Expeditious Discovery of Small-Molecule Thermoresponsive Ionic Liquid Materials: A Review
Abstract
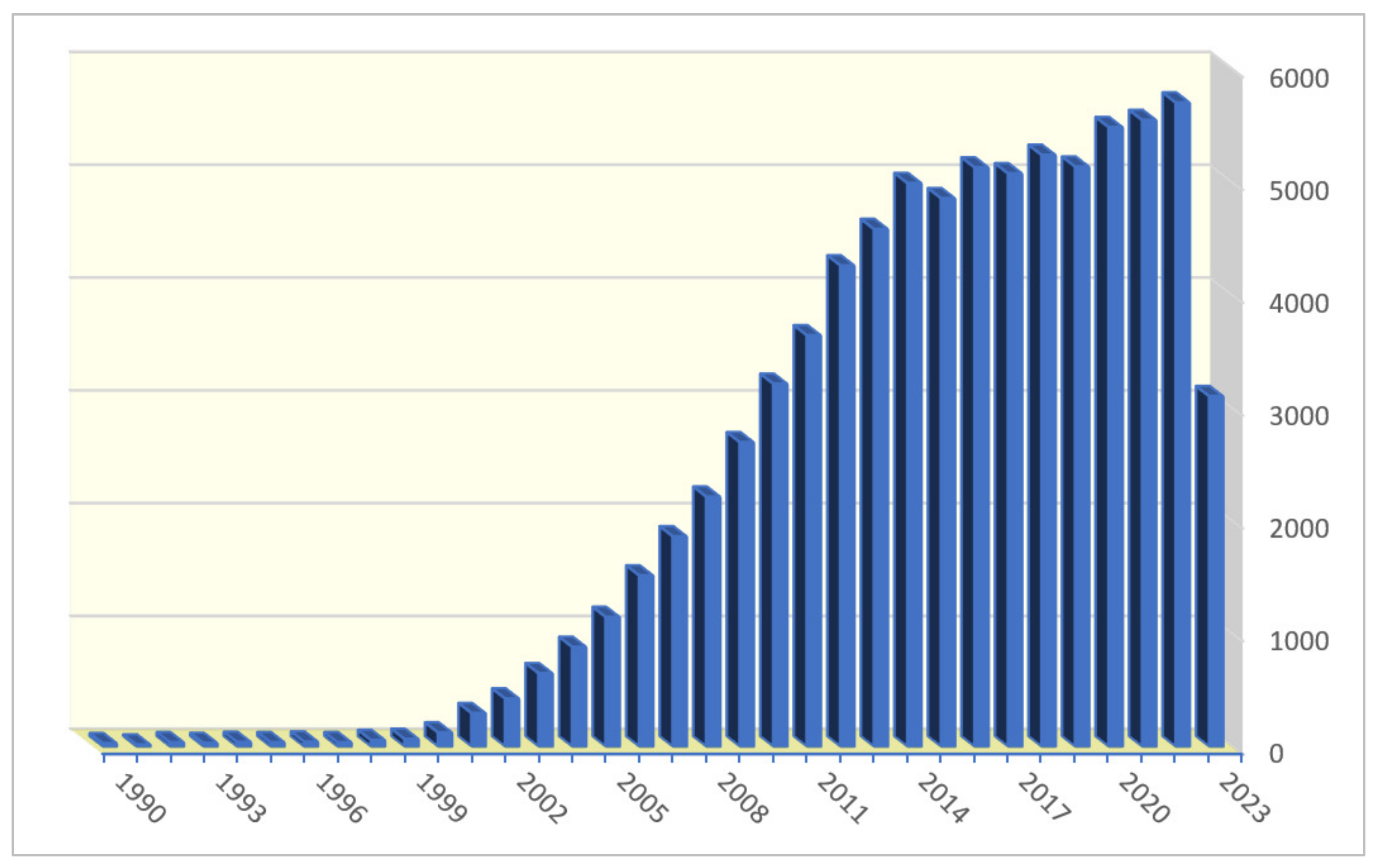
:1. Introduction
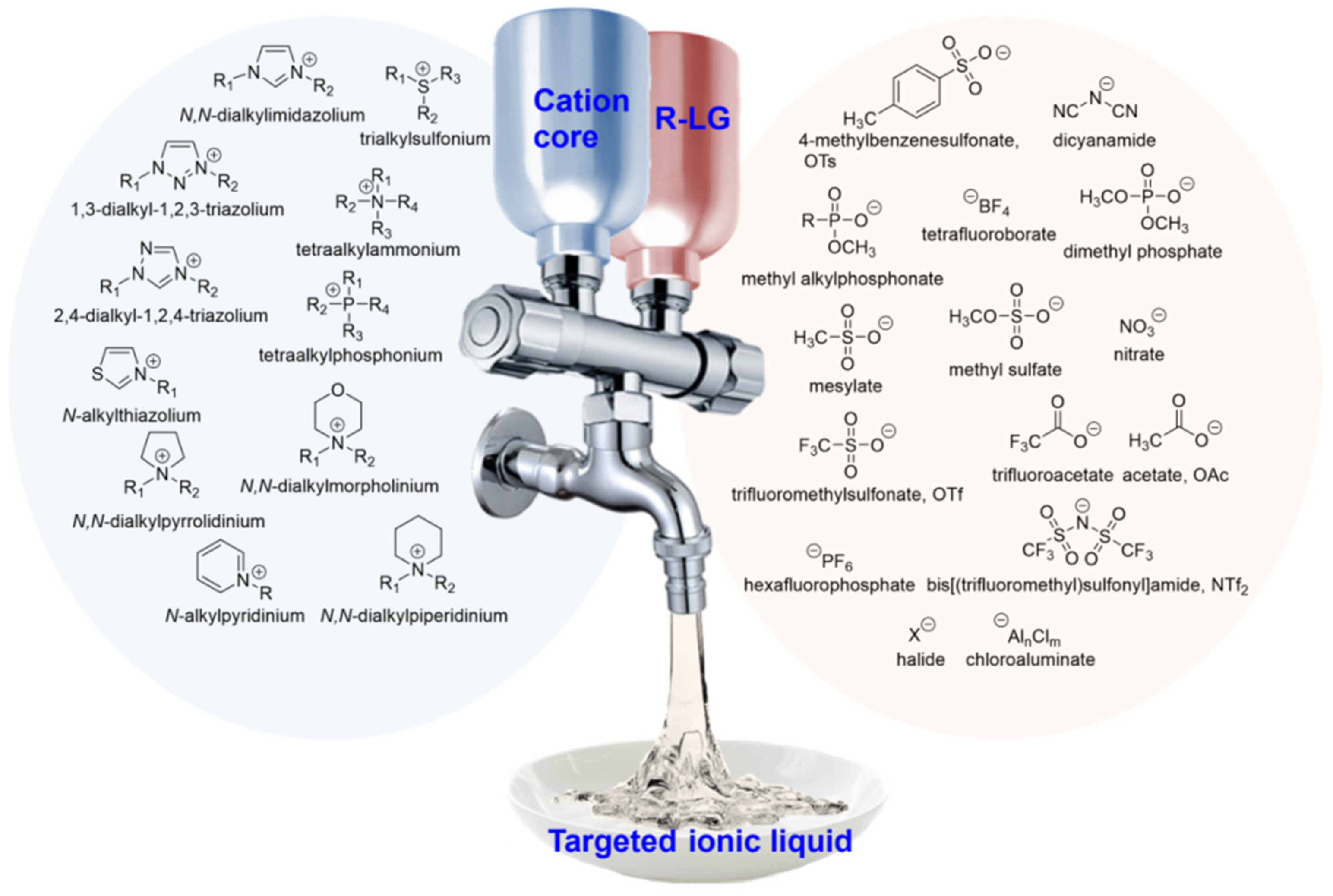
2. Ionic Liquids Are Designable and Structurally Tunable
2.1. Ionic Liquids as Attractive Reaction Media
2.2. Chiral Ionic Liquids and Supported Ionic Liquids
2.3. Zwitterionic Ionic Liquids
2.4. Task-Specific Ionic Liquids for CO2 Capture
2.5. Ionic Liquids as PCR Enhancers
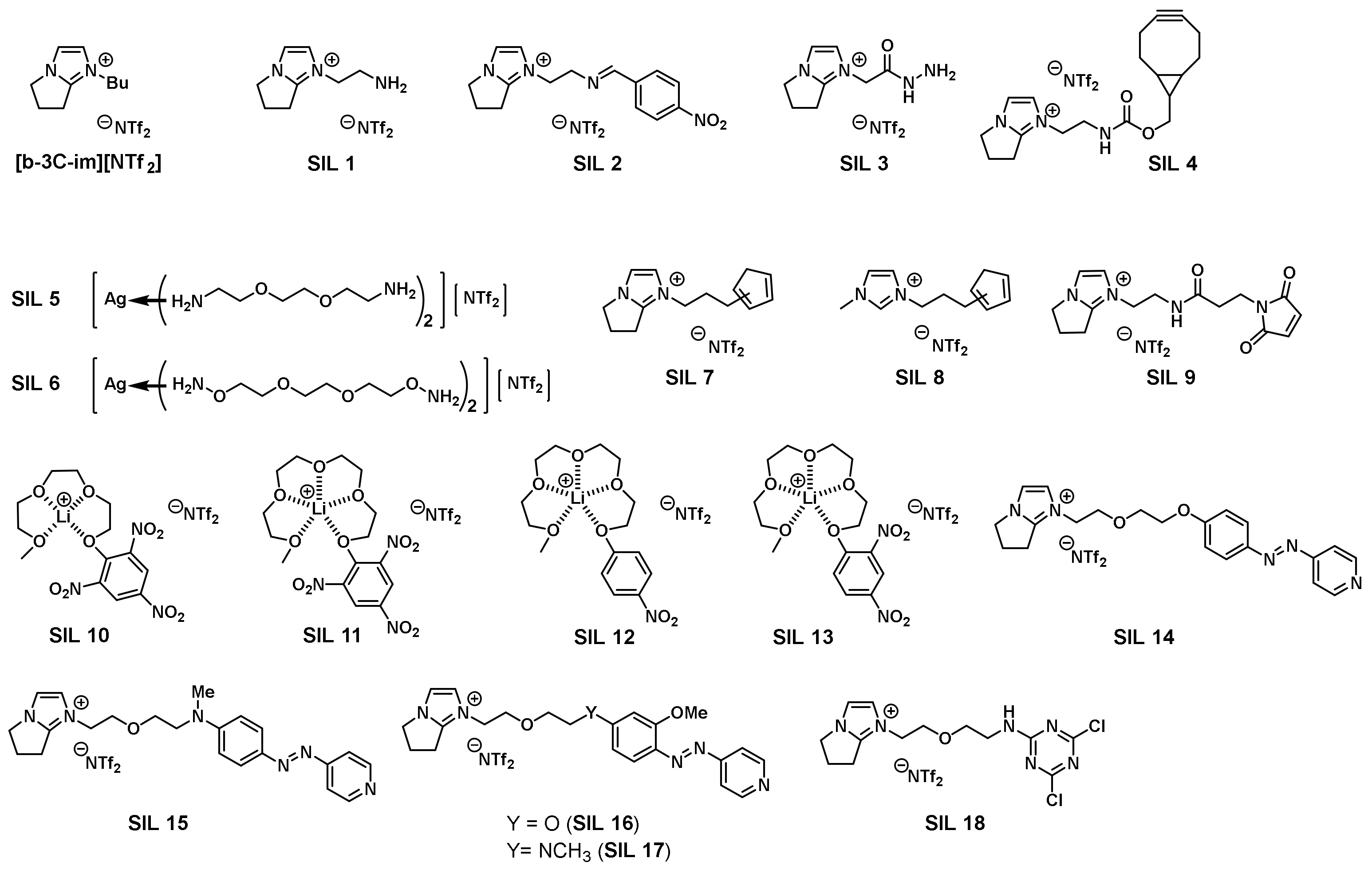
2.6. Functionalized Ionic Liquids
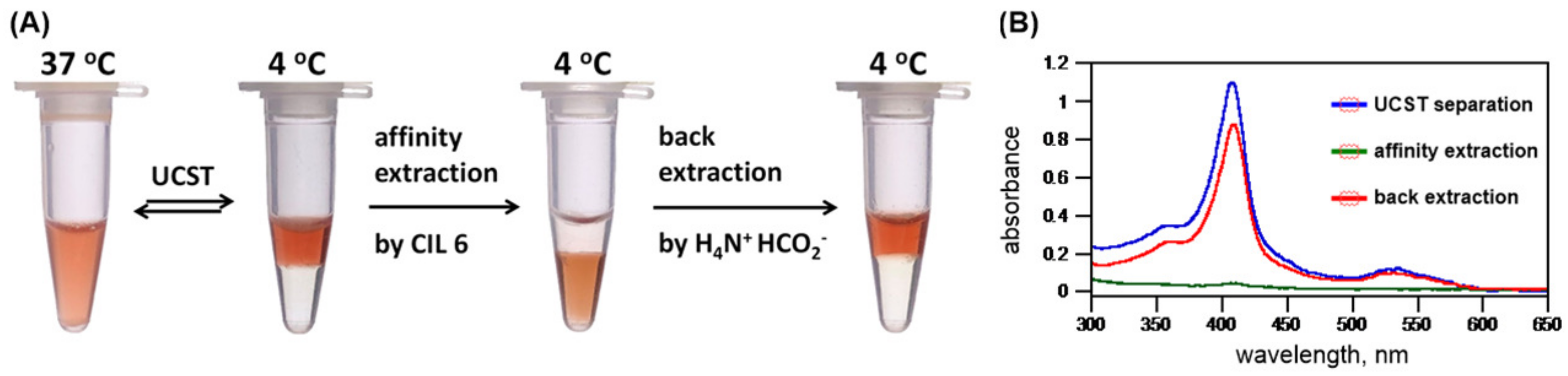
2.7. Affinity Ionic Liquids
3. Ionic Liquids Can Be Thermally Responsive
3.1. Thermoresponsive Ionic Liquids (TILs) Are Smart Materials
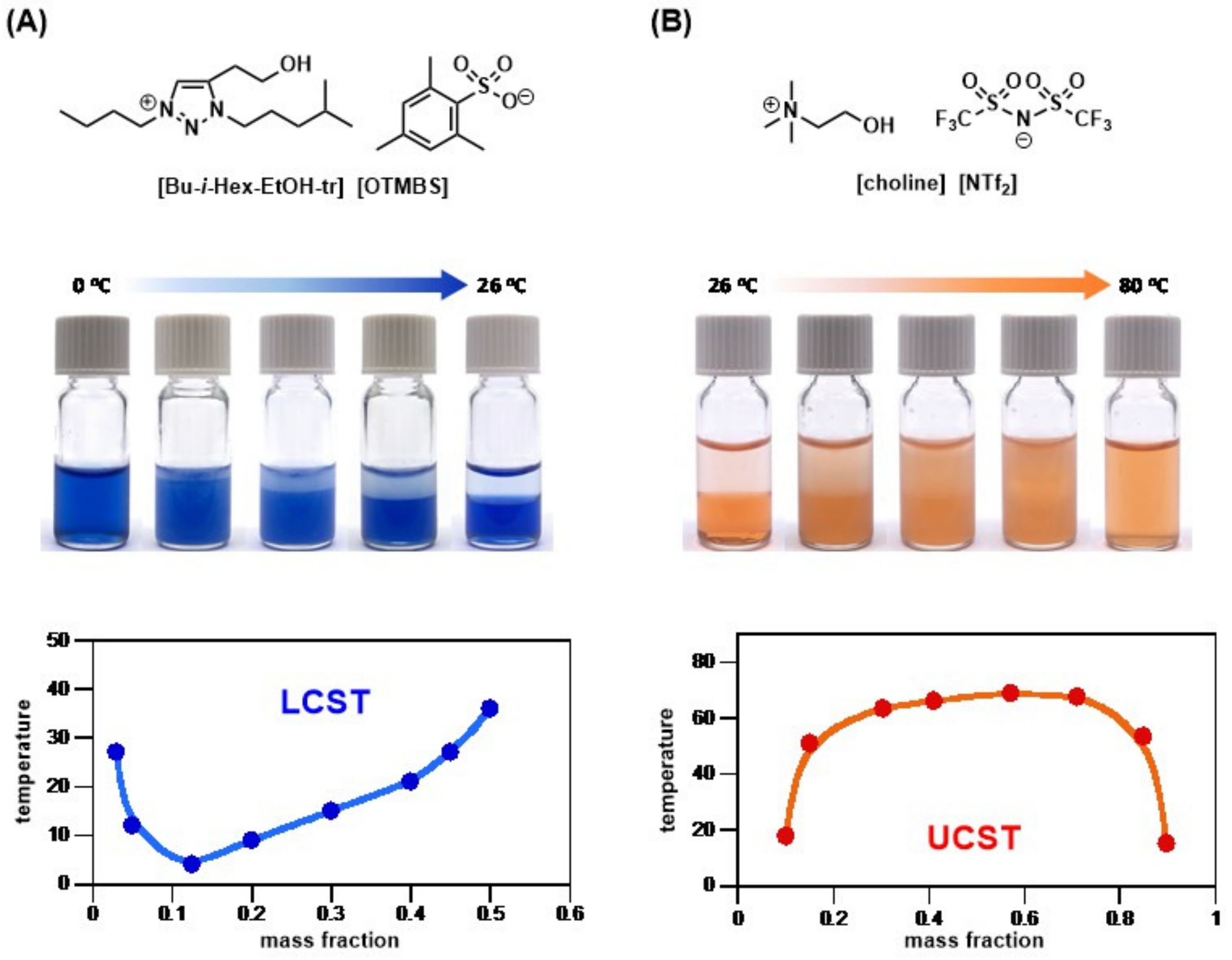
3.2. Ionic Liquids Are Thermally Sensitive Materials
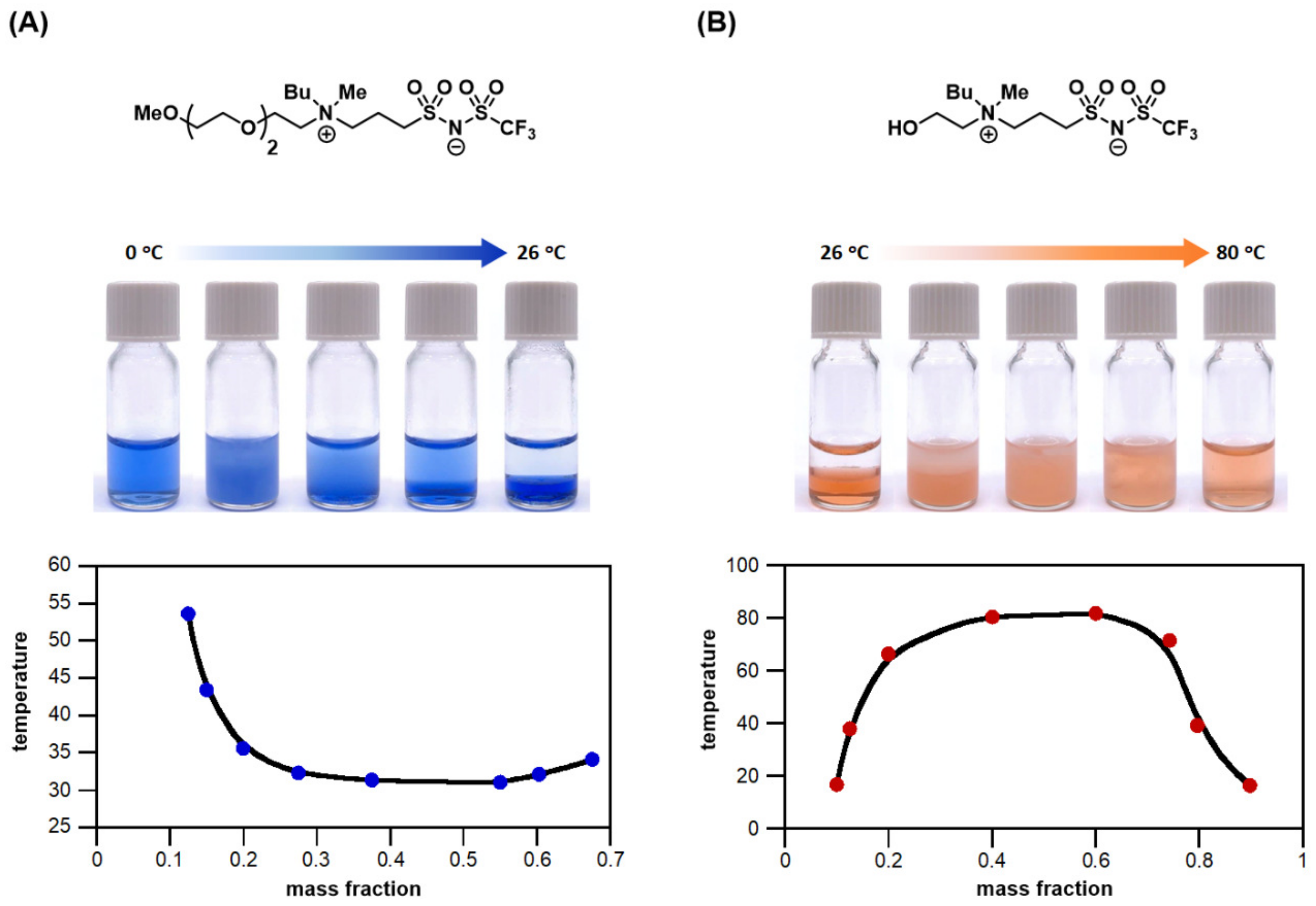
3.3. Zwitterionic Ionic Liquid Materials as TILs
3.4. Mechanism of Thermal Sensitivity
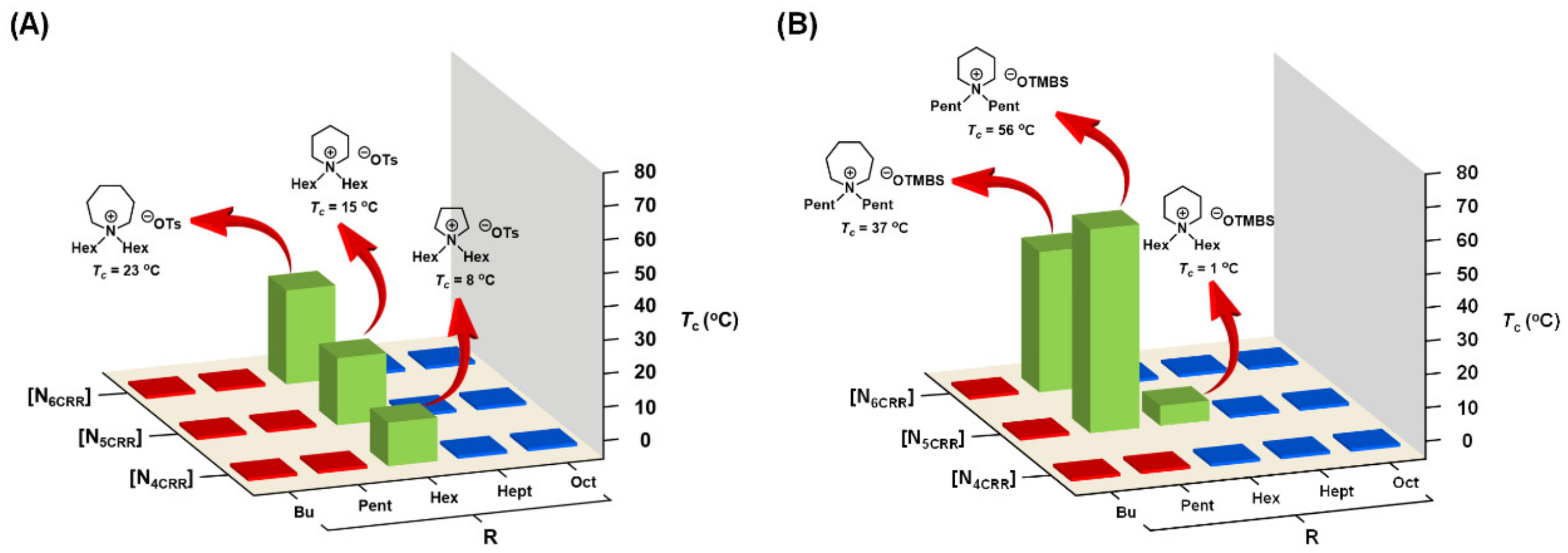
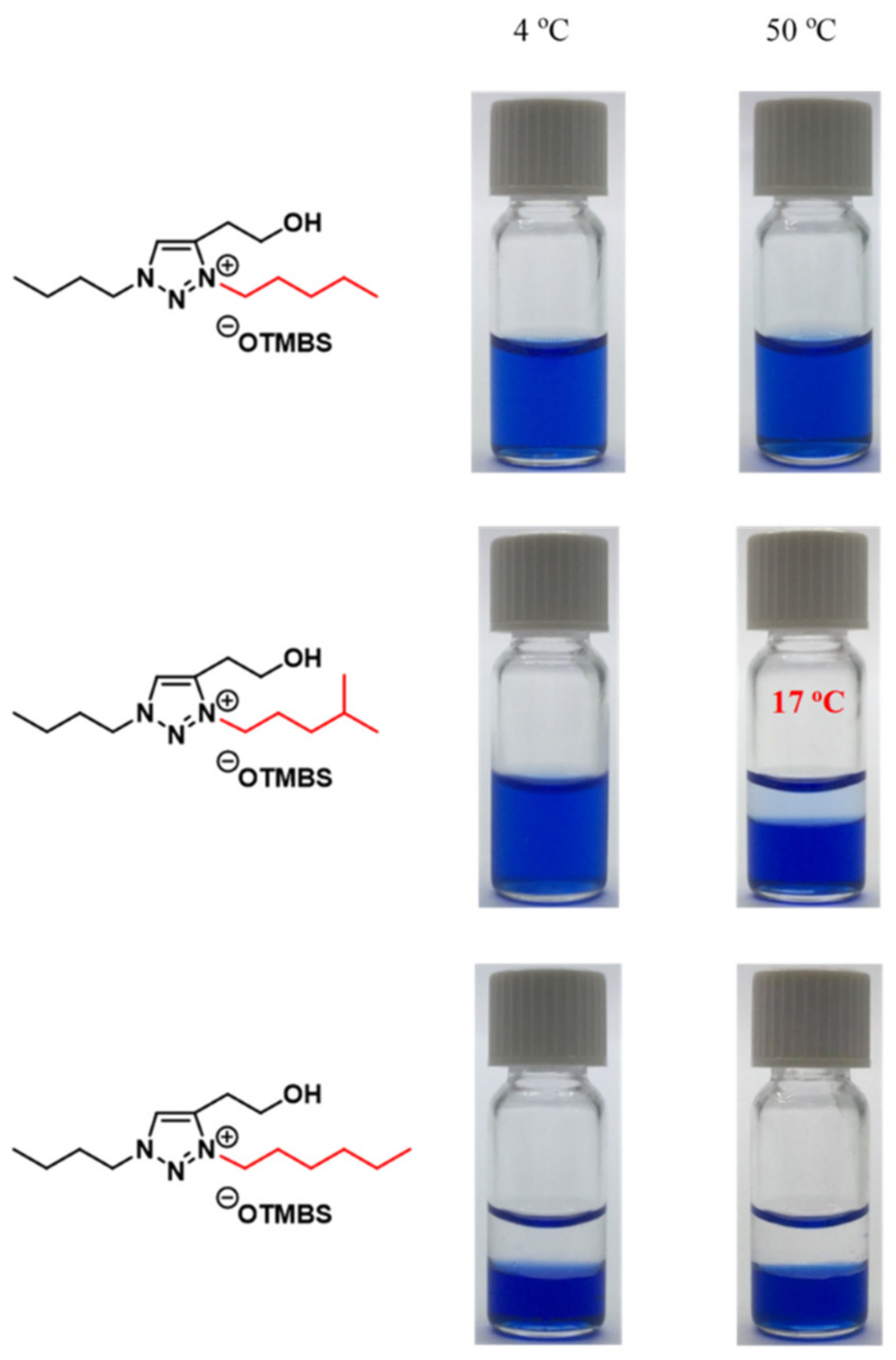
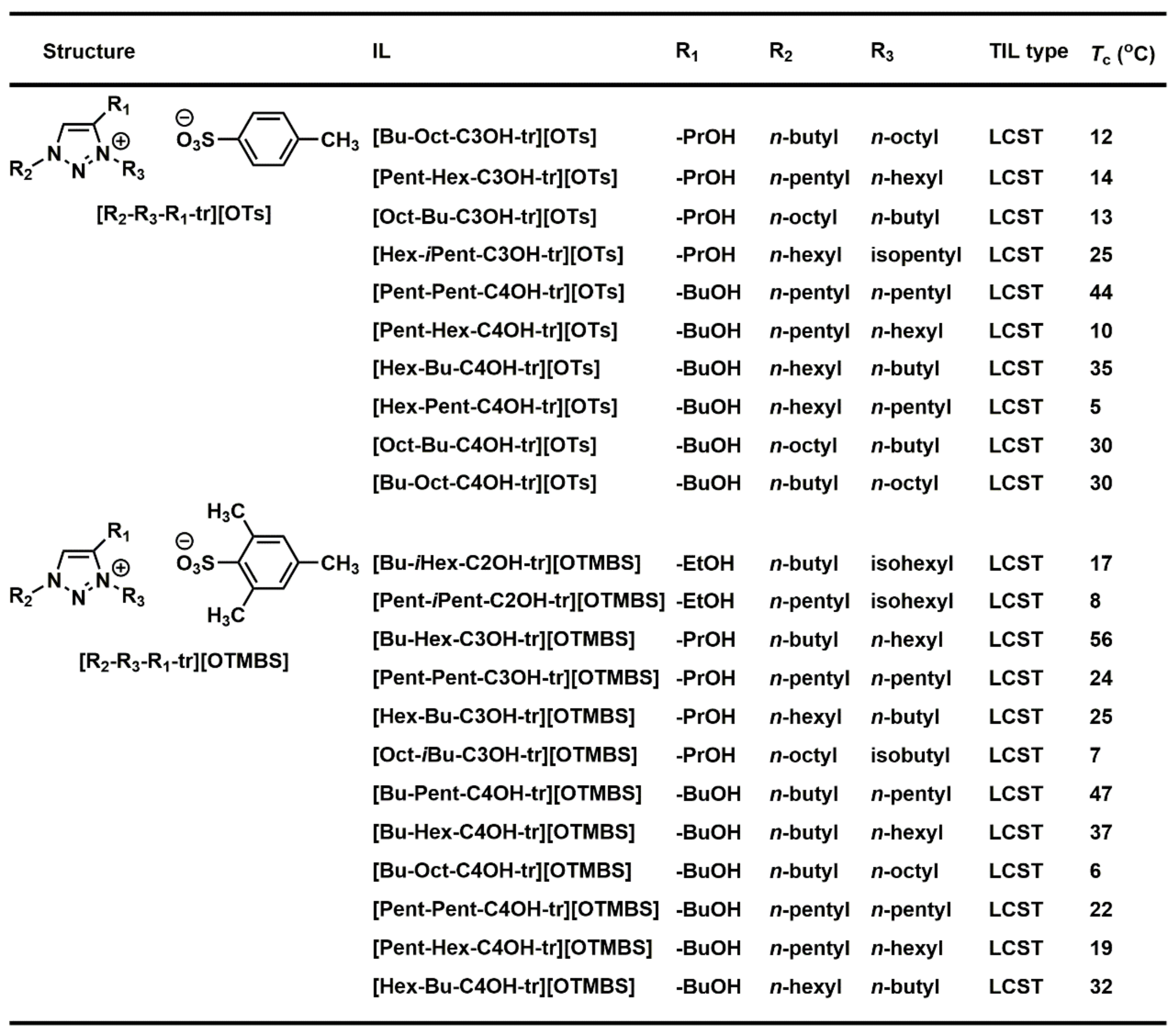
3.5. Combinatorial Discovery of Thermoresponsive Ionic Liquids
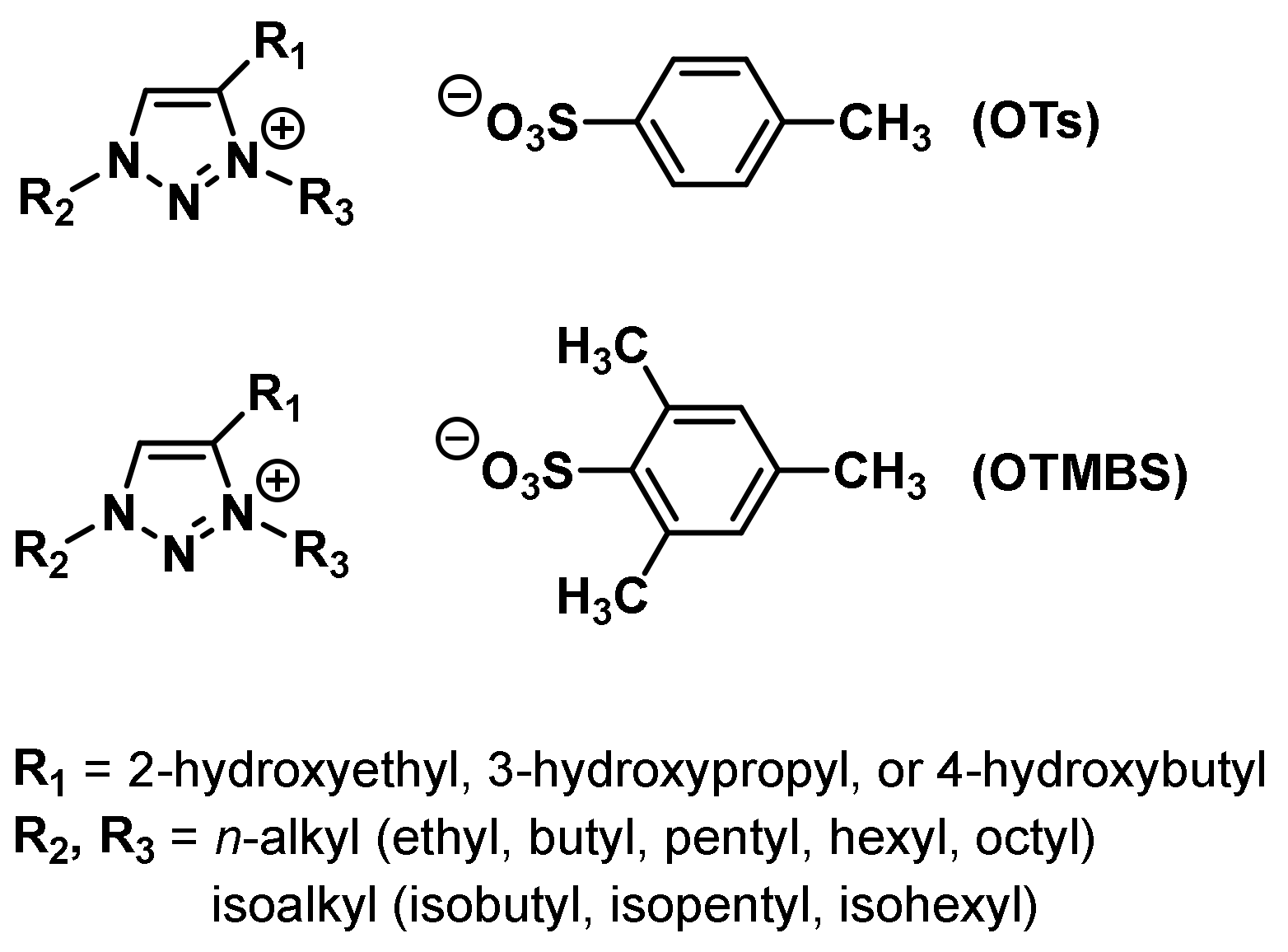
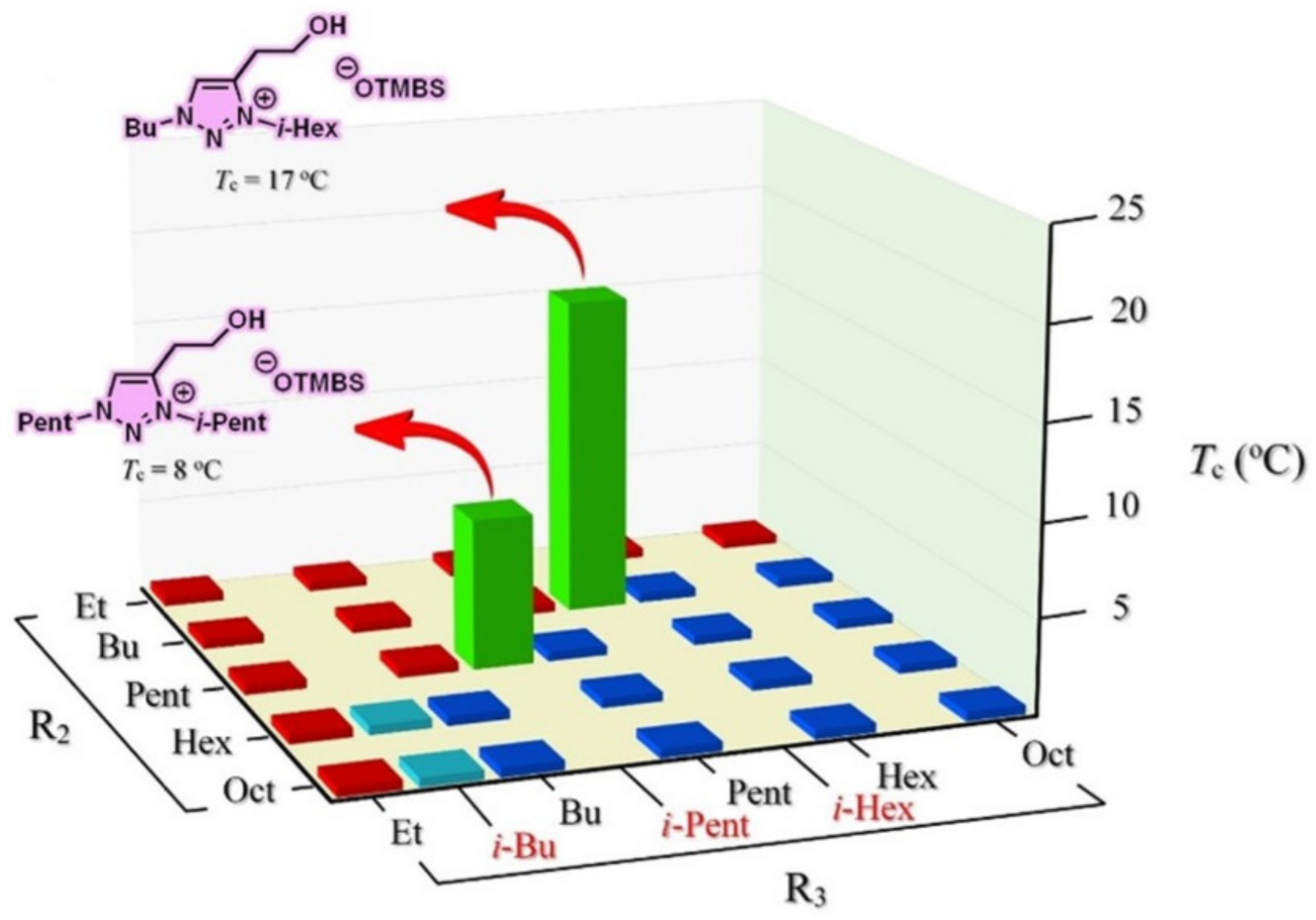
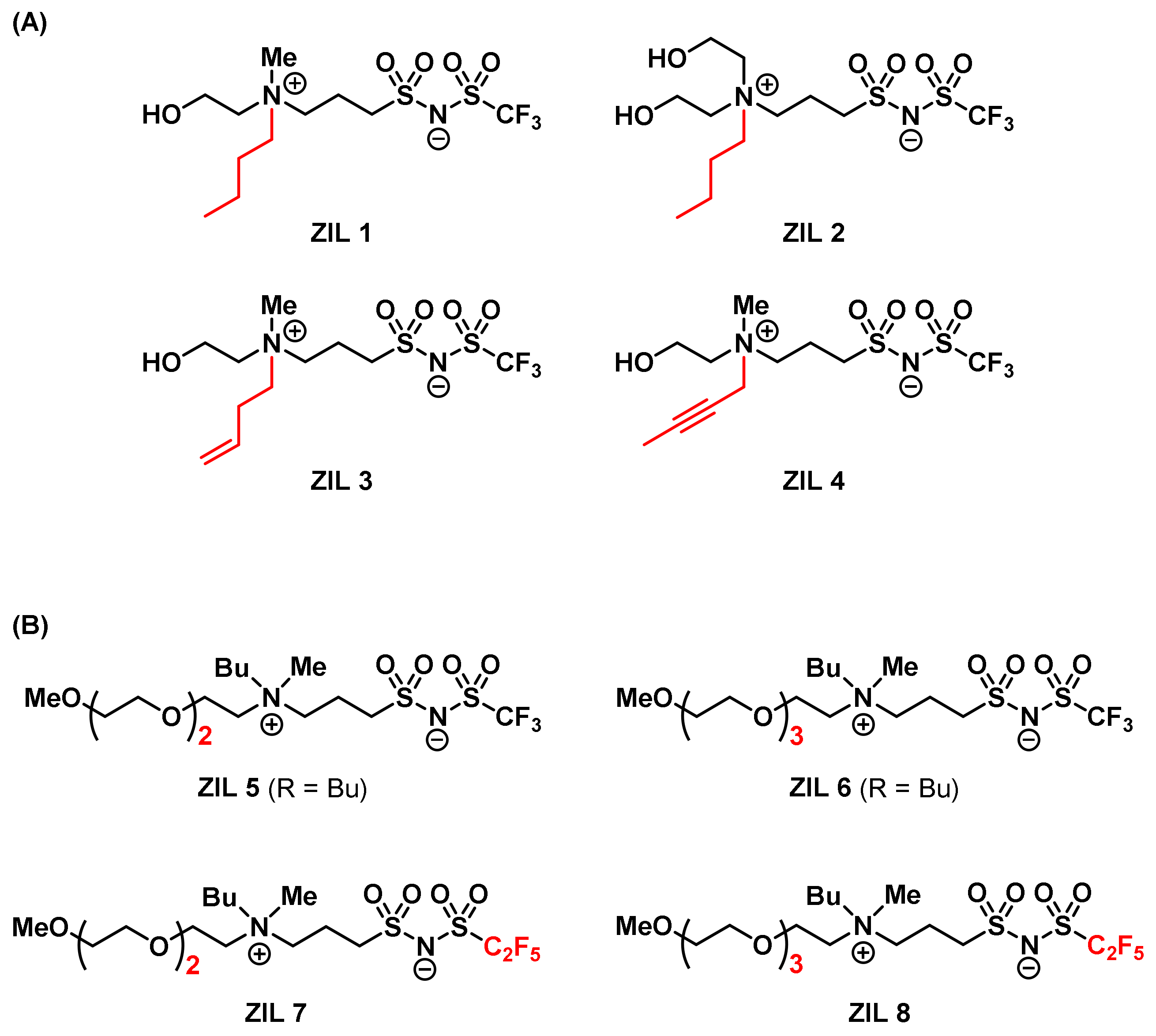
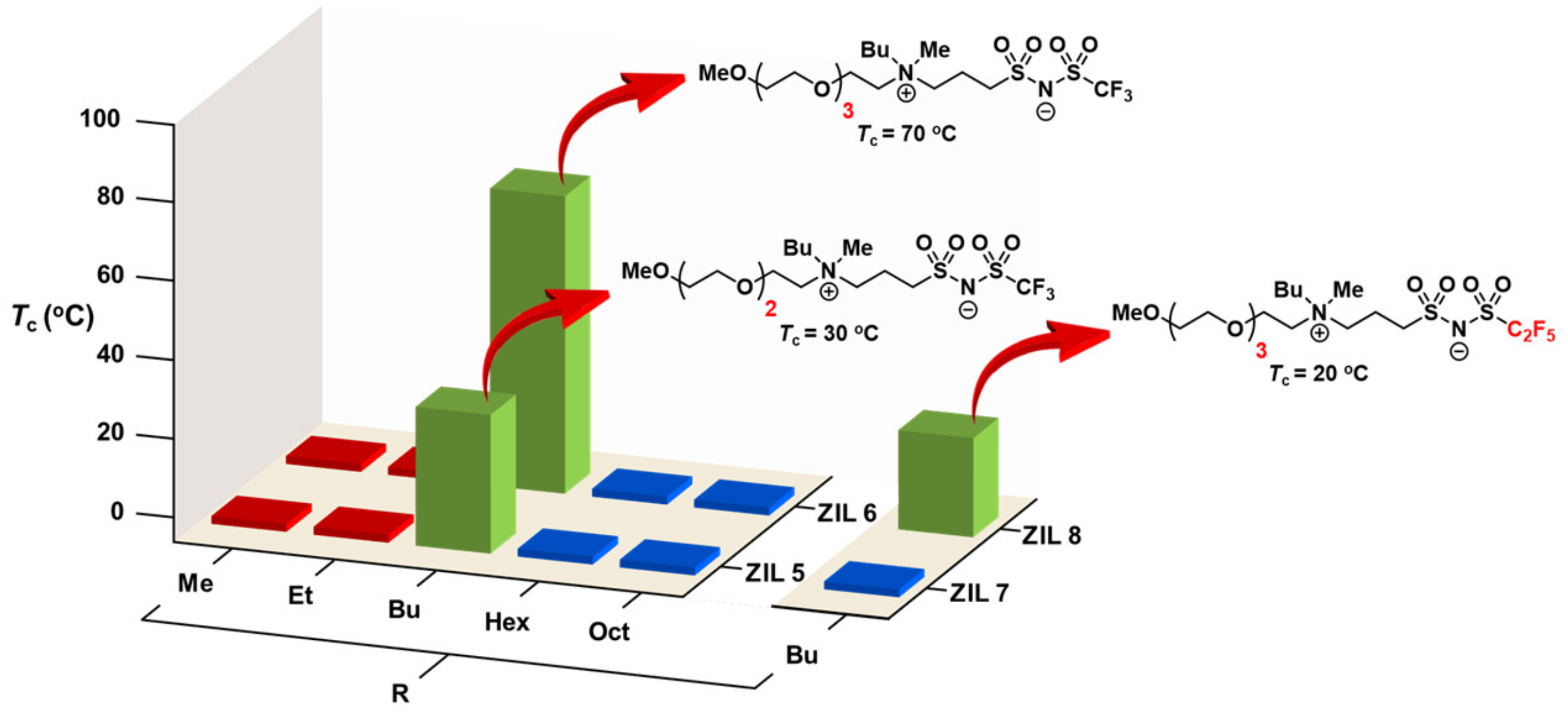
3.6. Combinatorial Discovery of Thermoresponsive Zwitterionic Ionic Liquids
3.7. Future Prospect of Thermoresponsive Ionic Liquid Materials
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaur, G.; Kumar, H.; Singla, M. Diverse applications of ionic liquids: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 351, 118556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.J.; Johan Jacquemin, J.; Hardacre, C. Industrial applications of ionic liquids. Molecules 2020, 25, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, J.S. A short history of ionic liquids—From molten salts to neoteric solvents. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Ionic liquids: A brief history. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan Beil, S.; Markiewicz, M.; Pereira, C.S.; Stepnowski, P.; Thöming, J.; Stolte, S. Toward the proactive design of sustainable chemicals: Ionic liquids as a prime example. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 13132–13173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Levisky, J.A.; Wilson, R.A.; Hussey, C.L. Dialkylimidazolium chloroaluminate melts: A new class of room-temperature ionic liquids for electrochemistry, spectroscopy and synthesis. Inorg. Chem. 1982, 21, 1263–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhôte, P.; Dias, A.