Ammonium–Amine Co-Activation: Promoting the Sulfurization of Azurite and Its Effect on Xanthate Adsorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
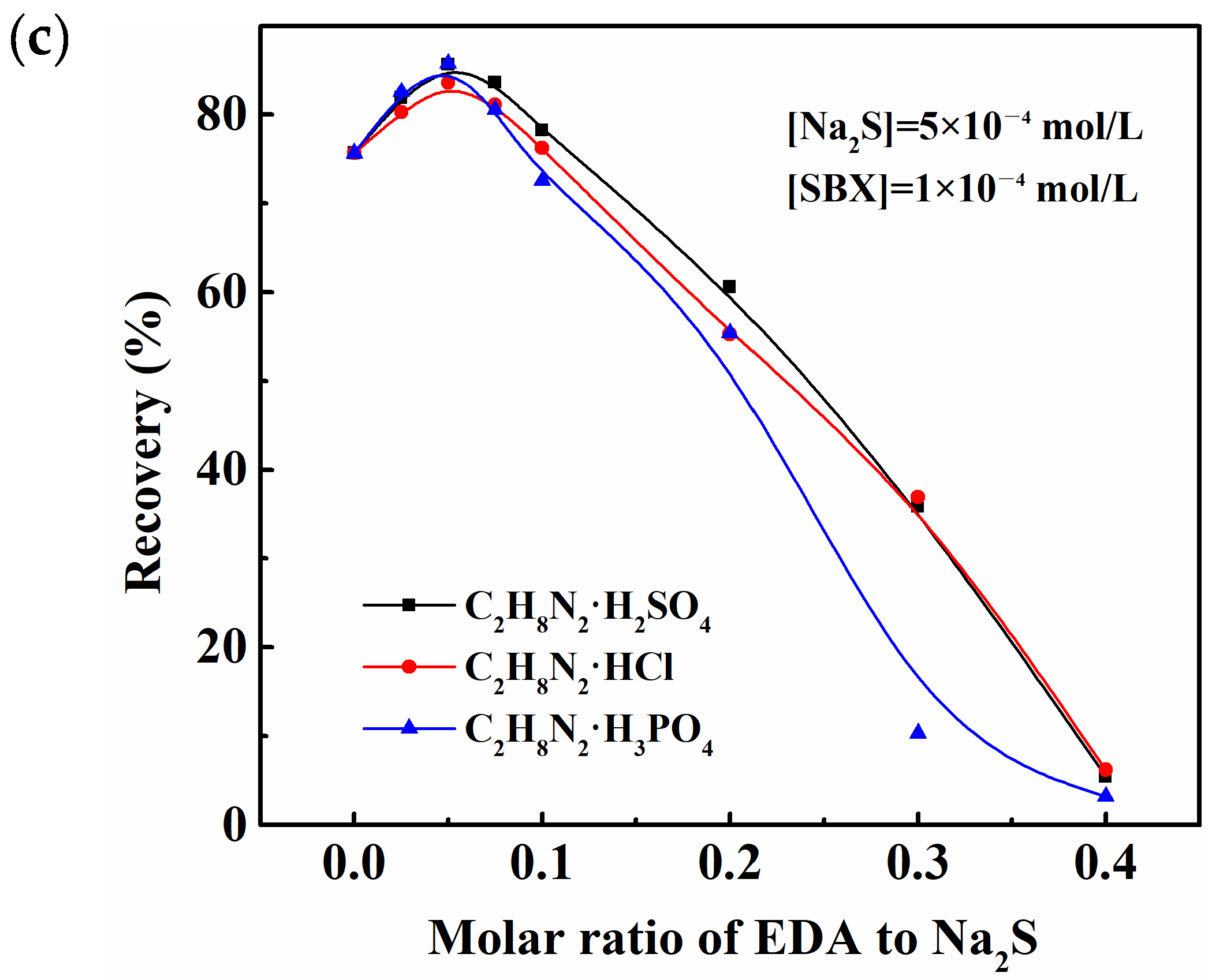
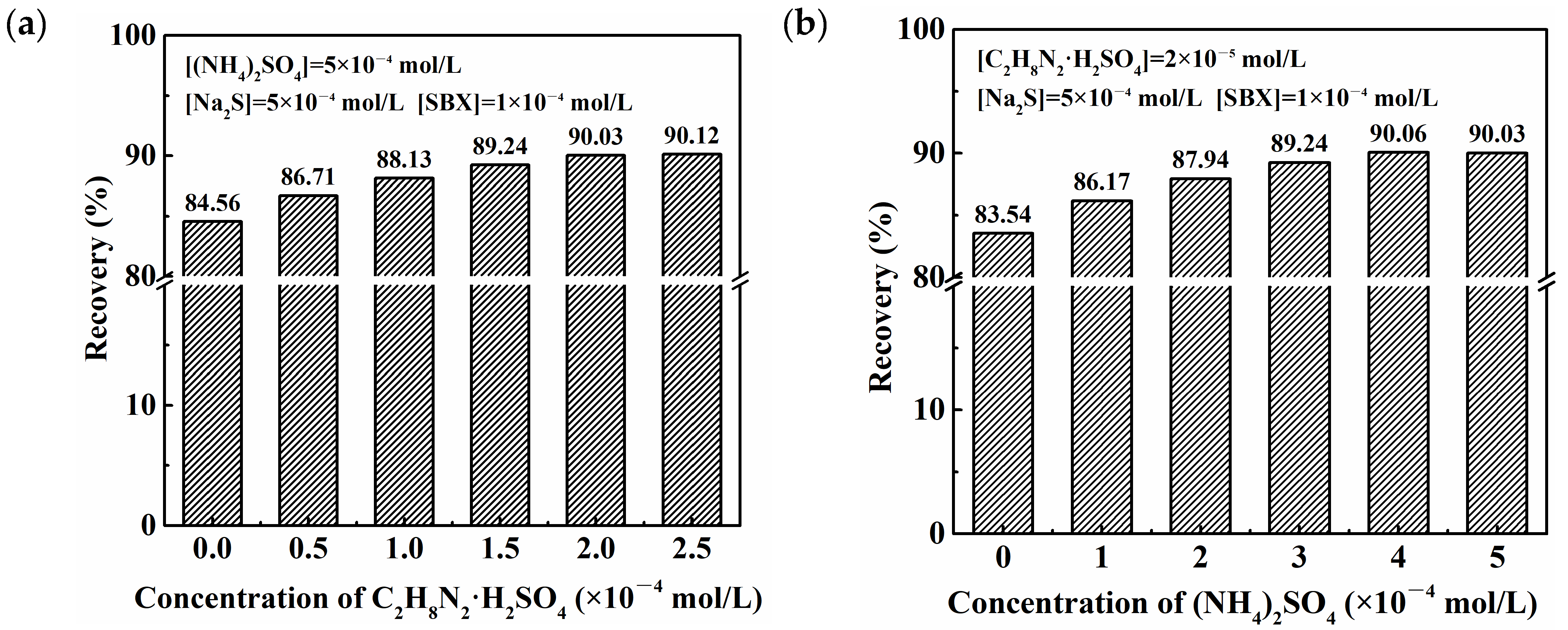
2.1. Floatability Studies
2.2. Sulfur-Containing Migration Analyses
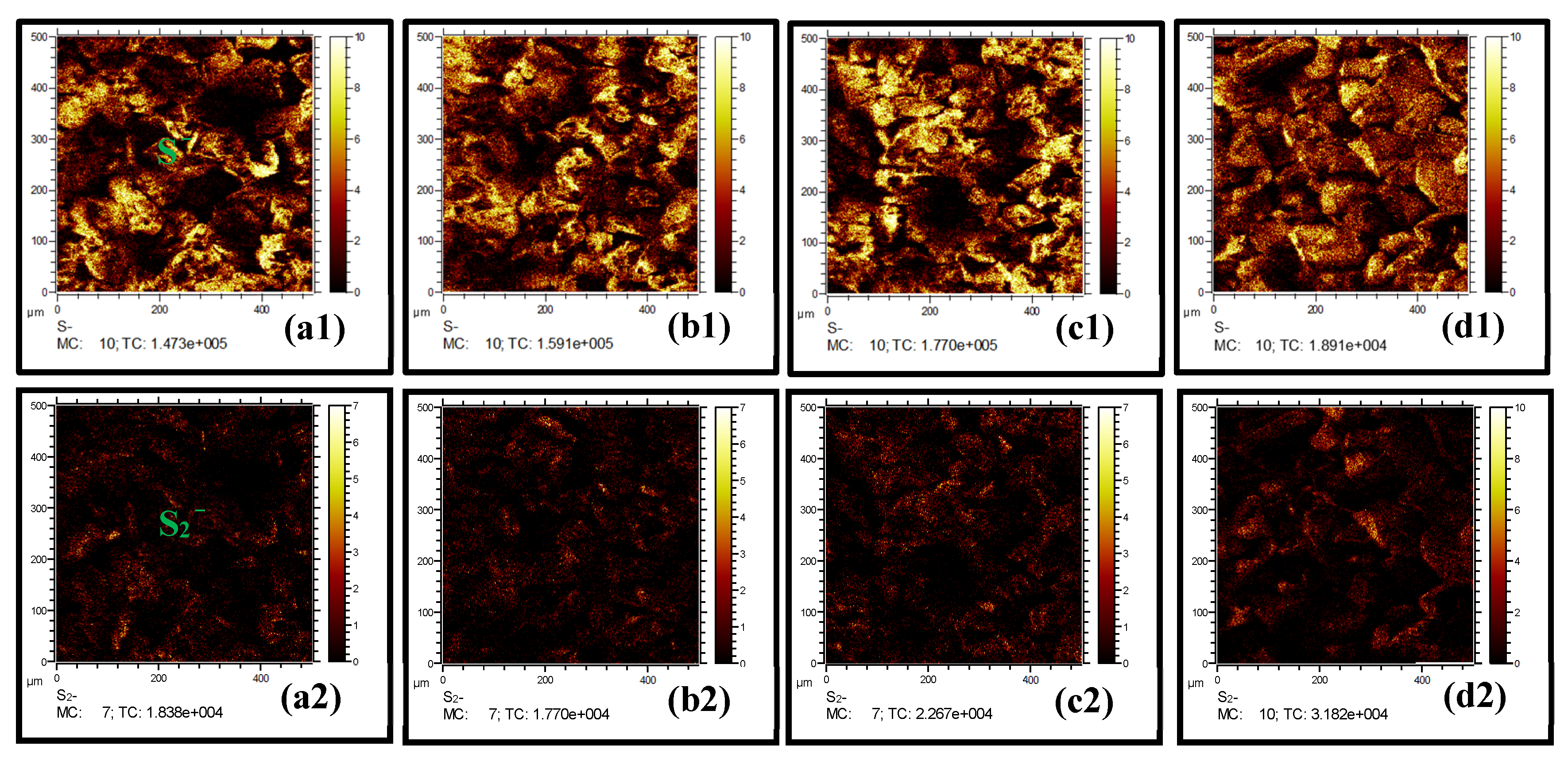
