Na+ Binding and Transport: Insights from Light-Driven Na+-Pumping Rhodopsin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ground-State Structure of KR2
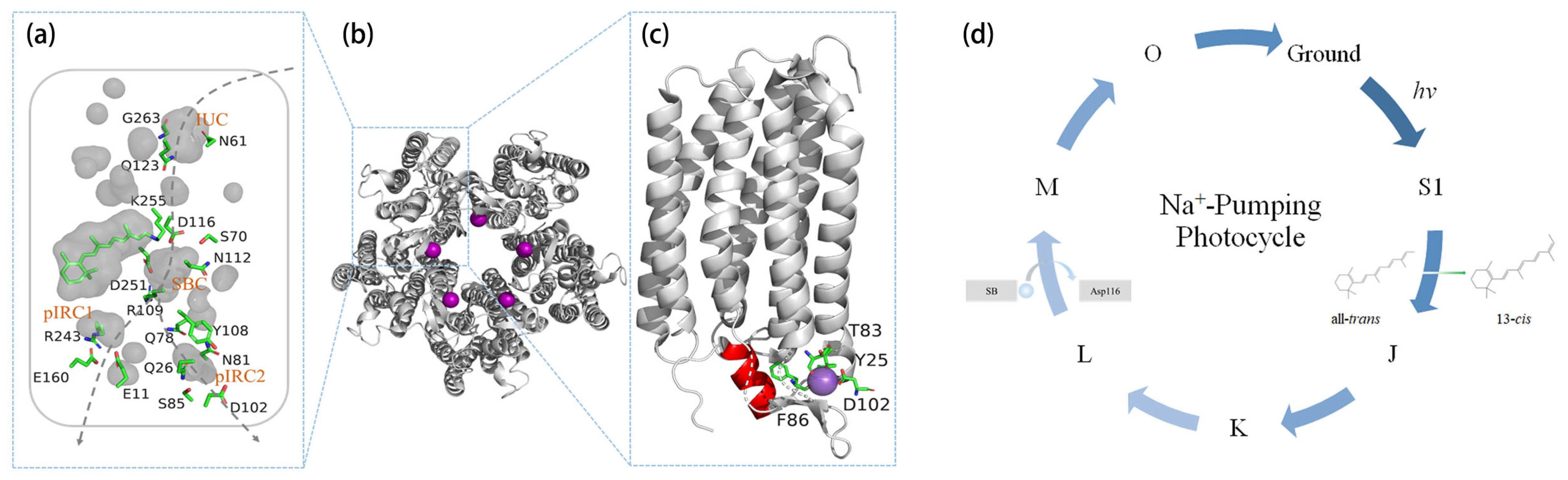
2.1. Na+ Translocation Pathway
2.2. Pentamerization
2.3. Initial Binding of Na+
2.4. N-Terminal Helix
3. Na+-Pumping Photocycle
3.1. Initial Steps of Retinal Isomerization
3.2. Relocation of Schiff Base H+
3.3. Transient Na+ Binding near the Schiff Base
3.4. The Timing of Na+ Release
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raghavan, M.; Fee, D.; Barkhaus, P.E. Generation and propagation of the action potential. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 160, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakim, K.G. Physiologic principles governing regulation and maintenance of electrolyte and fluid balance. J. Lancet 1954, 74, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muller, D.N.; Wilck, N.; Haase, S.; Kleinewietfeld, M.; Linker, R.A. Sodium in the microenvironment regulates immune responses and tissue homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.; Eisner, D.A. Regulation of Intracellular and Mitochondrial Sodium in Health and Disease. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterns, R.H. Disorders of plasma sodium—Causes, consequences, and correction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaumin, J.; DiBartola, S.P. Disorders of Sodium and Water Homeostasis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 47, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, T.K.; James, A.D.; Zaccagna, F.; Grist, J.T.; Deen, S.; Kennerley, A.; Riemer, F.; Kaggie, J.D.; Gallagher, F.A.; Gilbert, F.J.; et al. Sodium homeostasis in the tumour microenvironment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1872, 188304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blostein, R. Ion pumps. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1989, 1, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadsby, D.C. Ion channels versus ion pumps: The principal difference, in principle. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Ono, H.; Abe-Yoshizumi, R.; Yoshizawa, S.; Ito, H.; Kogure, K.; Kandori, H. A light-driven sodium ion pump in marine bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gushchin, I.; Shevchenko, V.; Polovinkin, V.; Kovalev, K.; Alekseev, A.; Round, E.; Borshchevskiy, V.; Balandin, T.; Popov, A.; Gensch, T.; et al. Crystal structure of a light-driven sodium pump. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.E.; Inoue, K.; Abe-Yoshizumi, R.; Kato, Y.; Ono, H.; Konno, M.; Hososhima, S.; Ishizuka, T.; Hoque, M.R.; Kunitomo, H.; et al. Structural basis for Na(+) transport mechanism by a light-driven Na(+) pump. Nature 2015, 521, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béjà, O.; Lanyi, J.K. Nature’s toolkit for microbial rhodopsin ion pumps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6538–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Konno, M.; Abe-Yoshizumi, R.; Kandori, H. The Role of the NDQ Motif in Sodium-Pumping Rhodopsins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 11536–11539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sineshchekov, O.A.; da Silva, G.F.; Spudich, J.L. In Vitro Demonstration of Dual Light-Driven Na(+)/H(+) Pumping by a Microbial Rhodopsin. Biophys. J. 2015, 109, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Ma, B.; Ji, L.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, D. Coexistence of light-driven Na(+) and H(+) transport in a microbial rhodopsin from Nonlabens dokdonensis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 172, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandori, H. Retinal Proteins: Photochemistry and Optogenetics. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 93, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandori, H.; Inoue, K.; Tsunoda, S.P. Light-Driven Sodium-Pumping Rhodopsin: A New Concept of Active Transport. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 10646–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.E.; Inoue, K.; Kandori, H.; Nureki, O. The light-driven sodium ion pump: A new player in rhodopsin research. Bioessays 2016, 38, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalev, K.; Polovinkin, V.; Gushchin, I.; Alekseev, A.; Shevchenko, V.; Borshchevskiy, V.; Astashkin, R.; Balandin, T.; Bratanov, D.; Vaganova, S.; et al. Structure and mechanisms of sodium-pumping KR2 rhodopsin. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalev, K.; Astashkin, R.; Gushchin, I.; Orekhov, P.; Volkov, D.; Zinovev, E.; Marin, E.; Rulev, M.; Alekseev, A.; Royant, A.; et al. Molecular mechanism of light-driven sodium pumping. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skopintsev, P.; Ehrenberg, D.; Weinert, T.; James, D.; Kar, R.K.; Johnson, P.J.M.; Ozerov, D.; Furrer, A.; Martiel, I.; Dworkowski, F.; et al. Femtosecond-to-millisecond structural changes in a light-driven sodium pump. Nature 2020, 583, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Inoue, K.; Ikeda, K.; Konno, M.; Singh, M.; Kataoka, C.; Abe-Yoshizumi, R.; Kandori, H.; Uchihashi, T. Oligomeric states of microbial rhodopsins determined by high-speed atomic force microscopy and circular dichroic spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamedov, M.D.; Mamedov, A.M.; Bertsova, Y.V.; Bogachev, A.V. A single mutation converts bacterial Na(+) -transporting rhodopsin into an H(+) transporter. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 2827–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, M.; Kato, Y.; Kato, H.E.; Inoue, K.; Nureki, O.; Kandori, H. Mutant of a Light-Driven Sodium Ion Pump Can Transport Cesium Ions. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Fukuda, M.; Jo, Y.; Wang, P.Y.; Paggi, J.M.; Inoue, M.; Byrne, E.F.X.; Kishi, K.E.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Structural basis for ion selectivity in potassium-selective channelrhodopsins. Cell 2023, 186, 4325–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Inoue, K.; Kandori, H. Kinetic Analysis of H(+)-Na(+) Selectivity in a Light-Driven Na(+)-Pumping Rhodopsin. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 5111–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Yang, Q.; Ma, B.; Li, L.; Kong, F.; Xiao, L.; Chen, D. K+-Dependent Photocycle and Photocurrent Reveal the Uptake of K+ in Light-Driven Sodium Pump. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe-Yoshizumi, R.; Inoue, K.; Kato, H.E.; Nureki, O.; Kandori, H. Role of Asn112 in a Light-Driven Sodium Ion-Pumping Rhodopsin. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 5790–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balashov, S.P.; Imasheva, E.S.; Dioumaev, A.K.; Wang, J.M.; Jung, K.H.; Lanyi, J.K. Light-driven Na(+) pump from Gillisia limnaea: A high-affinity Na(+) binding site is formed transiently in the photocycle. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 7549–7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomida, S.; Ito, S.; Mato, T.; Furutani, Y.; Inoue, K.; Kandori, H. Infrared spectroscopic analysis on structural changes around the protonated Schiff base upon retinal isomerization in light-driven sodium pump KR2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2020, 1861, 148190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, A.; Silapetere, A.; Grimm, C.; Heiser, F.; Ancina Moller, M.; Hegemann, P. Engineered Passive Potassium Conductance in the KR2 Sodium Pump. Biophys. J. 2019, 116, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garczarek, F.; Brown, L.S.; Lanyi, J.K.; Gerwert, K. Proton binding within a membrane protein by a protonated water cluster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3633–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garczarek, F.; Gerwert, K. Functional waters in intraprotein proton transfer monitored by FTIR difference spectroscopy. Nature 2006, 439, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.A.; Purdy, M.D.; Yeager, M. CryoEM maps are full of potential. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 58, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torino, S.; Dhurandhar, M.; Stroobants, A.; Claessens, R.; Efremov, R.G. Time-resolved cryo-EM using a combination of droplet microfluidics with on-demand jetting. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.S.; Ernst, O.P. Recent advances in biophysical studies of rhodopsins-Oligomerization, folding, and structure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2017, 1865, 1512–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouillette, C.G.; McMichens, R.B.; Stern, L.J.; Khorana, H.G. Structure and Thermal-Stability of Monomeric Bacteriorhodopsin in Mixed Phospholipid Detergent Micelles. Proteins-Struct. Funct. Genet. 1989, 5, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, A.; Kajimoto, K.; Fujisawa, T.; Tsukamoto, T.; Aizawa, T.; Kamo, N.; Jung, K.H.; Unno, M.; Demura, M.; Kikukawa, T. Functional importance of the oligomer formation of the cyanobacterial H(+) pump Gloeobacter rhodopsin. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Kinnebrew, M.; Schonenbach, N.S.; Aye, E.; Han, S. Functional Consequences of the Oligomeric Assembly of Proteorhodopsin. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gushchin, I.; Shevchenko, V.; Polovinkin, V.; Borshchevskiy, V.; Buslaev, P.; Bamberg, E.; Gordeliy, V. Structure of the light-driven sodium pump KR2 and its implications for optogenetics. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamizo, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Kikukawa, T.; Okamura, A.; Baba, H.; Unno, M. Low-temperature Raman spectroscopy of sodium-pump rhodopsin from Indibacter alkaliphilus: Insight of Na(+) binding for active Na(+) transport. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, G.F.; Goblirsch, B.R.; Tsai, A.L.; Spudich, J.L. Cation-Specific Conformations in a Dual-Function Ion-Pumping Microbial Rhodopsin. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 3950–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otomo, A.; Mizuno, M.; Inoue, K.; Kandori, H.; Mizutani, Y. Allosteric Communication with the Retinal Chromophore upon Ion Binding in a Light-Driven Sodium Ion-Pumping Rhodopsin. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hontani, Y.; Inoue, K.; Kloz, M.; Kato, Y.; Kandori, H.; Kennis, J.T. The photochemistry of sodium ion pump rhodopsin observed by watermarked femto- to submillisecond stimulated Raman spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 24729–24736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, H.; Inoue, K.; Abe-Yoshizumi, R.; Kandori, H. FTIR spectroscopy of a light-driven compatible sodium ion-proton pumping rhodopsin at 77 K. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 4784–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, C.; Silapetere, A.; Vogt, A.; Bernal Sierra, Y.A.; Hegemann, P. Electrical properties, substrate specificity and optogenetic potential of the engineered light-driven sodium pump eKR2. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kwon, S.K.; Jun, S.H.; Cha, J.S.; Kim, H.; Lee, W.; Kim, J.F.; Cho, H.S. Crystal structure and functional characterization of a light-driven chloride pump having an NTQ motif. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, T.; Shihoya, W.; Sugiura, M.; Yoshida, K.; Watari, M.; Tokano, T.; Yamashita, K.; Katayama, K.; Tsunoda, S.P.; Uchihashi, T.; et al. Structural insights into the mechanism of rhodopsin phosphodiesterase. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Kato, Y.; Kandori, H. Light-driven ion-translocating rhodopsins in marine bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajimoto, K.; Kikukawa, T.; Nakashima, H.; Yamaryo, H.; Saito, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Demura, M.; Unno, M. Transient Resonance Raman Spectroscopy of a Light-Driven Sodium-Ion-Pump Rhodopsin from Indibacter alkaliphilus. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 4431–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhardt, P.; Slavov, C.; Sormann, J.; Bamann, C.; Braun, M.; Wachtveitl, J. Temperature Dependence of the Krokinobacter rhodopsin 2 Kinetics. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Tsukamoto, T.; Demura, M.; Kikukawa, T. Real-time identification of two substrate-binding intermediates for the light-driven sodium pump rhodopsin. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, S.; Takeuchi, S.; Abe-Yoshizumi, R.; Inoue, K.; Ohtani, H.; Kandori, H.; Tahara, T. Ultrafast photoreaction dynamics of a light-driven sodium-ion-pumping retinal protein from Krokinobacter eikastus revealed by femtosecond time-resolved absorption spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 4481–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahara, S.; Takeuchi, S.; Abe-Yoshizumi, R.; Inoue, K.; Ohtani, H.; Kandori, H.; Tahara, T. Origin of the Reactive and Nonreactive Excited States in the Primary Reaction of Rhodopsins: pH Dependence of Femtosecond Absorption of Light-Driven Sodium Ion Pump Rhodopsin KR2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 4784–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusochek, P.A.; Scherbinin, A.V.; Bochenkova, A.V. Insights into the Early-Time Excited-State Dynamics of Structurally Inhomogeneous Rhodopsin KR2. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 8664–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asido, M.; Wachtveitl, J. Photochemistry of the Light-Driven Sodium Pump Krokinobacter eikastus Rhodopsin 2 and Its Implications on Microbial Rhodopsin Research: Retrospective and Perspective. J. Phys. Chem. B 2023, 127, 3766–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polland, H.J.; Franz, M.A.; Zinth, W.; Kaiser, W.; Kölling, E.; Oesterhelt, D. Early picosecond events in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys. J. 1986, 49, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathies, R.A.; Brito Cruz, C.H.; Pollard, W.T.; Shank, C.V. Direct observation of the femtosecond excited-state cis-trans isomerization in bacteriorhodopsin. Science 1988, 240, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Tanimoto, T.; Kandori, H. Water molecules in the schiff base region of bacteriorhodopsin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13312–13313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nango, E.; Royant, A.; Kubo, M.; Nakane, T.; Wickstrand, C.; Kimura, T.; Tanaka, T.; Tono, K.; Song, C.; Tanaka, R.; et al. A three-dimensional movie of structural changes in bacteriorhodopsin. Science 2016, 354, 1552–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomida, S.; Ito, S.; Inoue, K.; Kandori, H. Hydrogen-bonding network at the cytoplasmic region of a light-driven sodium pump rhodopsin KR2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2018, 1859, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakdetchai, O.; Eberhardt, P.; Asido, M.; Kaur, J.; Kriebel, C.N.; Mao, J.; Leeder, A.J.; Brown, L.J.; Brown, R.C.D.; Becker-Baldus, J.; et al. Probing the photointermediates of light-driven sodium ion pump KR2 by DNP-enhanced solid-state NMR. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, N.; Mizuno, M.; Kandori, H.; Mizutani, Y. Distortion and a Strong Hydrogen Bond in the Retinal Chromophore Enable Sodium-Ion Transport by the Sodium-Ion Pump KR2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 3430–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luecke, H.; Schobert, B.; Richter, H.T.; Cartailler, J.P.; Lanyi, J.K. Structure of bacteriorhodopsin at 1.55 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 291, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asido, M.; Eberhardt, P.; Kriebel, C.N.; Braun, M.; Glaubitz, C.; Wachtveitl, J. Time-resolved IR spectroscopy reveals mechanistic details of ion transport in the sodium pump Krokinobacter eikastus rhodopsin 2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 4461–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suomivuori, C.M.; Gamiz-Hernandez, A.P.; Sundholm, D.; Kaila, V.R.I. Energetics and dynamics of a light-driven sodium-pumping rhodopsin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7043–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murabe, K.; Tsukamoto, T.; Aizawa, T.; Demura, M.; Kikukawa, T. Direct Detection of the Substrate Uptake and Release Reactions of the Light-Driven Sodium-Pump Rhodopsin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 16023–16030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.F.; Inoue, K.; Ono, H.; Abe-Yoshizumi, R.; Wada, A.; Kandori, H. Time-resolved FTIR study of light-driven sodium pump rhodopsins. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 17694–17704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, T.; Nakatsuji, H. Light-Driven Proton, Sodium Ion, and Chloride Ion Transfer Mechanisms in Rhodopsins: SAC-CI Study. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 123, 1766–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimura, M.; Ishikita, H. Identification of intermediate conformations in the photocycle of the light-driven sodium-pumping rhodopsin KR2. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asido, M.; Kar, R.K.; Kriebel, C.N.; Braun, M.; Glaubitz, C.; Schapiro, I.; Wachtveitl, J. Transient Near-UV Absorption of the Light-Driven Sodium Pump Krokinobacter eikastus Rhodopsin 2: A Spectroscopic Marker for Retinal Configuration. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 6284–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, T.; Kinoue, K.; Seike, R.; Kikukawa, T.; Unno, M. Reisomerization of retinal represents a molecular switch mediating Na+ uptake and release by a bacterial sodium-pumping rhodopsin. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balashov, S.P. Protonation reactions and their coupling in bacteriorhodopsin. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2000, 1460, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhard, C.; Chizhov, I.; Siebert, F.; Engelhard, M. Microbial Halorhodopsins: Light-Driven Chloride Pumps. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 10629–10645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimányi, L.; Váró, G.; Chang, M.; Ni, B.; Needleman, R.; Lanyi, J.K. Pathways of proton release in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 8535–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogachev, A.V.; Bertsova, Y.V.; Verkhovskaya, M.L.; Mamedov, M.D.; Skulachev, V.P. Real-time kinetics of electrogenic Na(+) transport by rhodopsin from the marine flavobacterium Dokdonia sp. PRO95. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanyi, J.K. Bacteriorhodopsin. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2004, 66, 665–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanyi, J.K. 8.10 Light Capture and Energy Transduction in Bacterial Rhodopsins and Related Proteins. Compr. Biophys. 2012, 8, 206–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, S.; Iwaki, M.; Sugita, S.; Abe-Yoshizumi, R.; Iwata, T.; Inoue, K.; Kandori, H. Unique Hydrogen Bonds in Membrane Protein Monitored by Whole Mid-IR ATR Spectroscopy in Aqueous Solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Kriebel, C.N.; Eberhardt, P.; Jakdetchai, O.; Leeder, A.J.; Weber, I.; Brown, L.J.; Brown, R.C.D.; Becker-Baldus, J.; Bamann, C.; et al. Solid-state NMR analysis of the sodium pump Krokinobacter rhodopsin 2 and its H30A mutant. J. Struct. Biol. 2019, 206, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y. Spectroscopic Studies of Novel Microbial Rhodopsins from Fungi and Bacteria. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Guelph, Guelph, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, K.; Nomura, Y.; Kandori, H. Asymmetric Functional Conversion of Eubacterial Light-driven Ion Pumps. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 9883–9893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, M.; Thiel, V.; Takahashi, H.; Kojima, K.; Ward, D.M.; Bryant, D.A.; Sakai, M.; Yoshizawa, S.; Sudo, Y. Identification of a Functionally Efficient and Thermally Stable Outward Sodium-Pumping Rhodopsin (BeNaR) from a Thermophilic Bacterium. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2023, 71, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, Y.; Pedraza-Gonzalez, L.; Barneschi, L.; Inoue, K.; Olivucci, M.; Kandori, H. Pro219 is an electrostatic color determinant in the light-driven sodium pump KR2. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamedov, A.M.; Bertsova, Y.V.; Anashkin, V.A.; Mamedov, M.D.; Baykov, A.A.; Bogachev, A.V. Identification of the key determinant of the transport promiscuity in Na(+)-translocating rhodopsins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Del Carmen Marin, M.; Tomida, S.; Nakamura, R.; Nakajima, Y.; Olivucci, M.; Kandori, H. Red-shifting mutation of light-driven sodium-pump rhodopsin. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochiai, S.; Ichikawa, Y.; Tomida, S.; Furutani, Y. Covalent Bond between the Lys-255 Residue and the Main Chain Is Responsible for Stable Retinal Chromophore Binding and Sodium-Pumping Activity of Krokinobacter Rhodopsin 2. Biochemistry 2023, 62, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 6TK2 | 6XYT | |||
| Resolution (Å) | 2.5 | 2.1 | ||
| R-free (%) | 32.4 | 20.0 | ||
| B-factor (Å2) | ||||
| Protein | 41.7 | 58.9 | ||
| Water | 43.6 | 62.2 | ||
| Retinal | 36.7 | 56.9 | ||
| Na | 47.0 | 57.3 | ||
| Coordinating atoms of Na+ | Asn112-OD1 | 28.9 | Val67-O | 48.0 |
| Asp251-OD1 | 35.0 | Ser70-OG | 49.8 | |
| Asp251-OD2 | 38.2 | Asn112-OD1 | 52.6 | |
| Asp116-OD1 | 54.5 | |||
| Asp116-OD2 | 62.0 | |||
| Mutant | Description | Mutant | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E11A | Na+ pump activity lowered [11,12] Unstable [11,12] | Y25F | Na+ binding abolished [80] |
| H30A | H+ pump activity abolished [10] Photocycle slowed [81] | H30L | Na+ pump activity abolished [20] Unstable [20] |
| H30K | Na+ pump activity lowered [20] Pentamerization disrupted [20] | L32E | Leaky pump [32] |
| N61P | Na+ pump activity lowered [25] | N61L | K+ pump activity [25] |
| N61M | Similar to N61P [11] | N61Y | K+/Cs+ pump activity [12,25] |
| N61W | Pump activity abolished [25] | S64A | Pump activity lowered [62] |
| S70A | Na+ pump activity abolished [12] Photocurrents lowered [32] | S70V | Similar to S70A [32] |
| S70T | Na+ pump activity lowered [12] | L74A | Na+ pump activity lowered [21] |
| L75A | Na+ pump activity lowered [21] | L75K | Leaky pump [32] pKa of D251 increased [32] |
| Q78A | Na+ pump activity lowered [21] | Q78L | Function retained [21] |
| Q78Y | Similar to Q78A [21] | Q78W | Similar to Q78A [21] |
| D102N | Na+ binding abolished [12,80] Thermostability reduced [12] Equilibrium in K/L/M shifted [45] | D101N (IaNaR, D102 in KR2) | Na+ binding retained [42] |
| Y108A | Pentamerization retained [81] Pump activity abolished [21] | R109A | Pump activity abolished [10,31,32] Na+ binding abolished [10] K intermediate only [31] |
| R109K | D116-SB interaction weakened [31] Pump activity lowered [31] | R109N | Leaky pump [32] Pump activity abolished [32] |
| R109Q | Passive ion conductance [32] Residual Na+ pump activity [32] K intermediate prolonged; L/M absent [32] | R109Q (NdR2) | Leaky pump [32] |
| R108Q (NMR2, R109 in KR2) | Leaky pump [32] | R108Q (IaNaR, R109 in KR2) | R108–D250 interaction broken [42] |
| N112G | Na+ pump activity lowered [29] | N112A | Na+ pump activity abolished [10,12,29] O intermediate absent [14,29] |
| N112S | Similar to N112G [29] | N112C | Na+ pump activity abolished [29] |
| N112P | Na+ pump activity abolished [29] | N112D | Na+ binding abolished [10] Na+/H+ pump activity lowered [29] |
| N112T | K intermediate prolonged; O absent [29] Na+ pump activity lowered [29] | N112V | Na+ pump activity abolished [29] O intermediate accumulated [29] |
| N112E | Na+ pump activity abolished [29] | N112Q | Similar to N112P [29] |
| N112H | Pump activity abolished [29] K intermediate only [29] | N112L | Similar to N112P [29] |
| N112I | Similar to N112P [29] | N112M | Similar to N112P [29] |
| N112F | Similar to N112P [29] | N112K | Similar to N112H [29] |
| N112Y | Pump activity abolished [29] | N112R | Similar to N112Y [29] |
| N112W | Na+ pump activity abolished [29] H+ pump activity lowered [29] | N112D (NdR2) | Na+ binding abolished [82] O intermediate accumulated [82] Photocycle slowed [82] |
