Preparation of Biomass Carbon Composites MgO@ZnO@BC and Its Adsorption and Removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) in Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
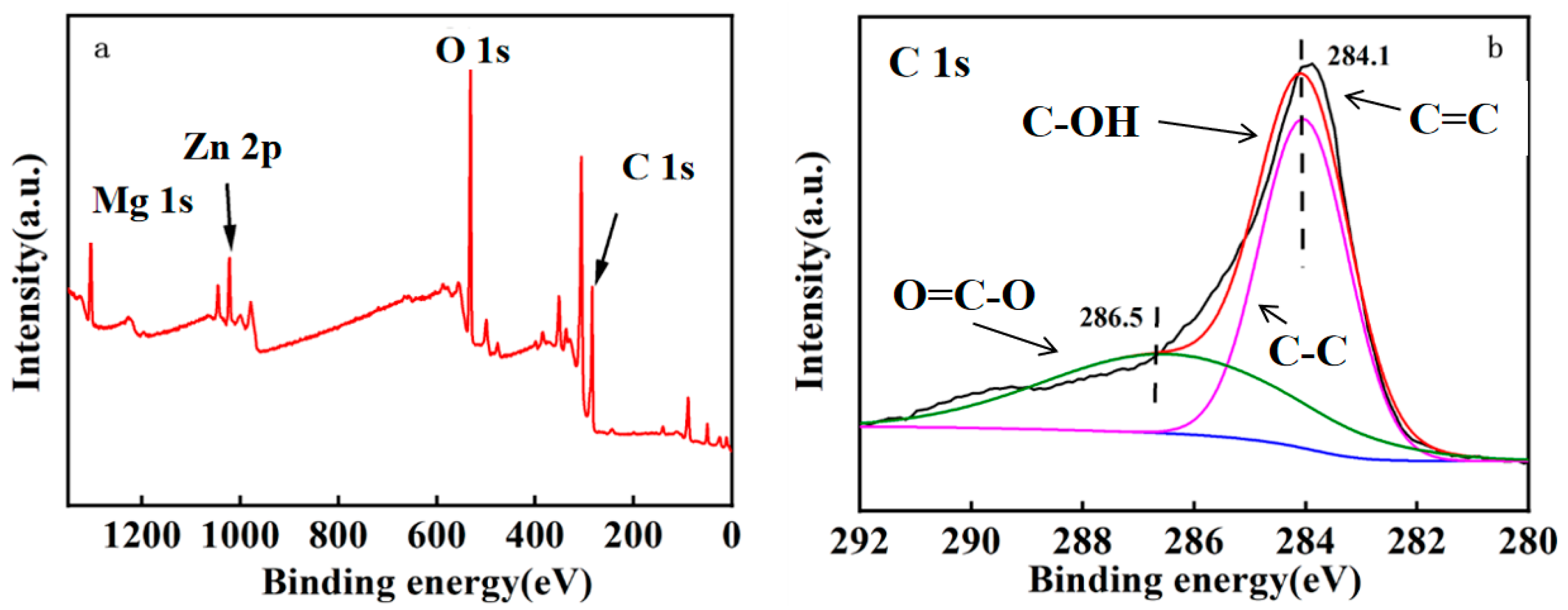
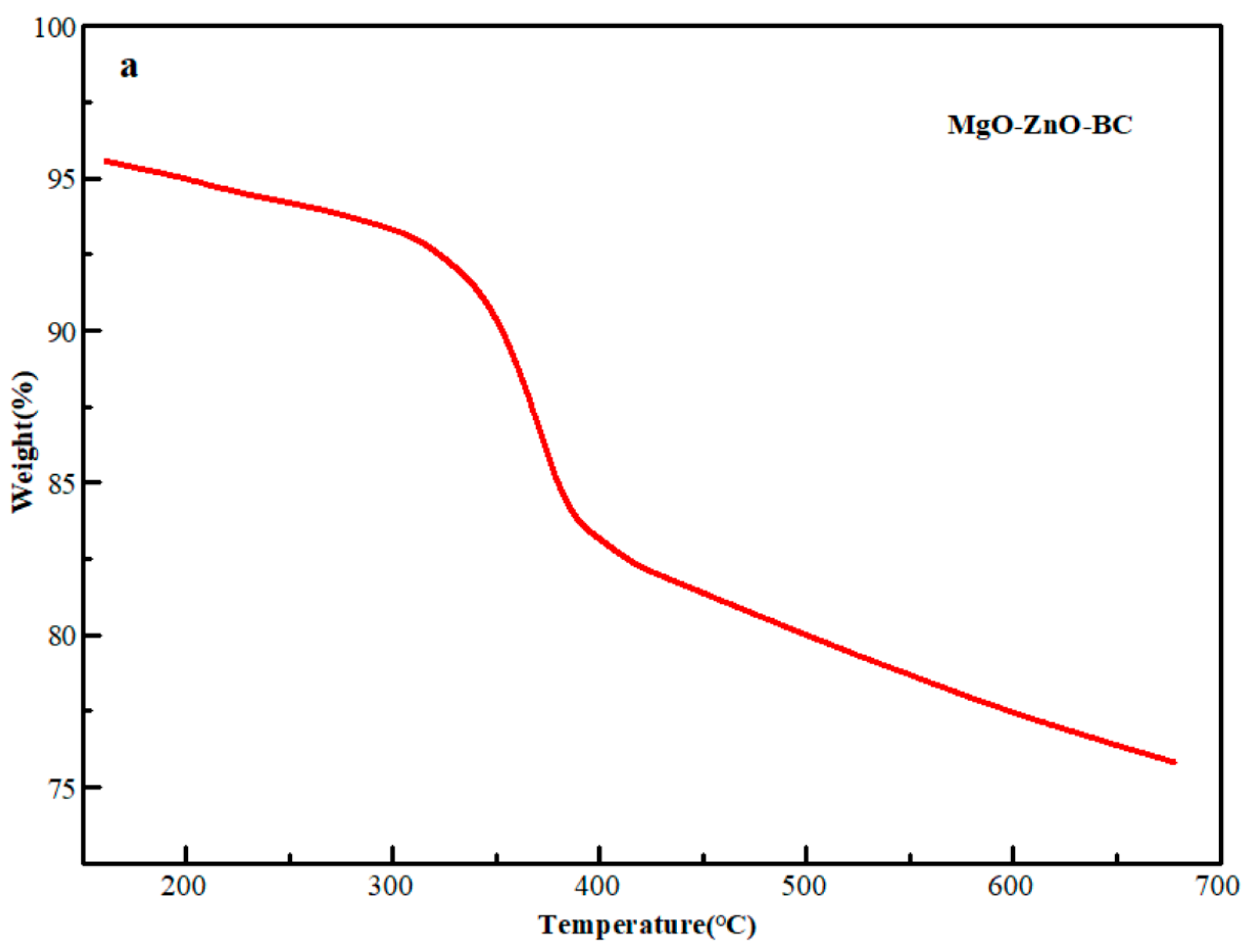
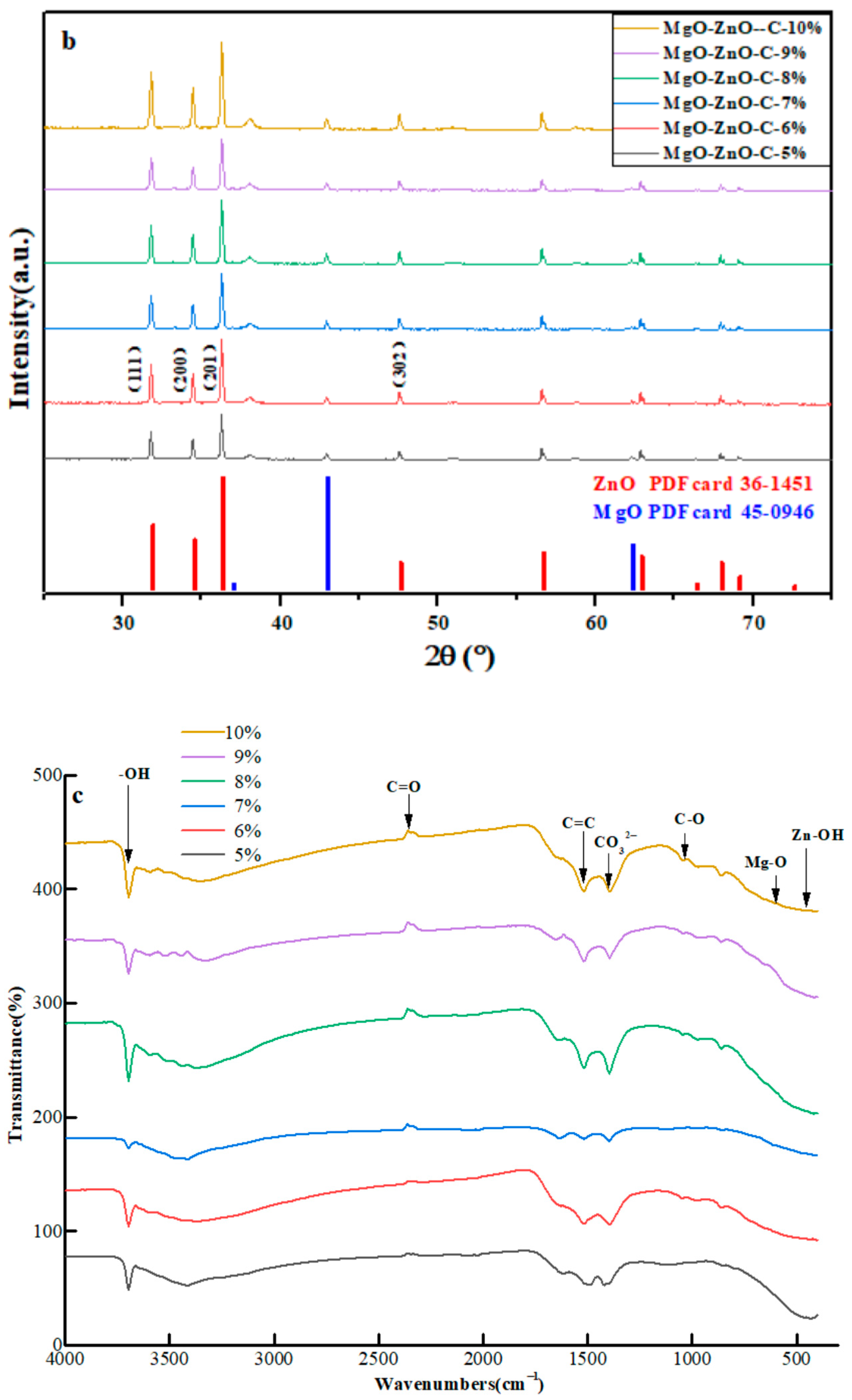
2.1. Characterization of MgO@ZnO@BC
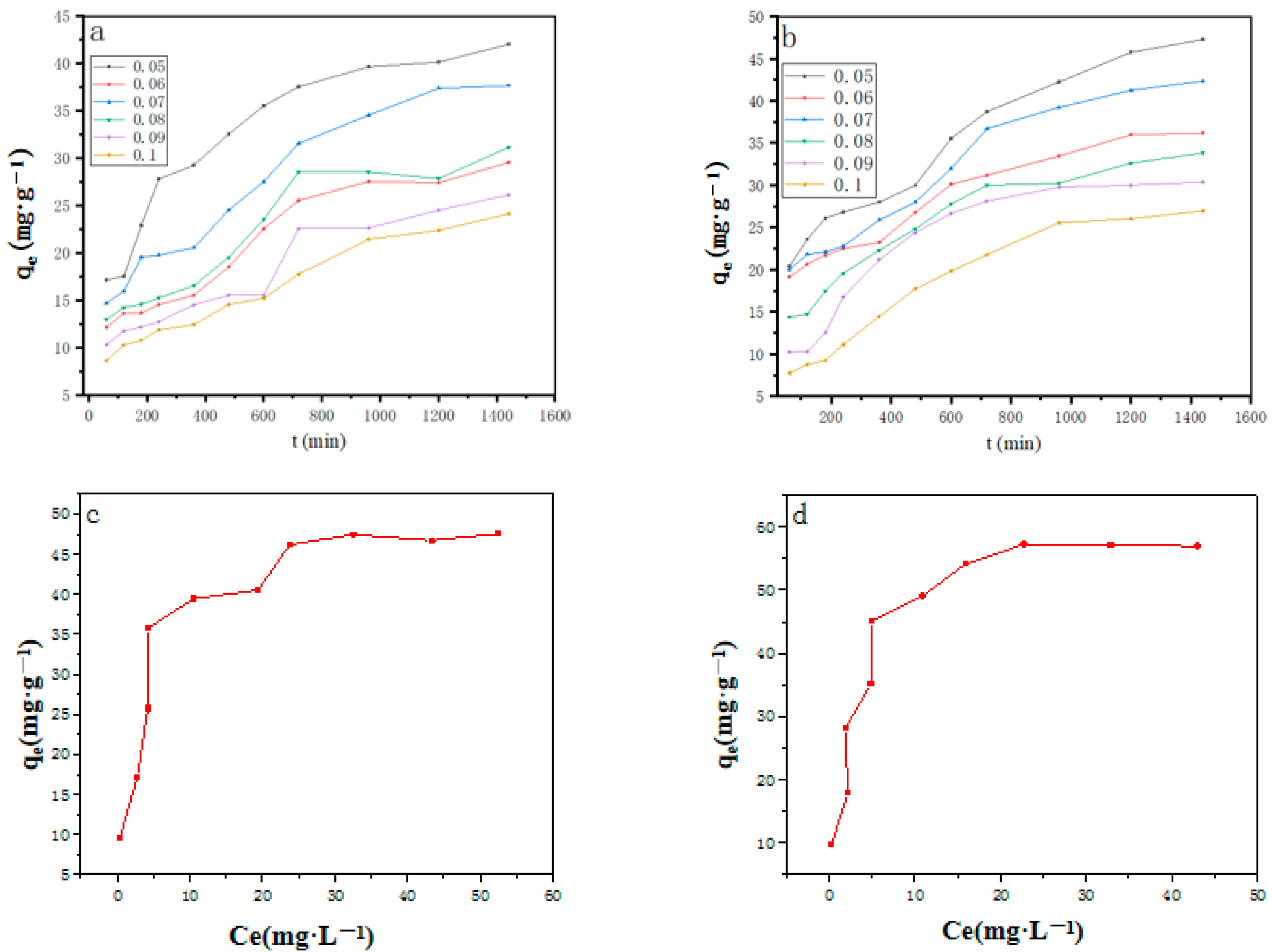
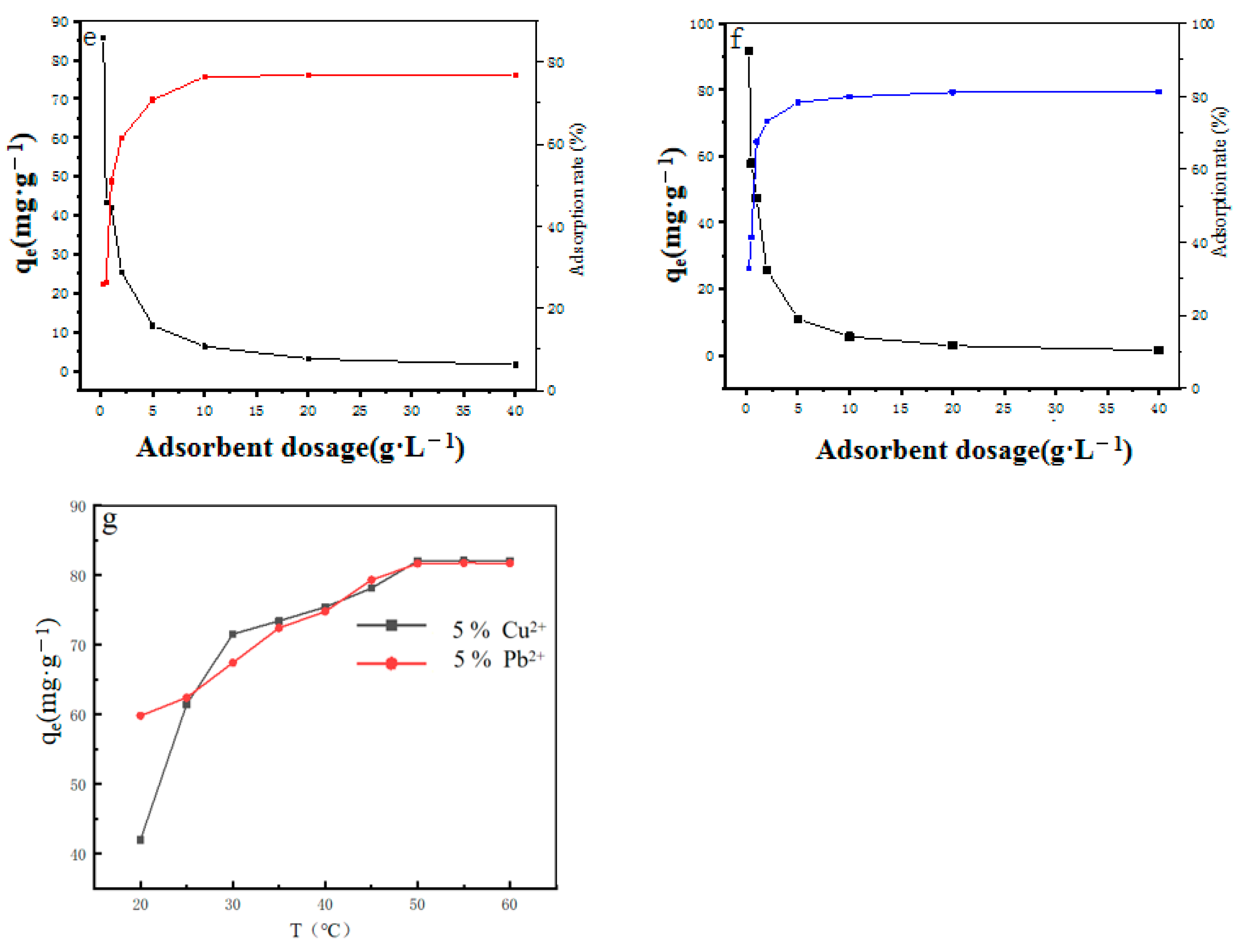
2.2. Adsorption Experiment
Influencing Factors of Adsorption Performance
2.3. Thermodynamic Model
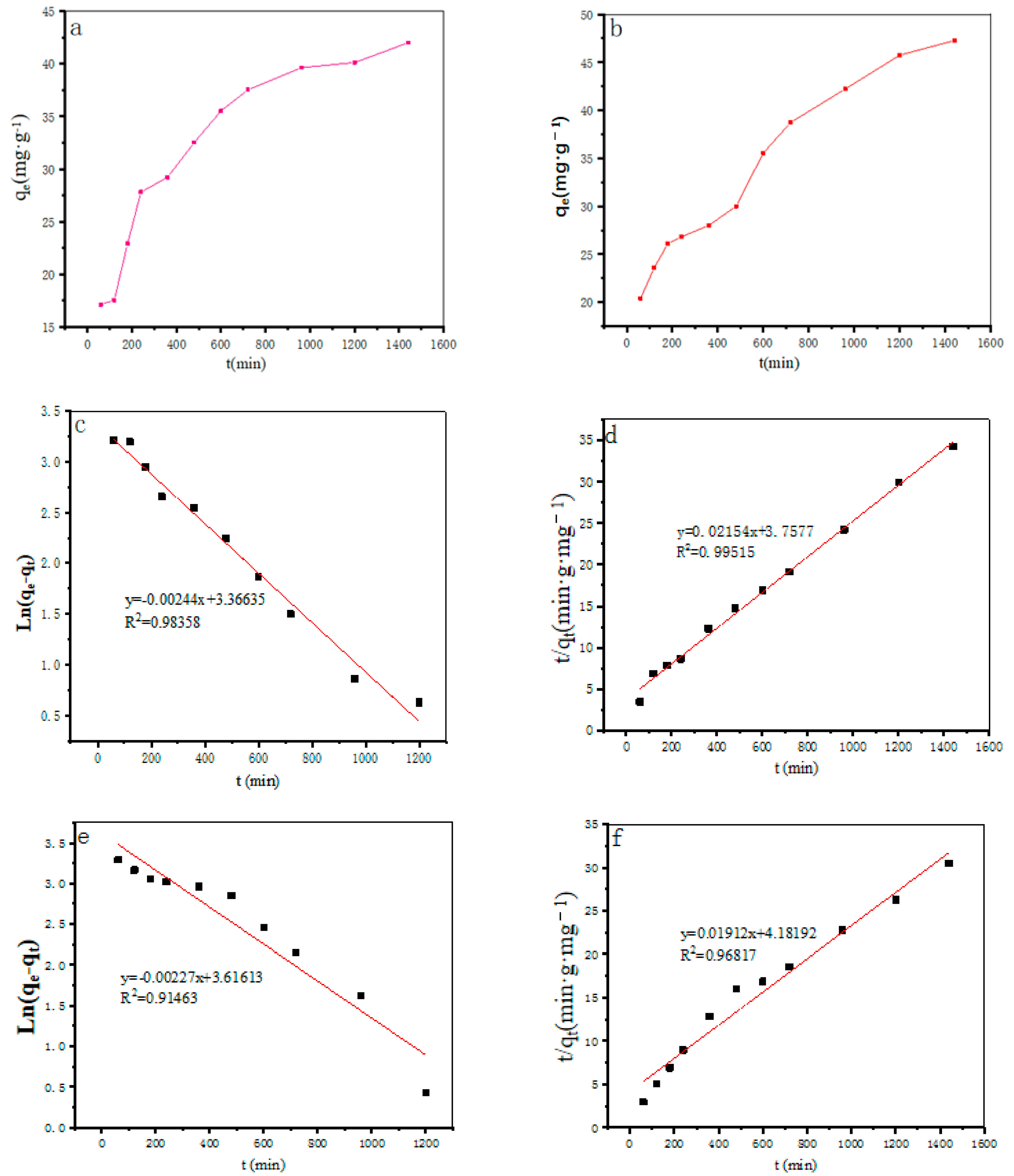
Adsorption Kinetics
2.4. Mechanism Analysis
- (1)
- Ion exchange: Mg2+ and Zn2+ are released from the MgO and ZnO groups loaded on the surface of biomass carbon to exchange ions with Pb2+ and Cu2+ in solution, resulting in PbO, CuO and Pb(OH)2, Cu(OH)2, etc., which are adsorbed on the surface of biomass carbon and participate in further precipitation reactions. This process is also one of the reactions for precipitation generation. Therefore, the role of ion exchange in the adsorption process needs to be further verified.
- (2)
- Precipitation: Pb(OH)2, Cu(OH)2 and other components have a certain solubility in aqueous solution, and then react with CO2 to produce further precipitation of alkaline lead carbonate based on Pb3(CO3)2(OH)2 and Cu2(OH)2CO3 and alkaline copper carbonate, greatly increasing the removal rate of Pb and Cu. At the same time, the pH of the system increases due to the action of MgO/Mg(OH)2 and CuO/Cu(OH)2, which reached favorable conditions for precipitation formation, especially on the surface of the adsorbent, thus allowing formation of lead and copper-containing precipitates in large quantities and adherence to the surface of the biochar, as well as binding to the adsorbent, thus allowing their removal from the solution through the filter membrane. Precipitation plays a major role in the adsorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) by MgO/Mg(OH)2 and CuO/Cu(OH)2-loaded materials.
- (3)
- The role of surface functional groups: C-containing functional groups such as C-O/C-N, C=O, and O=C-O, as well as some groups which share electrons with Pb(II) and Cu(II) during adsorption, combine with Pb(II) and Cu(II) to achieve removal. The addition of functional groups containing metal oxides by loading metal oxide also plays a role in the adsorption process.
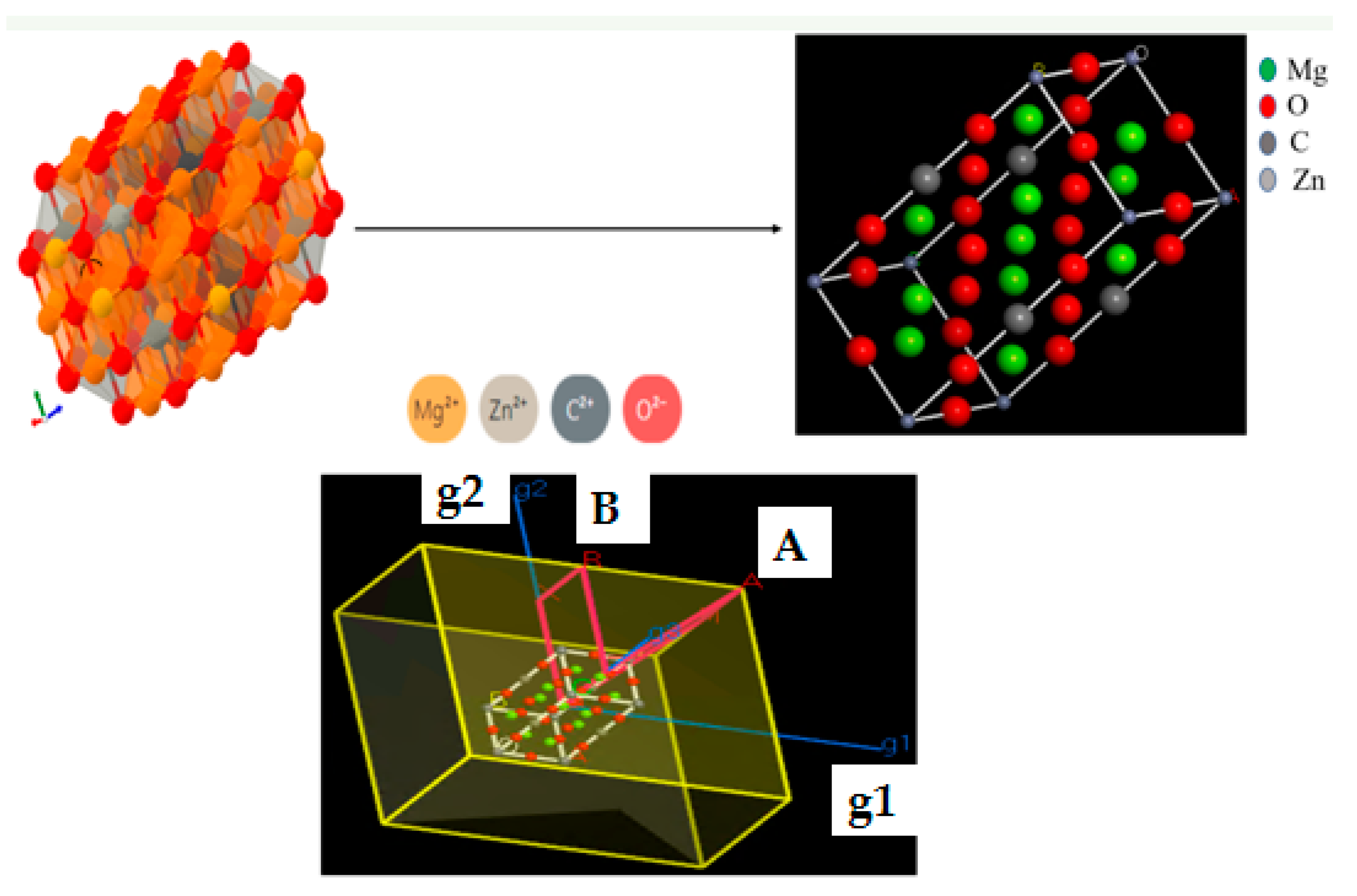
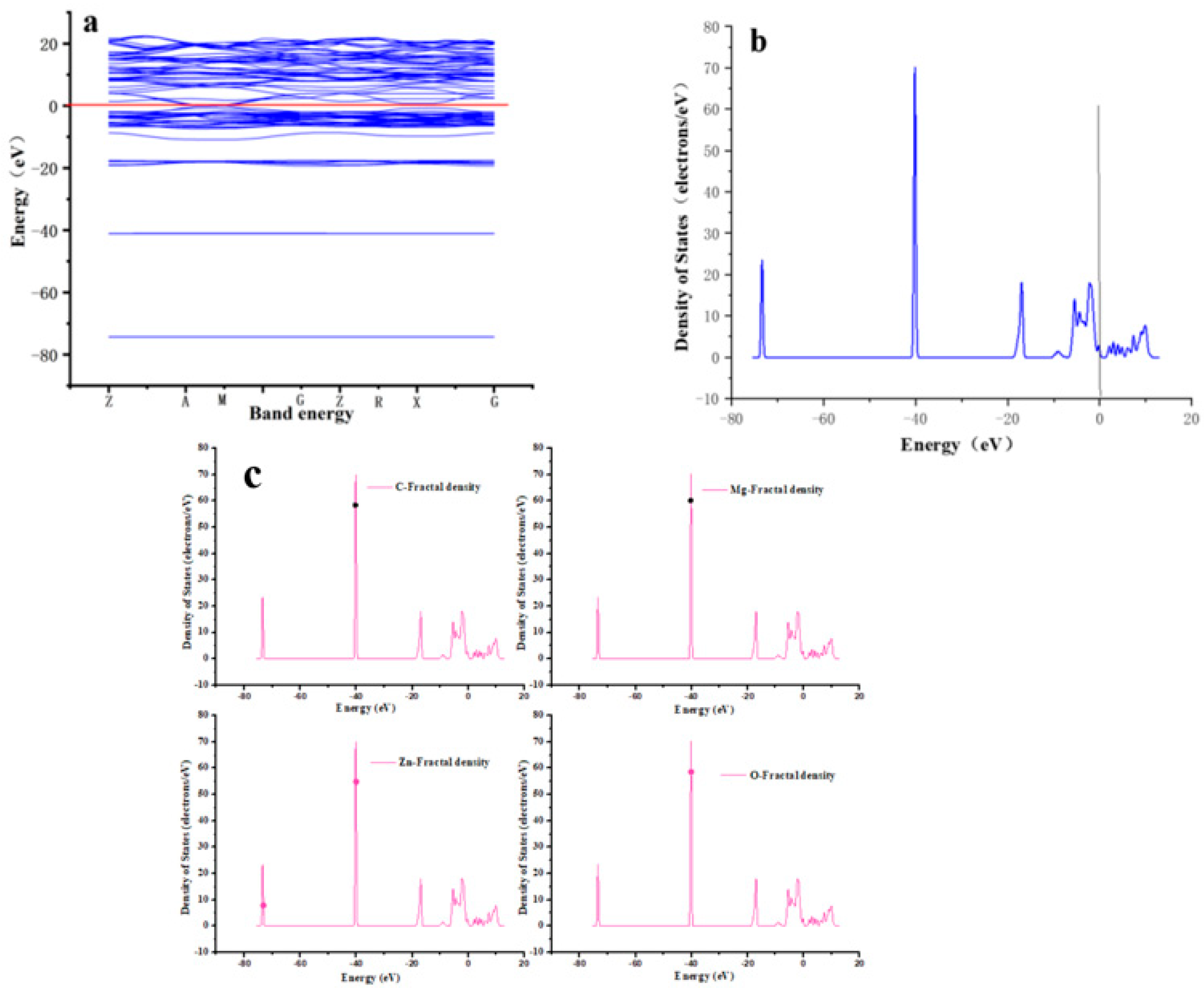
2.5. Chemical Simulation Calculations
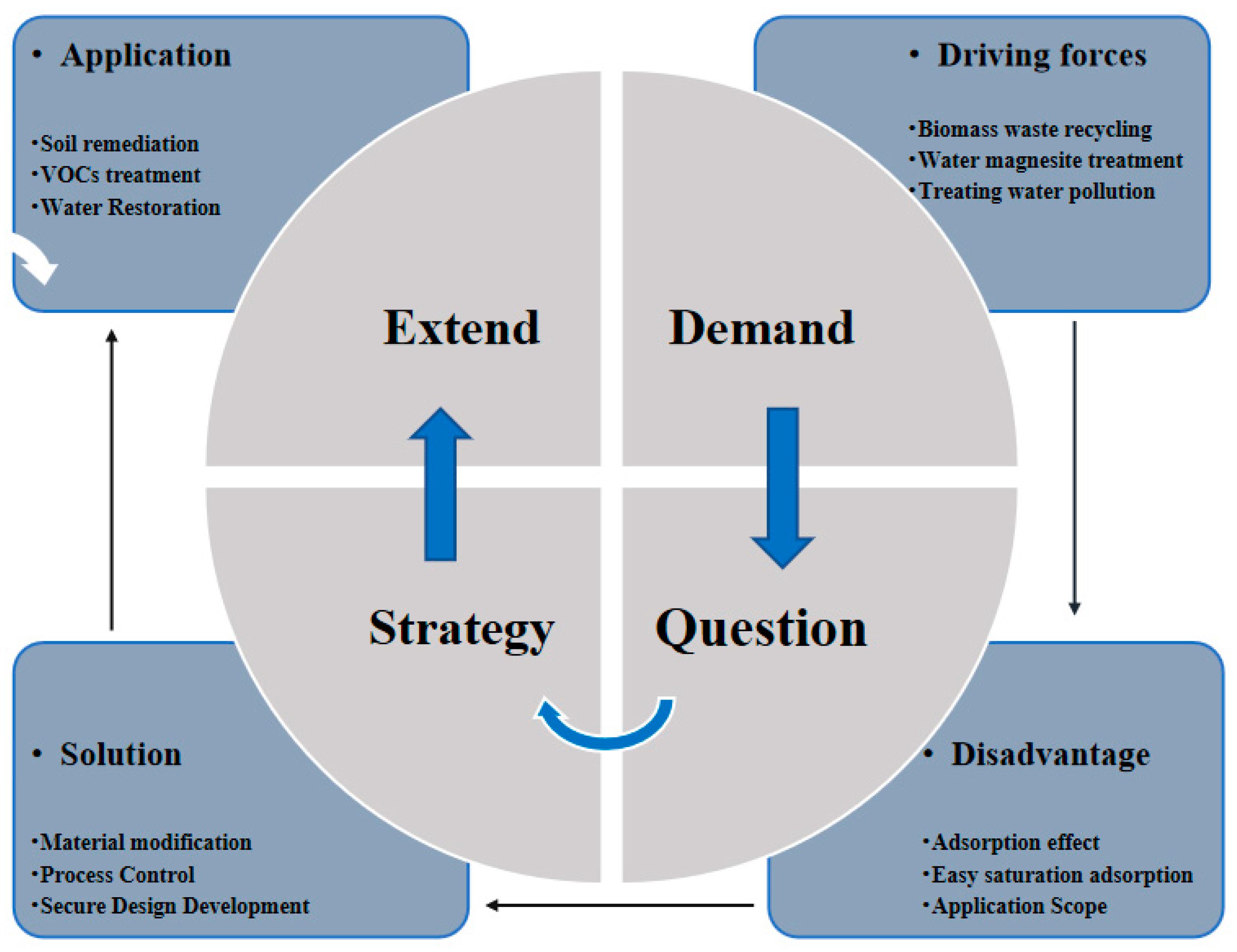
2.6. New Perspectives on Materials
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of MgO@ZnO@BC