2.3. Surface Morphology Characterizations
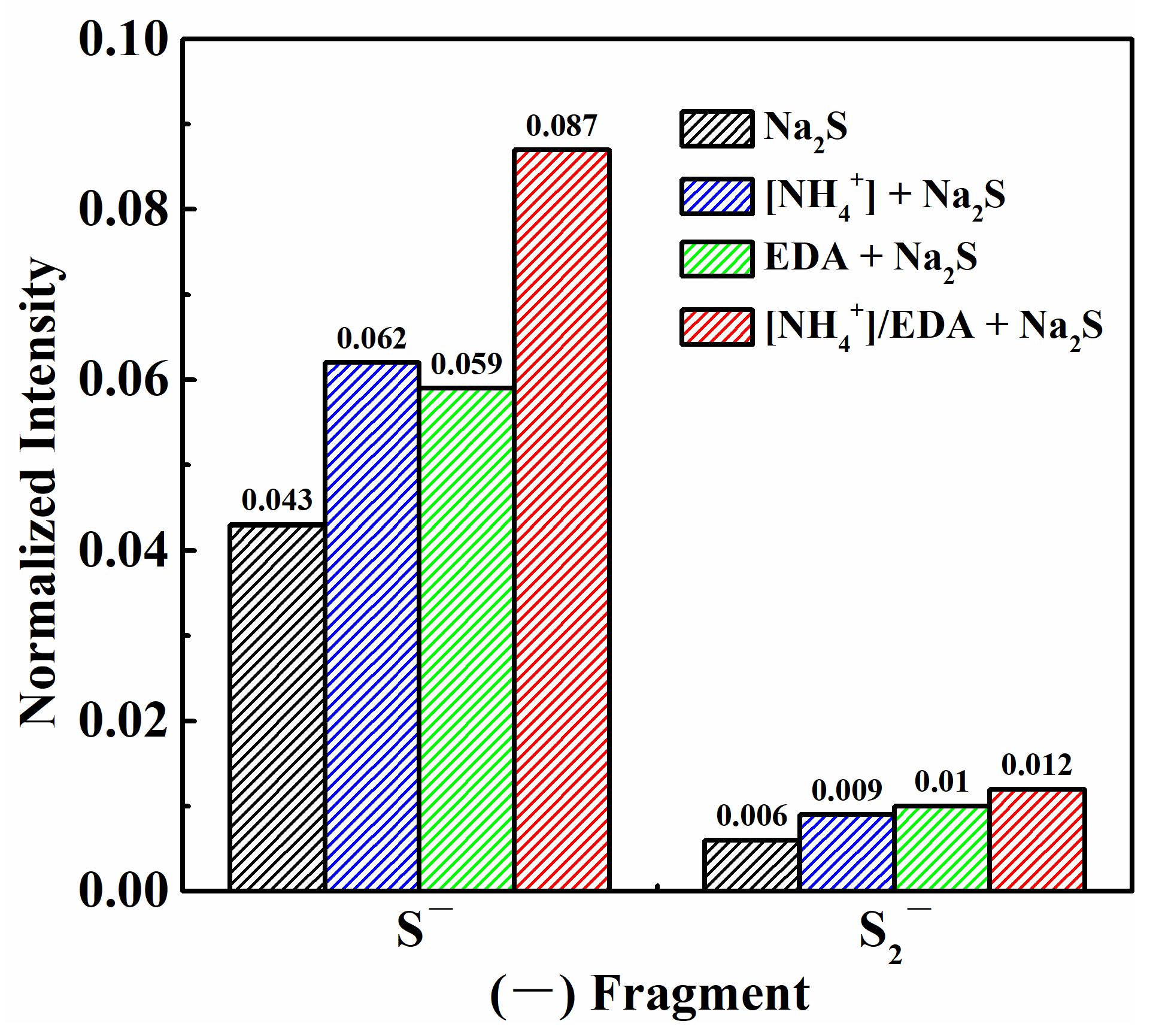
2.4. Product Composition Analyses
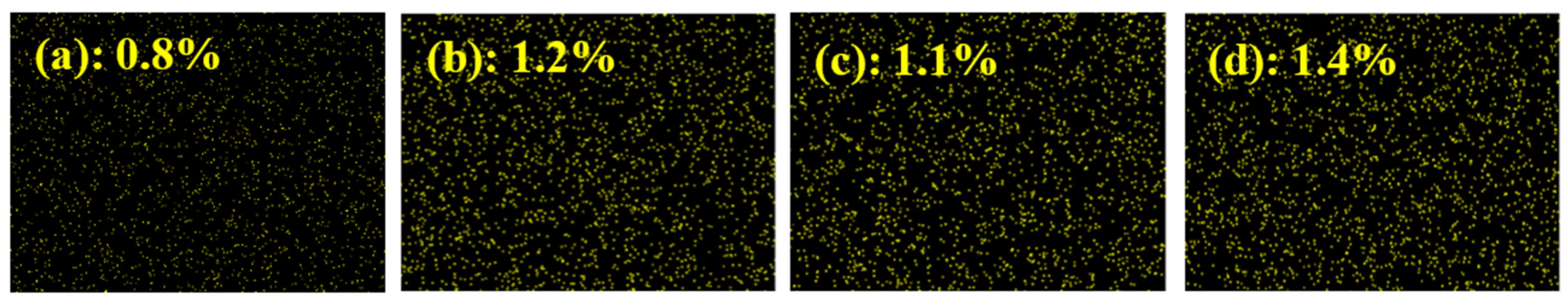
2.5. Xanthate Adsorption Studies
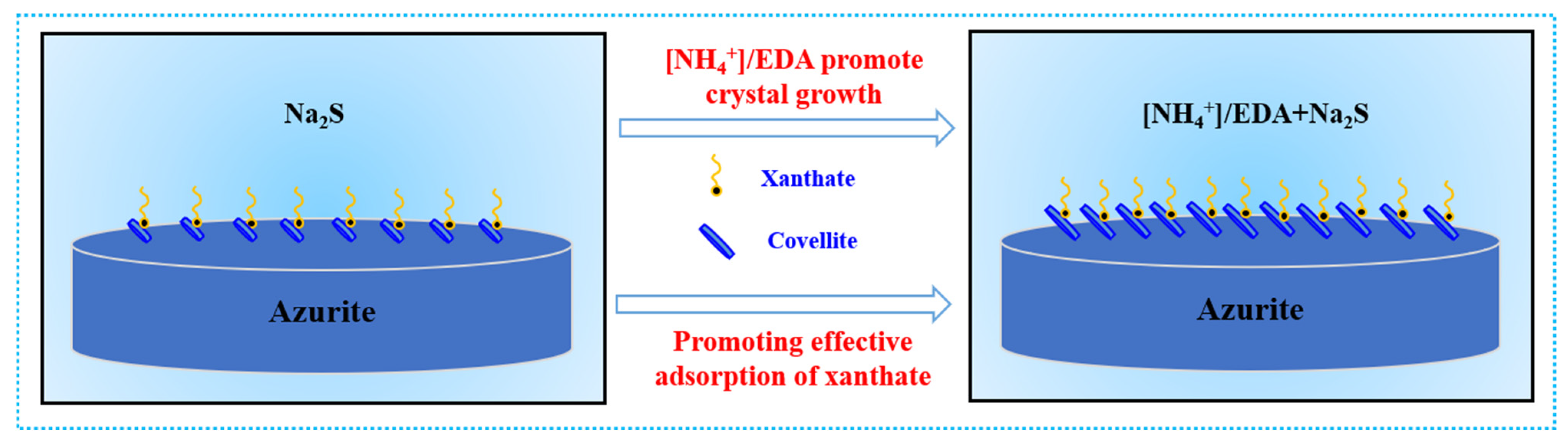
2.6. Mechanism of Ammonium–Amine Co-Activation in Promoting Sulfurization
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Flotation Tests
3.2.2. ToF-SIMS Analysis
3.2.3. Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) Analysis
3.2.4. FESEM-EDS and AFM Analyses
3.2.5. XRD Analysis
3.2.6. Ultraviolet–Visible Spectroscopy (UV-Vis) Measurement
4. Conclusions
- The combined ammonium–amine salts are an excellent activator for the sulfurization flotation of azurite. Compared with single ammonium (amine) salts, the combined ammonium–amine salts can improve the floatability of azurite to a greater extent and increase the flotation recovery by over 4 percentage points.
- Under the [NH4+]/EDA-Na2S system, an increased amount of copper sulfide components are generated on azurite. This phenomenon is closely related to improved adhesion stability.
- Pretreatment with [NH4+]/EDA does not change the phase composition of sulfurized products, which mainly exist in the form of covellite (syn-CuS), but substantially promotes the growth of a covellite crystal.
