Sequential Extraction and Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Monitoring in the Biorefining of Brewer’s Spent Grain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of BSG
| Non-Essential AAs | Concentration (mg/kg dm) | Essential AAs | Concentration (mg/kg dm) | Essential AAs for Adults (mg/kg/day) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspartic acid | 20 ± 1 | Histidine | 24 ± 1 | 10 |
| Glutamic acid | 43 ± 1 | Threonine | 15 ± 0 | 15 |
| Asparagine | 20 ± 0 | Methionine | 13 ± 1 | 10.4 |
| Serine | 18 ± 0 | Tryptophan | 14 ± 0 | 4 |
| Glutamine | 70 ± 2 | Valine | 38 ± 1 | 26 |
| Alanine | 29 ± 1 | Phenylalanine | 44 ± 1 | 25 |
| Arginine | 125 ± 2 | Isoleucine | 20 ± 1 | 20 |
| Glycine | 9 ± 0 | Leucine | 58 ± 1 | 39 |
| Tyrosine | 32 ± 1 | Lysine | 63 ± 1 | 30 |
| TOTAL | 335 ± 7 | TOTAL | 320 ± 7 | 184 |
| TAAs | 655 ± 14 | |||
2.2. Fractionation Process of BSG
2.3. ATR-FTIR Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Analytical Methods
3.2.1. Determination of Moisture, Lipid, Ash, Total Nitrogen, and Protein Content
3.2.2. Determination of β-Glucans, Starch, and Residual Sugars
3.2.3. Determination of Arabinoxylans, Lignin, and Cellulose
3.2.4. Determination of Total Polyphenols, Phenolic Acids, and Free Amino Acids
3.3. Fractionation of BSG
3.4. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2019. Moving Forward on Food Loss and Waste Reduction. Rome. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/ca6030en/ca6030en.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2023).
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affair. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2022. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2022/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2022.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2023).
- Jones, R.E.; Renouf, M.A.; Speight, R.E.; Blinco, J.L.; O’Hara, I.M. SeqFLoW: A systematic approach to identify and select food waste valorisation opportunities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 189, 106732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsegaye, B.; Jaiswal, S.; Jaiswal, A.K. Food Waste Biorefinery: Pathway towards Circular Bioeconomy. Foods 2021, 10, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statista. Beer Production Worldwide from 2008 to 2021, by Region. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/270270/worldwide-beer-production-by-region/ (accessed on 19 October 2023).
- The Brewers of Europe. European Beer Trends, 2022 Edition. Available online: https://brewersofeurope.org/site/index.php (accessed on 19 October 2023).
- Nyhan, L.; Sahin, A.W.; Schmitz, H.H.; Siegel, J.B.; Arendt, E.K. Brewers’ Spent Grain: An Unprecedented Opportunity to Develop Sustainable Plant-Based Nutrition Ingredients Addressing Global Malnutrition Challenges. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 10543–10564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assobirra. Annual Report. Available online: https://www.assobirra.it/annual-report-assobirra/ (accessed on 19 October 2023).
- Statista. Volume of By-Products Obtained from Brewing in Italy from 2018 to 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/936536/by-products-from-brewing-in-italy/ (accessed on 19 October 2023).
