Simultaneous Predictions of Chemical and Phase Equilibria in Systems with an Esterification Reaction Using PC-SAFT
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Algorithmic Approach
2.1. Thermodynamics of Chemical Reactions and Multiple Liquid Phase Equilibria
2.2. Algorithm Architecture
Algorithmic Structure
- 1-
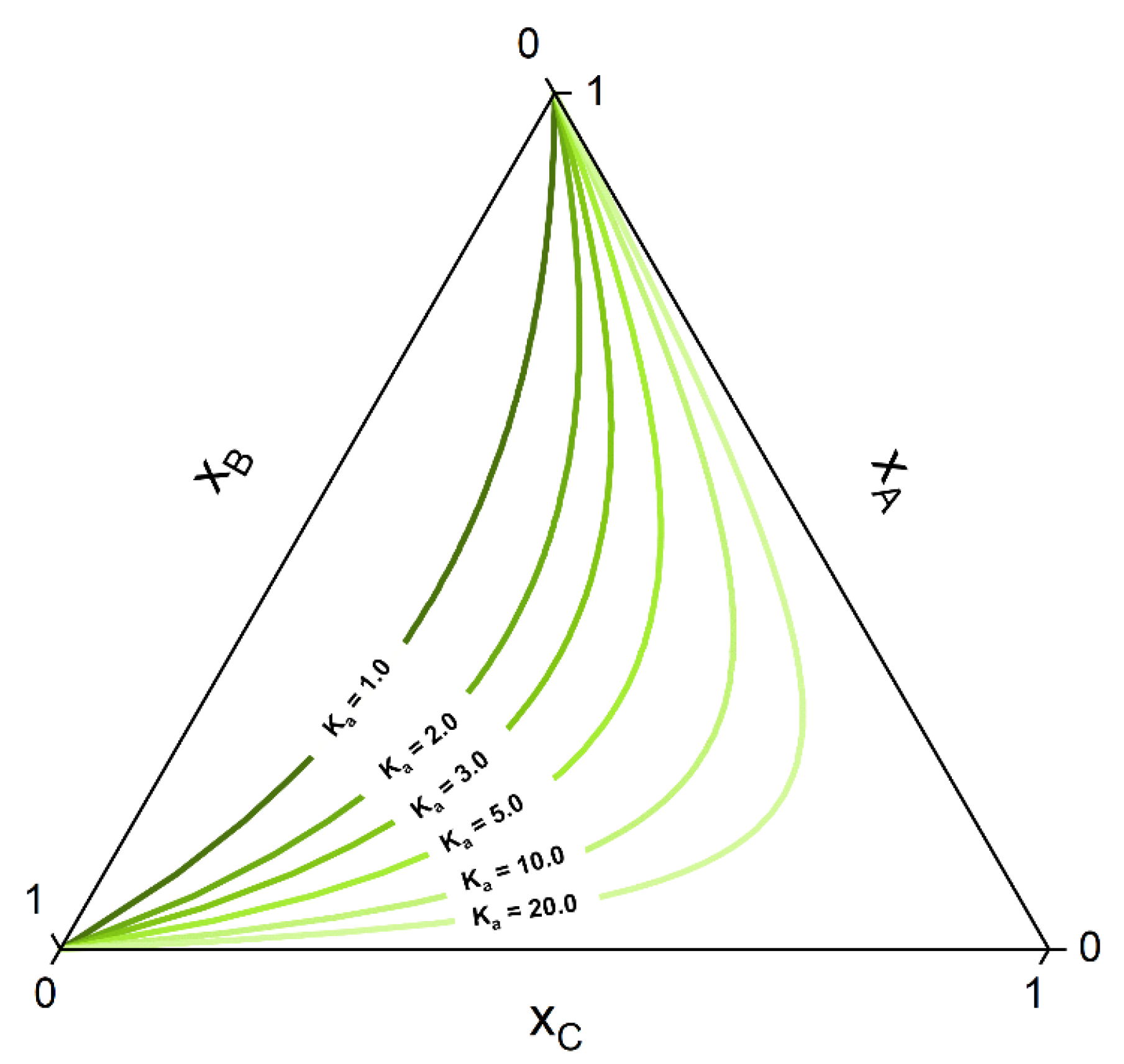
- First the feed composition , the temperature p and the pressure T is given. Initially, an homogeneous CE calculation is performed at these conditions, according to the stoichiometry of the defined key reactions . This is equivalent to moving the composition point, along a trajectory imposed by the stoichiometry called stoichiometry line, to the (hyper-)surface (composition ) where the CE condition for each key reaction is fulfilled (Equation (8)). For a simple reaction and the corresponding ternary phase diagram, this chemical equilibration step can be visualized in Figure 4.
