Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana: An Updated Overview of Their Sweetening Activity, Pharmacological Properties, and Safety Aspects
Abstract
1. Introduction
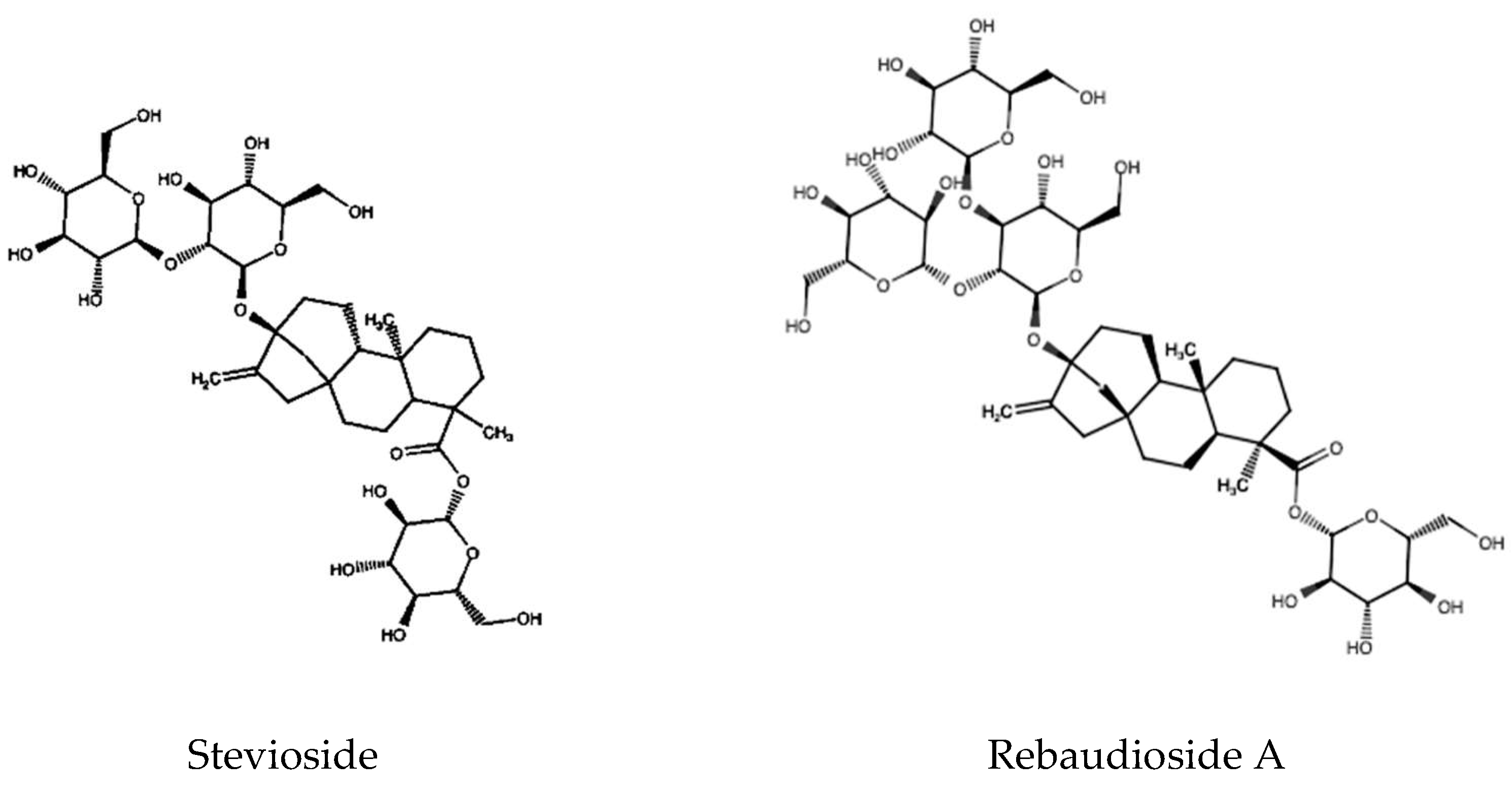
1.1. Chemical Structure of Steviol Glycosides
1.2. Pharmacokinetics
2. Steviol Glycosides as Noncaloric Sucrose Replacements and Noncariogenic Sweeteners
3. Pharmacological Properties of Steviol Glycosides
3.1. Antidiabetic Action
3.2. Antihypertensive Activity
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Property
3.4. Antioxidant Activity
3.5. Anticancer Action
3.6. Antidiarrheal Activity
3.7. Effect on Gut Microbiota
4. Safety Aspects
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kinghorn, A.D.; Djendoel Soejarto, D. Discovery of Terpenoid and Phenolic Sweeteners from Plants. Pure Appl. Chem. 2022, 74, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, P.; Ayoob, K.T.; Magnuson, B.A.; Wölwer-Rieck, U.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Rogers, P.J.; Rowland, I.; Mathews, R. Stevia Leaf to Stevia Sweetener: Exploring Its Science, Benefits, and Future Potential. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1186S–1205S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavarini, S.; Angelini, L.G. Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni as a Source of Bioactive Compounds: The Effect of Harvest Time, Experimental Site and Crop Age on Steviol Glycoside Content and Antioxidant Properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmachari, G.; Mandal, L.C.; Roy, R.; Mondal, S.; Brahmachari, A.K. Stevioside and Related Compounds–Molecules of Pharmaceutical Promise: A Critical Overview. Arch. Pharm. 2011, 344, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, E.; Kitazawa, K.; Ohori, Y.; Izawa, O.; Kakegawa, K.; Fujino, A.; Ui, M. In Vitro Metabolism of the Glycosidic Sweeteners, Stevia Mixture and Enzymatically Modified Stevia in Human Intestinal Microflora. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutapea, A.M.; Toskulkao, C.; Buddhasukh, D.; Wilairat, P.; Glinsukon, T. Digestion of Stevioside, a Natural Sweetener, by Various Digestive Enzymes. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 1997, 23, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, E.; Sakai, N.; Ohori, Y.; Kitazawa, K.; Izawa, O.; Kakegawa, K.; Fujino, A.; Ui, M. Absorption and Metabolism of Glycosidic Sweeteners of Stevia Mixture and Their Aglycone, Steviol, in Rats and Humans. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuns, J.M.C. Stevioside. Phytochemistry 2003, 64, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardana, C.; Simonetti, P.; Canzi, E.; Zanchi, R.; Pietta, P. Metabolism of Stevioside and Rebaudioside A from Stevia Rebaudiana Extracts by Human Microflora. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6618–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuns, J.M.C.; Augustijns, P.; Mols, R.; Buyse, J.G.; Driessen, B. Metabolism of Stevioside in Pigs and Intestinal Absorption Characteristics of Stevioside, Rebaudioside A and Steviol. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuns, J.M.C.; Buyse, J.; Vankeirsbilck, A.; Temme, E.H.M. Metabolism of Stevioside by Healthy Subjects. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 232, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, K.; Kasahara, D.; Yamamoto, F. Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion of Stevioside in Rats. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Japan 1986, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cardoso, V.N.; Barbosa, M.F.; Muramoto, E.; Mesquita, C.H.; Almeida, M.A. Pharmacokinetic Studies of 131I-Stevioside and Its Metabolites. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1996, 23, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuns, J.M.C.; Buyse, J.; Vankeirsbilck, A.; Temme, E.H.M.; Compernolle, F.; Toppet, S. Identification of Steviol Glucuronide in Human Urine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2794–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, A.; Boileau, A.C.; Winkler, P.C.; Compton, J.C.; Prakash, I.; Jiang, X.; Mandarino, D.A. Pharmacokinetics of Rebaudioside A and Stevioside after Single Oral Doses in Healthy Men. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, S54–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toskulkao, C.; Deechakawan, W.; Leardkamolkarn, V.; Glinsukon, T.; Buddhasukh, D. The Low Calorie Natural Sweetener Stevioside: Nephrotoxicity and Its Relationship to Urinary Enzyme Excretion in the Rat. Phytother. Res. 1994, 8, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.K.; Lee, Y.Y. Neurophysiological Symptoms and Aspartame: What Is the Connection? Nutr. NeuroSci. 2018, 21, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çadirci, K.; Özdemır Tozlu, Ö.; Türkez, H.; Mardınoğlu, A. The in Vitro Cytotoxic, Genotoxic, and Oxidative Damage Potentials of the Oral Artificial Sweetener Aspartame on Cultured Human Blood Cells. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.P.; Lin, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Wilson, Y.A.; Oyston, L.J.; Cotterell, J.; Qi, Y.; Khuong, T.M.; Bakhshi, N.; Planchenault, Y.; et al. Sucralose Promotes Food Intake through NPY and a Neuronal Fasting Response. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Compendium of Food Additive Specifications 68th Meeting; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2007; ISBN 9789251058664. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Drug Administration. GRAS Notice for Stevia Leaf Extract; FAO: Maryland, VI, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Barriocanal, L.A.; Palacios, M.; Benitez, G.; Benitez, S.; Jimenez, J.T.; Jimenez, N.; Rojas, V. Apparent Lack of Pharmacological Effect of Steviol Glycosides Used as Sweeteners in Humans. A Pilot Study of Repeated ExposuRes. in Some Normotensive and Hypotensive Individuals and in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetics. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 51, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatsudthipong, V.; Muanprasat, C. Stevioside and Related Compounds: Therapeutic Benefits beyond Sweetness. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 121, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, M.I.; Vincken, J.P.; Sanders, M.; Castro, C.; Stieger, M.; Agosin, E. Identification, Quantification, and Sensory Characterization of Steviol Glycosides from Differently Processed Stevia Rebaudiana Commercial Extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11797–11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muenprasitivej, N.; Tao, R.; Nardone, S.J.; Cho, S. The Effect of Steviol Glycosides on Sensory Properties and Acceptability of Ice Cream. Foods 2022, 11, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Cho, S. Consumer-Based Sensory Characterization of Steviol Glycosides (Rebaudioside A, D, and M). Foods 2020, 9, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwig, G.J.; te Poele, E.M.; Dijkhuizen, L.; Kamerling, J.P. Stevia Glycosides: Chemical and Enzymatic Modifications of Their Carbohydrate Moieties to Improve the Sweet-Tasting Quality. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 2016, 73, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielak, M.; Czarniecka-Skubina, E.; Głuchowski, A. Effect of Sugar Substitution with Steviol Glycosides on Sensory Quality and Physicochemical Composition of Low-Sugar Apple Preserves. Foods 2020, 9, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, S.; Wyrwisz, J.; Kurek, M.; Wierzbicka, A. Physical Properties of Muffins Sweetened with Steviol Glycosides as the Sucrose Replacement. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jooken, E.; Amery, R.; Struyf, T.; Duquenne, B.; Geuns, J.; Meesschaert, B. Stability of Steviol Glycosides in Several Food Matrices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10606–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, E.; Cagetti, M.G.; Ionescu, A.; Campus, G.; Lingström, P. An in Vitro and in Vivo Comparison of the Effect of Stevia Rebaudiana Extracts on Different Caries-Related Variables: A Randomized Controlled Trial Pilot Study. Caries Res. 2014, 48, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanela, N.L.M.; Bijella, M.F.T.B.; Rosa, O.P.d.S. The Influence of Mouthrinses with Antimicrobial Solutions on the Inhibition of Dental Plaque and on the Levels of Mutans Streptococci in Children. Pesqui. Odontol. Bras. 2002, 16, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, R.M. Oral Health: The Silent Epidemic. Public Health Rep. 2010, 125, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, V.P.; Dhillon, J.K. Dental Caries: A Disease Which Needs Attention. Indian J. Pediatr. 2018, 85, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Das, A.K.; Murphy, R.A.; Punwani, I.C.; Nasution, M.P.; Kinghorn, A.D. Evaluation of the Cariogenic Potential of the Intense Natural Sweeteners Stevioside and Rebaudioside A. Caries Res. 1992, 26, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabu, M.; Takase, M.; Toda, K.; Tanimoto, K.; Yasutake, A. Studies on Stevioside, Natural Sweetener. Effect on the Growth of Some Oral Microorganisms. Hiroshima Daigaku Shigaku Zasshi 1977, 9, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Giacaman, R.A.; Campos, P.; Muñoz-Sandoval, C.; Castro, R.J. Cariogenic Potential of Commercial Sweeteners in an Experimental Biofilm Caries Model on Enamel. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.M. Highlighting Diabetes—The Epidemic Continues. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Siddiqi, H.; Uribe, K.B.; Ostolaza, H.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, P.B.; Gregersen, S.; Alstrup, K.K.; Hermansen, K. Stevioside Induces Antihyperglycaemic, Insulinotropic and Glucagonostatic Effects in Vivo: Studies in the Diabetic Goto-Kakizaki (GK) Rats. Phytomedicine 2002, 9, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Chen, S.C.; Chan, P.; Chu, Y.L.; Yang, H.Y.; Cheng, J.T. Mechanism of the Hypoglycemic Effect of Stevioside, a Glycoside of Stevia Rebaudiana. Planta Med. 2005, 71, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudula, R.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Rolfsen, S.E.D.; Xiao, J.; Hermansen, K. Rebaudioside A Potently Stimulates Insulin Secretion from Isolated Mouse Islets: Studies on the Dose-, Glucose-, and Calcium-Dependency. Metabolism 2004, 53, 1378–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, C.; Zambonin, L.; Rizzo, B.; Maraldi, T.; Angeloni, C.; Dalla Sega, F.V.; Fiorentini, D.; Hrelia, S. Glycosides from Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni Possess Insulin-Mimetic and Antioxidant Activities in Rat Cardiac Fibroblasts. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 3724545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, B.; Zambonin, L.; Angeloni, C.; Leoncini, E.; Vieceli Dalla Sega, F.; Prata, C.; Fiorentini, D.; Hrelia, S. Steviol Glycosides Modulate Glucose Transport in Different Cell Types. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2013, 2013, 348169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lailerd, N.; Saengsirisuwan, V.; Sloniger, J.A.; Toskulkao, C.; Henriksen, E.J. Effects of Stevioside on Glucose Transport Activity in Insulin-Sensitive and Insulin-Resistant Rat Skeletal Muscle. Metabolism 2004, 53, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippaert, K.; Pironet, A.; Mesuere, M.; Sones, W.; Vermeiren, L.; Kerselaers, S.; Pinto, S.; Segal, A.; Antoine, N.; Gysemans, C.; et al. Steviol Glycosides Enhance Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function and Taste Sensation by Potentiation of TRPM5 Channel Activity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, J.M.; Król, E.; Krejpcio, Z. Steviol Glycosides Supplementation Affects Lipid Metabolism in High-Fat Fed STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats. Nutrients 2020, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotou, C.; Mihailidou, C.; Brauhli, G.; Katsarou, O.; Moutsatsou, P. Effect of Steviol, Steviol Glycosides and Stevia Extract on Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling in Normal and Cancer Blood Cells. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2018, 460, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, E.B.; de Assis Rocha Neves, F.; Duarte Da Costa, M.A.; Alves Do Prado, W.; de Araújo Funari Ferri, L.; Bazotte, R.B. Comparative Effects of Stevia Rebaudiana Leaves and Stevioside on Glycaemia and Hepatic Gluconeogenesis. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Perel, P.; Mensah, G.A.; Ezzati, M. Global Epidemiology, Health Burden and Effective Interventions for Elevated Blood Pressure and Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 785–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The Global Epidemiology of Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.S. Stevioside Effect on Renal Function of Normal and Hypertensive Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1992, 36, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.; Tomlinson, B.; Chen, Y.J.; Liu, J.C.; Hsieh, M.H.; Cheng, J.T. A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study of the Effectiveness and Tolerability of Oral Stevioside in Human Hypertension. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 50, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.; Xu, D.Y.; Liu, J.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Tomlinson, B.; Huang, W.P.; Cheng, J.T. The Effect of Stevioside on Blood Pressure and Plasma Catecholamines in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Life Sci. 1998, 63, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.N.; Wong, K.L.; Liu, J.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Cheng, J.T.; Chan, P. Inhibitory Effect of Stevioside on Calcium Influx to Produce Antihypertension. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 796–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleit, H.B. Chronic Inflammation. In Pathobiology of Human Disease: A Dynamic Encyclopedia of Disease Mechanisms; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonkaewwan, C.; Toskulkao, C.; Vongsakul, M. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Activities of Stevioside and Its Metabolite Steviol on THP-1 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunprajun, T.; Yimlamai, T.; Soodvilai, S.; Muanprasat, C.; Chatsudthipong, V. Stevioside Enhances Satellite Cell Activation by Inhibiting of NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway in Regenerating Muscle after Cardiotoxin-Induced Injury. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 2844–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushina, Y.; Akihisa, T.; Ukiya, M.; Hamasaki, Y.; Murakami-Nakai, C.; Kuriyama, I.; Takeuchi, T.; Sugawara, F.; Yoshida, H. Structural Analysis of Isosteviol and Related Compounds as DNA Polymerase and DNA Topoisomerase Inhibitors. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 2127–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, M.; Browne, R.; Ram, M.; Muti, P.; Freudenheim, J.; Carosella, A.M.; Armstrong, D. Correlates of Markers of Oxidative Status in the General Population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 154, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Grajales, S.; Ramos-Tovar, E.; Chávez-Estrada, E.; Alvarez-Suarez, D.; Hernández-Aquino, E.; Reyes-Gordillo, K.; Cerda-García-Rojas, C.M.; Camacho, J.; Tsutsumi, V.; Lakshman, M.R.; et al. Antioxidant and Immunomodulatory Activity Induced by Stevioside in Liver Damage: In Vivo, in Vitro and in Silico Assays. HHS Public Access. Life Sci. 2019, 224, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Aceves, L.M.; Dublán-García, O.; López-Martínez, L.X.; Novoa-Luna, K.A.; Islas-Flores, H.; Galar-Martínez, M.; García-Medina, S.; Hernández-Navarro, M.D.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M. Reduction of the Oxidative Stress Status Using Steviol Glycosides in a Fish Model (Cyprinus Carpio). Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2352594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotimi, S.O.; Rotimi, O.A.; Adelani, I.B.; Onuzulu, C.; Obi, P.; Okungbaye, R. Stevioside Modulates Oxidative Damage in the Liver and Kidney of High Fat/Low Streptozocin Diabetic Rats. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woźniak, Ł.; Marszałek, K.; Ska¸pska, S. Influence of Steviol Glycosides on the Stability of Vitamin C and Anthocyanins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11264–11269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žlabur, J.Š.; Dobričević, N.; Brnčić, M.; Barba, F.J.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Franco, D.; Atanasov, A.G.; Voća, S.; Brnčić, S.R. Evaluation of the Behavior of Phenolic Compounds and Steviol Glycosides of Sonicated Strawberry Juice Sweetened with Stevia (Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni). Molecules 2019, 24, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, C.E.; Lin, C.C.; Mariotto, A.B.; Siegel, R.L.; Stein, K.D.; Kramer, J.L.; Alteri, R.; Robbins, A.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Treatment and Survivorship Statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkin, D.M.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Pisani, P. Global Cancer Statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 74–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, E.J.; Babiker, H.M.; Weinberg, U.; Kirson, E.D.; von Hoff, D.D. Tumor-Treating Fields: A Fourth Modality in Cancer Treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaki, M.; Konoshima, T.; Kozuka, M.; Tokuda, H.; Takayasu, J.; Nishino, H.; Miyakoshi, M.; Mizutani, K.; Lee, K.H. Cancer Preventive Agents. Part 8: Chemopreventive Effects of Stevioside and Related Compounds. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, K.; Kitanaka, S.; Seo, S. Inhibitory Effect of Stevioside on Tumor Promotion by 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate in Two-Stage Carcinogenesis in Mouse Skin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 1488–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, K.; Matsui, H.; Shoda, T.; Uneyama, C.; Takada, K.; Takahashi, M. Assessment of the Carcinogenicity of Stevioside in F344 Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1997, 35, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonkaewwan, C.; Ao, M.; Toskulkao, C.; Rao, M.C. Specific Immunomodulatory and Secretory Activities of Stevioside and Steviol in Intestinal Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 3777–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velesiotis, C.; Kanellakis, M.; Vynios, D.H. Steviol Glycosides Affect Functional Properties and Macromolecular Expression of Breast Cancer Cells. IUBMB Life 2022, 74, 1012–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xia, Y.; Sui, X.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Steviol, a Natural Product Inhibits Proliferation of the Gastrointestinal Cancer Cells Intensively. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, K.; Fujii, A.; Nakano, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sato, M. Inhibitory Effects of Hot Water Extract of the Stevia Stem on the Contractile Response of the Smooth Muscle of the Guinea Pig Ileum. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, T.; Sato, N.; Arai, T.; Shiraishi, H.; Sato, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Kamio, Y. Bactericidal Activity of a Fermented Hot-Water Extract from Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni towards Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia Coli O157:H7 and Other Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria. Microbiol. Immunol. 1997, 41, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Matsuda, M.; Ohashi, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Nakagomi, O.; Abe, Y.; Mori, S.; Sato, N.; Okutani, K.; Shigeta, S. Analysis of Anti-Rotavirus Activity of Extract from Stevia Rebaudiana. Antivir. Res. 2001, 49, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, C.X.; Min, L.; Zhu, L.Y. Good or Bad: Gut Bacteria in Human Health and Diseases. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Pastor-Villaescusa, B.; Rueda-Robles, A.; Abadia-Molina, F.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J. Plausible Biological Interactions of Low- and Non-Calorie Sweeteners with the Intestinal Microbiota: An Update of Recent Studies. Nutrients 2020, 1, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalak, K.K.; Firrman, J.; Tomasula, P.M.; Nuñez, A.; Lee, J.J.; Bittinger, K.; Rinaldi, W.; Liu, L.S. Impact of Steviol Glycosides and Erythritol on the Human and Cebus Apella Gut Microbiome. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13093–13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, Ş.G.; Uçar, A.; Yılmaz, S. Do Steviol Glycosides Affect the Oxidative and Genotoxicity Parameters in BALB/c Mice? Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 45, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuns, J.M.C.; Malheiros, R.D.; Moraes, V.M.B.; Decuypere, E.M.P.; Compernolle, F.; Buyse, J.G. Metabolism of Stevioside by Chickens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodyingyuad, V.; Bunyawong, S. Effect of Stevioside on Growth and Reproduction. Hum. Reprod. 1991, 6, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Filho, R.M.; Uehara, O.A.; Minetti, C.A.S.A.; Valle, L.B.S. Chronic Administration of Aqueous Extract of Stevia Rebaudiana (Bert.) Bertoni in Rats: Endocrine Effects. Gen. Pharmacol. 1989, 20, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, G.A.; Heintz, M.M.; Borghoff, S.J.; Doepker, C.L.; Wikoff, D.S. Lack of Potential Carcinogenicity for Steviol Glycosides—Systematic Evaluation and Integration of Mechanistic Data into the Totality of Evidence. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 150, 112045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization. Safety Evaluation of Certain Food Additives; FAO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Younes, M.; Aquilina, G.; Engel, K.H.; Fowler, J.P.; Frutos Fernandez, M.J.; Fürst, P.; Gürtler, R.; Gundert-Remy, U.; Husøy, T.; Manco, M.; et al. Safety Evaluation of Glucosylated Steviol Glycosides as a Food Additive in Different Food Categories. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, J.D.; Carakostas, M.C.; Taylor, S.L. Steviol Glycoside Safety: Are Highly Purified Steviol Glycoside Sweeteners Food Allergens? Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 75, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkayastha, S.; Markosyan, A.; Prakash, I.; Bhusari, S.; Pugh, G.; Lynch, B.; Roberts, A. Steviol Glycosides in Purified Stevia Leaf Extract Sharing the Same Metabolic Fate. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualli, T.; Chaves, P.E.E.; Pereira, L.V.; Serpa, É.A.; Oliveira, L.F.S.D.; Machado, M.M. Steviol, the Active Principle of the Stevia Sweetener, Causes a Reduction of the Cells of the Immunological System Even ConsuMed. in Low Concentrations. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 42, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orellana-Paucar, A.M. Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana: An Updated Overview of Their Sweetening Activity, Pharmacological Properties, and Safety Aspects. Molecules 2023, 28, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031258
Orellana-Paucar AM. Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana: An Updated Overview of Their Sweetening Activity, Pharmacological Properties, and Safety Aspects. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031258
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrellana-Paucar, Adriana Monserrath. 2023. "Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana: An Updated Overview of Their Sweetening Activity, Pharmacological Properties, and Safety Aspects" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031258
APA StyleOrellana-Paucar, A. M. (2023). Steviol Glycosides from Stevia rebaudiana: An Updated Overview of Their Sweetening Activity, Pharmacological Properties, and Safety Aspects. Molecules, 28(3), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031258






