Novel Nanotherapeutics for Cancer Immunotherapy by PD-L1-Aptamer-Functionalized and Fexofenadine-Loaded Albumin Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
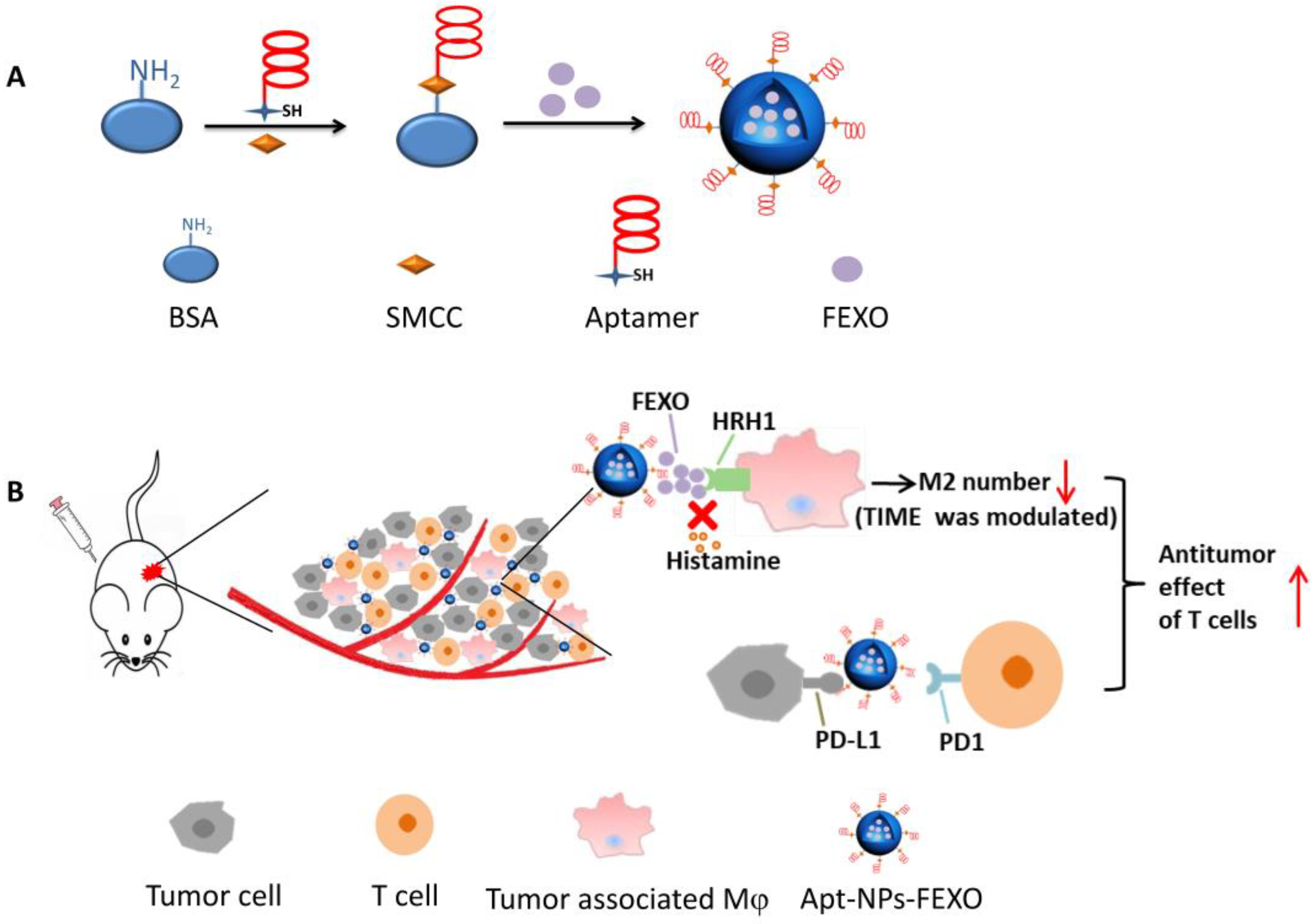
2.1. Conjugation of PD-L1 Aptamer to Albumin
2.2. Characterization of Nanoparticles
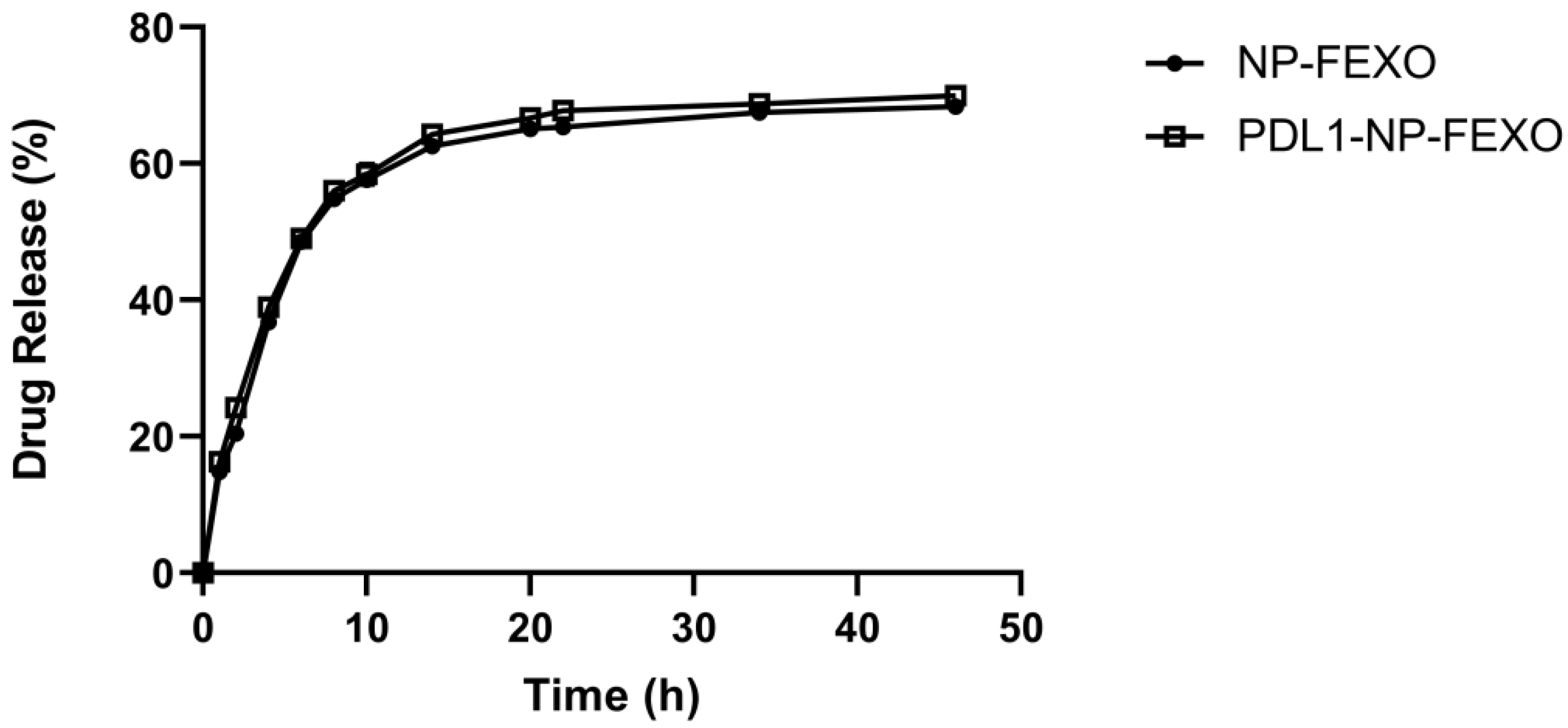
2.3. Release of FEXO from Nanoparticles
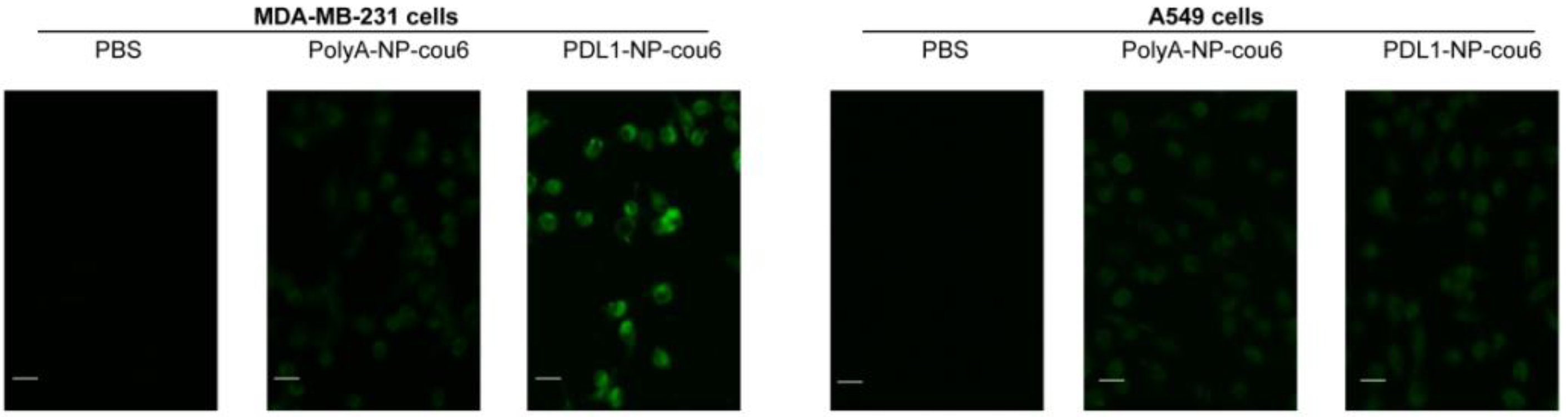
2.4. Affinity of PDL1-NP to PD-L1-Expressing Tumor Cells
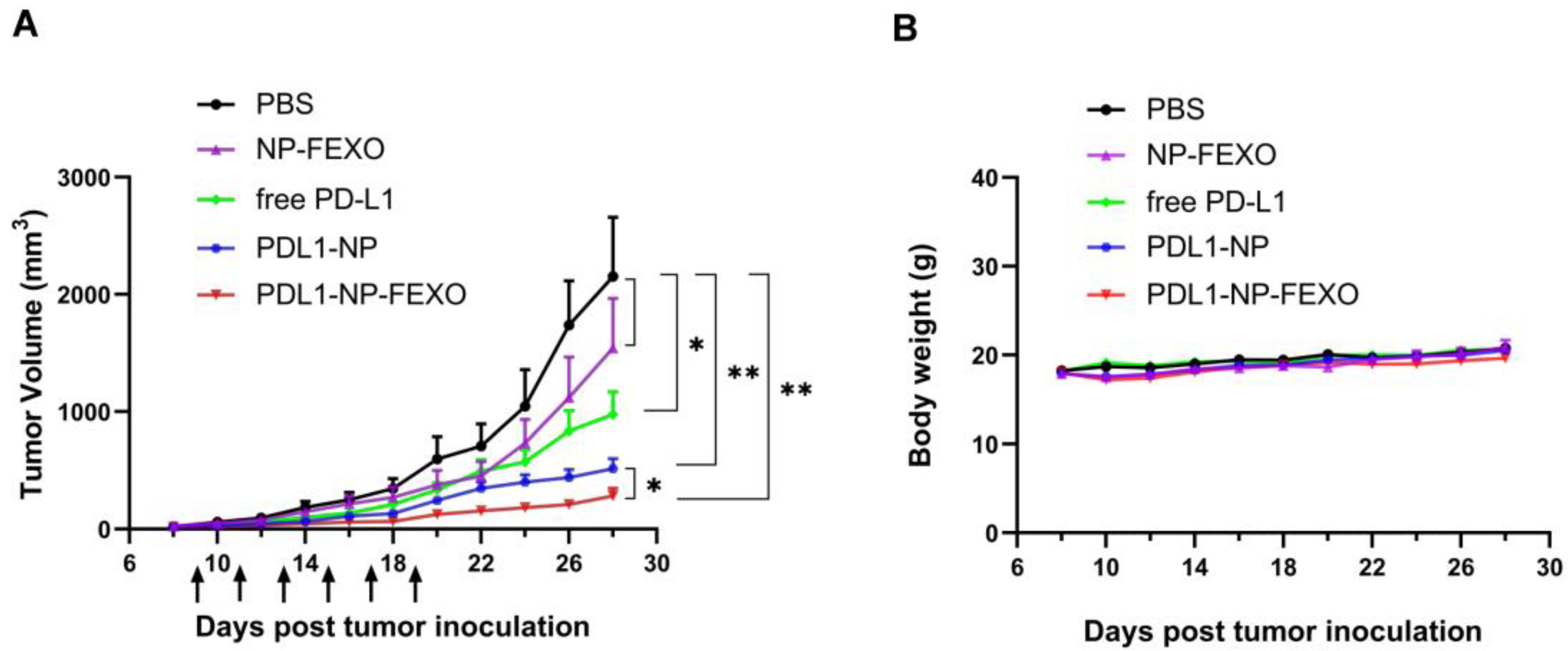
2.5. In Vivo Antitumor Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.2. Animals
4.3. Reagents
4.4. Conjugation of Aptamer to Albumin
4.5. Preparation of Aptamer-Modified Nanoparticles
4.6. Assessment of DNA Conjugation to Albumin
4.7. Characterization of Nanoparticles
4.8. Measurement of Drug-Loading Capacity and Drug Encapsulation Efficiency
4.9. Drug Release Study
4.10. Affinity of PDL1-NP to PD-L1-Expressing Tumor Cells
4.11. Animal Study
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.P.; Kurzrock, R. PD-L1 Expression as a Predictive Biomarker in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schütz, F.; Stefanovic, S.; Mayer, L.; von Au, A.; Domschke, C.; Sohn, C. PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway in Breast Cancer. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2017, 40, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Long, G.V.; Brady, B.; Dutriaux, C.; Maio, M.; Mortier, L.; Hassel, J.C.; Rutkowski, P.; McNeil, C.; Kalinka-Warzocha, E.; et al. Nivolumab in Previously Untreated Melanoma without BRAF Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizvi, N.A.; Mazières, J.; Planchard, D.; Stinchcombe, T.E.; Dy, G.K.; Antonia, S.J.; Horn, L.; Lena, H.; Minenza, E.; Mennecier, B.; et al. Activity and safety of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, for patients with advanced, refractory squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 063): A phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motzer, R.J.; Rini, B.I.; McDermott, D.F.; Redman, B.G.; Kuzel, T.M.; Harrison, M.R.; Vaishampayan, U.; Drabkin, H.A.; George, S.; Logan, T.F.; et al. Nivolumab for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Results of a Randomized Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Uram, J.