Abstract
In the search for crop protectants, amino acid ester conjugates have been widely investigated as potential antifungal agents. In this study, a series of rhein–amino acid ester conjugates were designed and synthesized in good yields, and their structures were confirmed by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and HRMS. The bioassay results revealed that most of the conjugates exhibited potent inhibitory activity against R. solani and S. sclerotiorum. In particular, conjugate 3c had the highest antifungal activity against R. solani with an EC50 value of 0.125 mM. For S. sclerotiorum, conjugate 3m showed the highest antifungal activity with an EC50 value of 0.114 mM. Satisfactorily, conjugate 3c exhibited better protective effects than that of the positive control, physcion, against powdery mildew in wheat. This research supports the role of rhein–amino acid ester conjugates as potential antifungal agents for plant fungal diseases.
1. Introduction
Fungicides play an irreplaceable role in protecting crops from pathogenic fungal infections and ensuring crop yield and quality [1,2]. Due to the long-term use of traditional fungicides, the emergence of drug-resistant strains and problems caused by the residue of these fungicides in the environment have become increasingly prominent [3,4]. Therefore, new antifungal agents with high efficiency, low toxicity and low environmental pollution must urgently be developed to address these challenges.
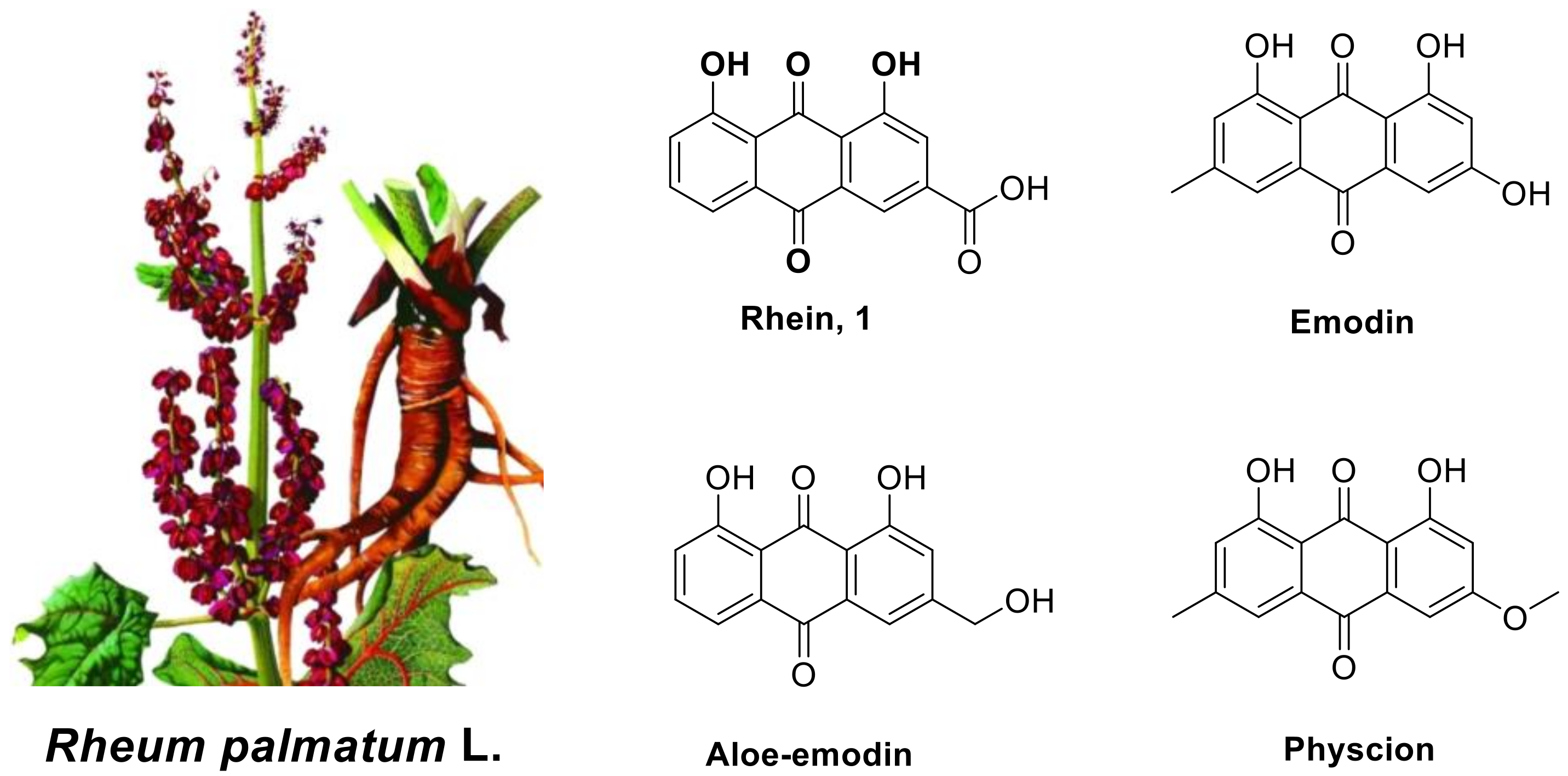
Natural products (NPs) have high chemical structure diversity, a wide range of biological activities and can easily be degraded by the environment, meaning that they play an important role in the development of crop protection agents [5,6]. The tuber of Rheum palmatum L. (Figure 1) is rich in 1,8-dihydroxy anthraquinones, and it is often used as a traditional folk medicine to treat rheumatoid arthritis, inflammation, cancer and cardiovascular diseases [7,8,9,10]. The active 1,8-dihydroxy anthraquinones in the tuber of Rheum palmatum L. are mainly rhein (1) and its analogs, which include emodin, aloeemodin, physcion (Figure 1) and so on [11,12,13]. This research mainly focused on the modification of the chemical structure and pharmacological activities of rhein. Our previous studies have shown that various simple derivatives of rhein exhibit certain insecticidal and antifungal activities, especially against some plant pathogens [14]. These findings suggest that rhein could be used as a lead structure for the discovery of new antifungal agents.
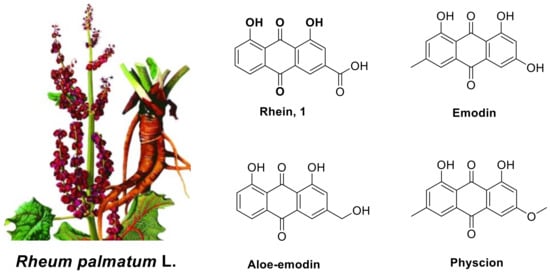
Figure 1.
The Rheum palmatum L. and the structures of rhein (1) and its active analogues emodin, aloe-emodin and physcion.
Amino acids are a class of active small molecules in organisms with important physiological and structural functions [15,16]. In addition, a significant number of amino acid or amino acid ester conjugates have been found in plants, in which a carboxylic group is usually conjugated with biologically active molecules via the amide bonds, such as hormones, flavonoids, vitamins, steroids and several heterocyclic compounds [17,18,19,20]. For this reason, many researchers have tried to conjugate active lead structures with amino acid (esters) moieties to find structures with better pharmacological or antifungal activities.