-P.; Papageorgiou, N.; Kalyanasundaram, K.; Grätzel, M. Hydrophobic, highly conductive ambient-temperature molten salts. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.D.; Long, T.E. Designing imidazole-based Ionic liquids and ionic liquid monomers for emerging technologies. Polym. Rev. 2009, 49, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiguel, S.; Dehaen, W.; Binnemans, K. Stability of ionic liquids in Brønsted-basic media. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5225–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological activity of ionic liquids and their application in pharmaceutics and medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danush, S.; Dutta, A. Machine learning-based framework for predicting toxicity of ionic liquids. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 72, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejazifar, M.; Lanaridi, O.; Bica-Schröder, K. Ionic liquid based microemulsions: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 303, 112264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonia, R.; Laali, K.K. Ionic liquid-mediated synthesis and functionalization of heterocyclic compounds. In Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry; Scriven, E.F.V., Ramsden, C.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 128, pp. 333–431. [Google Scholar]
- Brehm, M.; Pulst, M.; Kressler, J.; Sebastiani, D. Triazolium-based ionic liquids: A novel class of cellulose solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 3994–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadaf, R.N.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Daniel, T.; Lahoti, R.J.; Srinivasan, K.V. Room temperature ionic liquid promoted regioselective synthesis of 2-aryl benzimidazoles, benzoxazoles and benzthiazoles under ambient conditions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2004, 214, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Chopra, H.K. Synthesis and applications of carbohydrate based chiral ionic liquids as chiral recognition agents and organocatalysts. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 298, 111994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Feder-Kubis, J.; Tatarczak-Michalewska, M. Chiral ionic liquids: Structural diversity, properties and applications in selected separation techniques. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanni, M.; Soldaini, G.; Faggi, C.; Goti, A.; Cardona, F. Novel L-tartaric acid derived pyrrolidinium cations for the synthesis of chiral ionic liquids. Synlett 2009, 5, 747–750. [Google Scholar]
