Gut Microbiota Combined with Metabolomics Reveal the Mechanisms of Sika Deer Antler Protein on Cisplatin-Induced Hepatorenal Injury in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
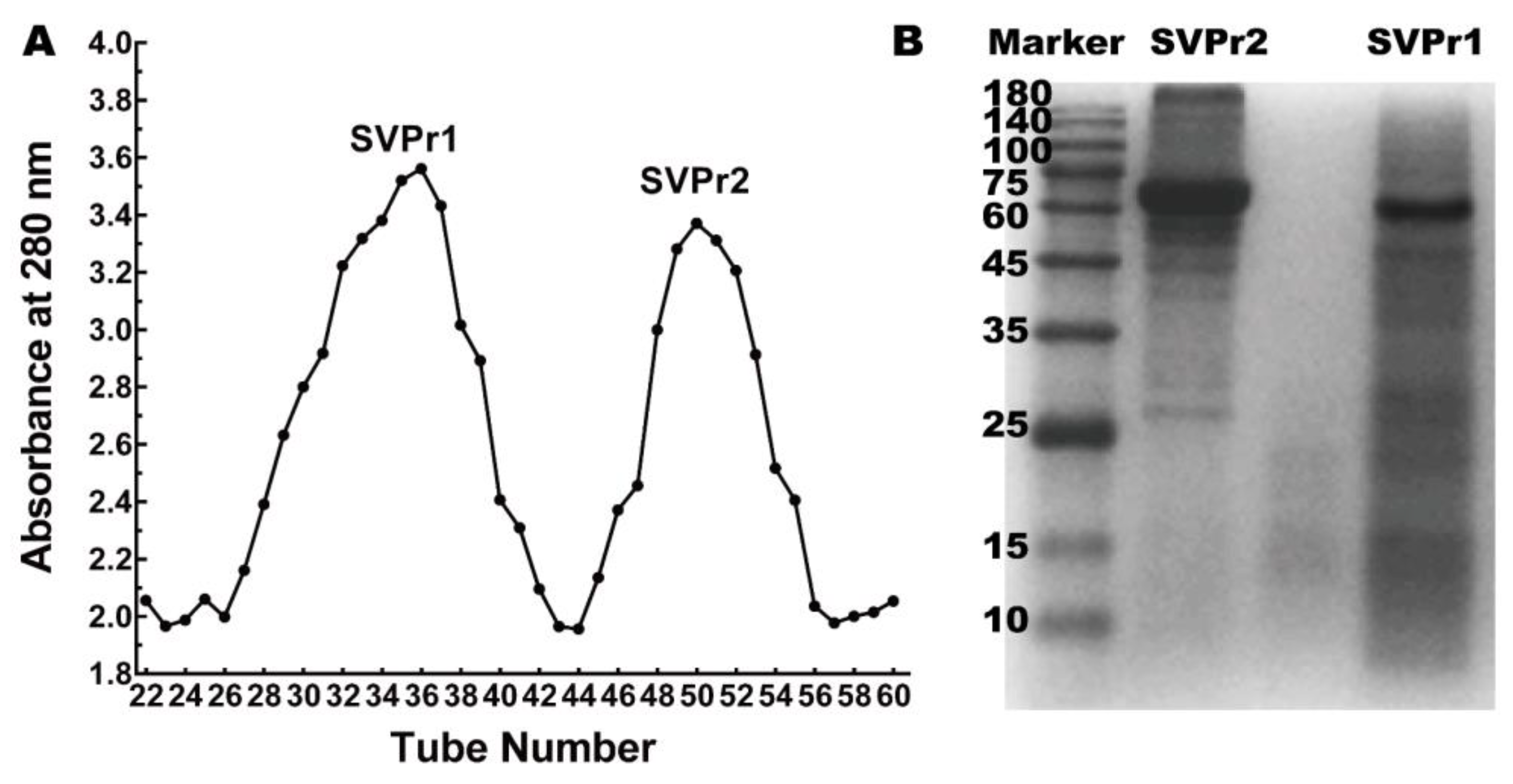
2.1. Isolation and Molecular Weight Identification of Sika Deer Antler Proteins
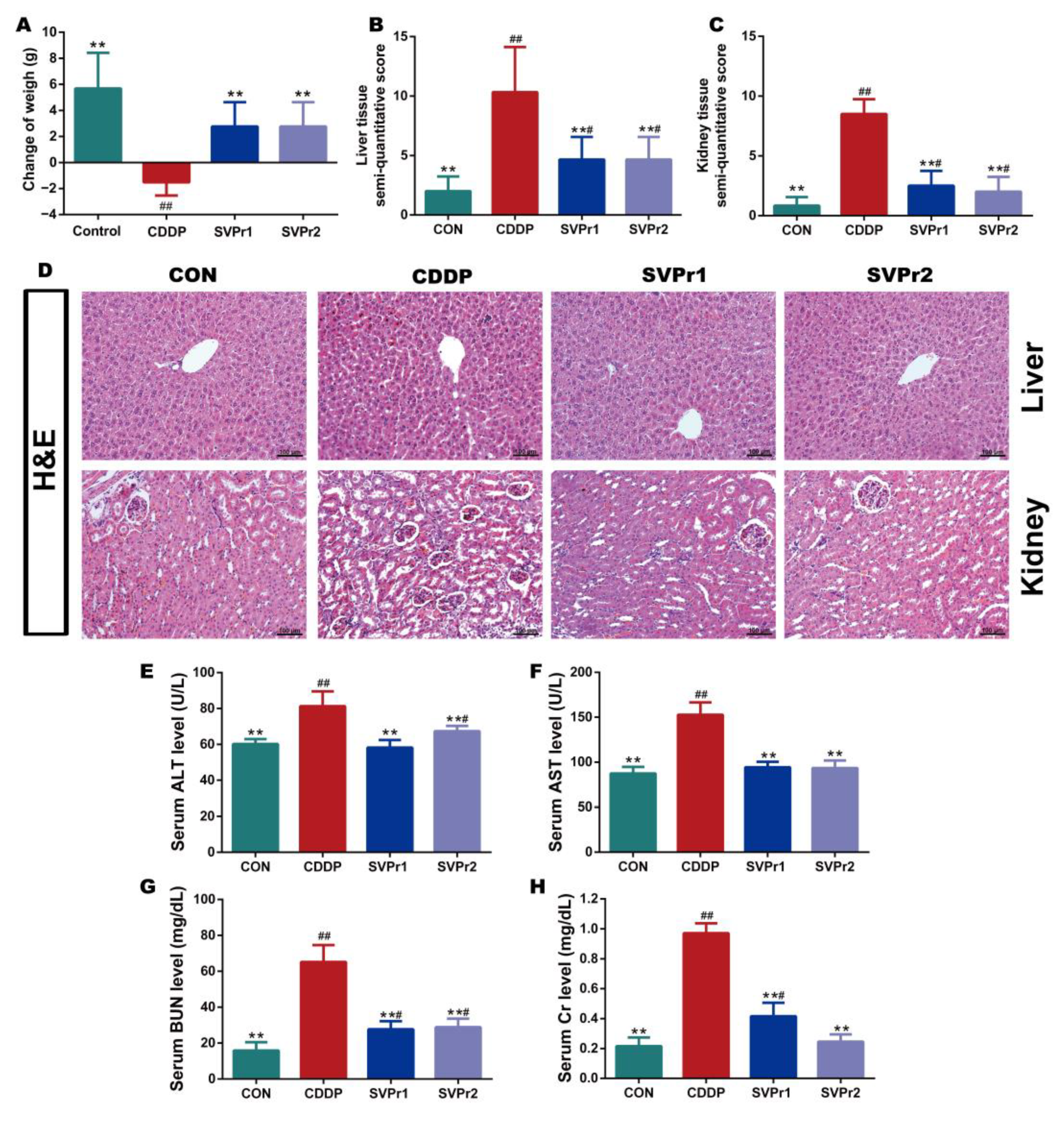
2.2. Protective Effects of SVPr1 and SVPr2 on Cisplatin-Induced Liver and Kidney Injury
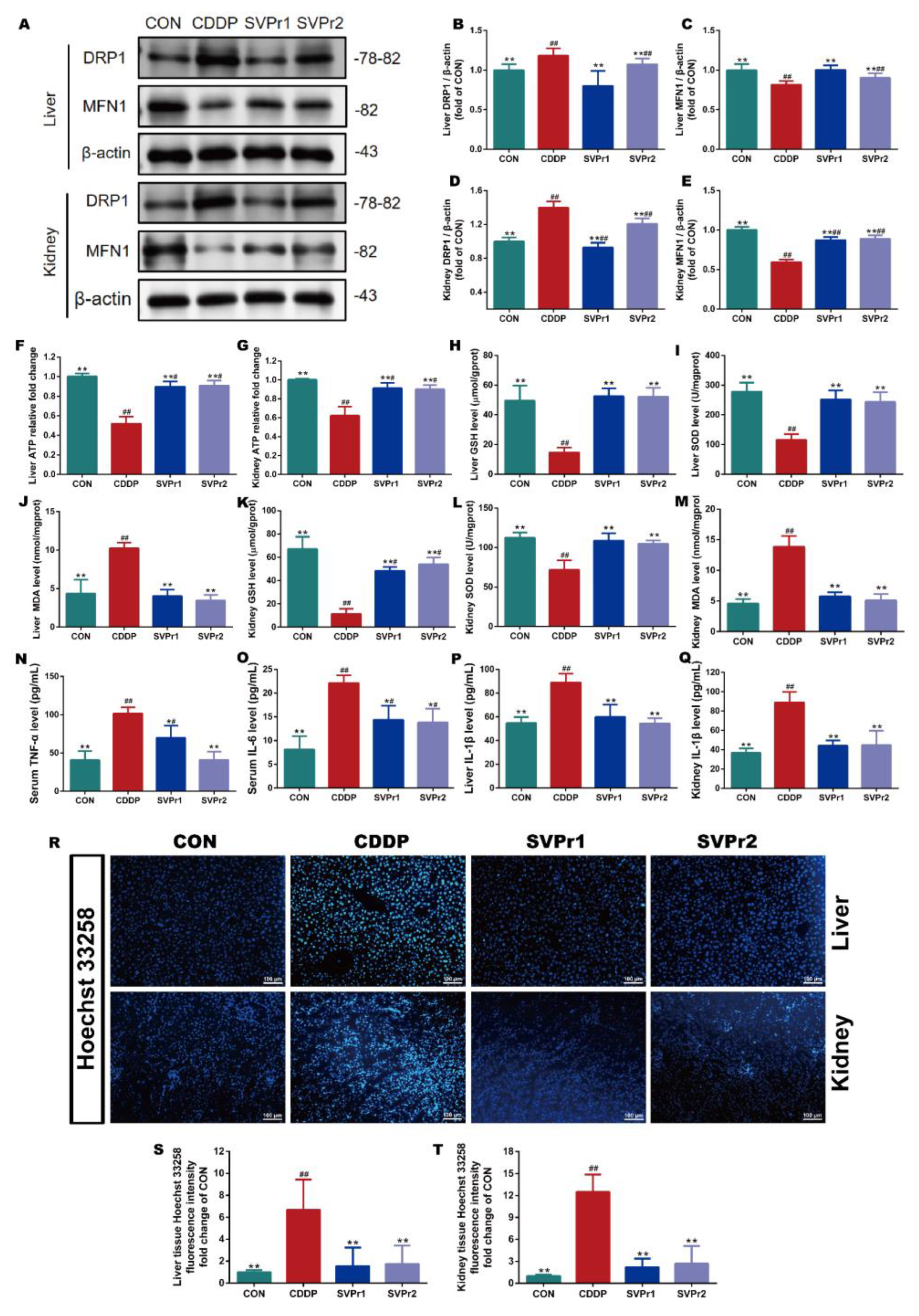
2.3. Effects of SVPr1 and SVPr2 on Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Cisplatin-Induced Liver and Kidney Injury
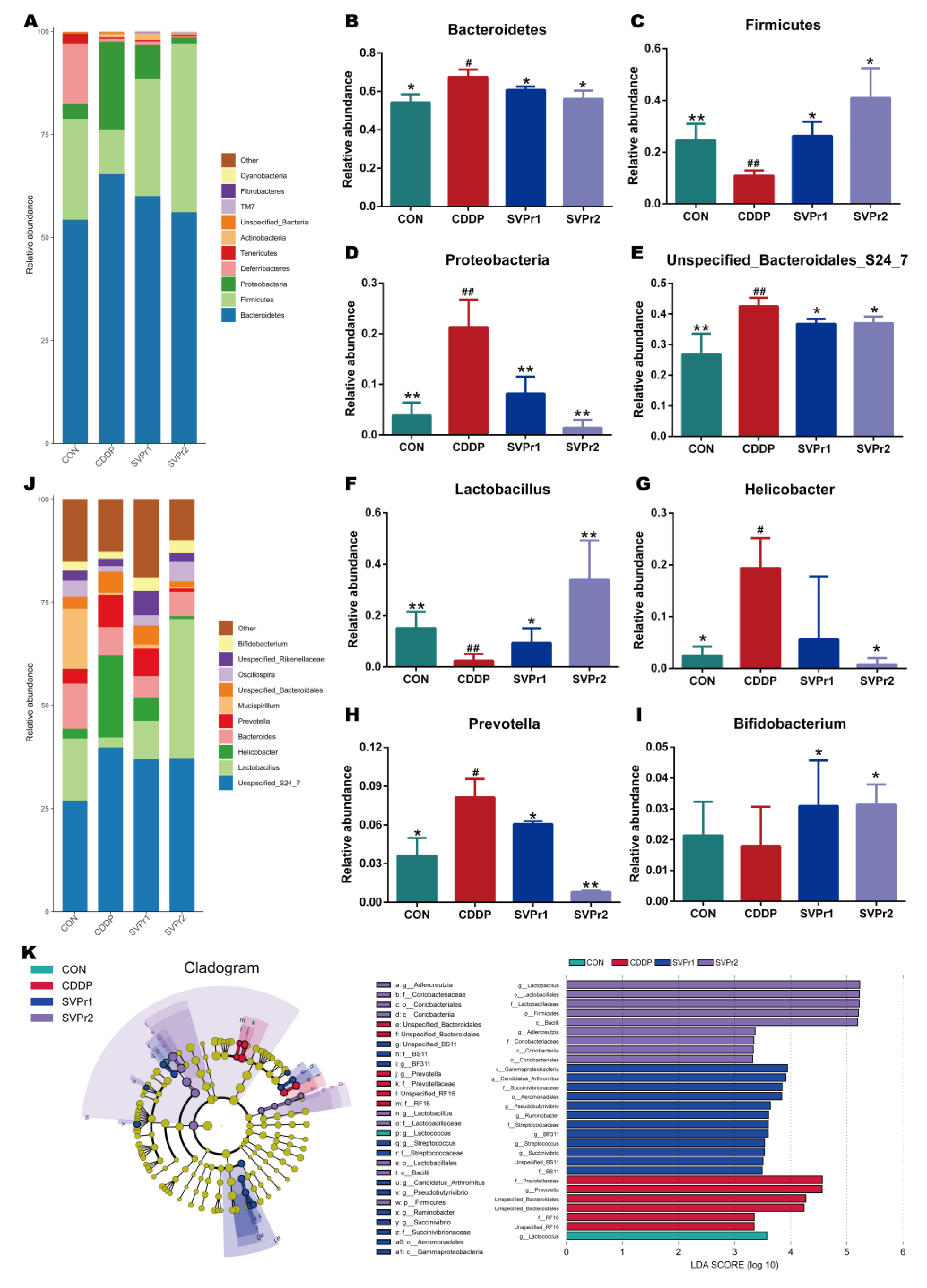
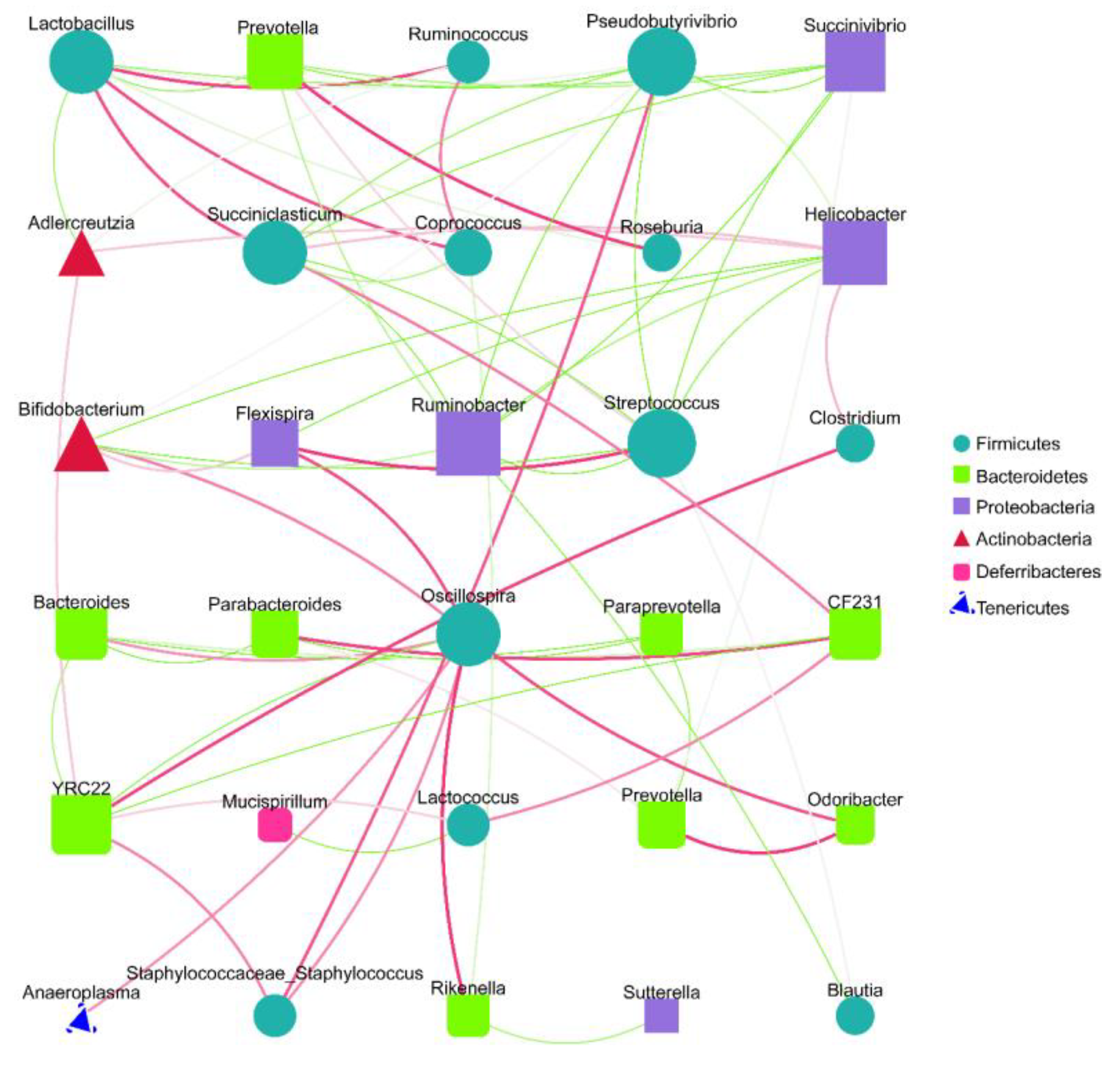
2.4. Effects of SVPr1 and SVPr2 on the Gut Microbiota of Mice with Cisplatin-Induced Liver and Kidney Injury
2.5. Effects of SVPr1 and SVPr2 on the Metabolites in Mice with Cisplatin-Induced Liver and Kidney Injury
2.6. Correlation Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Differential Metabolites in Cisplatin-Treated Mice Administered Sika Deer Antler Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Material and Reagents
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Extraction and Separation of Sika Deer Antler Protein
4.2.2. SDS-PAGE Analysis
4.2.3. Animals and Procedures
4.2.4. Determination of Liver and Kidney Injury Markers, Oxidative Stress Indicators, and Inflammatory Factors
4.2.5. Histopathological Analysis
4.2.6. Hoechst 33258 Fluorescent Staining
4.2.7. Assays for ATP Content
4.2.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.2.9. Metabolomics
4.2.10. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput 16S rRNA Sequencing
4.2.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ghosh, S. Cisplatin: The First Metal Based Anticancer Drug. Bioorg Chem. 2019, 88, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabla, N.; Huang, S.; Mi, Q.S.; Daniel, R.; Dong, Z. ATR-Chk2 Signaling in P53 Activation and DNA Damage Response during Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 6572–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, C.; Amorim, T.; Maqbool, M.; Lin, J.; Li, C.; Fang, C.; Xue, L.; Kwart, A.; Fang, H.; et al. Cisplatin-Mediated Upregulation of APE2 Binding to MYH9 Provokes Mitochondrial Fragmentation and Acute Kidney Injury. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Luo, L.; Xiong, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Xie, Y. VDAC1 Oligomerization May Enhance DDP-Induced Hepatocyte Apoptosis by Exacerbating Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial DNA Damage. FEBS Open Bio 2022, 12, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Livingston, M.J.; Safirstein, R.; Dong, Z. Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity: New Insights and Therapeutic Implications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litterst, C.L.; Gram, T.E.; Dedrick, R.L.; Leroy, A.F.; Guarino, A.M. Distribution and Disposition of Platinum Following Intravenous Administration of Cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum(II) (NSC 119875) to Dogs. Cancer Res. 1976, 36, 2340–2344. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.S.; Son, J.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Lim, H.J.; Ahn, M.Y.; Kwack, S.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, B.M.; et al. Hepatic Damage Exacerbates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Sprague-Dawley Rats. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. Part A 2018, 81, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galfetti, E.; Cerutti, A.; Ghielmini, M.; Zucca, E.; Wannesson, L. Risk Factors for Renal Toxicity after Inpatient Cisplatin Administration. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, J.; Jia, Y.; Wu, H.; Dong, H.; Leng, X. Deer Antler Extract Promotes Tibia Fracture Healing in Mice by Activating BMP-2/SMAD4 Signaling Pathway. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Li, H.; Jin, L.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; You, J.; Li, S.; Xu, Y. Deer Antler Base as a Traditional Chinese Medicine: A Review of Its Traditional Uses, Chemistry and Pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunhua, M.; Hongyan, L. Protective Effect of Pilose Antler Peptide on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, H.; Luo, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Sika Deer Antler Protein against Acetaminophen-Induced Nephrotoxicity by Activating Nrf2 and Inhibition FoxO1 via PI3K/Akt Signaling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 961–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, Y. Bioactive Components of Velvet Antlers and Their Pharmacological Properties. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 87, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; He, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J. The Proteins from Sika Deer Antler as Potential Modulators on Cisplatin-Induced Cytotoxicity in Human Embryonic Kidney 293 Cells. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1982–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Fan, M.; Choi, Y.J.; Choi, E.J.; Moon, S.H.; Debnath, T.; Yu, Y.; Lee, I.N.; Kim, E.K. Protective Effect of Sika Deer (Cervus Nippon) Velvet Antler Extract against Cisplatin-Induced Kidney and Liver Injury in a Prostate Cancer PC-3 Cell Xenograft Model. J. Chem. 2018, 2018, 6705156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, F.; Liang, S.; Zhang, W.; Guan, Y.; Shen, D.; et al. A Metagenome-Wide Association Study of Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, H.; Yang, W.; Zhao, S.; Jiang, M.; Xu, M.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y. Altered Gut Microbiota and Microbial Biomarkers Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernocchi, P.; Del Chierico, F.; Putignani, L. Gut Microbiota Profiling: Metabolomics Based Approach to Unravel Compounds Affecting Human Health. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idborg, H.; Pawelzik, S.C. Prostanoid Metabolites as Biomarkers in Human Disease. Metabolites 2022, 12, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Han, P.; Fu, J.; Yu, H.; Xu, H.; Hu, J.C.; Lu, J.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Bu, M.M.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Based Metabolites of Xiaoyao Pills (a Typical Traditional Chinese Medicine) Ameliorate Depression by Inhibiting Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Levels in Brain. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 313, 116555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Lai, X.; Wu, K.; Zhou, P.; Li, L.; Guo, Z.; Xu, S. Metabolomics Study of Fasudil on Cisplatin-Induced Kidney Injury. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20192940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Feng, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Pan, M.; He, F.; Wu, R.; Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. Gut Microbiota Accelerates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Liver Injury Associated with Robust Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Mice. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Qin, S.; Yuan, J.; Xie, X.; Wang, F.; Hu, S.; Yi, Y.; Chen, M. C-Phycocyanin Alleviated Cisplatin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation via Gut Microbiota-Metabolites Axis in Mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 996614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An Obesity-Associated Gut Microbiome with Increased Capacity for Energy Harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Wang, J.; Zhan, R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. Fecal Metabonomics Combined with 16S RRNA Gene Sequencing to Analyze the Changes of Gut Microbiota in Rats with Kidney-Yang Deficiency Syndrome and the Intervention Effect of You-Gui Pill. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 244, 112139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Ko, J.L.; Liao, J.M.; Huang, S.S.; Lin, M.Y.; Lee, L.H.; Chang, L.Y.; Ou, C.C. D-Methionine Alleviates Cisplatin-Induced Mucositis by Restoring the Gut Microbiota Structure and Improving Intestinal Inflammation. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835918821021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.; Li, C.; Zhong, Y.; Shi, J.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, X. FTIR Microspectroscopic Investigation of Lactobacillus Paracasei Apoptosis Induced by Cisplatin. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 252, 119542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zick, Y. Insulin Resistance: A Phosphorylation-Based Uncoupling of Insulin Signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2001, 11, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Rogers, A.B.; Whary, M.T.; Taylor, N.S.; Xu, S.; Feng, Y.; Keys, S. Helicobacter Bilis-Associated Hepatitis in Outbred Mice. Comp. Med. 2004, 54, 571–577. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Z.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Jia, N.Y.; Zhang, H. Helicobacter Pylori Infection Is Associated with Elevated Galactose-Deficient IgA1 in IgA Nephropathy. Ren. Fail. 2020, 42, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Shang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Gut Microbiome Characteristics in IgA Nephropathy: Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis from Observational Studies. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 904401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, C.Q.; Xing, H. Advances in Gut Microbiota of Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 9726786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Q.; Jia, W.; Xu, Y. Crosstalk between Gut Microbiota and Host Lipid Metabolism in a Mouse Model of Alcoholic Liver Injury by Chronic Baijiu or Ethanol Feeding. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Chen, Z.; Soutto, M.; Zhu, S.; Lu, H.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Peek, R.; Zhang, S.; El-Rifai, W. Helicobacter Pylori-Induced MiR-135b-5p Promotes Cisplatin Resistance in Gastric Cancer. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ji, G.E.; Park, M.S.; Seong, Y.J.; Go, Y.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Fang, Y.; Kim, M.G.; Oh, S.W.; Cho, W.Y.; et al. Probiotics Partially Attenuate the Severity of Acute Kidney Injury through an Immunomodulatory Effect. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 40, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Yao, Z.; Ni, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, S.; Chen, Z. Effect and Mechanism of Bifidobacterium Animalis B94 in the Prevention and Treatment of Liver Injury in Rats. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 914684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, S.; Song, Y.; Yuan, J.; Hu, S.; Chen, M.; Li, L. Alginate Oligosaccharide Alleviated Cisplatin-Induced Kidney Oxidative Stress via Lactobacillus Genus-FAHFAs-Nrf2 Axis in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 857242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Shan, A. Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG Ameliorates Deoxynivalenol-Induced Kidney Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Injury in Weaned Piglets. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 3905–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Yao, C.; Yan, R.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, K.; Ren, S.; Jiang, S.; Xia, J.; Li, S.; et al. Lactobacillus Acidophilus LA14 Alleviates Liver Injury. mSystems 2021, 6, e0038421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.W.; He, S.P.; Lan, J.G.; Zhu, W.Z. Honokiol Ameliorates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via Inhibition of Mitochondrial Fission. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 179, 3886–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaona-Gaona, L.; Molina-Jijón, E.; Tapia, E.; Zazueta, C.; Hernández-Pando, R.; Calderón-Oliver, M.; Zarco-Márquez, G.; Pinzón, E.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. Protective Effect of Sulforaphane Pretreatment against Cisplatin-Induced Liver and Mitochondrial Oxidant Damage in Rats. Toxicology 2011, 286, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, J.; Houten, S.M. The Lysine Degradation Pathway: Subcellular Compartmentalization and Enzyme Deficiencies. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2020, 131, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Ban, Z.; Tang, R.; Gan, Q.; Wu, S.; Guo, Y.; et al. The Lysine Catabolite Saccharopine Impairs Development by Disrupting Mitochondrial Homeostasis. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 580–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Gao, H.; Sun, J.; Tao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Hu, T.; Li, Z. Identification of Key Metabolites during Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Using an HPLC-TOF/MS-Based Non-Targeted Urine and Kidney Metabolomics Approach in Rats. Toxicology 2020, 431, 152366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Xiong, G.; Yang, S.; Li, S. Untargeted Metabolomics Reveals the Protective