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Kemberling, H.; Eyring, A.D.; Skora, A.D.; Luber, B.S.; Azad, N.S.; Laheru, D.; et al. PD-1 Blockade in Tumors with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamanishi, J.; Mandai, M.; Ikeda, T.; Minami, M.; Kawaguchi, A.; Murayama, T.; Kanai, M.; Mori, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Chikuma, S.; et al. Safety and Antitumor Activity of Anti-PD-1 Antibody, Nivolumab, in Patients With Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 4015–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botticelli, A.; Cirillo, A.; Strigari, L.; Valentini, F.; Cerbelli, B.; Scagnoli, S.; Cerbelli, E.; Zizzari, I.G.; Rocca, C.D.; D’Amati, G.; et al. Anti-PD-1 and Anti-PD-L1 in Head and Neck Cancer: A Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 705096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, R.; Chow, L.Q.; Dees, E.C.; Berger, R.; Gupta, S.; Geva, R.; Pusztai, L.; Pathiraja, K.; Aktan, G.; Cheng, J.D.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Patients With Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Phase Ib KEYNOTE-012 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2460–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizenga, D.E.; Szostak, J.W. A DNA Aptamer That Binds Adenosine and Atp. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.Z.; Chen, X.Y. Aptamer-based targeted therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 134, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singerman, L.J.; Masonson, H.; Patel, M.; Adamis, A.P.; Buggage, R.; Cunningham, E.; Goldbaum, M.; Katz, B.; Guyer, D. Pegaptanib sodium for neovascular age-related macular degeneration: Third-year safety results of the VEGF Inhibition Study in Ocular Neovascularisation (VISION) trial. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 92, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.H.; Rossi, J. Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: Current potential and challenges (vol 16, pg 181, 2017). Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, W.-Y.; Huang, B.-T.; Wang, J.-W.; Lin, P.-Y.; Yang, P.-C. A Novel PD-L1-targeting Antagonistic DNA Aptamer with Antitumor Effects. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, F.; Duan, J.; Yang, X.-D. Novel Complex of PD-L1 Aptamer and Albumin Enhances Antitumor Efficacy In Vivo. Molecules 2022, 27, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yao, F.; An, Y.; Li, X.; Duan, J.; Yang, X.-D. Novel Complex of PD-L1 Aptamer and Holliday Junction Enhances Antitumor Efficacy In Vivo. Molecules 2021, 26, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalbasi, A.; Ribas, A. Tumour-intrinsic resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Dai, L.-J.; Wu, S.-Y.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, D.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Shao, Z.-M. Spatial architecture of the immune microenvironment orchestrates tumor immunity and therapeutic response. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.M.; Marabelle, A.; Eggermont, A.; Soria, J.C.; Kroemer, G.; Zitvogel, L. Targeting the tumor microenvironment: Removing obstruction to anticancer immune responses and immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, D.C.; Shevde, L.A. The Tumor Microenvironment Innately Modulates Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Q.; Yao, J.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, X.; Saito, Y.; Fan, H.; Li, P.; et al. The allergy mediator histamine confers resistance to immunotherapy in cancer patients via activation of the macrophage histamine receptor H1. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 36–52.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunna, C.; Mengru, H.; Lei, W.; Weidong, C. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur. J. Pharm. 2020, 877, 173090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackute, J.; Zemaitis, M.; Pranys, D.; Sitkauskiene, B.; Miliauskas, S.; Vaitkiene, S.; Sakalauskas, R. Distribution of M1 and M2 macrophages in tumor islets and stroma in relation to prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Immunol. 2018, 19, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greish, K. Enhanced permeability and retention of macromolecular drugs in solid tumors: A royal gate for targeted anticancer nanomedicines. J. Drug Target. 2007, 15, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, J.M.; Tam, J.O.; Murthy, A.; Ingram, D.R.; Ma, L.L.; Travis, K.; Johnston, K.P.; Sokolov, K.V. Controlled Assembly of Biodegradable Plasmonic Nanoclusters for Near-Infrared Imaging and Therapeutic Applications. Acs Nano 2010, 4, 2178–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, H.; Brechbiel, M.W. Nano-sized MRI contrast agents with dendrimer cores. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 2271–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventola, C.L. Progress in Nanomedicine: Approved and Investigational Nanodrugs. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 742–755. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.H.; Han, H.K. Nanomedicines: Current status and future perspectives in aspect of drug delivery and pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farjadian, F.; Ghasemi, A.; Gohari, O.; Roointan, A.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Nanopharmaceuticals and nanomedicines currently on the market: Challenges and opportunities. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 93–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles in the clinic: An update. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2019, 4, e10143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prasad, M.; Lambe, U.P.; Brar, B.; Shah, I.; J, M.; Ranjan, K.; Rao, R.; Kumar, S.; Mahant, S.; Khurana, S.K.; et al. Nanotherapeutics: An insight into healthcare and multi-dimensional applications in medical sector of the modern world. Biomed. Pharm. 