Herein, in order to find higher antifungal rhein derivatives, a series of rhein–amino acid ester conjugates were designed and synthesized by conjugating rhein with L- or D-amino acid esters via an amide bond. The antifungal activities of all the synthesized compounds were tested in vitro and in vivo, and the primary structure–activity relationship was discussed.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
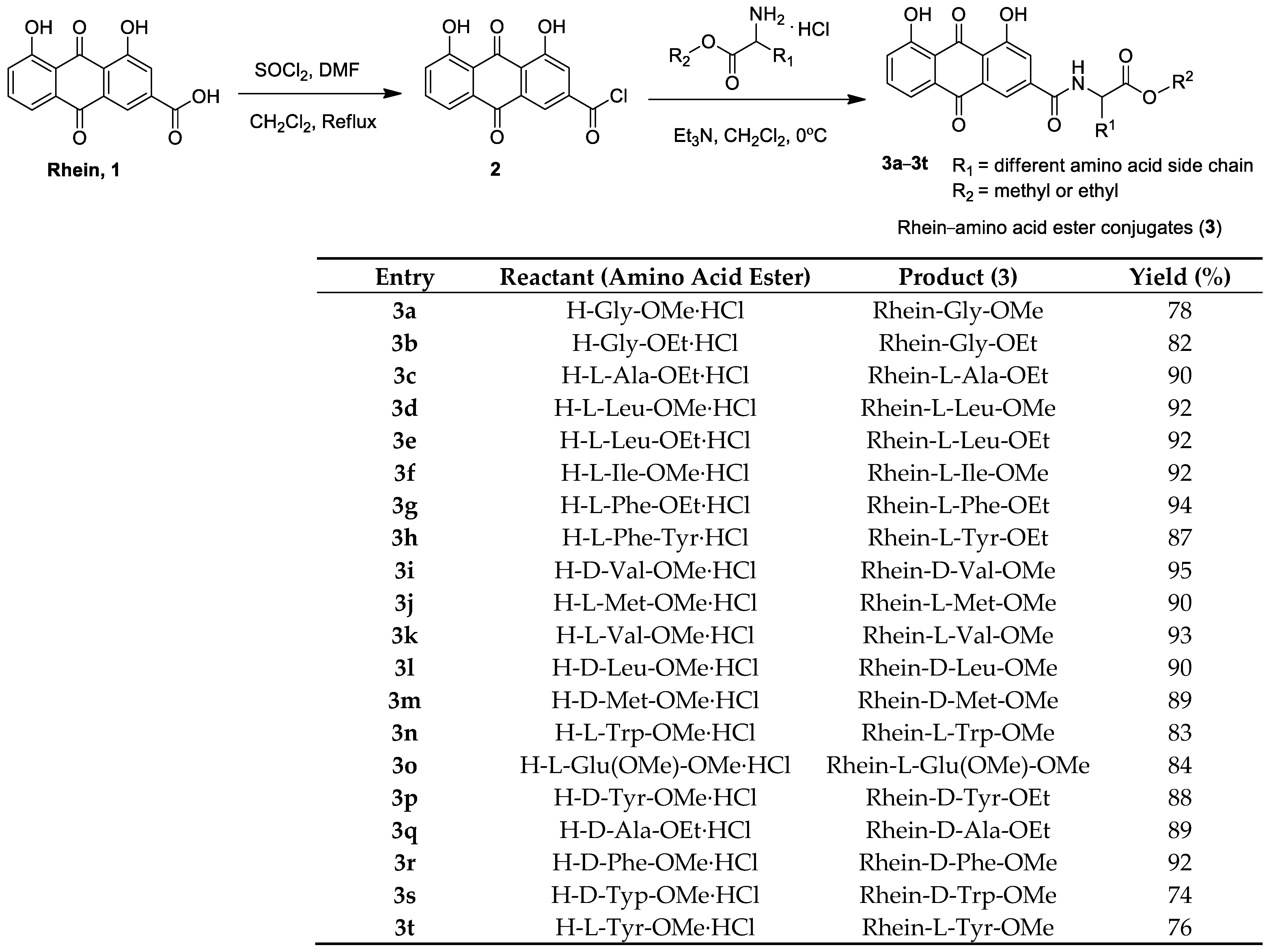
The synthetic route of rhein–amino acid ester conjugates 3a–3t is shown in Figure 2. Rhein was treated with SOCl2 at the reflux temperature in CH2Cl2 solution for 8 h, and intermediate 2 was afforded after the evaporation of the solvent. Then, intermediate 2 was allowed to react with the corresponding L- or D-amino acid esters in CH2Cl2 at 0 °C for 2 h to yield target compounds 3a–3t. The corresponding reactant (amino acid ester) was used in the synthesis of rhein–amino acid ester conjugates, and the yields are listed in Figure 2, indicating that the rhein–amino acid ester conjugates were obtained in good yields and varied from 74% to 94%.
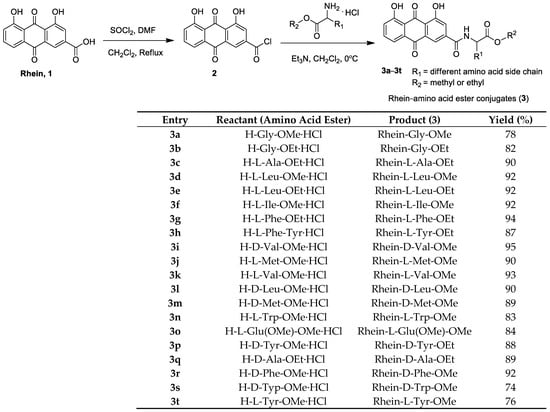
Figure 2.
Preparation of rhein–amino acid ester conjugates 3a–3t.
The structures of all the synthesized rhein–amino acid ester conjugates 3a–3t were effectively characterized by 1H NMR, 13C NMR and HRMS analyses (the corresponding spectra are available in the Supplementary Materials).
2.2. In Vitro Antifungal Activity
The in vitro antifungal activities of these rhein–amino acid ester conjugates 3a–3t were initially screened at 0.2 mM and 0.5 mM against four phytopathogenic fungi (Rhizoctonia solani, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Bipolaris maydis and Phytophthora capsici) using the mycelial growth rate method. The natural lead compound, rhein, was used as reference control. A commercial biofungicide, phenazine-1-carboxylic acid (PCA), was used as the positive control. The preliminary bioassay results of these conjugates against four phytopathogenic fungi are summarized in Table S1 and Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively.
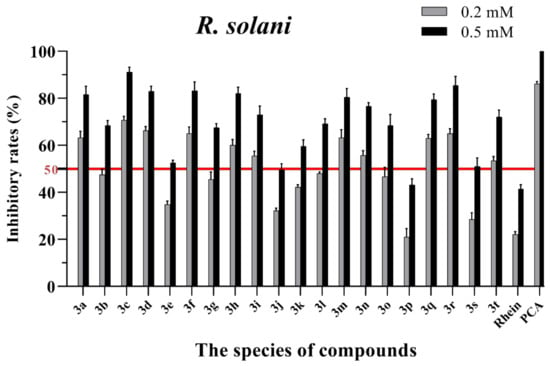
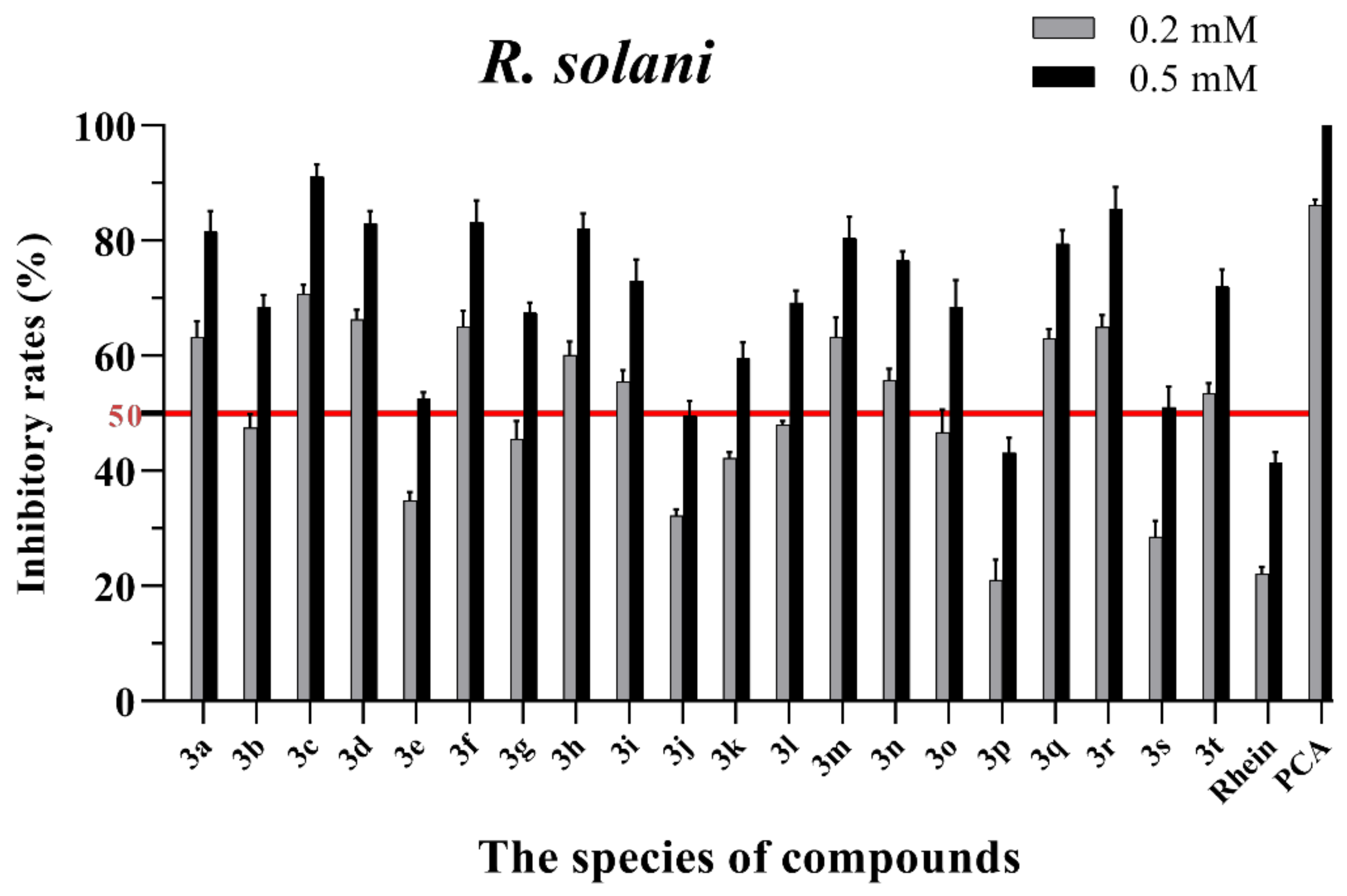
Figure 3.
