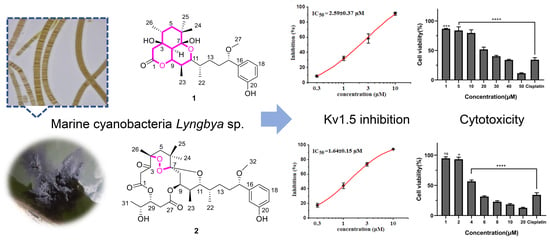
Structure Elucidation of Two Intriguing Neo-Debromoaplysiatoxin Derivatives from Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Showing Strong Inhibition of Kv1.5 Potassium Channel and Differential Cytotoxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
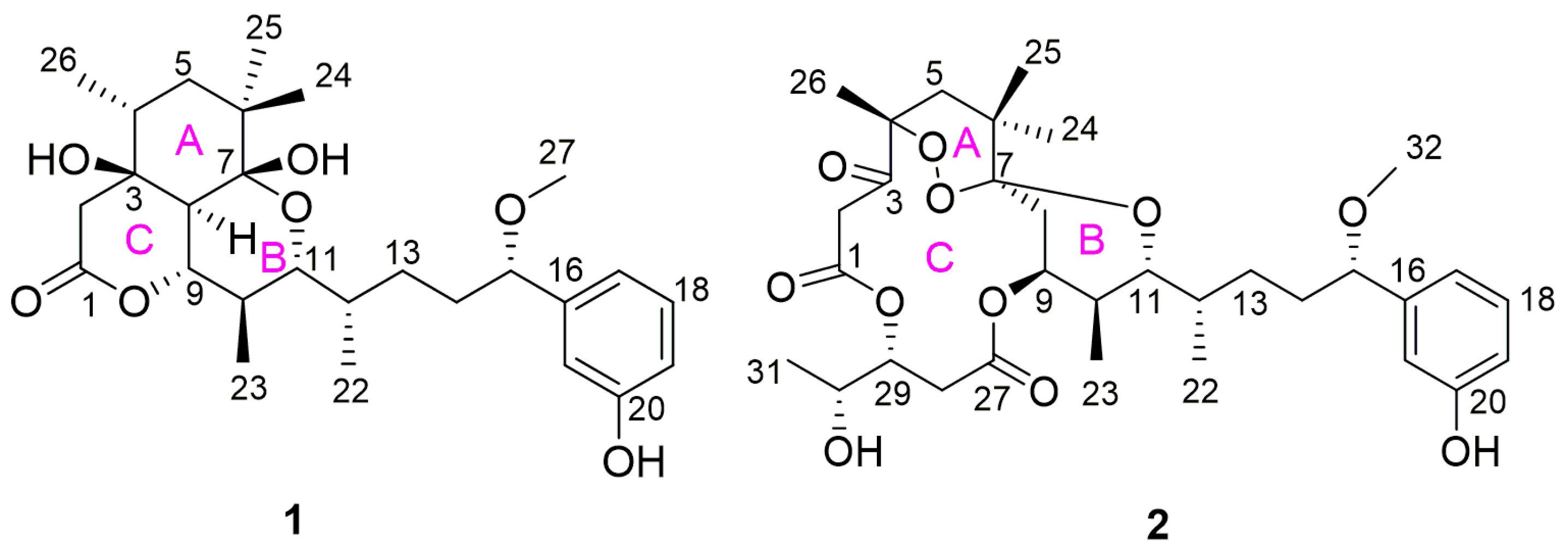
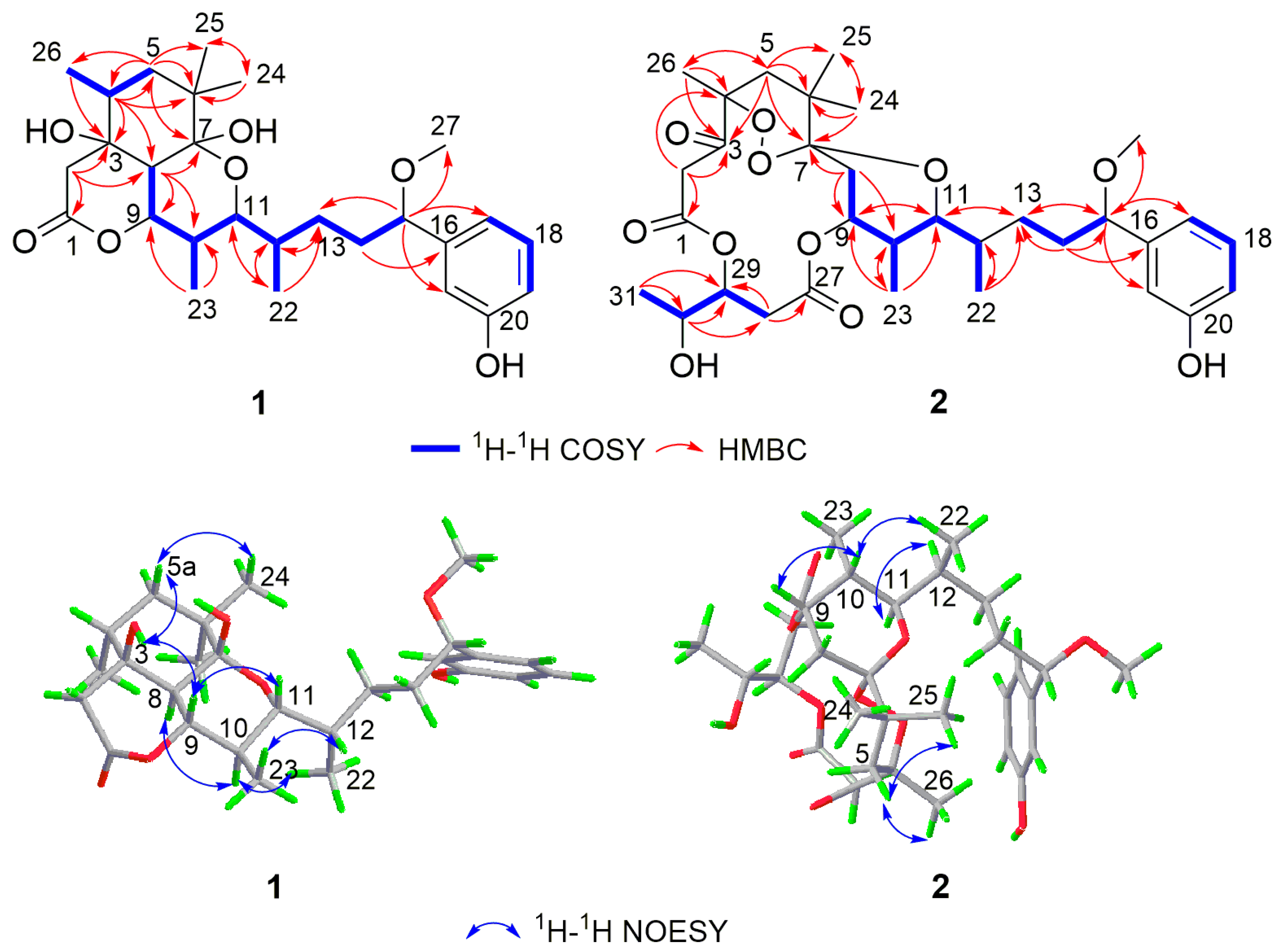
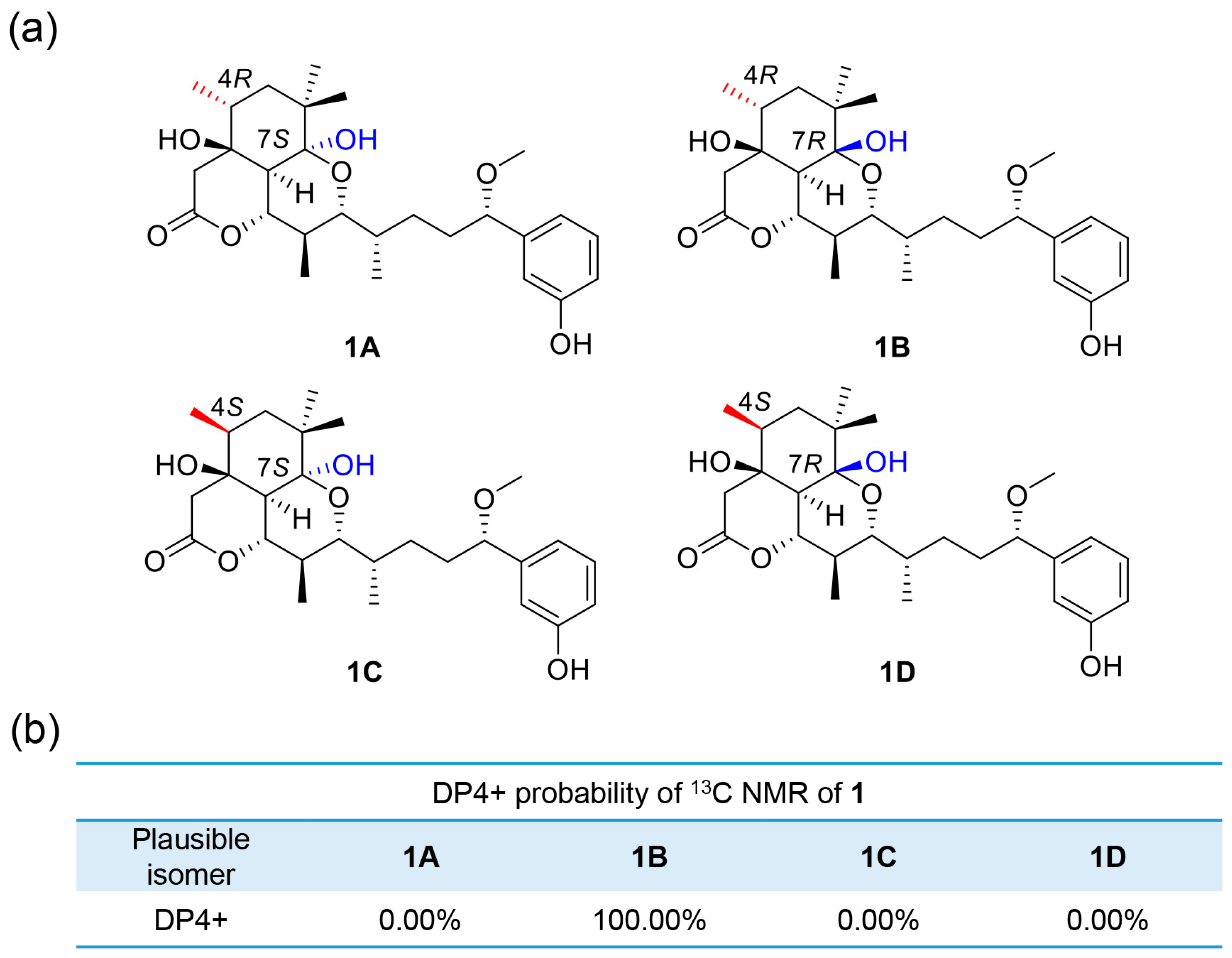
2.1. Structure Elucidation of Compounds
2.2. Bioactivities
2.2.1. Inhibitory Activities against Kv1.5
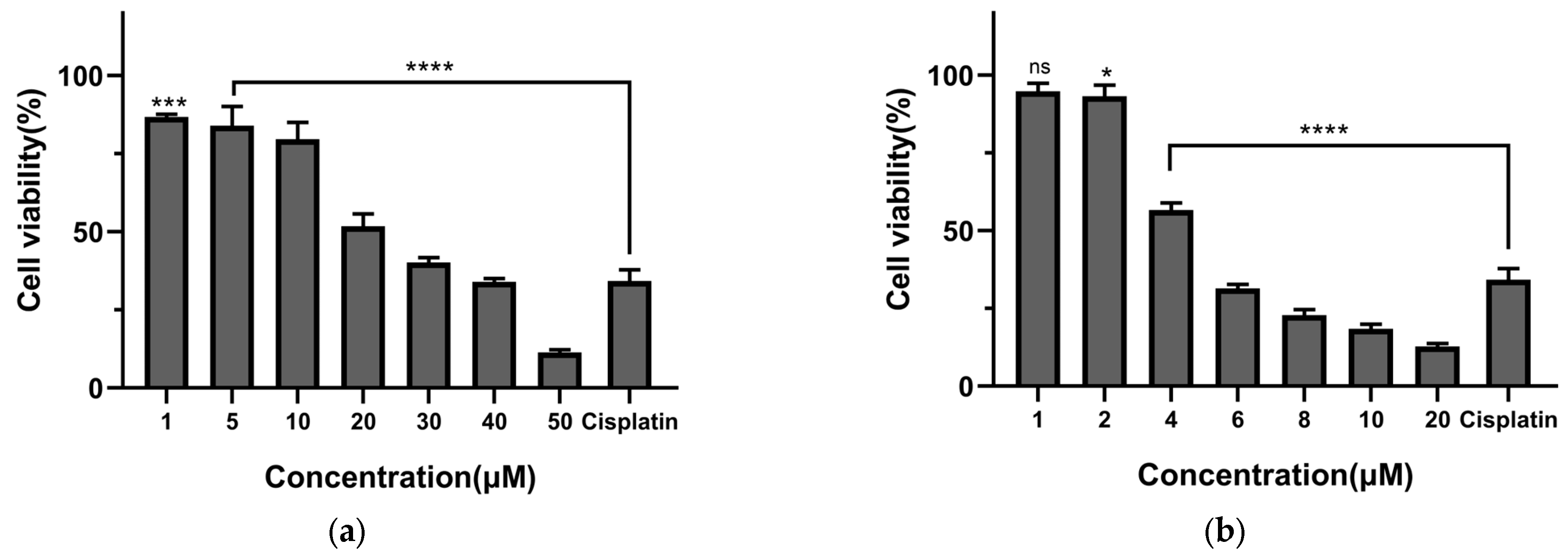
2.2.2. Cytotoxic Effects
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Theory and Calculation Details
3.5. Cell Culture
3.6. Ion Channel Inhibitory Experiment
3.7. Cell Viability Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamilton, T.L.; Bryant, D.A.; Macalady, J.L. The role of biology in planetary evolution: Cyanobacterial primary production in low-oxygen Proterozoic oceans. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuan, N.H.; An, T.T.; Shrestha, A.; Canh, N.X.; Sohng, J.K.; Dhakal, D. Recent advances in exploration and biotechnological production of bioactive compounds in three cyanobacterial genera: Nostoc, Lyngbya, and Microcystis. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.Z.; Zhang, T.; Yao, J.X.; Lu, J.; Liu, Z.W.; Ding, L.J. Recent advances in chemistry and bioactivity of marine cyanobacteria Moorea species. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 201, 112473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sini, P.; Dang, T.B.C.; Fais, M.; Galioto, M.; Padedda, B.M.; Luglie, A.; Iaccarino, C.; Crosio, C. Cyanobacteria, cyanotoxins, and neurodegenerative diseases: Dangerous liaisons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, J.S.; Tischbein, M.; Cox, P.A.; Stommel, E.W. Cyanotoxins and the nervous system. Toxins 2021, 13, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codd, G.A.