2000 (liver) 5000 (kidney) 200 (milk) |
| All other food-producing species | 300 (muscle) 500 (fat, except fish) 1000 (liver, except fish) 5000 (kidney, except fish) 200 (milk) | |
| Streptomycin | All ruminants, porcine, rabbit | 500 (muscle, fat, liver) 1000 (kidney) 200 (ruminants milk) |
| Analyte | Parent Ion (m/z) | Daughter Ion(s) (m/z) | Retention Time (min) | DP (V) | CE (eV) | CXP (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amikacin (AMI) | 586.4 | 163.1/425.3/264.0 | 3.12 | 113 | 36/27/34 | 13 |
| Apramycin (APR) | 540.3 | 217.0/199.3 | 3.18 | 119 | 33/32 | 13 |
| Dihydrostreptomycin (DHSTR) | 584.3 | 263.2/246.2/221.1 | 3.06 | 70 | 42/49/38 | 15 |
| Gentamicin (GEN) | 478.0 | 322.0/157.0 | 3.21 | 55 | 21/23 | 13 |
| Hygromycin B (HYG) | 528.3 | 352.3/177.4 | 3.02 | 62 | 33/41 | 13 |
| Kanamycin (KAN) | 485.0 | 163.0/324.0/205.0 | 3.13 | 60 | 32/21/34 | 13 |
| Neomycin (NEO) | 615.1 | 161.0/163.0/293.0 | 3.25 | 130 | 37/38/33 | 15 |
| Paromomycin (PAR) | 616.1 | 163.2/293.2/324.0 | 3.19 | 110 | 40/30/21 | 13 |
| Sisomicin (SIS) | 448.3 | 254.3/271.3 | 3.19 | 96 | 33/26 | 13 |
| Spectinomycin (SPC) | 351.0 | 333.2/207.0 | 2.93 | 132 | 24/28 | 15 |
| Streptomycin (STR) | 582.0 | 263.0/246.0/221.0 | 3.06 | 153 | 44/50/40 | 15 |
| Tobramycin (TOB) | 468.3 | 163.0/145.0 | 3.20 | 67 | 29/25 | 13 |
| Ribostamycin (RIB) * | 455.0 | 163.0 | 3.12 | 71 | 30 | 13 |
| Matrix | SPE Cartridges | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strata X | Strata X-CW | Strata X-AW | Oasis HLB | |
| Muscle | + | ++ | + | +++ |
| Kidney | ++ | + | + | +++ |
| Liver | + | ++ | ++ | +++ |
| Fat | ++ | + | ++ | +++ |
| Sausages | ++ | + | ++ | +++ |
| Shrimps | + | + | +++ | ++ |
| Fish | + | + | +++ | ++ |
| Honey | +++ | + | ++ | +++ |
| Milk | ++ | + | ++ | +++ |
| Eggs | + | ++ | +++ | ++ |
| Whey powder | ++ | + | ++ | +++ |
| Sour cream | + | + | ++ | +++ |
| Curd | + | + | ++ | +++ |
| Muscle | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyte | LOQ (µg/kg) | Validation Level (µg/kg) | Decision Limit CCα (µg/kg) | Repeatability *, (CV, %) | Within-Laboratory Reproducibility *, (CV, %) | Recovery * (%) | Matrix Effect * (CV, %) |
| AMI | 25.0 | 50 | 59.4 | 6.24 | 4.72 | 102 | 3 |
| APR | 10.0 | 1000 * | 1114 | 10.9 | 6.78 | 113 | 4 |
| DHSTR | 50.0 | 500 * | 586 | 6.39 | 7.31 | 102 | 3 |
| GEN | 10.0 | 50 * | 61.9 | 7.63 | 9.24 | 105 | 5 |