Mycelial growth % inhibition of chemicals against R. solani. The bold red line is the identity line with the inhibition rate of 50%.
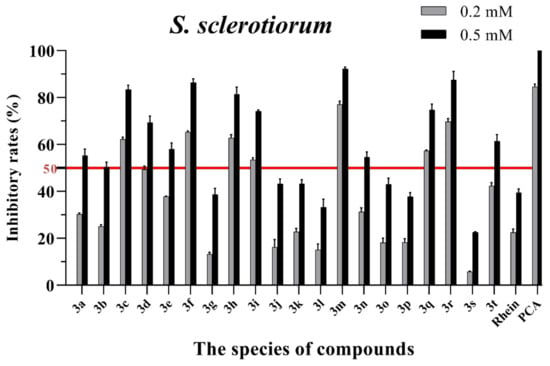
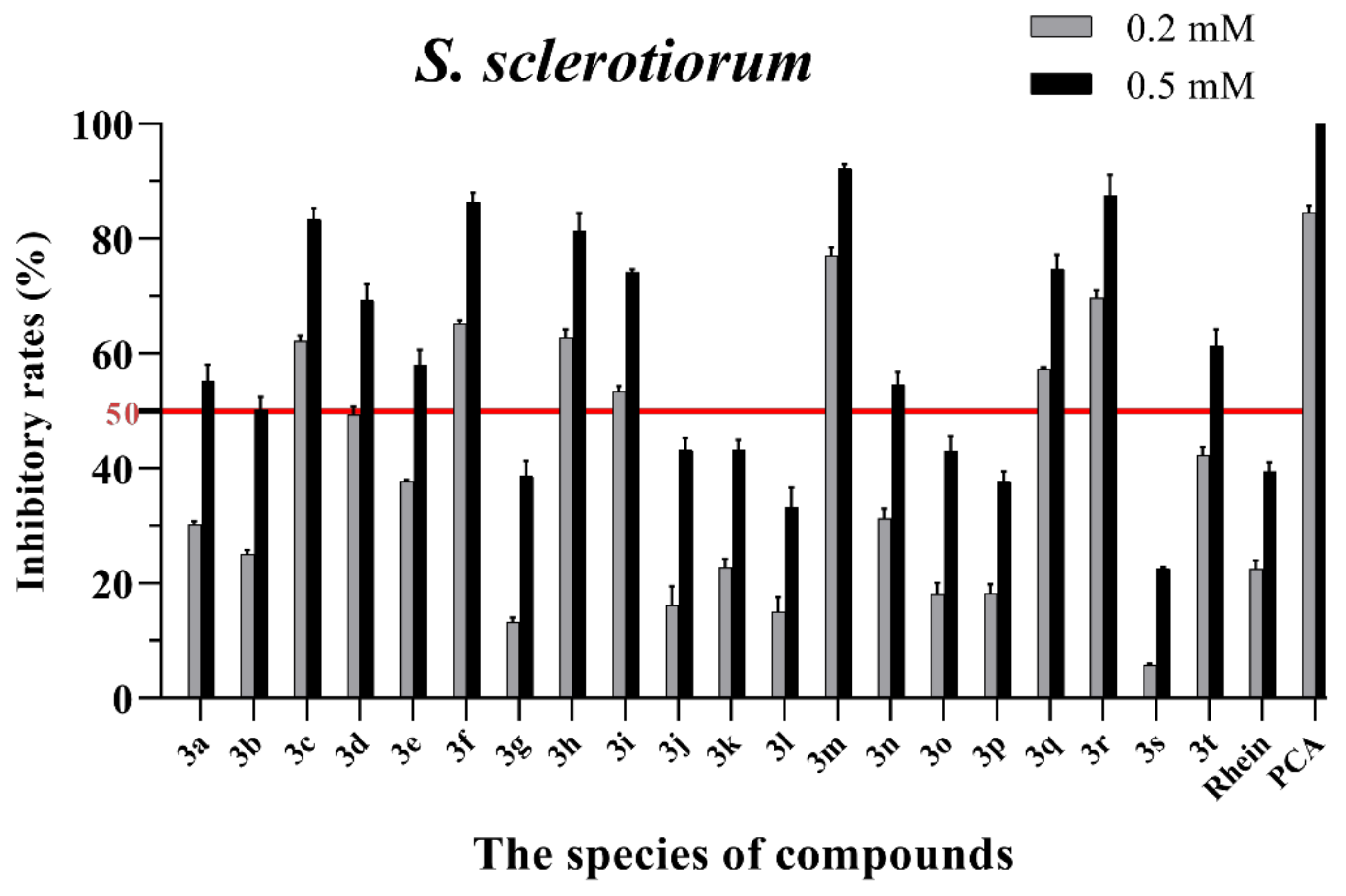
Figure 4.
Mycelial growth % inhibition of chemicals against S. sclerotiorum. The bold red line is the identity line with the inhibition rate of 50%.
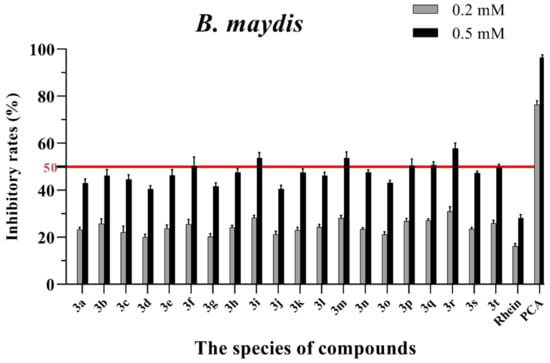
Figure 5.