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S. Cyanobacterial toxins: Risk management for health protection. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.K.; Kaur, P.; Leong, S.T.; Tan, L.T.; Prinsep, M.R.; Chu, J.J. Anti-Chikungunya viral activities of aplysiatoxin-related compounds from the marine cyanobacterium Trichodesmium erythraeum. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, Y.; Hanaki, Y.; Kita, M.; Hayakawa, K.; Irie, K.; Nokura, Y.; Nakazaki, A.; Nishikawa, T. Total synthesis and biological evaluation of oscillatoxins D, E, and F. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2021, 85, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikumori, M.; Yanagita, R.C.; Tokuda, H.; Suenaga, K.; Nagai, H.; Irie, K. Structural optimization of 10-methyl-aplog-1, a simplified analog of debromoaplysiatoxin, as an anticancer lead. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.N.; Liang, T.T.; Keen, L.J.; Fan, T.T.; Zhang, X.D.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S.P.; Lin, H.W. Two marine cyanobacterial aplysiatoxin polyketides, neo-debromoaplysiatoxin A and B, with K(+) channel inhibition activity. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.H.; Zhang, X.K.; Si, R.R.; Shen, S.C.; Liang, T.T.; Fan, T.T.; Chen, W.; Xu, L.H.; Han, B.N. Chemical and biological study of novel aplysiatoxin derivatives from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Toxins 2020, 12, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.C.; Wang, W.P.; Chen, Z.J.; Zhang, H.H.; Yang, Y.C.; Wang, X.L.; Fu, P.; Han, B.N. Absolute structure determination and Kv1.5 ion channel inhibition activities of new debromoaplysiatoxin analogues. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satake, M.; Iguchi, K.; Watanabe, R.; Uchida, H.; Nagai, H. Aplysiadione and aplysiaenal: Truncated biosynthetic intermediates of aplysiatoxins from a cyanobacterium. Results Chem. 2021, 3, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, K.; Satake, M.; Nishio, Y.; Zhang, B.T.; Kawashima, K.; Uchida, H.; Nagai, H. Debromooscillatoxins G and I from the Cyanobacterium Moorea producens. Int. J. Rev. Commun. Heterocycl. Chem. 2021, 102, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Yanagita, R.C.; Hamada, N.; Murakami, A.; Takahashi, H.; Saito, N.; Nagai, H.; Irie, K. A simple analogue of tumor-promoting aplysiatoxin is an antineoplastic agent rather than a tumor promoter: Development of a synthetically accessible protein kinase C activator with bryostatin-like activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7573–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, Y.; Rando, R.R. Structural basis of protein kinase C activation by tumor promoters. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griner, E.M.; Kazanietz, M.G. Protein kinase C and other diacylglycerol effectors in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2007, 7, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashida, Y.; Yanagita, R.C.; Takahashi, C.; Kawanami, Y.; Irie, K. Binding mode prediction of aplysiatoxin, a potent agonist of protein kinase C, through molecular simulation and structure-activity study on simplified analogs of the receptor-recognition domain. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4218–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulff, H.; Castle, N.A.; Pardo, L.A. Voltage-gated potassium channels as therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 982–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.H.; Wu, J.; Fan, T.T.; Zhang, H.H.; Gong, X.X.; Cao, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, H.W.; Han, B.N. Chemical and biological study of aplysiatoxin derivatives showing inhibition of potassium channel Kv1.5. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 7594–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.T.; Zhang, H.H.; Tang, Y.H.; Zhang, F.Z.; Han, B.N. Two new neo-debromoaplysiatoxins-a pair of stereoisomers exhibiting potent Kv1.5 ion channel inhibition activities. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.H.; Liang, T.T.; Fan, T.T.; Keen, L.J.; Zhang, X.D.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zeng, R.; Han, B.N. Neo-debromoaplysiatoxin C, with new structural rearrangement, derived from debromoaplysiatoxin. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 2151–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hada, K.; Araki, Y.; Nokura, Y.; Urabe, D.; Nishikawa, T. Collective synthesis of aplysiatoxin/oscillatoxin analogues by a bioinspired strategy. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 15618–15633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acton, N.; Roth, R.J. On the conversion of dihydroartemisinic acid into artemisinin. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 3610–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Gao, J.J.; Qin, X.J.; Hao, X.J.; He, H.P.; Liu, H.Y. Hedychins A and B, 6,7-dinorlabdane diterpenoids with a peroxide bridge from Hedychium forrestii. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.X.; Huang, H.B.; Shao, C.L.; Huang, H.R.; Jiang, J.Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y.J.; Li, M.F.; et al. Cytotoxic norsesquiterpene peroxides from the endophytic fungus Talaromyces flavus isolated from the mangrove plant Sonneratia apetala. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entzeroth, M.; Blackman, A.J.; Mynderse, J.S.; Moore, R.E. Structures and stereochemistries of oscillatoxin B, 31-noroscillatoxin B, oscillatoxin D, and 30-methyloscillatoxin D. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Watanabe, M.; Sato, S.; Kawaguchi, M.; Xiao, Y.-Y.; Hayashi, K.; Watanabe, R.; Uchida, H.; Satake, M. New aplysiatoxin derivatives from the Okinawan cyanobacterium Moorea producens. Tetrahedron 2019, 75, 2486–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzer, C.A.; Marnett, L.J. Cyclooxygenases: Structural and functional insights. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S29–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffan, N.; Grundmann, A.; Afiyatullov, S.; Ruan, H.; Li, S.M. FtmOx1, a non-heme Fe(II) and alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, catalyses the endoperoxide formation of verruculogen in Aspergillus fumigatus. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 4082–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.K.; Chen, W.L.; Sun, H.P.; You, Q.D. Kv1. 5 inhibitors for treatment of atrial fibrillation: A tradeoff between selectivity and non-selectivity. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1843–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, M.D.; Perkins, M.V. Structural diversity and chemical synthesis of peroxide and peroxide-derived polyketide metabolites from marine sponges. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 861–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Marine endoperoxides as antimalarial lead compounds. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Shen, J.H.; Luo, X.M.; Zhu, W.L.; Gu, J.D.; Ji, R.Y.; Jiang, H.L.; Chen, K.X. Molecular docking and 3-D-QSAR studies on the possible antimalarial mechanism of artemisinin analogues. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2002, 10, 2883–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.Y.; Ma, X.Y.; Cai, X.Q.; Yan, P.C.; Yue, L.; Lin, C.; Shao, W.W. Sesquiterpenoids from Curcuma wenyujin with anti-influenza viral activities. Phytochemistry 2013, 85, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, M.; Prachyawarakorn, V.; Aree, T.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. Cytotoxic sesquiterpenes from the endophytic fungus Pseudolagarobasidium acaciicola. Phytochemistry 2016, 122, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembitsky, V.M.; Gloriozova, T.A.; Poroikov, V.V. Natural peroxy anticancer agents. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.; Shaala, L.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.; Banjar, Z.M.; Badr, J.M.; McPhail, K.L.; Risinger, A.L.; Mooberry, S.L. 2,3-seco-2,3-dioxo-lyngbyatoxin A from a Red Sea strain of the marine cyanobacterium Moorea producens. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikumori, M.; Yanagita, R.C.; Tokuda, H.; Suzuki, N.; Nagai, H.; Suenaga, K.; Irie, K. Structure-activity studies on the spiroketal moiety of a simplified analogue of debromoaplysiatoxin with antiproliferative activity. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 5614–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimblat, N.; Zanardi, M.M.; Sarotti, A.M. Beyond DP4: An improved probability for the stereochemical assignment of isomeric compounds using quantum chemical calculations of NMR shifts. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12526–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
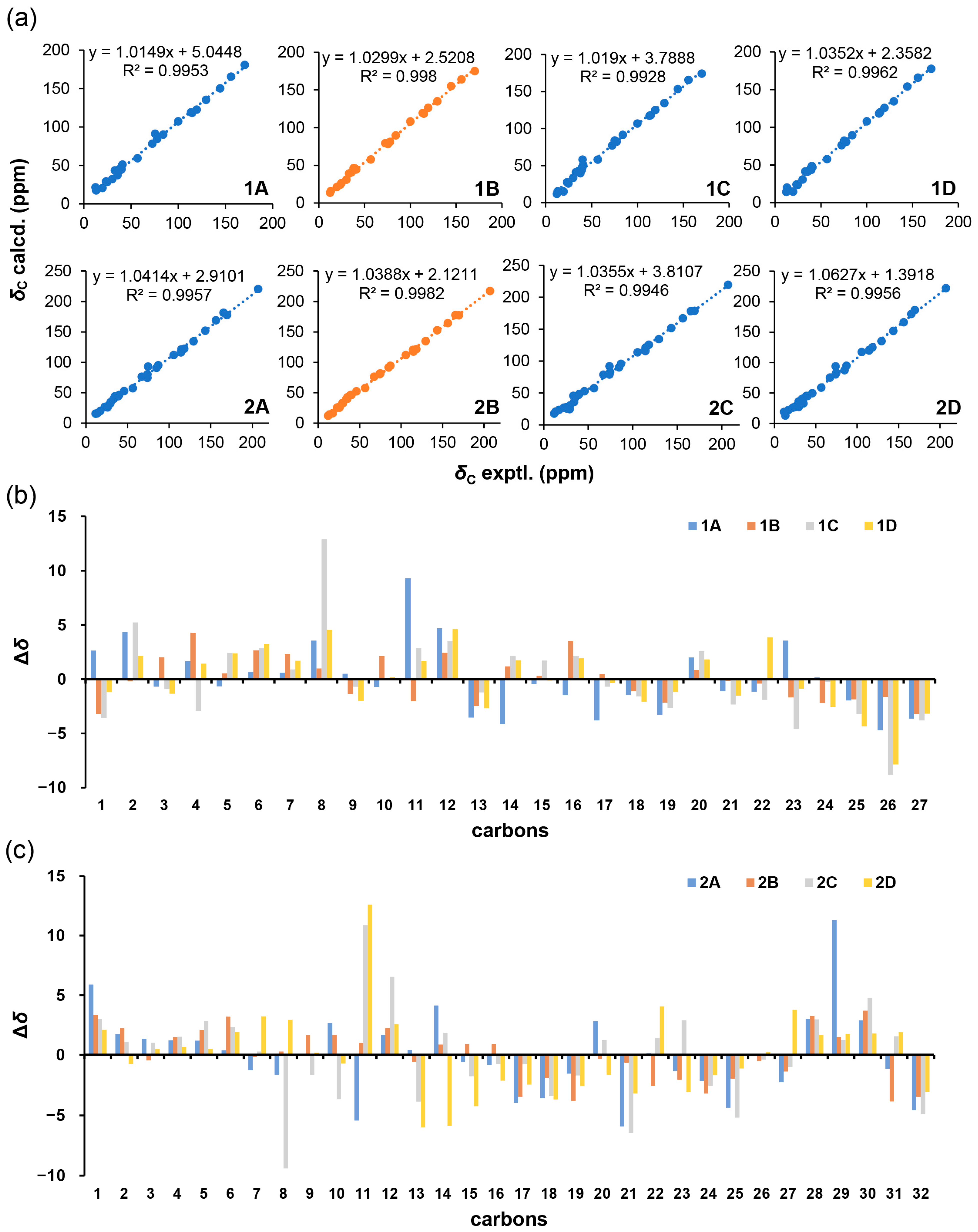
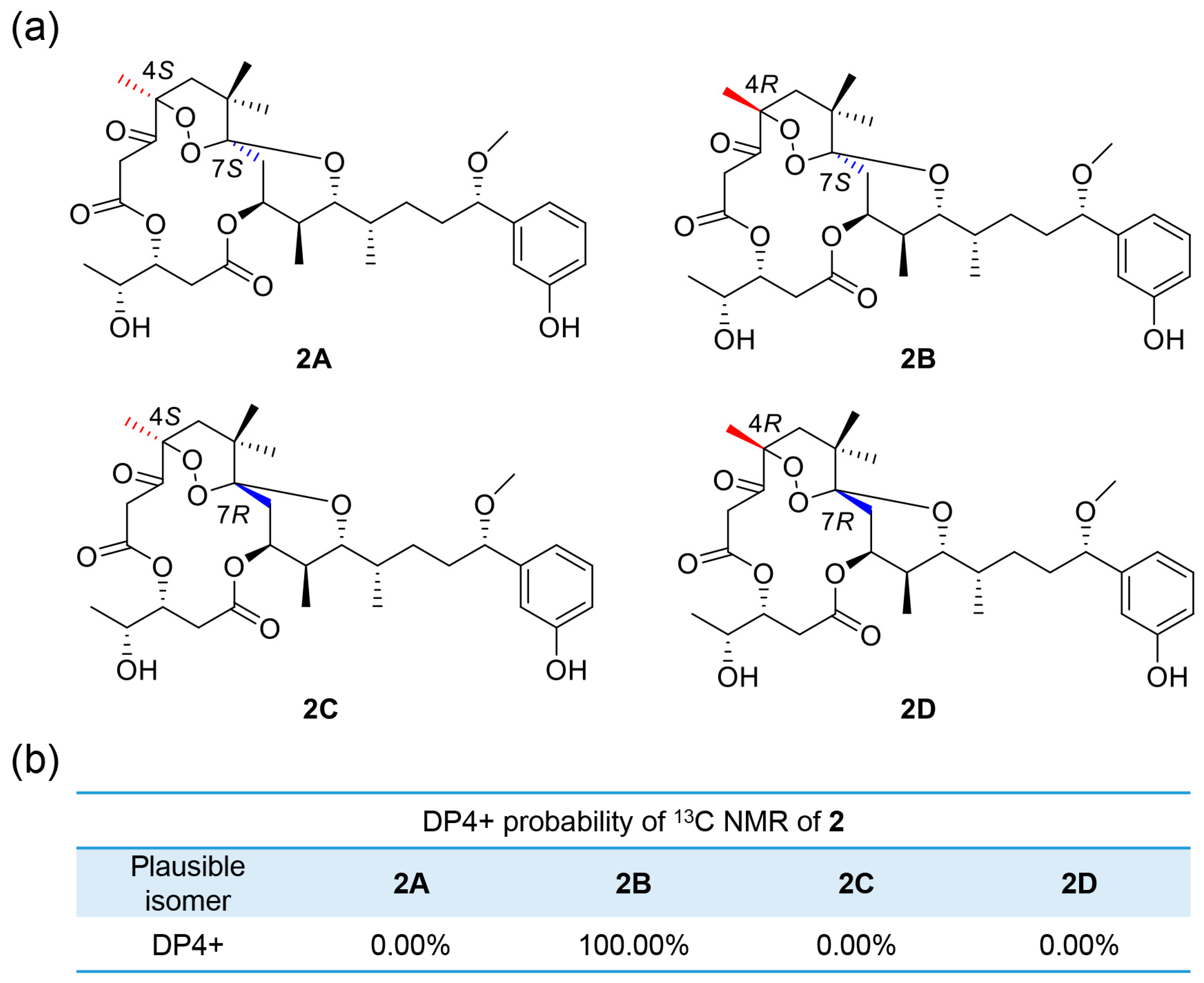
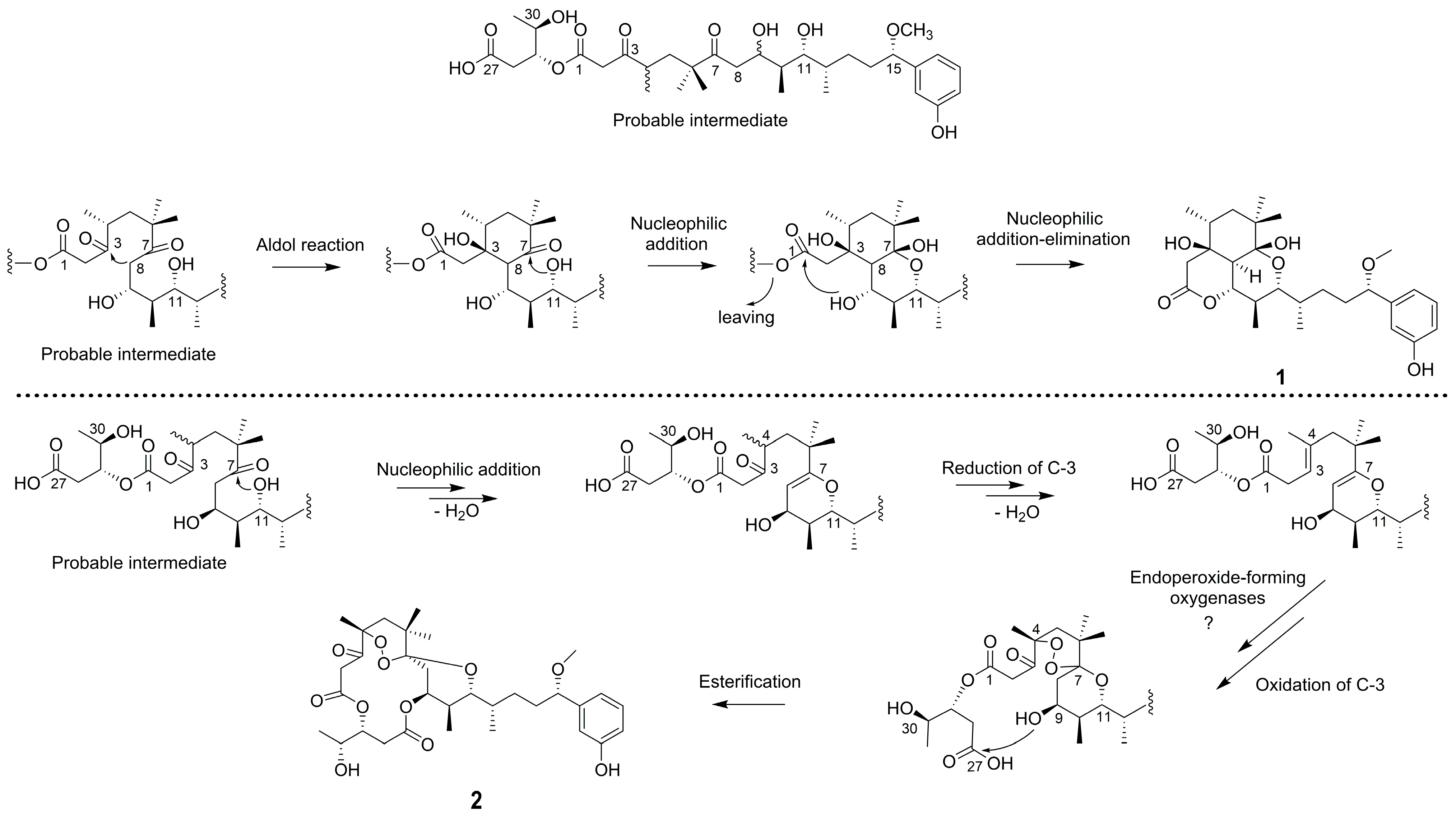
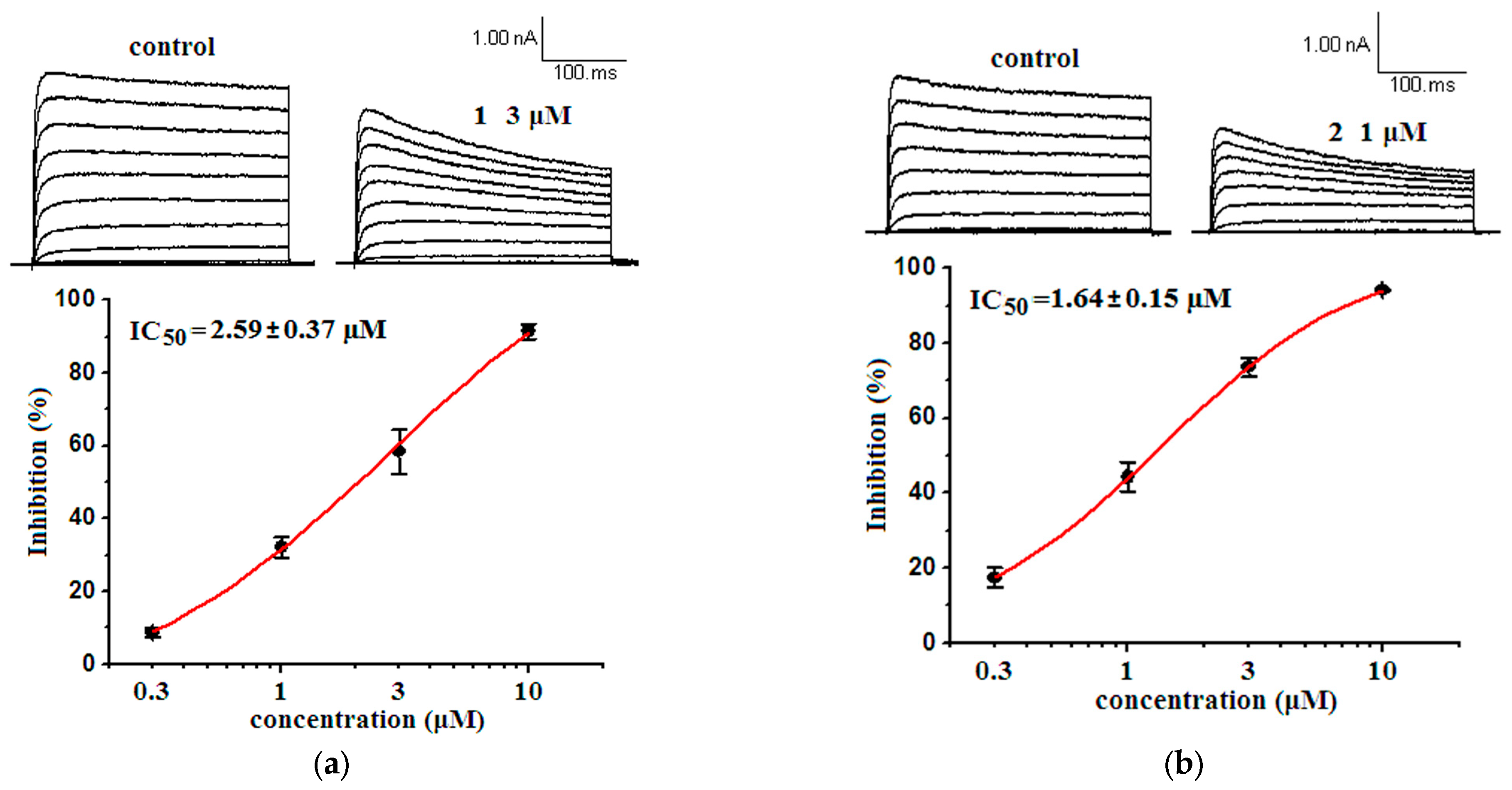
| Pos. | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δc, Type | δH, m (J in Hz) | δc, Type | δH, m (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 170.5, C | 165.5, C | ||
| 2 | 40.9, CH2 | a. 2.62, dd (17.7, 1.9) | 46.0, CH2 | a. 4.00, d (10.8) |
| b. 2.55, d (17.7) | b. 3.26, d (10.7) | |||
| 3 | 72.6, C | 207.2, C | ||
| 4 | 38.0, CH | 1.96, overlap | 87.2, C | |
| 5 | 40.1, CH2 | a. 2.02, dd (14.4, 5.8) | 40.2, CH2 | a. 2.27, d (13.8) |
| b. 1.21, dd (14.6, 2.1) | b. 1.44, d (13.8) | |||
| 6 | 39.5, C | 39.0, C | ||
| 7 | 100.1, C | 105.7, C | ||
| 8 | 40.2, CH | 1.96, overlap | 29.4, CH2 | a. 2.96, dd (14.8, 3.2) |
| b. 1.46, dd (14.8, 2.6) | ||||
| 9 | 77.6, CH | 4.54, t (10.7) | 74.2, CH | 4.71, q (2.8) |
| 10 | 39.3, CH | 1.78, m | 34.4, CH | 1.63, overlap |
| 11 | 75.5, CH | 3.55, dd (10.4, 1.9) | 74.1, CH | 3.61, dd (10.7, 1.9) |