- Kavalopoulos, M.; Stoumpou, V.; Christofi, A.; Mai, S.; Barampouti, E.M.; Moustakas, K.; Malamis, D.; Loizidou, M. Sustainable valorisation pathways mitigating environmental pollution from brewers’ spent grains. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sganzerla, W.G.; Ampese, L.C.; Mussatto, S.I.; Forster-Carneiro, T. A bibliometric analysis on potential uses of brewer’s spent grains in a biorefinery for the circular economy transition of the beer industry. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefin. 2021, 15, 1965–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazanfarzadeh, Z.; Ganesan, A.R.; Mariniello, L.; Conterno, L.; Kumaravel, V. Valorization of brewer’s spent grain for sustainable food packaging. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 385, 135726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, F.; Skov, P.V. Potentials and limitations of utilising brewer’s spent grain as a protein source in aquaculture feeds. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 357, 131986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Johansen, A.Z.; Mussatto, S.I. Evaluation of different pretreatment strategies for protein extraction from brewer’s spent grains. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 125, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.M.; Camina, J.L.; Borroni, V.; Péreza, E.E. Protein Recovery from Brewery Solid Wastes. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 134810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Gregor, T.; Wimmer, R. Utilising brewer’s spent grain as a source of cellulose nanofibres following separation of protein-based biomass. BioResources 2017, 12, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, A.; Piggott, C.O.; Fitzgerald, R.J. Characterisation of protein-rich isolates and antioxidative phenolic extracts from pale and black brewers’ spent grain. Int. J. Food Sci.Technol. 2013, 48, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, A.; Castiglione, F.; Ferro, M.; Colombo Dugoni, G.; Di Pietro, M.E.; Mannu, A.; Panzeri, W. Process for Biomass Treatment. Patent WO2020234761 A1, 26 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Outeiriño, D.; Costa-Trigo, I.; Paz, A.; Deive, F.J.; Rodríguez, A.; Domínguez, J.M. Biorefining brewery spent grain polysaccharides through biotuning of ionic liquids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outeiriño, D.; Costa-Trigo, I.; Pinheiro de Souza Oliveira, R.; Pérez Guerra, N.; Domínguez, J.M. A novel approach to the biorefinery of brewery spent grain. Process Biochem. 2019, 85, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radošević, K.; Železnjak, J.