Cross-Serological Reaction of Glandless Cottonseed Proteins to Peanut and Tree Nut Allergic IgE
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cottonseed Protein Extract Cross-Reacts with Peanut and Tree Nut IgE
2.2. 49 and 51 kDa Cottonseed Proteins Cross-React with Peanut and Tree Nut Allergic IgE
2.3. Cottonseed Vicilin and Legumin Proteins Cross-React with Peanut and Tree Nut IgE
2.4. Cottonseed Vicilin and Legumin Contain Sequences Similar to Peanut and Tree Nut IgE Epitopes
2.5. Cottonseed Vicilin and Legumin Models Reveal Potentially Surface Exposed IgE Cross-Reactive Epitopes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Gl Cottonseed Protein Preparation
4.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.4. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
4.5. Immunoblot
4.6. Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass-Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
4.7. Protein Sequence Analysis and Epitope Prediction
4.8. Protein Modeling
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yatsu, L.Y.; Hensarling, T.P.; Jacks, T.J. Extraction of Lipids from Cottonseed Tissue.6. Ultrastructural Morphology of Isolated Pigment Glands. J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 1974, 51, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Nam, S.; Zhang, H.; Olanya, O.M. Chemical Composition and Thermogravimetric Behaviors of Glanded and Glandless Cottonseed Kernels. Molecules 2022, 27, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathore, K.S.; Pandeya, D.; Campbell, L.M.; Wedegaertner, T.C.; Puckhaber, L.; Stipanovic, R.D.; Thenell, J.S.; Hague, S.; Hake, K. Ultra-Low Gossypol Cottonseed: Selective Gene Silencing Opens Up a Vast Resource of Plant-Based Protein to Improve Human Nutrition. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2020, 39, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Mattison, C.P.; Zhang, D.; Grimm, C.C. Vicilin and legumin storage proteins are abundant in water and alkali soluble protein fractions of glandless cottonseed. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, D.; Cao, H. Protein profiling of water and alkali soluble cottonseed protein isolates. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Freeland, D.M.H.; Nadeau, K.C. Food allergy: Immune mechanisms, diagnosis and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Holdford, D.; Bilaver, L.; Dyer, A.; Holl, J.L.; Meltzer, D. The economic impact of childhood food allergy in the United States. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkner, M.; Warren, C.; Gupta, R.S. Quality of Life in Food Allergy Patients and Their Families. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 2015, 62, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.S.; Warren, C.M.; Smith, B.M.; Jiang, J.; Blumenstock, J.A.; Davis, M.M.; Schleimer, R.P.; Nadeau, K.C. Prevalence and Severity of Food Allergies Among US Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e185630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benede, S.; Blazquez, A.B.; Chiang, D.; Tordesillas, L.; Berin, M.C. The rise of food allergy: Environmental factors and emerging treatments. EBioMedicine 2016, 7, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suther, C.; Moore, M.D.; Beigelman, A.; Zhou, Y. The Gut Microbiome and the Big Eight. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefle, S.L.; Nordlee, J.A.; Taylor, S.L. Allergenic foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1996, 36, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Smith, D. Open Sesame: Shedding light on an emerging global allergen. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 130, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeekens, J.M.; Bagley, K.; Kulis, M. Tree Nut Allergies: Allergen Homology, Cross-reactivity, and Implications for Therapy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiselhart, S.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Bublin, M. Tree nut allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, C.; Breiteneder, H. Peanut allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, N. Components of plant-derived food allergens: Structure, diagnostics, and immunotherapy. Allergol. Int. 2021, 70, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreskin, S.C.; Koppelman, S.J.; Andorf, S.; Nadeau, K.C.; Kalra, A.; Braun, W.; Negi, S.S.; Chen, X.; Schein, C.H. The importance of the 2S albumins for allergenicity and cross-reactivity of peanuts, tree nuts, and sesame seeds. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, F.J.; Clemente, A. 2S Albumin Storage Proteins: What Makes them Food Allergens? Open Biochem. J. 2008, 2, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, D.; Mattison, C.P. Quantitative comparison of the storage protein distribution in glandless and glanded cottonseeds. Agric. Environ. Lett. 2022, 7, e20076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, F.M.; Wilson, M.; Bock, S.A. Cottonseed hypersensitivity: New concerns over an old problem. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1988, 82, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, S.K.; Jordan, P.A.; Bahna, S.L. Eosinophilic esophagitis to unsuspected rare food allergen. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013, 111, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malanin, G.; Kalimo, K. Angioedema and urticaria caused by cottonseed protein in whole-grain bread. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1988, 82, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.F.; Kwan, S.H.; Lee, C.S.; Soh, Y.N.A.; Ho, Y.S.; Bi, X. Cottonseed Meal Protein Isolate as a New Source of Alternative Proteins: A Proteomics Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Punia, S.; Grasso, S.; Arrutia, F.; Choudhary, J.; Singh, S.; Verma, P.; Mahapatra, A.; Patil, S.; et al. Cottonseed: A sustainable contributor to global protein requirements. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wedegaertner, T. Genetics and Breeding for Glandless Upland Cotton With Improved Yield Potential and Disease Resistance: A Review. Front. Plant. Sci. 2021, 12, 753426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Cheng, H.N.; He, J. Initial Formulation of Novel Peanut Butter-like Products from Glandless Cottonseed. Foods 2023, 12, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, H.; Olk, D.C. Chemical Composition of Defatted Cottonseed and Soy Meal Products. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vita, R.; Mahajan, S.; Overton, J.A.; Dhanda, S.K.; Martini, S.; Cantrell, J.R.; Wheeler, D.K.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. The Immune Epitope Database (IEDB): 2018 update. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2019, 47, D339–D343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanos, C.; Urabe, H.; Tandang-Silvas, M.R.; Utsumi, S.; Mikami, B.; Maruyama, N. Crystal structure of the major peanut allergen Ara h 1. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 49, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Guo, F.; Chen, Y.W.; Howard, A.; Zhang, Y.Z. Crystal structure of Ara h 3, a major allergen in peanut. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudharson, S.; Kalic, T.; Hafner, C.; Breiteneder, H. Newly defined allergens in the WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Database during 01/2019-03/2021. Allergy 2021, 76, 3359–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radauer, C.; Breiteneder, H. Evolutionary biology of plant food allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalberse, R.C. Structural biology of allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiteneder, H.; Radauer, C. A classification of plant food allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Jin, T.; Lyu, S.C.; Nadeau, K.C.; McHugh, T. Almond (Prunus dulcis) Allergen Pru du 8, the First Member of a New Family of Food Allergens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8626–8631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabasser, S.; Pratap, K.; Kamath, S.; Taki, A.C.; Dang, T.; Koplin, J.; Perrett, K.; Hummel, K.; Radauer, C.; Breiteneder, H.; et al. Identification of vicilin, legumin and antimicrobial peptide 2a as macadamia nut allergens. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C. Kernel Rising: Cotton Could Soon Feed the World. Farm. J. 2020, 1–17. Available online: https://www.agweb.com/news/crops/crop-production/kernel-rising-cotton-could-soon-feed-world (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- He, Z.; Liu, S.; Nam, S.; Klasson, K.T.; Cheng, H.N. Molecular level characterization of the effect of roasting on the extractable components of glandless cottonseed by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattison, C.P.; Vant-Hull, B.; Bren-Mattison, Y.; Grimm, C.C. A cashew specific monoclonal antibody recognizing the small subunit of Ana o 3. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattison, C.P.; Desormeaux, W.A.; Wasserman, R.L.; Yoshioka-Tarver, M.; Condon, B.; Grimm, C.C. Decreased immunoglobulin E (IgE) binding to cashew allergens following sodium sulfite treatment and heating. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6746–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattison, C.P.; Grimm, C.C.; Wasserman, R.L. In vitro digestion of soluble cashew proteins and characterization of surviving IgE-reactive peptides. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
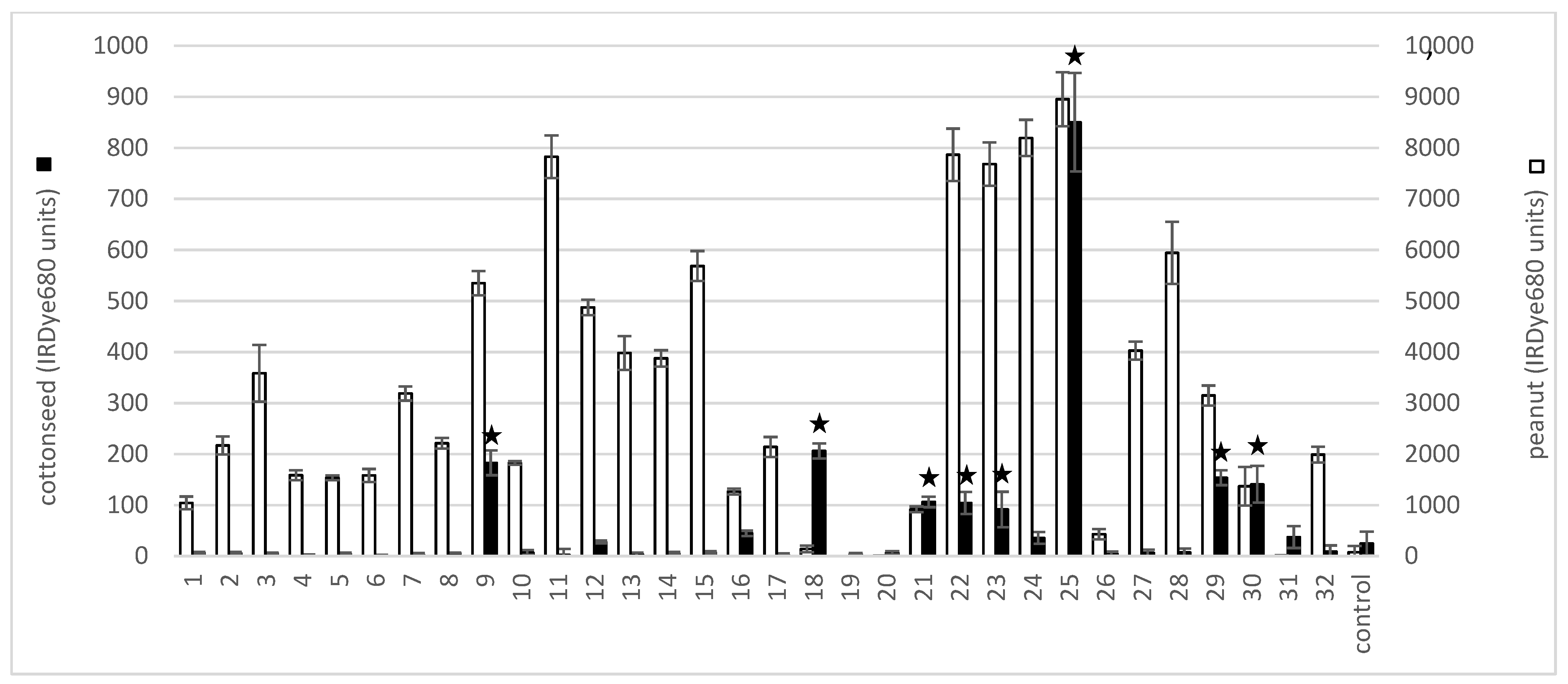


| Volunteer | Peanut | Almond | Hazelnut | Brazil Nut | Cashew | Pistachio | Walnut | Macadamia Nut | Pecan | Soy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 108.43 | ND | 0.28 | 0.1 | ND | ND | 0.1 | ND | ND | ND |
| 2 | 100 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 3 | 100 | 0.75 | 2.14 | 0.12 | 5.07 | 5.75 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 5.74 |
| 4 | 140.6 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 4.234 |
| 5 | 100 | 26.6 | 18.7 | 0.53 | 0.66 | 3.2 | 17.1 | 3.27 | 4.46 | 8.25 |
| 6 | 100 | 14.7 | 44 | 9.85 | 44.2 | 44.3 | 49.7 | 5.86 | 32.5 | 5.314 |
| 7 | 100 | 2.97 | 32.7 | 5.28 | 17.1 | 26.7 | 7.46 | ND | ND | 8.09 |
| 8 | 100 | 0.27 | 5.9 | ND | 10.8 | 4.63 | 0.54 | ND | ND | 5.11 |
| 9 * | 100 | ND | 100 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 38 |
| 10 | 100 | ND | 1.34 | 0.16 | 0.38 | 0.92 | 0.35 | ND | ND | ND |
| 11 | 15.19 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 12 | 43.2 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 13 | 0.35 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.422 |
| 14 | >100 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 15 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 51.4 | ND | ND | ND | 65.7 | ND |
| 16 | 1.678 | ND | 0.406 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 17 | 90.8 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 18 * | ND | ND | 18.9 | ND | ND | 3.14 | 25.4 | ND | ND | ND |
| 19 | 6.2 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 20 | 1.3 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 21 * | 2.9 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 22 * | 67.4 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 51.8 | 4.67 |
| 23 * | 47.4 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 24 | 74 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 25 * | 90.8 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 26 | 86.8 | ND | 11.7 | ND | ND | ND | 4.74 | ND | ND | 5.8 |
| 27 | 51.5 | ND | 20 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1.66 |