3.2. Material Characterization
3.3. Adsorption Studies
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Xiao, H.; Shahab, A.; Li, J.; Xi, B.; Sun, X.; He, H.; Yu, G. Distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments of Huixian coast wetland, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185, 109700. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Shahab, A.; Xi, B.; Chang, Q.; You, S.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Huang, H.; Li, X. Heavy metal pollution, ecological risk, spatial distribution, and source identification in sediments of the Lijiang River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gök, Ö.; Özcan, A.; Erdem, B.; Özcan, A.S. Prediction of the kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic parameters of adsorption of cop-per(II) ions onto 8-hydroxy quinoline immobilized bentonite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 317, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Fang, D.; Yang, L.; Wei, Z.; Tu, Y.; Shao, P.; Hua, Z.; Wang, Z.; Luo, X. Tailored construction of β-cyclodextrin covalently-supported tannic acid polymer nanosponge towards highly selective lead recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity to plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar]
- Morale Afghani, M.; Nezamzadeh Ejhieh, A. Efficient solid amino acid clinoptilolite nanoparticles adsorbent for Mn(II) removal: A comprehensive study on designing the experiments, thermodynamic and kinetic aspects. Solid State Sci. 2020, 101, 106124. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, W.; Yang, L.; Joseph, S.; Shi, W.; Bian, R.; Zheng, J.; Li, L.; Shan, S.; Pan, G. Utilization of biochar produced from invasive plant species to efficiently adsorb Cd (II) and Pb (II). Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 317, 124011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Bai, R. Removal of mercury (II) from aqueous solution with three commercial raw activated carbons. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2017, 43, 2273–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bediako, J.K.; Lin, S.; Sarkar, A.K.; Zhao, Y.; Choi, J.-W.; Song, M.-H.; Wei, W.; Reddy, D.H.K.; Cho, C.-W.; Yun, Y.-S. Benignly-fabricated crosslinked polyethylenimine/calcium-alginate fibers as high-performance adsorbents for effective recovery of gold. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Liu, M.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, G.; Song, C. Facile synthesis of size-controlled MIL-100(Fe) with an excellent adsorption capacity for ethylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, S.Y.; Liew, R.K.