The Phase Inversion Mechanism of the pH-Sensitive Reversible Invert Emulsion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
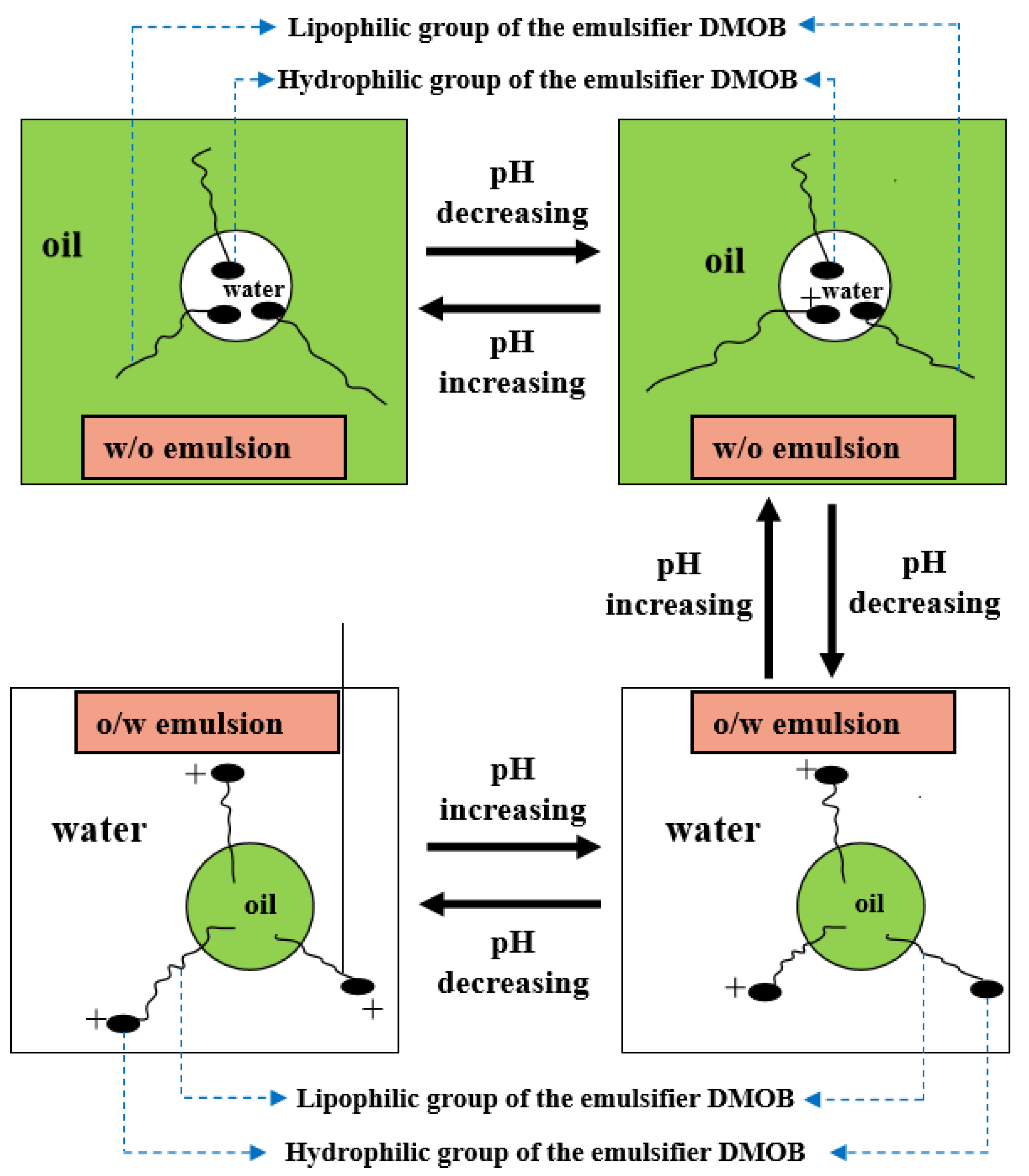
2.1. Characterization of Reversible Emulsion Phase Inversion Performance
2.2. Study on the Acid/Alkali Response Mechanism of Reversible Emulsifiers
2.2.1. Response of the Electrical Properties of Oil–Water Interface to Acid/Alkali
2.2.2. Response of the Emulsifier’s HLB Value to Acid/Alkali
HLB Values Required for Emulsifying Cottonseed Oil and Kerosene into O/W Emulsions
- (1)
- Through experiments, it was determined that the ratio of oleic acid to sodium oleate, which could emulsify cottonseed oil and deionized water into a water-in-oil emulsion and had the best stability was 23:11. The HLB value of this composite emulsifier (6.5) was the HLB value required for the emulsification of cottonseed oil into a water-in-oil emulsion, that is, E was 6.5.