- Sawant, A.D.; Raut, D.G.; Darvatkar, N.B.; Salunkhe, M.M. Recent developments of task-specific ionic liquids in organic synthesis. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2011, 4, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Dubreuil, J.; Bazureau, J.P. Rate accelerations of 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions in ionic liquids. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 7351–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, M.; Hirao, M.; Ito-Akita, K.; Ohno, H. Ion conduction in zwitterionic-type molten salts and their polymers. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.C.; Jensen, J.L.; Ntai, I.; Tran, K.L.T.; Weaver, K.J.; Forbes, D.C.; Davis, J.H., Jr. Novel brønsted acidic ionic liquids and their use as dual solvent-catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 5962–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.-L.; Chen, T.-U.; Cheng, T.-H.; Lin, Y.-D. Ionic Liquid and Viscose Composition. Patent TW I472545B, 11 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, X.M.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Hu, X.B.; Xu, Y. Protic ionic liquids for the selective absorption of H2S from CO2: Thermodynamic analysis. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 4232–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, G.; Bhoria, N.; AlHallaq, S.; Abdala, A.; Mittal, V. Polymer membranes for acid gas removal from natural gas. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 158, 333–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, E.D.; Mayton, R.D.; Ntai, I.; Davis, J.H., Jr. CO2 capture by a task-specific ionic liquid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 926–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.K.; Khokarale, S.G.; Bui, T.Q.; Mikkola, J.-P.T. Ionic liquids: Potential materials for carbon dioxide capture and utilization. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiki, R.K.; Gelfand, D.H.; Stoffel, S.; Scharf, S.J.; Higuchi, R.; Horn, G.T.; Mullis, K.B.; Erlich, H.A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 1988, 4839, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Laššáková, S.; Korabečná, M.; Neužil, P. PCR past, present and future. Biotechniques 2020, 69, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, U.H.; Bachmann, H.S.; Peters, J.; Siffert, W. PCR-amplification of GC-rich regions: ‘Slowdown PCR’. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1312–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of GC-rich templates. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2019, 2, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. Dimethyl sulfoxide targets phage RNA polymerases to promote transcription. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 333, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; e Silva, F.A.; Quental, M.V.; Mondal, D.; Mara, G.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic-liquid-mediated extraction and separation processes for bioactive compounds: Past, present, and future trends. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6984–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buljubasic, F.; Buchbauer, G. The scent of human diseases: A review on specific volatile organic compounds as diagnostic biomarkers. Flavour Fragr. J. 2015, 30, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suerbrey, G. The use of quartz oscillators for weighing thin layers and for microweighing. Zeit. Phys. 1959, 155, 206–222. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Yuan, C.-Y.; Warmack, R.J.; Barnes, C.E.; Dai, S. Ionic liquids: A new class of sensing materials for detection of organic vapors based on the use of a quartz crystal microbalance. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 2172–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchatip, S.; Ananthanawat, C.; Sithigorngul, P.; Sangvanich, P.; Rengpipat, S.; Hoven, V.P. Detection of the shrimp pathogenic bacteria, Vibrio harveyi, by a quartz crystal microbalance-specific antibody based sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, R.E.; Cooper, M.A. A survey of the 2010 quartz crystal microbalance literature. J. Mol. Recognit. 2012, 25, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Sun, L.; Huang, P.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Zou, Y.; Chu, H.; Yan, E.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; et al. A pyridine vapor sensor based on metal-organic framework-modified quartz crystal microbalance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Li, H.-Y.; Chang, I.-N.; Chu, Y.-H. Affinity ionic liquids for chemoselective gas sensing. Molecules 2018, 23, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.-C.; Tseng, M.-J.; Chu, Y.-H. Affinity ionic liquid. Chem. Commun. 