- 2-
- 3-
- Third, CE is performed for each of the single phases provided by step 2. This is equivalent to moving each single phase, according to the reaction stoichiometry, to the chemical equilibrium (hyper-)surface. The overall feed composition will move as well; however, it will in general not lie to the chemical equilibrium (hyper-)surface as with the single phases. This third step will finally provide good initial point for the final reactive flash calculation.
- 4-
- Finally, rigorous reactive flash calculation according to the strategy proposed in the last section is applied. After final convergence, two equilibrium points that satisfy Equations (7) and (8) are returned (Figure 6).
3. Results
3.1. The Reaction Systems Considered in This Work
3.2. PC-SAFT Parameters for the Considered Reaction Systems
3.3. The Reaction Equilibrium Constants Ka of the Considered Chemical Reactions
3.4. Prediction Results of the CPE Problem for Both Reactions under Study
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. PC-SAFT
References
- Toikka, A.M.; Samarov, A.A.; Toikka, M.A. Phase and chemical equilibria in multicomponent fluid systems with a chemical reaction. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2015, 84, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmehling, J.; Kolbe, B. Thermodynamik, 2nd überarbeitete Auflage ed; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1992; ISBN 3527285474. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.M.; van Ness, H.C.; Abbott, M.M. Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, 7th ed.; McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2005; ISBN 0073104450. [Google Scholar]
- Prausnitz, J.M.; de Azevedo, E.G.; Lichtenthaler, R.N. Molecular Thermodynamics of Fluid-Phase Equilibria, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1999; ISBN 0139777458. [Google Scholar]
- Sundmacher, K.; Kienle, A. Reactive Distillation: Status and Future Directions; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; ISBN 3527305793. [Google Scholar]
- Górak, A.; Sorensen, E. Distillation: Fundamentals and Principles; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 0123865484. [Google Scholar]
- Górak, A.; Olujic, Z. Distillation: Equipment and Processes; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 0123868793. [Google Scholar]
- Serafimov, L.A.; Pisarenko, Y.A.; Kulov, N.N. Coupling chemical reaction with distillation: Thermodynamic analysis and practical applications. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, T.; Blahusiak, M.; Babic, K.; Schuur, B. Reactive extraction and recovery of levulinic acid, formic acid and furfural from aqueous solutions containing sulphuric acid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 185, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, G. Modeling the liquid–liquid equilibrium for the recovery of carboxylic acids from aqueous solutions. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2006, 241, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.; Waluga, T. Reactive extraction. In Process Intensification by Reactive and Membrane-Assisted Separations, 2nd ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-3-11-072045-7. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, D.A.; Ng, K.M. Synthesis of reactive crystallization processes. AIChE J. 1997, 43, 1737–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, M.A.; Salami, H.; Harris, P.R.; Lagerman, C.E.; Yang, X.; Bommarius, A.S.; Grover, M.A.; Rousseau, R.W. Reactive crystallization: A review. React. Chem. Eng. 2021, 6, 364–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenig, E.Y.; Schneider, R.; Górak, A. Reactive absorption: Optimal process design via optimal modelling. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenig, E.Y.; Górak, A. Reactive absorption. In Integrated Chemical Processes: Synthesis, Operation, Analysis, and Control; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 265–311. [Google Scholar]
- Kunze, A.-K. Reactive absorption. In Process Intensification by Reactive and Membrane-assisted Separations, 2nd ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-3-11-072045-7. [Google Scholar]
- Skiborowski, M.; Górak, A. Hybrid separation processes. In Process Intensification by Reactive and Membrane-assisted Separations, 2nd ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-3-11-072045-7. [Google Scholar]
- Schembecker, G.; Tlatlik, S. Process synthesis for reactive separations. Chem. Eng. Process. 2003, 42, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, M.F.; Huss, R.S.; Doherty, M.F. Green chemical engineering aspects of reactive distillation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5325–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.K. Chemistry of Active Coacervate Droplets: Liquid Droplets as a Minimal Model of Life. Ph.D. Thesis, Radboud University Nijmegen, Nijmegen, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima, K.K.; Baaij, J.F.; Spruijt, E. Reversible generation of coacervate droplets in an enzymatic network. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Park, K.; Lee, H.; Jang, S.; Song, H.-C.; Shin, H.-C.; Park, J.J.; Park, J.; Maken, S. Purification of native and modified enzymes using a reactive aqueous two-phase system. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2004, 10, 384–388. [Google Scholar]