Effect of a Traditional Chinese Herbal Decoction on Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. Ecam 2020, 2020, 8524132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, U.H.; Hartung, E.A.; Concors, S.; Hernandez, P.T.; Wang, Z.; Perry, C.; Baur, J.A.; Denburg, M.R.; Hancock, W.W.; Gade, T.P.; et al. Tissue Metabolic Profiling Shows That Saccharopine Accumulates during Renal Ischemic-Reperfusion Injury, While Kynurenine and Itaconate Accumulate in Renal Allograft Rejection. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinschen, M.M.; Palygin, O.; El-Meanawy, A.; Domingo-Almenara, X.; Palermo, A.; Dissanayake, L.V.; Golosova, D.; Schafroth, M.A.; Guijas, C.; Demir, F.; et al. Accelerated Lysine Metabolism Conveys Kidney Protection in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla, P.; Andrade, M.J.; Peña, F.J.; Rodríguez, A.; Estévez, M. An in Vitro Assay of the Effect of Lysine Oxidation End-Product, α-Aminoadipic Acid, on the Redox Status and Gene Expression in Probiotic Lactobacillus Reuteri PL503. Amino Acids 2022, 54, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Cai, J.; Zhao, S.; Ma, A. Lactobacillus Casei Modulates Inflammatory Cytokines and Metabolites during Tuberculosis Treatment: A Post Hoc Randomized Controlled Trial. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 31, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, J.Q.; Huang, W.Q.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Xu, F.G. Renal Medulla Is More Sensitive to Cisplatin than Cortex Revealed by Untargeted Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Chen, J.; Qin, S.; Liao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Xu, F. Tryptophan Pathway-Targeted Metabolomics Study on the Mechanism and Intervention of Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hu, T.; Gao, H.; Zhai, J.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, L.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Qu, X. Altered Metabolic Profiles and Biomarkers Associated with Astragaloside IV-Mediated Protection against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats: An HPLC-TOF/MS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Study. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 183, 114299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas, B.; Richard, M.L.; Leducq, V.; Pham, H.P.; Michel, M.L.; Da Costa, G.; Bridonneau, C.; Jegou, S.; Hoffmann, T.W.; Natividad, J.M.; et al. CARD9 Impacts Colitis by Altering Gut Microbiota Metabolism of Tryptophan into Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligands. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes Barragan, L.; Chai, J.N.; Tianero, M.D.; Di Luccia, B.; Ahern, P.P.; Merriman, J.; Cortez, V.S.; Caparon, M.G.; Donia, M.S.; Gilfillan, S.; et al. Lactobacillus Reuteri Induces Gut Intraepithelial CD4+CD8αα+ T Cells. Science 2017, 357, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzosek, L.; Ciocan, D.; Hugot, C.; Spatz, M.; Dupeux, M.; Houron, C.; Lievin-Le Moal, V.; Puchois, V.; Ferrere, G.; Trainel, N.; et al. Microbiota Tryptophan Metabolism Induces Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation and Improves Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury. Gut 2021, 70, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hj, P. Riboflavin (Vitamin B-2) and Health. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, I.; Chibber, S.; Naseem, I. Ameliorative Effect of Riboflavin on the Cisplatin Induced Nephrotoxicity and Hepatotoxicity under Photoillumination. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q. A New Mechanism for Ginsenoside Rb1 to Promote GLUCOSE Uptake, Regulating Riboflavin Metabolism and Redox Homeostasis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
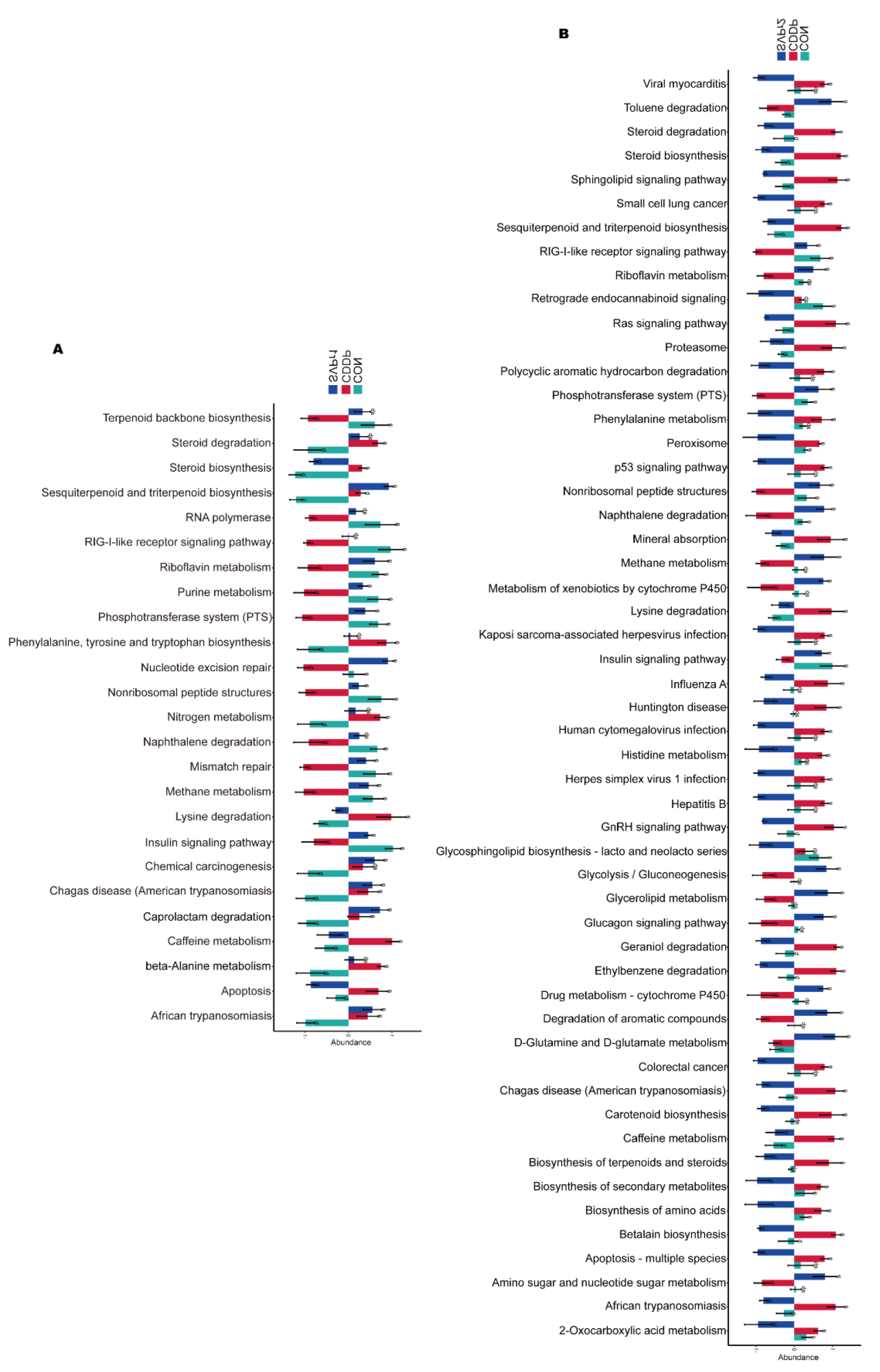




| No. | Metabolite | Formula | KEGG ID | p-Value | VIP | Trend Up/Down |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arachidonic acid | C20H32O2 | C00219 | 0.006 | 2.206 | down |
| 2 | Nervonic acid | C24H46O2 | C08323 | 0.011 | 1.968 | up |
| 3 | Taurochenodeoxycholic acid | C26H45NO6S | C05465 | 0.014 | 1.854 | up |
| 4 | Acetyl-L-carnitine | C9H17NO4 | C02571 | 0.014 | 1.845 | down |
| 5 | L-Lysine | C6H14N2O2 | C00047 | 0.019 | 1.731 | down |
| 6 | Taurocholic acid | C26H45NO7S | C05122 | 0.020 | 1.701 | down |
| 7 | L-2-Aminoadipic acid | C6H11NO4 | C00956 | 0.026 | 1.591 | down |
| 8 | 4-Methylphenol | C7H8O | C01468 | 0.027 | 1.572 | down |
| 9 | L-Saccharopine | C11H20N2O6 | C00449 | 0.029 | 1.536 | down |
| 10 | Cytosine | C4H5N3O | C00380 | 0.036 | 1.447 | up |
| 11 | Nicotinamide | C6H6N2O | C00153 | 0.036 | 1.440 | up |
| 12 | L-Kynurenine | C10H12N2O3 | C00328 | 0.037 | 1.434 | down |
| 13 | D-Ribulose 5-phosphate | C5H11O8P | C00199 | 0.037 | 1.428 | up |
| 14 | Taurine | C2H7NO3S | C00245 | 0.038 | 1.418 | down |
| 15 | Pregnenolone | C21H32O3 | C01953 | 0.038 | 1.417 | down |
| 16 | Cortolone | C21H34O5 | C05481 | 0.038 | 1.417 | up |
| 17 | Glutathione | C10H17N3O6S | C00051 | 0.039 | 1.411 | up |
| 18 | Xanthurenic Acid | C10H7NO4 | C02470 | 0.040 | 1.394 | up |
| 19 | 3-Methylindole | C9H9N | C08313 | 0.042 | 1.376 | down |
| 20 | Riboflavin | C17H20N4O6 | C00255 | 0.043 | 1.369 | down |
| 21 | O-Acetyl-L-carnitine | C9H17NO4 | C02571 | 0.048 | 1.319 | down |