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, Y.W.; Yek, P.N.Y.; Mahari, W.A.W.; Lee, X.Y.; Han, C.S.; Vo, D.V.N.; Van Le, Q.; et al. Valorization of biomass waste to engineered activated biochar by microwave pyrolysis: Progress, challenges, and future directions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124401. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, Y.J. Hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchically structured birnessite-type MnO2/biochar composites for the adsorptive removal of Cu(II) from aqueous media. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Zeng, Q.; Tie, B.; Lei, M.; Yang, J.; Luo, S.; Song, Z. Manganese dioxide nanosheet suspension: A novel absorbent for cadmium(II) contamination in waterbody. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 456, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, H. Heavy metal removal from water by magnetite nanorods. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamari, A.; Ngah, W.S.W. Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of lead and copper uptake by H2SO4 modified Chitosan. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 73, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Chowdhary, P.; Gnansounou, E.; Chaturvedi, P. Biochar and environmental sustainability: Emerging trends and techno-economic perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, W.; Fu, J.; Mao, X.; Kang, Q.; Ran, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; et al. Microwave assisted preparation of activated carbon from biomass: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 92, 958–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Gu, H.; Gu, S.; Xiong, M.; Zhang, D.; Qi, R.; Chen, W. Novel FeO-C/S (IV) system: Toward the interaction between FeO-C internal electrolysis and soft for p-nitrophenol degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 268, 118615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Song, N.; Li, X. High-performance supercapacitors and batteries derived from activated banana-peel with porous structures. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 222, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfabad, E.M.; Ding, J.; Cui, K.; Kohandehghan, A.; Kalisvaart, W.P.; Hazelton, M.; Mitlin, D. High-Density Sodium and Lithium Ion Battery Anodes from Banana Peels. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7115–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Lu, W.; Chen, C.; Tan, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, C. Optimized synthesis of banana peel derived porous carbon and its application in lithium sulfur batteries. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 112, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Ou, R.; Lu, Y.; Yuan, A.; Liu, J.; Gu, J.; Hu, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, F. Record-high capture of volatile benzene and toluene enabled by activator implant-optimized banana peel-derived engineering carbonaceous adsorbents. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, H. Activated banana peel carbon: A potential adsorbent for Rhodamine B decontamination from aqueous system. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, J.; Shafique, U.; Zaman, W.U.; Salman, M.; Dar, A.; Anwar, S. Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) from water by adsorption on peels of banana. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1752–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Saeed, K. Decontamination of Cr(VI) and Mn(II) from aqueous media by untreated and chemically treated banana peel: A comparative study. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3586–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro-Silva, E.; Pipi, A.R.F.; Magdalena, A.G.; Piacenti-Silva, M. Application of Langmuir and Freundlich models in the study of banana peel as bioadsorbent of copper (II) in aqueous medium. Rev. Mater. 2020, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, L.L.; Liu, W.J.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, H. Magnesium oxide embedded nitrogen self-doped biochar composites: Fast and high-efficiency adsorption of heavy metals in an aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10081–10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarska, A.A.; Klapiszewski, Ł.; Jesionowski, T. Recent development in the synthesis, modification and application of Mg(OH)2 and MgO: A review. Powder Technol. 2017, 319, 373–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zou, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; He, X.; Fan, Z.; Ren, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, D. Synthesis of high surface area, mesoporous MgO nanosheets with excellent adsorption capability for Ni(II) via a distillation treating. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 438, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Shafey, A.M. Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles from plant leaf extracts and their applications: A review. Green Process. Synth. 2020, 9, 304–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhang, H.; Shahab, A.; Zeng, H.; Zeng, H.; Bacha, A.