The Study of a Novel Paeoniflorin-Converting Enzyme from Cunninghamella blakesleeana
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
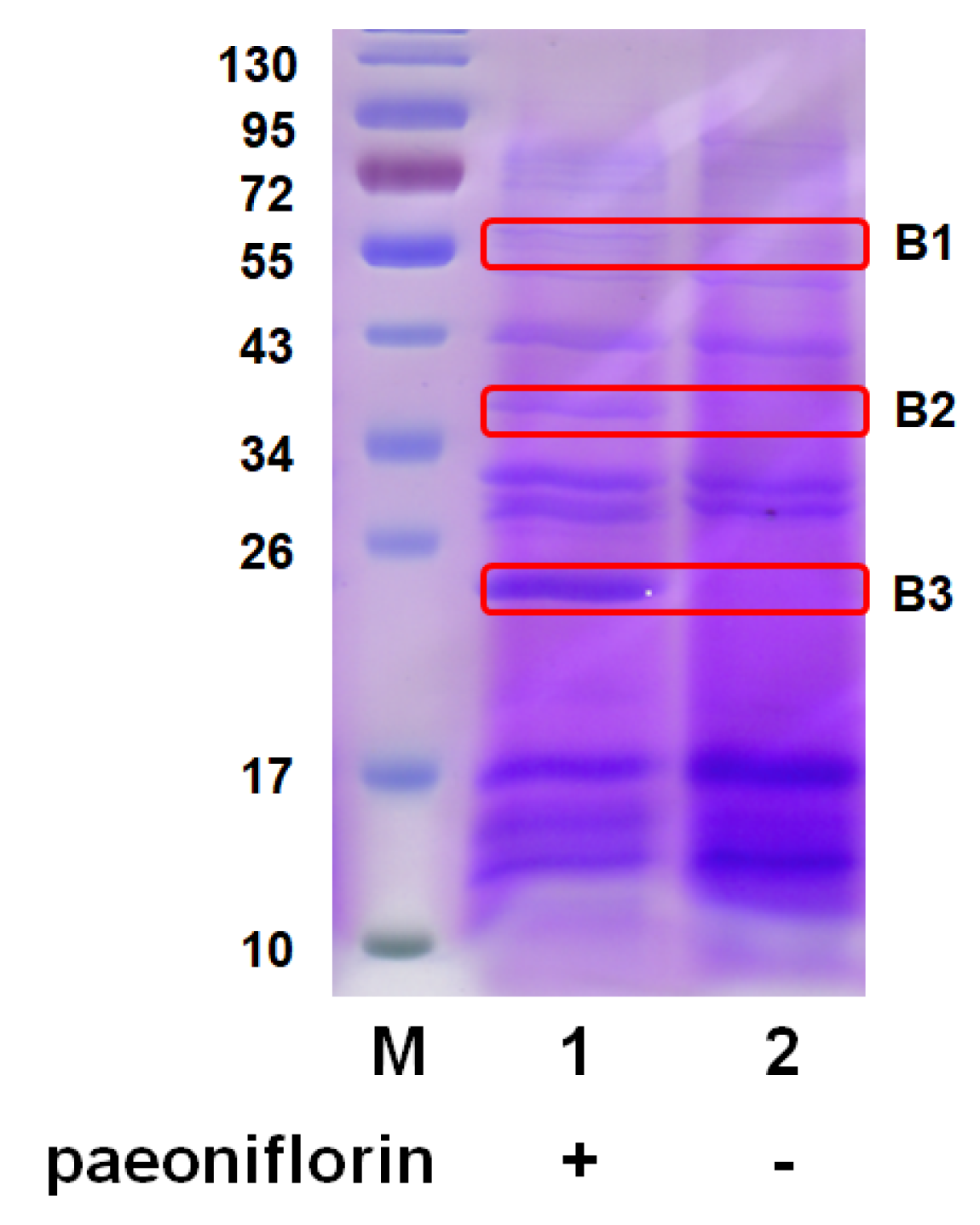
2.1. MS Analysis to Determine Exoenzyme for Paeoniflorin Transformation
2.2. Transcriptomics Analysis of the Paeoniflorin-Induced Cunninghamella blakesleeana
2.3. Comparative Analysis between Protein MS and Transcriptomics
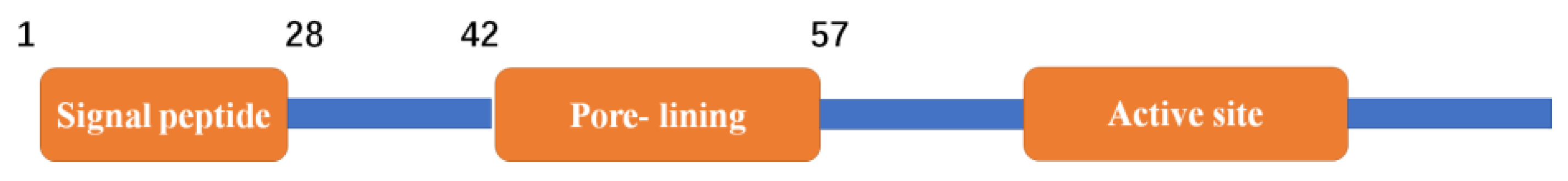
2.4. Cloning of Full-Length G6046 and Its Truncations
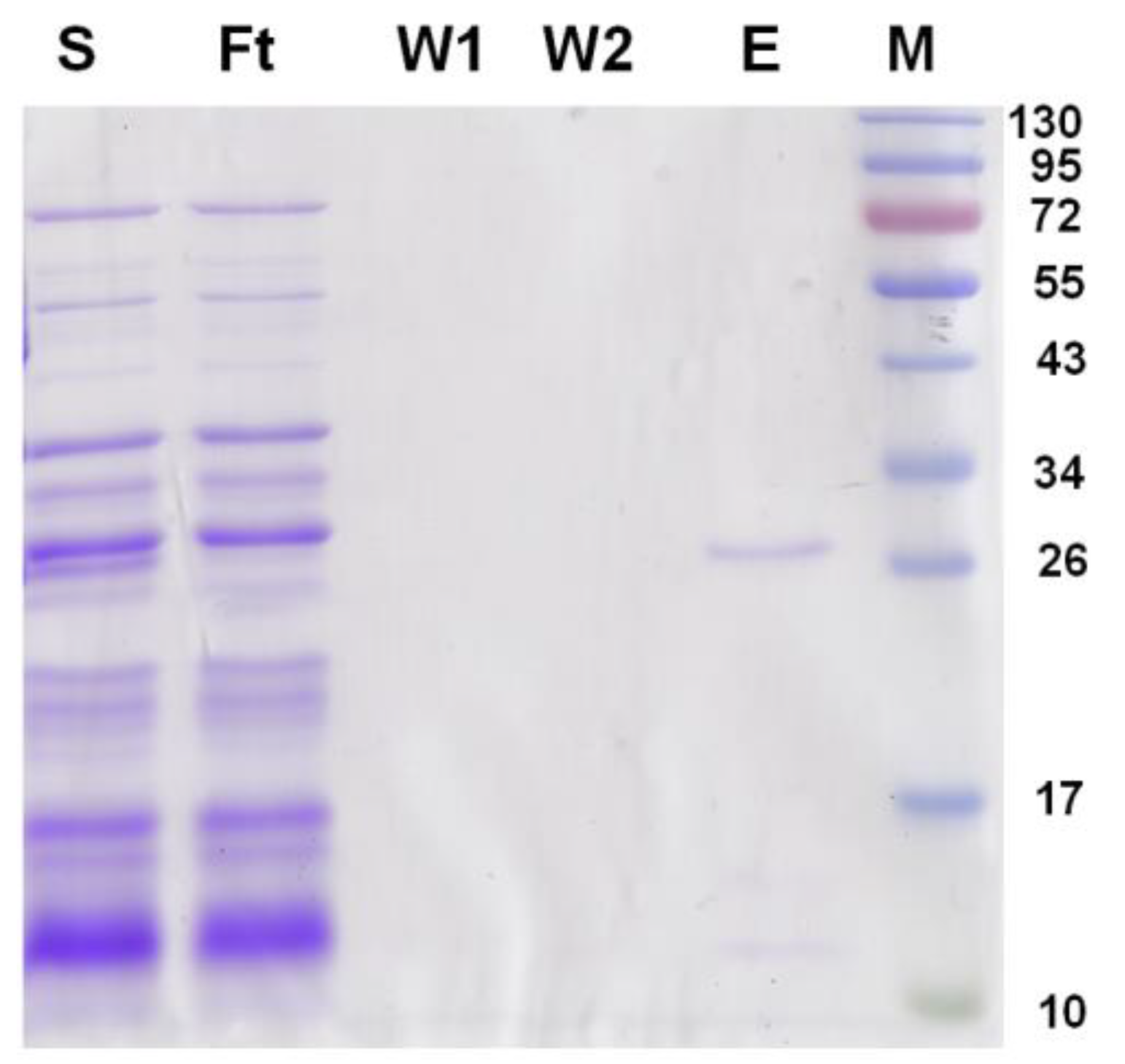
2.5. Expression and Purification of G6046 from E. coli
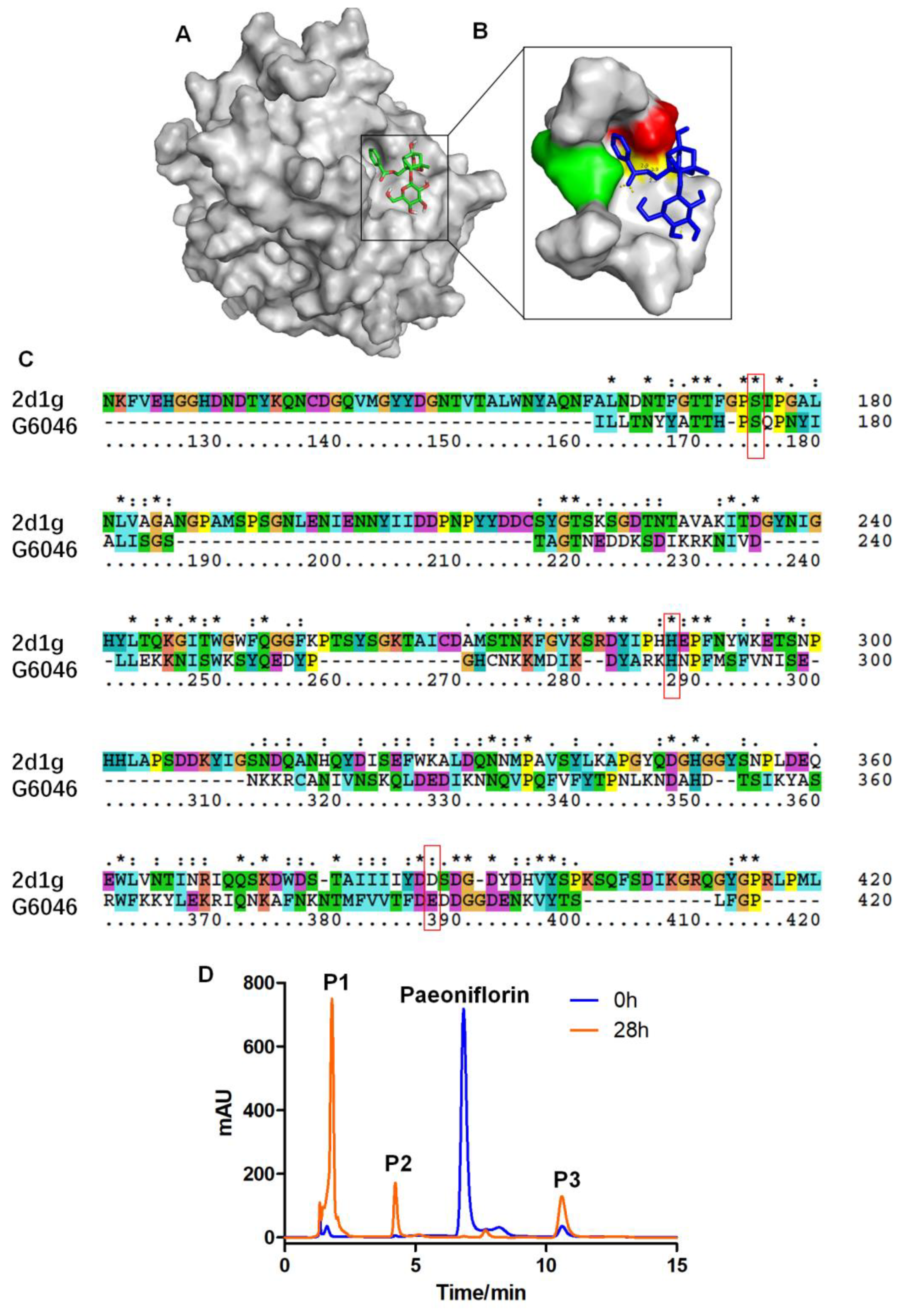
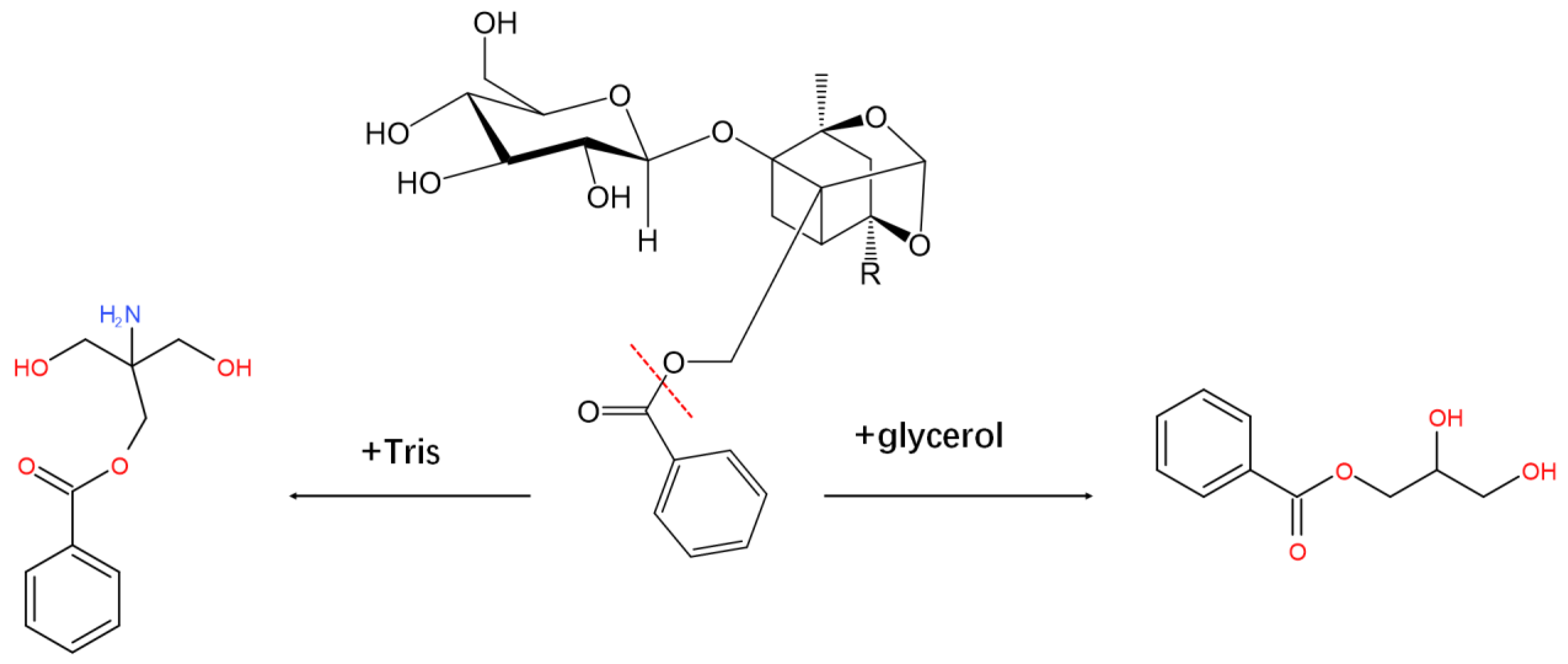
2.6. Activity Assay
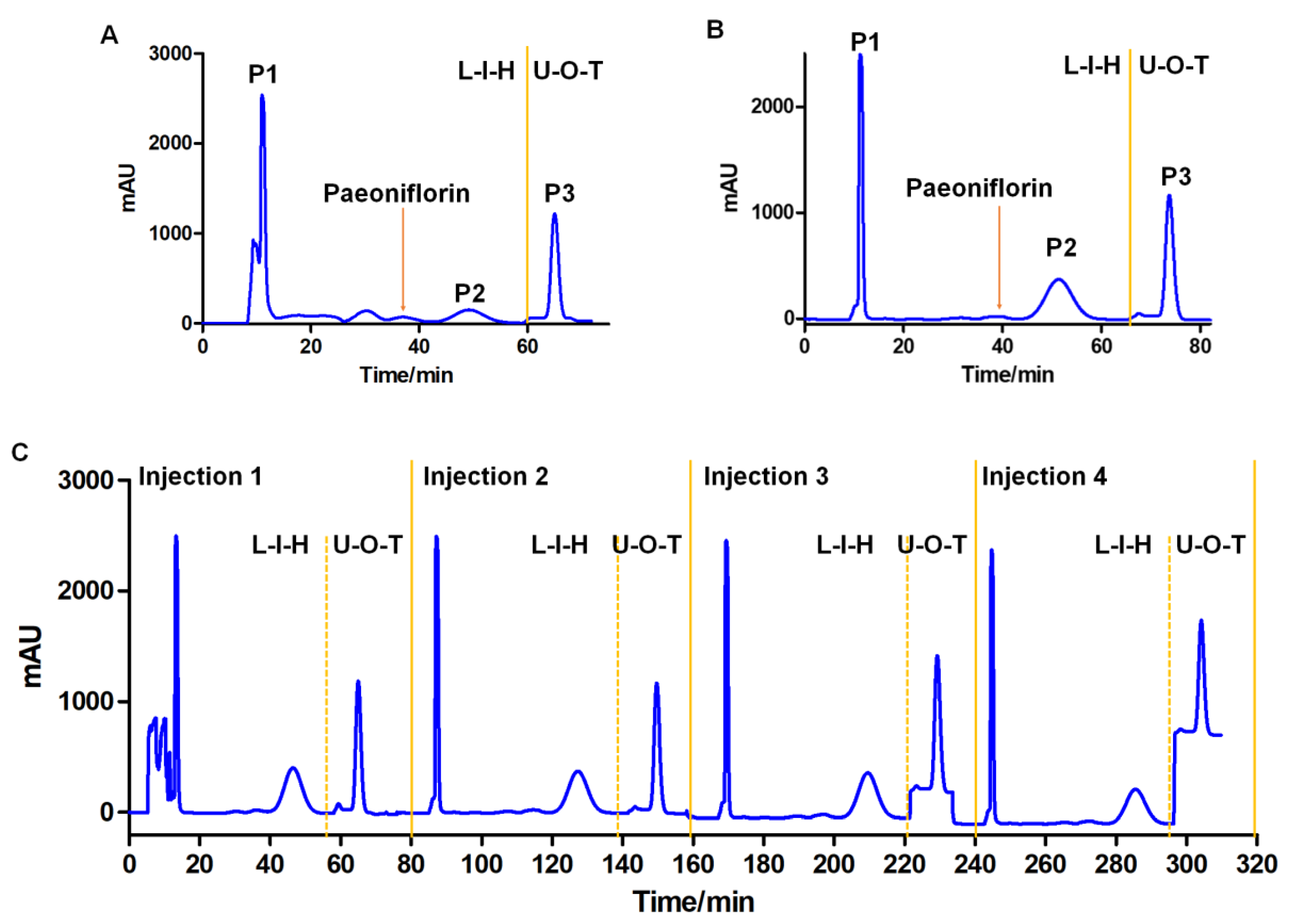
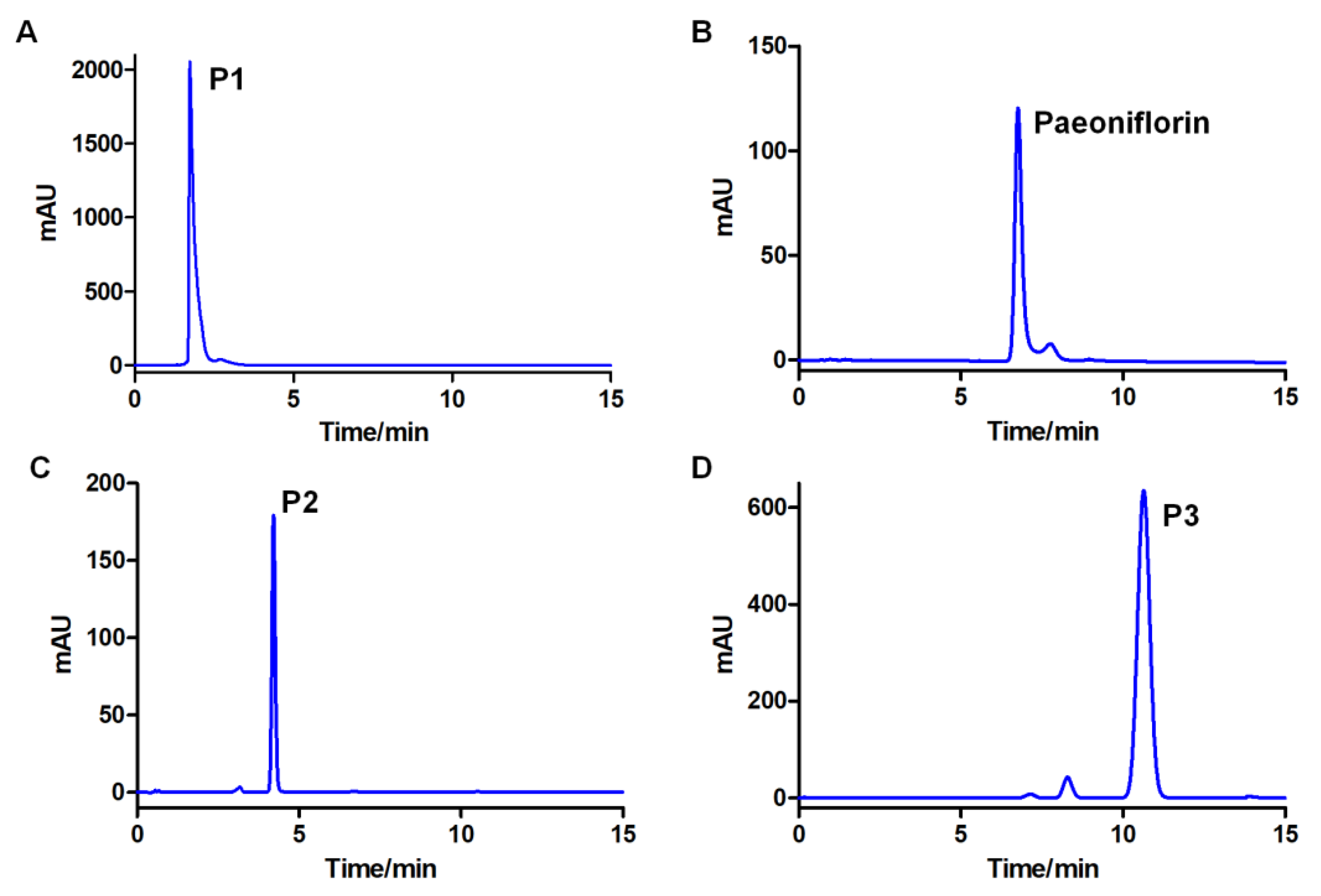
2.7. Selection of Solvent System and CCC Separation
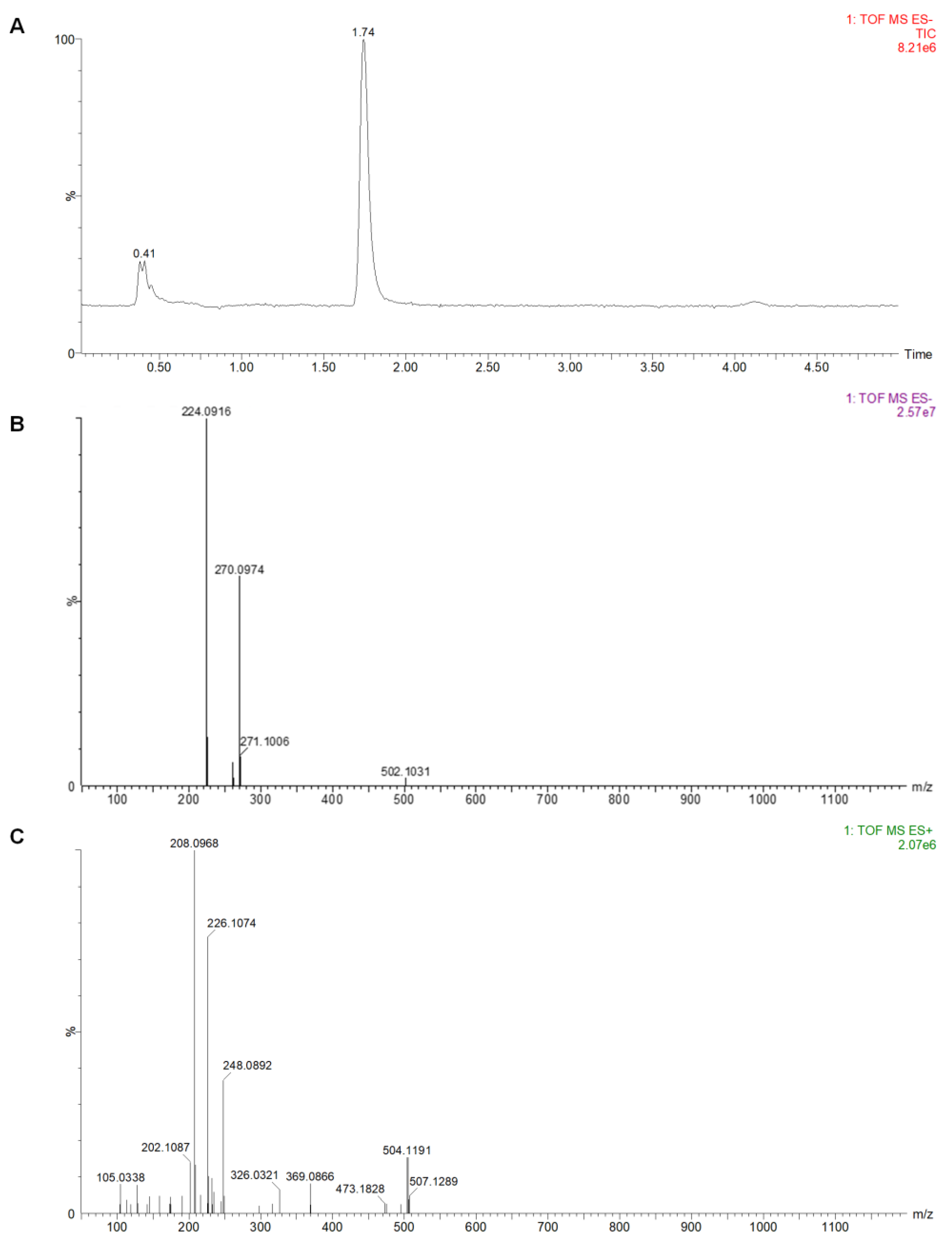
2.8. UPLC-Q-TOF-MS Analysis of the Conversion Products
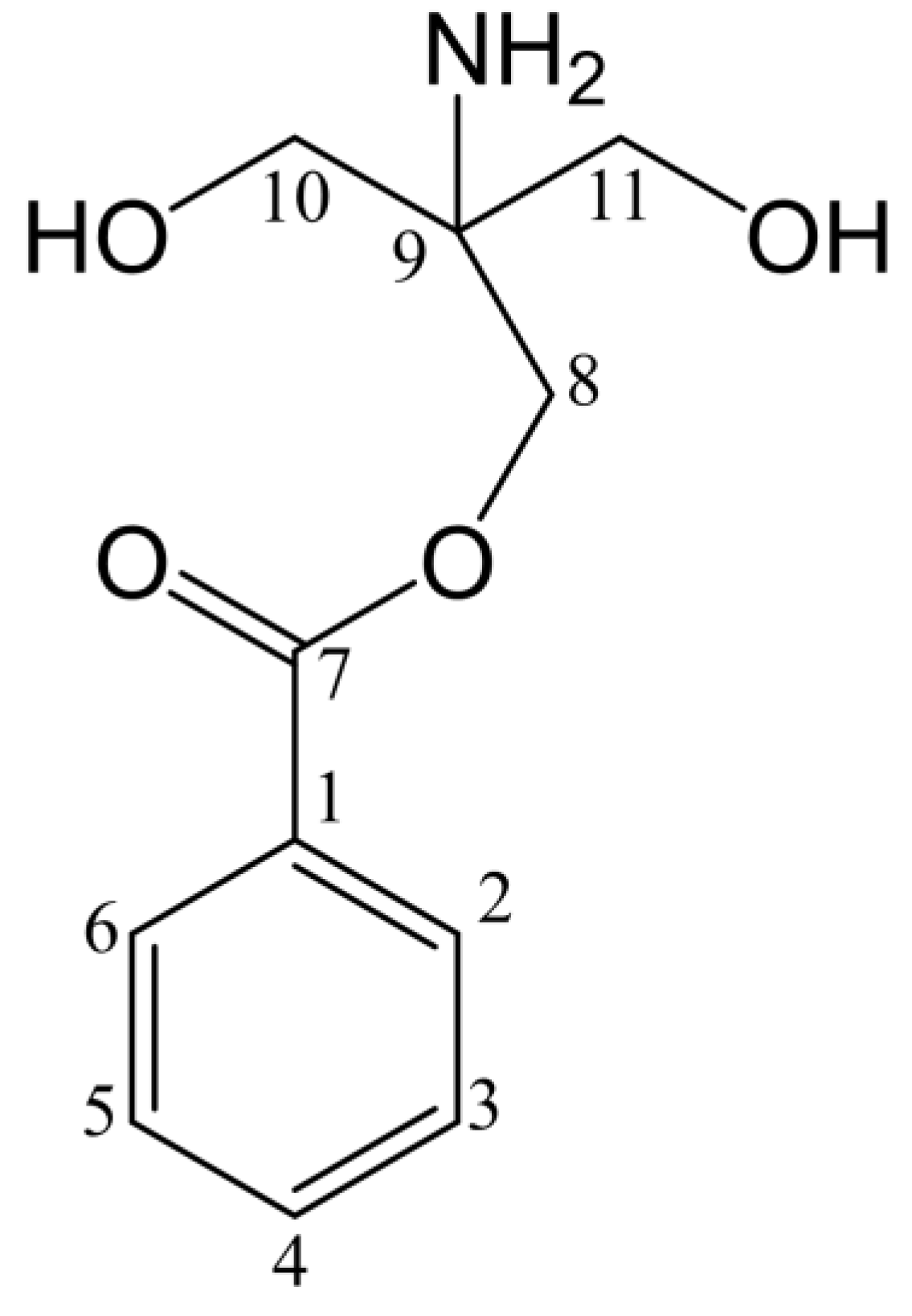
2.9. Structural Identification by NMR
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains and Culture Medium
4.2. Reagents and Materials
4.3. Biotransformation by Cunninghamella blakesleeana
4.4. Identification of Proteins in Culture Medium after Paeoniflorin Induction
4.5. Transcriptomic Analysis
4.6. Construction of the G6046 Expression Vectors
4.7. Expression and Purification of G6046 and Truncations in E. coli BL21 (DE3)
4.8. HPLC Analysis of the Biotransformation Activity
4.9. HPCCC Separation of the Converting Products
4.10. Identification of the Separates by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and NMR
4.11. Paeoniflorin AutoDock Vina Docking Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, S.J.; Wang, R.; Shi, Y.H.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.T. Primary safety evaluation of sulfated paeoniae radix alba. Yao Xue Xue Bao Acta Pharm. Sin. 2012, 47, 486–491. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Jing, L.; Chen, C.; Shao, M.; Fan, Q.; Diao, J.; Liu, Y.; Lv, Z.; Sun, X. Danzhi Xiaoyao San ameliorates depressive-like behavior by shifting toward serotonin via the downregulation of hippocampal indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 160, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.B.; Sun, Y.X.; Ma, X.L.; Xue, X.X.; Zhang, W.T.; Wu, Z.Q.; Ouyang, Y.L.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, W.M.; Guo, S.Z.; et al. Effects of Sini San used alone and in combination with fluoxetine on central and peripheral 5-HT levels in a rat model of depression. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 33, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.L.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.B.; Li, R.Y.; Chen, C.; Wei, S.Z.