- (2)
- Through experiments, it was determined that the ratio of oleic acid to sodium oleate was 11:23, which could emulsify kerosene and deionized water to form a W/O emulsion and had the best stability. The HLB value of this compound emulsifier (12.5) was the HLB value required for the emulsification of kerosene into a W/O emulsion, and F was 12.5.
Influence of Acid/Alkali on the Reversible Emulsifier’s HLB Value
- (1)
- Effect of the acid solution on the HLB value of the reversible emulsifier
- (2)
- Influence of alkali on the reversible emulsifier’s HLB value
2.2.3. The Reversible Emulsion’s Multi-Repeat Phase Conversion Performance
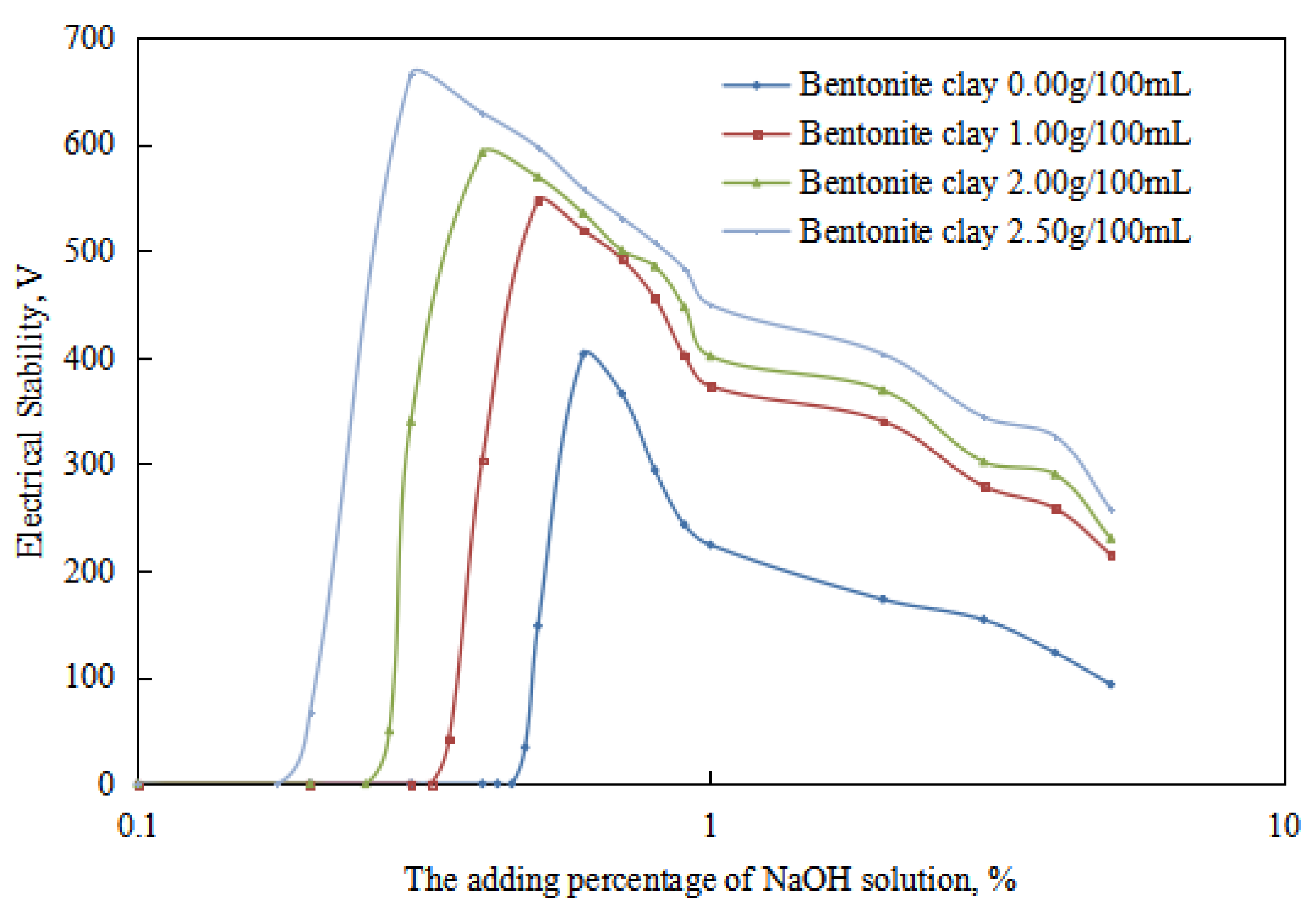
2.3. Study on the Influencing Mechanism of Organic Clay on Reversible Emulsion
2.3.1. Influence of Organic Clay on Acid-Induced Phase Transition
2.3.2. Influence of Organic Clay on Base-Induced Phase Transition
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experimental Apparatus
3.3. Experimental Method
3.3.1. Determination of the HLB Value for Reversible Emulsifiers
- (1)
- Calculation of the HLB value of composite emulsifier
- (2)
- Preparation of the emulsion
- (3)
- HLB value for emulsification of cottonseed oil and kerosene into an O/W emulsion
- (4)
- HLB value of emulsifiers with different dosages of acid/alkali
3.3.2. Preparation of the Initial Reversible Emulsion
3.3.3. Study on the Phase Inversion Performance of Reversible Emulsions
3.3.4. Study on the Stability of Reversible Emulsions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langevin, D. Recent Advances on Emulsion and Foam Stability. Langmuir 2023, 39, 3821–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcclements, D.J. Critical review of techniques and methodologies for characterization of emulsion stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 611–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jiang, G.; Fu, Y.; Yang, J.; He, Y.; Dong, T. pH-responsive water-in-oil emulsions with reversible phase inversion behavior stabilized by a novel dynamic covalent surfactant. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 364, 120004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, Q.; Li, Q.; Huang, H.; Ni, W.; Wang, Q.; Xin, X.; Zhao, B.; Chen, G. Preparation of Multifunctional Surfactants Derived from Sodium Dodecylbenzene Sulfonate and Their Use in Oil-Field Chemistry. Molecules 2023, 28, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Huang, F.; Song, S.; Ai, G.; Xin, X.; Zhao, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Recent advances in g-C3N4-based materials and their application in energy and environmental sustainability. Molecules 2023, 28, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Song, W.; Shi, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, X.; Xu, D.-L.; Li, Z. CO2-Switchable Emulsification and Demulsification of Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 11, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalvy, J.; Armes, S.; Binks, B.; Rodrigues, J.; Unali, G. Use of sterically-stabilised polystyrene latex particles as a pH-responsive particulate emulsifier to prepare surfactant-free oil-in-water emulsions. Chem. Commun. 2003, 15, 1826–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sznitowska, M.; Janicki, S.; Dabrowska, E.; Zurowska-Pryczkowska, K. Submicron emulsions as drug carriers: Studies on destabilization potential of various drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Ali, S. New opportunities for the drilling industry through innovative emulsifier chemistry. In Proceedings of the SPE International Conference on Oilfield Chemistry, Houston, TX, USA, 5–7 February 2003; p. SPE-80247-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Qi, G.; Yu, T.; Xin, X.; Zhao, B.; Chen, G. Oil-Soluble Exogenous Catalysts and Reservoir Minerals Synergistically Catalyze the Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil. Molecules 2023, 28, 6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyaa Allogo, C.