-U.; Nabi, I.; Siddique, J.; Ullah, H. Efficient performance of magnesium oxide loaded biochar for the significant removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 221, 112426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouda, A.; Hassan, S.E.D.; Saied, E.; Hamza, M.F. Photocatalytic degradation of real textile and tannery effluent using biosynthesized magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgO-NPs), heavy metal adsorption, phytotoxicity, and antimicrobial activity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105346. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.-J.; Jiang, H.; Tian, K.; Ding, Y.-W.; Yu, H.-Q. Mesoporous Carbon Stabilized MgO Nanoparticles Synthesized by Pyrolysis of MgCl2 Preloaded Waste Biomass for Highly Efficient CO2 Capture. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9397–9403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, R.; Kumar, S.D.; Jayalakshmi, A.; Singaravelu, G.; Govindaraju, K.; Kumar, V.G. Green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity. Indian J. Geo Mar. Sci. 2019, 48, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, M.; Shang, Y.; Yang, G.; Liu, B.; Yang, B. Facile synthesis of hollow mesoporous MgO spheres via spray-drying with improved adsorption capacity for Pb(II) and Cd(II). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18825–18833. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, M.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Lu, P.; Liu, J.; Dong, F. Sol–gel preparation and enhanced photocatalytic performance of Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamanickam, D.; Shanthi, M. Photocatalytic degradation of an organic pollutant by zinc oxide—Solar process. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, S1858–S1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modwi, A.; Khezami, L.; Taha, K.; Al-Duaij, O.; Houas, A. Fast and high efficiency adsorption of Pb(II) ions by Cu/ZnO composite. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.; Wu, X.; Zeng, X.C. Adsorption of O2, H2, CO, NH3, and NO2 on ZnO nanotube: A density functional theory study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 5747–5755. [Google Scholar]
- He, A.L.; Wang, X.Q.; Wu, R.Q.; Lu, Y.H.; Feng, Y.P. Adsorption of an Mn atom on a ZnO sheet and nanotube: A density functional theory study. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 175501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, R.; Xie, S.; Wang, J.; Ji, Z. Synthesis of octahedral-like ZnO/ZnFe2O4 heterojunction photocatalysts with superior photocatalytic activity. Solid State Sci. 2019, 96, 105901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliangsuwan, A.; Phonchai, A.; Bunkoed, O. A magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer hierarchical composite adsorbent embedded with a zinc oxide carbon foam nanocomposite for the extraction of sulfonamides. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107443–107451. [Google Scholar]