| HYG | 25.0 | 50 | 64.2 | 8.72 | 8.01 | 99.0 | 4 |
| KAN | 10.0 | 100 * | 110 | 9.25 | 9.14 | 103 | 5 |
| NEO | 10.0 | 500 * | 509 | 9.88 | 7.73 | 104 | 7 |
| PAR | 10.0 | 500 * | 517 | 9.20 | 7.91 | 89.6 | 4 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 62.0 | 7.99 | 5.58 | 101 | 5 |
| SPC | 50.0 | 300 * | 327 | 7.23 | 8.38 | 104 | 2 |
| STR | 25.0 | 500 * | 543 | 13.9 | 13.1 | 101 | 3 |
| TOB | 10.0 | 50 | 56.7 | 7.27 | 5.44 | 103 | 3 |
| Kidney | |||||||
| AMI | 10.0 | 50 | 58.1 | 9.91 | 6.21 | 108 | 5 |
| APR | 10.0 | 20,000 * | 21,642 | 3.52 | 9.25 | 96.8 | 4 |
| DHSTR | 10.0 | 1000 * | 1093 | 9.50 | 9.37 | 102 | 8 |
| GEN | 10.0 | 750 * | 851 | 4.66 | 10.8 | 105 | 6 |
| HYG | 50.0 | 50 | 62.8 | 4.26 | 7.03 | 87.4 | 9 |
| KAN | 10.0 | 2500 * | 2769 | 4.66 | 5.90 | 95.1 | 8 |
| NEO | 10.0 | 9000 * | 10,632 | 12.5 | 10.8 | 109 | 4 |
| PAR | 10.0 | 1500 * | 1740 | 9.59 | 7.19 | 113 | 5 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 53.5 | 8.86 | 5.65 | 107 | 5 |
| SPC | 25.0 | 5000 * | 5967 | 4.31 | 5.79 | 92.3 | 3 |
| STR | 10.0 | 1000 * | 1195 | 7.45 | 8.82 | 89.0 | 3 |
| TOB | 10.0 | 50 | 64.7 | 10.4 | 4.42 | 105 | 4 |
| Liver | |||||||
| AMI | 50.0 | 50 | 63.0 | 13.0 | 11.8 | 104 | 6 |
| APR | 10.0 | 10,000 * | 12,097 | 11.0 | 11.4 | 107 | 4 |
| DHSTR | 10.0 | 500 * | 621 | 9.59 | 11.8 | 110 | 3 |
| GEN | 10.0 | 200 * | 246 | 10.4 | 7.99 | 112 | 7 |
| HYG | 25.0 | 50 | 57.9 | 6.37 | 5.78 | 101 | 4 |
| KAN | 10.0 | 600 * | 702 | 7.07 | 4.49 | 108 | 5 |
| NEO | 100 | 5500 * | 5971 | 11.5 | 9.77 | 115 | 5 |
| PAR | 50.0 | 1500 * | 1814 | 10.4 | 9.44 | 112 | 4 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 68.1 | 13.6 | 11.9 | 102 | 7 |
| SPC | 25.0 | 2000 * | 2462 | 14.0 | 12.2 | 109 | 4 |
| STR | 10.0 | 500 * | 594 | 12.0 | 11.4 | 103 | 6 |
| TOB | 10.0 | 50 | 69.9 | 10.3 | 8.88 | 105 | 5 |
| Fat | |||||||
| AMI | 10.0 | 50 | 67.1 | 5.51 | 12.2 | 85.6 | 3 |
| APR | 10.0 | 1000 * | 1194 | 4.28 | 5.78 | 107 | 4 |
| DHSTR | 10.0 | 500 * | 537 | 5.75 | 9.02 | 87.2 | 8 |
| GEN | 10.0 | 50 * | 61.3 | 9.28 | 7.75 | 109 | 6 |
| HYG | 10.0 | 50 | 69.5 | 8.05 | 8.26 | 106 | 4 |
| KAN | 10.0 | 100 * | 117 | 6.97 | 4.49 | 97.3 | 6 |
| NEO | 10.0 | 500 * | 604 | 7.08 | 8.25 | 101 | 8 |
| PAR | 10.0 | 50 | 51.8 | 8.95 | 7.12 | 88.5 | 6 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 63.7 | 5.58 | 6.44 | 89.4 | 6 |
