Development of Innovative Vitamin D Enrichment Designs for Two Typical Italian Fresh Cheeses: Burrata and Giuncata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Laboratory-Scale Development of VD3 Enrichment Systems
2.1.1. Enrichment Design for Giuncata Cheese
2.1.2. Enrichment Design for Burrata Cheese
2.2. Assessment of the Distribution of the Bioactive Compound into Cheese Matrixes
2.2.1. Distribution of VD3 into Giuncata Cheese Matrix
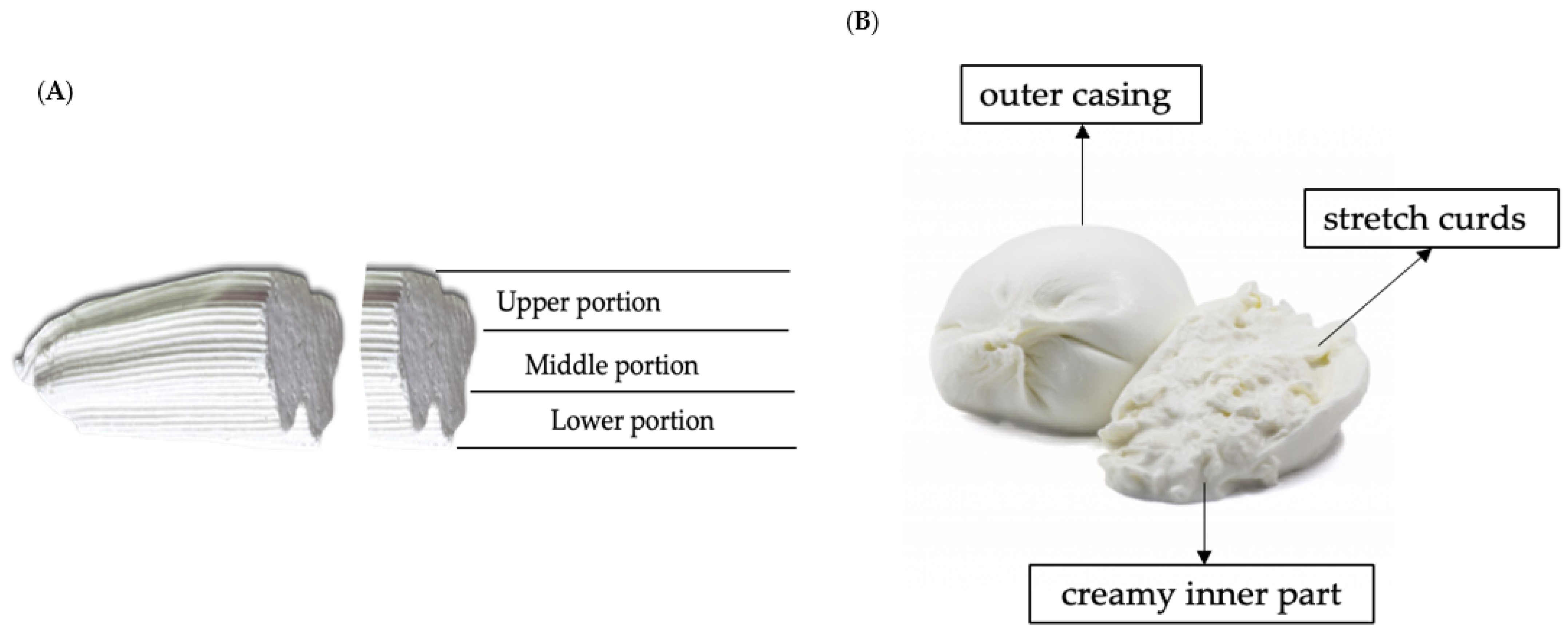
2.2.2. Distribution of VD into Burrata Cheese Matrix
2.3. Industrial-Scale Application: Homogeneity of the Production Batch
2.3.1. Giuncata Cheese
2.3.2. Burrata Cheese
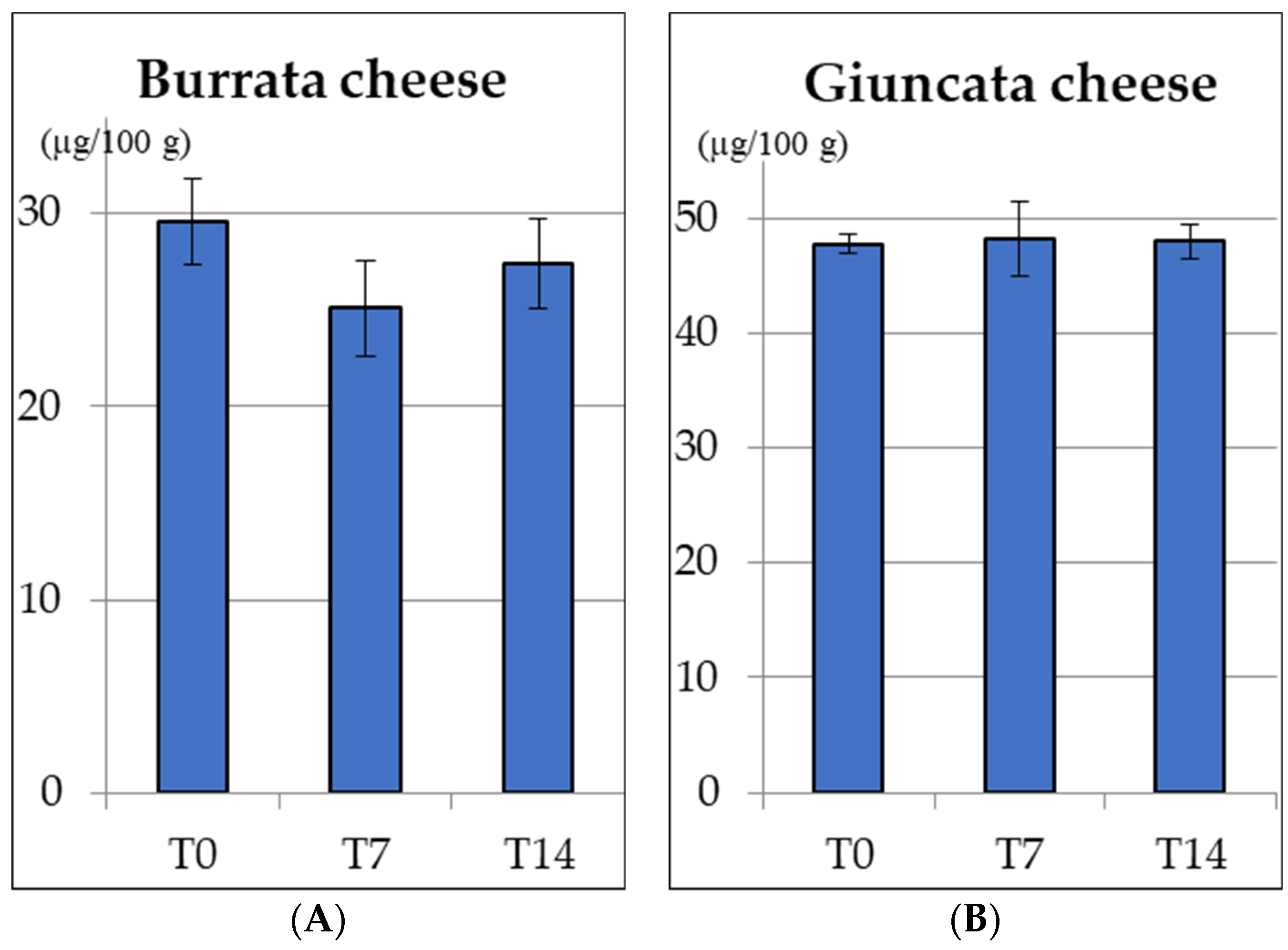
2.4. Stability of Vitamin D in Fortified Cheese
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cheese Samples and Compositional Analyses
4.3. Design of Vitamin D Enrichment Systems in Cheese: Laboratory-Scale Optimization
4.4. VD3 Enrichment System for Giuncata Cheese
4.5. VD3 Enrichment System for Burrata Cheese
4.6. Determination of Vitamin D through HPLC Analyses
4.7. Homogeneity Study of Production Batches and Assessment of the Distribution of the Bioactive Compound into Cheese Matrixes
4.8. Stability of Vitamin D in Fortified Cheeses
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Divakar, U.; Sathish, T.; Soljak, M.; Bajpai, R.; Dunleavy, G.; Visvalingam, N.; Nazeha, N.; Soh, C.K.; Christopoulos, G.; Car, J. Prevalence of Vitamin D Deficiency and Its Associated Work-Related Factors among Indoor Workers in a Multi-Ethnic Southeast Asian Country. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palacios, C.; Gonzalez, L. Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem? J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, N. Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, F.H.; Majumder, R.; Torabi, R.; Saeg, F.; Hoffman, R.; Cirillo, J.D.; Greiffenstein, P. Vitamin D insufficiency is prevalent in severe COVID-19. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radujkovic, A.; Hippchen, T.; Tiwari-Heckler, S.; Dreher, S.; Boxberger, M.; Merle, U. Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, P.-J.; Gysemans, C.; Verstuyf, A.; Mathieu, C. Vitamin D’s Effect on Immune Function. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, E.K.; Thenappan, T.; Bhargava, M.; Chen, Y. Does Vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19? Clin. Med. 2020, 20, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, R.; Hussein, M.H.; Toraih, E.A.; Elshazli, R.M.; Jardak, C.; Sultana, N.; Youssef, M.R.; Omar, M.; Attia, A.S.; Fawzy, M.S.; et al. Vitamin D insufficiency as a potential culprit in critical COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, M.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Perspective: Improving Vitamin D status in the management of COVID-19. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, E.; Rhodes, J.; Kenny, R.A. Vitamin D and inflammation: Potential implications for severity of Covid-19. Ir. Med. J. 2020, 113, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Nzekoue, F.K.; Alesi, A.; Vittori, S.; Sagratini, G.; Caprioli, G. Development of functional whey cheese enriched in vitamin D3: Nutritional composition, fortification, analysis, and stability study during cheese processing and storage. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozenfeld, Y.; Beam, J.; Maier, H.; Haggerson, W.; Boudreau, K.; Carlson, J.; Medows, R. A model of disparities: Risk factors associated with COVID-19 infection. Int. J. Equity Health 2020, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, V.K.; Bashir, K.; Aggarwal, M. Vitamin D microencapsulation and fortification: Trends and technologies. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. 2020, 196, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaque, M.S. Can adverse effects of excessive Vitamin D supplementation occur without developing hypervitaminosis D? J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 180, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tippetts, M.; Martini, S.; Brothersen, C.; McMahon, D.J. Fortification of cheese with Vitamin D3 using dairy protein emulsions as delivery systems. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 4768–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganesan, B.; Brothersen, C.; McMahon, D.J. Fortification of Cheddar cheese with Vitamin D does not alter cheese flavor perception. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 3708–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boivin-Piché, J.; Vuillemard, J.C.; St-Gelais, D. Vitamin D-fortified Cheddar type cheese produced from concentrated milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4140–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crevier, B.; Bélanger, G.; Vuillemard, J.C.; St-Gelais, D. Production of cottage cheese fortified with vitamin D. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 5212–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manios, Y.; Moschonis, G.; Mavrogianni, C.; van den Heuvel, E.G.H.M.; Singh-Povel, C.M.; Kiely, M.; Cashman, K.D. Reduced-fat Gouda-type cheese enriched with Vitamin D 3 effectively prevents vitamin D deficiency during winter months in postmenopausal women in Greece. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalidi, B.; Chiu, W.; Rousseau, D.; Vieth, R. Bioavailability and safety of vitamin D3 from pizza baked with fortified mozzarella cheese: A randomized controlled trial. Can. J. Diet. Pract. Res. 2015, 76, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzekoue, F.K.; Alesi, A.; Vittori, S.; Sagratini, G.; Caprioli, G. Development of a functional whey cheese (ricotta) enriched in phytosterols: Evaluation of the suitability of whey cheese matrix and processing for phytosterols supplementation. LWT 2021, 139, 110479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratulat, I.; Britten, M.; Salmieri, S.; Fustier, P.; St-Gelais, D.; Champagne, C.P.; Lacroix, M. Enrichment of cheese with Vitamin D3 and vegetable omega-3. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 13, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Cerbo, A.; Miraglia, D.; Marino, L.; Stocchi, R.; Loschi, A.R.; Fisichella, S.; Rea, S. “Burrata di Andria” PGI Cheese: Physicochemical and Microbiological Features. Foods 2020, 9, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, M.; Quintieri, L.; De Angelis, E.; Monaci, L.; Logrieco, A.F.; Caputo, L.; Mule, G. Yield improvement of the Italian fresh Giuncata cheese by laccase–induced protein crosslink. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 100, 104555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciotti, U.; Massaro, A.; Galiano, A.; Garganese, F. Cheese Fortification: Review and Possible Improvements. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 38 (Suppl. S1), 474–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, M.; Han, J.; Britten, M.; Champagne, C.P.; Fustier, P. Cheese fortification. In Handbook of Food Fortification and Health; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 71–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, D.; Sidhom, G.; Whiting, S.J.; Rousseau, D.; Vieth, R. The bioavailability of Vitamin D from fortified cheeses and supplements is equivalent in adults. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feeney, E.L.; Lamichhane, P.; Sheehan, J.J. The cheese matrix: Understanding the impact of cheese structure on aspects of cardiovascular health–A food science and a human nutrition perspective. Int. J. Dairy Techol. 2021, 74, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontecha, J.; Calvo, M.V.; Juarez, M.; Gil, A.; Martínez-Vizcaino, V. Milk and dairy product consumption and cardiovascular diseases: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S164–S189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, N.; Elderkin, A.L.; Kiel, D.P.; Khosla, S. Managing fragility fractures during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemb, P.; Bergman, P.; Camargo, C.A.; Cavalier, E.; Cormier, C.; Courbebaisse, M.; Hollis, B.; Joulia, F.; Minisola, S.; Pilz, S.; et al. Vitamin D deficiency and the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 133–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; McInnes, I.B.; McMurray, J.J. Obesity is a risk factor for severe COVID-19 infection: Multiple potential mechanisms. Circulation 2020, 142, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liang, W.; Zhong, H.; He, J.; Chen, Z.; He, G.; Song, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; et al. Risk factors associated with COVID-19 infection: A retrospective cohort study based on contacts tracing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, R.E.; Adab, P.; Cheng, K.K. COVID-19: Risk factors for severe disease and death. BMJ 2020, 368, m1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parohan, M.; Yaghoubi, S.; Seraji, A.; Javanbakht, M.H.; Sarraf, P.; Djalali, M. Risk factors for mortality in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Aging Male 2020, 23, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 19th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists Inc.: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval-Castilla, O.; Lobato-Calleros, C.; Aguirre-Mandujano, E.; Vernon-Carter, E.J. Microstructure and texture of yoghurt as influenced by fat replacers. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Quantity (g) | Concentrations (µg/g) | Total Quantity of VD3 (µg) | Proportions (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | 500 | 0.45 ± 0.0 | 225 ± 0.5 | 100 |
| Cheese | 130 | 0.76 ± 0.01 | 98.8 ± 1.3 | 43.9 ± 0.6 |
| Whey | 370 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 125.8 ± 3.7 | 55.9 ± 1.6 |
| Adhesiveness (J) | Firmness (N) | Cohesiveness | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control yogurt | 5.3 ± 1.1 J | 0.8 ± 0.1 N | 0.8 ± 0.0 |
| 5 min blending | 4.5 ± 0.5 J | 0.7 ± 0.0 N | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| 10 min blending | 4.3 ± 0.4 J | 0.7 ± 0.0 N | 0.8 ± 0.2 |
| Giuncata Cheese | Upper Part | Middle Part | Lower Part | Whole Cheese | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.48 ± 0.01 | 0.49 ± 0.01 | 0.48 ± 0.00 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | µg/g | |
| Burrata Cheese | Outer Casing | Stretch Curds | Creamy Inner Part | Whole Cheese | Units |
| 0.0 ± 0.0 a | 0.15 ± 0.04 b | 0.52 ± 0.02 c | 0.32 ± 0.02 | µg/g |
| Burrata | Giuncata | |
|---|---|---|
| 239 ± 9 Kcal | 186 ± 6 Kcal |
| 21.2 ± 0.8 g | 15.0 ± 0.6 g |
| of which saturated fats | 15 ± 0.6 g | 9.8 ± 0.4 g |
| 1.5 ± 0.0 g | 1.8 ± 0.1 g |
| of which sugar | 0.7 ± 0.0 g | 0.6 ± 0.0 g |
| 12.3 ± 0.4 g | 11.2 ± 0.2 g |
| 0.3 ± 0.0 g | 0.7 ± 0.0 g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santanatoglia, A.; Nzekoue, F.K.; Alesi, A.; Ricciutelli, M.; Sagratini, G.; Suo, X.; Torregiani, E.; Vittori, S.; Caprioli, G. Development of Innovative Vitamin D Enrichment Designs for Two Typical Italian Fresh Cheeses: Burrata and Giuncata. Molecules 2023, 28, 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031049
Santanatoglia A, Nzekoue FK, Alesi A, Ricciutelli M, Sagratini G, Suo X, Torregiani E, Vittori S, Caprioli G. Development of Innovative Vitamin D Enrichment Designs for Two Typical Italian Fresh Cheeses: Burrata and Giuncata. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031049
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantanatoglia, Agnese, Franks Kamgang Nzekoue, Alessandro Alesi, Massimo Ricciutelli, Gianni Sagratini, Xinying Suo, Elisabetta Torregiani, Sauro Vittori, and Giovanni Caprioli. 2023. "Development of Innovative Vitamin D Enrichment Designs for Two Typical Italian Fresh Cheeses: Burrata and Giuncata" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031049
APA StyleSantanatoglia, A., Nzekoue, F. K., Alesi, A., Ricciutelli, M., Sagratini, G., Suo, X., Torregiani, E., Vittori, S., & Caprioli, G. (2023). Development of Innovative Vitamin D Enrichment Designs for Two Typical Italian Fresh Cheeses: Burrata and Giuncata. Molecules, 28(3), 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031049