2009, 48, 7503–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Gong, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J. Affinity ionic liquids for the rapid liquid–liquid extraction purification of hexahistidine tagged proteins. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 146, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.-C.; Yuan, T.-C.; Li, Z.; Chu, Y.-H. Crowned ionic liquids for biomolecular interaction analysis. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10811–10815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirumurugan, P.; Matosiuk, D.; Jozwiak, K. Click chemistry for drug development and diverse chemical–biology applications. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4905–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, C.J. The discovery of crown ethers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1988, 27, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüdiger, V.; Schneider, H.-J.; Solov’ev, V.P.; Kazachenko, V.P.; Raevsky, O.A. Crown ether–ammonium complexes: Binding mechanisms and solvent effects. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 1999, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, Y.; Shohei, S.; Men, Y.-J.; Yuan, J.-Y.; Ohno, H. Thermoresponsive polyelectrolytes derived from ionic liquids. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 2163–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tucker, Z.D.; Wang, Y.; Ashfeld, B.L.; Luo, T. Ionic liquid enables highly efficient low temperature desalination by directional solvent extraction. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Ikari, R.; Nakamura, N.; Ohno, H.; Fujita, K. Distribution of cytochrome c in LCST-type ionic liquid/water mixtures controlled by applied potential and temperature. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, G96–G100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Ohno, H. Thermoresponsive ionic liquid/water mixtures for separation and purification technologies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-H.; Huang, H.-H. Exploiting α-benzylated 1,4-butanesultones to expedite the discovery of small-molecule, LCST-type sulfobetaine zwitterionic materials. Mater. Adv. 2023, 4, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-S. Structural Engineering and Optimization of Zwitterionic Salts for Expeditious Discovery of Thermoresponsive Materials. Molecules 2022, 27, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Ma, W.; Theyssen, N.; Chen, C.; Hou, Z. Temperature-responsive ionic liquids: Fundamental behaviors and catalytic applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6881–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Li, X.; Lee, D.; Li, J.; Yun, J.; Jiang, C.; Li, Z.; Lee, S.W. Thermoresponsive ionic liquid for electrochemical low-grade heat harvesting. Nano Energy 2023, 105, 108022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasbrenner, H.; Weingaertner, H. Phase separation and critical point of an aqueous electrolyte solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1989, 93, 3378–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullius, J.E.L.; Suarez, P.A.Z.; Einloft, S.; de Souza, R.F.; Dupont, J.; Fischer, J.; De Cian, A. Selective catalytic hydrodimerization of 1,3-butadiene by palladium compounds dissolved in ionic liquids. Organometallics 1998, 17, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, P.J.; Ellis, D.J.; Welton, T. A temperature-controlled reversible ionic liquid—Water two phase—Single phase protocol for hydrogenation catalysis. Can. J. Chem. 2001, 79, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nockemann, P.; Thijs, B.; Pittois, S.; Thoen, J.; Glorieux, C.; Hecke, K.V.; Meervelt, L.V.; Kirchner, B.; Binnemans, K. Task-specific ionic liquid for solubilizing metal oxides. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 20978–20992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukaya, Y.; Sekikawa, K.; Murata, K.; Nakamura, N.; Ohno, H. Miscibility and phase behavior of water–dicarboxylic acid type ionic liquid mixed systems. Chem. Commun. 2007, 29, 3089–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, K.; Ohno, H. LCST-type phase changes of a mixture of water and ionic liquids derived from amino acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1852–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, Y.; Saita, S.; Murata, K.; Nakamura, N.; Ohno, H. Extraction of proteins with temperature sensitive and reversible phase change of ionic liquid/water mixture. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, Y.; Ohno, H. Temperature-responsive ionic liquid/water interfaces: Relation between hydrophilicity of ions and dynamic phase change. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 5063–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nockemann, P.; Binnemans, K.; Thijs, B.; Parac-Vogt, T.N.; Merz, K.; Mudring, A.