| SPC | 25.0 | 500 * | 563 | 9.43 | 5.78 | 100 | 7 |
| STR | 25.0 | 500 * | 615 | 8.74 | 9.12 | 102 | 4 |
| TOB | 10.0 | 50 | 51.7 | 6.68 | 10.6 | 84.7 | 7 |
| Sausages | |||||||
| AMI | 25.0 | 50 | 68.4 | 13.2 | 7.94 | 87.9 | 6 |
| APR | 25.0 | 50 | 64.7 | 10.3 | 9.68 | 82.8 | 4 |
| DHSTR | 25.0 | 50 | 53.8 | 9.84 | 10.7 | 94.5 | 7 |
| GEN | 10.0 | 50 | 56.6 | 7.98 | 9.58 | 102 | 6 |
| HYG | 50.0 | 50 | 67.9 | 8.85 | 10.3 | 106 | 5 |
| KAN | 10.0 | 50 | 57.3 | 11.3 | 9.36 | 97.2 | 5 |
| NEO | 25.0 | 50 | 51.8 | 4.71 | 6.13 | 96.5 | 4 |
| PAR | 25.0 | 50 | 70.3 | 7.09 | 9.15 | 99.4 | 5 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 54.9 | 10.8 | 11.4 | 107 | 5 |
| SPC | 25.0 | 50 | 55.8 | 11.7 | 10.9 | 115 | 6 |
| STR | 50.0 | 50 | 69.2 | 10.0 | 10.1 | 89.6 | 5 |
| TOB | 25.0 | 50 | 71.6 | 9.64 | 7.86 | 112 | 5 |
| Shrimps | |||||||
| AMI | 10.0 | 50 | 68.7 | 7.68 | 9.12 | 103 | 8 |
| APR | 25.0 | 50 | 51.9 | 11.5 | 10.9 | 89.4 | 6 |
| DHSTR | 10.0 | 50 | 57.9 | 9.25 | 5.56 | 87.2 | 7 |
| GEN | 10.0 | 50 | 64.3 | 4.58 | 4.30 | 100 | 5 |
| HYG | 50.0 | 50 | 73.8 | 6.79 | 9.55 | 114 | 4 |
| KAN | 10.0 | 50 | 71.6 | 5.52 | 10.3 | 110 | 9 |
| NEO | 25.0 | 50 | 55.9 | 9.93 | 12.8 | 109 | 5 |
| PAR | 10.0 | 50 | 57.6 | 11.7 | 7.42 | 98.8 | 6 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 62.5 | 10.8 | 11.8 | 106 | 6 |
| SPC | 25.0 | 50 | 65.9 | 6.65 | 9.48 | 97.3 | 4 |
| STR | 50.0 | 50 | 58.9 | 7.48 | 10.1 | 89.5 | 4 |
| TOB | 10.0 | 50 | 74.9 | 5.43 | 12.6 | 118 | 9 |
| Fish | |||||||
| AMI | 10.0 | 50 | 68.9 | 9.32 | 8.15 | 104 | 4 |
| APR | 10.0 | 50 | 54.3 | 7.45 | 9.37 | 87.0 | 4 |
| DHSTR | 10.0 | 50 | 55.4. | 8.82 | 7.18 | 93.6 | 8 |
| GEN | 10.0 | 50 * | 59.0 | 3.96 | 9.22 | 108 | 6 |
| HYG | 10.0 | 50 | 68.1 | 6.74 | 8.57 | 103 | 8 |
| KAN | 10.0 | 50 | 67.3 | 9.48 | 10.4 | 97.4 | 7 |
| NEO | 10.0 | 50 | 59.1 | 6.34 | 11.8 | 105 | 10 |
| PAR | 10.0 | 50 | 60.8 | 4.59 | 6.25 | 117 | 8 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 67.1 | 7.61 | 7.12 | 83.5 | 4 |
| SPC | 25.0 | 50 | 56.0 | 10.3 | 8.87 | 109 | 5 |
| STR | 25.0 | 50 | 71.3 | 9.78 | 7.56 | 89.4 | 10 |
| TOB | 10.0 | 50 | 54.7 | 7.42 | 10.7 | 101 | 5 |
| Honey | |||||||
| AMI | 10.0 | 50 | 67.2 | 11.7 | 9.84 | 106 | 7 |
| APR | 10.0 | 50 | 70.6 | 10.7 | 11.5 | 110 | 3 |
| DHSTR | 10.0 | 50 | 68.4 | 5.29 | 4.71 | 110 | 8 |
