A Comprehensive Review of Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting Bruton Tyrosine Kinase: Synthetic Approaches and Clinical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Signaling Pathway of BTK
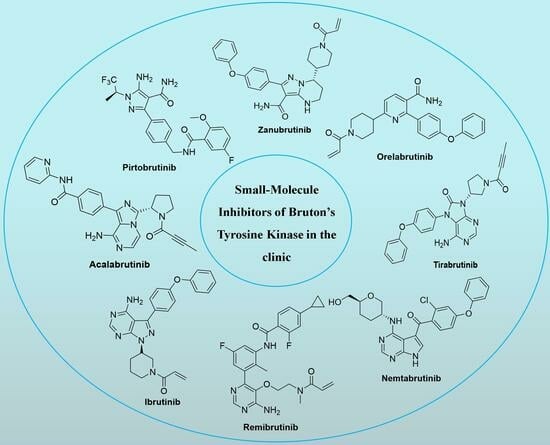
3. Representative Small-Molecule BTK Inhibitors in the Clinic
3.1. Aminopyrimidines
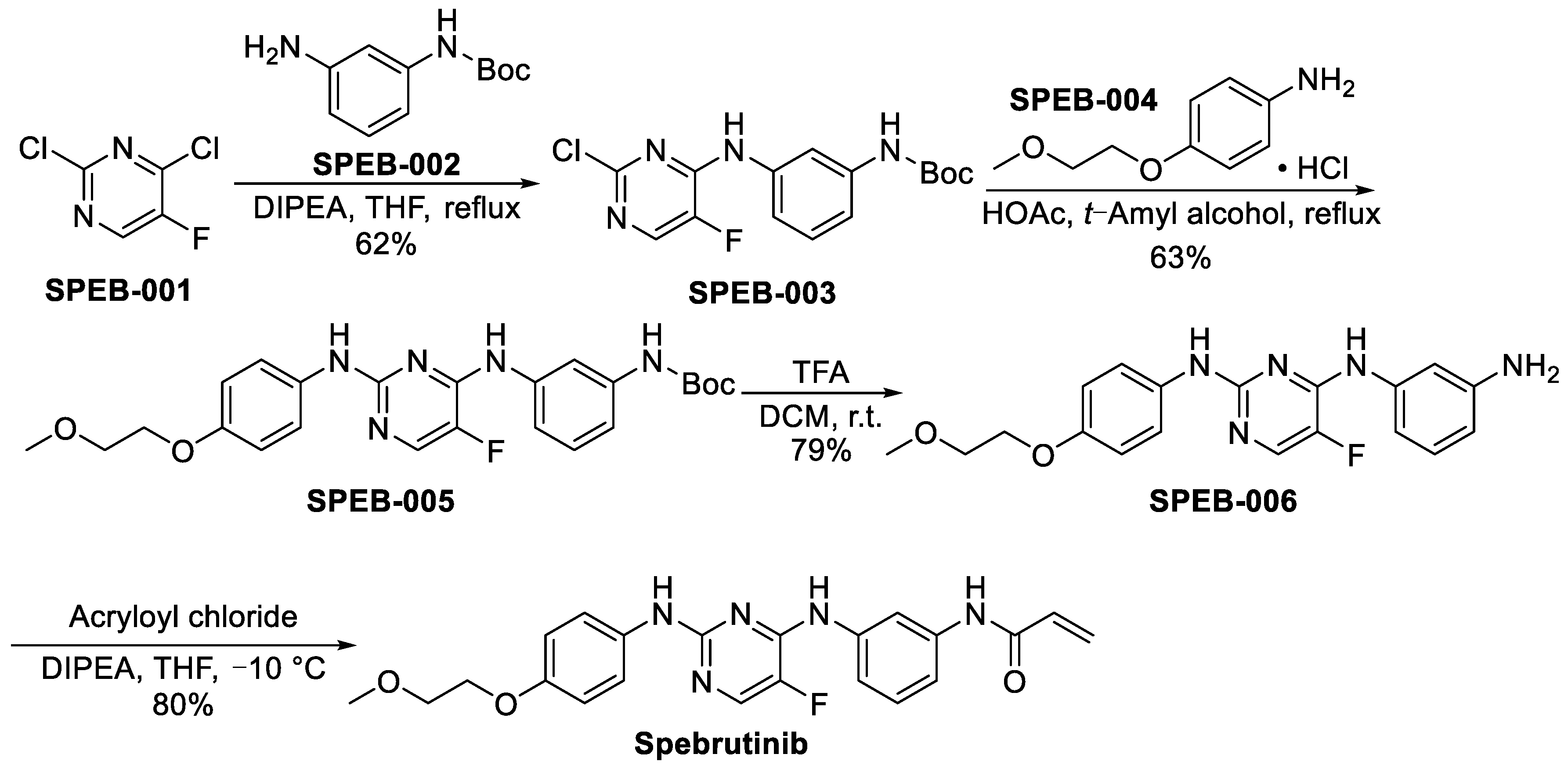
3.1.1. Spebrutinib (CC-292)
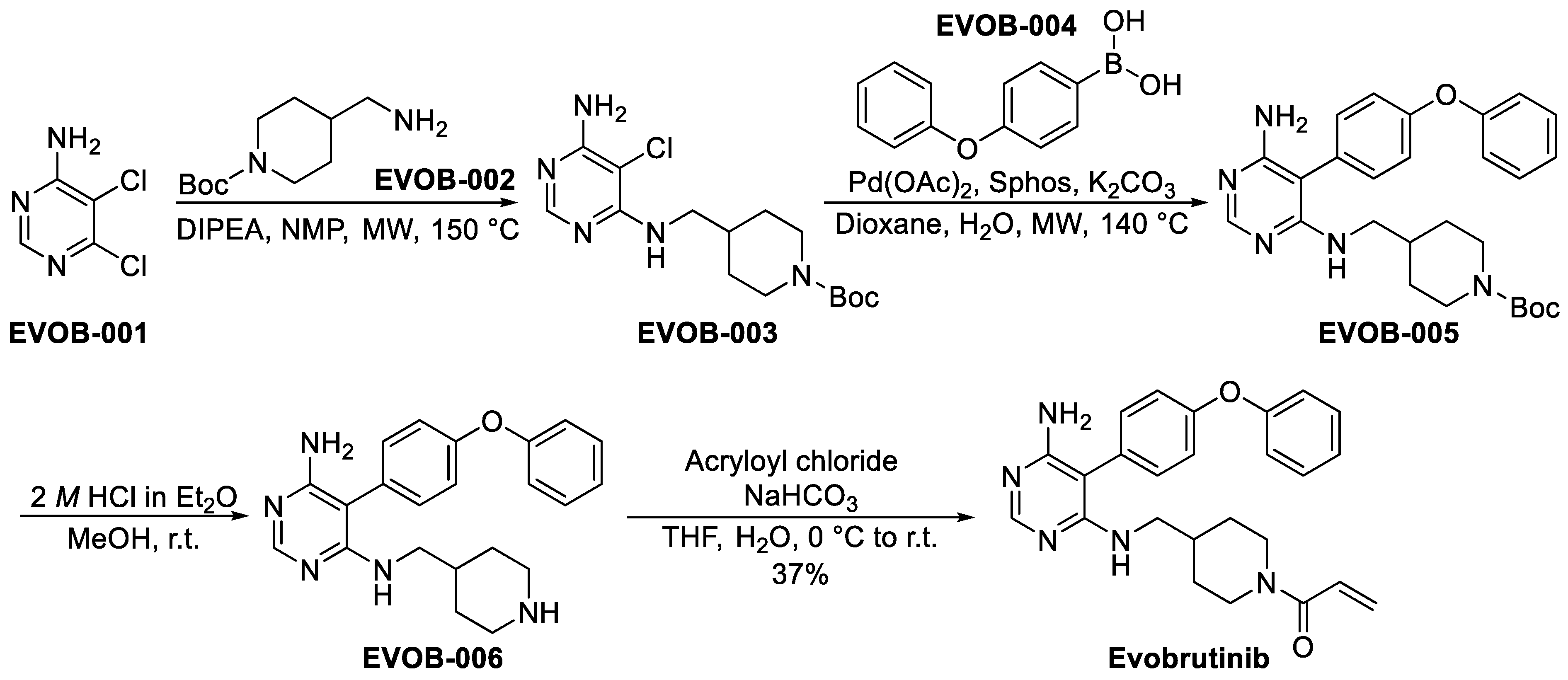
3.1.2. Evobrutinib (M-2951)
3.1.3. Remibrutinib (LOU-064)
3.2. Pyrimidine-Fused Bicyclic Heterocycles
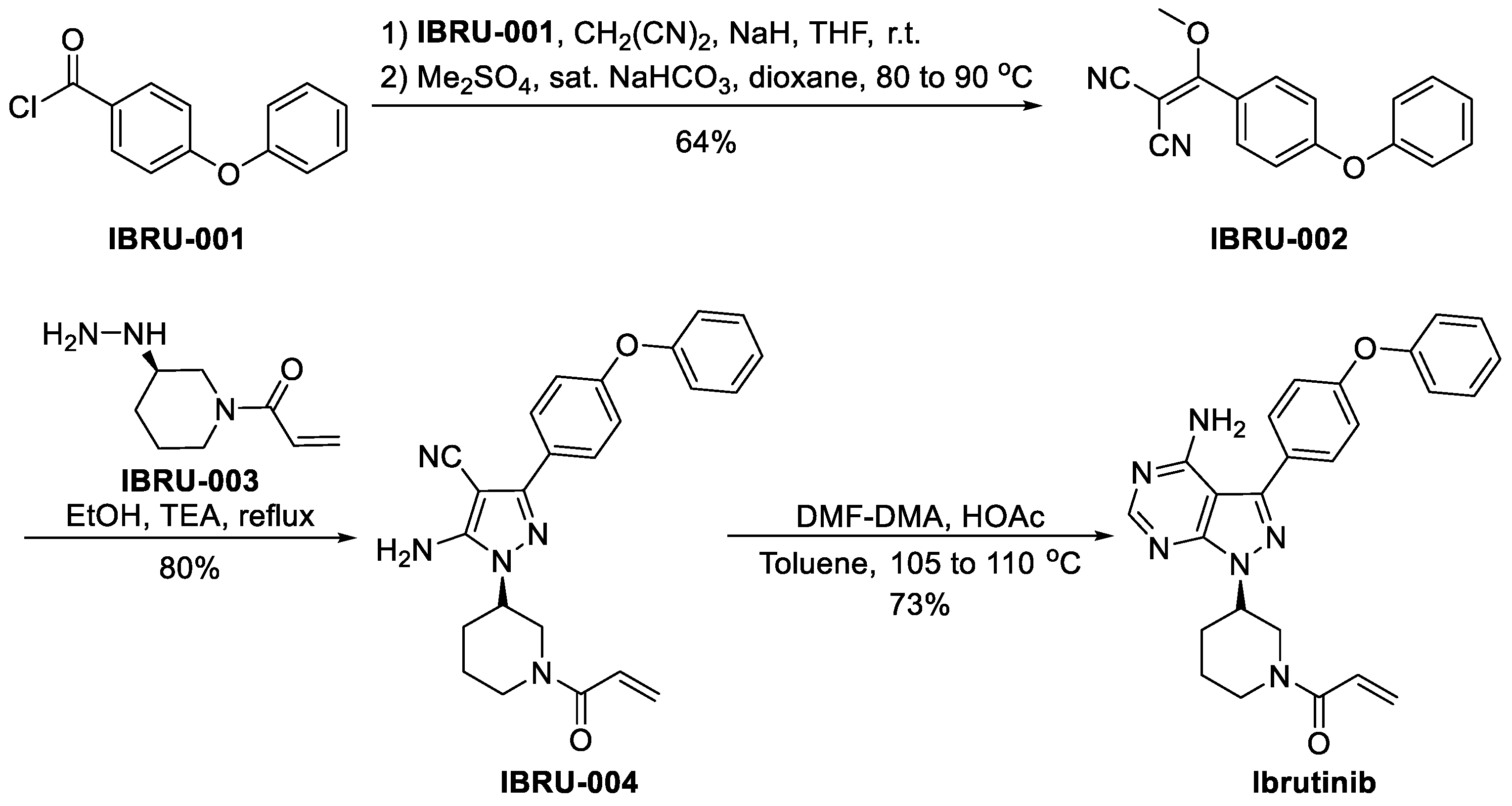
3.2.1. Ibrutinib (Imbruvica, PCI-32765)
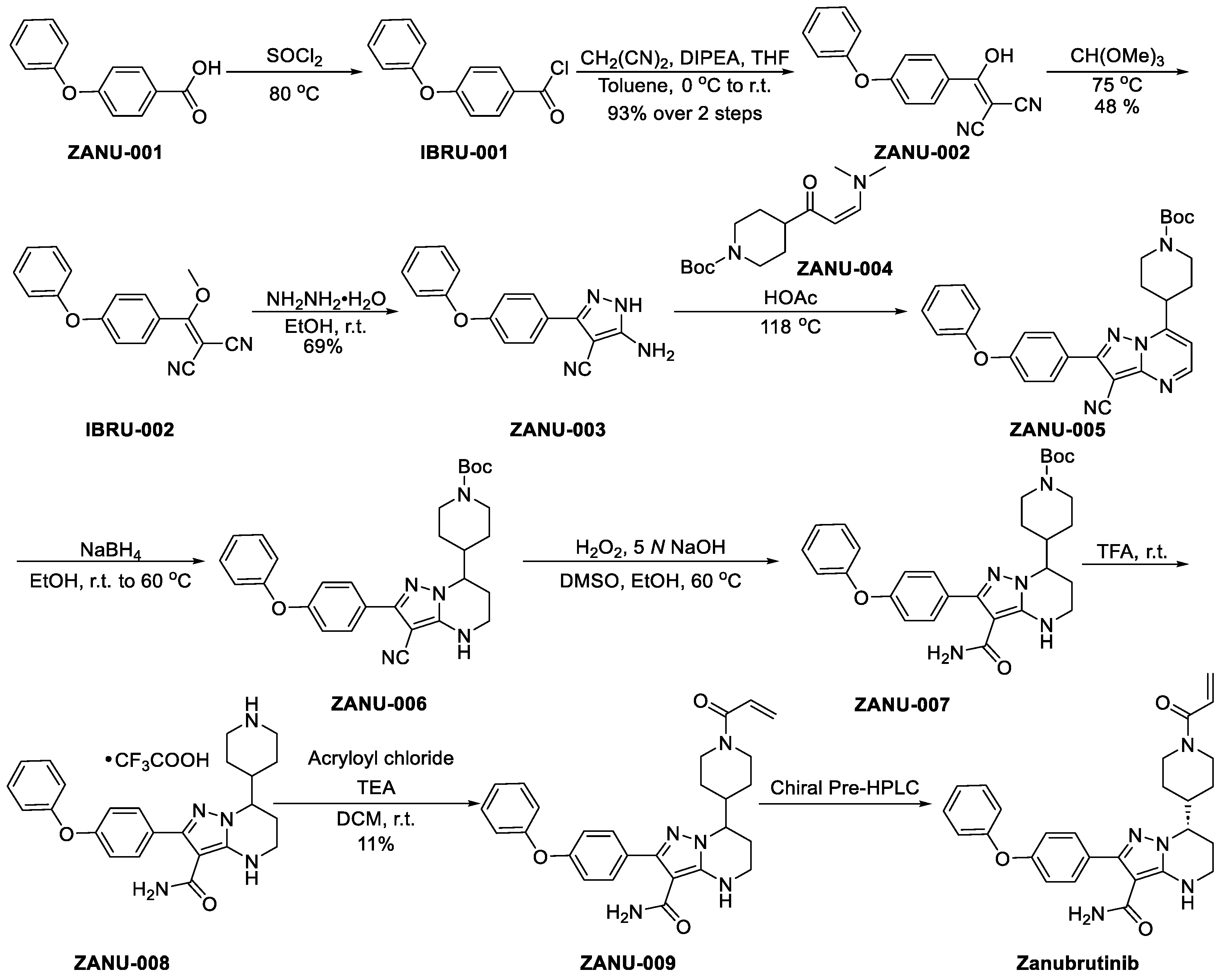
3.2.2. Zanubrutinib (Brukinsa, BGB-3111)
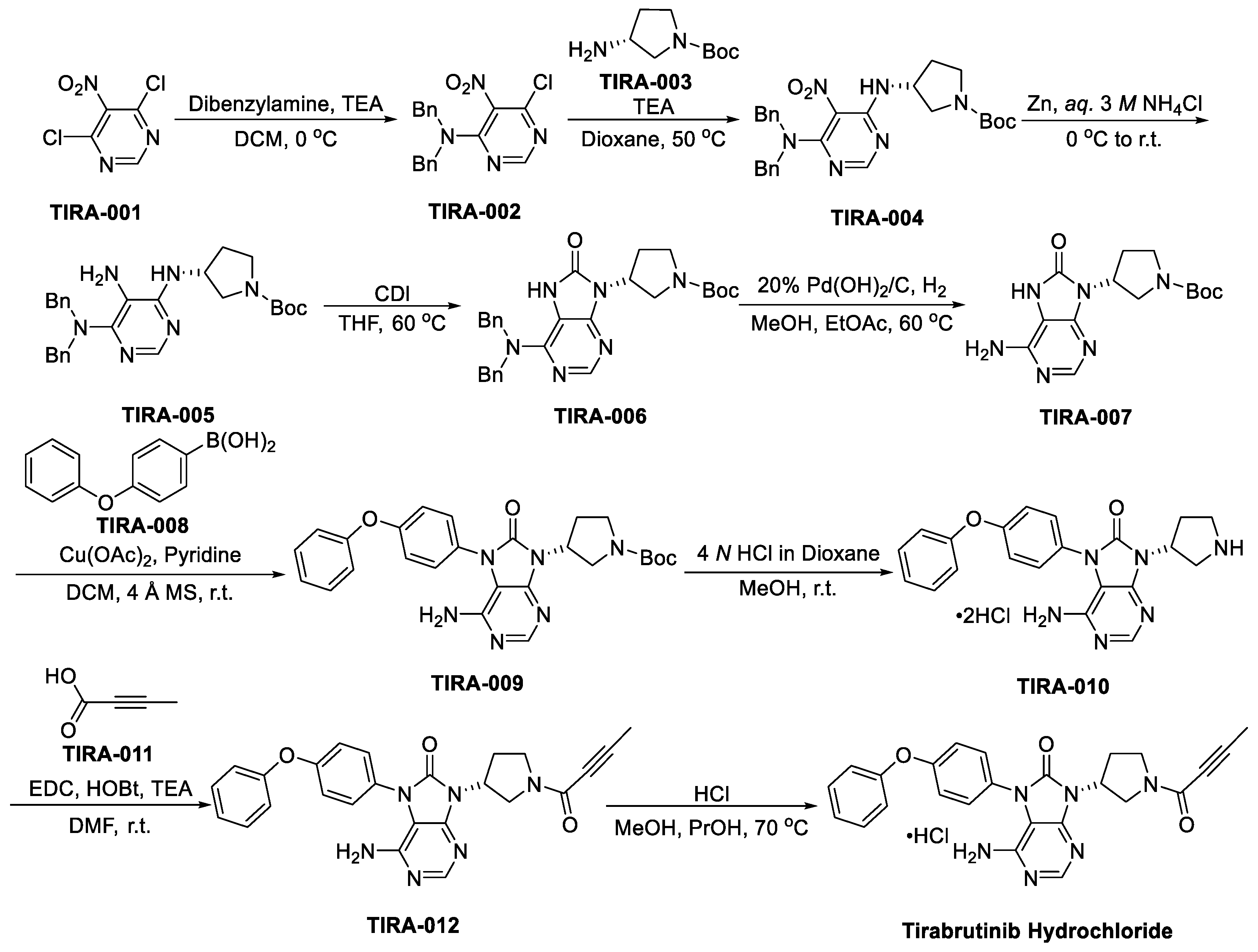
3.2.3. Tirabrutinib (Velexbru, ONO/GS-4059)
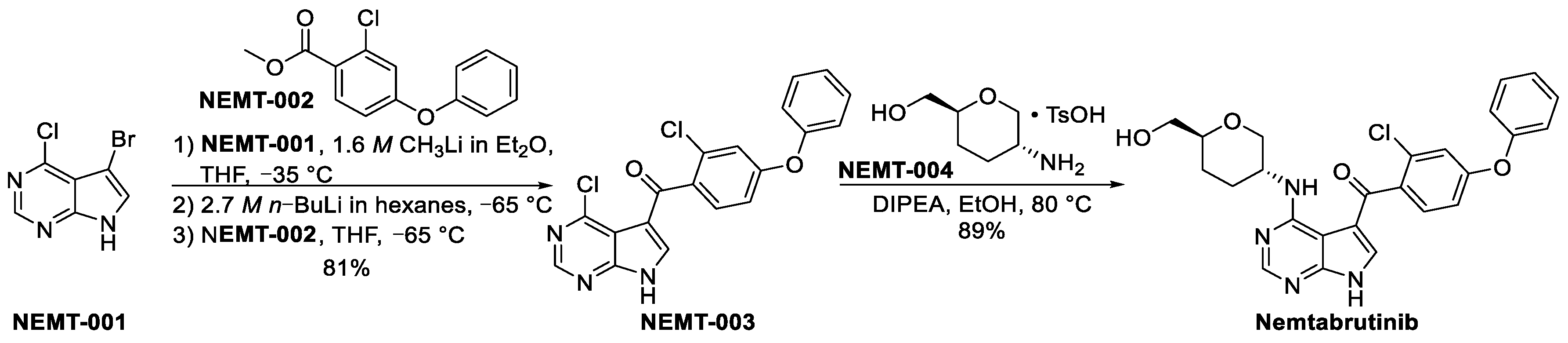
3.2.4. Nemtabrutinib (MK-1026)
3.2.5. Rilzabrutinib (PRN-1008)
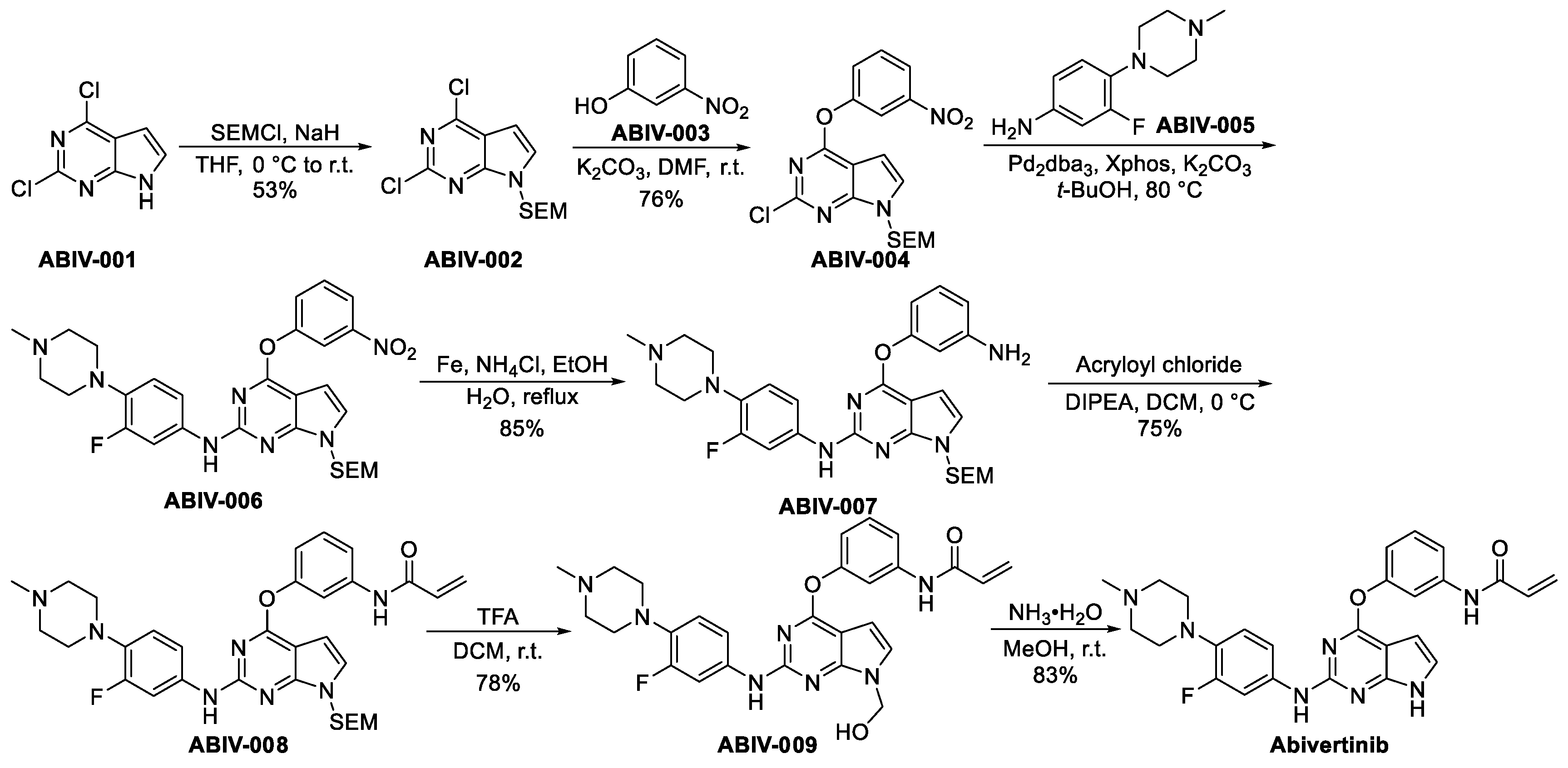
3.2.6. Abivertinib (AC-0010)
3.3. Benzopyrroles
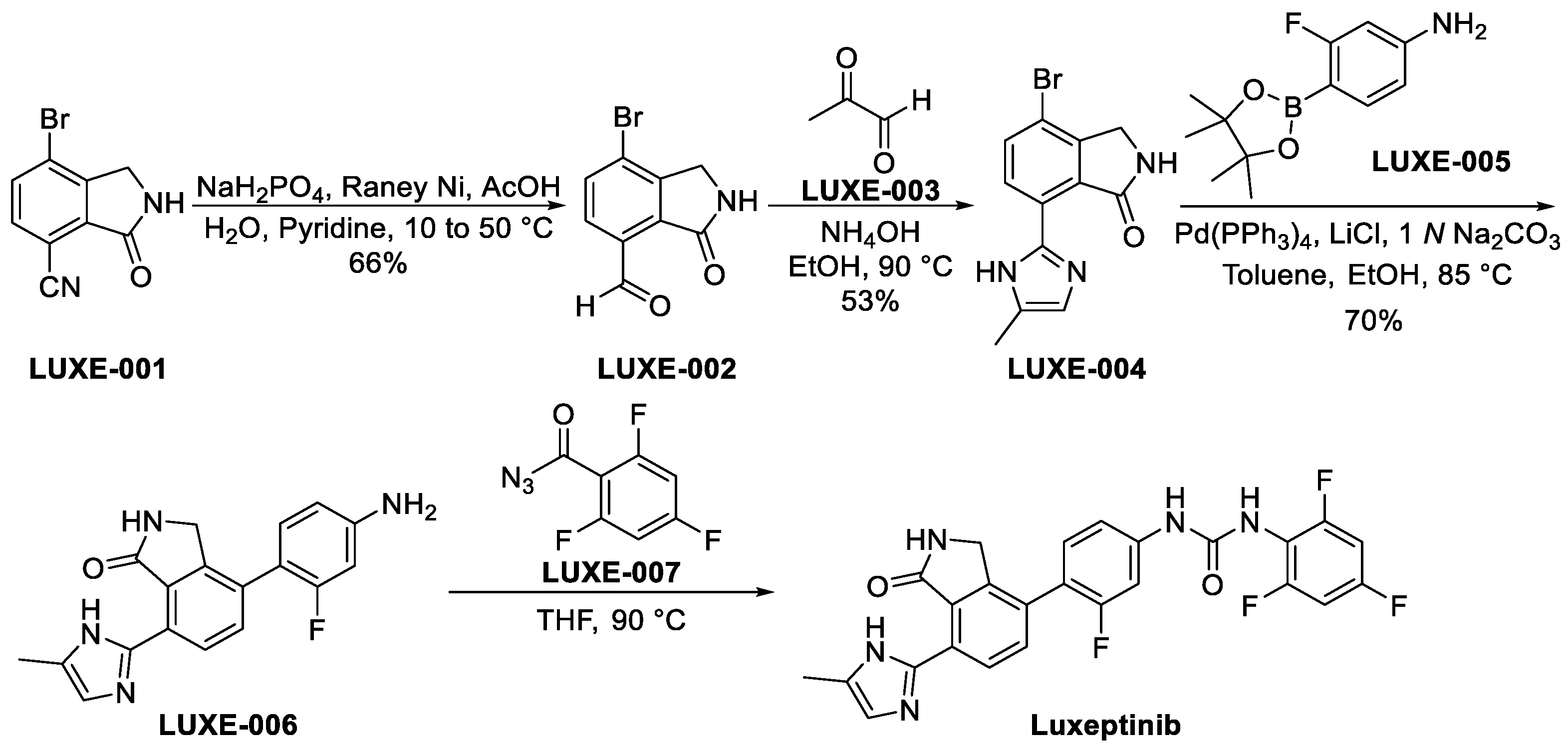
3.3.1. Luxeptinib (CG-806)
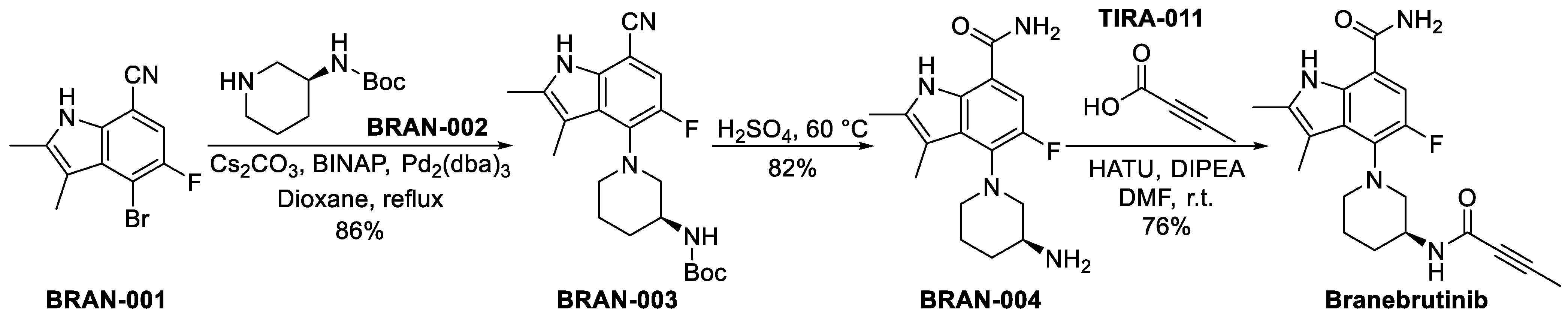
3.3.2. Branebrutinib (BMS-986195)
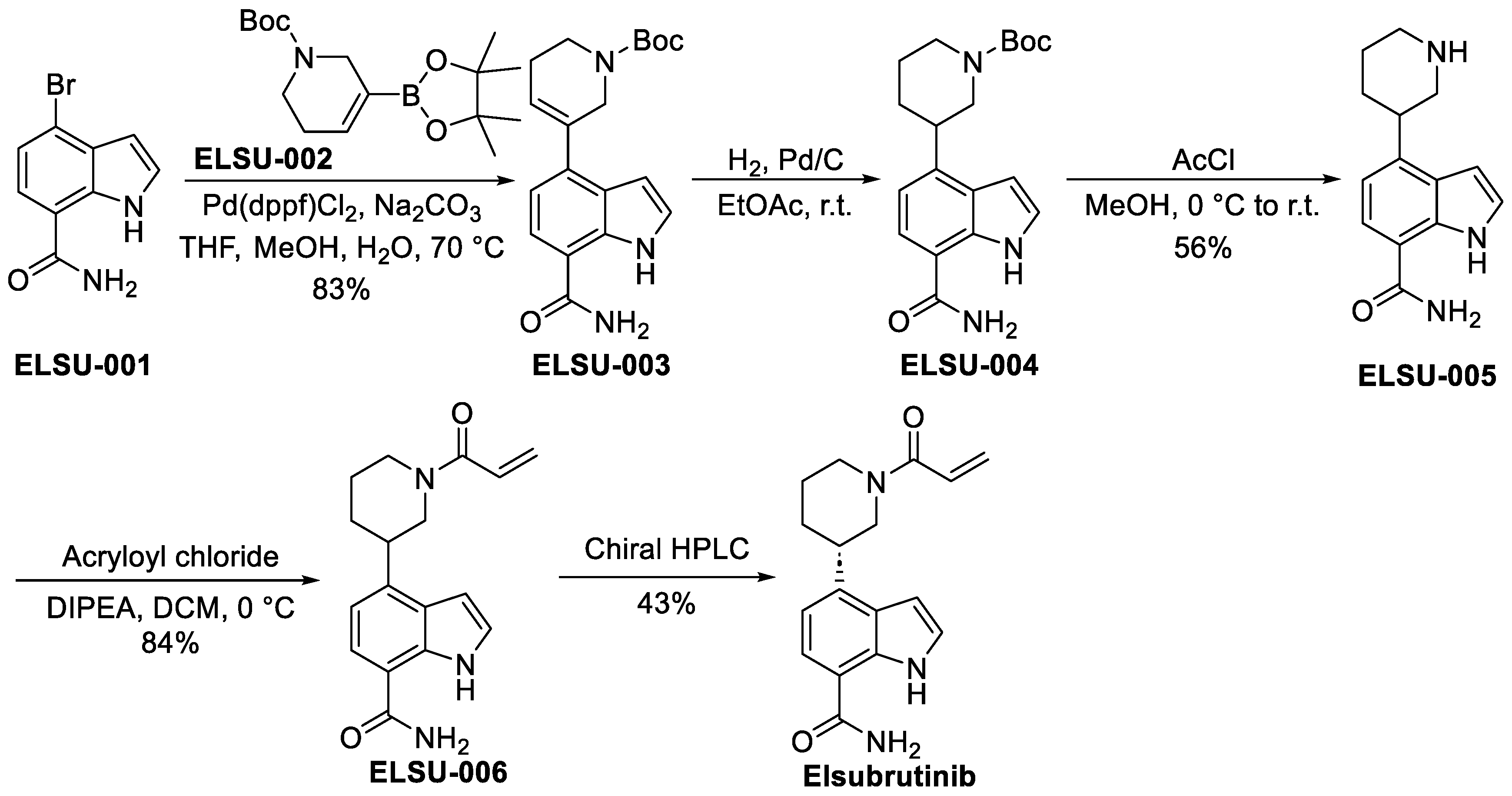
3.3.3. Elsubrutinib (ABBV-105)
3.4. Pyrazine-Fused Bicyclic Heterocycles
3.4.1. Acalabrutinib (Calquence, ACP-196)
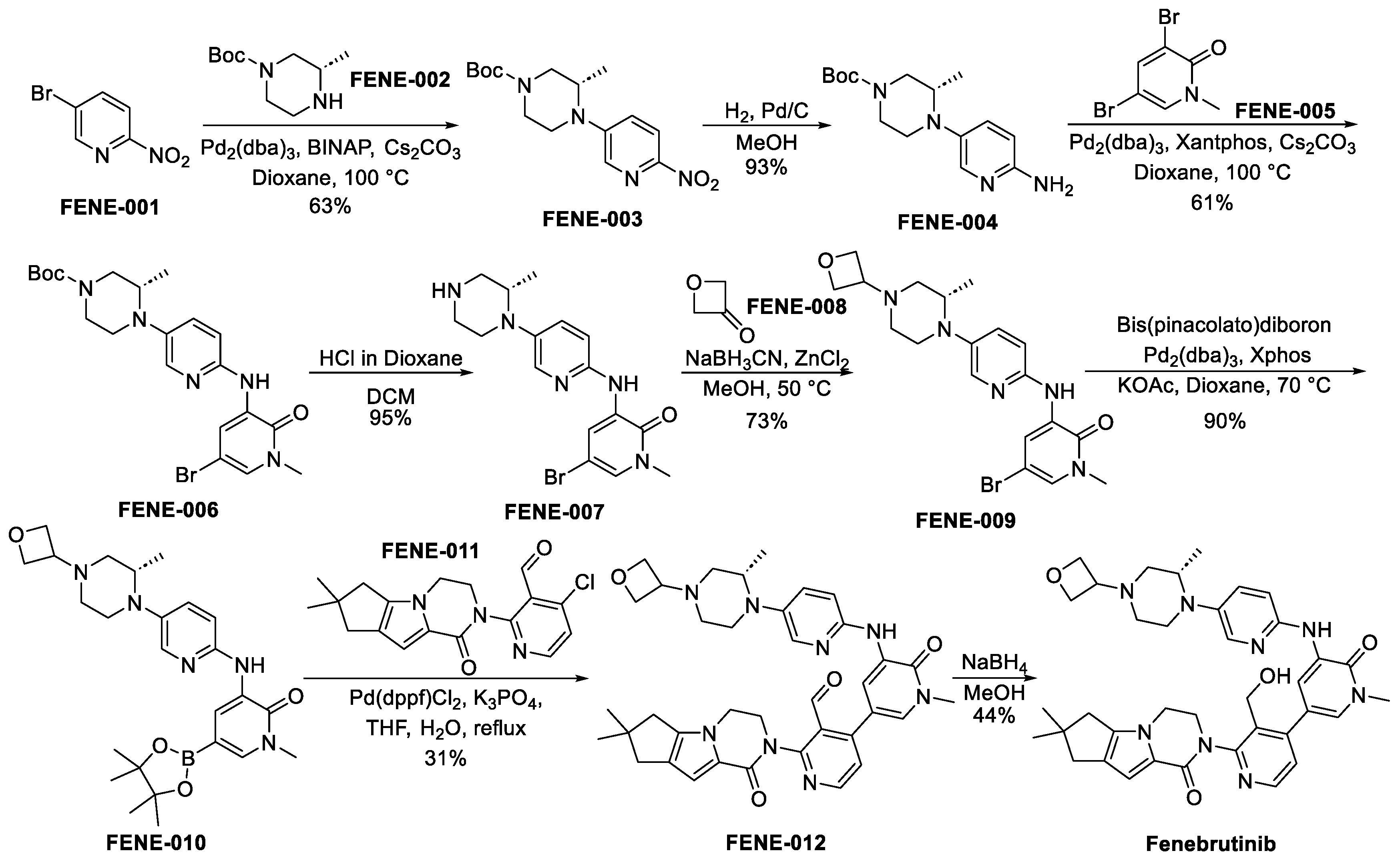
3.4.2. Fenebrutinib (GDC-0853)
3.5. Others
3.5.1. Orelabrutinib (ICP-022)
3.5.2. Pirtobrutinib (Jaypirca, LOXO-305)
3.5.3. Tolebrutinib (SAR-442168)
4. Challenge and Prospective
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pal Singh, S.; Dammeijer, F.; Hendriks, R.W. Role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Padron, E.J.; Rammohan, K.W.; Goodman, C.F. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors: The next frontier of B-cell-targeted therapies for cancer, autoimmune disorders, and multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Wiestner, A. Targeting B cell receptor signalling in cancer: Preclinical and clinical advances. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 148–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Duan, W.; Cu, X.; Liang, C.; Xin, M. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors in treating cancer: A patent review (2010–2018). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 217–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gong, H.; Meng, F. Recent advances in BTK inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alu, A.; Lei, H.; Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. BTK inhibitors in the treatment of hematological malignancies and inflammatory diseases: Mechanisms and clinical studies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Claro, R.A.; McGinn, K.M.; Verdun, N.; Lee, S.L.; Chiu, H.J.; Saber, H.; Brower, M.E.; Chang, C.J.; Pfuma, E.; Habtemariam, B.; et al. FDA approval: Ibrutinib for patients with previously treated mantle cell lymphoma and previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3586–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paydas, S. Management of adverse effects/toxicity of ibrutinib. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 136, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, C.; Tsui, S.T.; Liu, D. Second-generation inhibitors of Bruton tyrosine kinase. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perutelli, F.; Montalbano, M.C.; Boccellato, E.; Coscia, M.; Vitale, C. Beyond ibrutinib: Novel BTK inhibitors for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2022, 34, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, A.N.; Jimeno, A. Zanubrutinib: A new BTK inhibitor for treatment of relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Drugs Today 2020, 56, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zain, R.; Vihinen, M. Structure-function relationships of covalent and non-covalent btk inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 694853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.B.; Shah, N.N.; Alencar, A.J.; Gerson, J.N.; Patel, M.R.; Fakhri, B.; Jurczak, W.; Tan, X.N.; Lewis, K.L.; Fenske, T.; et al. MCL-133 Pirtobrutinib, a highly selective, non-covalent (reversible) BTK inhibitor in previously treated mantle cell lymphoma: Updated results from the phase 1/2 BRUIN study. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022, 22, S394–S395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, J.; Bar-Or, A.; Turner, T.J.; Wiendl, H. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors for multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 19, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.K.; Tester, R.; Aslanian, S.; Karp, R.; Sheets, M.; Labenski, M.T.; Witowski, S.R.; Lounsbury, H.; Chaturvedi, P.; Mazdiyasni, H.; et al. Inhibition of BTK with CC-292 provides early pharmacodynamic assessment of activity in mice and humans. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 346, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, P.H.; Kivitz, A.J.; Ma, J.; Korish, S.; Sutherland, D.; Li, L.; Azaryan, A.; Kosek, J.; Adams, M.; Capone, L.; et al. Spebrutinib (CC-292) affects markers of B cell activation, chemotaxis, and osteoclasts in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from a mechanistic study. Rheumatol. Ther. 2020, 7, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozkiewicz, D.; Hermanowicz, J.M.; Kwiatkowska, I.; Krupa, A.; Pawlak, D. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors (BTKIs): Review of preclinical studies and evaluation of clinical trials. Molecules 2023, 28, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Petter, R.; Tester, R.W.; Kluge, A.F. 2,4-Disubstituted Pyrimidines Useful as Kinase Inhibitors. U.S. Patent 8338439B2, 25 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Petter, R.; Wayne Tester, R.; Kluge, A.F. Heteroaryl Compounds and Uses Thereof. WO2011090760A1, 28 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey, R. Phase II trial of evobrutinib in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafoux, D.; Davis, H.M.; Frank, K.E.; Friedman, M.M.; Herold, J.M.; Hoemann, M.Z.; Huntley, R.; Osuma, A.; Sheppard, G.; Somal, G.K.; et al. Primary Carboxamides as BTK Inhibitors. CN105530932A, 27 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Haselmayer, P.; Camps, M.; Liu-Bujalski, L.; Nguyen, N.; Morandi, F.; Head, J.; O’Mahony, A.; Zimmerli, S.C.; Bruns, L.; Bender, A.T.; et al. Efficacy and pharmacodynamic modeling of the BTK inhibitor evobrutinib in autoimmune disease models. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 2888–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodous, B.L.; Liu-Bujalski, L.; Jones, R.; Bankston, D. Compositions and Methods for the Production of Pyrimidine and Pyridine Compounds with BTK Inhibitory Activity. WO 2012170976A2, 30 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Angst, D.; Gessier, F.; Janser, P.; Vulpetti, A.; Wälchli, R.; Beerli, C.; Littlewood-Evans, A.; Dawson, J.; Nuesslein-Hildesheim, B.; Wieczorek, G.; et al. Discovery of LOU064 (remibrutinib), a potent and highly selective covalent inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 5102–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, M.; End, P.; Cabanski, M.; Schuhler, C.; Jakab, A.; Kistowska, M.; Kinhikar, A.; Maiolica, A.; Sinn, A.; Fuhr, R.; et al. Remibrutinib (LOU064): A selective potent oral BTK inhibitor with promising clinical safety and pharmacodynamics in a randomized phase I trial. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 1756–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.; Berger, W.; Giménez-Arnau, A.; Hayama, K.; Jain, V.; Reich, A.; Haemmerle, S.; Lheritier, K.; Walsh, P.; Xia, S.; et al. Remibrutinib, a novel BTK inhibitor, demonstrates promising efficacy and safety in chronic spontaneous urticaria. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 1498–1506.E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honigberg, L.A.; Smith, A.M.; Sirisawad, M.; Verner, E.; Loury, D.; Chang, B.; Li, S.; Pan, Z.; Thamm, D.H.; Miller, R.A.; et al. The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor PCI-32765 blocks B-cell activation and is efficacious in models of autoimmune disease and B-cell malignancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13075–13080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davids, M.S.; Brown, J.R. Ibrutinib: A first in class covalent inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ding, N.; Gao, H.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Hwang, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. PROTAC-induced BTK degradation as a novel therapy for mutated BTK C481S induced ibrutinib-resistant B-cell malignancies. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. Method for Preparing Ibrutinib. CN103626774A, 12 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, C.S.; Trotman, J.; Opat, S.; Burger, J.A.; Cull, G.; Gottlieb, D.; Harrup, R.; Johnston, P.B.; Marlton, P.; Munoz, J.; et al. Phase 1 study of the selective BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib in B-cell malignancies and safety and efficacy evaluation in CLL. Blood 2019, 134, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, F.; Ma, S. Use of BTK inhibitors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL): A practical guidance, Blood Lymphat. Cancer 2022, 12, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.X.; Zhu, H.Y.; Li, X.T.; Xia, Y.; Miao, K.R.; Zhao, S.S.; Wu, Y.J.; Wang, L.; Xu, W.; Li, J.Y. The impacts of zanubrutinib on immune cells in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiwei, W.; Yunhang, G. Fused Heterocyclic Compounds as Protein Kinase Inhibitors. U.S. Patent 20170073349A1, 16 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, S. Tirabrutinib: First approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Kong, H.; Li, C.; Dong, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Han, S.; Lei, T.; Yang, H. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors in primary central nervous system lymphoma-evaluation of anti-tumor efficacy and brain distribution. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1975–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, H.S.; Jayne, S.; Rule, S.A.; Cartron, G.; Morschhauser, F.; Macip, S.; Karlin, L.; Jones, C.; Herbaux, C.; Quittet, P.; et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with CLL treated with the selective Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ONO/GS-4059. Blood 2017, 129, 2808–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munakata, W.; Ando, K.; Hatake, K.; Fukuhara, N.; Kinoshita, T.; Fukuhara, S.; Shirasugi, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Ichikawa, S.; Ohmachi, K.; et al. Phase I study of tirabrutinib (ONO-4059/GS-4059) in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies in Japan. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1686–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Yoshizawa, T. Purinone Derivative. WO2011152351A1, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Woyach, J.; Flinn, I.W.; Awan, F.T.; Eradat, H.; Brander, D.; Tees, M.; Parikh, S.A.; Phillips, T.; Wang, W.; Reddy, N.M.; et al. P682: Nemtabrutinib (MK-1026), a non-covalent inhibitor of wild-type and C481s mutated Bruton tyrosine kinase for B-cell malignancies: Efficacy and safety of the phase 2 dose-expansion bellwave-001 study. HemaSphere 2022, 6, 578–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Flinn, I.W.; Awan, F.T.; Eradat, H.; Brander, D.; Tees, M.; Parikh, S.A.; Phillips, T.J.; Ghori, R.; Reddy, N.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nemtabrutinib, a wild-type and C481S-mutated Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor for B-Cell malignancies: Updated analysis of the open-label phase 1/2 dose-expansion bellwave-001 study. Blood 2022, 140, 7004–7006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhowski, E.M.; Ravikrishnan, J.; Gordon, B.; Yu, L.; Misra, S.; Walker, B.; Eathiraj, S.; Sampath, D.; Rogers, K.A.; Byrd, J.C.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of combination nemtabrutinib and venetoclax in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Corry, J.; Desmond, R.; Di Maso, M.J. Synthesis of BTK Inhibitor and Intermediates Thereof. WO2022251404A1, 1 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.F.; Krishnarajah, J.; Nunn, P.A.; Hill, R.J.; Karr, D.; Tam, D.; Masjedizadeh, M.; Funk, J.O.; Gourlay, S.G. A phase I trial of PRN1008, a novel reversible covalent inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 2367–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.; Bradshaw, J.; Bisconte, A.; Tam, D.; Owens, T.; Brameld, K.; Smith, P.; Funk, J.; Goldstein, D.; Nunn, P. Preclinical characterization of PRN1008, a novel reversible covalent inhibitor of BTK that shows efficacy in a RAT model of collagen-induced arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, T.D.; Brameld, K.A.; Verner, E.J.; Ton, T.