Hydrothermal Synthesis of Bismuth Ferrite Hollow Spheres with Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
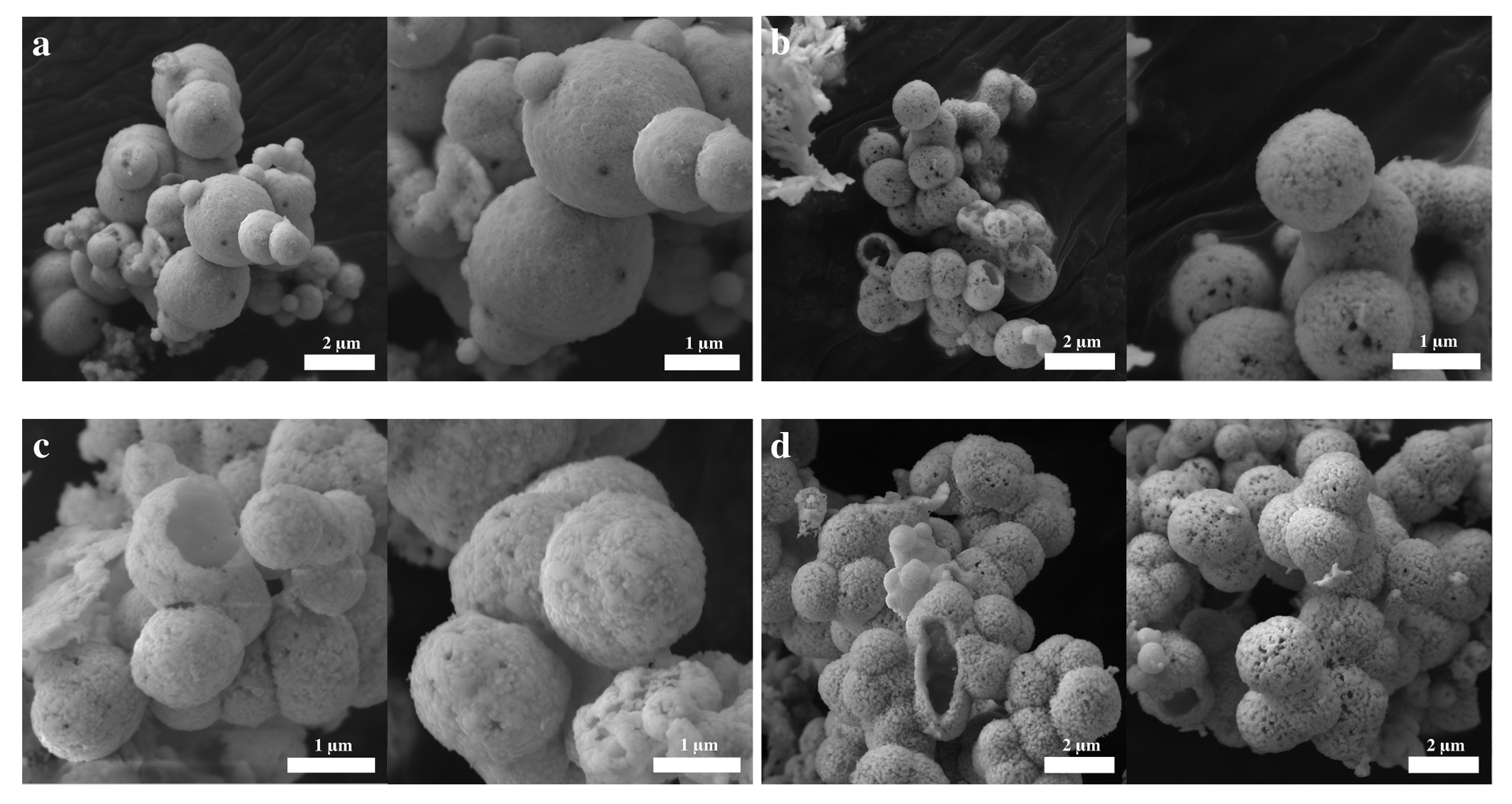
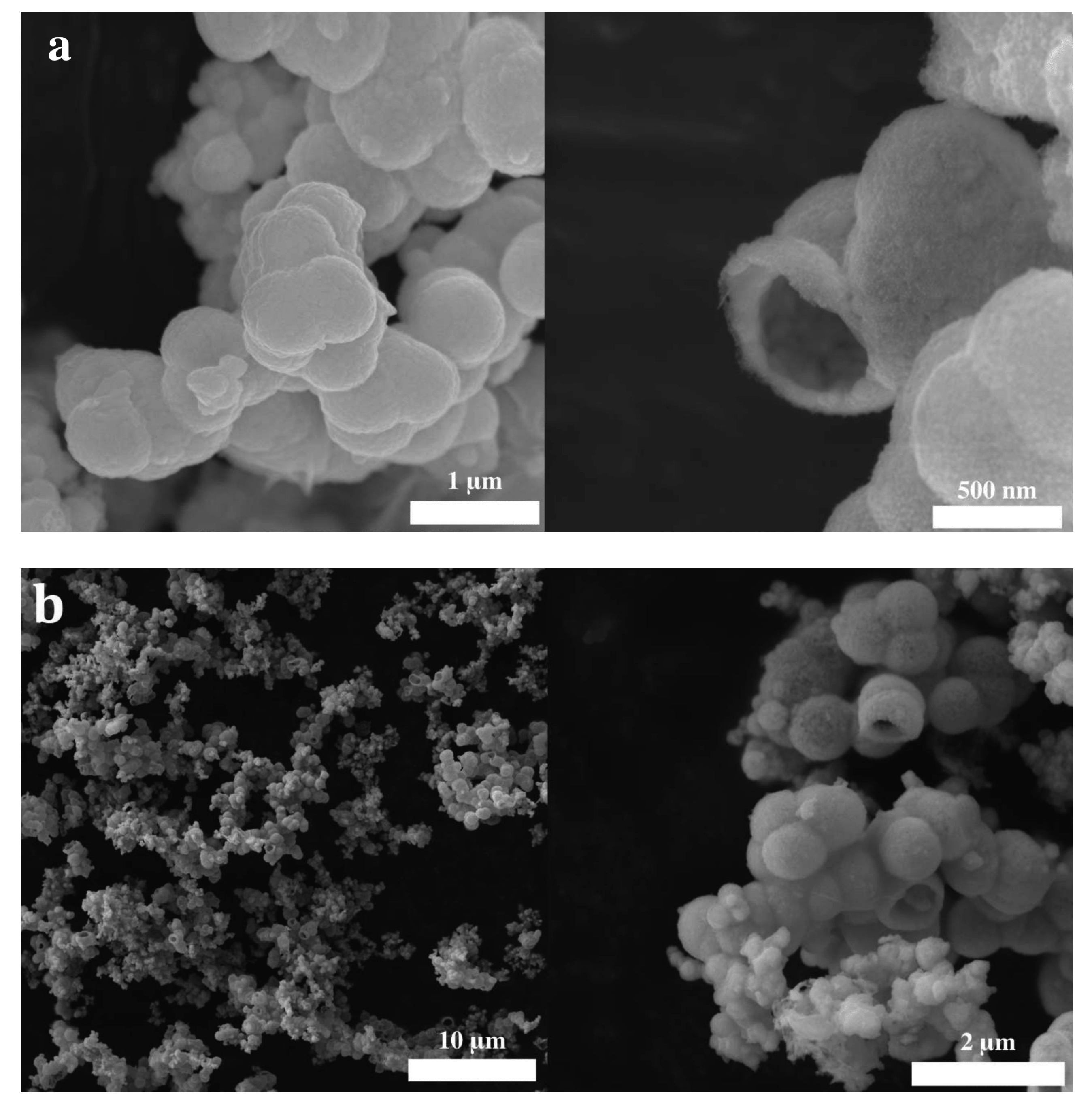
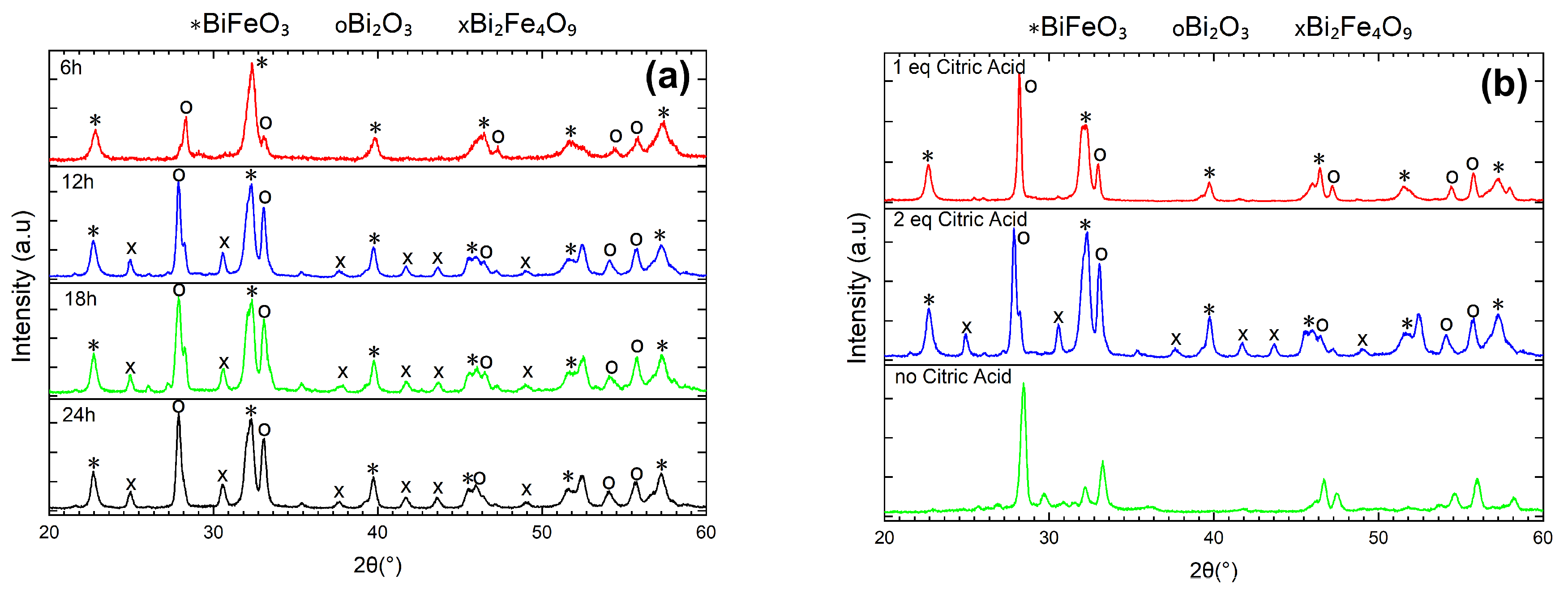
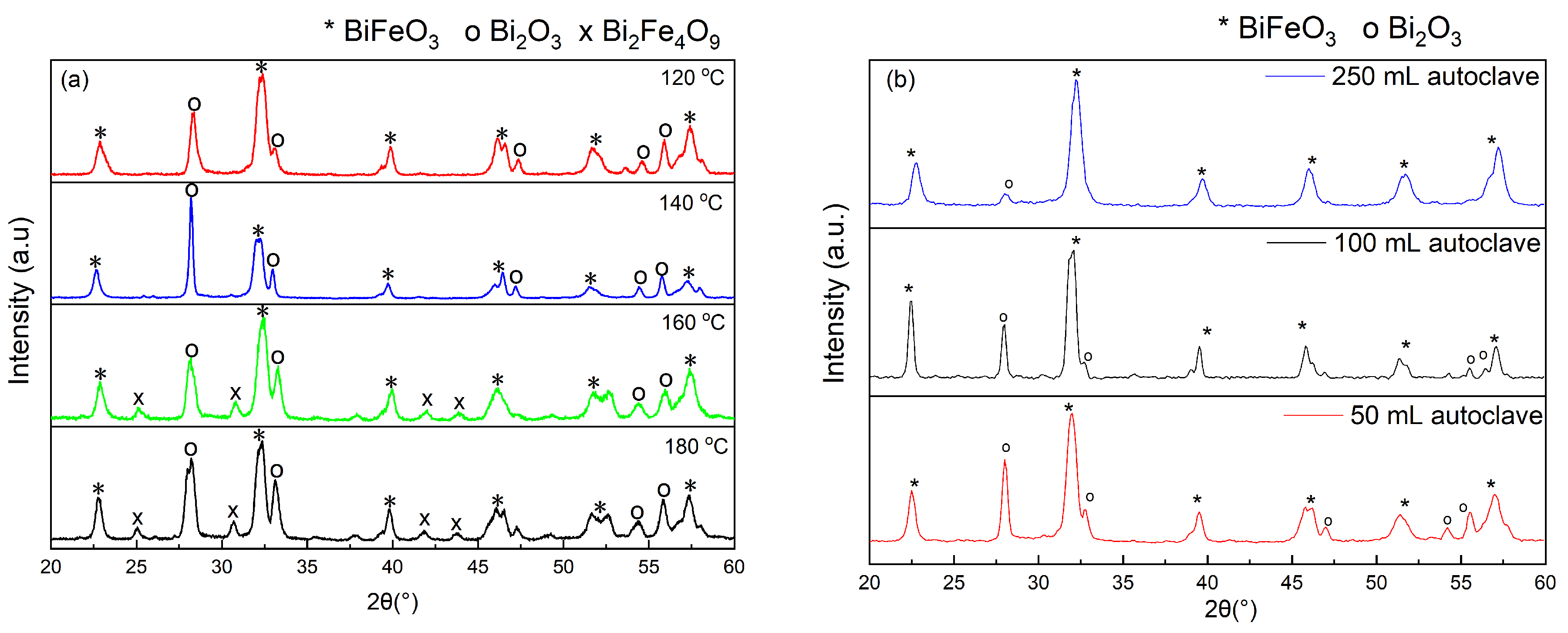
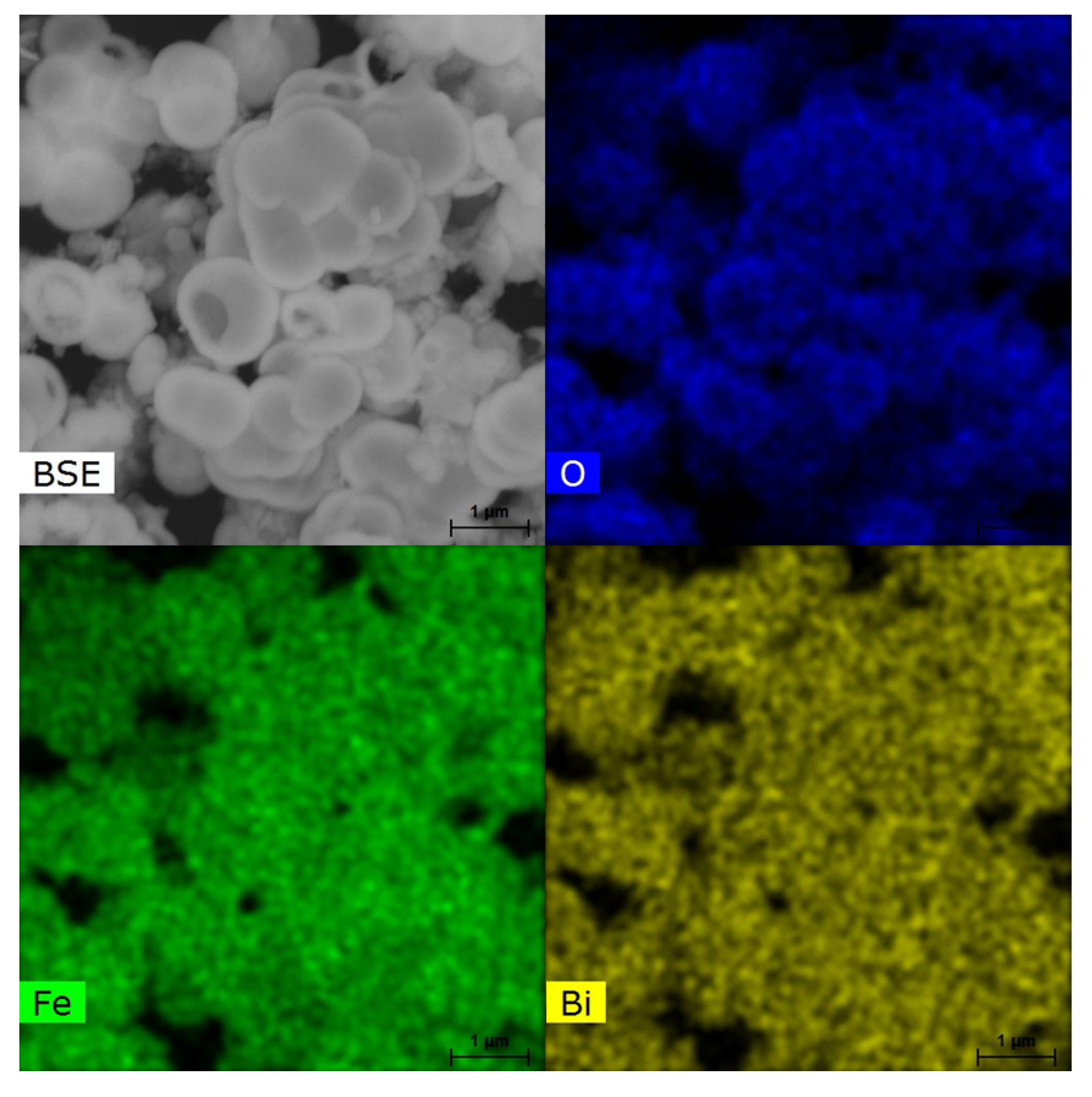
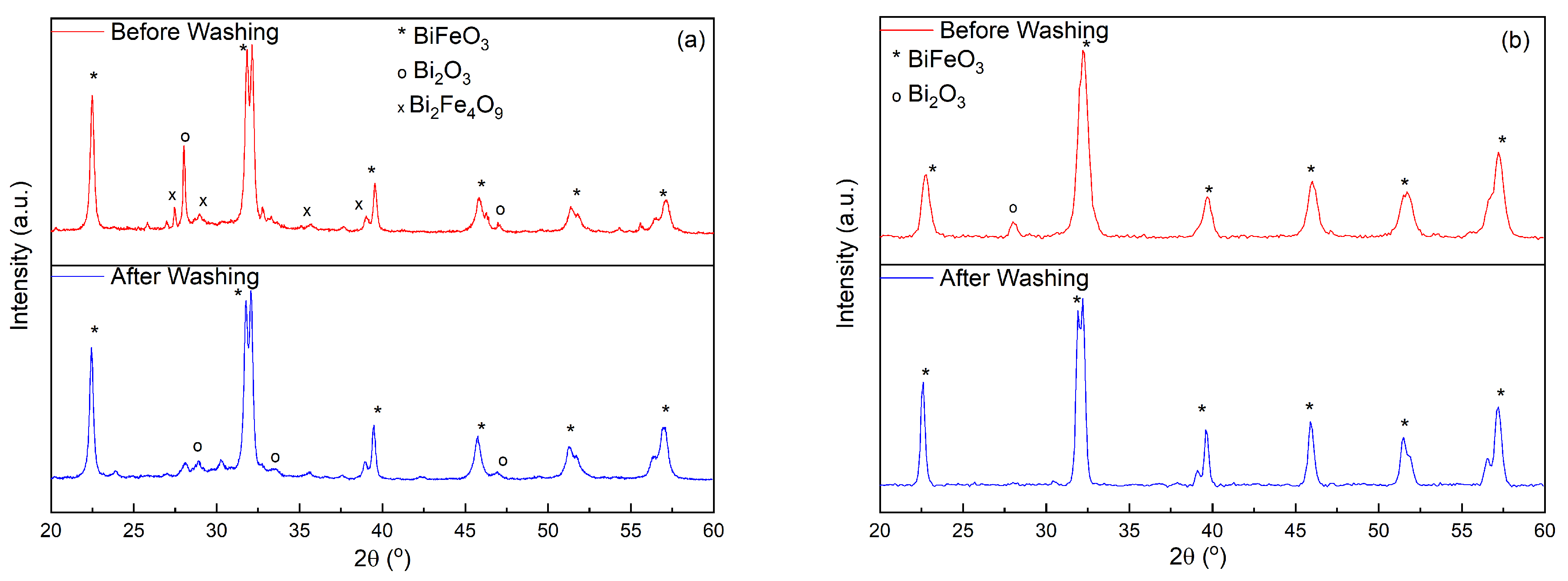
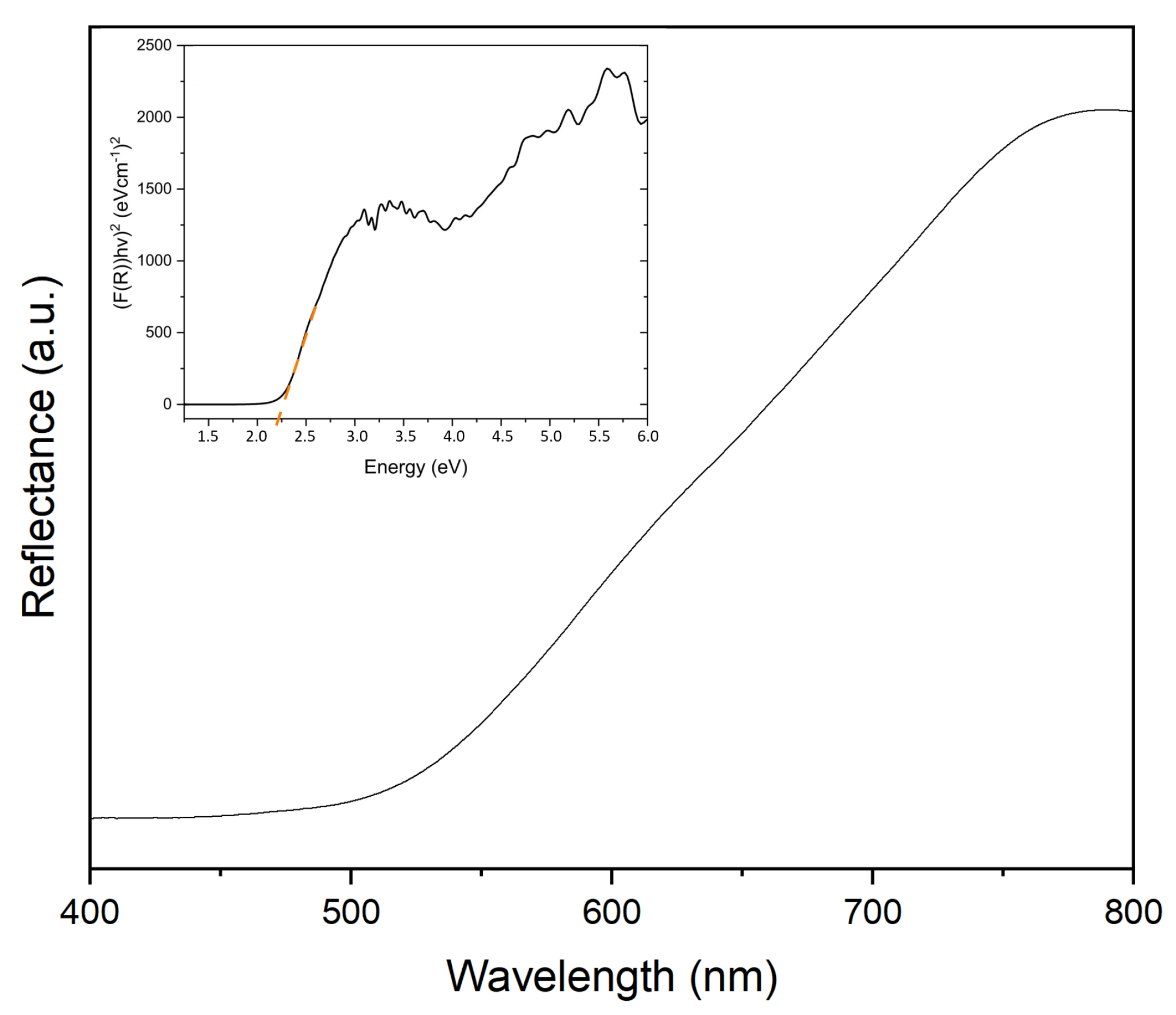
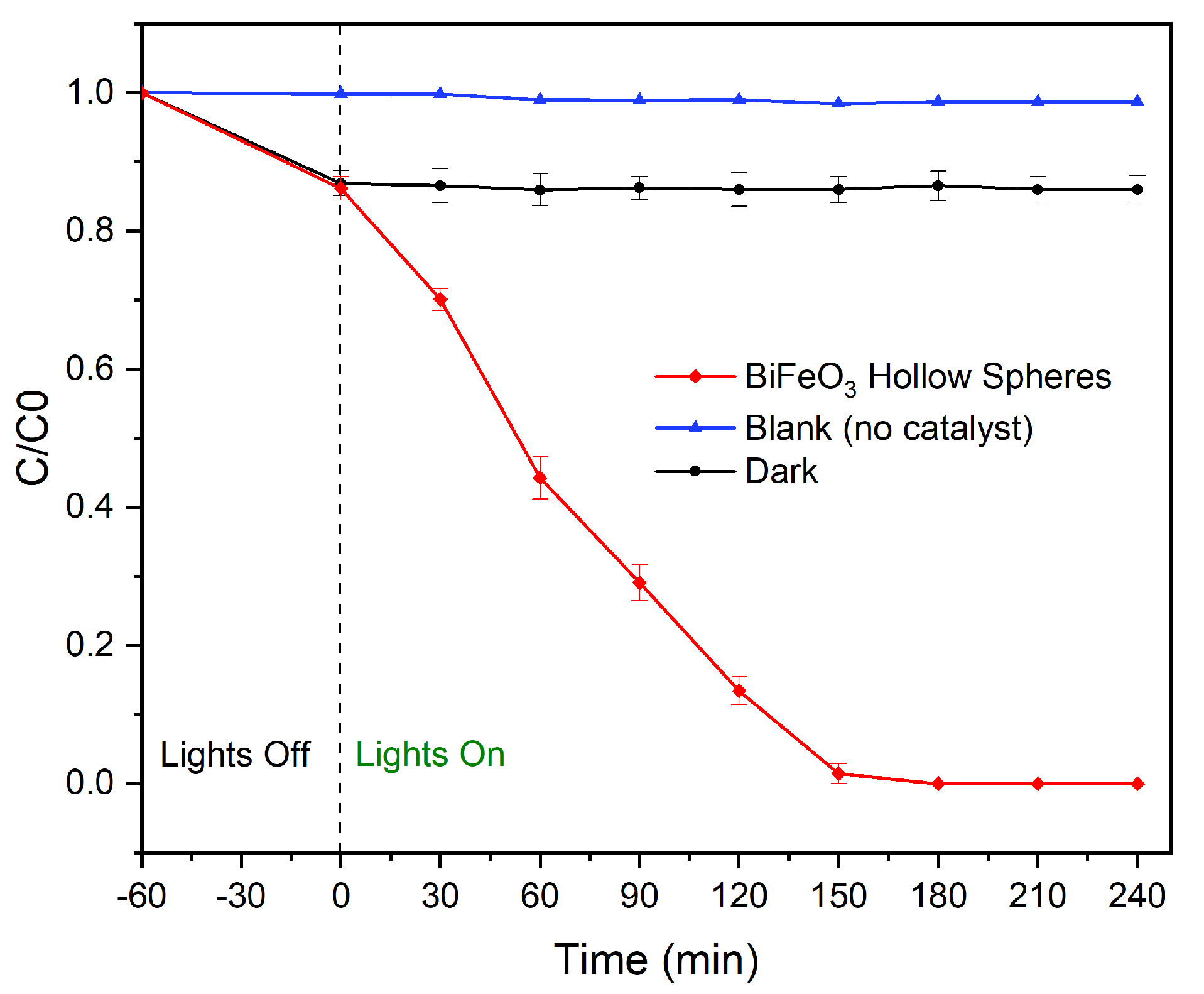
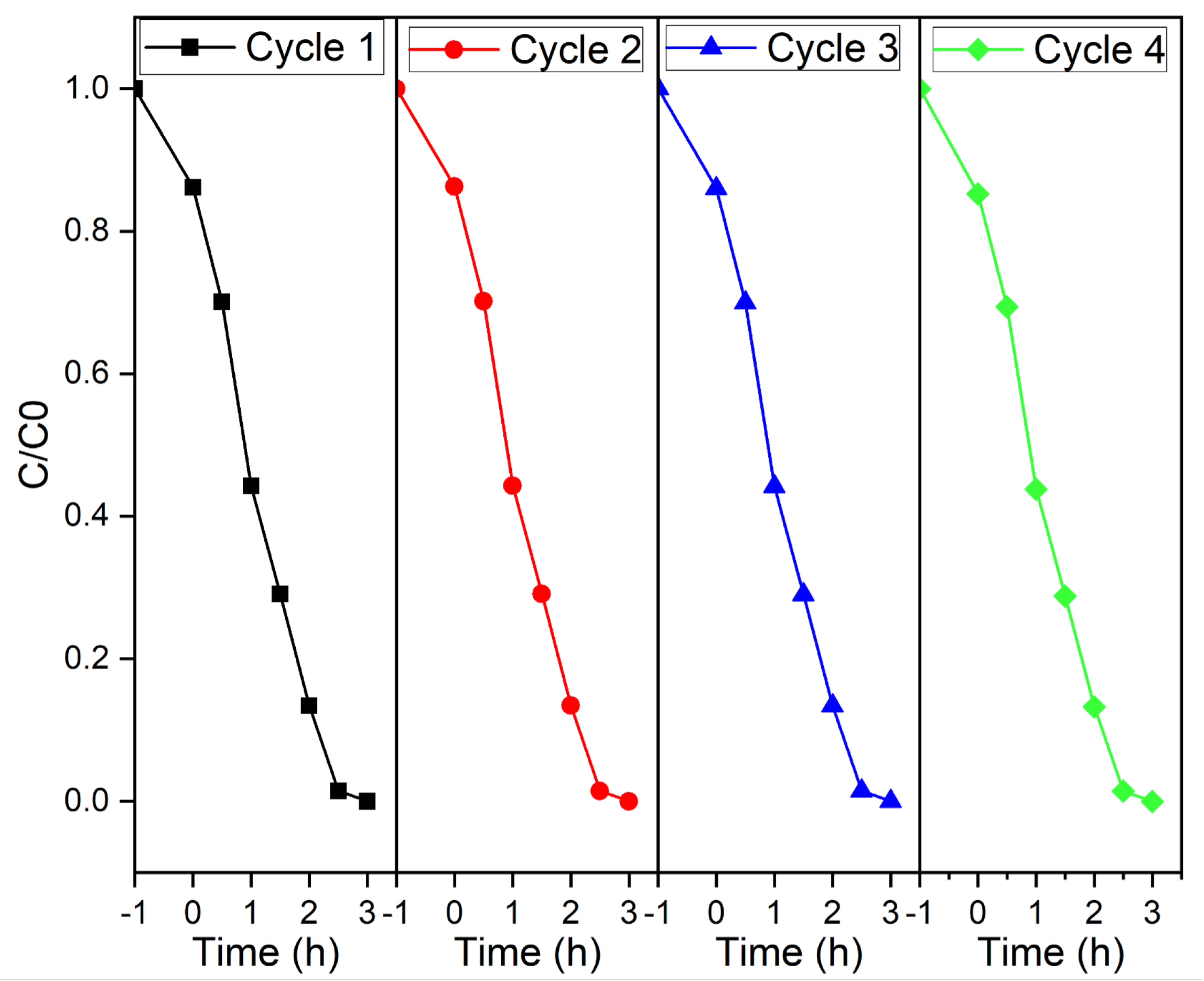
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of BiFeO Hollow Spheres
3.2. Characterization Techniques and Equipment
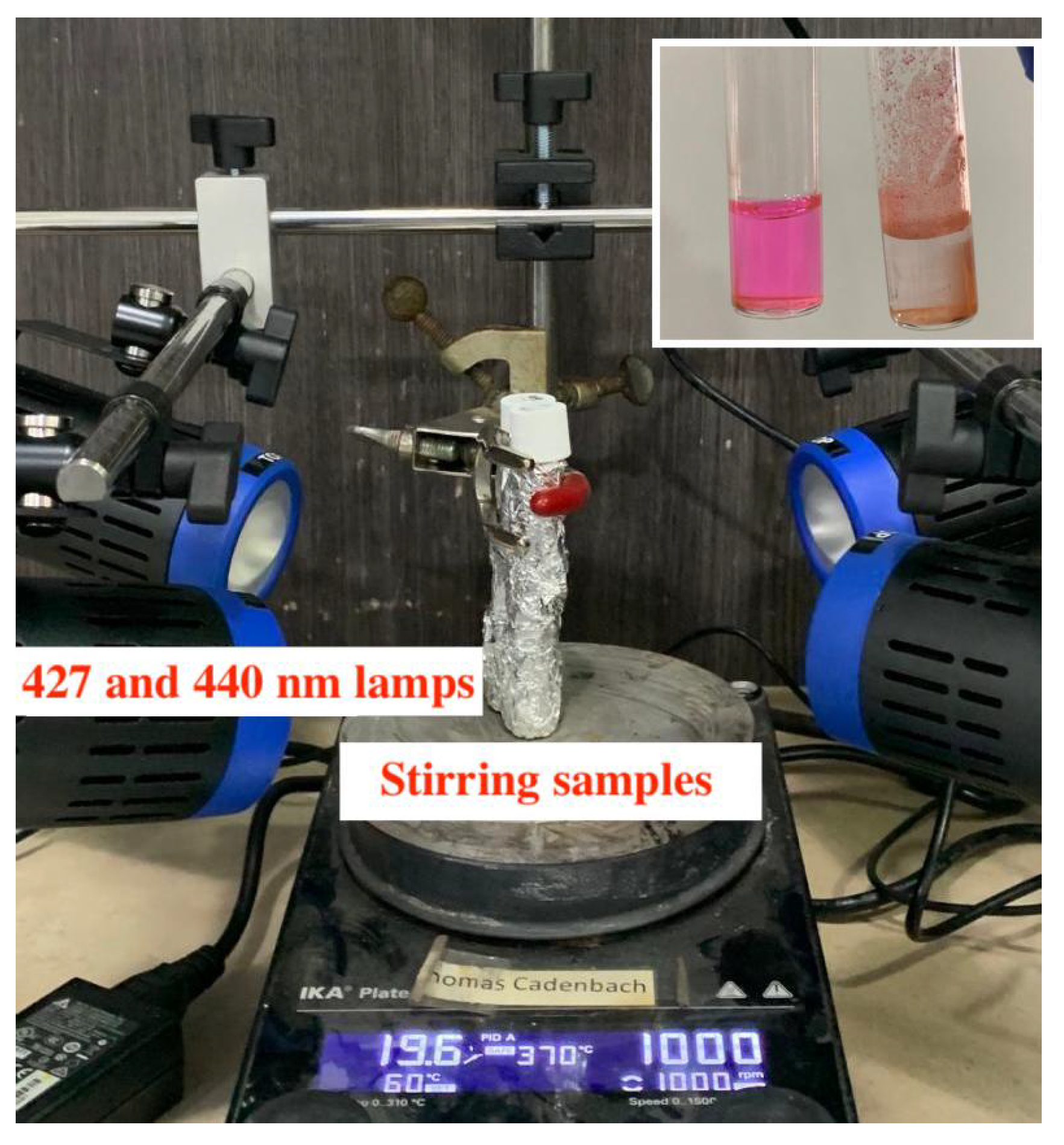
3.3. Photocatalytic Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ismail, A.A.; Bahnemann, D.W. Photochemical splitting of water for hydrogen production by photocatalysis: A review. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 128, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahnemann, D. Photocatalytic water treatment: Solar energy applications. Sol. Energy 2004, 77, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, F.D.; Attia, M.F.; Whitehead, D.C.; Alexis, F. Nanotechnology for Environmental Remediation: Materials and Applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arora, G.; Yadav, M.; Gaur, R.; Gupta, R.; Yadav, P.; Dixit, R.; Sharma, R.K. Fabrication, functionalization and advanced applications of magnetic hollow materials in confined catalysis and environmental remediation. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 10967–11003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y. Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Hollow Micro-/Nanostructures. Chem. Rev. 2016, 16, 10983–11060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, M.; Fang, X.; Wu, L. Fabrication and application of inorganic hollow spheres. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5472–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Fang, L.; Dong, W.; Zheng, F.; Shen, M. Enhanced photocatalytic activity and ferromagnetism in Gd doped BiFeO 3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 21390–21396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Chen, Z.; Niu, F.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, L.; Sun, X.; Huang, Y. Shape-controlled preparation of bismuth ferrite by hydrothermal method and their visible-light degradation properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 648, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Lu, C. High efficient ultraviolet photocatalytic activity of BiFeO3 nanoparticles synthesized by a chemical coprecipitation process. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2010, 21, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefi, N.; Masoudpanah, S.M.; Hasheminiasari, M. Microwave-assisted solution combustion synthesis of BiFeO3 powders. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 86, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, R.I. Perovskite Oxides Prepared by Hydrothermal and Solvothermal Synthesis: A Review of Crystallisation, Chemistry, and Compositions. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 9041–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.Y.; Jing, Z.Z.; Huang, J.F.; Yun, J. Synthesis of hierarchical hollow spherical CdS nanostructures by microwave hydrothermal process. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, s89–s94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Wu, Y. PEG-directed microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of spherical α-Ni(OH)2 and NiO architectures. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 2567–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matras-Postolek, K.; Sovinska, S.; Wyrazik, M.; Bogdal, D. Microwave-assisted synthesis and the surface modification of 1-D dimensional ZnS:Mn nanocrystals for polymer applications. In Proceedings of the 18th International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry, Online, 1 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zhu, J.J. Microwave-assisted synthesis of Sb2Se3 submicron rods, compared with those of Bi2Te3 and Sb2Te3. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 085604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volanti, D.P.; Orlandi, M.O.; Andrés, J.; Longo, E. Efficient microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of CuO sea urchin-like architectures via a mesoscale self-assembly. CrystEngComm 2010, 12, 1696–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z. Self-templated microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of two-dimensional holey hydroxyapatite nanosheets for efficient heavy metal removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 30076–30086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, M.; Wang, D.; Zhou, L.; Yu, N.; Zhang, P.; Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Qiu, G. Urchin-like m-LaVO4 and m-LaVO4/Ag microspheres: Synthesis and characterization. Mater. Charact. 2014, 98, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghazzawi, W.; Danish, E.; Alnahdi, H.; Salam, M.A. Rapid microwave-assisted hydrothermal green synthesis of rGO/NiO nanocomposite for glucose detection in diabetes. Synth. Met. 2020, 267, 116401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, J.M.; Michel, C.; Gerson, R.; James, W.J. Ferroelectric BiFeO3 X-ray and neutron diffraction study. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1971, 32, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip’ev, V.S.; Smolyaninov, N.P.; Fesenko, E.G.; Belyaev, I.N. Formation of BiFeOs and Determination of Unit Cell. Kristallografiya 1960, 5, 958. [Google Scholar]
- Aishwarya, K.; Jeniffer, I.H.; Maruthasalamoorthy, S.; Nirmala, R.; Punithavelan, N.; Navamathavan, R. Review—State of the Art of the Multifunctional Bismuth Ferrite: Synthesis Method and Applications. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 043010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponraj, C.; G., V.; Daniel, J. A review on the visible light active BiFeO3 nanostructures as suitable photocatalyst in the degradation of different textile dyes. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 7, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan, G.; Scott, J.F. Physics and Applications of Bismuth Ferrite. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2463–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sati, P.C.; Chhoker, S.; Sajal, V. Electron spin resonance studies and improved magnetic properties of Gd substituted BiFeO3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, S.; Zhuanghao, Z.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.X.; Liang, G.X.; Luo, J.T.; Ping, F. Critical review: Bismuth ferrite as an emerging visible light active nanostructured photocatalyst. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 6375–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Q.; Niu, F.; Huang, X.; Qin, L.; Huang, Y. A review: Preparation of bismuth ferrite nanoparticles and its applications in visible-light induced photocatalyses. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2015, 40, 97–109. [Google Scholar]
- Haruna, A.; Abdulkadir, I.; Idris, S.O. Photocatalytic activity and doping effects of BiFeO3 nanoparticles in model organic dyes. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fei, L.; Yuan, J.; Hu, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Visible light responsive perovskite BiFeO3 pills and rods with dominant {111}c facets. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tan, G.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Ren, H.; Xia, A. Microwave hydrothermal synthesis of BiFeO3: Impact of different surfactants on the morphology and photocatalytic properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2014, 25, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casut, C.; Malaescu, I.; Marin, C.N.; Miclau, M. The Effect of Bi2O3 and Fe2O3 Impurity Phases in BiFeO3 Perovskite Materials on Some Electrical Properties in the Low-Frequency Field. Materials 2022, 15, 4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valant, M.; Axelsson, A.K.; Alford, N. Peculiarities of a Solid-State Synthesis of Multiferroic Polycrystalline BiFeO3. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 5431–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Liang, H.; Qu, Y.; Jing, L. BiFeO3/Bi2Fe4O9 S-scheme heterojunction hollow nanospheres for high-efficiency photocatalytic o-chlorophenol degradation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 319, 121893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, S.; Khan, I.; Zhang, F.M.; Khan, S.; Khan, A.; Khan, S.; Sadiq, S.; Rafiq, M.; Saghir, S.; Sun, X.J. Synthesis of mediator free hollow BiFeO3 spheres/porous g-C3N4 Z-scheme photocatalysts for CO2 conversion and Alizarin Red S degradation. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2023, 162, 107534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Meng, J.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Hu, Y.; Di, A.; Wu, Y.; Chen, G. Novel formation of Bi@BiFe-glycolate hollow spheres and their conversion into Bi2O3/BiFeO3 composite hollow spheres with enhanced activity and durability in visible photocatalysis. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 10697–10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenbach, T.; Benitez, M.J.; Tirado, S.A.; Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Debut, A.; Vizuete, K. Adsorption enhanced photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B using GdxBi1-xFeO3@SBA-15 (x = 0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15) nanocomposites under visible light irradiation. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 29139–29148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenbach, T.; Santillan, P.; Morales, A.L.; Benitez, M.J.; Moncada, F.; Lascano, L.; Costa-Vera, C.; Ochoa-Herrera, V.; Vizuete, K.; Debut, A. Synthesis of doped and undoped Bi1-xMxFeO3 porous networks (M = La, Gd, Nd; x = 0, 0.03, 0.05, 0.10) with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 416, 113334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostwald, W. Lehrbuch der Allgemeinen Chemie. Bd. 2. Stöchiometrie 1896, 2, 705–742. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkendall, E. Rates of diffusion of copper and zinc in alpha brass. Trans. AIME 1939, 133, 186–203. [Google Scholar]
- Cadenbach, T.; Benitez, M.J.; Morales, A.L.; Vera, C.C.; Lascano, L.; Quiroz, F.; Debut, A.; Vizuete, K. Nanocasting synthesis of BiFeO3 nanoparticles with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 1822–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Rajendar, V.; Shekar, M.; Park, S. Particle size effects on the photocatalytic activity of BiFeO3 particles. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2018, 13, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, J.; Samantilleke, A.; Parpot, P.; Fernandes, F.; Pastor, M.; Correia, A.; Luís, E.; Chivanga Barros, A.; Teixeira, V. Visible light induced enhanced photocatalytic degradation of industrial effluents (Rhodamine B) in aqueous media using TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cadenbach, T.; Sanchez, V.; Chiquito Ríos, D.; Debut, A.; Vizuete, K.; Benitez, M.J. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Bismuth Ferrite Hollow Spheres with Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 5079. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135079
Cadenbach T, Sanchez V, Chiquito Ríos D, Debut A, Vizuete K, Benitez MJ. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Bismuth Ferrite Hollow Spheres with Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):5079. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135079
Chicago/Turabian StyleCadenbach, Thomas, Valeria Sanchez, Daniela Chiquito Ríos, Alexis Debut, Karla Vizuete, and Maria J. Benitez. 2023. "Hydrothermal Synthesis of Bismuth Ferrite Hollow Spheres with Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity" Molecules 28, no. 13: 5079. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135079
APA StyleCadenbach, T., Sanchez, V., Chiquito Ríos, D., Debut, A., Vizuete, K., & Benitez, M. J. (2023). Hydrothermal Synthesis of Bismuth Ferrite Hollow Spheres with Enhanced Visible-Light Photocatalytic Activity. Molecules, 28(13), 5079. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135079