- Vaizogullar, A.I. Heterostructured MgO/ZnO photocatalysts: Synthesis, Characterization and UV Light-Induced Photocatalytic Activity Using Model Pollutant 2,6-dichlorophenol. Kinet. Catal. 2018, 59, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.B.; Lohani, P.C.; Kim, A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles decorated tungsten oxide nanorods as high-performance supercapacitor electrode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 804, 139884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Hao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Jiang, L. The selective heavy metal ions adsorption of zinc oxide nanoparticles from dental wastewater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 534, 110750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.T.; Antony, R. Green synthesis of silver doped nano metal oxides of zinc copper for antibacterial proper-ties, adsorption, catalytic hydrogenation photodegradation of aromatics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, R.; De, S. Removal of copper(II) from aqueous solution using zinc oxide nanoparticle impregnated mixed matrix hollow fiber membrane. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.B.; Kim, A.A.; Lohani, P.C.; Yoo, D.J.; Kim, H.J. Assembling zinc cobalt hydroxide/ternary sulfides heterostructure and iron oxide nanorods on three-dimensional hollow porous carbon nanofiber as high energy density hybrid supercapacitor. J. Energy Storage 2023, 60, 106713. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Geng, Z.; Cai, M. High-pressure hydrogen storage and optimizing fabrication of corncob-derived activated carbon. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 194, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Hao, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, K.; Zheng, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, L. Tea polyphenols functionalized and reduced graphene oxide-ZnO composites for selective Pb2+ removal and enhanced antibacterial activity. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jothirani, R.