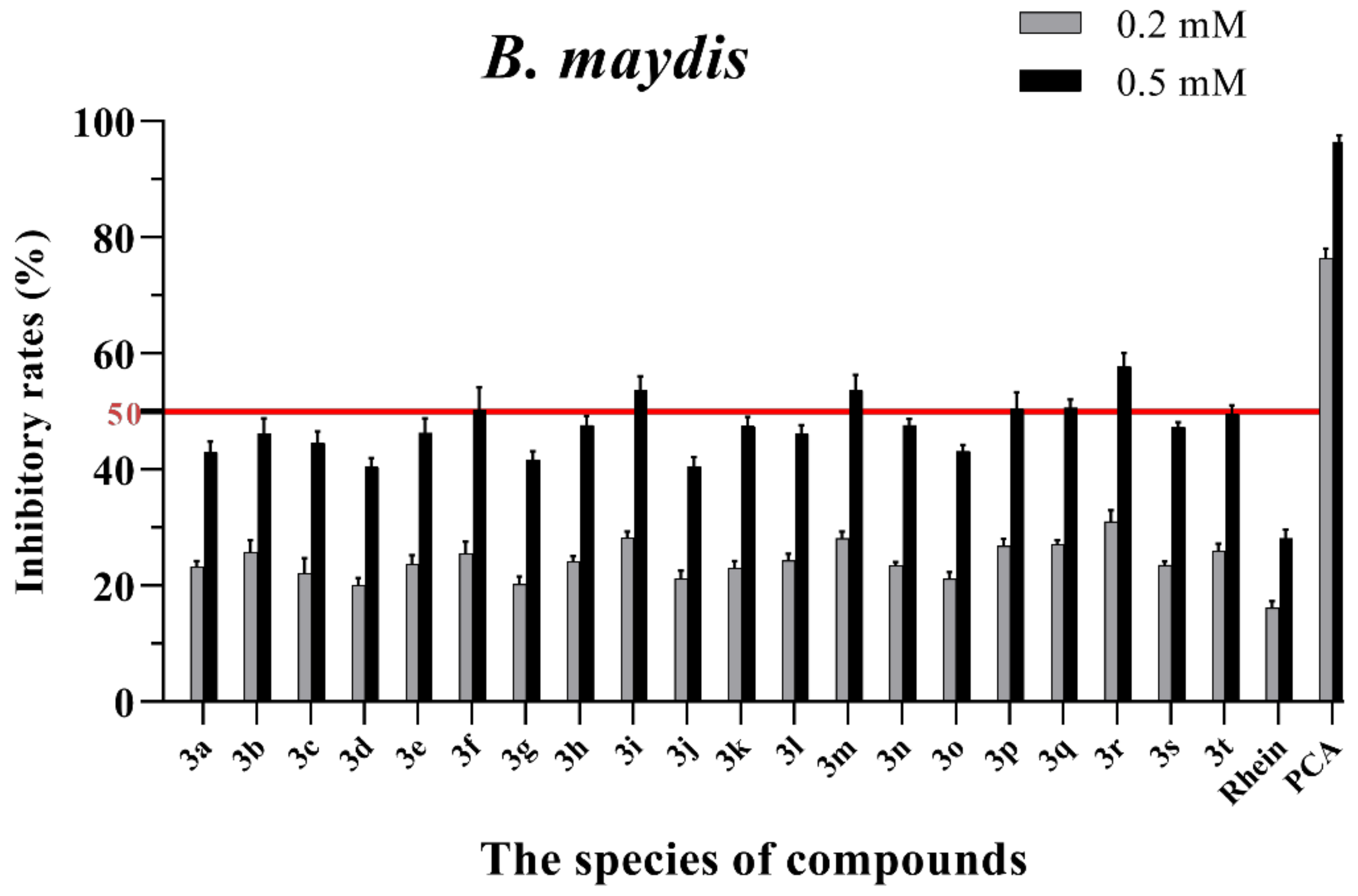
Mycelial growth % inhibition of chemicals against B. maydis. The bold red line is the identity line with the inhibition rate of 50%.
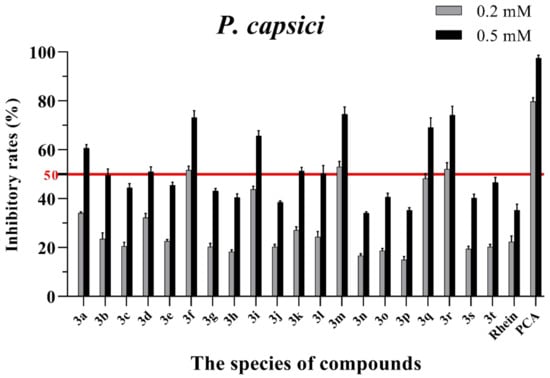
Figure 6.
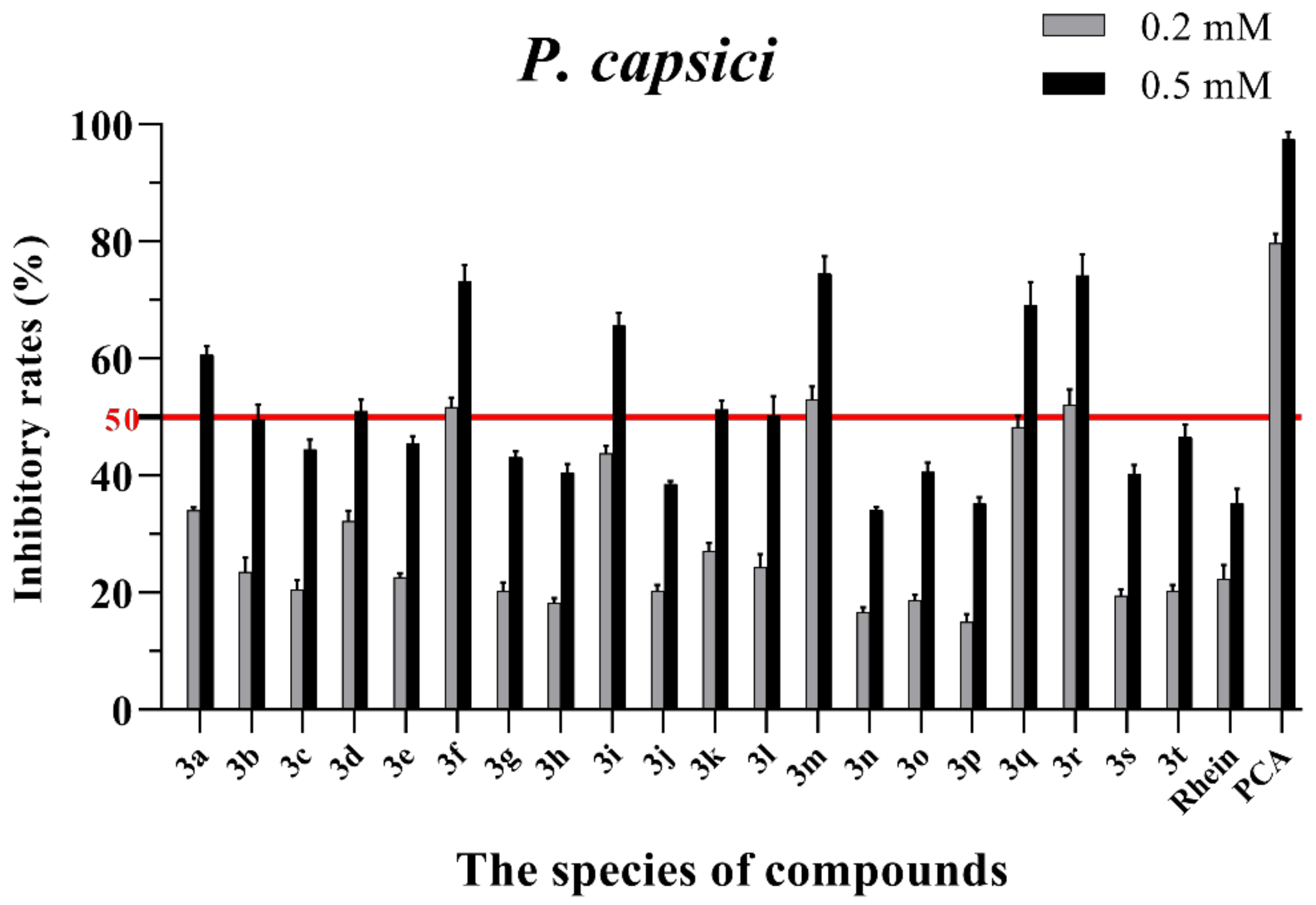
Mycelial growth % inhibition of chemicals against P. capsici. The bold red line is the identity line with the inhibition rate of 50%.
As seen in Figure 3, all of the conjugates exhibited moderate-to-good antifungal activities against R. solani at the concentration of 0.2 mM (this concentration of rhein was equal to 56.8 mg/L). Among all 20 conjugates, 11 conjugates, 3a, 3c, 3d, 3f, 3h, 3i, 3m, 3n, 3q, 3r and 3t, showed an efficacy over 50% against R. solani at 0.2 mM. In particular, at 0.5 mM (this concentration of rhein was equal to 142.1 mg/L), most of the conjugates showed great antifungal activities against R. solani, and compound 3c (rhein-L-Ala-OEt) exhibited excellent antifungal activities against R. solani with an inhibition rate of more than 90%. The data in Figure 4 indicated that seven conjugates (3c, 3f, 3h, 3i, 3m, 3q and 3r) out of the twenty tested conjugates showed moderate-to-strong antifungal activities against S. sclerotiorum with an efficacy over 50% at 0.2 mM. In particular, compound 3m (rhein-D-Met-OMe) exhibited excellent antifungal activities against S. sclerotiorum with an inhibition rate of more than 90% at 0.5 mM. As seen in Figure 5 and Figure 6, almost all the conjugates presented poor antifungal activities against B. maydis and P. capsici, among which only compounds 3f, 3m and 3r showed an efficacy over 50% against P. capsici at 0.2 mM. Through this analysis of the preliminary antifungal activities results, it was inferred that these rhein–amino acid ester conjugates can be used as antifungal lead structures against R. solani and S. sclerotiorum.