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Masjedizadeh, M.R.; Bradshaw, J.M.; Hill, R.J.; Tam, D.; et al. Discovery of reversible covalent Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors PRN473 and PRN1008 (rilzabrutinib). J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 5300–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, D.F.; Patsatsi, A.; Stavropoulos, P.; Baum, S.; Zeeli, T.; Kern, J.S.; Roussaki-Schulze, A.V.; Sinclair, R.; Bassukas, I.D.; Thomas, D.; et al. Proof of concept for the clinical effects of oral rilzabrutinib, the first Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor for pemphigus vulgaris: The phase II BELIEVE study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, T.; Verner, E. Pyrazolopyrimidine Compounds as Kinase Inhibitors. WO2014039899A1, 3 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, L.; Tang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Hua, Y.; Weng, B.; Mo, X.; Bao, Y.; Teng, L.; et al. Discovery of a novel, selective and irreversible inhibitor (abivertinib) of mutated EGFR and T790M-induced resistance for the treatment of NSCLC. Med. Drug Discov. 2020, 6, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Huang, Z.; Han, L.; Gong, Y.; Xie, C. Mechanisms and management of 3rd-generation EGFR-TKI resistance in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (review). Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Xi, B. Novel Pyrrolopyrimidine Compounds as Inhibitors of Protein Kinases. U.S. Patent 20150210702A1, 30 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, W.G.; Howell, S.B.; Zhang, H.; Rastgoo, N.; Local, A.; Kurtz, S.E.; Lo, P.; Bottomly, D.; Wilmot, B.; McWeeney, S.K.; et al. Luxeptinib (CG-806) targets FLT3 and clusters of kinases operative in acute myeloid leukemia. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Zhang, H.; Sivina, M.; Vaca, A.; Thompson, P.A.; Jain, N.; Ferrajoli, A.; Estrov, Z.E.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. CG-806, a first-in-class pan-FLT3/pan-BTK Inhibitor, exhibits broad signaling inhibition in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 2019, 134, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.M.; Hong, Y. Methods for Treating Patients with Hematologic Malignancies. WO2018156578A1, 30 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.R.; Na, J.E.; Min, I.S.; Cha, H.J. 2,3-Dihydro-isoindole-1-on Derivative as BTK Kinase Suppressant, and Pharmaceutical Composition Including Same. U.S. Patent 20150336934A1, 26 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, W.G.; Cho, J.M.; Hong, Y. Methods for Treating Patients with Hematologic Malignancies. CN110621665A, 27 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Watterson, S.H.; Liu, Q.; Beaudoin Bertrand, M.; Batt, D.G.; Li, L.; Pattoli, M.A.; Skala, S.; Cheng, L.; Obermeier, M.T.; Moore, R.; et al. Discovery of branebrutinib (BMS-986195): A strategy for identifying a highly potent and selective covalent inhibitor providing rapid in vivo inactivation of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK). J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 3228–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catlett, I.M.; Nowak, M.; Kundu, S.; Zheng, N.; Liu, A.; He, B.; Girgis, I.G.; Grasela, D.M. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of branebrutinib (BMS-986195), a covalent, irreversible inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase: Randomised phase I, placebo-controlled trial in healthy participants. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, C.; Xanthopoulos, C.; Kostareli, E. The role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in the immune system and disease. Immunology 2021, 164, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goess, C.; Harris, C.M.; Murdock, S.; McCarthy, R.W.; Sampson, E.; Twomey, R.; Mathieu, S.; Mario, R.; Perham, M.; Goedken, E.R.; et al. ABBV-105, a selective and irreversible inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, is efficacious in multiple preclinical models of inflammation. Mod. Rheumatol. 2019, 29, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, R.; Friedman, A.; Drescher, E.; Singhal, A.; Cortes-Maisonet, G.; Doan, T.; Lu, W.; Wang, Z.; Nader, A.; Housley, W.; et al. Safety and efficacy of elsubrutinib or upadacitinib alone or in combination (ABBV-599) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response or intolerance to biological therapies: A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 2022, 4, E395–E406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafoux, D.; Davis, H.M.; Frank, K.E.; Friedman, M.M. Primary Carboxamides as BTK Inhibitors. WO2014210255A1, 31 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, D. Acalabrutinib (ACP-196): A selective second-generation BTK inhibitor. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, C.Y.; Seymour, J.F.; Wang, M.L. Mantle Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, S.E.M.; Montraveta, A.; Niemann, C.U.; Mora-Jensen, H.; Gulrajani, M.; Krantz, F.; Mantel, R.; Smith, L.L.; McClanahan, F.; Harrington, B.K.; et al. The bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib demonstrates potent on-target effects and efficacy in two mouse models of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barf, T.A.; Gerardus, C.J.; Maria, J.; Man, D.A.; Antonius, P.; Oubrie, A.A. Oubrie. 4-Imidazopyridazin-1-yl-benzamides and 4-imidazotriazin-1-yl-benzamides as BTK-Inhibitors. WO2013010868A1, 24 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Erickson, R.I.; Schutt, L.K.; Tarrant, J.M.; McDowell, M.; Liu, L.; Johnson, A.R.; Lewin-Koh, S.C.; Hedehus, M.; Ross, J.; Carano, R.A.; et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase small molecule inhibitors induce a distinct pancreatic toxicity in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 360, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isenberg, D.; Furie, R.; Jones, N.S.; Guibord, P.; Galanter, J.; Lee, C.; McGregor, A.; Toth, B.; Rae, J.; Hwang, O.