Removal of Chromium Species by Adsorption: Fundamental Principles, Newly Developed Adsorbents and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cr Removal: The Developed Adsorbents
2.1. Carbon Materials
2.1.1. ACs
2.1.2. CMS
2.1.3. CNTs-Based Composites
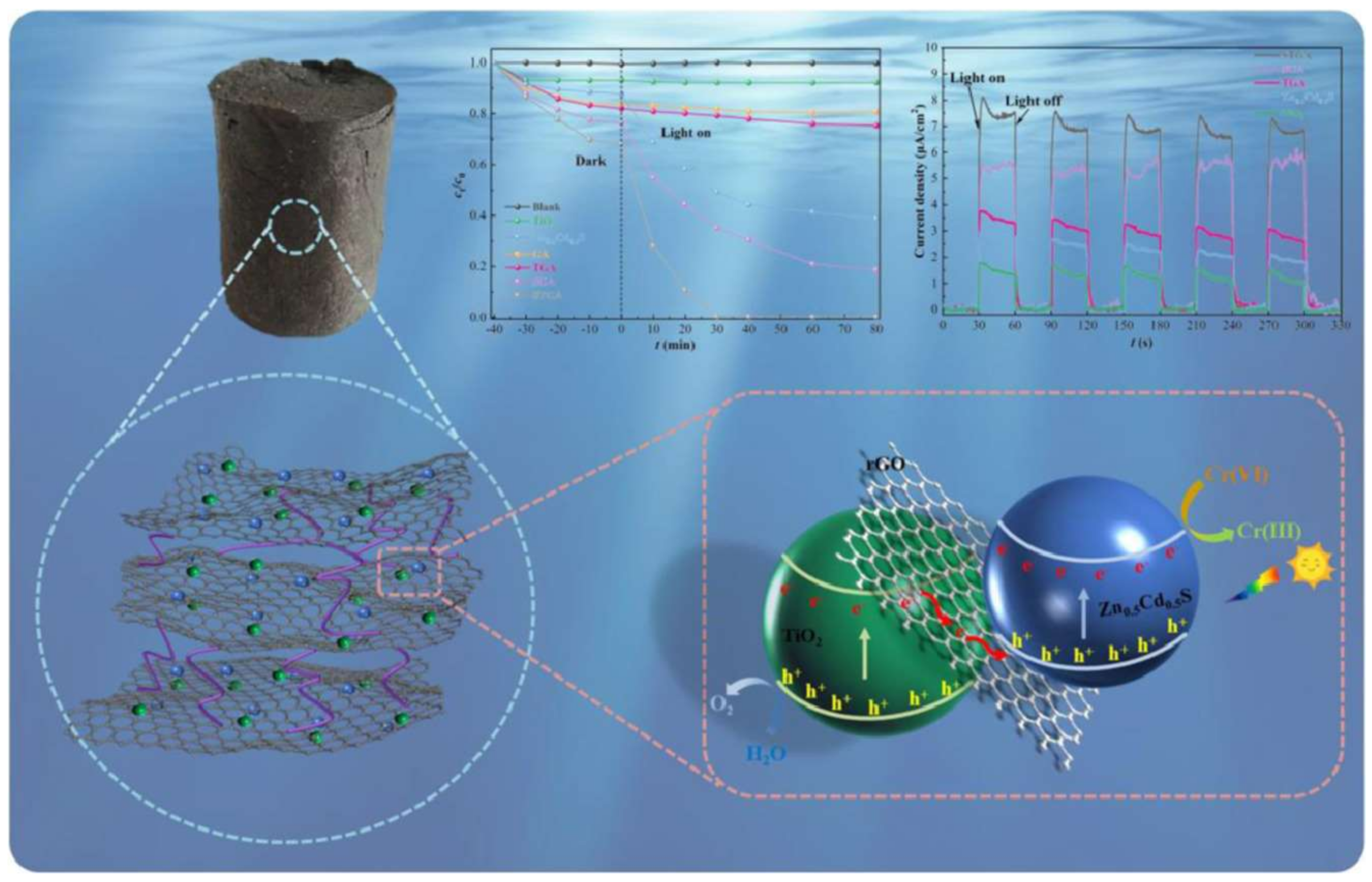
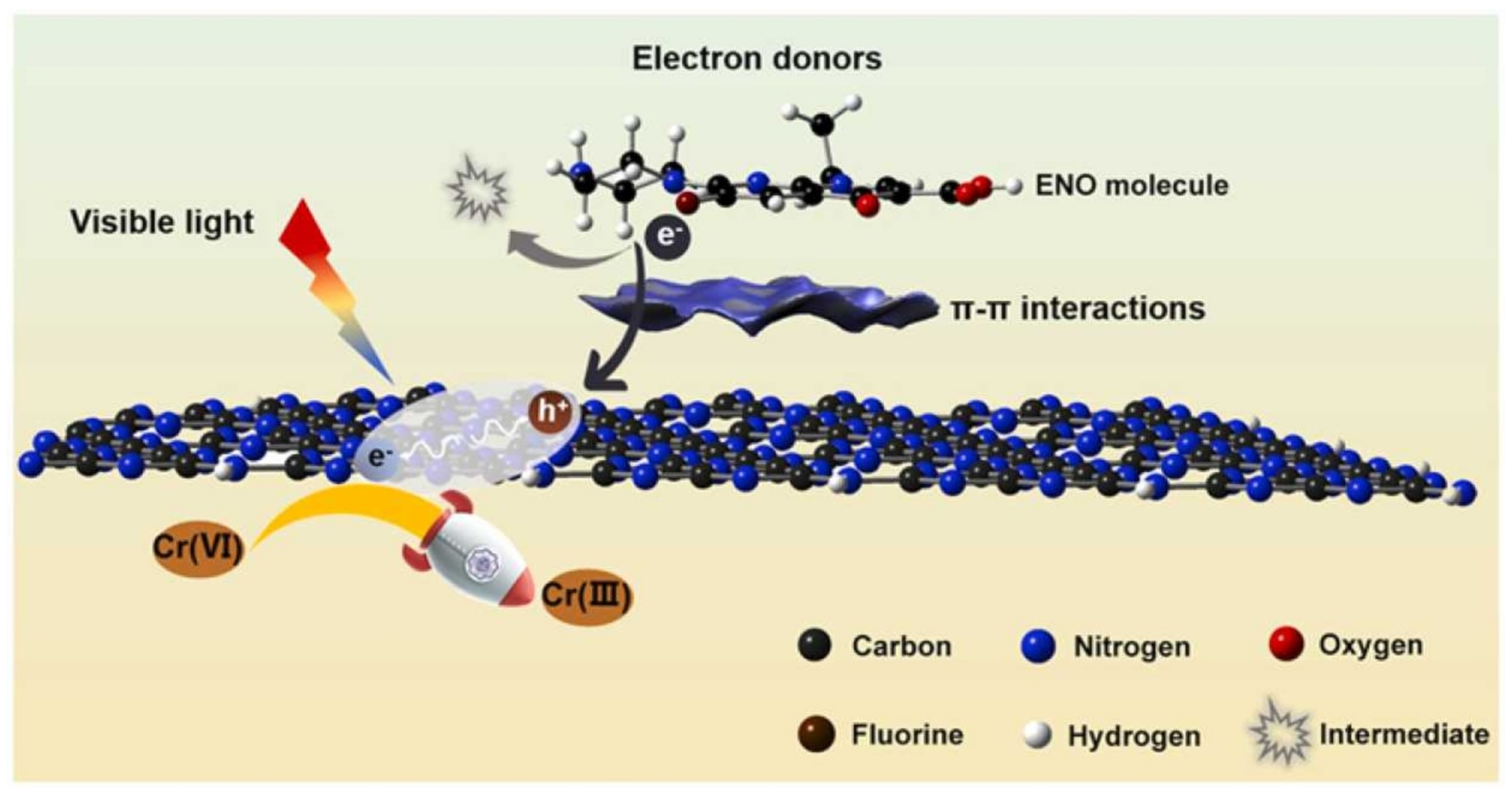
2.1.4. Gr and GO-Based Composites

2.2. Silicon-Based Materials
2.3. Resins
2.4. Iron-Based Adsorbents
2.4.1. Iron Oxyhydroxide (FeOOH) and Its Derivatives
2.4.2. Magnetic Adsorbents
2.5. Polymers
2.6. Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs)
2.7. Titanates
2.8. Reductive Adsorbents
2.9. Montmorillonite
2.10. Biological Adsorbents
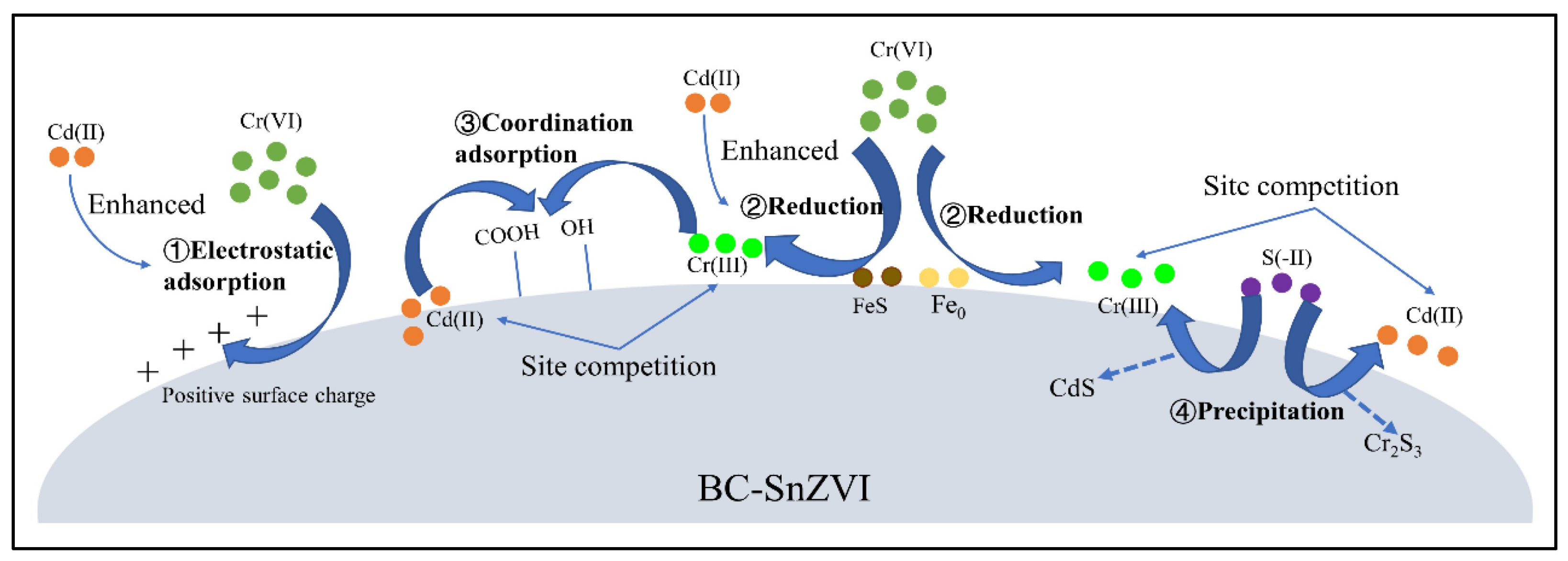
2.11. Three-Dimensional (3D) Nanocomposites
2.12. Hydrogels and Aerogels
2.13. Frameworks
| Cr Species | Type of Adsorbent | Adsorption Conditions | Adsorption Capacities | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr(VI) | FeMnOx/MWCNTs | C0 = 50 mg/L; adsorbent dose: 1 g/L; contact time: 60 min; pH: 2.0 | 47.25 mg/g | [34] |
| Cr(III) | GO@CZ | C0 = 30 mg/L; adsorbent dose: 300 mg/L; contact time: 60 min; pH = 7.0 | 285.71 mg/g | [43] |
| Cr(VI) | Gr-Si-PPy | C0 = 100 mg/L; adsorbent dose: 400 mg/L; T = 25 °C; contact time: 60 min; pH: 2.0 | 429.2 mg/g | [47] |
| Cr(VI) | GO@SiO2@C@Ni-400 | C0 = 20 mg/L; T = 25 °C; adsorbent dose: 0.15 g/L; pH = 3.0 | 299.20 mg/g | [50] |
| Cr(VI) | GO-NiFe LDH | C0 = 20 mg/L; T = 30 °C; contact time: 280 min; adsorbent dose: 80 mg/L | 53.6 mg/g | [51] |
| Cr(VI) | Fe3O4-GO | C0 = 600 mg/L; T = 25 °C; adsorbent dose: 125 mg/L; pH = 6.0 | 280.6 mg/g | [55] |
| Cr(VI) | TSGA | C0 = 50 mg/L; T = 25 °C; adsorbent dose: 800 mg/L; contact time: 40 min; pH = 2.0 | 100% removal | [60] |
| Cr(VI) | APTES-NPSi | C0 = 200 mg/L; T = 25 °C; adsorbent dose: 5 mg; contact time: 180 min; pH = 2.0 | 103.75 mg/g | [64] |
| Cr(VI) | MnFe-LDH/MnFe2O3@3DNF | C0 = 300 mg/L; T = 25 °C; contact time: 120 min; adsorbent dose: 5 mg; pH = 2.0 | 564.88 mg/g | [121] |
| Cr(VI) | 3D porous CoFe2O4@SiO2-NH2 | C0 = 150 mg/L; contact time: 600 min; adsorbent dose: 1 g/L; T = 25 °C; pH = 2.0 | 126.8 mg/g | [138] |
| Cr(VI) | TCMR | C0 = 150 mg/L; contact time: 360 min; adsorbent dose: 2 g/L; T = 25 °C; pH = 5.0 | 27.04 mg/g | [150] |
| Cr(VI) | Rice husk | C0 = 100 mg/L; contact time: 60 min; adsorbent dose: 50 g/L; T = 25 °C; pH = 5.0–6.0 | 30 mg/g | [158] |
| Cr(VI) | BCS and BCW | C0 = 320 mg/L; contact time: 24 h; adsorbent dose: 4 g/L; T = 25 °C; pH = 2.0 | 24.6 mg/g for BCS, 23.6 mg/g for BCW | [159] |
| Cr(VI) | SDBC | C0 = 100 mg/L; contact time: 24 h; adsorbent dose: 1 g/L; T = 25 °C; pH = 5.0 | 688~738 μmol/g | [161] |
| Cr(VI) | ZBC | C0 = 100 mg/L; contact time: 600 min; adsorbent dose: 4 g/L; T = 25 °C; pH = 1.0 | 33.87 mg/g | [175] |
| Cr(VI) | PEI/SA | C0 = 240 mg/L; contact time: 300 min; adsorbent dose: 400 mg/L; T = 25 °C; pH = 2.0 | 678.67 mg/g | [178] |
| Cr(VI) | CGP | C0 = 100 mg/L; contact time: 800 min; adsorbent dose: 2 g/L; T = 25 °C; pH = 2.0 | 386.40 mg/g | [180] |
| Cr(VI) | Fe-BDC | C0 = 50 mg/L; contact time: 60 min; adsorbent dose: 50 mg; T = 25 °C; pH = 5.5 | 100 mg/g | [187] |
| Cr(VI) | (Fe/Co)-BDC | C0 = 50 mg/L; contact time: 60 min; adsorbent dose: 50 mg; T = 20 °C; pH = 5.3 | 588 mg/g | [188] |
| Cr(VI) | Pectin-hydrogel-crosslinked Fe-based MOFs | C0 = 50 mg/L; contact time: 60 min; adsorbent dose: 20 mg; T = 50 °C; pH = 3.0 | 825.97 mg/g | [189] |
| Cr(VI) | Co/Zn-based ZIF | C0 = 15.0 mg/L; contact time: 30 min; adsorbent dose: 33 mg; T = 25 °C; pH = 6.5 | 69.4 mg/g | [191] |
| Cr(VI) | NH2-SBA-15 | C0 = 25.0 mg/L; contact time: 4 h; adsorbent dose: 100 mg; T = 30 °C; pH = 2.0 | Removal efficiency of 88% | [192] |
| Cr(VI) | Ficus carica bast fiber | C0 = 350.0 mg/L; contact time: 210 min; adsorbent dose: 0.5 g; T = 25 °C; pH = 3.0 | 19.68 mg/g | [193] |
| Cr(VI) and Cr(III) | Canadian peat and coconut fiber | C0 = 250.0 mg/L; contact time: 20 h; adsorbent dose: 1.0 g; T = 25 °C; pH = 1.5 | 19.21 mg/g for Cr(III) and 9.54 mg/g for Cr(VI), respectively | [194] |
3. Novel Adsorption Technologies
3.1. Continuous Fluidized Bed Process
3.2. Membrane Technology
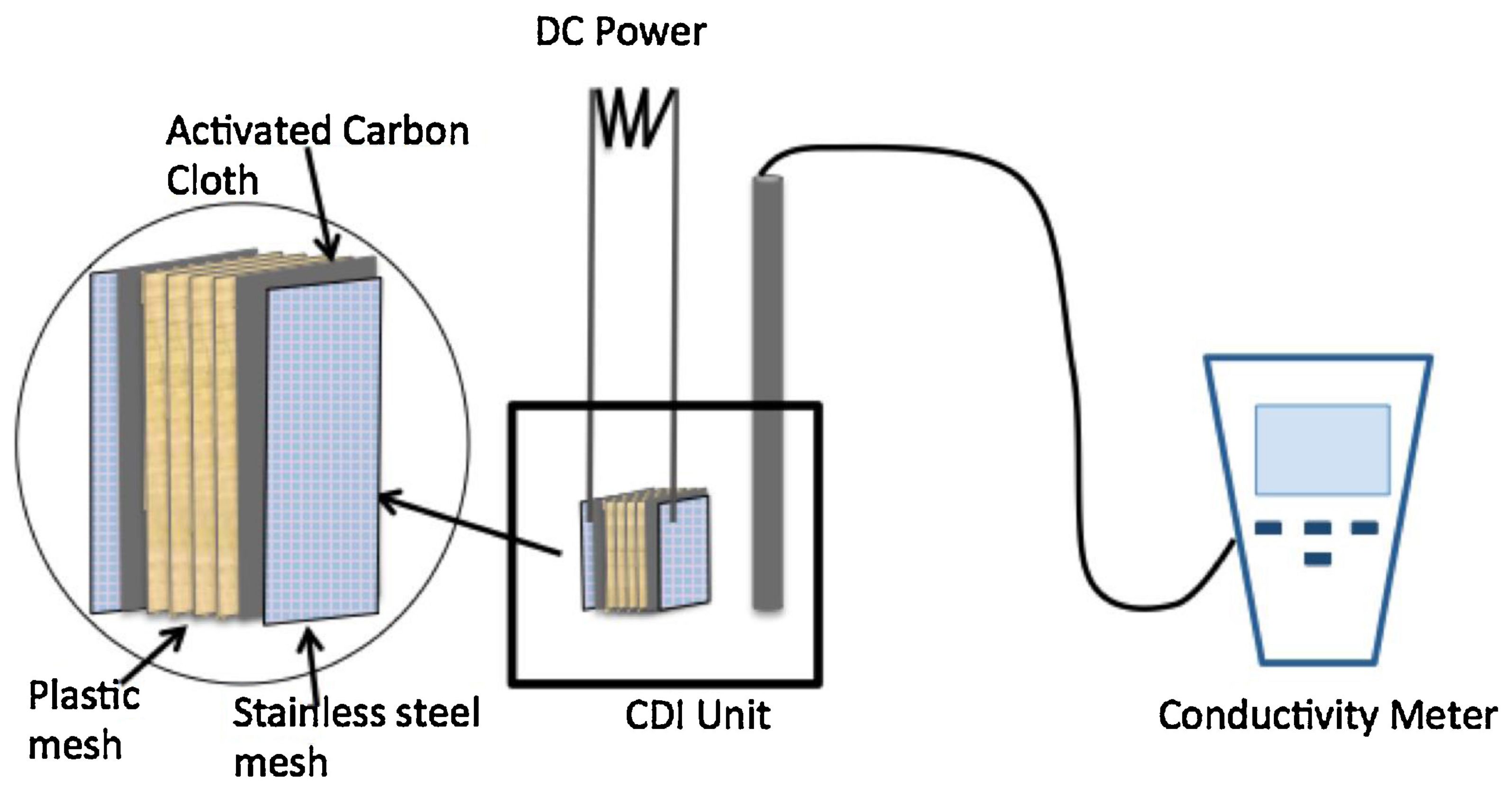
3.3. Capacitive Deionization (CDI)
4. Mechanism Studies
4.1. Adsorbent–Adsorbate Interactions
4.2. Analyses of Adsorption Process
| Type of Cr | Type of Adsorbent | Applicable Kinetic Model | Applicable Isotherm Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr(VI) | MCMs | The pseudo-second-order model | The Langmuir model | [22] |
| Cr(VI) | FeMnOx/MWCNTs | The pseudo-second-order model | The Langmuir model | [34] |
| Cr(VI) | Gr-Si-PPy | The pseudo-second-order model | The Langmuir model | [47] |
| Cr(VI) | nZVI-MSC | The pseudo-first-order model | Not provided | [61] |
| Cr(VI) | nFeOOH@D001 | The pseudo-second-order model | The Langmuir model | [73] |
| Cr(VI) | FeBC | The intra-particle diffusion model | Not provided | [79] |
| Cr(VI) | Fe2(SO4)3@Egeria najas based biochar | The pseudo-second-order model | The Langmuir model | [86] |
| Cr(VI) | PPy-MSFA | The pseudo-second-order model | The Langmuir model | [98] |
| Cr(VI) | SnZVI@EPS | The pseudo-second-order model | Not provided | [107] |
| Cr(VI) | Zn/Al-LDHs | The pseudo-second-order model | The Langmuir model | [116] |
| Cr(VI) | PANI-Mg/Al LDHs | The pseudo-second-order model | The Langmuir model | [118] |
| Cr(VI) | Crayfish shell biochar–Fe composite | The pseudo-second-order model | The Langmuir model | [134] |
| Cr(VI) | EDTA/GO/CS | The pseudo-second-order model | The Freundlich model | [166] |
| Cr(VI) | ZBC | The pseudo-second-order model | The Langmuir model | [175] |
| Cr(VI) | PEI-modified Juncus effuses | The pseudo-second-order model | The Freundlich model | [176] |
| Cr(VI) | Co/Zn based ZIF | Not provided | The Langmuir model | [191] |
| Cr(VI) | PANI/EVOH | The pseudo-second-order model | The Freundlich model | [197] |
| Cr(VI) | Pd@LNP/FP | The pseudo-first-order model | Not provided | [198] |
| Cr(VI) | PEI functionalized magnetic hydrochar | The Elovich model | The Freundlich model | [206] |
| Cr(VI) | CVN | The pseudo-second-order model | The Langmuir model | [208] |
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Zhang, X.H.; Koropchak, J.A. Thermospray methods for rapid, sensitive, and nonchromatographic speciation of chromium oxidation states. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3046–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proctor, D.M.; Thompson, C.M.; Suh, M.; Harris, M.A. A response to “A quantitative assessment of the carcinogenicity of hexavalent chromium by the oral route and its relevance to human exposure”. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.Y.; Lin, X.F.; Yu, H.W.; Li, S.X.; Huang, X.G. Visible-light photoreduction, adsorption, matrix conversion and membrane separation for ultrasensitive chromium determination in natural water by X-ray fluorescence. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 226, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorade, I.B.; Thakur, V.R.; Patil, S.S. Assessment of heavy metal content in sediment of Godavari River basin. Eur. Acad. Res. 2014, 2, 3560–3584. [Google Scholar]