In order to understand the antifungal activity of the more active conjugates against R. solani and S. sclerotiorum more clearly, the conjugates with inhibition rates of >50% at a concentration of 0.2 mM against these two fungi (shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4) were further assayed to determine their median effective concentrations (EC50). The results are presented in Table 1. The results showed that 11 conjugates (3a, 3c, 3d, 3f, 3h, 3i, 3m, 3n, 3q, 3r and 3t) exhibited potent antifungal activity against R. solani with EC50 values between 0.125 and 0.197 mM, but these values were lower than that of PCA (EC50 = 0.083 mM). Additionally, conjugate 3c had the highest antifungal activity with an EC50 value of 0.125 mM. For S. sclerotiorum, conjugate 3m (rhein-D-Met-OMe) showed the highest antifungal activity with an EC50 value of 0.114 mM, but this value was lower than PCA (EC50 = 0.088 mM).

Table 1.
EC50 values of effective compounds against R. solani and S. sclerotiorum in vitro (mM).
2.3. In Vivo Antifungal Activity against Powdery Mildew in Wheat
The antifungal activity of conjugate 3c against powdery mildew in wheat was evaluated at 0.4 mM and 0.2 mM. As shown in Table 2, in terms of its curative activity, conjugate 3c exhibited potent antifungal activity against powdery mildew in wheat with control efficiencies of 84.4% and 61.2% at 0.4 mM and 0.2 mM, respectively, which were similar values to those of the control agent, physcion (87.4% at 0.4 mM, and 67.2% at 0.2 mM). In terms of its protective activity, conjugate 3c had antifungal activity of 66.7% and 53.8% against powdery mildew in wheat at 0.4 mM and 0.2 mM, respectively, which were higher values than those of the control agent, physcion (54.2% at 0.4 mM, and 38.4% at 0.2 mM).

Table 2.
Protective and curative activities of compound 3c in vivo.
Presently, extensive studies regarding the biological activities of amino acid ester conjugates are being carried out based on the conjugation of amino acid esters with an active lead structure. Zhang designed and synthesized a series of novel amino acid ester-coupled caffeoylquinic acid derivatives, and the biological evaluation suggested that some amino acid ester-coupled derivatives exhibited varying degrees of lipid-lowering effects on oleic acid-elicited lipid accumulation in HepG2 liver cells [18]. Studies have shown that some curcumin–amino acid conjugates exhibit enhanced anti-inflammatory properties with potency higher than that of standard NSAID references (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, indomethacin, and ibuprofen) [21]. In our previous research, to improve the bioactivities of PCA (a biofungicide), a series of PCA–amino acid ester conjugates have been successfully prepared, some of which were shown to be more effective against Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn than PCA [22]. In this study, using natural rhein as a lead structure, 20 rhein–amino acid ester conjugates were successfully prepared, and the antifungal activities of these conjugates were initially determined. The current results confirmed that some rhein–amino acid ester conjugates have potent antifungal activities against R. solani and S. sclerotiorum, and they can be used as lead structures for the development of antifungal agents.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Instruments
All chemicals and reagents were commercially purchased and used directly without further purification. Flash column chromatography and analytical thin layer chromatography (TLC) were performed using silica gel 60 (200–300 mesh) and silica gel aluminum sheets F254 (Qingdao Marine Chemical Ltd., Qingdao, China), respectively. The melting points of all the compounds were determined using a WRR melting point apparatus (Shanghai Jingke Industrial Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China) and were uncorrected. Then, 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra were recorded in CDCl3 or DMSO-d6 solution at 400 MHz for 1H and 101 MHz for 13C on a Bruker Avance III HD 500 MHz NMR Spectrometer (Bruker (Beijing) Scientific Technology Co. Ltd., Beijing, China) using tetramethylsilane (TMS) as an internal standard. High-resolution mass spectra were obtained using a Bruker APEX IV Fourier-transform mass spectrometer (Bruker (Beijing) Scientific Technology Co. Ltd., Beijing, China).
3.2. Test Fungus
Plant pathogenic fungi, including Rhizoctonia solani, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Bipolaris maydis, and Phytophthora capsici, were provided by the Institute of Pesticide Research, Yangtze University, China. These four fungi were grown on potato dextrose agar (PDA) plates at 25 °C and maintained at 4 °C with periodic subculturing. The susceptible wheat variety, Chanceller and the tested pathogenic fungi, Blumeria graminis, isolated from a wheat plant infected with powdery mildew, were provided by the Institute for Plant Protection and Soil Sciences, Hubei Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
3.3. Preparation of 4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carbonyl Chloride (2)
According to our previous literature report [23], rhein 1 (10 mmol), 30 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane, and 2~3 drops of DMF as a catalyst were added into a single-port bottle for stirring. Then, thionyl chloride (15 mmol) was slowly added to the flask and heated to reflux until the solid disappeared completely. The reflux reaction continued for 8 h, and the solvent was removed on a rotary evaporator to obtain 2 for the next step.
3.4. General Procedure for Preparation of Rhein–Amino Acid Ester Conjugates (3a–3t)
4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carbonyl chloride 2 (10 mmol) dissolved in 10 mL of anhydrous CH2Cl2 was added dropwise to a solution of glycine methyl ester hydrochloride (10 mmol), and triethylamine (22 mmol) was used as the attaching acid agent in 50 mL of CH2Cl2 at 0 °C. The mixture was refluxed for 2 h until the reaction was complete. Then, the solvent was evaporated under vacuum, and the crude product was purified via column chromatography to obtain a pure rhein–glycine methyl ester conjugate (3a). Conjugates 3b–3t were also obtained in the same way.
3.4.1. Rhein-Gly-OMe (3a): Methyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)acetate
Yellow solid; yield: 78%; m.p, 219~222 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.05 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.98 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 8.16 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.88 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.79 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.74 (t, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.35 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 6.82 (s, 1H, CONH), 4.29 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, acylamino-CH2), 3.84 (s, 3H, CH3). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 209.29, 192.69, 164.30, 162.84, 162.72, 161.46, 137.72, 137.37, 133.49, 133.48, 125.04, 123.45, 120.46, 117.42, 111.67, 96.50, 52.70, 41.91. HRMS calcd for C18H13NO7 [M + H]+: 356.0765, found 356.0765.
3.4.2. Rhein-Gly-OMe (3b): Ethyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)acetate
Yellow solid; yield: 82%; m.p, 211~214 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.05 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.98 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.15 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.87 (dd, J = 7.6, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.78 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.76–7.70 (m, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.34 (dd, J = 8.4, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 6.85 (s, 1H, CONH), 4.33–4.28 (m, 2H, CH2CH3), 4.27 (d, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, acylamino-CH2), 1.34 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, CH3). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.69, 181.01, 169.54, 164.91, 162.82, 162.70, 141.55, 137.71, 134.11, 133.44, 125.01, 123.42, 120.44, 117.63, 117.44, 115.80, 61.95, 42.06, 14.18.
HRMS calcd for C19H15NO7 [M + H]+: 370.0921, found 370.0923.
3.4.3. Rhein-L-Ala-OEt (3c): (R)-Ethyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)propanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 90%; m.p, 223~225 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.04 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.98 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.14 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.88 (dd, J = 7.6, J =1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.77 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.76–7.70 (m, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.34 (dd, J = 8.4, J =1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 6.92 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, CONH), 4.79 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, CH), 4.28 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2CH3), 1.58 (d, J = 4.8, 3H, CHCH3), 1.36–1.30 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, CH2CH3). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.70, 181.08, 172.73, 164.30, 162.82, 162.71, 141.87, 137.69, 134.08, 133.46, 125.01, 123.42, 120.44, 117.56, 117.44, 115.82, 61.90, 48.91, 18.53, 14.17. HRMS calcd for C20H17NO7 [M + H]+: 384.1078, found 384.1080.