-V.; Menon, P.C.; Rajesh, R.N.; Cordoyiannis, G.; Thoen, J.; et al. Temperature-driven mixing-demixing behavior of binary mixtures of the ionic liquid choline bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide and water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukayaab, Y.; Ohno, H. Hydrophobic and polar ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Kuroda, K.; Sato, D.; Kunimura, H.; Ohno, H. Effects of polarity, hydrophobicity, and density of ionic liquids on cellulose solubility. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 32276–32282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depuydt, D.; Liu, L.; Glorieux, C.; Dehaena, W.; Binnemans, K. Homogeneous liquid–liquid extraction of metal ions with non-fluorinated bis(2-ethylhexyl)phosphate ionic liquids having a lower critical solution temperature in combination with water. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14183–14186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J. Tunable LCST-type phase behavior of [FeCl4]−–based ionic liquids in water. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieno, Y.; Kohno, Y.; Saita, S.; Ohno, H. Design and control of LCST behaviour of zwitterion/aqueous Brønsted acid mixtures. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 12262–12265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oba, Y.; Okuhata, M.; Osakai, T.; Mochida, T. Solvate and protic ionic liquids from aza-crown ethers: Synthesis, thermal properties, and LCST behavior. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 3118–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero-Martinez, N.C.; Cortes-Huerto, R.; Benedetto, A.; Ballone, P. Thermoresponsive ionic liquid/water mixtures: From nanostructuring to phase separation. Molecules 2022, 27, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nockemann, P.; Thijs, B.; Parac-Vogt, T.N.; Hecke, K.V.; Meervelt, L.V.; Tinant, B.; Hartenbach, I.; Schleid, T.; Ngan, V.T.; Nguyen, M.T.; et al. Carboxyl-functionalized task-specific ionic liquids for solubilizing metal oxides. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 9987–9999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Pei, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Understanding the mechanism of LCST phase separation of mixed ionic liquids in water by MD simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 23238–23245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-H.; Hwang, C.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Tseng, M.-J. Combinatorial discovery of thermoresponsive cycloammonium ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 11855–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.-H.; Cheng, M.-F.; Chiang, Y.