-M.; Allias, B.; Tayebi, R.; Baraque, A.; Lansot, J.Y.; Diogo, J. Reversible Fluids and Mud Breaker Technology Outperforms Productivity and Injectivity in West Africa–Fit to Purpose and Designed for Success. In Proceedings of the SPE International Conference and Exhibition on Formation Damage Control, Lafayette, LA, USA, 23–24 February 2022; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Green, T.; Headley, J.; Scott, P.; Brady, S.; Haynes, L.; Pardo, C.; Dick, M. Minimizing formation damage with a reversible invert emulsion drill-in fluid. In Proceedings of the SPE/IADC Middle East Drilling Technology Conference and Exhibition, Manama, Bahrain, 22–24 October 2021; p. SPE-72283-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.; Singh, A.K.; Bidwai, N.; Indulkar, S.; Gupta, V. Innovative Surfactant Chemistry Offers the Performance Advantages to Invert Emulsion Drilling Fluids While Drilling Under Challenging Environments. In Proceedings of the SPE International Conference on Oilfield Chemistry, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 6–7 December 2021; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, S.; Natsepnskaya, A.; Okromelidze, G.; Garshina, O.; Khvotscin, P.; Grebneva, F.; Nekrasova, I. The Innovative approach to use of emulsion drilling fluid–reversible inverted drilling fluid. In Proceedings of the SPE Arctic and Extreme Environments Technical Conference and Exhibition, Moscow, Russia, 15–17 October 2013; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Dou, M.; Ma, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, B.; Chen, G. Enhanced sorption for the oil spills by SDS-modified rice straw. Gels 2023, 9, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.D. Reversible invert emulsion drilling fluids-a quantum leap in technology. In Proceedings of the IADC/SPE Asia Pacific Drilling Technology Conference and Exhibition, Jakarta, Indonesia, 7–9 September 1998; p. SPE-47772-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, M.; Svoboda, C.; Jones, M. Reversible invert emulsion system used to significantly increase water injection rates in an open hole, stand-alone screen completion in West Africa. In Proceedings of the SPE European Formation Damage Conference and Exhibition, The Hague, The Netherlands, 13–14 May 2003; p. SPE-82278-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Luyster, M.R.; Patel, A.D.; Ali, S.A. Development of a delayed-chelating cleanup technique for openhole gravel-pack horizontal completions using a reversible invert emulsion drill-in system. In Proceedings of the SPE International Conference and Exhibition on Formation Damage Control, Lafayette, LA, USA, 15–17 February 2006; p. SPE-98242-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Frenier, W.; Brady, M.; Al-Harthy, S.; Arangath, R.; Chan, K.S.; Flamant, N.; Samuel, M. Hot oil and gas wells can be stimulated without acids. SPE Prod. Facil. 2004, 19, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jin, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, L. pH-responsive drilling fluid with high-temperature and high-density performance. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 851097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, E.; Dosunmu, A.; Oriji, B.; Iyuke, S. Impact of reversible invert emulsion drilling fluid rheology on productivity. In Proceedings of the SPE Nigeria Annual International Conference and Exhibition, Lagos, Nigeria, 4–6 August 2015; p. SPE-178308-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Jiang, G.; Yang, J.; He, Y.; Fu, Y. Synthesis of a Novel pH-Responsive Emulsifier Based on Dynamic Covalent Bond and Its Application in Reversible Oil-Based Drilling Fluids. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Civil Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 313–323. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, B.; Xu, P.; Xu, M.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S. Synthesis and plugging effect of inverse emulsion polymerization microspheres (OPME) for oil-based drilling fluids. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, X.; Wang, X.; Xin, Y.; Liu, K.; Gao, L.; Du, D. The phase inversion mechanism of the pH-sensitive reversible invert emulsion from w/o to o/w. Open Phys. 2020, 18, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Alqam, M. The role of asphaltenes, resins and other solids in the stabilization of water in oil emulsions and its effects on oil production in Saudi oil fields. Fuel 2000, 79, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Masliyah, J.H. Effect of pH on adsorption and desorption of clay particles at oil–water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 181, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salager, J.-L.; Forgiarini, A.; Marquez, L.; Pena, A.; Pizzino, A.; Rodriguez, M.P.; Rondon-Gonzalez, M. Using emulsion inversion in industrial processes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 108, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salager, J.-L.; Márquez, L.; Pena, A.A.; Rondón, M.; Silva, F.; Tyrode, E. Current phenomenological know-how and modeling of emulsion inversion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 2665–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, N.; Tyrode, E.; Mira, I.; Márquez, L.; Rodríguez, M.-P.; Salager, J.-L. Emulsion catastrophic inversion from abnormal to normal morphology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S. Effect of mixing protocol on formation of fine emulsions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 3009–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.A.; Costa, J.M.R.; Menezes, R.R.; Ferreira, H.S.; Neves, G.d.A.; Ferreira, H.C. Studies of new occurrences of bentonite clays in the State of Paraíba for use in water based drilling fluids. Rem Rev. Esc. Minas 2013, 66, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vipulanandan, C.; Mohammed, A. Effect of nanoclay on the electrical resistivity and rheological properties of smart and sensing bentonite drilling muds. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 130, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Pang, S.; An, Y. Deep eutectic solvents for enhancing the rheological behavior of polymers and clays in polymeric water-based drilling fluids. Energy Fuel 2023, 37, 4391–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Masliyah, J.H. Solids-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions: Scavenging of emulsion droplets by fresh oil addition. Colloids Surf. A 1993, 75, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Masliyah, J.H. Adsorption and desorption of clay particles at the oil-water interface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 168, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, D. Encyclopedia of Emulsion Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, L.; Lu, S.; Cao, G. Stability and demulsification of emulsions stabilized by asphaltenes or resins. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 271, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Dosage of Organic Clay (g/100 mL) | Feasibility of Preparing the Initial O/W Emulsion | Feasibility of Acid-Induced Phase Transition | Feasibility of Alkali-Induced Phase Transition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 1.00 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2.00 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2.50 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3.00 | Yes | No | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, F.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X. The Phase Inversion Mechanism of the pH-Sensitive Reversible Invert Emulsion. Molecules 2023, 28, 7407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217407
Liu F, Li Y, Li X, Wang X. The Phase Inversion Mechanism of the pH-Sensitive Reversible Invert Emulsion. Molecules. 2023; 28(21):7407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217407
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Fei, Yongfei Li, Xiaqing Li, and Xuewu Wang. 2023. "The Phase Inversion Mechanism of the pH-Sensitive Reversible Invert Emulsion" Molecules 28, no. 21: 7407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217407
APA StyleLiu, F., Li, Y., Li, X., & Wang, X. (2023). The Phase Inversion Mechanism of the pH-Sensitive Reversible Invert Emulsion. Molecules, 28(21), 7407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217407