2018, 97, 1521–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, B.; Mady, O.Y.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Haggag, Y.A. pH-sensitive nanoparticles containing 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin as an improved anti-cancer option for colon cancer. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggag, Y.; Elshikh, M.; El-Tanani, M.; Bannat, I.M.; McCarron, P.; Tambuwala, M.M. Nanoencapsulation of sophorolipids in PEGylated poly(lactide-co-glycolide) as a novel approach to target colon carcinoma in the murine model. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; He, J.; Gong, W.; Zhou, N.; Zhou, S.; Lai, Z.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, W.; et al. TLS11a Aptamer/CD3 Antibody Anti-Tumor System for Liver Cancer. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Tan, X.; Tu, K.; Tong, X.; Qi, L. Aptamer Functionalized Cisplatin-Albumin Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Positive Cervical Cancer. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Watanabe, R.; Choyke, P.L. Improving conventional enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effects; what is the appropriate target? Theranostics 2013, 4, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.K.; Oberdorster, G.; Biswas, P. Characterization of size, surface charge, and agglomeration state of nanoparticle dispersions for toxicological studies. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, M.; Rehman, M.U.; Kamal, Z.; Alzhrani, R.M.; Alshehri, S.; Alamri, A.H.; Bakkari, M.A.; Sabei, F.Y.; Safhi, A.Y.; Mohammed, A.M.; et al. Formulation development of lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles of doxorubicin and its in-vitro, in-vivo and computational evaluation. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1025013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binsalamah, Z.M.; Paul, A.; Khan, A.A.; Prakash, S.; Shum-Tim, D. Intramyocardial sustained delivery of placental growth factor using nanoparticles as a vehicle for delivery in the rat infarct model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2667–2678. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, M.; Silva, L.; Carvalho, I.; Amaral, R.; de Paula, M.; Swiech, K.; Bastos, J.; Paschoal, J.; Emery, F.; dos Reis, R.; et al. Targeted uptake of folic acid-functionalized polymeric nanoparticles loading glycoalkaloidic extract in vitro and in vivo assays. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 192, 111106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.J.; Park, J.Y.; Cho, Y.L.; Chae, J.R.; Cho, H.; Kang, W.J. In vivo positron emission tomography imaging for PD-L1 expression in cancer using aptamer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 620, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Fang, Y.C.; Li, J. PD-L1 expression levels on tumor cells affect their immunosuppressive activity. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 5399–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajor, M.; Graczyk-Jarzynka, A.; Marhelava, K. PD-L1 CAR effector cells induce self-amplifying cytotoxic effects against target cells (vol 10, e002500, 2022). J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e002500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; You, M.; Pu, Y.; Liu, H.; Ye, M.; Tan, W. Recent developments in protein and cell-targeted aptamer selection and applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4117–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pednekar, P.P.; Jadhav, K.R.; Kadam, V.J. Aptamer-dendrimer bioconjugate: A nanotool for therapeutics, diagnosis, and imaging. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 1273–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Pieve, C.; Blackshaw, E.; Missailidis, S.; Perkins, A.C. PEGylation and biodistribution of an anti-MUC1 aptamer in MCF-7 tumor-bearing mice. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, M.R.; Wan, H.T. Discussion about several potential drawbacks of PEGylated therapeutic proteins. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrobel, D.; Appelhans, D.; Signorelli, M.; Wiesner, B.; Fessas, D.; Scheler, U.; Voit, B.; Maly, J. Interaction study between maltose-modified PPI dendrimers and lipidic model membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1848, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, R.; Sethiya, N.K.; Gulbake, A.S.; Mehra, N.K.; Murty, U.; Gulbake, A. A review on albumin as a biomaterial for ocular drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Miles, D.; Gianni, L.; Krop, I.E.; Welslau, M.; Baselga, J.; Pegram, M.; Oh, D.-Y.; Diéras, V.; Guardino, E.; et al. Trastuzumab emtansine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Hah, S.S. Binding of uranyl ion by a DNA aptamer attached to a solid support. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4020–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, N.; Sun, Y.; Xie, J.; Teng, L. Preparation and Evaluation of in vitro Self-assembling HSA Nanoparticles for Cabazitaxel. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, L.; Lee, R.; Sun, Y.; Cai, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Lu, J.; Meng, Q.; Teng, L.; Wang, D.; et al. Cabazitaxel-loaded human serum albumin nanoparticles as a therapeutic agent against prostate cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 3451–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, P.; Bhushan, R. Enantioseparation of (RS)-fexofenadine and enhanced detection as the diastereomeric amide and anhydride derivatives using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 32, e4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.-Q.; Gao, C.-D.; Hu, S.-F.; Ren, J.-L.; Zhao, L.-H.; Sun, R.-C. Xylan-Modified-Based Hydrogels with Temperature/pH Dual Sensitivity and Controllable Drug Delivery Behavior. Materials 2017, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, F.; An, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Duan, J.; Yang, X.