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, B.; et al. Paeonia lactiflora Pall. protects against ANIT-induced cholestasis by activating Nrf2 via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 5061–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.P.; Yin, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Song, Y.W.; Li, D.D. A Protective Role of Paeoniflorin in Fluctuant Hyperglycemia-Induced Vascular Endothelial Injuries through Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Reduction of PKC beta 1. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 5647219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Chen, M.; Wan, H.Q.; Chen, X.Q.; Li, C.F.; Zhu, J.X.; Liu, Q.; Xu, G.H.; Yi, L.T. Paeoniflorin exerts antidepressant-like effects through enhancing neuronal FGF-2 by microglial inactivation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 274, 114046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamutdinova, I.T.; Jin, Y.C.; Kim, J.S.; Yean, M.H.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, H.G.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, K.C. Paeonol and paeoniflorin, the main active principles of Paeonia albiflora, protect the heart from myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Du, P.; Wang, J. Paeoniflorin ameliorates acute myocardial infarction of rats by inhibiting inflammation and inducible nitric oxide synthase signaling pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 3937–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, Z.; Chen, L.; Fu, Q.; Ji, W.; Wang, S.; Liang, Z.; Qu, R.; Kong, L.; Ma, S. Paeoniflorin attenuates amyloid-beta peptide-induced neurotoxicity by ameliorating oxidative stress and regulating the NGF-mediated signaling in rats. Brain Res. 2013, 1498, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, K.; Huang, B.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, F.F. Protective Effect of Paeoniflorin on A beta(25-35)-Induced SH-SY5Y Cell Injury by Preventing Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, C.Y.; Mao, C.J.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.P.; Liu, S.; Hu, L.F.; Liu, C.F. Neuroprotective Effects of Paeoniflorin on 6-OHDA-Lesioned Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2923–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, C.; Fan, Y.; Yan, P.; Shi, D.; Zhang, Y. Neuroprotection by Paeoniflorin in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2017, 116, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Li, Z. Neuroprotective effect of paeoniflorin on H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by modulation of reactive oxygen species and the inflammatory response. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1768–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.B.; Zhao, Z.X.; Peng, R.; Pan, L.B.; Fu, J.; Ma, S.R.; Han, P.; Cong, L.; Zhang, Z.W.; Sun, L.X.