| GEN | 10.0 | 50 | 68.8 | 9.15 | 7.41 | 95.4 | 9 |
| HYG | 50.0 | 50 | 57.3 | 8.76 | 5.59 | 91.2 | 4 |
| KAN | 10.0 | 50 | 65.5 | 11.9 | 8.36 | 109 | 6 |
| NEO | 10.0 | 50 | 69.0 | 5.40 | 2.71 | 86.3 | 6 |
| PAR | 10.0 | 50 | 57.1 | 4.62 | 4.15 | 114 | 6 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 59.7 | 3.11 | 10.5 | 107 | 6 |
| SPC | 10.0 | 50 | 67.3 | 8.27 | 7.71 | 89.7 | 4 |
| STR | 10.0 | 50 | 52.9 | 12.0 | 9.05 | 98.1 | 4 |
| TOB | 10.0 | 50 | 57.1 | 8.26 | 5.95 | 106 | 5 |
| Milk | |||||||
| AMI | 10.0 | 50 | 71.3 | 10.4 | 8.54 | 111 | 5 |
| APR | 25.0 | 50 | 59.0 | 4.82 | 5.70 | 103 | 5 |
| DHSTR | 10.0 | 200 * | 261 | 7.62 | 6.88 | 105 | 5 |
| GEN | 10.0 | 100 * | 127 | 7.48 | 8.43 | 98.4 | 6 |
| HYG | 25.0 | 50 | 60.8 | 8.58 | 6.92 | 105 | 7 |
| KAN | 10.0 | 150 * | 172 | 5.52 | 6.13 | 103 | 6 |
| NEO | 10.0 | 1500 * | 1690 | 10.0 | 8.66 | 100 | 8 |
| PAR | 10.0 | 50 | 67.6 | 9.28 | 9.39 | 110 | 6 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 57.9 | 5.57 | 8.74 | 105 | 5 |
| SPC | 50.0 | 200 * | 262 | 9.08 | 9.96 | 109 | 9 |
| STR | 10.0 | 200 * | 257 | 10.1 | 8.74 | 104 | 6 |
| TOB | 10.0 | 50 | 64.8 | 4.83 | 4.54 | 99.2 | 12 |
| Eggs | |||||||
| AMI | 10.0 | 50 | 71.9 | 7.03 | 7.97 | 109 | 5 |
| APR | 10.0 | 50 | 64.2 | 4.55 | 5.02 | 102 | 8 |
| DHSTR | 10.0 | 50 | 57.8 | 8.01 | 8.70 | 108 | 8 |
| GEN | 10.0 | 50 | 60.8 | 8.94 | 9.96 | 108 | 15 |
| HYG | 50.0 | 50 | 67.1 | 8.92 | 9.41 | 97.3 | 7 |
| KAN | 10.0 | 50 | 55.3 | 6.74 | 10.1 | 102 | 7 |
| NEO | 10.0 | 500 * | 587 | 9.47 | 10.8 | 112 | 8 |
| PAR | 10.0 | 200 * | 229.0 | 11.7 | 11.2 | 108 | 13 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 57.1 | 10.0 | 9.60 | 101 | 8 |
| SPC | 50.0 | 100 | 131 | 4.79 | 6.44 | 88.6 | 8 |
| STR | 10.0 | 50 | 58.3 | 7.37 | 5.13 | 110 | 5 |
| TOB | 10.0 | 50 | 68.1 | 5.22 | 5.81 | 103 | 13 |
| Whey Powder | |||||||
| AMI | 25.0 | 50 | 65.8 | 8.57 | 11.2 | 114 | 5 |
| APR | 50.0 | 50 | 58.1 | 6.99 | 10.8 | 94.3 | 7 |
| DHSTR | 10.0 | 50 | 63.0 | 8.80 | 6.25 | 96.5 | 11 |
| GEN | 10.0 | 50 | 67.1 | 10.2 | 9.13 | 87.4 | 7 |
| HYG | 100 | 100 | 118 | 8.43 | 5.70 | 85.9 | 5 |
| KAN | 25.0 | 50 | 54.6 | 10.8 | 8.24 | 107 | 8 |
| NEO | 100 | 250 | 271 | 12.0 | 10.6 | 104 | 7 |
| PAR | 25.0 | 50 | 56.3 | 9.16 | 7.89 | 116 | 8 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 58.1 | 8.96 | 8.54 | 97.8 | 6 |
| SPC | 50.0 | 100 | 128 | 10.0 | 11.8 | 100 | 6 |