-H. Combinatorial discovery of small-molecule 1,2,3-triazolium ionic liquids exhibiting lower critical solution temperature phase transition. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-Y. Structural fine-tuning of zwitterionic salts for the discovery of LCST-type thermoresponsive materials. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 7286–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, L.; Huang, H.-H.; Wu, J.; Zhou, X.; Yan, X.; Jia, J.; Yue, T.; Chu, Y.-H.; Yan, B. Biosafety-inspired structural optimization of triazolium ionic liquids based on structure-toxicity relationships. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-H.; Jia, J.; Ren, L.; Wang, S.; Yue, T.; Yan, B.; Chu, Y.-H. A zwitterionic solution for smart ionic liquids to evade cytotoxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, P.; Pan, X.; Chen, C.-Y.; Li, H.-Y.; Yan, X.; Li, C.; Chu, Y.-H.; Yan, B. Emerging Impacts of Ionic Liquids on Eco-Environmental Safety and Human Health. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 13609–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maculewicz, J.; Swiacka, K.; Stepnowski, P.; Dołzonek, J.; Białk-Bielinska, A. Ionic liquids as potentially hazardous pollutants: Evidences of their presence in the environment and recent analytical developments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, N.; Ota, K.; Miura, Y.; Shin, H.; Yamamoto, M. Sulfobetaine polymers for effective permeability into multicellular tumor spheroids (MCTSs). J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.-Y.; Chu, Y.-H. Expeditious Discovery of Small-Molecule Thermoresponsive Ionic Liquid Materials: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 6817. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196817
Li H-Y, Chu Y-H. Expeditious Discovery of Small-Molecule Thermoresponsive Ionic Liquid Materials: A Review. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6817. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196817
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hsin-Yi, and Yen-Ho Chu. 2023. "Expeditious Discovery of Small-Molecule Thermoresponsive Ionic Liquid Materials: A Review" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6817. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196817
APA StyleLi, H.-Y., & Chu, Y.-H. (2023). Expeditious Discovery of Small-Molecule Thermoresponsive Ionic Liquid Materials: A Review. Molecules, 28(19), 6817. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196817