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Based Pharmacokinetics and the Antidepressant Mechanism of Paeoniflorin. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.T.; Huang, W.S.; Tsai, H.Y.; Lee, M.M.; Chen, Y.F. In vivo microdialysis and in vitro HPLC analysis of the impact of paeoniflorin on the monoamine levels and their metabolites in the rodent brain. Biomed. Taiwan 2019, 9, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.X.; Fu, J.; Ma, S.R.; Peng, R.; Yu, J.B.; Cong, L.; Pan, L.B.; Zhang, Z.G.; Tian, H.; Che, C.T.; et al. Gut-brain axis metabolic pathway regulates antidepressant efficacy of albiflorin. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5945–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akao, T.; Shu, Y.Z.; Matsuda, Y.; Hattori, M.; Namba, T.; Kobashi, K. Metabolism of paeoniflorin and related compounds by human intestinal bacteria. IV. Formation and structures of adducts of a metabolic intermediate with sulfhydryl compounds by Lactobacillus brevis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1988, 36, 3043–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huan, G.; Zhang, L.S.; Song, J.N.; Dong, B. Absorption and biotransformation of four compounds in the Guizhi decoction in the gastrointestinal tracts of rats. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 39, 332–338. [Google Scholar]
- Takeda, S.; Isono, T.; Wakui, Y.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Amagaya, S.; Maruno, M. Absorption and excretion of paeoniflorin in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.X.; Goto, E.; Akao, T.; Tani, T. Interaction between Shaoyao-Gancao-Tang and a alteration of paeoniflorin metabolism by intestinal laxative with respect to bacteria in rats. Phytomedicine 2007, 14, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikal, O.A.; Akao, T.; Takeda, S.; Hattori, M. Pharmacokinetic study of paeonimetabolin I, a major metabolite of paeoniflorin from paeony roots. Biol. Amp; Pharm. Bull. 1997, 20, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhan, J.; Guo, H.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, D. Microbial transformation of artemisinin by Cunninghamella echinulata and Aspergillus niger. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 4519–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer-Brown, W.; Miranda-CasoLuengo, R.; Wolfe, K.H.; Byrne, K.P.; Murphy, C.D. The CYPome of the model xenobiotic-biotransforming fungus Cunninghamella elegans. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goncalves, M.D.; Tomiotto-Pellissier, F.; de Matos, R.L.N.; Assolini, J.P.; da Silva Bortoleti, B.T.; Concato, V.M.; Silva, T.F.; Rafael, J.A.; Pavanelli, W.R.; Conchon-Costa, I.; et al. Recent Advances in Biotransformation by Cunninghamella Species. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021, 22, 1035–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ma, X.; Huo, C.; Yu, S.; Wang, Q. Microbiological transformation of paeoniflorin and albiflorin. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2010, 35, 872–875. [Google Scholar]