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A.; Narayan, A.S.; Dutta, A. Ultrasonic modified corn pith for the sequestration of dye from aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 39, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, R.; Muthukumaran, K.; Selvaraju, N. Enhanced Pb (II) ions removal by using magnetic NiO/Biochar composite. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yang, D.P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Kang, Z.; Lin, C.; Jia, N.; Luque, R. Waste eggshell membrane-templated CuO-ZnO nanocomposites with enhanced adsorption, catalysis and antibacterial properties for water purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, F.-K.; Hsiao, C.-T.; Kao, H.-M.; Sue, Y.-C.; Lin, K.-W.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, X.-H.; Wan, L.; Hsu, M.-H.; Hwu, J.R.; et al. Size-adjustable annular ring-functionalized mesoporous silica as effective and selective adsorbents for heavy metal ions. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 25686–25689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, W.-P. A novel modified method for the efficient removal of Pb and Cd from wastewater by biochar: Enhanced the ion exchange and precipitation capacity. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 754, 142150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.X.; Jiang, H. Amino modification of biochar for enhanced adsorption of copper ions from synthetic wastewater. Water Res. 2014, 48, 396–405. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Chen, B.; Lin, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhan, J.; Shen, Q.; Pan, X. Adsorption of heavy metal from aqueous solution by dehydrated root powder of long-root Eichhornia crassipes. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2016, 18, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Wu, D.; Lu, J.; Shan, C.; Ren, Y.; Li, T.; Lv, L.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W. Temperature regulated adsorption and desorption of heavy metals to A-MIL-121: Mechanisms and the role of exchangeable protons. Water Res. 2020, 189, 116599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskui, F.N.; Aghdasinia, H.; Sorkhabi, M.G. Adsorption of Cr (III) using an Iranian natural nanoclay: Applicable to tannery wastewater: Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.B.; Awasthi, G.P.; Kim, H.J. Novel insight into the adsorption of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) ions by MOF derived Co-Al layered double hydroxide @hematite nanorods on 3D porous carbon nanofiber network. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, R.; Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Kim, S.; Wan, L.; Nguyen, N.S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Simon, G.P.; Wang, H. Thermoresponsive Amphoteric Metal–Organic Frameworks for Efficient and Reversible Adsorption of Multiple Salts from Water. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1802767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudel, M.B.; Shin, M.; Kim, H.J. Interface engineering of MIL-88 derived MnFe-LDH and MnFe2O3 on three-dimensional carbon nanofibers for the efficient adsorption of Cr(VI), Pb(II), and As(III) ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Deng, S.; Cagnetta, G.; Wang, W.; Meng, P.; Liu, D.; Yu, G. Regeneration of chitosan-based adsorbents used in heavy metal adsorption: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xia, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G.; Cai, W.; Hu, W. Adsorption of cadmium(II) in wastewater by magnesium oxide modified biochar. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104059. [Google Scholar]

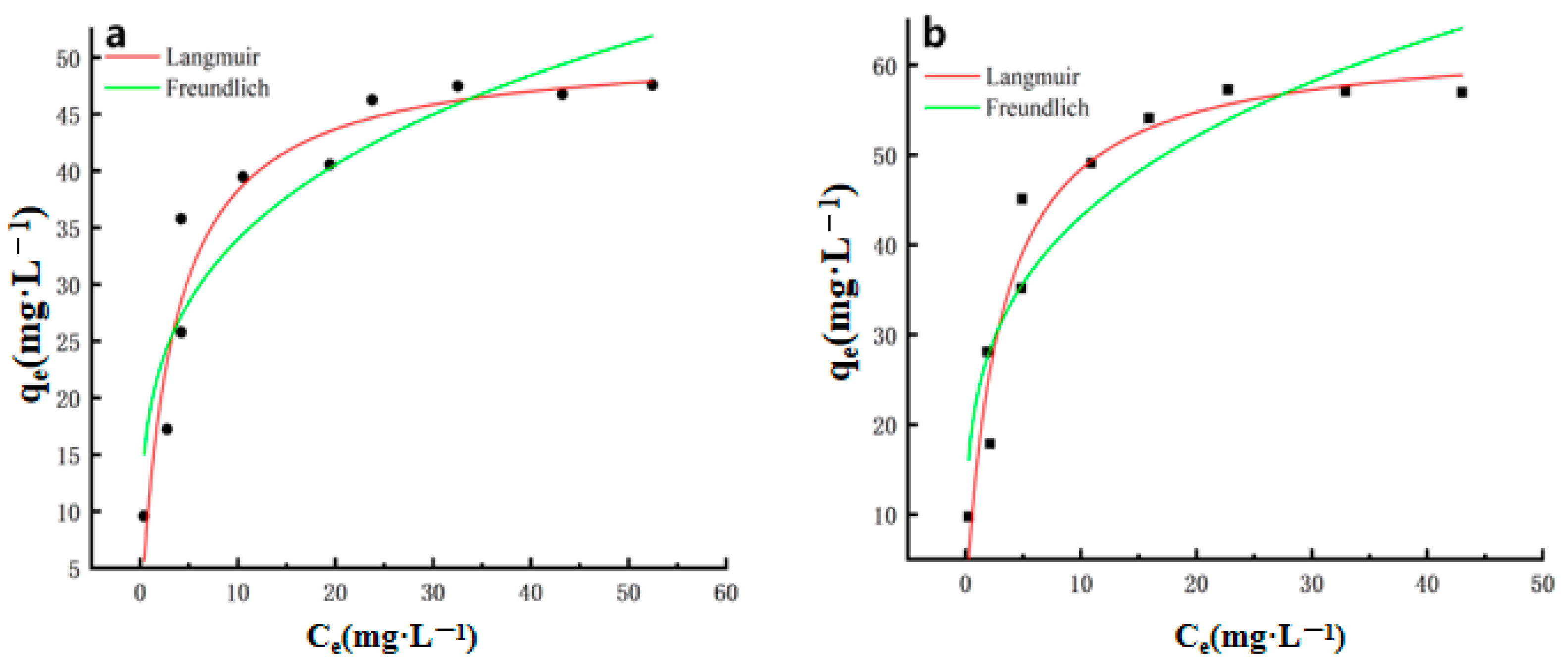

| Adsorbent | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg·g−1) | KL (L·mg−1) | R2 | KF (mg1−n·Ln·g−1) | n | R2 | |
| Cu2+ | 50.89628 | 0.30251 | 0.92517 | 18.85133 | 3.91068 | 0.8653 |
| Pb2+ | 63.00477 | 0.33164 | 0.94099 | 23,0983 | 3.68433 | 0.8688 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Wei, Q.; Tian, C.; Li, D.; Li, H.; Qin, G.; Hu, K.; Zhang, Q. Preparation of Biomass Carbon Composites MgO@ZnO@BC and Its Adsorption and Removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) in Wastewater. Molecules 2023, 28, 6982. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196982
Yang J, Wei Q, Tian C, Li D, Li H, Qin G, Hu K, Zhang Q. Preparation of Biomass Carbon Composites MgO@ZnO@BC and Its Adsorption and Removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) in Wastewater. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6982. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196982
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jie, Qing Wei, Changan Tian, Dong Li, Hongming Li, Guangchao Qin, Kunhong Hu, and Qinyan Zhang. 2023. "Preparation of Biomass Carbon Composites MgO@ZnO@BC and Its Adsorption and Removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) in Wastewater" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6982. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196982
APA StyleYang, J., Wei, Q., Tian, C., Li, D., Li, H., Qin, G., Hu, K., & Zhang, Q. (2023). Preparation of Biomass Carbon Composites MgO@ZnO@BC and Its Adsorption and Removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) in Wastewater. Molecules, 28(19), 6982. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196982