- Campos-García, V.R.; Benavides, J.; González-Valdez, J. Reactive aqueous two-phase systems for the production and purification of PEGylated proteins. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 54, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schick, D.; Bierhaus, L.; Strangmann, A.; Figiel, P.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C. Predicting CO2 solubility in aqueous and organic electrolyte solutions with ePC-SAFT advanced. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2023, 567, 113714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NguyenHuynh, D.; Mai, C.T.Q.; Tran, S.T.K.; Nguyen, X.T.T.; Baudouin, O. Modelling of phase behavior of ammonia and its mixtures using the mg-SAFT. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2020, 523, 112689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogeorgis, G.M.; Folas, G.K. Thermodynamic Models for Industrial Applications: From Classical and Advanced Mixing Rules to Association Theories; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 0470747544. [Google Scholar]
- Danzer, A.; Enders, S. Comparison of two modelling approaches for the interfacial tension of binary aqueous mixtures. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrmann, D.; Danzer, A.; Sadowski, G. Generalized Diffusion–Relaxation Model for Solvent Sorption in Polymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 15766–15781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caram, H.S.; Scriven, L.E. Non-unique reaction equilibria in non-ideal systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1976, 31, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othmer, H.G. Nonuniqueness of equilibria in closed reacting systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1976, 31, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidemann, R.A. Non-uniqueness in phase and reaction equilibrium computations. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1978, 33, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, S.; Doherty, M.F. Theory of phase equilibria in multireaction systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1995, 50, 3201–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, D.; Doherty, M.F. A new set of composition variables for the representation of reactive-phase diagrams. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1987, 413, 459–464. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Smith, W.R.; Chapman, G.R. Global optimality conditions and their geometric interpretation for the chemical and phase equilibrium problem. SIAM J. Optim. 1995, 5, 813–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chapman, G.R.; Smith, W.R. On the geometry of chemical reaction and phase equilibria. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1996, 118, 77–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.R.; Missen, R.W. Strategies for solving the chemical equilibrium problem and an efficient microcomputer-based algorithm. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1988, 66, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.V.; Missen, R.W.; Smith, W.R. General optimality criteria for multiphase multireaction chemical equilibrium. AIChE J. 1993, 39, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.R. The computation of chemical equilibria in complex systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1980, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleznik, F.J.; Gordon, S. Calculation of complex chemical equilibria. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1968, 60, 27–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Wareck, J.S. Computation of physical and chemical equilibria—Alternate specifications. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1986, 10, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, D.; Doherty, M.F. Theory of phase diagrams and azeotropic conditions for two-phase reactive systems. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1987, 413, 443–458. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, D.; Doherty, M.F. The influence of equilibrium chemical reactions on vapor—Liquid phase diagrams. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1988, 43, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharov, V.T. Open evaporation of solutions of reacting substances. Zh. Fiz. Khim 1970, 44, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Zharov, V.T.; Pervukhin, O.K. Structure of the Vapor–liquid Equilibrium Diagrams of Reactive Systems: II. Methanol–Formic Acid–Methyl Formate–Water System. Zh. Fiz. Khim 1972, 46, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Wasylkiewicz, S.K.; Ung, S. Global phase stability analysis for heterogeneous reactive mixtures and calculation of reactive liquid–liquid and vapor–liquid–liquid equilibria. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2000, 175, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okasinski, M.J.; Doherty, M.F. Thermodynamic behavior of reactive azeotropes. AIChE J. 1997, 43, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, S.; Doherty, M.F. Necessary and sufficient conditions for reactive azeotropes in multireaction mixtures. AIChE J. 1995, 41, 2383–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, S.; Doherty, M.F. Vapor-liquid phase equilibrium in systems with multiple chemical reactions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1995, 50, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.M.; Floudas, C.A. Global optimization for the phase and chemical equilibrium problem: Application to the NRTL equation. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1995, 19, 1111–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.M.; Floudas, C.A. Global optimization for the phase stability problem. AIChE J. 1995, 41, 1798–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.M.; Floudas, C.A. GLOPEQ: A new computational tool for the phase and chemical equilibrium problem. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1997, 21, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali-Farahani, F.; Seader, J.D. Use of homotopy-continuation method in stability analysis of multiphase, reacting systems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2000, 24, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanas, C.; Stenby, E.H.; Yan, W. Calculation of multiphase chemical equilibrium by the modified RAND method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 11983–11995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stateva, R.P.; Wakeham, W.A. Phase equilibrium calculations for chemically reacting systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 5474–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, R.V.; Chien, H.H. Simultaneous chemical and phase equilibrium calculation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1973, 12, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coatléven, J.; Michel, A. A successive substitution approach with embedded phase stability for simultaneous chemical and phase equilibrium calculations. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2022, 168, 108041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Bishnoi, P.R.; Kalogerakis, N. A method for the simultaneous phase equilibria and stability calculations for multiphase reacting and non-reacting systems. Fluid Ph. Equilibria 1991, 63, 65–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Johnson, S.M.; Dantzig, G.B. Chemical Equilibrium in Complex Mixtures. J. Chem. Phys. 1958, 28, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Proust, C.; Gomez, F.; Luart, D.; Len, C. The prediction multi-phase, multi reactant equilibria by minimizing the Gibbs energy of the system: Review of available techniques and proposal of a new method based on a Monte Carlo technique. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 216, 115433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulocheris, V.; Panteli, M.; Petropoulou, E.; Louli, V.; Voutsas, E. Modeling of Simultaneous Chemical and Phase Equilibria in Systems Involving Non-reactive and Reactive Azeotropes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 8836–8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, A.M.M.; Kulik, D.A.; Smith, W.R.; Saar, M.O. An overview of computational methods for chemical equilibrium and kinetic calculations for geochemical and reactive transport modeling. Pure Appl. Chem. 2017, 89, 597–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanas, C.; Stenby, E.H.; Yan, W. Calculation of simultaneous chemical and phase equilibrium by the method of Lagrange multipliers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 174, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. A Review on Global Optimization Methods for Phase Equilibrium Modeling and Calculations. Open Thermodyn. J. 2011, 5, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toikka, A.M.; Toikka, M.A. Solubility and critical phenomena in reactive liquid–liquid systems. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toikka, M.A.; Toikka, A.M. Peculiarities of phase diagrams of reactive liquid–liquid systems. Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 85, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toikka, A.M.; Toikka, M.A.; Trofimova, M.A. Chemical equilibrium in a heterogeneous fluid phase system: Thermodynamic regularities and topology of phase diagrams. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2012, 61, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toikka, A.M.; Toikka, M.A.; Pisarenko, Y.A.; Serafimov, L.A. Vapor-liquid equilibria in systems with esterification reaction. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2009, 43, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromov, D.; Toikka, A. Toward formal analysis of thermodynamic stability: Le Chatelier—Brown principle. Entropy 2020, 22, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toikka, A.M.; Jenkins, J.D. Conditions of thermodynamic equilibrium and stability as a basis for the practical calculation of vapour–liquid equilibria. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 89, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorovits, B.I.; Toikka, A.M.; Pisarenko, Y.A.; Serafimov, L.A. Thermodynamics of heterogeneous systems with chemical interaction. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2006, 40, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toikka, M.A.; Kuzmenko, P.; Samarov, A.; Trofimova, M. Phase behavior of the oleic acid–methanol–methyl oleate–water mixture as a promising model system for biodiesel production: Brief data review and new results at 303.15 K and atmospheric pressure. Fuel 2022, 319, 123730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senina, A.; Samarov, A.; Toikka, M.; Toikka, A. Chemical equilibria in the quaternary reactive mixtures and liquid phase splitting: A system with n-amyl acetate synthesis reaction at 318.15 K and 101.3 kPa. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 118246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toikka, M.A.; Tsvetov, N.S.; Toikka, A.M. Experimental study of chemical equilibrium and vapor-liquid equilibrium calculation for chemical-equilibrium states of the n-propanol-acetic acid-n-propyl acetate-water system. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2013, 47, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarov, A.; Prikhodko, I.; Shner, N.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C.; Toikka, A. Liquid–Liquid Equilibria for Separation of Alcohols from Esters Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride: Experimental Study and Thermodynamic Modeling. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 6049–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarov, A.; Naumkin, P.; Toikka, A. Chemical equilibrium for the reactive system acetic acid+ n-butanol+ n-butyl acetate+ water at 308.15 K. Fluid Ph. Equilibria 2015, 403, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golikova, A.; Samarov, A.; Trofimova, M.; Rabdano, S.; Toikka, M.; Pervukhin, O.; Toikka, A. Chemical equilibrium for the reacting system acetic acid–ethanol–ethyl acetate–water at 303.15 K, 313.15 K and 323.15 K. J. Solut. Chem. 2017, 46, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, S.; Hasse, H. Thermodynamics of phase and chemical equilibrium in a strongly nonideal esterification system. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2005, 50, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechert, O.; Husham, M.; Sadowski, G.; Zeiner, T. Solvent effects on esterification equilibria. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 3000–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangler, A.; Canales, R.; Held, C.; Luong, T.Q.; Winter, R.; Zaitsau, D.H.; Verevkin, S.P.; Sadowski, G. Co-solvent effects on reaction rate and reaction equilibrium of an enzymatic peptide hydrolysis. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 11317–11326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajardo-Parra, N.; Akrofi-Mantey, H.O.; Ascani, M.; Cea-Klapp, E.; Garrido, J.M.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C. Osmolyte effect on enzymatic stability and reaction equilibrium of formate dehydrogenase. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2022, 24, 27930–27939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangler, A.; Böttcher, D.; Hüser, A.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C. Prediction and Experimental Validation of Co-Solvent Influence on Michaelis Constants: A Thermodynamic Activity-Based Approach. Chem. A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 16418–16425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangler, A.; Bunse, M.J.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C. Thermodynamic activity-based Michaelis constants. In Kinetics of Enzymatic Synthesis; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 27–49. [Google Scholar]