- Felts, R.L.; Reilly, T.J.; Tanner, J.J. Structure of Francisella tularensis AcpA: Prototype of a unique superfamily of acid phosphatases and phospholipases C. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 30289–30298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, Y. Golden rules and pitfalls in selecting optimum conditions for high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A. 2005, 1065, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xu, X.; Xie, C.; Xie, Z.; Yang, M. Isolation and Purification of Paeoniflorin and Albiflorin from Radix Paeoniae Rubra by High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2013, 36, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.E.; Pei, H.R.; Huo, L.S.; Hu, G.H.; Ito, Y. Development and evaluation of a spiral tube column for counter-current chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 2611–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casati, S.; Ciuffreda, P.; Santaniello, E. Synthesis of enantiomerically pure (R)-and (S)-1-benzoyloxypropane-2,3-diol and revision of the stereochemical outcome of the Candida antarctica lipase-catalyzed benzoylation of glycerol. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2011, 22, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Liu, M.; Shi, X.; Yang, W.; Kong, D.; Duan, K.; Wang, Q. Pharmacokinetic properties of paeoniflorin, albiflorin and oxypaeoniflorin after oral gavage of extracts of Radix Paeoniae Rubra and Radix Paeoniae Alba in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wei, S.; Wei, Z.; Li, R.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xiao, X. Comparative pharmacokinetic study of paeoniflorin and albiflorin after oral administration of Radix Paeoniae Rubra in normal rats and the acute cholestasis hepatitis rats. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Wan, M.; Zhou, D.; Gao, J.; Zhu, Y.; Bi, K. LC-MS/MS determination and pharmacokinetic study of albiflorin and paeoniflorin in rat plasma after oral administration of Radix Paeoniae Alba extract and Tang-Min-Ling-Wan. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, M.; Shu, Y.Z.; Shimizu, M.; Hayashi, T.; Morita, N.; Kobashi, K.; Xu, G.J.; Namba, T. Metabolism of paeoniflorin and related compounds by human intestinal bacteria. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1985, 33, 3838–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shu, Y.Z.; Hattori, M.; Akao, T.; Kobashi, K.; Kagei, K.; Fukuyama, K.; Tsukihara, T.; Namba, T. Metabolism of paeoniflorin and related compounds by human intestinal bacteria. II. Structures of 7S- and 7R-paeonimetabolines I and II formed by Bacteroides fragilis and Lactobacillus brevis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 3726–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsiu, S.L.; Lin, Y.T.; Wen, K.C.; Hou, Y.C.; Chao, P.D. A deglucosylated metabolite of paeoniflorin of the root of Paeonia lactiflora and its pharmacokinetics in rats. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Sun, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y. Metabolic study of paeoniflorin and total paeony glucosides from Paeoniae Radix Rubra in rats by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with sequential mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 32, e4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, H.; Purushothaman, S.; Pullaguri, N.; Bhargava, Y.; Bhargava, A. Sodium benzoate induced developmental defects, oxidative stress and anxiety-like behaviour in zebrafish larva. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xue, P.; Zhang, H.; Tan, C.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; et al. Gut brain interaction theory reveals gut microbiota mediated neurogenesis and traditional Chinese medicine research strategies. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1072341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.J.; Lin, C.H.; Lane, H.Y. Ketamine, benzoate, and sarcosine for treating depression. Neuropharmacology 2023, 223, 109351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, A.; Fujita, Y.; Iyo, M.; Hashimoto, K. Effects of sodium benzoate on pre-pulse inhibition deficits and hyperlocomotion in mice after administration of phencyclidine. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2015, 27, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scaglia, F.; Carter, S.; O’Brien, W.E.; Lee, B. Effect of alternative pathway therapy on branched chain amino acid metabolism in urea cycle disorder patients. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2004, 81 (Suppl. S1), S79–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmachari, S.; Jana, A.; Pahan, K. Sodium benzoate, a metabolite of cinnamon and a food additive, reduces microglial and astroglial inflammatory responses. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5917–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahan, K. Immunomodulation of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by cinnamon metabolite sodium benzoate. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2011, 33, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.; Modi, K.K.; Roy, A.; Anderson, J.A.; van Breemen, R.B.; Pahan, K. Up-regulation of neurotrophic factors by cinnamon and its metabolite sodium benzoate: Therapeutic implications for neurodegenerative disorders. J. Neuroimmune Pharm. 2013, 8, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Yang, R.; Tan, Y. Exploring the role and mechanism of sodium benzoate in CUMS-induced depression model of rats. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2020, 41, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.H.; Chen, P.K.; Chang, Y.C.; Chuo, L.J.; Chen, Y.S.; Tsai, G.E.; Lane, H.Y. Benzoate, a D-amino acid oxidase inhibitor, for the treatment of early-phase Alzheimer disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howley, E.; Bestwick, M.; Fradley, R.; Harrison, H.; Leveridge, M.; Okada, K.; Fieldhouse, C.; Farnaby, W.; Canning, H.; Sykes, A.P.; et al. Assessment of the Target Engagement and D-Serine Biomarker Profiles of the D-Amino Acid Oxidase Inhibitors Sodium Benzoate and PGM030756. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 3279–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Mawla, A.M.; Schmidt, W.; Beerhues, L. Cinnamic acid is a precursor of benzoic acids in cell cultures of Hypericum androsaemum L. but not in cell cultures of Centaurium erythraea RAFN. Planta 2001, 212, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Hou, J.; Meng, Q.; Yang, M.; Kurihara, H.; Tian, J. Novel antidepressant candidate RO-05 modulated glucocorticoid receptors activation and FKBP5 expression in chronic mild stress model in rats. Neuroscience 2015, 290, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Xing, Y.; Zuo, D.; Wu, Y.; Tian, J.; Meng, Q.; Yang, M. In vitro and in vivo characterization of PA01, a novel promising triple reuptake inhibitor. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 138, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Potassium 2-(1-hydroxypentyl)-benzoate improves depressive-like behaviors in rat model. Acta Pharm Sin. B 2018, 8, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponchiado, R.; Sorrentino, J.M.; Olegario, N.; Oliveira, S.S.; Cordenonsi, L.M.; Silveira, G.P.; Fuentefria, A.M.; Mendez, A.S.L.; Steppe, M.; Garcia, C.V. Microbial transformation of ambrisentan to its glycosides by Cunninghamella elegans. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C. RNA-Seq identification of candidate defense genes by analyzing Mythimna separata feeding-damage induced systemic resistance in balsas teosinte. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2019, 76, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjellqvist, B.; Basse, B.; Olsen, E.; Celis, J.E. Reference points for comparisons of two-dimensional maps of proteins from different human cell types defined in a pH scale where isoelectric points correlate with polypeptide compositions. Electrophoresis 1994, 15, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, D.W.A.; Jones, D.T. The PSIPRED Protein Analysis Workbench: 20 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W402–W407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, A.K.H.; Holzknecht, M.; Cappuccio, E.; Dorigatti, I.; Kreidl, K.; Naschberger, A.; Rupp, B.; Gstach, H.; Jansen-Durr, P. Expression, Purification, Crystallization, and Enzyme Assays of Fumarylacetoacetate Hydrolase Domain-Containing Proteins. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2019, 148, e59729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, H.; Ma, X.; Pan, Y.; Han, T.; Lu, Z.; Wu, R.; Cao, X.; Zheng, J. Separation and purification of lanosterol, dihydrolanosterol, and cholesterol from lanolin by high-performance counter-current chromatography dual-mode elution method. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaaboul, F.; Cao, C.; Raza, H.; Jun, Z.Z.; Xu, Y.J.; Liu, Y.F. The Triacylglycerol Profile of Oil Bodies and Oil Extracted from Argania spinosa Using the UPLC Along with the Electrospray Ionization Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (LC-Q-TOF-MS). J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cao, X.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, G. Untargeted metabolomics coupled with chemometrics approach for Xinyang Maojian green tea with cultivar, elevation and processing variations. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Clone | Vector | Restriction Site | Cell Strain | Expression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G6046-22b | pET22b | NdeI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | Inclusion body | |
| G6046-28b | pET28b | NdeI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | Inclusion body | |
| MBP-G6046 | pET28b | NcoI | NdeI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | Inclusion body |
| T4L-G6046 | pET28b | NcoI | BamHI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | Inclusion body |
| G6046-NΔ57-22b | pET22b | NdeI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | Inclusion body | |
| G6046-NΔ57-28b | pET28b | NdeI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | Inclusion body | |
| MBP-G6046-NΔ57 | pET28b | NcoI | NdeI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | Inclusion body |
| T4L-G6046-NΔ57 | pET28b | NcoI | BamHI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | Inclusion body |
| G6046-NΔ82-22b | pET22b | NdeI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | √ | |
| G6046-NΔ82-28b | pET28b | NdeI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | Inclusion body | |