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Slivac, I.; Srček, V.G. Comparative in vitro study of cholinium-based ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents toward fish cell line. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 131, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeko-Pivač, A.; Tišma, M.; Žnidaršič-Plazl, P.; Kulisic, B.; Sakellaris, G.; Hao, J.; Planinić, M. The Potential of Brewer’s Spent Grain in the Circular Bioeconomy: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 870744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, O.; Marrocchi, A. Process for treating of Brewing Industry by-products. Patent WO2023012841 A1, 9 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bravi, E.; De Francesco, G.; Sileoni, V.; Perretti, G.; Galgano, F.; Marconi, O. Brewing By-Product Upcycling Potential: Nutritionally Valuable Compounds and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA, European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Dietary Reference Values for protein. EFSA J. 2011, 20, 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Sileoni, V.; Alfeo, V.; Bravi, E.; Belardi, I.; Marconi, O. Upcycling of a by-product of the brewing production chain as an ingredient in the formulation of functional shortbreads. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 98, 105292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchami, M.; Agnihotri, S.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Aqueous ethanol organosolv process for the valorization of Brewer’s spent grain (BSG). Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanho, M.N.; De Souza do Prado, K.; De Paiva, J.M.F. Developing thermoplastic corn starch composites filled with brewer’s spent grain for applications in biodegradable films. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA, European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to barley beta-glucans and lowering of blood cholesterol and reduced risk of (coronary) heart disease pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Ho, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Marconi, O.; Marrocchi, A.; Kim, C.J. Brewers’ spent grain (BSG)-based green dielectric materials for low-voltage operating solution-processed organic field-effect transistors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 15194–15199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA, European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to arabinoxylan produced from wheat endosperm and reduction of post-prandial glycaemic responses (ID 830) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Kuhn, D.D.; Ogejo, J.A.; O’Keefe, S.F.; Fraguas, C.F.; Wiersema, B.D.; Jin, Q.; Yu, D.; Huang, H. Wet fractionation process to produce high protein and high fiber products from brewer’s spent grain. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 117, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.P.S.; Bhandari, S.; Bhatta, D.; Poudel, A.; Bhattarai, S.; Yadav, P.; Ghimire, N.; Paudel, P.; Paudel, P.; Shrestha, J.; et al. Biochar application: A sustainable approach to improve soil health. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 11, 100498. [Google Scholar]
- Naibaho, J.; Korzeniowska, M.; Wojdyło, A.; Figiel, A.; Yang, B.; Laaksonen, O.; Foste, M.; Vilu, R.; Viiard, E. Fiber modification of brewers’ spent grain by autoclave treatment to improve its properties as a functional food ingredient. LWT 2021, 149, 111877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naibaho, J.; Butula, N.; Jonuzi, E.; Korzeniowska, M.; Laaksonen, O.; Föste, M.; Kütt, M.L.; Yang, B. Potential of brewers’ spent grain in yogurt fermentation and evaluation of its impact in rheological behaviour, consistency, microstructural properties and acidity profile during the refrigerated storage. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaguey-Hernández, Y.; Tapia-Ignacio, C.; Aguilar-Arteaga, K.; González-Olivares, L.G.; Castañeda-Ovando, E.P.; Cruz-Cansino, N.; Ojeda-Ramirez, D.; Castañeda-Ovando, A. Thermoplastic biofilms obtained from an arabinoxylan-rich fraction from brewers’ spent grain: Physicochemical characterization and thermal analysis. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 13, 14035–14047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grams, J. Surface Analysis of Solid Products of Thermal Treatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 161, 105429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellebois, T.; Gaiani, C.; Planchon, S.; Renaut, J.; Soukoulis, C. Impact of heat treatment on the acid induced gelation of brewers’ spent grain protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.; Mohamed, F.M.; Lu, N.A.L.M.I.; Sarman, N.S.P.; Samsudin, S.N.S. Computer-assisted analysis of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectra for characterization of various treated and untreated agriculture biomass. BioResources 2012, 7, 5367–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Brewery Convention Method Collection. Moisture Content of Spent Grain, 12.2. In Analytica EBC; Fachverlag Hans Carl GmbH: Nurnberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- European Brewery Convention Method Collection. Fatty substances in cereal adjuncts, 6.10. In