Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolomics to Reveal the Protection of Coptisine against Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury via Anti-Inflammation and Antioxidant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
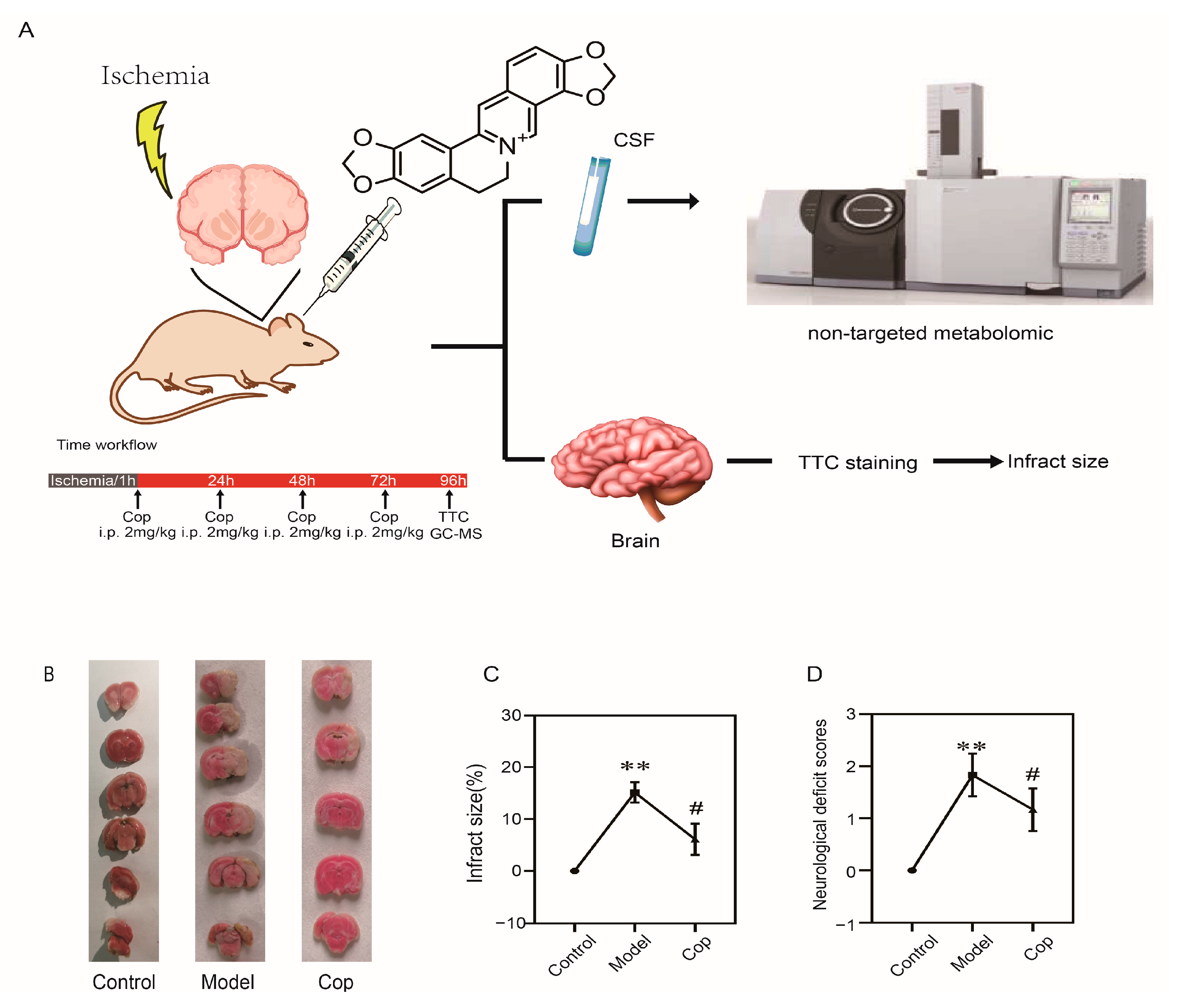
2.1. Protective Effect of Cop on Cerebral IR
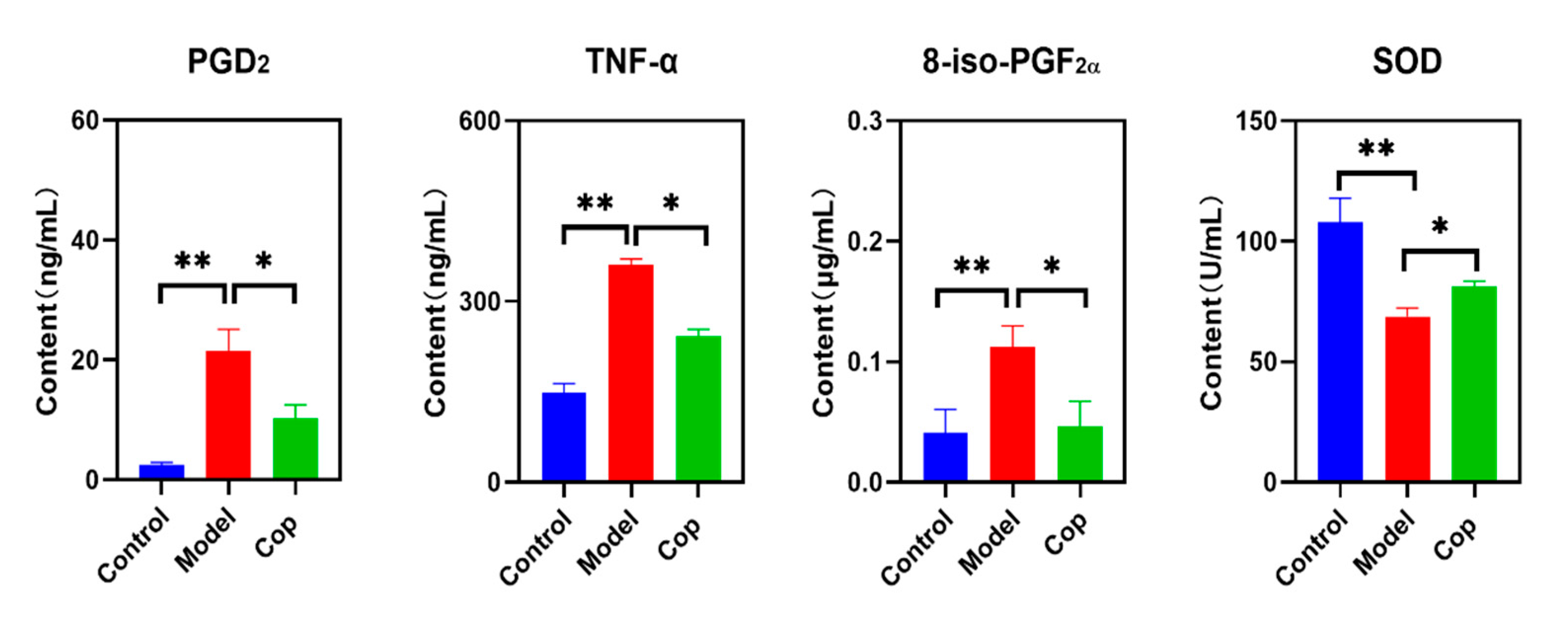
2.2. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Cop in Response to Cerebral IR
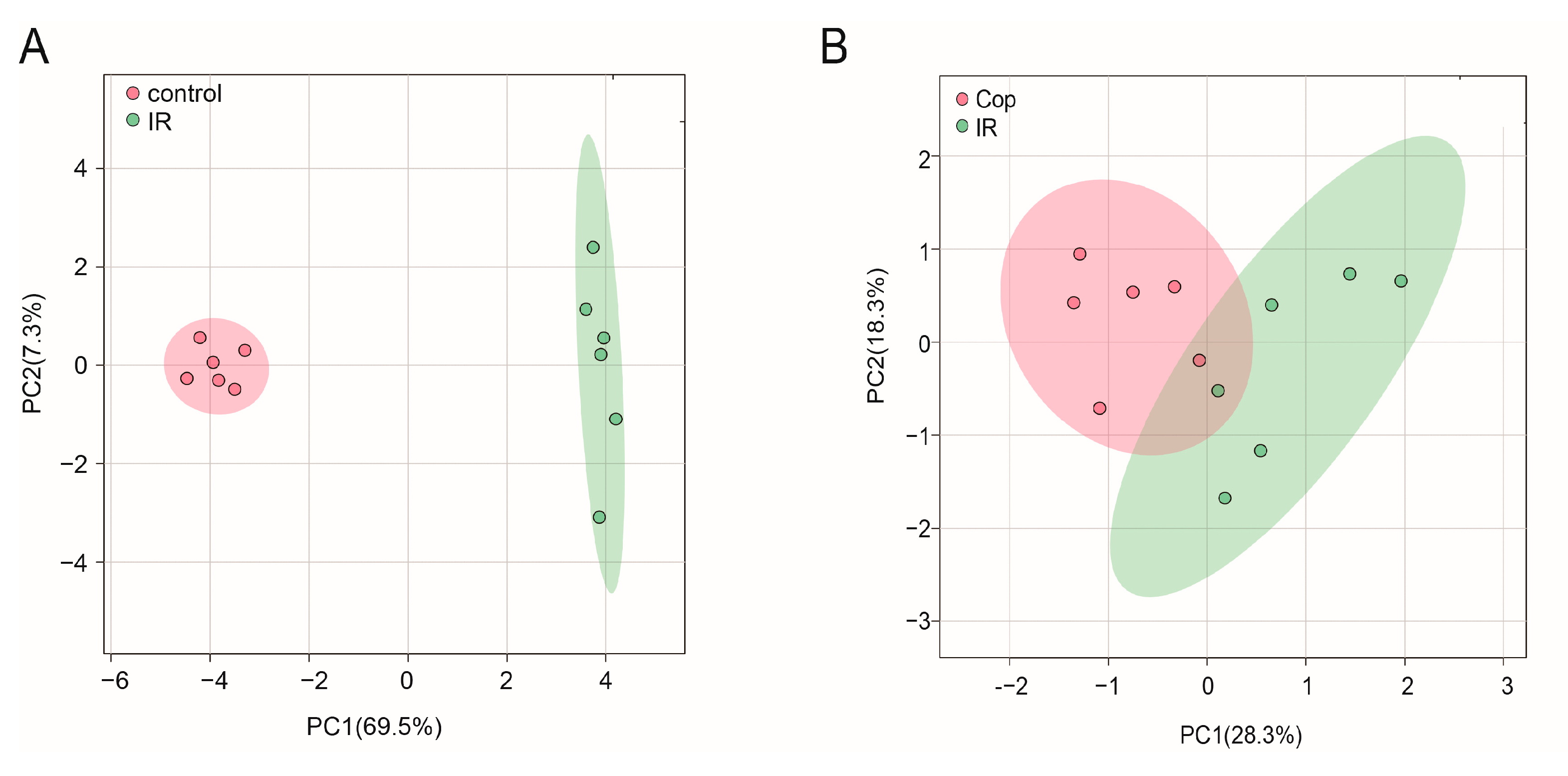
2.3. GC–MS Analysis
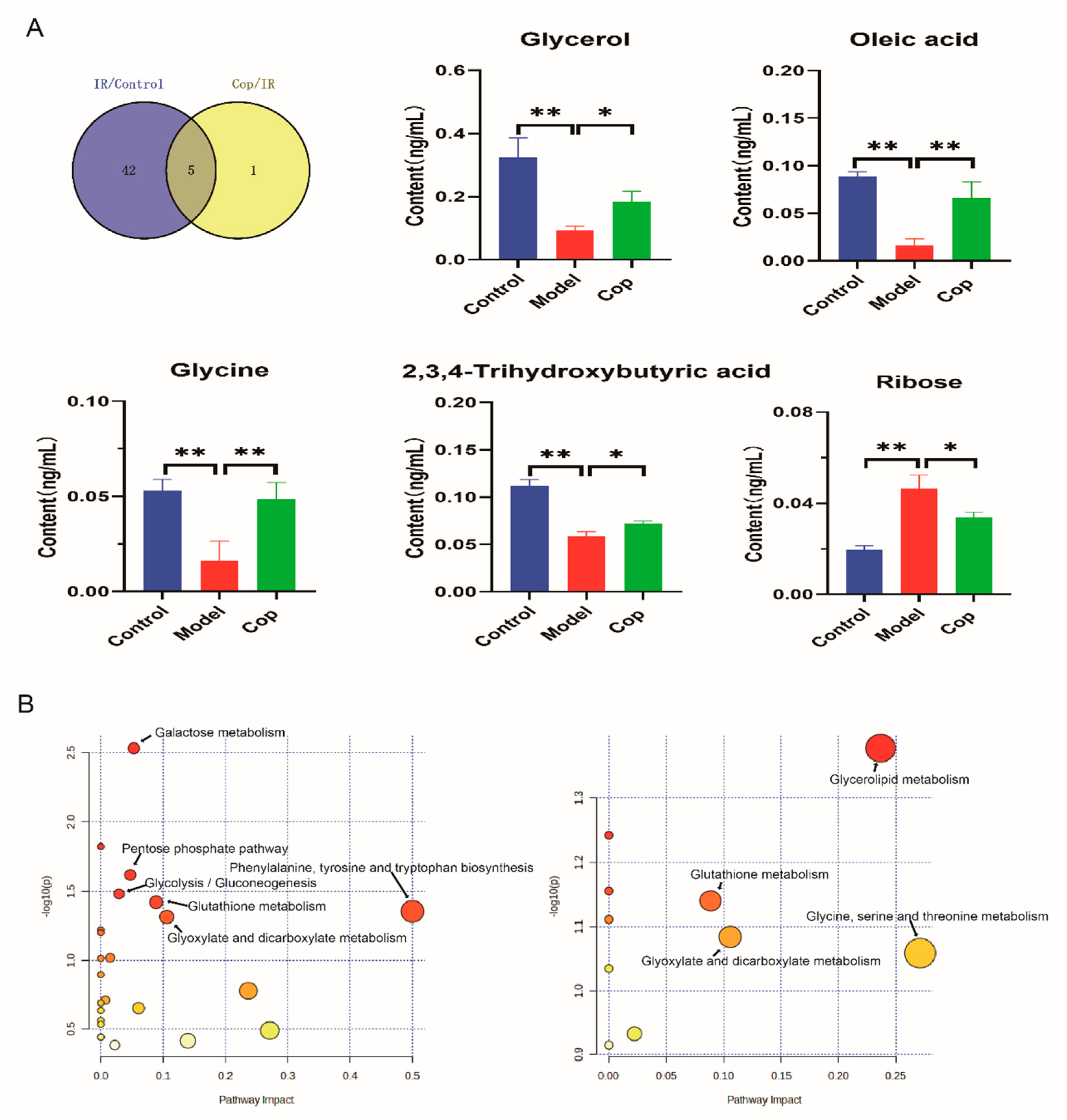
2.4. Screen in Metabolites from GC–MS Data as Potential Biomarkers between Control, Model, and Cop-Treated Groups
2.5. Analysis of Metabolic Pathway Enrichment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Reagents
4.2. Animal Care
4.3. Transient Focal Cerebral IR and Animal Treatment
4.4. Neurological Function Measurement
4.5. Sample Collection
4.6. Sample Preparation and GC–MS Analysis
4.7. Qualitative Identification of Metabolites and Raw Data Preprocessing
4.8. Measurement of Brain PGD2, TNF-α, 8-iso-PGF2α and SOD
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2023 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 147, e93–e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marko, M.; Posekany, A.; Szabo, S.; Scharer, S.; Kiechl, S.; Knoflach, M.; Serles, W.; Ferrari, J.; Lang, W.; Sommer, P.; et al. Trends of r-tPA (Recombinant Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator) Treatment and Treatment-Influencing Factors in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Su, X.; Lu, F.; Zong, R.; Ding, S.; Liu, J.; Wilson, G.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Serum and brain metabolomic study reveals the protective effects of Bai-Mi-Decoction on rats with ischemic stroke. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1005301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.F.; Zheng, F.; Su, L.J.; Zhang, D.W.; Liu, Y.N.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Gong, S.S.; Kou, J.P. Metabolomic Profiling of Brain Protective Effect of Edaravone on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 814942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Chen, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Feng, Y. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Profiling Reveals the Protective Effect of Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. & Maxim.) Harms Combined With Gastrodia elata Blume on Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 619076. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedemann, T.; Ying, Y.; Wang, W.; Kramer, E.R.; Schumacher, U.; Fei, J.; Schroder, S. Neuroprotective Effect of Coptis chinensis in MPP[Formula: See text] and MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Models. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Luo, C.; Ni, C.; Xie, J.; Su, Z.; Chen, J.; et al. Coptisine ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via improving intestinal barrier dysfunction and suppressing inflammatory response. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 896, 173912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gong, S.; Li, K.; Wu, G.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Su, Z.; et al. Coptisine protects against hyperuricemic nephropathy through alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress and mitochondrial apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.G.; Park, C.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.Y.; Keum, Y.S.; Hyun, J.W.; Kwon, T.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Hong, S.H. Inhibition of oxidative stress induced-cytotoxicity by coptisine in V79-4 Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts through the induction of Nrf-2 mediated HO-1 expression. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.R.; Ma, H.; Zou, Z.Y.; He, K.; Xiao, Y.B.; Wang, Y.; Feng, M.; Ye, X.L.; Li, X.G. Activation of Akt and JNK/Nrf2/NQO1 pathway contributes to the protective effect of coptisine against AAPH-induced oxidative stress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Zhang, X.; Qu, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y. Coptisine induces G2/M arrest in esophageal cancer cell via the inhibition of p38/ERK1/2/claudin-2 signaling pathway. Pharmazie 2021, 76, 202–207. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Jiang, P.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Huang, T.; Ye, X.; Li, X. Coptisine-induced apoptosis in human colon cancer cells (HCT-116) is mediated by PI3K/Akt and mitochondrial-associated apoptotic pathway. Phytomedicine 2018, 48, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Sun, C.; Yao, D.; Wang, C.Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yuan, C.S. Novel surface imprinted magnetic mesoporous silica as artificial antibodies for efficient discovery and capture of candidate nNOS-PSD-95 uncouplers for stroke treatment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedemann, T.; Schumacher, U.; Tao, Y.; Leung, A.K.; Schroder, S. Neuroprotective Activity of Coptisine from Coptis chinensis (Franch). Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 827308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.L.; Fang, L.H.; Qin, H.L.; Lv, Y.; Du, G.H. Analysis of the mechanisms underlying the vasorelaxant action of coptisine in rat aortic rings. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2012, 40, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Tao, B.B.; Yang, Y.Y.; Du, L.S.; Yang, S.S.; He, X.J.; Zhu, Y.W.; Yan, J.K.; Yang, Q. The IDO inhibitor coptisine ameliorates cognitive impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2015, 43, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasa, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamashina, K.; Yagishita-Kyo, N.; Maruyama, K.; Awaji, T.; Takei, Y.; Hirasawa, A.; Yoshikawa, K. A peripheral lipid sensor GPR120 remotely contributes to suppression of PGD(2)-microglia-provoked neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in the mouse hippocampus. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Cai, C.; Wang, X.; Deng, L.; He, B.; Zhou, W.; Cui, Y. DL-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP) alleviates poststroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) by suppressing neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 987293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elesber, A.A.; Best, P.J.; Lennon, R.J.; Mathew, V.; Rihal, C.S.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. Plasma 8-iso-prostaglandin F2alpha, a marker of oxidative stress, is increased in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Free. Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, K.; Popeda, M.; Price, B.; Bienkowski, M.; Fahlstrom, A.; Drummond, K.; Adamides, A.A. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 8-iso-prostaglandin F2alpha as potential predictors of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga Cabeza, O.; Zhang, Z.; Smith Khoury, E.; Sheldon, R.A.; Sharma, A.; Zhang, F.; Slusher, B.S.; Kannan, R.M.; Kannan, S.; Ferriero, D.M. Neuroprotective effects of a dendrimer-based glutamate carboxypeptidase inhibitor on superoxide dismutase transgenic mice after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 148, 105201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulart, V.A.M.; Sena, M.M.; Mendes, T.O.; Menezes, H.C.; Cardeal, Z.L.; Paiva, M.J.N.; Sandrim, V.C.; Pinto, M.C.X.; Resende, R.R. Amino Acid Biosignature in Plasma among Ischemic Stroke Subtypes. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8480468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; Zhao, X.S.; Fan, T.P.; Qi, H.X.; Li, D. Glycine Improves Ischemic Stroke Through miR-19a-3p/AMPK/GSK-3beta/HO-1 Pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liao, X.Y.; Pan, M.X.; Tang, J.C.; Chen, S.F.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, P.X.; Lu, L.J.; Zou, Y.Y.; Qin, X.P.; et al. Glycine Exhibits Neuroprotective Effects in Ischemic Stroke in Rats through the Inhibition of M1 Microglial Polarization via the NF-kappaB p65/Hif-1alpha Signaling Pathway. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1704–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo-Hernandez, E.; Tello, V.; Arroyo, A.A.; Dominguez-Prieto, M.; de Castro, F.; Tabernero, A.; Medina, J.M. Oleic acid synthesized by stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD-1) in the lateral periventricular zone of the developing rat brain mediates neuronal growth, migration and the arrangement of prospective synapses. Brain Res. 2014, 1570, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vascellari, S.; Palmas, V.; Melis, M.; Pisanu, S.; Cusano, R.; Uva, P.; Perra, D.; Madau, V.; Sarchioto, M.; Oppo, V.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Metabolome Alterations Associated with Parkinson’s Disease. Msystems 2020, 5, e00561-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulieu, J.; Costa, G.; Renaud, J.; Moitie, A.; Glemet, H.; Sergi, D.; Martinoli, M.G. The Neuroinflammatory and Neurotoxic Potential of Palmitic Acid Is Mitigated by Oleic Acid in Microglial Cells and Microglial-Neuronal Co-cultures. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3000–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Lee, D.; Kim, H. Neuroprotective effects of oleic acid in rodent models of cerebral ischaemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhao, S.; Hong, J.; Li, W.; Wang, X. Protective Effects of Kaempferol on D-Ribose-Induced Mesangial Cell Injury. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7564207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; He, T.; Wei, Y.; He, R. D-ribose is elevated in T1DM patients and can be involved in the onset of encephalopathy. Aging 2019, 11, 4943–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Bhat, O.M.; Li, G.; Dempsey, S.K.; Zhang, Q.; Ritter, J.K.; Li, W.; Li, P.L. Lysosomal regulation of extracellular vesicle excretion during d-ribose-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in podocytes. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q.; Ritter, J.; Li, W.; Li, P.L. D-Ribose Induces Podocyte NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Glomerular Injury via AGEs/RAGE Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Li, S.; Huang, W.; Xiang, L.; Liu, D.; Hu, Y.; Wang, P.; Lu, X.; et al. Coptisine from Coptis chinensis blocks NLRP3 inflammasome activation by inhibiting caspase-1. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 147, 104348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wei, H.; Chen, C.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, J.; Tan, Y.; Zeng, L. Coptisine attenuates post-infectious IBS via Nrf2-dependent inhibition of the NLPR3 inflammasome. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 26, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.Y.; Pan, P.H.; Li, J.R.; Ou, Y.C.; Liao, S.L.; Chen, W.Y.; Kuan, Y.H.; Chen, C.J. Glycerol Improves Intracerebral Hemorrhagic Brain Injury and Associated Kidney Dysfunction in Rats. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shin, J.A.; Lee, E.M.; Nam, M.; Park, E.M. Noggin-mediated effects on metabolite profiles of microglia and oligodendrocytes after ischemic insult. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 224, 115196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Kong, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Lai, M. GC-MS-based metabolomics identifies an amino acid signature of acute ischemic stroke. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 642, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H.; He, D.; Chen, L.; Dong, C.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Qin, Y.H.; Yu, R.; Ahmed, R.; Kuang, J.J.; Zhang, X.W. GC-MS based metabolomics strategy to distinguish three types of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Wei, Y.; Yu, H.; Ma, X.; Yan, S.; Zhao, L.; Ding, L.; Cheng, J.; Feng, H. Erythritol Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Activating Nrf2 Antioxidant Capacity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 13080–13092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hartog, G.J.; Boots, A.W.; Adam-Perrot, A.; Brouns, F.; Verkooijen, I.W.; Weseler, A.R.; Haenen, G.R.; Bast, A. Erythritol is a sweet antioxidant. Nutrition 2010, 26, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, J.; Li, M.; Ma, L.; Li, X. Coptisine ameliorates renal injury in diabetic rats through the activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Yao, Z.Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.H.; Luo, M.; Dong, M.M.; Zhou, G.P. Mechanism of Electroacupuncture Against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Reducing Inflammatory Response and Cell Pyroptosis by Inhibiting NLRP3 and Caspase-1. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 822088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Kita, Y.; Kohira, T.; Yoshida, K.; Hamano, F.; Tokuoka, S.M.; Shimizu, T. A comprehensive quantification method for eicosanoids and related compounds by using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry with high speed continuous ionization polarity switching. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 995, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Qi, A.; Liu, L.; Cai, C.; Xu, H. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolomics to Reveal the Protection of Coptisine against Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury via Anti-Inflammation and Antioxidant. Molecules 2023, 28, 6350. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176350
Zhang J, Qi A, Liu L, Cai C, Xu H. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolomics to Reveal the Protection of Coptisine against Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury via Anti-Inflammation and Antioxidant. Molecules. 2023; 28(17):6350. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176350
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Junjie, Ao Qi, Lulu Liu, Chun Cai, and Hui Xu. 2023. "Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolomics to Reveal the Protection of Coptisine against Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury via Anti-Inflammation and Antioxidant" Molecules 28, no. 17: 6350. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176350
APA StyleZhang, J., Qi, A., Liu, L., Cai, C., & Xu, H. (2023). Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolomics to Reveal the Protection of Coptisine against Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury via Anti-Inflammation and Antioxidant. Molecules, 28(17), 6350. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176350