| D116A | Pump activity abolished [10] Red-shifted absorption peak [10] | D116N | Pump activity abolished [10] Red-shifted absorption peak [10,32] Red-shift intermediate only [10,72] |
| D116E | Na+ pump activity abolished [10] Weak Glu-SB hydrogen bond [31] | D116T | Pump activity abolished [83] |
| D116N (NdR2) | Red-shifted absorption peak [82] | D116T (NdR2) | Red-shifted absorption peak [82] 9-cis-retinal [82] |
| D116N (GLR) | Red-shifted absorption peak [30] Unstable at pH below 3.5 [30] | D115N (IaNaR, D116 in KR2) | HOOP intensity of K intermediate decreased [42] |
| D101N (BeNaR, D116 in KR2) | Red-shifted absorption peak [84] Pump activity abolished [84] | Q123A | Na+ pump activity lowered [10] Na+ uptake slowed [14] |
| Q123V | Na+ uptake slowed [14] | Q123D | H+ pump activity enhanced [10] |
| Q123E | Similar to Q123D [10] | Q123D (Dokdonia sp. PRO95) | Na+ pump activity lowered [24] H+ pump activity [24] |
| Q123E (Dokdonia sp. PRO95) | H+ pump [24] | Y154A | Pentamerization disrupted [81] |
| Y154F | Na+ pump activity lowered [20] Pentamerization disrupted [20] | E160A | Na+ pump activity lowered [11,12] Unstable [11,12] |
| E160Q | Unstable [10] | P219R | Pump activity lowered [85] Blue-shift absorption peak [85] |
| R243A | Na+ pump activity lowered [11,12] Unstable [11,12] | R243Q | Similar to R243A [11] |
| D251A | Pump activity abolished [10] | D251N | Similar to D251A [10,32] |
| D251E | Pump activity abolished [10] Leaky pump [32] | D251N (NdR2) | Photocycle slowed [82] O-like intermediate absent [82] |
| D251E (GLR) | Na+ binds [30] Red-shifted absorption peak [30] | D250N (IaNaR, D251 in KR2) | R108–D250 interaction broken [42] |
| D230N (BeNaR, D251 in KR2) | Pump activity abolished [84] | C253S (Dokdonia sp. PRO95) | H+ pump activity [86] |
| S254A | Red-shifted absorption peak [87] K+ pump activity [20] | K255A | Na+ pump activity abolished [88] |
| K255G | Na+ pump activity abolished [88] O intermediate absent [88] | G263L | Pump activity lowered [11] |
| G263F | Na+ pump activity lowered [11] H+ pump activity abolished [11] K+/Cs+ pump activity [25] | G263W | K+ pump activity [12] |
| N61Y/G263W | Pump activity abolished [12] | N61P/G263F | K+ pump activity [25] |
| N61Y/G263F | Similar to N61P/G263F [25] | N61P/G263W | K+ pump activity over Na+ [12,25] |
| N61L/G263F | K+/Cs+ pump activity [25] | N61L/G263W | Similar to N61Y/G263W [25] |
| N61P/G263W (NdR2) | K+ pump activity [28] Na+ affinity decreased [28] | S70A/R109Q | Pump activity abolished [32] Leaky pump [32] |
| F72G/D116T | Cl− pump [83] | F72G/D102N/ D116T | Cl− pump activity enhanced [83] Cl−-dependence color [83] Red-shifted intermediate only [83] |
| E90Q/E91Q/ D98N/D102N | Na+ binding abolished [10] | D102N/N112D/D116T/Q123D | Na+ pump activity abolished [83] |
| D102N/N112D/D116T/Q123E | Similar to D102N/N112D/D116T/Q123D [83] | D102N/D116T | Cl− pump [83] Cl−-dependence color [83] |
| R109Q/D251N | Pump activity restored [32] | R109Q/D251N | Leaky pump [32] |
| N112D/D116T/Q123D | Na+ pump activity abolished [83] | N112D/D116T/Q123E | Similar to N112D/D116T/Q123D [83] |
| D116E/Q123D | Na+ pump activity abolished [10] | P219T/S254A | Red-shifted absorption peak [87] Photocycle slowed [87] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Chen, D. Na+ Binding and Transport: Insights from Light-Driven Na+-Pumping Rhodopsin. Molecules 2023, 28, 7135. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207135
Yang Q, Chen D. Na+ Binding and Transport: Insights from Light-Driven Na+-Pumping Rhodopsin. Molecules. 2023; 28(20):7135. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207135
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qifan, and Deliang Chen. 2023. "Na+ Binding and Transport: Insights from Light-Driven Na+-Pumping Rhodopsin" Molecules 28, no. 20: 7135. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207135
APA StyleYang, Q., & Chen, D. (2023). Na+ Binding and Transport: Insights from Light-Driven Na+-Pumping Rhodopsin. Molecules, 28(20), 7135. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207135