Analytica EBC; Fachverlag Hans Carl GmbH: Nurnberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; AOAC Int.: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- European Brewery Convention Method Collection. Total Nitrogen of Malt: Kjeldahl Method, 4.3.1. In Analytica EBC; Fachverlag Hans Carl GmbH: Nurnberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- European Brewery Convention Method Collection. High Molecular Weight β-Glucan Content of Malt: Enzymatic Method, 4.16.1. In Analytica EBC; Fachverlag Hans Carl GmbH: Nurnberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Marconi, O.; Tomasi, I.; Sileoni, V.; Bonciarelli, U.; Guiducci, M.; Maranghi, S.; Perretti, G. Effects of Growth Conditions and Cultivar on the Content and Physiochemical Properties of Arabinoxylan in Barley. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Crocker, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass. In Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP); National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagent. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagnari, F.; Galieni, A.; D’Egidio, S.; Falcinelli, B.; Pagnani, G.; Pace, R.; Pisante, M.; Paolo, B. Effects of sprouting and salt stress on polyphenol composition and antiradical activity of einkorn, emmer and durum wheat. Ital. J. Agron. 2017, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, O.; Mayer, H.; Chiacchieroni, F.; Ricci, E.; Perretti, G.; Fantozzi, P. The influence of glumes on malting and brewing of hulled wheats. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2013, 71, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, F.; Kim, C.; Marrocchi, A.; Vaccaro, L. Green solvent-processed organic electronic devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 15027–15047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocchi, A.; Adriaensens, P.; Bartollini, E.; Barkakati, B.; Carleer, R.; Chen, J.; Hensley, D.K.; Petrucci, C.; Tassi, M.; Vaccaro, L. Novel cross-linked polystyrenes with large space network as tailor-made catalyst supports for sustainable media. Eur. Pol. J. 2015, 73, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börjesson, M.; Westman, G.; Larsson, A.; Ström, A. Thermoplastic and Flexible Films from Arabinoxylan. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härdelin, L.; Ström, A.; Di Maio, E.; Iannace, S.; Larsson, A. Microcellular foaming of arabinoxylan and PEGylated arabinoxylan with supercritical CO2. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
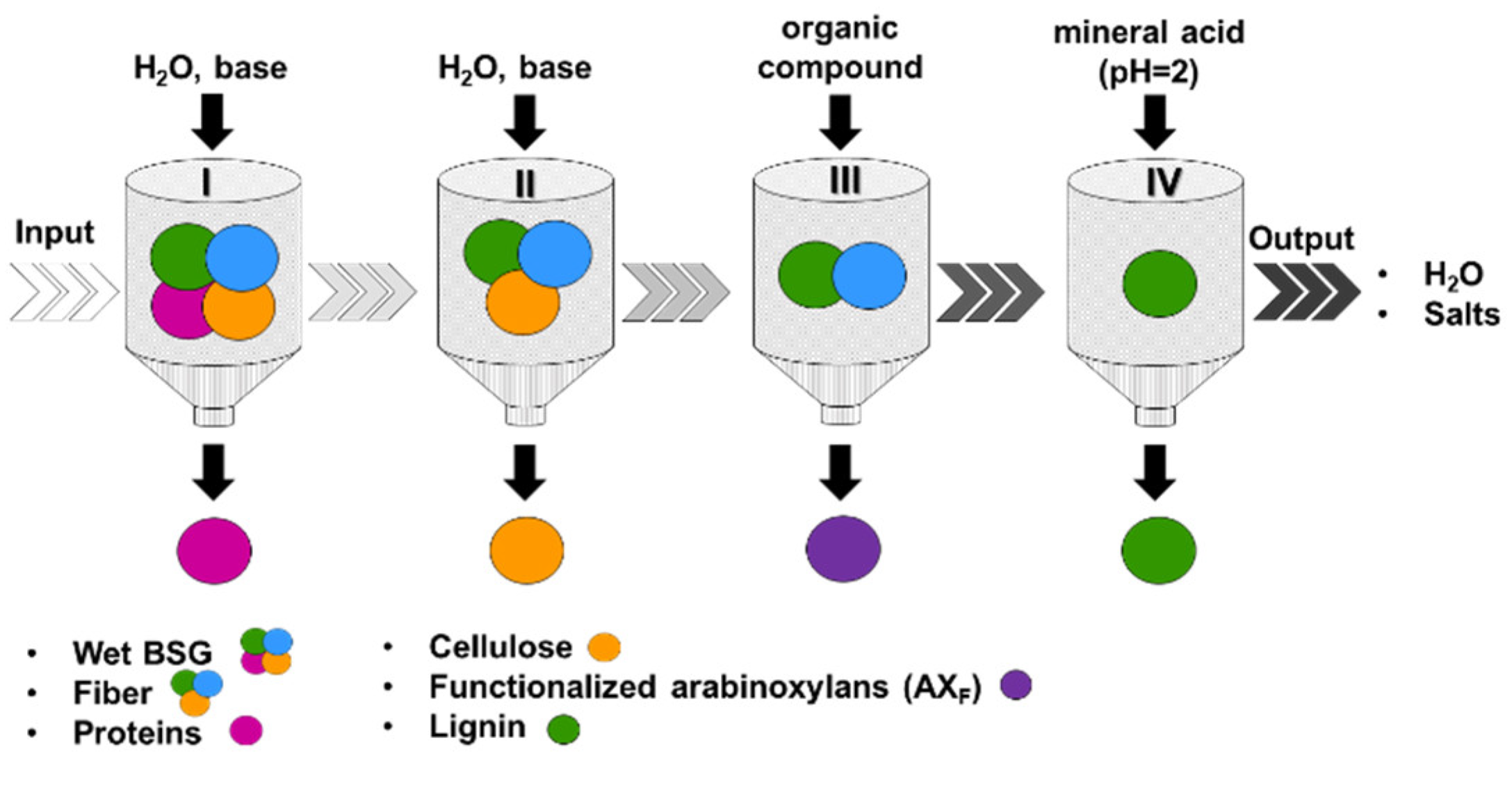
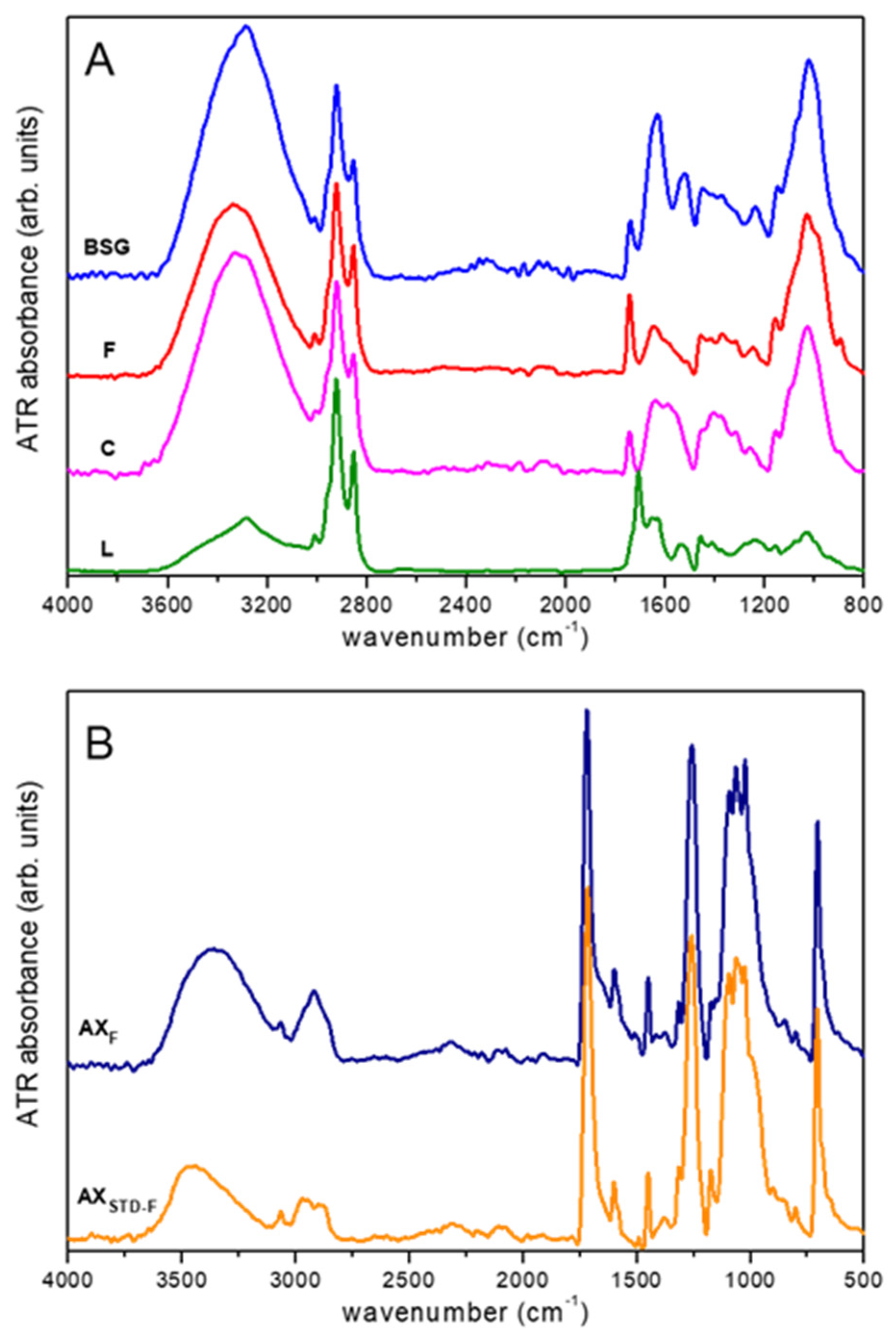
| BSG Components | Concentration (% dm 2) |
|---|---|