- An, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. Heavy metals and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of the Yangtze river estuary, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Huang, X.; Gong, J.; Ma, L.; Qian, J. Influence of aquifer heterogeneity on Cr(VI) diffusion and removal from groundwater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 3918–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Ji, M. Cr (VI) removal by a new type of anion exchange resin DEX-Cr: Adsorption affecting factors, isotherms, kinetics, and desorption regeneration. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusku, O.; Rivas, B.L.; Urbano, B.F.; Arda, M.; Kabay, N.; Bryjak, M. A comparative study of removal of Cr(VI) by ion exchange resins bearing quaternary ammonium groups. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhu, B.; Xu, H.; Zhu, L. Tertiary amine block copolymer containing ultrafiltration membrane with pH-dependent macromolecule sieving and Cr(VI) removal properties. Desalination 2015, 355, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alothman, Z.A.; Naushad, M.; Ali, R. Kinetic, equilibrium isotherm and thermodynamic studies of Cr(VI) adsorption onto low-cost adsorbent developed from peanut shell activated with phosphoric acid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 3351–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Ali, I.; Saleh, T.A.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Agarwal, S. Chromium removal from water by activated carbon developed from waste rubber tires. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangabhashiyam, S.; Suganya, E.; Selvaraju, N. Packed bed column investigation on hexavalent chromium adsorption activated carbon prepared from Swietenia Mahogani fruit shells. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 13048–13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, Y.; Namrata, G.; Ramgopal, U. Ni(II) adsorption characteristics of commercial activated carbon from synthetic electroless plating solutions. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 13807–13817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.L.; Xu, L.; Kano, N.; Imaizumi, H. Adsorption of heavy metal onto activated carbon modified with potassium permanganate. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2014, 47, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, A.; Redzwan, G.; Sahu, J.N.; Mukherjee, S.; Sen Gupta, B.; Hashim, M.A. Hexavalent chromium adsorption by a novel activated carbon prepared by microwave activation. Bioresources 2014, 9, 1498–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boustila, H.; Boutillara, Y.; Velasco, L.F.; Djellali, A.; Tazibet, S. Tailoring activated carbon properties for Pb(II) and Cr(VI) removal from water in continuous mode. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2022, 45, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.Z.; Li, X.M. Enhance Cr(VI) removal by quaternary amine-anchoring activated carbons. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 58, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qian, Y.; Ma, J.; Mao, M.; Qian, L.; An, D. New insights into the cooperative adsorption behavior of Cr(VI) and humic acid in water by powdered activated carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 153081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyan, S.M.; Prabhu, S.V.; Ambio, T.A.; Gomadurai, C. A statistical modeling and optimization for Cr(VI) adsorption from aqueous media via teff straw-based activated carbon: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 7998069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, B.; Chen, H.; Xue, S.; Deng, J.; Tao, H. Ultrafast and efficient removal of aqueous Cr(VI) using iron oxide nanoparticles supported on Bermuda grass-based activated carbon. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseh, N.; Khosravi, R.; Rumman, G.A.; Ghadirian, M.; Eslami, H.; Khoshnamvand, M.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Khosravi, A. Adsorption of Cr(VI) ions onto powdered activated carbon synthesized from Peganum harmala seeds by ultrasonic waves activation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.G.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, J.T.; Qiao, W.M.; Long, D.H.; Ling, L.C. Effective removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by adsorption on mesoporous carbon microspheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 462, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Cai, J.; Aikelaimu, A.; Li, Y. Removal of Cr (III) from aqueous solutions by carbon lignin-based composite. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Fu, F.; Zhang, L.; Tang, B. Insight into efficient co-removal of Se(IV) and Cr(VI) by magnetic mesoporous carbon microspheres: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, F.; Tang, B. Adsorption and redox conversion behaviors of Cr(VI) on goethite/carbon microspheres and akaganeite/carbon microspheres composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xing, J.; Xu, P.; Chang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Usman, K.M. Activated carbon microsphere from sodium lignosulfonate for Cr(VI) adsorption evaluation in wastewater treatment. Polymers 2020, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, A.P.; Bergmann, C.P.; Fagan, S.B. Carbon nanotubes functionalized with titanium complexes for hexavalent chromium adsorption: An ab initio approach. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2017, 1113, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.J.; Chen, C. Adsorption of chlorophenols from aqueous solutions by pristine and surface functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 43, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Song, K.; Luo, W.; Yang, J. Adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) by hydroxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes: Effects of humic acid and surfactants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12746–12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Jing, Z.; Duan, Y.; Li, J. Ultrafast removal of Cr(VI) ions using polyamine modified carbon nanotubes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 133, 104265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.H.; Chai, L.Y.; Li, Q.Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Mohammad, A. Preparation and characterization of magnetic Fe3O4/CNT nanoparticles by RPO method to enhance the efficient removal of Cr(VI). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7175–7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.M.A.; Den, W.; Kuo, H.-W. Elucidating the mass transfer mechanism of Cr-VI adsorption by encapsulated chitosan-carbon nanotubes-iron beads in packed-bed columns. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, N.; Wu, H.; Li, W.; Fang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Qian, X. Flexible design of carbon nanotubes grown on carbon nanofibers by PECVD Chock for enhanced Cr(VI) adsorption capacity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 207, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Wu, Y.; Liu, N.; Yan, C. Adsorption behavior of Cr(VI) and As(III) on multiwall carbon nanotubes modified by iron-manganese binary oxide (FeMnOx/MWCNTs) from aqueous solution. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, Z.; Farrokhnia, A.; Lemraski, E.G.; Moafi, Z.; Sabzezari, M. Performance evaluation of nanocomposite magnetic mono-tosyl-b-cyclodextrin conjugated carbon nanotubes-iron oxide in removal of Cr(III) from aqueous solutions using Taguchi method. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2022, 96, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A. Preparation and characterization of chitin/magnetite/multiwalled carbon nanotubes magnetic nanocomposite for toxic hexavalent chromium removal from solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 233, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Fan, J.; Jiang, J.H.; Wang, J.J. pH/temperature dependent selective removal of trace Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by imidazolium ionic liquid functionalized magnetic carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 47165–47173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Fatema Tuj, Z.; Mahdi, M.M.; Mahmudunnabi, D.M.; Choudhury, T.R.; Alam, M.Z.; Nurnabi, M. Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide for removal of Cr(III) from tannery effluent. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 244, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Cao, Z.-F.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Yu, J.-G. Graphene oxide-Bicine composite as a novel adsorbent for removal of various contaminants from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, K.; Hardian, R.; Kumar, V.; Viswanatha, R.; Kumar, S.; Singh, A.; Santosh, M.; Szekely, G. Composite nanofiltration membrane comprising one-dimensional erdite, two-dimensional reduced graphene oxide, and silkworm pupae binder. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 22, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Naik, T.S.S.K.; Anil, A.G.; Khasnabis, S.; Nath, B.; Basavaraju, U.; Kumar, V.; Garg, V.K.; Subramanian, S.; Singh, J.; et al. A novel CaO nanocomposite cross linked graphene oxide for Cr(VI) removal and sensing from wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Anil, A.G.; Khasnabis, S.; Kumar, V.; Nath, B.; Adiga, V.; Naik, T.S.S.K.; Subramanian, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, J.; et al. Sustainable removal of Cr(VI) using graphene oxide-zinc oxide nanohybrid: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamics. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Kumar, D. Adsorption of Cr(III) and Cu(II) on hydrothermally synthesized graphene oxide-calcium-zinc nanocomposite. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 4560–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.J.; Chen, F.N.; Wei, J.Z.; Zhang, F.M.; Pang, S.Y. Preparation of magnetic triethylene tetramine-graphene oxide ternary nanocomposite and application for Cr (VI) removal. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 66, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, W.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Ma, H.; Jiang, G. Zero-valent iron nanoparticles embedded into reduced graphene oxide-alginate beads for efficient chromium (VI) removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 506, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Xu, X.; Kan, Y.; Zhao, P. Magnetic graphene oxide functionalized by poly dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride for efficient removal of Cr(VI). J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 91, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Jiang, X.; Luo, H.; Geng, J. Synthesis of graphene/SiO2@polypyrrole nanocomposites and their application for Cr(VI) removal in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Fan, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y. Highly efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water based on graphene oxide incorporated flower-like MoS2 nanocomposite prepared in situ hydrothermal synthesis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 13882–13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Si, C.; Gao, H. The adsorption performance of MoS2 nano-rod by combined with graphene oxide for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. Mater. Sci.-Medzg. 2022, 28, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Song, G.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, K.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Chen, C. Construction of novel graphene-based materials GO@SiO2@C@Ni for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 557, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, B.; You, W.; Yu, J.; Ho, W. 3D hierarchical graphene oxide-NiFe LDH composite with enhanced adsorption affinity to Congo red, methyl orange and Cr(VI) ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Qin, X.; Wang, K.; Peng, Y.; Wang, P.; Jiang, G. Nanoscale zero valent iron supported on MgAl-LDH-decorated reduced graphene oxide: Enhanced performance in Cr(VI) removal, mechanism and regeneration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Dong, J.; Chi, Z.; Huang, H. Reduced graphene oxide-nano zero value iron (rGO-nZVI) micro-electrolysis accelerating Cr(VI) removal in aquifer. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 73, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-P.; Lv, Y.-T.; Guan, J.-F.; Khoso, F.M.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Chen, J.; Li, W.-J.; Yu, J.-G. Rational design of three-dimensional graphene/graphene oxide-based architectures for the efficient adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 343, 117709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, J.; Cao, B.; Liu, X.; Lin, Z.; Yang, C.; Wu, R.; Su, X.; Wang, X. Facile synthesis of recycling Fe3O4/graphene adsorbents with potassium humate for Cr(VI) removal. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 560, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, N.; Lande, A.; Abu-Danso, E.; Iqbal, J.; Bhatnagar, A. A comparative study of magnetic chitosan (Chi@Fe3O4) and graphene oxide modified magnetic chitosan (Chi@Fe3O4GO) nanocomposites for efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; He, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Song, Z. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide/chitosan composite aerogel with high adsorption performance for Cr(VI) by a new crosslinking route. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Yang, W.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y. Amino-assisted AHMT anchored on graphene oxide as high performance adsorbent for efficient removal of Cr(VI) and Hg(II) from aqueous solutions under wide pH range. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y. Highly efficient and ultrafast removal of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution to ppb level by poly(allylamine hydrochloride) covalently cross-linked amino-modified graphene oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, R.; Xu, K.; Luo, H. Efficient removal of Cr(VI) by a 3D Z-scheme TiO2-ZnxCd1-xS graphene aerogel via synergy of adsorption and photocatalysis under visible light. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.M. Zero-valent iron particles embedded on the mesoporous silica-carbon for chromium (VI) removal from aqueous solution. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2016, 18, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qian, L.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Han, L.; Shang, X.; Li, J.; Gu, M.; Chen, M. Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported by attapulgite produced at different acid modification: Synthesis mechanism and the role of silicon on Cr(VI) removal. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Shang, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Su, A.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Han, L.; Yan, J.; Chen, M. Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) by silicon rich biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Ma, W.; Li, Y.; He, Z.; Hu, H. Effective removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution based on APTES modified nanoporous silicon prepared from kerf loss silicon waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 10899–10909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, A.; Taki, A.; Asamoto, H.; Minamisawa, H.; Yamada, K. Kinetic, isotherm, and equilibrium investigation of Cr(VI) Ion adsorption on amine-functionalized porous silica beads. Polymers 2022, 14, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.; Peng, S.; Zhou, C. Synthesis of calcium silicate hydrate from coal gangue for Cr(VI) and Cu(II) removal from aqueous solution. Molecules 2021, 26, 6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bian, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, Z. Chelation resin efficient removal of Cu(II), Cr(III), Ni(II) in electroplating wastewater. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2018, 26, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Yue, Q.; Kan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, B. Research on adsorption of Cr(VI) by Poly-epichlorohydrin-dimethylamine (EPIDMA) modified weakly basic anion exchange resin D301. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, R.; Er, E.; Delibas, A. Synthesis of novel resin containing carbamothiolylimidamide group and application for Cr(VI) removal. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 963–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Yin, X.; Chen, L.; He, X.; Lin, Z.; Liu, C.; Ning, S.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y. An integrated process for removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from electroplating wastewater by ion exchange and reduction-precipitation based on a silica-supported pyridine resin. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yue, Q.; Zhang, P.; Kong, W.; Jin, B.; Xu, X.; Gao, B. Co-monomer polymer anion exchange resin for removing Cr(VI) contaminants: Adsorption kinetics, mechanism and performance. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, Z.; Shao, S.; Jiao, W.; Liu, Y. High-gravity intensified preparation of D201 resin-hydrated iron oxide nanocomposites for Cr(VI) removal. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yin, W.; Bu, H.; Zeng, W.; Li, P.; Zheng, X.; Chiang, P.; Wu, J. A facile modification of cation exchange resin by nano-sized goethite for enhanced Cr(VI) removal from water. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Zhong, D.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, N. A novel sulfide-modified nanoscale zero valent iron supported on porous anion exchange resin composite for Cr(VI) effective removal from waste. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 794, 139494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toli, A.; Mystrioti, C.; Xenidis, A.; Papassiopi, N. Continuous Flow Process for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solutions using resin supported zero-valent iron. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhong, D.; Xu, Y.; Luo, H.; Zeng, S. Nano zero-valent iron supported by macroporous styrene ion exchange resin for enhanced Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2022, 43, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, H.T.; Pehlivan, E. Evaluation of anion-exchange resins on the removal of Cr(VI) polluted water: Batch ion-exchange modeling. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Maji, P.K.; Sarkar, S. Detailed investigation of effective trace Cr(VI) removal mechanism by anion exchange resin with phenol-formaldehyde matrix. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 111, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Dai, M.; Hou, X.; Peng, C. Active biochar-supported iron oxides for Cr(VI) removal from groundwater: Kinetics, stability and the key role of FeO in electron-transfer mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Li, R.; Shen, N.; Li, J.; Shen, J.; Sun, X.; Han, W. Enhanced sequestration of chelated Cr(III) from aqueous by Al-containing ferrihydrite: New expectation of overall removal of various heavy metal complexes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wei, X.; Yin, H.; Zhu, M.; Luo, H.; Dang, Z. Synergistic removal of Cr(VI) by S-nZVI and organic acids: The enhanced electron selectivity and pH-dependent promotion mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Xie, T.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Su, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized ferrous sulfide@extracellular polymeric substance for Cr(VI) removal: Characterization, performance, and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.J.; Lu, J.W.; Ding, Z.C.; Li, N.; Fu, F.L.; Tang, B. Cr(VI) removal by mesoporous FeOOH polymorphs: Performance and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 82118–82130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Fu, F.L.; Cheng, Z.H.; Tang, B. Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by FeOOH supported on Amberlite IR120 resin. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 17767–17773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Fu, F.; Yu, P.; Sun, G. Properties and mechanism of Cr(VI) adsorption and reduction by K2FeO4 in presence of Mn(II). Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Ning, P. Adsorption properties and mechanism of Cr(VI) by Fe2(SO4)3 modified biochar derived from Egeria najas. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 645, 128938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.Y.; He, P.; Niu, W.L.; Wu, Y.J.; Ai, L.H.; Gou, X.L. Synthesis of a-Fe2O3 nanofibers for applications in removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, I.; Alvarez, J.A.; Villar, P.; Pascual, A.; Herrero, L. Foundry sands as low-cost adsorbent material for Cr (VI) removal. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, K.; Anantharaman, N. Removal of chromium(VI) ions from aqueous solutions and industrial effluents using magnetic Fe3O4 nano-particles. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2009, 27, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Deng, Q.; Wang, H.M.; Kang, S.H.; Yang, Y.; Ng, D.H.L.; Cai, W.P.; Wang, G.Z. Synthesis and characterization of nanostructured Fe3O4 micron-spheres and their application in removing toxic Cr ions from polluted water. Chem. A Eur. J. 2012, 18, 13418–13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhou, S.M.; Lou, S.Y.; Yuan, L.; Gao, T.; Wu, X.P.; Shi, X.J.; Wang, K. Synthesis of high saturation magnetization superparamagnetic Fe3O4 hollow microspheres for swift chromium removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4913–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Shen, H.Y.; Li, Q.; Xia, Q.H. Adsorption studies on Cr(VI) in wastewater by NH2-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 magnetic composites. Acta Chim. Sin. 2009, 67, 1509–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Shen, H.Y.; Pan, S.D.; Hu, M.Q. Synthesis, characterization and properties of ethylenediamine-functionalized Fe3O4 magnetic polymers for removal of Cr(VI) in wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Li, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, S. Rubra-like MnFe2O4 Microsphere: A high efficiency microwave reduction catalyst for Cr(VI) removal from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.X.; Hu, P.Z.; Jiang, M.Y.; Huang, X.L.; Shen, T.; Ge, W.W.; Pan, S.D.; Shen, H.Y. Adsorption mechanism investigation of tetraethylenepentamine-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 magnetic polymers in Cu(II), Cr(VI) co-existing water system. Acta Chim. Sin. 2011, 69, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Shen, H.Y.; Pan, S.D.; Hu, M.Q.; Xia, Q.H. Preparation and characterization of amino-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 magnetic polymer adsorbents for removal of chromium(VI) ions. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5291–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Qiu, G.M.; Cao, H.Y.; Jin, R.F. Removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions using Fe3O4 magnetic polymer microspheres functionalized with amino groups. Materials 2015, 8, 8378–8391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.; Yan, C.J.; Luo, W.J. Polypyrrole coated secondary fly ash-iron composites: Novel floatable magnetic adsorbents for the removal of chromium (VI) from wastewater. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasinszki, T.; Krebsz, M.; Kotai, L.; Sajo, I.E.; Homonnay, Z.; Kuzmann, E.; Kiss, L.F.; Vaczi, T.; Kovacs, I. Nanofurry magnetic carbon microspheres for separation processes and catalysis: Synthesis, phase composition, and properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 7353–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Xu, X.; Ren, Z.F.; Gao, B.Y. Removal of phosphate and chromium(VI) from liquids by an amine-crosslinked nano-Fe3O4 biosorbent derived from corn straw. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 47237–47248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.T.; Yang, L.R.; Dong, T.T.; Liu, Z.N.; Liu, H.Z. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using amino-modified Fe3O4-SiO2-chitosan magnetic microspheres with high acid resistance and adsorption capacity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, H.; Irani, M.; Hosseini, L.; Rahimi, A.; Aliabadi, M. Removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions using chitosan/MWCNT/Fe3O4 composite nanofibers-batch and column studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.C.; Tang, Q.Z.; Dong, S.Y.; Chai, L.Y.; Wang, H.Y. Single-step synthesis of magnetic chitosan composites and application for chromate (Cr(VI)) removal. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewska, M.; Chibowski, S.; Urban, T. Synthetic polyacrylamide as a potential flocculent to remove commercial chromium(III) oxide from aqueous suspension. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.K.; Wang, Y.M.; Wu, N.M.; Chen, Q.C.; Wu, K. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by a novel HEA/AMPS copolymer hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1511–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, X.; Yi, Y.; Ma, J.; Ning, P. Formulation of NZVI-supported lactic acid/PAN membrane with glutathione for enhanced dynamic Cr(VI) removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xie, T.; Liu, H.; Su, Z.; Huanga, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Li, X. Covering extracellular polymeric substances to enhance the reactivity of sulfidated nanoscale zerovalent iron toward Cr(VI) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 448, 137610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Muhammad, H.; Laipan, M.; Fan, X.; Guo, J.; Li, Y. Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) and Mo(VI) from polluted water using L-cysteine doped polypyrrole/bentonite composite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 217, 106387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, D. Selective removal of Cr(III) from aqueous solution using cross-linked polyethylenimine: Experimental optimization and modeling. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, B.F.; Mahdavi, H.; Rad, M.F.; Baghdadi, M. Using design-expert to optimize the properties of a polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane through the incorporation of NH2-MIL-53(Fe) and PVP for maximum Cr(VI) removal and flux. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 3875–3889. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, J.; Yang, Q.; Gong, W.; Li, M.; Cao, B. Simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and phenol from water using silica-di-block polymer hybrids: Adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics. Polymers 2022, 14, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z. Efficient removal of Cr (VI) by magnetic and recyclable calcined CoFe-LDH/g-C3N4 via the synergy of adsorption and photocatalysis under visible light. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, B.; Ho, W. Hierarchical porous Ni/Co-LDH hollow dodecahedron with excellent adsorption property for Congo red and Cr(VI) ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, F.; Ma, J. Adsorption behavior of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) on aged microplastics in antibiotics-heavy metals coexisting system. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Li, A. Green strategy with high iron utilization for Cr(VI) removal via sodium polyacrylate-based hydrogel. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.D.; Zhao, Y.P.; Li, S.F.; Fan, X.; Wei, X.Y.; Zong, Z.M. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by calcined Zn/Al-LDHs. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.J.; Zhu, X.P.; Lan, L.M.; Zuo, H.B. Removal of chromium from laboratory wastewater using preparation-adsorption technology with a Mg/Al/Cr layered compound. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85595–85602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.R.; Gao, Y.; Tan, X.L.; Chen, C.L. Polyaniline-modified Mg/Al layered double hydroxide composites and their application in efficient removal of Cr(VI). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4361–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Du, T.; Yue, T.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J. Demand-oriented construction of Mo3S13-LDH: A versatile scavenger for highly selective and efficient removal of toxic Ag(I), Hg(II), As(III), and Cr(VI) from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, P. CuBi2O4/calcined ZnAlBi-LDHs heterojunction: Simultaneous removal of Cr (VI) and tetracycline through effective adsorption and photocatalytic redox. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.B.; Shin, M.; Kim, H.J. Interface engineering of MIL-88 derived MnFe-LDH and MnFe2O3 on three-dimensional carbon nanofibers for the efficient adsorption of Cr(VI), Pb(II), and As(III) ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manea, Y.K.; Khan, A.M.; Wani, A.A.; Saleh, M.A.S.; Qashqoosh, M.T.A.; Shahadat, M.; Rezakazemi, M. In-grown flower like Al-Li/Th-LDH@CNT nanocomposite for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of MG dye and selective adsorption of Cr (VI). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xiong, C.; Ying, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Ding, J.; Lu, J. Facile synthesis of a MOF-derived magnetic CoAl-LDH@chitosan composite for Pb (II) and Cr (VI) adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 449, 137722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gong, Z.; Zhuo, Z.; Zhong, X.; Zhou, M.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Tunning the defects in lignin-derived-carbon and trimetallic layered double hydroxides composites (LDH@LDC) for efficient removal of U(VI) and Cr (VI) in aquatic environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 132113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, T.; Huang, T.; Sun, W.; Qiao, S.; Liu, W. Insights into interactions of Cr(III) and organic matters during adsorption onto titanate nanotubes: Differential absorbance and DFT study. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Fan, Q.H.; Tan, X.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, C.L.; Xu, A.W.; Wang, X.K. A core-shell structure of polyaniline coated protonic titanate nanobelt composites for both Cr(VI) and humic acid removal. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Huang, X.; Luo, Y.; Yuan, H.; Ren, T.; Li, X.; Xu, D.; Guo, X.; Wu, Y. Fluorescent chitosan-based hydrogel incorporating titanate and cellulose nanofibers modified with carbon dots for adsorption and detection of Cr(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, Z.; Han, J.; Wei, Z.; Yang, L.; Lu, M.; Ma, T.; Yang, L. An all-in-one photocatalyst: Photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) and anchored adsorption of Cr(III) over mesoporous titanium@sulfonated carbon hollow hemispheres. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Liu, J. The simultaneous reduction and adsorption for V(V) and Cr(VI) anionic species in aqueous solution by polyethyleneimine cross-linked titanate nanotubes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 299, 121682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Shi, C. Creation of oxygen vacancies to activate lanthanum-doped bismuth titanate nanosheets for efficient synchronous photocatalytic removal of Cr(VI) and methyl orange. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 314, 113613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Chai, S.; Zhang, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, X. Facile integration of FeS and titanate nanotubes for efficient removal of total Cr from aqueous solution: Synergy in simultaneous reduction of Cr(VI) and adsorption of Cr(III). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122834. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.T.; Ge, W.Z.; Nie, Y.X.; Wang, Y.X.; Zeng, F.G.; Qiao, Y. Highly efficient detoxification of Cr(VI) by brown coal and kerogen: Process and structure studies. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 150, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.T.; Ge, W.Z.; Yue, F.; Wang, Y.X.; Pedersen, C.M.; Zeng, F.G.; Qiao, Y. Mechanism study of Cr(III) immobilization in the process of Cr(VI) removal by Huolinhe lignite. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 152, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Dong, F.-X.; Li, Y.; Guo, P.-R.; Kong, L.-J.; Chu, W.; Diao, Z.-H. Synchronous removal of Cr(VI) and phosphates by a novel crayfish shell biochar-Fe composite from aqueous solution: Reactivity and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.L.; Gao, X.; Wu, C.N.; Xie, R.; Feng, S.J.; Chen, C.L. Facile preparation of amino functionalized graphene oxide decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the adsorption of Cr(VI). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 384, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Jia, Y. Removal combined with reduction of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by Fe-ethylene glycol complex microspheres. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.L.; Ding, Q.Q.; Zhou, H.J.; Zhao, Z.F.; Liu, G.; Wang, G.Z. An adsorption-reduction synergistic effect of mesoporous Fe/SiO2-NH2 hollow spheres for the removal of Cr(VI) ions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 27039–27046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Ge, X.; Wang, X. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal by hierarchical CoFe2O4@SiO2-NH2 via reduction and adsorption processes. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 13686–13692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, B.; Ren, H.; Chen, S.; Luo, C.; Li, Q.; Yang, W.; Yan, K. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous systems using Fe-P slag as a reducing agent. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 211, 105875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, H. Industrial lignins: The potential for efficient removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 10467–10481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Gao, X.; Che, H.; Wang, P.; Ao, Y. In-depth insight into the mechanism on photocatalytic synergistic removal of antibiotics and Cr (VI): The decisive effect of antibiotic molecular structure. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 313, 121443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Xu, B.; Yang, P. Rhombic TiO2 grown on g-C3N4 nanosheets towards fast charge transfer and enhanced Cr(VI) and NO removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 111, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eladlani, N.; Dahmane, E.M.; Ablouh, E.-H.; Ouahrouch, A.; Rhazi, M.; Taourirte, M.; Neffa, M. “Chitosan/montmorillonite” nanocomposites: Adsorption of Cr(III). J. Water Chem. Technol. 2019, 41, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.F.; Hua, Y.Y.; Su, X.; Komarneni, S.; Ma, S.J.; Wang, Y.J. Cr(VI) adsorption by montmorillonite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 124, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Chen, N.; Yu, Y.; Feng, C.P.; Ning, Q.; Hu, W.W. Chromium(VI) removal from aqueous solution using a new synthesized adsorbent. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 4537–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.S.; Rong, H.W.; Zeng, G.M. New trends in removing heavy metals from wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6509–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fiol, N.; Villaescusa, I.; Poch, J. New approach in modeling Cr(VI) sorption onto biomass from metal binary mixtures solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Cepoi, L.; Chiriac, T.; Culicov, O.A.; Frontasyeva, M.; Pavlov, S.; Kirkesali, E.; Akshintsev, A.; Rodlovskaya, E. Spirulina platensis as biosorbent of chromium and nickel from industrial effluents. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 11103–11110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, M.; Dastidar, M.G. Biosorption of Cr (VI) by resting cells of fusarium solani. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2011, 8, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Duan, X.; Tie, J. One-pot synthesis of a magnetic Zn/iron-based sludge/biochar composite for aqueous Cr(VI) adsorption. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, M.; Rawat, A.P.; Giri, K.; Rai, J.P.N. Cr(VI) sorption by free and immobilised chromate-reducing bacterial cells in PVA-alginate matrix: Equilibrium isotherms and kinetic studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5198–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Bankar, A.; Kumar, A.R.; Gosavi, S.; Zinjarde, S. Removal of hexavalent chromium ions by Yarrowia lipolytica cells modified with phyto-inspired Fe0/Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 146, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, S.H.; Onal, S.; Ozdemir, G. Biosorption of chromium, cadmium, and cobalt from aqueous solution by immobilized living cells of chryseomonas luteola TEM 05. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2009, 39, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joutey, N.T.; Bahafid, W.; Sayel, H.; Ananou, S.; El Ghachtouli, N. Hexavalent chromium removal by a novel Serratia proteamaculans isolated from the bank of Sebou River (Morocco). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 3060–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco-Reigosa, N.; Pena-Rodriguez, S.; Novoa-Munoz, J.C.; Arias-Estevez, M.; Fernandez-Sanjurjo, M.J.; Alvarez-Rodriguez, E.; Nunez-Delgado, A. Arsenic, chromium and mercury removal using mussel shell ash or a sludge/ashes waste mixture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2670–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kothiyal, N.C. Use of activated dry flowers (ADF) of Alstonia Scholaris for chromium (Vl) removal: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8986–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D.; Vankar, P.S. Efficient biosorption of chromium(VI) ion by dry Araucaria leaves. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2321–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhanardakani, S.; Parvizimosaed, H.; Olyaie, E. Heavy metals removal from wastewaters using organic solid waste-rice husk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5265–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytak, A.; Oleszczuk, P.; Dobrowolski, R. Sorption and desorption of Cr(VI) ions from water by biochars in different environmental conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5985–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Sun, H.W. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution by UV-mutant Bacillus subtilis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7450–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.S.; Wang, H.; Fang, S.E.; Zhang, W.H.; Qiu, R.L. Pb(II), Cr(VI) and atrazine sorption behavior on sludge-derived biochar: Role of humic acids. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 16031–16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Xiu, Y.F.; Zhu, H.M. Selective removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by adsorption on mangosteen peel. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5930–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, S.; Finfrock, Y.Z.; Ye, Z.; Feng, Y.; Li, X. Iron-modified biochar-based bilayer permeable reactive barrier for Cr(VI) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Xu, Z.; You, S.; Komarek, M.; Alessi, D.S.; Yuan, X.; Palansooriya, K.N.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W. Machine learning exploration of the direct and indirect roles of Fe impregnation on Cr(VI) removal by engineered biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Cao, X.; Li, T.; Cui, X.; Cui, Z. Co-removal effect and mechanism of Cr(VI) and Cd(II) by biochar-supported sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron in a binary system. Molecules 2022, 27, 4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, H.J.; Liu, P.P.; Fang, W.; Geng, J.J. A novel modified graphene oxide/chitosan composite used as an adsorbent for Cr(VI) in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 87, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.L.; Deng, S.B.; Wu, R.; Hong, S.Q.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Yu, G. Highly efficient removal of hexavalent chromium from electroplating wastewater using aminated wheat straw. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 8797–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-N.; Guo, J.-Z.; Wu, C.; Huan, W.-W.; Chen, L.; Li, B. Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) by cation functionalized bamboo hydrochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; He, J.J.; Shi, W.X.; Liu, D.M.; Chi, H.Z.; Cui, F.Y.; Wang, W. Microstructured macroporous adsorbent composed of polypyrrole modified natural corncob-core sponge for Cr(VI) removal. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 59292–59298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Chen, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Mei, M.; Li, J. Co-pyrolysis of polyester and cotton via thermogravimetric analysis and adsorption mechanism of Cr(VI) removal by carbon in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 354, 118902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.H.; Hu, J.T.; Han, Z.S.; Diesel, E.; Wang, Z.X.; Zheng, Z.; Ba, C.Y.; Langer, J.; Economy, J. Interactions of Cr(VI) with hybrid anion exchange/porous carbon fibers in aqueous solution at natural pH. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.G.; Liu, S.B.; Yin, Y.C.; Zeng, G.M.; Tan, X.F.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.J.; Jiang, L.H.; Ding, Y.; et al. Investigation of the adsorption-reduction mechanisms of hexavalent chromium by ramie biochars of different pyrolytic temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Fan, W.; Yi, X.W.; Wang, Z.H.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.J.; Gu, H.B. Dithiocarbamate-modified starch derivatives with high heavy metal adsorption performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, C.; Yu, F.; Zhou, H. Investigation of black liquor-derived carbon for removal of Cr(VI): Comparison with lignin-derived carbon. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 642, 128730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Feng, H.; Jia, P.; An, Q.; Ma, M. Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by a novel ZnO-sludge biochar composite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 83045–83059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Li, M.; Lin, T.; Su, K.; Yang, H.; Chen, J. Efficient removal and detoxification of Cr(VI) by PEI-modified Juncus effuses with a natural 3D network structure. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Song, W.; Wu, Z.; Chen, W.; Cui, J.; Yao, Y. Cationic polyacrylamide aerogel intercalated molybdenum disulfide for enhanced removal of Cr(VI) and organic contaminants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 294, 121188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Tian, Y.; Kong, L.; Cai, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W.; Wen, B. Shapeable amino-functionalized sodium alginate aerogel for high-performance adsorption of Cr(VI) and Cd(II): Experimental and theoretical investigations. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W.; Li, Y.; Cai, G. A novel 3D superelastic polyethyleneimine functionalized chitosan aerogels for selective removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution: Performance and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tang, C.; Fu, S.; Tam, K.C.; Zong, Y. Cellulose-based aerogel beads for efficient adsorption-reduction-sequestration of Cr(VI). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Du, X.; Cheng, X.; Du, Z.; Wang, H. Fabrication of MXene/PEI functionalized sodium alginate aerogel and its excellent adsorption behavior for Cr(VI) and Congo Red from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Yuan, W.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ao, C.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. Iron-loaded carbon aerogels derived from bamboo cellulose fibers as efficient adsorbents for Cr(VI) removal. Polymers 2021, 13, 4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, R.; Chen, J.; Lan, J.; Li, S.; Zhou, M.; Zeng, T.; Hou, H. Microscopic mechanism about the selective adsorption of Cr(VI) from salt solution on nitrogen-doped carbon aerogel microsphere pyrolysis products. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, D.; Jiang, H.; Qi, Y.; Wang, S.; Jia, Y.; Wang, W. Preparation of covalent triazine-based framework for efficient Cr(VI) removal from water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 632, 127757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.Z.X.; Dahanayaka, M.; Liu, B.; Law, A.W.