| No. | Metabolite | Formula | KEGG ID | p-Value | VIP | Trend Up/Down |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L-Saccharopine | C11H20N2O6 | C00449 | 0.005 | 2.271 | down |
| 2 | L-Lysine | C6H14N2O2 | C00047 | 0.006 | 2.241 | down |
| 3 | Riboflavin | C17H20N4O6 | C00255 | 0.006 | 2.213 | down |
| 4 | Acetophenone | C8H8O | C07113 | 0.010 | 2.011 | up |
| 5 | Taurocholic acid | C26H45NO7S | C05122 | 0.011 | 1.956 | down |
| 6 | L-Kynurenine | C10H12N2O3 | C00328 | 0.013 | 1.881 | down |
| 7 | D-Ribulose 5-phosphate | C5H11O8P | C00199 | 0.018 | 1.739 | up |
| 8 | 3-Methylindole | C9H9N | C08313 | 0.020 | 1.694 | down |
| 9 | Indole | C8H7N | C00463 | 0.021 | 1.677 | down |
| 10 | L-Tryptophan | C11H12N2O2 | C00078 | 0.021 | 1.670 | up |
| 11 | Xanthurenic Acid | C10H7NO4 | C02470 | 0.023 | 1.639 | up |
| 12 | L-Adrenaline | C9H13NO3 | C00788 | 0.023 | 1.632 | down |
| 13 | Deoxycorticosterone | C21H30O3 | C03205 | 0.026 | 1.591 | up |
| 14 | 3-Hydroxybutyric acid | C4H8O3 | C01089 | 0.029 | 1.533 | down |
| 15 | Arachidonic acid | C20H32O2 | C00219 | 0.032 | 1.500 | down |
| 16 | Cortisol | C21H30O5 | C00735 | 0.034 | 1.472 | down |
| 17 | Palmitoleic Acid | C16H30O2 | C08362 | 0.036 | 1.447 | down |
| 18 | Taurochenodeoxycholic acid | C26H45NO6S | C05465 | 0.038 | 1.418 | down |
| 19 | Acetoacetate | C4H6O3 | C00164 | 0.042 | 1.374 | down |
| 20 | Aconitic acid | C6H6O6 | C00417 | 0.047 | 1.327 | down |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J. Gut Microbiota Combined with Metabolomics Reveal the Mechanisms of Sika Deer Antler Protein on Cisplatin-Induced Hepatorenal Injury in Mice. Molecules 2023, 28, 6463. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186463
Wang L, Li L, Wang Z, Zhang P, Zhang J. Gut Microbiota Combined with Metabolomics Reveal the Mechanisms of Sika Deer Antler Protein on Cisplatin-Induced Hepatorenal Injury in Mice. Molecules. 2023; 28(18):6463. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186463
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lulu, Lei Li, Zhenyi Wang, Pu Zhang, and Jing Zhang. 2023. "Gut Microbiota Combined with Metabolomics Reveal the Mechanisms of Sika Deer Antler Protein on Cisplatin-Induced Hepatorenal Injury in Mice" Molecules 28, no. 18: 6463. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186463
APA StyleWang, L., Li, L., Wang, Z., Zhang, P., & Zhang, J. (2023). Gut Microbiota Combined with Metabolomics Reveal the Mechanisms of Sika Deer Antler Protein on Cisplatin-Induced Hepatorenal Injury in Mice. Molecules, 28(18), 6463. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186463