| 28 | 42.67 | ND | ND | ND | 11.3 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 9.49 |
| 29 * | 99.3 | 10.4 | 27.2 | 9.32 | 82.6 | ND | 24 | ND | ND | 13.2 |
| 30 * | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 15.5 | ND |
| 31 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | 38.6 | ND | ND | ND |
| 32 | 41 | ND | ND | ND | 10.6 | ND | ND | ND | 2.22 | 4.34 |
| 51 kDa Band | ||||||||
| Accession | Score | Mass | Matches | Match (sig) | Sequences | Seq (sig) | emPAI | Description |
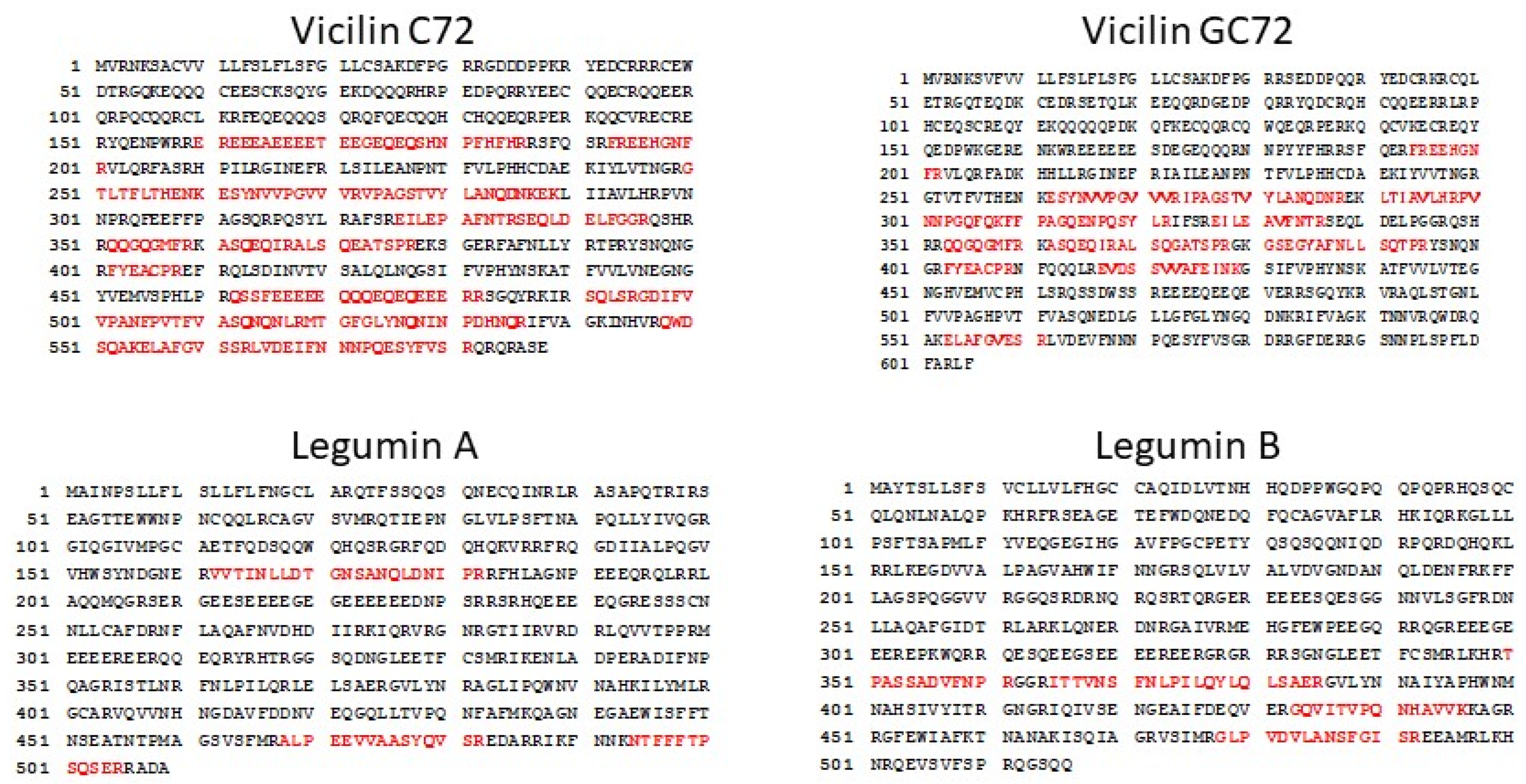
| VCLB_GOSHI | 8731 | 70,598 | 320 | 320 | 21 | 21 | 3.8 | Vicilin C72 OS = Gossypium hirsutum OX = 3635 PE = 2 SV = 1 |
| VCLA_GOSHI | 886 | 71,861 | 52 | 52 | 11 | 11 | 1.24 | Vicilin GC72-A OS = Gossypium hirsutum OX = 3635 PE = 3 SV = 1 |
| LEGB_GOSHI | 275 | 59,072 | 11 | 11 | 4 | 4 | 0.39 | Legumin B OS = Gossypium hirsutum OX = 3635 GN = LEGB PE = 2 SV = 1 |
| LEGA_GOSHI | 226 | 58,902 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0.18 | Legumin A OS = Gossypium hirsutum OX = 3635 GN = LEGA PE = 2 SV = 2 |
| 49 kDa band | ||||||||
| Accession | Score | Mass | Matches | Match (sig) | Sequences | Seq (sig) | emPAI | Description |
| VCLB_GOSHI | 9443 | 70,598 | 339 | 339 | 20 | 20 | 3.49 | Vicilin C72 OS = Gossypium hirsutum OX = 3635 PE = 2 SV = 1 |
| VCLA_GOSHI | 911 | 71,861 | 43 | 43 | 9 | 9 | 0.96 | Vicilin GC72-A OS = Gossypium hirsutum OX = 3635 PE = 3 SV = 1 |
| LEGA_GOSHI | 193 | 58,902 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0.18 | Legumin A OS = Gossypium hirsutum OX = 3635 GN = LEGA PE = 2 SV = 2 |
| LEGB_GOSHI | 95 | 59,072 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0.18 | Legumin B OS = Gossypium hirsutum OX = 3635 GN = LEGB PE = 2 SV = 1 |
| Name | Source | Accession | Query Cover | E Value | Percent Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GC72 | Cotton | A0A1U8LQ34 | 99% | 0 | 72.39 |
| Jug r 2 2.0101 | English walnut | Q9SEW4 | 78% | 1.00 × 10−127 | 45.53 |
| Car i 2.0101 | Pecan | B3STU4 | 84% | 2.00 × 10−120 | 44.47 |
| Cor a 11.0101 | Hazelnut | Q8S4P9 | 82% | 2.00 × 10−107 | 39.39 |
| Ara h 1 (P41B) | Peanut | P43238 | 72% | 1.00 × 10−77 | 35.87 |
| Pis v 3.0101 | Pistachio | B4X640 | 84% | 1.00 × 10−88 | 32.96 |
| Ana o 1.0101 | Cashew | Q8L5L5 | 84% | 1.00 × 10−86 | 31.89 |
| Name | Source | Accession | Query Cover | E Value | Percent Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pis v 2.0101 | Pistachio | B7P073 | 89% | 3.00 × 10−168 | 54.06 |
| Cor a 9.0101 | Hazelnut | Q8W1C2 | 98% | 1.00 × 10−144 | 47.49 |
| Jug n 4.0101 | Black walnut | A0A1L6K371 | 98% | 8.00 × 10−150 | 46.32 |
| Car i 4.0101 | Pecan | B5KVH4 | 98% | 3.00 ×10−146 | 46.15 |
| Jug r 4.0101 | English walnut | Q2TPW5 | 98% | 5.00 × 10−139 | 45.42 |
| Legumin A | Cotton | XP_016701249.1 | 90% | 5.00 × 10−138 | 45.05 |
| Ana o 2.0101 | Cashew | Q8GZP6 | 97% | 8.00 × 10−141 | 45.04 |