- Jaworek, M.W.; Gajardo-Parra, N.F.; Sadowski, G.; Winter, R.; Held, C. Boosting the kinetic efficiency of formate dehydrogenase by combining the effects of temperature, high pressure and co-solvent mixtures. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 208, 112127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, M.L. The isothermal flash problem. Part I. Stability. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1982, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, M.L. The isothermal flash problem. Part II. Phase-split calculation. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1982, 9, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaifi, N.M.; Englezos, P. Prediction of multiphase equilibrium using the PC-SAFT equation of state and simultaneous testing of phase stability. Fluid Ph. Equilibria 2011, 302, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boston, J.F.; Britt, H.I. A radically different formulation and solution of the single-stage flash problem. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1978, 2, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zhu, K.; Yuan, W.; Chien, H.H. An algorithm for simultaneous chemical and phase equilibrium calculation. AIChE J. 1989, 35, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, S.I. Chemical and Engineering Thermodynamics, 3rd ed.; Section 8.5; J. Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.R.; Missen, R.W. Chemical Reaction Equilibrium Analisis: Theory and Algorithms; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Ascani, M.; Held, C. Thermodynamics for reactive separations. In Process Intensification by Reactive and Membrane-Assisted Separations, 2nd ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-3-11-072045-7. [Google Scholar]
- Storonkin, A.V. Thermodynamics of Heterogeneous Systems; Part 1&2; Publishing House of Leningrad University: Leningrad, Russia, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Ascani, M.; Pabsch, D.; Klinksiek, M.; Gajardo-Parra, N.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C. Prediction of pH in multiphase multicomponent systems with ePC-SAFT advanced. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 8436–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascani, M.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C. Calculation of Multiphase Equilibria Containing Mixed Solvents and Mixed Electrolytes: General Formulation and Case Studies. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2022, 67, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broyden, C.G. A class of methods for solving nonlinear simultaneous equations. Math. Comput. 1965, 19, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Blair, M. DNAD, a simple tool for automatic differentiation of Fortran codes using dual numbers. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2013, 184, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M. Heterogen Katalysierte Reaktivdestillation: Stoffdaten, Experimente, Simulation und Scale-up am Beispiel der Synthese von Hexylacetat. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgard, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, M.; Hasse, H. Phase equlibria for hexyl acetate reactive distillation. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2005, 50, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Hasse, H. Chemical equilibrium and reaction kinetics of heterogeneously catalyzed n-hexyl acetate esterification. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 4123–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, R.; Stuart, J. Mutual binary solubilities: Water-alcohols and water-esters. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1986, 31, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, R.; Stuart, J.; Tabak, M. Mutual solubility of water and aliphatic alcohols. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1984, 29, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toikka, M.A.; Vernadskaya, V.; Samarov, A. Solubility, liquid-liquid equilibrium and critical states for quaternary system acetic acid–n-amyl alcohol–n-amyl acetate–water at 303.15 K and atmospheric pressure. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2018, 471, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, M.M.; Bernardo-Gil, M.G. Liquid—Liquid equilibria for the systems: Water/1-pentanol/acetic acid and water/1-hexanol/acetic acid. Fluid Ph. Equilibria 1991, 62, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameretti, L.F.; Sadowski, G. Modeling of aqueous amino acid and polypeptide solutions with PC-SAFT. Chem. Eng. Process. 2008, 47, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.; Sadowski, G. Application of the perturbed-chain SAFT equation of state to associating systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 5510–5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tihic, A.; Kontogeorgis, G.M.; von Solms, N.; Michelsen, M.L. Applications of the simplified perturbed-chain SAFT equation of state using an extended parameter table. Fluid Ph. Equilibria 2006, 248, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabsch, D.; Lindfeld, J.; Schwalm, J.; Strangmann, A.; Figiel, P.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C. Influence of solvent and salt on kinetics and equilibrium of esterification reactions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 263, 118046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, H.; Voges, M.; Held, C.; Albert, J. Measuring and Predicting the Extraction Behavior of Biogenic Formic Acid in Biphasic Aqueous/Organic Reaction Mixtures. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8982–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmehling, J.; Onken, U.; Arlt, W. Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data Collection: Organic Hydroxy Compounds: Alcohols and Phenols (Chemistry Data Series, Volume 1, Part 2b); DECHEMA Research Institute: Frankfurt, Germany, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.; Liang, S. Phase and reaction equilibria of acetic acid–1-pentanol–water–n-amyl acetate system at 760 mm Hg. Fluid Ph. Equilibria 1998, 149, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Chen, S.-L.; Kang, C.-H.; Lin, H. Simultaneous chemical and phase equilibria for mixtures of acetic acid, amyl alcohol, amyl acetate, and water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 4383–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.; Sadowski, G. Perturbed-chain SAFT: An equation of state based on a perturbation theory for chain molecules. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 1244–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanzig, R.W. High-temperature equation of state by a perturbation method. I. Nonpolar gases. J. Chem. Phys. 1954, 22, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuarrie, D.A. Statistical Mechanics; Sterling Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 1891389157. [Google Scholar]
- Wertheim, M.S. Fluids with highly directional attractive forces. I. Statistical thermodynamics. J. Stat. Phys. 1984, 35, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertheim, M.S. Fluids with highly directional attractive forces. II. Thermodynamic perturbation theory and integral equations. J. Stat. Phys. 1984, 35, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertheim, M.S. Fluids with highly directional attractive forces. III. Multiple attraction sites. J. Stat. Phys. 1986, 42, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertheim, M.S. Fluids with highly directional attractive forces. IV. Equilibrium polymerization. J. Stat. Phys. 1986, 42, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Component | Ref. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 1.2047 | * | 353.95 | 2 | 2425.7 | 0.04509 | [104] |
| Acetic acid | 1.3402 | 3.8582 | 311.59 | 2 | 3044.4 | 0.07555 | [105] |
| 1-Pentanol | 3.6260 | 3.4508 | 247.28 | 2 | 2252.1 | 0.01033 | [105] |
| 1-Hexanol | 3.5146 | 3.6735 | 262.32 | 2 | 2538.9 | 0.00575 | [105] |
| Pentyl Acetate | 4.7077 | 3.4729 | 234.57 | 2 | 0.0 | 0.04509 | [106] |
| Hexyl Acetate | 4.8847 | 3.5834 | 241.42 | 2 | 0.0 | 0.04509 | [107] |
| Component 1 | Component 2 | kij,298.15/- | kij,T/K | Property Used for Estimation | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Acetic acid | −0.1247 | - | VLE-binary | [107] |
| Water | 1-Pentanol | 0.001604 | 0.00016 | LLE-binary | [108] |
| Water | Pentyl Acetate | −0.0228 | - | LLE-binary | This work (using data from [100]) |
| Water | 1-Hexanol | 0.010105 | 0.000404 | LLE-binary | [108] |
| Water | Hexyl Acetate | −0.01 | 0.0015 | LLE-binary | This work (using data from [100]) |
| Acetic acid | 1-Pentanol | −0.1 | - | LLE-ternary | This work (using data from [103]) |
| Acetic acid | 1-Hexanol | −0.033 | - | LLE-ternary | This work (using data from [103]) |
| Acetic acid | Pentyl Acetate | −0.1 | - | LLE-ternary | This work (using data from [102]) |
| Acetic acid | Hexyl Acetate | −0.08 | −0.0004 | LLE-ternary | This work (using data from [98]) |
| 1-Pentanol | Pentyl Acetate | −0.0095 | - | VLE-binary | This work (using data from [109]) |
| 1-Hexanol | Hexyl Acetate | −0.0042 | - | VLE-binary | This work (using data from [98]) |
| Component | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.4000 | 3.2000 | 200.00 | 2 | 2500.0 | 0.05 |
| B | 1.0800 | 3.0000 | 400.00 | 2 | 2500.0 | 0.05 |
| C | 2.8000 | 3.8000 | 280.00 | 0 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ascani, M.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C. Simultaneous Predictions of Chemical and Phase Equilibria in Systems with an Esterification Reaction Using PC-SAFT. Molecules 2023, 28, 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041768
Ascani M, Sadowski G, Held C. Simultaneous Predictions of Chemical and Phase Equilibria in Systems with an Esterification Reaction Using PC-SAFT. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041768
Chicago/Turabian StyleAscani, Moreno, Gabriele Sadowski, and Christoph Held. 2023. "Simultaneous Predictions of Chemical and Phase Equilibria in Systems with an Esterification Reaction Using PC-SAFT" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041768
APA StyleAscani, M., Sadowski, G., & Held, C. (2023). Simultaneous Predictions of Chemical and Phase Equilibria in Systems with an Esterification Reaction Using PC-SAFT. Molecules, 28(4), 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041768