| STR | 50.0 | 100 | 116 | 11.8 | 13.8 | 93.7 | 5 |
| TOB | 10.0 | 50 | 55.8 | 8.67 | 9.60 | 99.1 | 8 |
| Sour cream | |||||||
| AMI | 50.0 | 50 | 55.3 | 9.13 | 10.9 | 87.6 | 4 |
| APR | 50.0 | 50 | 57.2 | 7.64 | 8.46 | 91.4 | 3 |
| DHSTR | 25.0 | 50 | 60.8 | 10.8 | 7.68 | 109 | 7 |
| GEN | 25.0 | 50 | 64.1 | 9.64 | 12.5 | 99.8 | 6 |
| HYG | 50.0 | 100 | 115 | 8.25 | 9.36 | 106 | 6 |
| KAN | 25.0 | 50 | 54.9 | 7.55 | 10.5 | 117 | 7 |
| NEO | 250 | 250 | 279 | 6.84 | 11.3 | 108 | 10 |
| PAR | 50.0 | 100 | 128 | 14.2 | 8.56 | 94.7 | 6 |
| SIS | 50.0 | 50 | 57.3 | 9.46 | 9.97 | 96.8 | 7 |
| SPC | 50.0 | 100 | 121 | 8.67 | 7.56 | 83.7 | 4 |
| STR | 50.0 | 100 | 119 | 9.12 | 10.6 | 100 | 8 |
| TOB | 50.0 | 50 | 57.6 | 9.45 | 11.7 | 110 | 7 |
| Curd | |||||||
| AMI | 100 | 100 | 109 | 4.56 | 9.10 | 83.9 | 8 |
| APR | 25.0 | 50 | 54.3 | 8.12 | 7.54 | 102 | 7 |
| DHSTR | 10.0 | 50 | 57.8 | 11.6 | 7.49 | 96.4 | 5 |
| GEN | 50.0 | 50 | 60.9 | 5.79 | 10.3 | 84.0 | 8 |
| HYG | 100 | 100 | 117 | 6.45 | 7.96 | 88.7 | 6 |
| KAN | 50.0 | 50 | 65.7 | 10.5 | 9.81 | 103 | 13 |
| NEO | 100 | 250 | 262 | 9.86 | 8.30 | 118 | 8 |
| PAR | 100 | 100 | 117 | 8.64 | 8.76 | 105 | 8 |
| SIS | 10.0 | 50 | 65.9 | 10.8 | 11.3 | 96.1 | 6 |
| SPC | 50.0 | 100 | 124 | 13.5 | 7.99 | 94.7 | 6 |
| STR | 25.0 | 100 | 131 | 8.25 | 10.1 | 83.0 | 6 |
| TOB | 10.0 | 50 | 54.3 | 7.51 | 9.36 | 87.5 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowacka-Kozak, E.; Gajda, A.; Gbylik-Sikorska, M. Analysis of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics: A Challenge in Food Control. Molecules 2023, 28, 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124595
Nowacka-Kozak E, Gajda A, Gbylik-Sikorska M. Analysis of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics: A Challenge in Food Control. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124595
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowacka-Kozak, Ewelina, Anna Gajda, and Małgorzata Gbylik-Sikorska. 2023. "Analysis of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics: A Challenge in Food Control" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124595
APA StyleNowacka-Kozak, E., Gajda, A., & Gbylik-Sikorska, M. (2023). Analysis of Aminoglycoside Antibiotics: A Challenge in Food Control. Molecules, 28(12), 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124595