| Ara h 3.0101 | Peanut | O82580 | 92% | 6.00 × 10−98 | 35.85 |
| Epitope | Antigen | Organism |
|---|---|---|
| GC72 vicilin | ||
| VNTPGQFEDFFPASS | Ara h 1 | Arachis hypogaea (peanut) |
| YAEIKRGAMMVPHYNSKATV | Jug r 2 | Juglans regia (English walnut) |
| ARLARGDIFVIPAGHPIAIT | Jug r 2 | Juglans regia (English walnut) |
| QDIFVIPAGYPVVVN | Beta-conglycinin alpha subunit 2 | Glycine max (soybean) |
| C72 vicilin | ||
| SMPVNTPGQFEDFFP | Ara h 1 | Arachis hypogaea (peanut) |
| VNTPGQFEDFFPASS | Ara h 1 | Arachis hypogaea (peanut) |
| PVNTPGQFEDFFPASSRDQS | Ara h 1 | Arachis hypogaea (peanut) |
| SMPVNTPGQFEDFFPASSRD | Ara h 1 | Arachis hypogaea (peanut) |
| Legumin A | ||
| NQLDQMPRRFYLAGN | Gly m 6 | Glycine max (soybean) |
| GDIIAFPAGVAHWSY | Jug r 4 | Juglans regia (English walnut) |
| GDIIALPAGVAHWCY | Cor a 9 | Corylus avellana (European hazelnut) |
| FQISREDARKIKFNN | Ana o 2 | Anacardium occidentale (cashew) |
| LDRTPRKFHLAGNPK | Ana o 2 | Anacardium occidentale (cashew) |
| QDRHQKIRRFRRGDI | Ana o 2 | Anacardium occidentale (cashew) |
| QNQLDQVPRRFYLAG | Pru du 6 | Prunus dulcis (almond) |
| Legumin B | ||
| FGMIFPGCPSTYQEP | Gly m 6 | Glycine max (soybean) |
| AFQISREEARRLKYN | Cor a 9 | Corylus avellana (European hazelnut) |
| GDIIALPAGVAHWCY | Cor a 9 | Corylus avellana (European hazelnut) |
| IESWDPNNQQFQCAG | Jug r 4 | Juglans regia (English walnut) |
| PHWNLNAHSVVYALR | Jug r 4 | Juglans regia (English walnut) |
| YANQLDENPRHFYLA | Cor a 9 | Corylus avellana (European hazelnut) |
| AIPAGVAHWCYNEGN | Ana o 2 | Anacardium occidentale (cashew) |
| LKWLQLSVEKGVLYK | Ana o 2 | Anacardium occidentale (cashew) |
| LSVCFLILFHGCLAS | Ana o 2 | Anacardium occidentale (cashew) |
| RWGQRDNGIEETICTMRLKENINDP | Ana o 2 | Anacardium occidentale (cashew) |
| QFRCAGVALVRHTIQ | Ana o 2 | Anacardium occidentale (cashew) |
| ERGVLQNNALMVPHWNFNAS | Pis v 5 | Pistacia vera (pistachio) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mattison, C.P.; He, Z.; Zhang, D.; Dupre, R.; Lloyd, S.W. Cross-Serological Reaction of Glandless Cottonseed Proteins to Peanut and Tree Nut Allergic IgE. Molecules 2023, 28, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041587
Mattison CP, He Z, Zhang D, Dupre R, Lloyd SW. Cross-Serological Reaction of Glandless Cottonseed Proteins to Peanut and Tree Nut Allergic IgE. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041587
Chicago/Turabian StyleMattison, Christopher P., Zhongqi He, Dunhua Zhang, Rebecca Dupre, and Steven W. Lloyd. 2023. "Cross-Serological Reaction of Glandless Cottonseed Proteins to Peanut and Tree Nut Allergic IgE" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041587
APA StyleMattison, C. P., He, Z., Zhang, D., Dupre, R., & Lloyd, S. W. (2023). Cross-Serological Reaction of Glandless Cottonseed Proteins to Peanut and Tree Nut Allergic IgE. Molecules, 28(4), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041587