-D. Targeted Therapy of Colon Cancer by Aptamer-Guided Holliday Junctions Loaded with Doxorubicin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2119–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Duan, J.; Yang, X.-D. Targeted Treatment of Colon Cancer with Aptamer-Guided Albumin Nanoparticles Loaded with Docetaxel. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6737–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

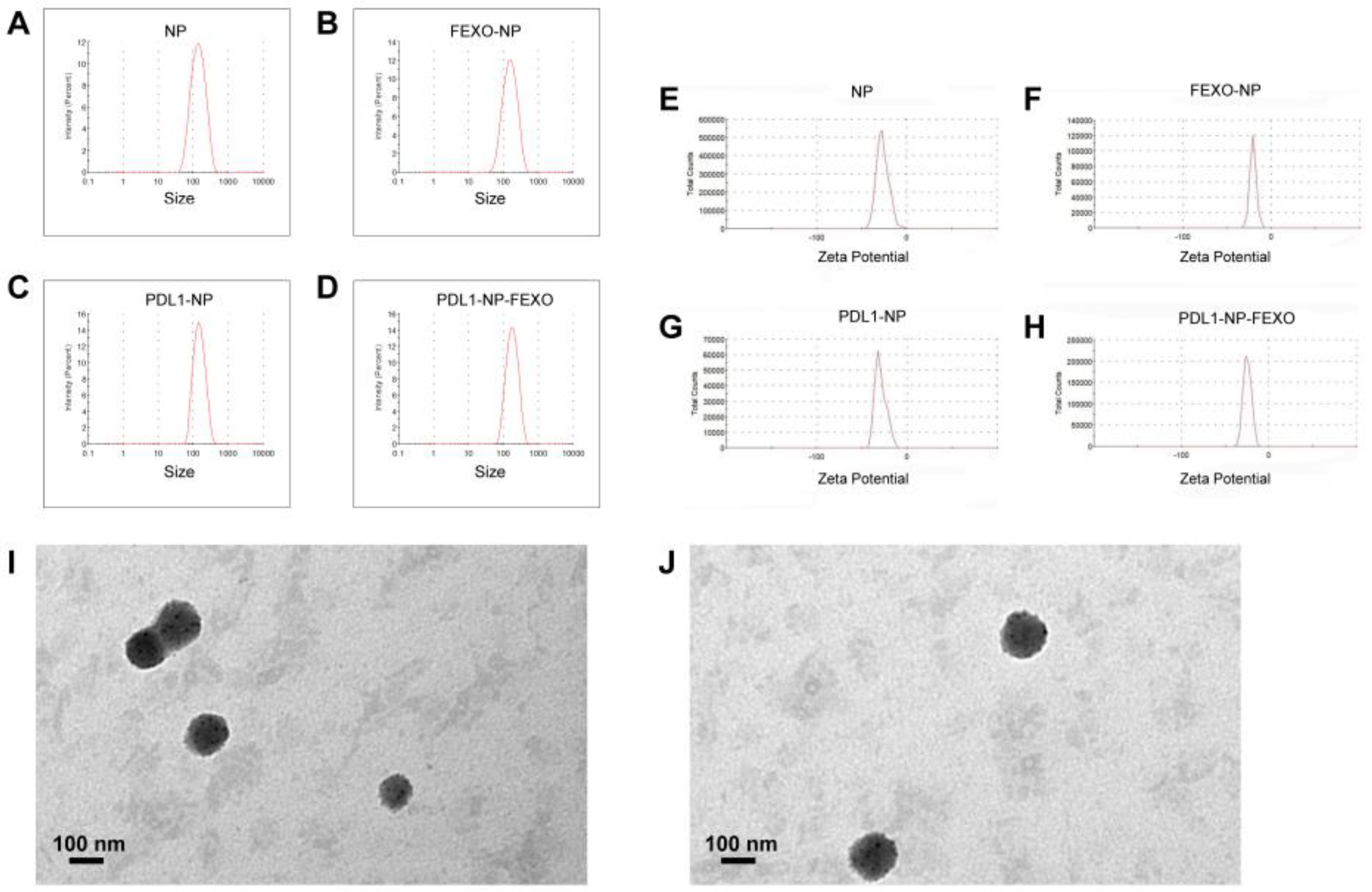

| Formulation | Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NP | 117.9 ± 2.7 | 0.254 ± 0.018 | −25.5 ± 1.04 |
| PDL1-NP | 135.5 ± 1.95 | 0.234 ± 0.031 | −30.7 ± 1.32 |
| NP-FEXO | 123.2 ± 3.39 | 0.247 ± 0.024 | −20.8 ± 0.53 |
| PDL1-NP-FEXO | 154.6 ± 2.92 | 0.222 ± 0.011 | −24.1 ± 0.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, X.; Yao, F.; An, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, X.-D. Novel Nanotherapeutics for Cancer Immunotherapy by PD-L1-Aptamer-Functionalized and Fexofenadine-Loaded Albumin Nanoparticles. Molecules 2023, 28, 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062556
Lai X, Yao F, An Y, Li X, Yang X-D. Novel Nanotherapeutics for Cancer Immunotherapy by PD-L1-Aptamer-Functionalized and Fexofenadine-Loaded Albumin Nanoparticles. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062556
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Xialian, Fengjiao Yao, Yacong An, Xundou Li, and Xian-Da Yang. 2023. "Novel Nanotherapeutics for Cancer Immunotherapy by PD-L1-Aptamer-Functionalized and Fexofenadine-Loaded Albumin Nanoparticles" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062556
APA StyleLai, X., Yao, F., An, Y., Li, X., & Yang, X.-D. (2023). Novel Nanotherapeutics for Cancer Immunotherapy by PD-L1-Aptamer-Functionalized and Fexofenadine-Loaded Albumin Nanoparticles. Molecules, 28(6), 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062556