- The abundant copper sulfide components promote the adsorption of additional xanthate on azurite in the [NH4+]/EDA-Na2S system.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, Y.; Lin, R.; Xiong, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, M.; Duan, X. The Effect of Copper Sulfide Stoichiometric Coefficient and Morphology on Electrochemical Performance. Molecules 2023, 28, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Su, C.; Ma, Y.; Yu, X.; Peng, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Fang, J.; Shen, P.; Liu, D. Role of ammonium sulfate in sulfurization flotation of azurite: Inhibiting the formation of copper sulfide colloid and its mechanism. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Wei, Q.; Jiao, F.; Yang, C.; Liu, R. Utilization of polysaccharides as depressants for the flotation separation of copper/lead concentrate. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2020, 30, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Yang, W.; Wen, S.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Han, G. Flotation of copper oxide minerals: A review. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wen, S.; Feng, Q. Surface characterization of azurite modified with sodium sulfide and its response to flotation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Lin, S.; Zhang, C.; Sun, W.; Chen, D.; Wang, R.; Chen, J. Surface modification of malachite with tetraam-minecopper (II) and its effect on sulfidation flotation. Miner. Eng. 2022, 189, 107882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wen, S.; Feng, Q.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y. Utilization of high-gradient magnetic separation–secondary grinding–leaching to improve the copper recovery from refractory copper oxide ores. Miner. Eng. 2019, 136, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wen, J.; Tan, G.; Liu, G.; Wu, B. Experimental studies and pilot plant tests for acid leaching of low-grade copper oxide ores at the Tuwu Copper Mine. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conejeros, V.; Pérez, K.; Jeldres, R.; Castillo, J.; Hernández, P.; Toro, N. Novel Treatment for mixed copper ores: Leaching ammonia—Precipitation—Flotation (l.a.p.f.). Miner. Eng. 2020, 149, 106242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, S.; Cao, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhong, H. Structural modification of hydroxamic acid collectors to enhance the flotation performance of malachite and associated mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 344, 117959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, P.; Sun, W. Adsorption mechanism and flotation behavior of ammonium salt of N-Nitroso-N-phenylhydroxyamine on malachite mineral. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 583, 152489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Han, L.; Li, C. Flotation separation performance of malachite from calcite with new chelating collector and its adsorption mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 255, 117732. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Zhu, Z.; Yin, W.; He, J. Effective flotation separation of malachite from quartz with a selective collector: Collection abil-ity, separation performance and adsorption mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wen, S.; Han, G.; Feng, Q. Interaction mechanism of copper ions with the surface of sulfidized malachite and its response to flotation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. 2022, 647, 129127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wen, S.; Cao, Q. Copper sulfide species formed on malachite surfaces in relation to flotation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 48, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Song, S.; Li, H.; Ai, G. Sulfidization flotation performance of malachite in the presence of calcite. Miner. Eng. 2019, 132, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, S.; Goldfarb, J.; Laskowski, J. Sulphidizing reactions in the flotation of oxidized copper minerals, I. Chemical factors in the sulphidization of copper oxide. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1974, 1, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, S.; Soto, H.; Goldfarb, J. Sulphidizing reactions in the flotation of oxidized copper minerals, II. Role of the adsorption and oxidation of sodium sulphide in the flotation of chrysocolla and malachite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1974, 1, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.; Adamec, E.; Lee, L. Sulfidization and flotation of chrysocolla and brochantite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1984, 12, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Chander, S. Kinetics of sulfidization of malachite in hydrosulfide and tetrasulfide solutions. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1999, 37, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Q.; Yin, W.; Yang, B.; Cao, S.; Sun, H.; Ma, Y.; Chen, K. Improving surface sulfidization of azurite with ammonium bisul-fate and its contribution to sulfidization flotation. Miner. Eng. 2021, 171, 107072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Wu, D.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z.; Wen, S.; Huang, L.; Chen, H. Corrosion activation by ammonium fluoride enhances the separation of chrysocolla and quartz by sulfidation flotation. Miner. Eng. 2022, 189, 107864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Mao, Y.; Deng, J.; Wen, S. Activation mechanism of ammonium ions on sulfidation of malachite (–201) surface by DFT study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 410, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Wen, S. Surface modification of malachite with ethanediamine and its effecton sulfidization flotation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Wu, D.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Huang, L. A DFT-based method to determine the ammonium-induced activation and sulfidation pathway of tenorite, J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. E. 2022, 132, 104221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Jia, X.; Yang, S.; Li, J.; Ning, S. Sulfidization mechanism in malachite flotation: A heterogeneous solid-liquid reaction that yields CuxSy phases grown on malachite. Miner. Eng. 2020, 154, 106420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Ao, S.; Pei, B.; Liu, D.; Li, J. Reexamining the Role of Ammonium Ions in the Sulfidization, Xanthate-Flotation of Malachite. Minerals 2020, 10, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Ma, Y.; Su, C.; Lai, H.; Shen, P.; Liu, D.; Pei, B. New insight into enhancing sulfurization of azurite with ethylenediamine and its response to xanthate adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 389, 122865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Liu, J.; Wen, S.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y. Effect of ammonium salt on the stability of surface sulfide layer of smithsonite and its flotation performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 514, 145851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wen, S.; Deng, J.; Zhao, W. Combined DFT and XPS investigation of enhanced adsorption of sulfide species onto cerussite by surface modification with chloride. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 425, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sulfurization Time (Min) | Sulfurization System | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na2S | [NH4+]-Na2S | EDA-Na2S | [NH4+]/EDA-Na2S | |
| 1 | 13.27 | 11.80 | 11.32 | 10.54 |
| 3 | 9.07 | 6.55 | 5.07 | 4.31 |
| 5 | 7.59 | 4.52 | 4.83 | 3.26 |
| 7 | 7.66 | 4.58 | 4.81 | 3.27 |
| 10 | 7.89 | 4.84 | 4.85 | 3.29 |
| 15 | 8.09 | 4.87 | 4.86 | 3.29 |
| 30 | 8.64 | 4.90 | 4.91 | 3.30 |
| 60 | 9.55 | 5.32 | 5.26 | 3.45 |
| Element. | Cu | Fe | CaO | Al2O3 | MgO | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 53.85 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 0.18 | 0.88 |
| Reagent | Chemical Formula | Purity | Function | Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfuric | H2SO4 | 98% | Purifying sulfurized products | Tiefeng |
| Sodium hydroxide | NaOH | 99% | pH regulator | Aladdin |
| Sodium sulfide | Na2S·9H2O | 99% | Activator | Aladdin |
| Ammonium sulfate | (NH4)2SO4 | 99% | Regulator | Aladdin |
| Diammonium hydrogen phosphate | (NH4)2HPO4 | 99% | Regulator | Aladdin |
| ammonium chloride | NH4Cl | 99% | Regulator | Aladdin |
| ammonium carbonate | (NH4)2CO3 | 99% | Regulator | Aladdin |
| Ethylenediamine sulfate | C2H8N2·H2SO4 | 99% | Regulator | Aladdin |
| Ethylenediamine hydrochloride | C2H8N2·2HCl | 99% | Regulator | Aladdin |
| Ethylenediamine phosphate | C2H8N2·H3PO4 | Industrial grade | Regulator | Tiefeng |
| Sodium butyl xanthate | C4H9OCSSNa | 90% | Collector | Aladdin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, C.; Liu, D.; Cai, J.; Shen, P. Ammonium–Amine Co-Activation: Promoting the Sulfurization of Azurite and Its Effect on Xanthate Adsorption. Molecules 2023, 28, 7376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217376
Su C, Liu D, Cai J, Shen P. Ammonium–Amine Co-Activation: Promoting the Sulfurization of Azurite and Its Effect on Xanthate Adsorption. Molecules. 2023; 28(21):7376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217376
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Chao, Dianwen Liu, Jinpeng Cai, and Peilun Shen. 2023. "Ammonium–Amine Co-Activation: Promoting the Sulfurization of Azurite and Its Effect on Xanthate Adsorption" Molecules 28, no. 21: 7376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217376
APA StyleSu, C., Liu, D., Cai, J., & Shen, P. (2023). Ammonium–Amine Co-Activation: Promoting the Sulfurization of Azurite and Its Effect on Xanthate Adsorption. Molecules, 28(21), 7376. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217376






