Phosphatidylcholine-Specific Phospholipase C as a Promising Drug Target
Abstract
:1. Introduction
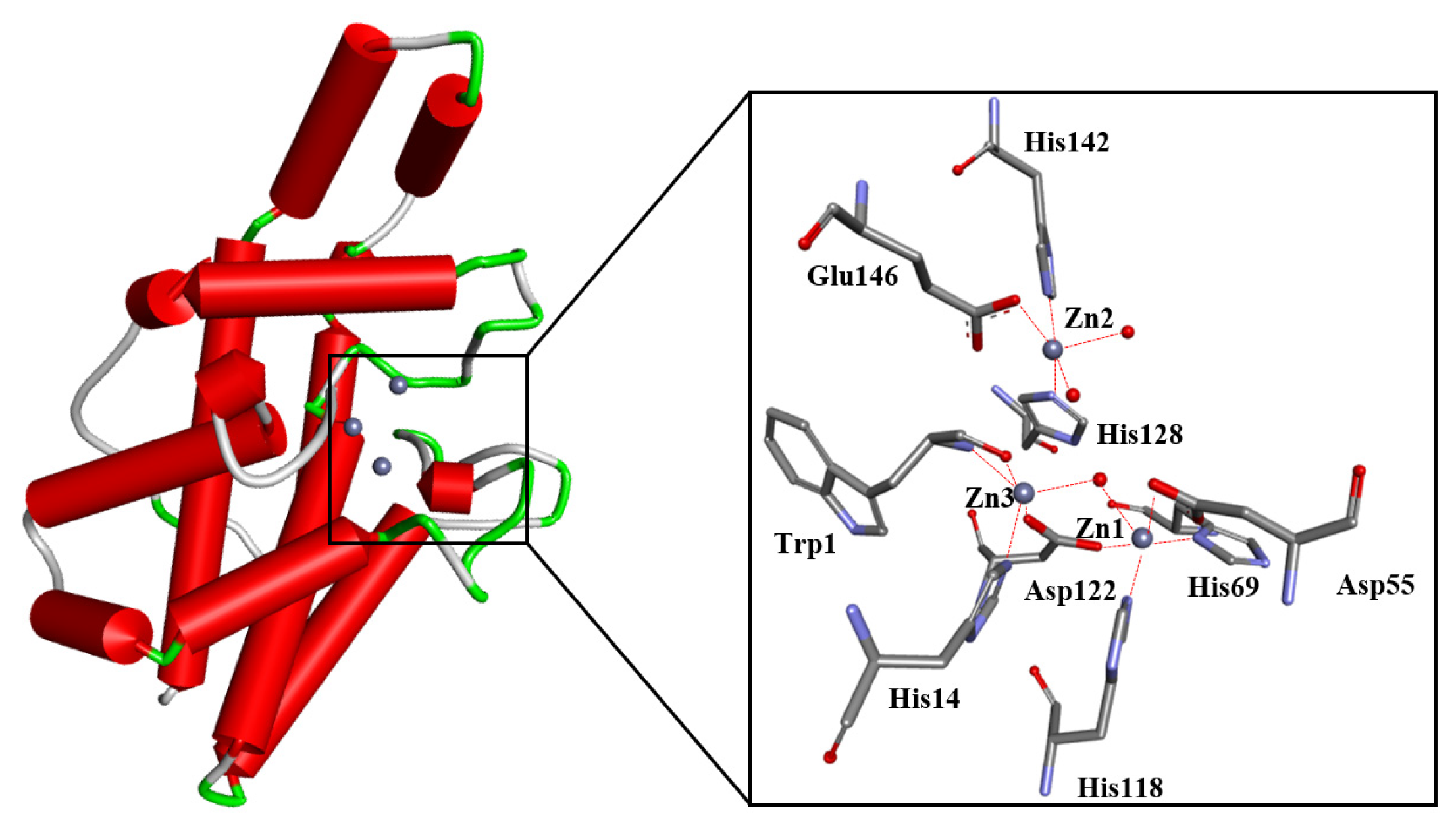
2. Pathological Implications of PC-PLC
2.1. Cancer
2.2. Atherosclerosis
2.3. Inflammation
2.4. Neuronal Cell Death
3. Discovery and Development of PC-PLC Inhibitors
3.1. 2-Aminohydroxamic Acids
3.2. Phospholipid Analogues
3.3. Xanthates
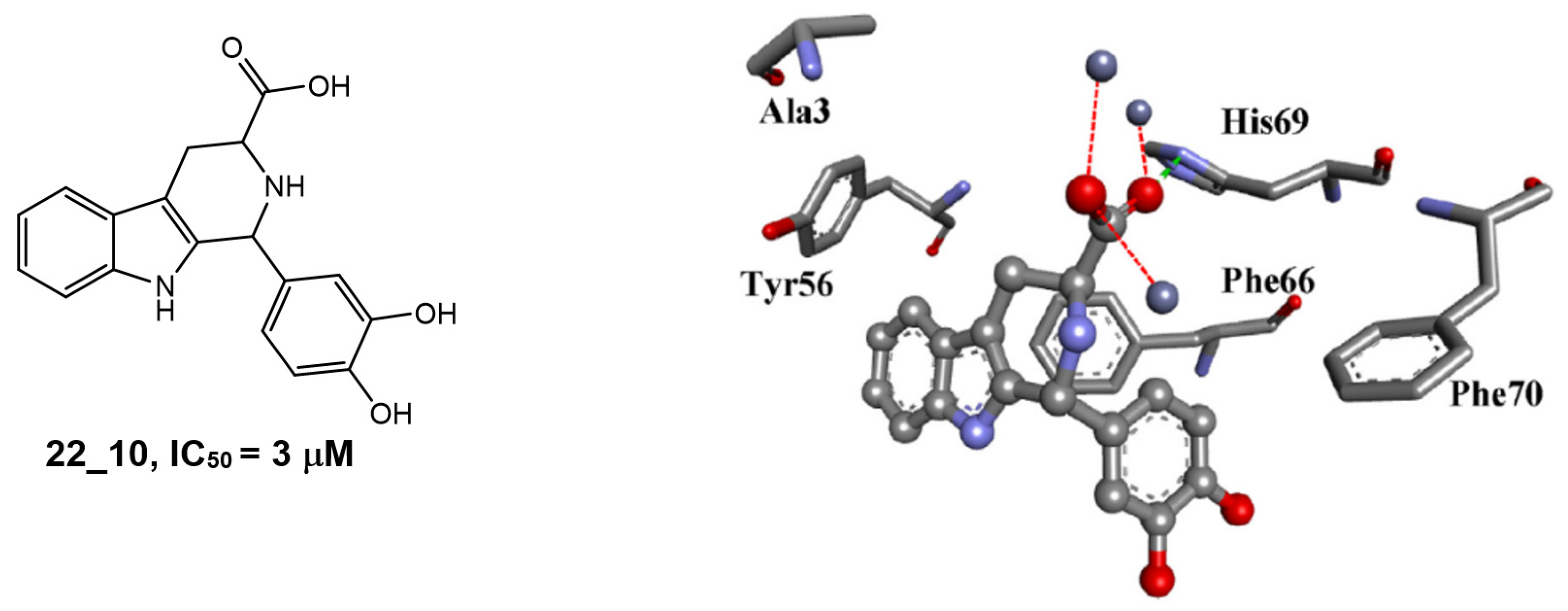
3.4. Pyrido[3,4-b]indoles
3.5. Morpholinobenzoic Acids
3.6. 1,4-Oxazepines
3.7. N,N′-Dihydroxyureas
| Compound | Chemical Structure | IC50/Ki | Assay | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-aminohydroxamic acid 6 | 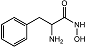 | IC50 = 4 μM | Chromogenic-based assay | [59] |
| 2-aminohydroxamic acid 18 | 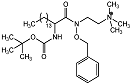 | IC50 = 2 μM | Chromogenic-based assay | [58] |
| Phospholipid analogue 7 | 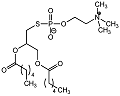 | Ki = 7 μM | pH-based assay | [60] |
| Dihydroxy phospholipid 7 | 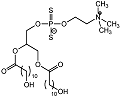 | Ki = 5.4 μM | Chromogenic-based assay | [61] |
| D609 | 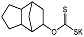 | Ki = 6.4 μM | Radiometric enzyme assay | [62] |
| Potassium O-decyl xanthate |  | Ki = 10 μM | Chromogenic-based assay | [64] |
| 1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole 22_10 |  | IC50 = 3.1 μM | Amplex Red assay | [8] |
| 2-morpholinobenzoic acid 84 | 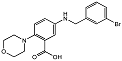 | IC50 = 3.7 μM | Amplex Red assay | [8] |
| Morpholinobenzene 10k |  | IC50 = 1.1 μM | Amplex Red assay | [70] |
| 2-morpholinobenzene hydroxamic acid 9i | 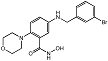 | Unknown | Amplex Red assay | [71] |
| R-7ABO | 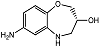 | Unknown | Amplex Red assay | [73] |
| S-7ABO | 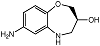 | Unknown | Amplex Red assay | [73] |
| 2,7-dihydroxytropolone | 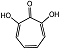 | Ki(pH = 7.3) = 16 μMKi(pH = 9.5) = 23 μM | Chromogenic-based assay | [79] |
| N,N′-dihydroxyurea 10 | 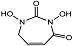 | Ki(pH = 7.3) = 388 μMKi(pH = 9.5) = 53 μM | Chromogenic-based assay | [79] |
3.8. Univalent Anions
4. PC-PLC Enzymatic Assays
5. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vines, C.M. Phospholipase C. In Calcium Signaling; Islam, M.S., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 235–254. [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway, N.D. The role of phosphatidylcholine and choline metabolites to cell proliferation and survival. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.P.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, X.C. Sphingomyelin synthases 1 and 2 exhibit phosphatidylcholine phospholipase C activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafesse, F.G.; Huitema, K.; Hermansson, M.; van der Poel, S.; van den Dikkenberg, J.; Uphoff, A.; Somerharju, P.; Holthuis, J.C.M. Both Sphingomyelin Synthases SMS1 and SMS2 Are Required for Sphingomyelin Homeostasis and Growth in Human HeLa Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17537–17547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hough, E.; Hansen, L.K.; Birknes, B.; Jynge, K.; Hansen, S.; Hordvik, A.; Little, C.; Dodson, E.; Derewenda, Z. High-resolution (1.5 Å) crystal structure of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Nature 1989, 338, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.A.; Shorr, R.G.L.; Bomalaski, J.S. Antibodies prepared to Bacillus cereus phospholipase C crossreact with a phosphatidylcholine preferring phosoholipase C in mammalian cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 140, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, L.; Xiao, D.M.; Little, C. Increased arachidonic acid metabolites from cells in culture after treatment with the phosphatidylcholine-hydrolyzing phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Prostaglandins 1987, 34, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurtivong, C.; Pilkington, L.I.; van Rensburg, M.; White, R.M.; Brar, H.K.; Rees, S.; Paulin, E.K.; Xu, C.S.; Sharma, N.; Leung, I.K.H.; et al. Discovery of novel phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C drug-like inhibitors as potential anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 187, 111919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Cancer Key Facts. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 22 March 2023).
- Meisamy, S.; Bolan, P.J.; Baker, E.H.; Bliss, R.L.; Gulbahce, E.; Everson, L.I.; Nelson, M.T.; Emory, T.H.; Tuttle, T.M.; Yee, D.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy of locally advanced breast cancer: Predicting response with in vivo 1H MR spectroscopy-a pilot study at 4 T. Radiology 2004, 233, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola-Leyva, A.; López-Cara, L.C.; Ríos-Marco, P.; Ríos, A.; Marco, C.; Carrasco-Jiménez, M.P. Choline kinase inhibitors EB-3D and EB-3P interferes with lipid homeostasis in HepG2 cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, T.; Wildes, F.; Penet, M.F.; Winnard, P.T., Jr.; Glunde, K.; Artemov, D.; Ackerstaff, E.; Gimi, B.; Kakkad, S.; Raman, V.; et al. Choline kinase overexpression increases invasiveness and drug resistance of human breast cancer cells. NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reo, N.V.; Goecke, C.M.; Narayanan, L.; Jarnot, B.M. Effects of perfluoro-n-octanoic acid, perfluoro-n-decanoic acid, and clofibrate on hepatic phosphorus metabolism in rats and guinea pigs in vivo. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1994, 124, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xingzhong, W.U.; Lu, H.; Zhou, L.A.N.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H. Changes of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C in hepatocarcinogenesis and in the proliferation and differentiation of rat liver cancer cells. Cell Biol. Int. 1997, 21, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, E.; Innominato, P.F.; Mariggio, M.A.; Maffucci, T.; Iacobelli, S.; Falasca, M. The mechanism involved in the regulation of phospholipase Cgamma1 activity in cell migration. Oncogene 2002, 21, 6520–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, D.W.; Tompkins, C.; Brewer, J.; Ball, A.; Coon, M.; Morris, V.; Waggoner, D.; Singer, J.W. Phospholipase C δ-4 overexpression upregulates ErbB1/2 expression, Erk signaling pathway, and proliferation in MCF-7 cells. Mol. Cancer 2004, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paris, L.; Cecchetti, S.; Spadaro, F.; Abalsamo, L.; Lugini, L.; Pisanu, M.E.; Iorio, E.; Natali, P.G.; Ramoni, C.; Podo, F. Inhibition of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C downregulates HER2 overexpression on plasma membrane of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podo, F.; Paris, L.; Cecchetti, S.; Spadaro, F.; Abalsamo, L.; Ramoni, C.; Ricci, A.; Pisanu, M.E.; Sardanelli, F.; Canese, R.; et al. Activation of Phosphatidylcholine-Specific Phospholipase C in Breast and Ovarian Cancer: Impact on MRS-Detected Choline Metabolic Profile and Perspectives for Targeted Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnoli, M.; Granata, A.; Nicoletti, R.; Krishnamachary, B.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Canese, R.; Podo, F.; Canevari, S.; Iorio, E.; Mezzanzanica, D. Choline Metabolism Alteration: A Focus on Ovarian Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisanu, M.E.; Ricci, A.; Paris, L.; Surrentino, E.; Liliac, L.; Bagnoli, M.; Canevari, S.; Mezzanzanica, D.; Podo, F.; Iorio, E.; et al. Monitoring response to cytostatic cisplatin in a HER2(+) ovary cancer model by MRI and in vitro and in vivo MR spectroscopy. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaro, F.; Ramoni, C.; Mezzanzanica, D.; Miotti, S.; Alberti, P.; Cecchetti, S.; Iorio, E.; Dolo, V.; Canevari, S.; Podo, F. Phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C activation in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6541–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cancer Research UK, Types of Skin Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/skin-cancer/types (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Xie, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liao, E.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Pennypacker, S.D. Phospholipase C-gamma1 is required for the epidermal growth factor receptor-induced squamous cell carcinoma cell mitogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 397, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, D.; Tan, Y.; Yang, X.; Qiao, J.; Yu, C.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, L. Phospholipase C gamma 1 is a potential prognostic biomarker for patients with locally advanced and resectable oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 43, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchetti, S.; Bortolomai, I.; Ferri, R.; Mercurio, L.; Canevari, S.; Podo, F.; Miotti, S.; Iorio, E. Inhibition of Phosphatidylcholine-Specific Phospholipase C Interferes with Proliferation and Survival of Tumor Initiating Cells in Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallego, O. Nonsurgical treatment of recurrent glioblastoma. Curr. Oncol. 2015, 22, e273–e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birzu, C.; French, P.; Caccese, M.; Cerretti, G.; Idbaih, A.; Zagonel, V.; Lombardi, G. Recurrent Glioblastoma: From Molecular Landscape to New Treatment Perspectives. Cancers 2020, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Shi, Z. Phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCG1) overexpression is associated with tumor growth and poor survival in IDH wild-type lower-grade gliomas in adult patients. Lab. Investig. 2022, 102, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratti, S.; Marvi, M.V.; Mongiorgi, S.; Obeng, E.O.; Rusciano, I.; Ramazzotti, G.; Morandi, L.; Asioli, S.; Zoli, M.; Mazzatenta, D.; et al. Impact of phospholipase C β1 in glioblastoma: A study on the main mechanisms of tumor aggressiveness. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.E.; Mezzapelle, R. The Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 in Cell Proliferation and Tissue Regeneration. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Azad, B.B.; Nimmagadda, S. The intricate role of CXCR4 in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2014, 124, 31–82. [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio, L.; Cecchetti, S.; Ricci, A.; Pacella, A.; Cigliana, G.; Bozzuto, G.; Podo, F.; Iorio, E.; Carpinelli, G. Phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C inhibition down- regulates CXCR4 expression and interferes with proliferation, invasion and glycolysis in glioma cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) Key Facts. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Kawakami, A.; Aikawa, M.; Nitta, N.; Yoshida, M.; Libby, P.; Sacks, F.M. Apolipoprotein CIII-induced THP-1 cell adhesion to endothelial cells involves pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein- and protein kinase C alpha-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Su, L.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Miao, J. Targeting annexin A7 by a small molecule suppressed the activity of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C in vascular endothelial cells and inhibited atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E−/− mice. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Su, L.; Huang, B.; Wang, L.; Su, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Miao, J. D609 inhibits progression of preexisting atheroma and promotes lesion stability in apolipoprotein e−/− mice: A role of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Jing, Q.; Meng, N.; Su, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Miao, J.; Zhao, J. Regulation of apoptosis and autophagy by sphingosylphosphorylcholine in vascular endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 2827–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Lu, W.; Zhao, J.; Su, L.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Miao, J. Phosphatidylethanolamine binding protein 1 in vacular endothelial cell autophagy and atherosclerosis. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 5005–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schütze, S.; Machleidt, T.; Krönke, M. The role of diacylglycerol and ceramide in tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 signal transduction. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1994, 56, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Jones, C.; Zhang, G. The Role of Phospholipase C Signaling in Macrophage-Mediated Inflammatory Response. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 5201759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schütze, S.; Potthoff, K.; Machleidt, T.; Berkovic, D.; Wiegmann, K.; Krönke, M. TNF activates NF-kappa B by phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C-induced “acidic” sphingomyelin breakdown. Cell 1992, 71, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütze, S.; Berkovic, D.; Tomsing, O.; Unger, C.; Krönke, M. Tumor necrosis factor induces rapid production of 1′2′diacylglycerol by a phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 174, 975–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosoff, P.M.; Savage, N.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 stimulates diacylglycerol production in T lymphocytes by a novel mechanism. Cell 1988, 54, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2016 Neurological Disorders Collaborator Group. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders during 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Maher, P.; Schubert, D. Phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C regulates glutamate-induced nerve cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7748–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Du, C.Q.; Wang, S.S.; Xie, K.; Zhang, S.L.; Miao, J.Y. D609 induces vascular endothelial cells and marrow stromal cells differentiation into neuron-like cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 442–446. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Xie, K.; Huo, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Miao, J. Suppressing phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C and elevating ROS level, NADPH oxidase activity and Rb level induced neuronal differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 100, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Peng, H.; Kim, D.-I.; Kunkel, M.; Powis, G.; Zalkow, L.H. Structure–activity relationship of Aza-steroids as PI-PLC inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2001, 9, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Peng, H.; Zalkow, L.H.; Li, Y.H.; Zhu, C.; Powis, G.; Kunkel, M. 3β-Hydroxy-6-aza-cholestane and related analogues as phosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) inhibitors with antitumor activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2000, 8, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynisson, J.; Court, W.; O’Neill, C.; Day, J.; Patterson, L.; McDonald, E.; Workman, P.; Katan, M.; Eccles, S.A. The identification of novel PLC-γ inhibitors using virtual high throughput screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3169–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynisson, J.; Jaiswal, J.K.; Barker, D.; D’mello, S.A.N.; Denny, W.A.; Baguley, B.C.; Leung, E.Y. Evidence that phospholipase C is involved in the antitumour action of NSC768313, a new thieno[2,3-b]pyridine derivative. Cancer Cell Int. 2016, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.; Yu, Y.U.; Kim, Y.C. Inhibition of phospholipase Cγ1 and cancer cell proliferation by lignans and flavans from Machilus thunbergii. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powis, G.; Seewald, M.J.; Gratas, C.; Melder, D.; Riebow, J.; Modest, E.J. Selective inhibition of phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C by cytotoxic ether lipid analogues. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 2835–2840. [Google Scholar]
- Drings, P.; Günther, I.; Gatzemeier, U.; Ulbrich, F.; Khanavkar, B.; Schreml, W.; Lorenz, J.; Brugger, W.; Schick, H.D.; von Pawel, J.; et al. Final Evaluation of a Phase II Study on the Effect of Edelfosine (an Ether Lipid) in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Bronchogenic Carcinoma. Oncol. Res. Treat. 1992, 15, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, W.R.; Berdel, W.E.; Geller, R.B.; Brochstein, J.A.; Beveridge, R.A.; Dalton, W.S.; Miller, K.B.; Lazarus, H.M. A phase II trial of autologous bone marrow transplantation (ABMT) in acute leukemia with edelfosine purged bone marrow. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1996, 416, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- González-Bulnes, P.; González-Roura, A.; Canals, D.; Delgado, A.; Casas, J.; Llebaria, A. 2-Aminohydroxamic acid derivatives as inhibitors of Bacillus cereus phosphatidylcholine preferred phospholipase C PC-PLCBc. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 8549–8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Roura, A.; Navarro, I.; Delgado, A.; Llebaria, A.; Casas, J. Disclosing new inhibitors by finding similarities in three-dimensional active-site architectures of polynuclear zinc phospholipases and aminopeptidases. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004, 43, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.F.; Wong, Y.L.; Wagman, A.S. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Phospholipid Analogs as Inhibitors of the Bacterial Phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 4821–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, C.L.; Li, H.; Martin, S.F. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of water-soluble phospholipid analogues as inhibitors of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 7298–7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amtmann, E. The antiviral, antitumoural xanthate D609 is a competitive inhibitor of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1996, 22, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sauer, G.; Amtmann, E.; Melber, K.; Knapp, A.; Müller, K.; Hummel, K.; Scherm, A. DNA and RNA virus species are inhibited by xanthates, a class of antiviral compounds with unique properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3263–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Roura, A.; Casas, J.; Llebaria, A. Synthesis and phospholipase C inhibitory activity of D609 diastereomers. Lipids 2002, 37, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.A.; Addo, J.K.; Deokar, H.; Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Suttle, D.P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Buolamwini, J.K. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Modeling Studies of New Pyrido[3,4-b]indole Derivatives as Broad-Spectrum Potent Anticancer Agents. Drug Des. 2017, 6, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashok, P.; Chander, S.; Smith, T.K.; Prakash Singh, R.; Jha, P.N.; Sankaranarayanan, M. Biological evaluation and structure activity relationship of 9-methyl-1-phenyl-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole derivatives as anti-leishmanial agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 84, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamiz, A.P.; Whittemore, E.R.; Woodward, R.M.; Upasani, R.B.; Keana, J.F.W. Structure-activity relationship for a series of 2-substituted 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indoles: Potent subtype-selective inhibitors of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.K.; Jain, P.C.; Anand, N.; Dua, P.R. Agents acting on the central nervous system. 15. 2-Substituted 1,2,3,4,6,7,12,12a-octahydropyrazino [2′,1′:6,1]pyrido[3,4-b]indoles. New class of central nervous system depressants. J. Med. Chem. 1973, 16, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Savi, C.; Bradbury, R.H.; Rabow, A.A.; Norman, R.A.; de Almeida, C.; Andrews, D.M.; Balard, P.; Buttar, D.; Callis, R.J.; Currie, G.S.; et al. Optimization of a Novel Binding Motif to (E)-3-(3,5-Difluoro-4-((1R,3R)-2-(2-fluoro-2-methylpropyl)-3-methyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indol-1-yl)phenyl)acrylic Acid (AZD9496), a Potent and Orally Bioavailable Selective Estrogen Receptor Downregulator and Antagonist. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8128–8140. [Google Scholar]
- Pilkington, L.I.; Sparrow, K.; Rees, S.W.P.; Paulin, E.K.; van Rensburg, M.; Xu, C.S.; Langley, R.J.; Leung, I.K.H.; Reynisson, J.; Leung, E.; et al. Development, synthesis and biological investigation of a novel class of potent PC-PLC inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 191, 112162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, S.W.P.; Leung, E.; Reynisson, J.; Barker, D.; Pilkington, L.I. Development of 2-Morpholino-N-hydroxybenzamides as anti-proliferative PC-PLC inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 114, 105152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Langley, R.J.; Eurtivong, C.; Leung, E.; Dixon, R.J.; Paulin, E.K.; Rees, S.W.P.; Pilkington, L.I.; Barker, D.; Reynisson, J.; et al. An optimised MALDI-TOF assay for phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Su, L.; Li, K.; Zhao, B. Discovery of novel PC-PLC activity inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2020, 95, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.Q.; Wei, C.X.; Li, F.N.; Sun, Z.G.; Quan, Z.S. Design and synthesis of 10-alkoxy-5, 6-dihydro-triazolo[4,3-d]benzo[f][1,4]oxazepine derivatives with anticonvulsant activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3080–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.E.; Kurukulasuriya, R.; Sinz, C.; Lombardo, M.; Bender, K.; Parker, D.; Sherer, E.C.; Costa, M.; Dingley, K.; Li, X.; et al. Discovery and development of benzo-[1,2,4]-triazolo-[1,4]-oxazepine GPR142 agonists for the treatment of diabetes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2947–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapegin, A.; Kalinin, S.; Angeli, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Krasavin, M. Unprotected primary sulfonamide group facilitates ring-forming cascade en route to polycyclic [1,4]oxazepine-based carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 76, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Jin, B.; Sha, S.; Wu, X.; Sangani, C.B.; Wang, S.F.; Qiao, F.; Lu, A.M.; Lv, P.C.; et al. 6,7-Dihydrobenzo[f]benzo[4,5]imidazo[1,2-d][1,4]oxazepine derivatives as selective inhibitors of PI3Kα. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dols, P.P.M.A.; Folmer, B.J.B.; Hamersma, H.; Kuil, C.W.; Lucas, H.; Ollero, L.; Rewinkel, J.B.M.; Hermkens, P.H.H. SAR study of 2,3,4,14b-tetrahydro-1H-dibenzo[b,f]pyrido[1,2-d][1,4]oxazepines as progesterone receptor agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.F.; Follows, B.C.; Hergenrother, P.J.; Franklin, C.L. A Novel Class of Zinc-Binding Inhibitors for the Phosphatidylcholine-Preferring Phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 4509–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakre, S.E.; Little, C. Inhibition of Bacillus cereus phospholipase C by univalent anions. Biochem. J. 1982, 203, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aalmo, K.; Hansen, L.; Hough, E.; Jynge, K.; Krane, J.; Little, C.; Storm, C.B. An anion binding site in the active centre of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Biochem. Int. 1984, 8, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hergenrother, P.J.; Martin, S.F. Determination of the Kinetic Parameters for Phospholipase C (Bacillus cereus) on Different Phospholipid Substrates Using a Chromogenic Assay Based on the Quantitation of Inorganic Phosphate. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 251, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, A.; Gong, S.; Faigle, M.; Neumeister, B. Critical evaluation of p-nitrophenylphosphorylcholine (p-NPPC) as artificial substrate for the detection of phospholipase C. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2000, 26, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingjie, Z.; Cailan, Z.; Richard, P.H. Choline oxidase: A useful tool for high-throughput assays of acetylcholinesterase, phospholipase D, phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C, and sphingomyelinase. In Advances in Nucleic Acid and Protein Analysis, Manipulation, and Sequencing; Limbach, P.A., Owicki, J.C., Raghavachari, R., Tan, W., Eds.; Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE): San Jose, CA, USA, 2000; Volume 3926, pp. 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Diwu, Z.; Panchuk-Voloshina, N.; Haugland, R.P. A stable nonfluorescent derivative of resorufin for the fluorometric determination of trace hydrogen peroxide: Applications in detecting the activity of phagocyte NADPH oxidase and other oxidases. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 253, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, J.G.; Jaffe, J.S.; Schulman, E.S.; Raible, D.G. A highly sensitive fluorescent micro-assay of H2O2 release from activated human leukocytes using a dihydroxyphenoxazine derivative. J. Immunol. Methods 1997, 202, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, C.; Mizuno, S.; Kado, S.; Sakane, F. Development of a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry based enzyme activity assay for phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 526, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eurtivong, C.; Leung, E.; Sharma, N.; Leung, I.K.H.; Reynisson, J. Phosphatidylcholine-Specific Phospholipase C as a Promising Drug Target. Molecules 2023, 28, 5637. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155637
Eurtivong C, Leung E, Sharma N, Leung IKH, Reynisson J. Phosphatidylcholine-Specific Phospholipase C as a Promising Drug Target. Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5637. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155637
Chicago/Turabian StyleEurtivong, Chatchakorn, Euphemia Leung, Nabangshu Sharma, Ivanhoe K. H. Leung, and Jóhannes Reynisson. 2023. "Phosphatidylcholine-Specific Phospholipase C as a Promising Drug Target" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5637. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155637
APA StyleEurtivong, C., Leung, E., Sharma, N., Leung, I. K. H., & Reynisson, J. (2023). Phosphatidylcholine-Specific Phospholipase C as a Promising Drug Target. Molecules, 28(15), 5637. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155637