-K.; Zhou, K. Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks as capacitive deionization electrodes for water desalination and Cr(VI) adsorption: A molecular simulation study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 546, 149080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Qin, L.; Lai, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Xiao, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M. Recent advances in the application of water-stable metal-organic frameworks: Adsorption and photocatalytic reduction of heavy metal in water. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzalat, O.; Wong, D.; Elsayed, M.A. Nano-porous composites of activated carbon-metal organic frameworks (Fe-BDC@AC) for rapid removal of Cr (VI): Synthesis, adsorption, mechanism, and kinetics studies. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 1924–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzalat, O.; Tantawy, H.; Mokhtar, M.; Baraka, A. Nano-porous bimetallic organic frameworks (Fe/Co)-BDC, a breathing MOF for rapid and capacitive removal of Cr-oxyanions from water. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Mohamed, A.K. Novel derived pectin hydrogel from mandarin peel based metal-organic frameworks composite for enhanced Cr(VI) and Pb(II) ions removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pang, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Song, G.; Alharbi, N.S.; Rabah, S.O. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-based nanomaterials for the capture of heavy metal ions and radionuclides: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nqombolo, A.; Munonde, T.S.; Makhetha, T.A.; Moutloali, R.M.; Nomngongo, P.N. Cobalt/zinc based metal organic frameworks as an effective adsorbent for improved removal of As(V) and Cr(VI) in a wide pH range. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Zhou, J.X.; Jin, Y.P.; Cao, J.L.; Yilihan, P.; Wen, Y.J.; Wu, Y.Y. Mechanisms of chromium and arsenite adsorption by amino-functionalized SBA-15. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 1859–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Pathania, D.; Agarwal, S.; Sharma, S. Removal of Cr(VI) onto Ficus carica biosorbent from water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2632–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henryk, K.; Jaroslaw, C.; Witold, Z. Peat and coconut fiber as biofilters for chromium adsorption from contaminated wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Moreno, N.; Navia, R.; Querol, X. Study of a Chilean petroleum coke fluidized bed combustion fly ash and its potential application in copper, lead and hexavalent chromium removal. Fuel 2010, 89, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, K.; Xu, H. Self-assembly modified-mushroom nanocomposite for rapid removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution with bubbling fluidized bed. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.D.; Yan, S.; Weng, W.; Xiao, R. Cost effective nanofiber composite membranes for Cr(VI) adsorption with high durability. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 44723–44731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; An, B.; Chen, H.; Chu, J.; Ma, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Z. Botryoidal nanolignin channel stabilized ultrasmall PdNP incorporating with filter membrane for enhanced removal of Cr(VI) via synergetic filtration and catalysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 296, 121409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Xing, W.; Luo, K.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Jin, W.; Wang, J.; Tang, W. Effective and continuous removal of Cr(VI) from brackish wastewater by flow-electrode capacitive deionization (FCDI). J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 326, 129417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Lu, L.; Cai, Z.X.; Ren, Z.J. Individual and competitive removal of heavy metals using capacitive deionization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, M.S.; Balomajumder, C. Simultaneous electrosorptive removal of chromium(VI) and fluoride ions by capacitive deionization (CDI): Multicomponent isotherm modeling and kinetic study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 186, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, M.S.; Balomajumder, C.; Tiwari, A.K. Acid treated RHWBAC electrode performance for Cr(VI) removal by capacitive deionization and CFD analysis study. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, M.S.; Balomajumder, C. Removal of Cr(VI) and fluoride by membrane capacitive deionization with nanoporous and microporous Limonia acidissima (wood apple) shell activated carbon electrode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 195, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhu, L. Investigation of adsorption/desorption behavior of Cr(VI) at the presence of inorganic and organic substance in membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI). J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 78, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanraj, P.; AllwinEbinesar, J.S.S.; Amala, J.; Bhuvaneshwari, S. Biocomposite based electrode for effective removal of Cr (VI) heavy metal via capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2020, 207, 775–789. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zeng, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Z. Ultra-high selective removal of CR and Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using polyethyleneimine functionalized magnetic hydrochar: Application strategy and mechanisms insight. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 448, 137464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Tang, W.; Gu, X. Competitive kinetics of Ni(II)/Co(II) and Cr(VI)/P(V) adsorption and desorption on goethite: A unified thermodynamically based model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.L.; Liu, S.Q.; Xu, M.; Peng, J.; Li, J.Q.; Zhai, M.L. Synthesis of novel aminated cellulose microsphere adsorbent for efficient Cr(VI) removal. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016, 125, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Xin, Y.-N.; Zou, J.; Khoso, F.M.; Liu, Y.-P.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Peng, S.; Yu, J.-G. Removal of Chromium Species by Adsorption: Fundamental Principles, Newly Developed Adsorbents and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2023, 28, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020639
Liu B, Xin Y-N, Zou J, Khoso FM, Liu Y-P, Jiang X-Y, Peng S, Yu J-G. Removal of Chromium Species by Adsorption: Fundamental Principles, Newly Developed Adsorbents and Future Perspectives. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020639
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bo, Ya-Nan Xin, Jiao Zou, Fazal Muhammad Khoso, Yi-Ping Liu, Xin-Yu Jiang, Sui Peng, and Jin-Gang Yu. 2023. "Removal of Chromium Species by Adsorption: Fundamental Principles, Newly Developed Adsorbents and Future Perspectives" Molecules 28, no. 2: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020639
APA StyleLiu, B., Xin, Y.-N., Zou, J., Khoso, F. M., Liu, Y.-P., Jiang, X.-Y., Peng, S., & Yu, J.-G. (2023). Removal of Chromium Species by Adsorption: Fundamental Principles, Newly Developed Adsorbents and Future Perspectives. Molecules, 28(2), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020639