| MBP-G6046-NΔ82 | pET28b | NcoI | NdeI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | Inclusion body |
| T4L-G6046-NΔ82 | pET28b | NcoI | BamHI | XhoI | BL21 (DE3) | Inclusion body |
| Solvent System Ethyl Acetate/n-Butanol/Water (v/v) | P1 (K1) | Paeoniflorin | P2 (K2) | P3 (K3) | α | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Kp) | Kp/K1 | K2/Kp | ||||
| 3/2.5/5 | 0.35 | 0.68 | 0.73 | 2.76 | 1.94 | 1.07 |
| 3/2/5 | 0.24 | 0.54 | 0.59 | 2.94 | 2.25 | 1.09 |
| 2/3/5 | 0.43 | 1.03 | 1.18 | 3.52 | 2.39 | 1.14 |
| 1/4/5 | 0.68 | 1.22 | 1.89 | 7.35 | 1.79 | 1.54 |
| No. | δC (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 131.57 | |
| 2 | 128.63 | 7.77 (m, 2H) |
| 3 | 127.72 | 7.44 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H) |
| 4 | 135.64 | 7.50 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H) |
| 5 | 127.72 | 7.44 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H) |
| 6 | 128.63 | 7.77 (m, 2H) |
| 7 | 167.76 | |
| 8 | 72.94 | 3.67 (s, 2H) |
| 9 | 60.99 | |
| 10 | 63.08 | 3.67 (s, 2H) |
| 11 | 63.56 | 3.67 (s, 2H) |
| No. | δC (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 130.38 | |
| 2 | 129.64 | 8.00 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H) |
| 3 | 129.09 | 7.53 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H) |
| 4 | 133.64 | 7.66 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H) |
| 5 | 129.09 | 7.53 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H) |
| 6 | 129.64 | 8.00 (d, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H) |
| 7 | 166.24 | |
| 8 | 66.82 | 4.18 (dd, J = 11.1, 4.0 Hz, 1H) |
| 4.31 (dd, J = 11.1, 6.3 Hz, 1H) | ||
| 9 | 69.79 | 3.80 (q, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H) |
| 10 | 63.08 | 3.45 (hept, J = 5.8 Hz, 2H) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Y.; Pei, H.; Cao, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, J. The Study of a Novel Paeoniflorin-Converting Enzyme from Cunninghamella blakesleeana. Molecules 2023, 28, 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031289
Ye Y, Pei H, Cao X, Liu X, Li Z, Wang B, Pan Y, Zheng J. The Study of a Novel Paeoniflorin-Converting Enzyme from Cunninghamella blakesleeana. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031289
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Yiheng, Hairun Pei, Xueli Cao, Xueying Liu, Zhanghan Li, Biying Wang, Yan Pan, and Jimin Zheng. 2023. "The Study of a Novel Paeoniflorin-Converting Enzyme from Cunninghamella blakesleeana" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031289
APA StyleYe, Y., Pei, H., Cao, X., Liu, X., Li, Z., Wang, B., Pan, Y., & Zheng, J. (2023). The Study of a Novel Paeoniflorin-Converting Enzyme from Cunninghamella blakesleeana. Molecules, 28(3), 1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031289