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and pharmacodynamic effects of the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor fenebrutinib (GDC-0853) in systemic lupus erythematosus: Results of a phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1835–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.; Christopher, H.; Meire, B.; Alexandra, G.; James, C.; Adam, J.; Amit, B.-O. Fenebrutinib demonstrates the highest potency of Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors (BTKis) in phase 3 clinical development for multiple sclerosis (MS). Neurology 2021, 96, 4437. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, J.J.; Treon, S.P. What is new in the treatment of Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia? Leukemia 2019, 33, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, J.J.; Johnson, A.R.; Misner, D.L.; Belmont, L.D.; Castanedo, G.; Choy, R.; Coraggio, M.; Dong, L.; Eigenbrot, C.; Erickson, R.; et al. Discovery of GDC-0853: A potent, selective, and noncovalent Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor in early clinical development. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2227–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, S. Orelabrutinib: First approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Song, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Liu, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, J.; Gao, S.; Ding, K. Safety, tolerability and efficacy of orelabrutinib, once a day, to treat Chinese patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small cell leukemia. Blood 2019, 134, 4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Li, J.; Miao, Y. Evaluating orelabrutinib as a novel treatment option for relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia in China. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2022, 23, 1979–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiangyang, C.; Yingxiang, G.; Chong, L.; Haihong, N. Substituted Nicotinimide Inhibitors of btk and Their Preparation and Use in the Treatment of Cancer, Inflammation and Autoimmune Disease. WO2015048662A2, 2 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, E.B.; Rosendahal, M.S.; Rothenberg, S.M.; Andrews, S.W.; Brandhuber, B.J. Loxo-305, a highly selective and non-covalent next generation BTK inhibitor, inhibits diverse BTK C481 substitution mutations. Blood 2019, 134, 4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.L.; Mato, A.R.; Pena, C.; Roeker, L.E.; Coombs, C.C. The potential of pirtobrutinib in multiple B-cell malignancies. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2022, 13, 20406207221101697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Shah, N.N.; Jurczak, W.; Cheah, C.Y.; Pagel, J.