| Moisture | 83.5 ± 0.2 3 |
| Total nitrogen | 3.62 ± 0.02 |
| Proteins | 22.64 ± 0.12 |
| Lipids | 7.33 ± 0.23 |
| Ash | 3.51 ± 0.02 |
| Starch | 6.8 ± 0.9 |
| Residual sugars | 2.7 ± 0.0 |
| Total fiber | 56.54 ± 1.3 |
| β-glucans | 0.54 ± 0.07 |
| Cellulose | 19.78 ± 0.82 |
| Arabinoxylans | 17.11 ± 1.86 |
| Total lignin | 19.65 ± 0.25 |
| Soluble lignin | 1.42 ± 0.07 |
| Insoluble lignin | 18.23 ± 0.32 |
| Polyphenol | Concentration (mg GAE g−1 dm) |
|---|---|
| FP | 0.84 ± 0.03 |
| BP | 6.35 ± 0.34 |
| TOTAL | 7.41 ± 0.12 |
| Free Phenolic Acids | Concentration (µg g−1 dm) |
| α-resorcylic acid | 17.1 ± 2.2 |
| Syringic acid | 24.7 ± 2.7 |
| Homovanillic acid | 47.5 ± 3.1 |
| p-Coumaric acid | 10.0 ± 0.6 |
| Salicylic acid | 19.8 ± 0.7 |
| Ferulic acid | 21.1 ± 1.4 |
| Sinapic acid | 11.7 ± 0,9 |
| TOTAL | 151.9 ± 7.8 |
| Bound Phenolic Acids | Concentration (µg g−1 dm) |
| α-resorcylic acid | 13.9 ± 1.8 |
| p-hydroxybenzoic acid | 4.7 ± 0.6 |
| Vanillic acid | 11.9 ± 0.3 |
| Caffeic acid | 27.3 ± 1.4 |
| p-coumaric acid | 170.9 ± 6.7 |
| Salicylic acid | 126.1 ± 4.1 |
| Ferulic acid | 247.1 ± 6.4 |
| Sinapic acid | 42.2 ± 3.0 |
| TOTAL | 630.1 ± 93.4 |
| Total phenolic acids | 782.0 ± 5.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belardi, I.; Marrocchi, A.; Alfeo, V.; Sileoni, V.; De Francesco, G.; Paolantoni, M.; Marconi, O. Sequential Extraction and Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Monitoring in the Biorefining of Brewer’s Spent Grain. Molecules 2023, 28, 7992. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247992
Belardi I, Marrocchi A, Alfeo V, Sileoni V, De Francesco G, Paolantoni M, Marconi O. Sequential Extraction and Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Monitoring in the Biorefining of Brewer’s Spent Grain. Molecules. 2023; 28(24):7992. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247992
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelardi, Ilary, Assunta Marrocchi, Vincenzo Alfeo, Valeria Sileoni, Giovanni De Francesco, Marco Paolantoni, and Ombretta Marconi. 2023. "Sequential Extraction and Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Monitoring in the Biorefining of Brewer’s Spent Grain" Molecules 28, no. 24: 7992. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247992
APA StyleBelardi, I., Marrocchi, A., Alfeo, V., Sileoni, V., De Francesco, G., Paolantoni, M., & Marconi, O. (2023). Sequential Extraction and Attenuated Total Reflection–Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Monitoring in the Biorefining of Brewer’s Spent Grain. Molecules, 28(24), 7992. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247992