3.4.4. Rhein-L-Leu-OMe (3d): (R)-Methyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-4-methylpentanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 92%; m.p, 177~179 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.05 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.98 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.13 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.88 (dd, J = 7.6, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.77 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.76–7.71 (m, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.35 (dd, J = 8.4, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 6.70 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, CONH), 4.88 (dd, J = 11.2, J = 5.6 Hz, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.80 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.81–1.70 (m, 3H, CH2CH(CH3)2), 1.04–0.97 (m, 6H, CH(CH3)2). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.68, 181.11, 173.18, 164.61, 162.83, 162.71, 141.76, 137.71, 134.08, 133.44, 125.04, 123.50, 120.45, 117.59, 117.38, 115.82, 52.59, 51.47, 41.76, 25.03, 22.82, 22.02. HRMS calcd for C22H21NO7 [M + H]+: 412.1391, found 412.1393.
3.4.5. Rhein-L-Leu-OEt (3e): (R)-Ethyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-4-methylpentanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 92%; m.p, 145~147 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.02 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.97 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.11 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.86 (dd, J = 7.6, J =1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.76–7.68 (m, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 7.33 (dd, J = 8.4, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 6.82 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, CONH), 4.85 (m, 1H, acylamino-CH), 4.26 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2CH3), 1.83–1.67 (m, 3H, CH2CH(CH3)2), 1.33 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, CH2CH3), 1.01 (dd, J = 6.0, J = 4.4 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.63, 181.04, 172.85, 164.61, 162.79, 162.65, 141.83, 137.68, 134.00, 133.42, 125.00, 123.43, 120.42, 117.50, 117.44, 115.79, 61.73, 51.56, 41.74, 25.04, 22.86, 22.03, 14.19. HRMS calcd for C23H23NO7 [M + H]+: 426.1547, found 426.1552.
3.4.6. Rhein-L-Ile-OMe (3f): (2R,3R)-Methyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-3-methylpentanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 92%; m.p, 162~164 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.06 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.98 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.14 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.89 (dd, J = 7.6, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.74 (dd, J = 12.0, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 7.35 (dd, J = 8.4, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 6.79 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, CONH), 4.83 (dd, J = 8.4, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.80 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.11–2.01 (m, 1H, acylamino-CHCH, 1.26 (s, 2H, CH2), 1.05–0.95 (m, 6H, CH3CH(CH2CH3)). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.70, 181.08, 172.14, 165.93, 164.67, 162.83, 162.70, 142.00, 137.72, 134.12, 133.46, 125.03, 123.36, 120.45, 117.47, 99.99, 57.15, 52.40, 38.24, 25.42, 15.53, 11.61. HRMS calcd for C22H21NO7 [M + H]+: 412.1391, found 412.1397.
3.4.7. Rhein-L-Phe-OEt (3g): (R)-Ethyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-3-phenylpropanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 94%; m.p, 178~180 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.04 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.98 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.06 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.87 (dd, J = 7.6, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.76–7.69 (m, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.66 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.37–7.26 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.20–7.14 (m, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 6.74 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, CONH), 5.10–5.01 (m, 1H, acylamino-CH), 4.25 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2CH3), 3.36–3.25 (m, 2H, acylamino-CHCH2), 1.30 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, CH3). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.68, 180.96, 171.19, 164.43, 162.80, 162.66, 141.88, 137.70, 135.56, 134.11, 133.45, 129.35, 128.74, 127.40, 124.98, 123.18, 120.42, 117.58, 117.52, 115.79, 61.92, 53.84, 37.90, 14.16. HRMS calcd for C26H21NO7 [M + H]+: 460.1391, found 460.1398.
3.4.8. Rhein-L-Tyr-OEt (3h): (R)-Ethyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 87%; m.p, 192~194 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.04 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.98 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.07 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.87 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.76–7.71 (m, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.68 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.34 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.03 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 6.79 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 6.70 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, CONH), 5.03 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, acylamino-CH), 4.25 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, acylamino-CHCH2), 3.22 (dd, J = 14.8, J = 5.6 Hz, 2H, CH2CH3), 1.31 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, CH3). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.68, 180.96, 171.19, 164.43, 162.80, 162.66, 141.88, 137.70, 135.56, 134.11, 133.45, 129.35, 128.74, 127.40, 124.98, 124.84, 123.18, 120.42, 117.52, 115.79, 61.92, 53.84, 37.90, 14.16. HRMS calcd for C26H21NO8 [M + H]+: 476.134, found 476.1348.
3.4.9. Rhein-D-Val-OMe (3i): (S)-Methyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-3-methylbutanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 95%; m.p, 177~180 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.05 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.97 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.14 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.88 (dd, J = 7.5, J =1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.74 (dd, J = 11.6, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 7.34 (dd, J = 8.4, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 6.80 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, CONH), 4.80 (dd, J = 8.4, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.81 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.39–2.23 (m, 1H, acylamino-CHCH), 1.04 (dd, J = 6.8, J = 5.6 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.67, 181.05, 172.20, 164.87, 162.81, 162.68, 142.01, 137.72, 134.10, 133.44, 125.02, 123.36, 120.44, 117.57, 117.49, 115.80, 57.83, 52.46, 31.64, 19.02, 18.07. HRMS calcd for C21H19NO7 [M + H]+: 398.1234, found 398.1242.
3.4.10. Rhein-L-Met-OMe (3j): (R)-Methyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-4-(methylthio)butanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 90%; m.p, 184~186 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.04 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.97 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.16 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.90–7.84 (m, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.79–7.70 (m, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 7.37–7.31 (m, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.18 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, CONH), 5.02–4.94 (m, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.83 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.63 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2SCH3), 2.38–2.16 (m, 2H, acylamino-CHCH), 2.14 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 3H, SCH3). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.67, 181.04, 172.08, 164.63, 162.82, 162.69, 141.55, 137.74, 134.09, 133.42, 125.04, 123.45, 120.46, 117.63, 117.47, 115.79, 52.87, 52.44, 31.25, 30.13, 15.59. HRMS calcd for C21H19NO7S [M + H]+: 430.0955, found 430.0966.
3.4.11. Rhein-L-Val-OMe (3k): (R)-Methyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-4-methylbutanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 93%; m.p, 194~195 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.04 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.97 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.14 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.90–7.84 (m, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.73 (dd, J = 10.4, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 7.34 (dd, J = 8.4, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 6.79 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, CONH), 4.79 (dd, J = 8.8, J = 4.8 Hz, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.81 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.40–2.28 (m, 1H, acylamino-CHCH), 1.04 (dd, J = 6.8, J = 5.6 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.66, 181.04, 172.19, 164.87, 162.81, 162.67, 142.00, 137.73, 134.09, 133.43, 125.03, 123.36, 120.45, 117.56, 117.48, 115.79, 57.82, 52.48, 31.64, 19.03, 18.07. HRMS calcd for C21H19NO7 [M + H]+: 398.1234, found 398.1241
3.4.12. Rhein-D-Leu-OMe (3l): (S)-Methyl 2-(4,5-dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-4-methylpentanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 90%; m.p, 177~178 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.01 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.96 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.11 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.86 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.73 (dd, J = 11.2, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 7.34 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 6.78 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, CONH), 4.92–4.80 (m, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.80 (s, 3H, CH3), 1.84–1.68 (m, 3H, acylamino-CHCH2CH), 1.01 (dd, J = 5.6, J = 4.0 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.62, 181.06, 173.28, 164.63, 162.80, 162.65, 141.71, 137.71, 134.01, 133.40, 125.04, 123.49, 120.44, 117.53, 117.41, 115.78, 52.62, 51.47, 41.68, 25.03, 22.85, 21.99. HRMS calcd for C22H21NO7 [M + H]+: 412.139, found 412.1395.
3.4.13. Rhein-D-Met-OMe (3m): (S)-Methyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-4-(methylthio)butanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 89%; m.p, 190~193 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.02 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.96 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.14 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.86 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.78–7.69 (m, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 7.34 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.22 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, CONH), 5.01–4.94 (m, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.83 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.63 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2SCH3), 2.38–2.17 (m, 2H, acylamino-CHCH), 2.15 (s, 3H, SCH3). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.63, 181.00, 172.13, 164.65, 162.81, 162.66, 141.54, 137.73, 134.06, 133.39, 125.03, 123.44, 120.45, 117.60, 117.48, 115.77, 52.87, 52.43, 31.25, 30.14, 15.58. HRMS calcd for C21H19NO7S [M + H]+: 430.0955, found 430.0958.