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Fakhri, B.; Eyre, T.A.; Lamanna, N.; Patel, M.R.; et al. Pirtobrutinib in relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies (BRUIN): A phase 1/2 study. Lancet 2021, 397, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Mi, X.; Thompson, M.C.; Montoya, S.; Notti, R.Q.; Afaghani, J.; Durham, B.H.; Penson, A.; Witkowski, M.T.; Lu, S.X.; et al. Mechanisms of resistance to noncovalent Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, A.D.A.; Charles, E.; Jared, F.; Scott, F.; Nicholas, M. Processes and Intermediates for the Preparation of (S)-5-amino-3-(4-((5-fluoro-2-methoxybenzamido)methyl)phenyl)-1-(1,1,1-trifluoropropane-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide. WO2022056100A1, 17 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Francesco, M.; Wong, M.; LaStant, J.; Finkle, D.; Loewenstein, N.; Macsata, R.; Lindstrom, M.; Shu, J.; Ton, T.; Zhu, J. PRN2246, a potent and selective blood brain barrier penetrating BTK inhibitor, exhibits efficacy in central nervous system immunity. Mult. Scler. J. 2017, 23, 989. [Google Scholar]
- Ringheim, G.E.; Wampole, M.; Oberoi, K. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors and autoimmune diseases: Making sense of BTK inhibitor specificity profiles and recent clinical trial successes and failures. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 662223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, D.S.; Arnold, D.L.; Vermersch, P.; Bar-Or, A.; Fox, R.J.; Matta, A.; Turner, T.; Wallström, E.; Zhang, X.; Mareš, M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of tolebrutinib, an oral brain-penetrant BTK inhibitor, in relapsing multiple sclerosis: A phase 2b, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlandi, R.; Gajofatto, A. Tolebrutinib. Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor treatment of multiple sclerosis. Drugs Future 2022, 47, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueffer, L.E.; Joseph, R.E.; Andreotti, A.H. Reining in BTK: Interdomain interactions and their importance in the regulatory control of BTK. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 655489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, D.M.; Owens, T.D. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. CN106459049A, 22 February 2017. [Google Scholar]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Wen, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y. A Comprehensive Review of Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting Bruton Tyrosine Kinase: Synthetic Approaches and Clinical Applications. Molecules 2023, 28, 8037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248037
Zhang Q, Wen C, Zhao L, Wang Y. A Comprehensive Review of Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting Bruton Tyrosine Kinase: Synthetic Approaches and Clinical Applications. Molecules. 2023; 28(24):8037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248037
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qi, Changming Wen, Lijie Zhao, and Yatao Wang. 2023. "A Comprehensive Review of Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting Bruton Tyrosine Kinase: Synthetic Approaches and Clinical Applications" Molecules 28, no. 24: 8037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248037
APA StyleZhang, Q., Wen, C., Zhao, L., & Wang, Y. (2023). A Comprehensive Review of Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting Bruton Tyrosine Kinase: Synthetic Approaches and Clinical Applications. Molecules, 28(24), 8037. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28248037