3.4.14. Rhein-L-Trp-OMe (3n): (R)-Methyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 83%; m.p, 173~175 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.89 (s, 2H, anthraquinone-OH), 10.87 (s, 1H, indole-NH), 9.35 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, indole-H), 8.12 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.81 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.76–7.71 (m, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 7.57 (s, 1H, indole-H), 7.40 (dd, J = 8.4, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.34 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, indole-H), 7.23 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H, indole-H), 7.07 (s, 1H, indole-H), 7.00 (s, 1H, CONH), 4.76–7.70 (m, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.67 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.34–3.26 (m, 2H, CH2-indole). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 191.93, 181.46, 172.61, 164.77, 161.85, 161.53, 141.27, 138.02, 136.59, 134.05, 133.71, 127.50, 124.97, 124.15, 123.11, 121.50, 119.90, 118.94, 118.48, 118.21, 116.50, 111.96, 110.31, 54.54, 52.53, 26.97. HRMS calcd for C27H20N2O7 [M + H]+: 485.1343, found 485.1349.
3.4.15. Rhein-L-Glu(OMe)-OMe (3o): (R)-Dimethyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)pentanedioate
Yellow solid; yield: 84%; m.p, 171~173 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 11.95 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.91 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.09 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.81 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.70 (dd, J = 10.4, J = 4.8 Hz, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 7.50 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.30 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, CONH), 4.85–4.78 (m, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.81 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 3H, CH3), 3.73 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.58–2.50 (m, 2H, CHCH2CH2), 2.33–2.28 (m, 2H, CHCH2). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.52, 180.84, 173.73, 172.02, 164.86, 162.71, 162.54, 141.48, 137.67, 133.89, 133.31, 124.94, 123.43, 120.37, 117.60, 117.44, 115.68, 52.82, 52.69, 52.14, 30.26, 26.80. HRMS calcd for C22H19NO9 [M + H]+: 442.1133, found 442.1136.
3.4.16. Rhein-D-Tyr-OEt (3p): (S)-Ethyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 88%; m.p, 221~222 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.89 (s, 2H, anthraquinone-OH), 9.30 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-H) 9.26 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 8.10 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.82 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.78–7.68 (m, 2H, Ar-H), 7.40 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.10 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 6.67 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 6.65 (s, H, CONH), 4.66–4.53 (m, 1H, acylamino-CH), 4.11 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, acylamino-CHCH2), 3.07–3.01 (m, 2H, CH2CH3), 1.16 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 3H, CH3). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 191.98, 181.59, 171.89, 164.81, 161.86, 161.53, 156.44, 141.36, 138.05, 134.18, 133.82, 130.49, 127.91, 125.01, 123.03, 119.92, 118.35, 118.14, 116.62, 115.51, 61.13, 55.38, 35.92, 14.50. HRMS calcd for C26H21NO8 [M + H]+: 476.134, found 476.1346.
3.4.17. Rhein-D-Ala-OEt (3q) (S)-Ethyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)propanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 89%; m.p, 236~237 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.03 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.98 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.14 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.87 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.75 (d, J = 15.2 Hz, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 7.34 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 6.93 (s, 1H, CONH), 4.79 (s, 1H, acylamino-CH), 4.28 (d, J = 6.8 Hz, 2H, CH2CH3), 1.57 (d, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H, acylamino-CHCH3), 1.33 (t, J = 6.4 Hz, 3H, CH3). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 191.96, 181.54, 172.76, 164.57, 161.87, 161.58, 141.33, 138.05, 134.11, 133.76, 125.00, 123.13, 119.92, 118.26, 118.19, 116.56, 61.07, 49.13, 17.02, 14.55. HRMS calcd for C20H17NO7 [M + H]+: 384.1078, found 384.1079.
3.4.18. Rhein-D-Phe-OMe (3r) (S)-Methyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-3-phenylpropanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 92%; m.p, 201~202 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 12.03 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 11.96 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-OH), 8.05 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.86 (dd, J = 7.6, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.76–7.69 (m, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.66 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.37–7.27 (m, 4H, Ar-H), 7.16 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.15 (s, 1H, Ar-H), 6.72 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, CONH), 5.17–5.04 (m, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.81 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.31– 3.25 (m, 2H, acylamino-CH2). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ 192.66, 180.95, 171.62, 164.45, 162.80, 162.64, 141.77, 137.73, 135.48, 134.09, 133.42, 129.28, 128.82, 127.47, 125.00, 123.22, 120.43, 117.59, 117.50, 115.77, 53.82, 52.66, 37.85. HRMS calcd for C25H19NO7 [M + H]+: 446.1234, found 446.1236.
3.4.19. Rhein-D-Trp-OMe (3s) (S)-Methyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 74%; m.p, 196~198 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.89 (s, 2H, anthraquinone-OH), 10.87 (s, 1H, indole-NH), 9.35 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, indole-H), 8.12 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.82 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.78–7.70 (m, 2H, anthraquinone-H), 7.58 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, indole-H), 7.40 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.34 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, indole-H), 7.23 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H, indole-H), 7.07 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, indole-H), 7.00 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 1H, CONH), 4.78–4.68 (m, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.67 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.33–3.25 (m, 2H, CH2-indole). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 191.99, 181.59, 172.58, 164.81, 161.87, 161.54, 141.30, 138.05, 136.59, 134.16, 133.82, 127.51, 125.01, 124.13, 123.11, 121.49, 119.93, 118.94, 118.48, 118.34, 118.18, 116.63, 111.96, 110.32, 54.53, 52.53, 26.96. HRMS calcd for C27H20N2O7 [M + H]+: 485.1343, found 485.1350.
3.4.20. Rhein-L-Tyr-OMe (3t) (R)-Methyl 2-(4,5-Dihydroxy-9,10-dioxo-9,10-dihydroanthracene-2-carboxamido)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate
Yellow solid; yield: 76%; m.p, 233~234 °C; 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 11.90 (s, 2H, anthraquinone-OH), 9.31 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 9.27 (s, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 8.09 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.88–7.80 (m, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.76 (dd, J = 7.6, J = 1.0 Hz, 1H, anthraquinone-H), 7.71 (d, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.41 (dd, J = 8.4, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H, Ar-H), 7.09 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ar-H), 6.67 (s, H, Ar-OH), 6.65 (s, H, CONH), 4.66–4.60 (m, 1H, acylamino-CH), 3.66 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.08–3.02 (m, 2H, acylamino-CHCH2). 13C-NMR (101 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ 191.92, 181.64, 172.37, 164.80, 161.91, 161.64, 156.44, 141.27, 138.02, 134.21, 133.84, 130.46, 127.94, 125.04, 123.10, 119.89, 118.40, 118.06, 116.66, 115.54, 55.27, 52.50, 35.86. HRMS calcd for C25H19NO8 [M + H]+: 462.1183, found 462.1186.
3.5. In Vitro Antifungal Bioassay
The primary antifungal activities of all the target compounds against Rhizoctonia solani, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Bipolaris maydis and Phytophthora capsici were evaluated using a mycelium growth rate method reported in our previously published literature report [24,25]. Briefly, a solution of the tested compound (25 or 10 mmol) in 5 mL of sterile water containing 0.1% Tween 80 and 0.1 mL of DMSO was fully mixed with 45 mL of 50 °C melted PDA agar to provide a culture medium containing a 0.5 mM or 0.2 mM tested compound and 0.2% (v/v) DMSO. Then, it was poured into a sterilized Petri dish (ca. 16 mL on each plate). The control blank assay was performed with 0.2% DMSO in sterile aqueous 1% Tween 80. A biofungicide phenazine-1-carboxylic acid (PCA) was used as the positive control. A hyphal plug (d = 6 mm) was taken from the growing margin of the test fungus on each subcultured Petri dish and placed on the amended PDA. Each experiment was repeated three times. The inoculated Petri dishes were kept in an incubator at 25 °C for 72 h, after which, the diameter of each fungal colony was measured, and the percentage inhibition was calculated. The relative inhibitory rates (I) of the tested compounds were calculated using the following formula: I (%) = [(C − T)/(C − 6)] × 100, where C represents the average colony diameter (mm) during the blank assay, and T represents the average colony diameter (mm) during the test.
The target compounds with higher initial activities were further assayed to determine the EC50 values according to the method described above. Based on the screening results, a series of test concentrations of the compound was set and evaluated to determine its inhibitory rate against the fungi. The log dose–response curves allowed for the determination of the EC50 value for the bioassay using probit analysis.
3.6. In Vivo Protective and Curative Antifungal Bioassay
The control efficacy (protective and curative activity) of compound 3c against powdery mildew in wheat was assessed with pot experiments according to the method described in the literature with some modifications [26]. First, wheat seeds were grown in plastic pots (20 cm diameter) with about 15 plants per pot. After three weeks, plants in the three-leaf stage were used in antifungal activity experiments. For the protection assay, compound 3c solutions as well as the positive control physcion with different concentrations (0.4 and 0.2 mM) (containing 0.1% Tween 80 as the surfactant) were sprayed on the leaves of wheat on the first day. After 24 h, powdery mildew spores were inoculated into the leaves of wheat. Wheat seedlings sprayed with water were used as negative controls. Then, the plants were placed in a greenhouse at 25 °C with 100% relative humidity. After 7 days of greenhouse culture, the disease index of the wheat seedlings was measured. The grading standard of powdery mildew in wheat was used according to the method presented in the literature: Disease index (CK or PT) = ∑ (the number of leaves at each grade × the corresponding grade)/(the total number of leaves × the superlative grade). The protective efficacy of the tested compound was calculated according to the following formula: Relative control efficacy I (%) = (CK − PT)/CK × 100, where CK is the disease index of the negative control and PT is the disease index of the treatment group. For the curative assay, the powdery mildew spores were inoculated into the leaves for 24 h before the leaves were sprayed with the solutions under examination. The rest of the procedures were the same as the above.
3.7. Statistical Analysis
The collected data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism (Version 8.3.0) software.
4. Conclusions
In summary, a series of rhein–amino acid ester conjugates were obtained in good yields by conjugating rhein with L- or D-amino acid esters via an amide bond, and their structures were confirmed by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and HRMS. The bioassay results revealed that most of the conjugates exhibited potent inhibitory activity against R. solani and S. sclerotiorum. In particular, conjugate 3c had the highest antifungal activity against R. solani, with an EC50 value of 0.125 mM. For S. sclerotiorum, conjugate 3m showed the highest antifungal activity, with an EC50 value of 0.114 mM. Satisfactorily, conjugate 3c exhibited better protective effects than those of the positive control physcion against wheat powdery mildew. This research provides support for rhein–amino acid esters conjugates as potential antifungal agents for plant fungal diseases.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules28052074/s1, Tables S1 and S2: Fungicidal activity; Figures S1–S60: 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, and HRMS spectra of compounds 3a–3t.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.Z. and J.L.; methodology, X.Z., S.C., Y.T. and Y.Z.; formal analysis, J.S.; investigation, X.Z., S.C., L.Y. and M.W.; writing—original draft preparation, S.C., X.Z. and L.L.; writing—review and editing, X.Z., M.W. and J.L.; supervision, J.L. and X.Z.; funding acquisition, J.L. and X.Z.; project administration, J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (NO. 2018YFD0200500), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO. 31672069) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (NO. 2022M710917).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or the Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
We declare no conflicts of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References
- Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.; Duan, X.; He, W.; Si, H.; Wang, P.; Cheng, S.; Luo, H.; Rao, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Novel Citral-thiazolyl Hydrazine Derivatives as Promising Antifungal Agents against Phytopathogenic Fungi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 14512–14519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Su, H.; Yang, X.; Sun, T.; Lu, X.; Shi, F.; Duan, H.; Liu, X.; Ling, Y. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity of Novel Fungicides Containing a 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroquinoline Scaffold and Acting as Laccase Inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 1776–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.D.; Ma, K.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Sun, Y.; Shang, X.F.; Zhao, Z.M.; Wang, R.X.; Chen, Y.J.; Zhu, J.K.; Liu, Y.Q. Design, Synthesis, and Antifungal Evaluation of 8-Hydroxyquinoline Metal Complexes against Phytopathogenic Fungi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 11096–11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, F.P. Pesticides, environment, and food safety. Food Energy Secur. 2017, 6, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorsbach, B.A.; Sparks, T.C.; Cicchillo, R.M.; Garizi, N.V.; Hahn, D.R.; Meyer, K.G. Natural products: A strategic lead generation approach in crop protection discovery. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2301–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, T.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, M.; Huang, M.; Deng, L.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y. Natural products-based pesticides: Design, synthesis and pesticidal activities of novel fraxinellone derivatives containing N-phenylpyrazole moiety. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 117, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viayna, E.; Sola, I.; Bartolini, M.; Simone, A.D.; Tapia-Rojas, C.; Serrano, F.G.; Sabate, R.; Juárez-Jiménez, J.; Pérez, B.; Luque, F.J.; et al. Synthesis and Multitarget Biological Profiling of a Novel Family of Rhein Derivatives As Disease-Modifying Anti-Alzheimer Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 2549–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Qi, X.; Yan, Y.; Qi, J.; Qian, N.; Guo, L.; Li, C.; Wang, F.; Huang, P.; Zhou, H.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of rhein amides as inhibitors of osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, G.; Yang, C.; Wang, B. Novel Rhein Analogues as Potential Anticancer Agents. Chemmedchem 2011, 6, 2294–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suneela, D.; Dipmala, P. Synthesis and pharmacokinetic profile of rhein-boswellic acid conjugate. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 7582–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.F.; Zhao, Z.M.; Li, J.C.; Yang, J.Z.; Liu, Y.Q.; Dai, L.X.; Zhang, Z.J.; Yang, Z.G.; Miao, X.L.; Yang, C.J.; et al. Insecticidal and antifungal activities of Rheum palmatum L. anthraquinones and structurally related compounds. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 137, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.K.; Singh, S.S.; Verm, S.; Kumar, S. Antifungal activity of anthraquinone derivatives from Rheum emodi. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 72, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.K.; Yue, Z.Z.; Li, J.X.; Tan, C.; Miao, Z.H.; Tan, W.F.; Yang, C.H. Natural product-based design, synthesis and biological evaluation of anthra[2,1-d]thiazole-6,11-dione derivatives from rhein as novelantitumour agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 84, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hsiang, T.; Huang, R.; Qi, J.; Gan, T.; Chang, Y.; Li, J. Antifungal and insecticidal activities of rhein derivatives: Synthesis, characterization and preliminary structure–activity relationship studies. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 4140–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yu, L.H.; Hsiang, T.; Huang, D.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Du, X.; Li, J. The influence of steric configuration of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid-amino acid conjugates on fungicidal activity and systemicity. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019. 75, 3323–3330. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.L.T.; Hsiang, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Du, X.; Yin, J.; Li, J. An efficient overexpression method for studying genes in Ricinus that transport vectorized agrochemicals. Plant Methods 2022, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todoroki, Y.; Narita, K.; Muramatsu, T.; Shimomura, H.; Ohnishi, T.; Mizutani, M.; Ueno, K.; Hirai, N. Synthesis and biological activity of amino acid conjugates of abscisic acid. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, D.Y.; Shang, H.; Jia, Y.; Xu, X.D.; Tian, Y.; Guo, P. Amino acid ester-coupled caffeoylquinic acid derivatives as potential hypolipidemic agents: Synthesis and biological evaluation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Zhao, C. Synthesis of l-ascorbic acid-amino acid-norcantharidin conjugates and their biological activity evaluation in vitro. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 5455–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, K.P.; Kumara, H.K.; Ullas, B.J.; Shivakumara, J.; Gowda, D.C. Amino acids conjugated quinazolinone-Schiff’s bases as potential antimicrobial agents: Synthesis, SAR and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 90, 103093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.S.; Girgis, A.S.; Thomas, S.J.; Capito, J.E.; George, R.F.; Salman, A.; El-Manawaty, M.A.; Samir, A. Synthesis, pharmacological profile and 2D-QSAR studies of curcumin-amino acid conjugates as potential drug candidates. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 196, 112293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Q.; Li, J. Synthesis and bioactivities of amino acid ester conjugates of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5384–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Z.; Yao, Z.; Wu, Q.; Du, X.; Li, J. Design, synthesis and biological activity of hydroxybenzoic acid ester conjugates of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Huang, D.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, M.; Yao, Z.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Li, J. Design, Synthesis, Phloem Mobility, and Bioactivities of a Series of Phenazine-1-Carboxylic Acid-Amino Acid Conjugates. Molecules 2018, 23, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Huang, G.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, J. Screening Effective Antifungal Substances from the Bark and Leaves of Zanthoxylum avicennae by the Bioactivity-Guided Isolation Method. Molecules 2019, 24, 4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang Min Xiao, Y.; Hsiang, T.; Hu, C.; Li, J. Systemic fungicidal activity of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid-valine conjugate against tobacco sore shin and its translocation and accumulation in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.). Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).