| 12 | 33.0, CH | 1.71, hept (6.1) | 33.7, CH | 1.28, overlap |
| 13 | 30.1, CH2 | a. 1.36, m | 29.9, CH2 | a. 1.25, overlap |
| b. 1.25, overlap | b. 1.21, m | |||
| 14 | 35.8, CH2 | a. 1.83, m | 35.2, CH2 | a. 1.81, m |
| b. 1.62, overlap | b. 1.65, overlap | |||
| 15 | 84.2, CH | 4.01, t (6.6) | 85.0, CH | 4.04, dd (8.5, 5.2) |
| 16 | 144.4, C | 143.6, C | ||
| 17 | 119.5, CH | 6.82, dt (7.5, 1.2) | 118.4, CH | 6.85, overlap |
| 18 | 129.8, CH | 7.20, t (7.8) | 129.5, CH | 7.20, t (8.0) |
| 19 | 114.8, CH | 6.74, ddd (8.1, 2.6, 1.0) | 114.8, CH | 6.78, dt (8.4, 1.4) |
| 20 | 156.0, C | 156.4, C | ||
| 21 | 113.5, CH | 6.77, t (2.0) | 114.5, CH | 6.85, overlap |
| 22 | 13.1, CH3 | 0.82, d (6.6) | 12.0, CH3 | 0.71, d (6.6) |
| 23 | 12.3, CH3 | 1.01, d (6.4) | 13.6, CH3 | 0.74, d (6.9) |
| 24 | 23.4, CH3 | 0.83, s | 25.6, CH3 | 0.85, s |
| 25 | 24.8, CH3 | 1.06, s | 26.2, CH3 | 1.12, s |
| 26 | 19.7, CH3 | 1.08, d (7.7) | 22.8, CH3 | 1.28, s |
| 27 | 56.8, CH3 | 3.20, s | 169.8, C | |
| 28 | 35.2, CH2 | a. 2.79, dd (16.9, 1.5) | ||
| b. 2.70, dd (16.9, 10.9) | ||||
| 29 | 75.0, CH | 5.33, dd (10.7, 4.7) | ||
| 30 | 67.4, CH | 3.95, m | ||
| 31 | 17.4, CH3 | 1.15, d (6.4) | ||
| 32 | 56.7, CH3 | 3.25, s | ||
| 3-OH | 4.35, d (2.0) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Chen, N.; Fu, P.; Wang, W.; Bian, S.; Zhang, H.; Shen, S.; Han, B. Structure Elucidation of Two Intriguing Neo-Debromoaplysiatoxin Derivatives from Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Showing Strong Inhibition of Kv1.5 Potassium Channel and Differential Cytotoxicity. Molecules 2023, 28, 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062786
Chen Z, Chen N, Fu P, Wang W, Bian S, Zhang H, Shen S, Han B. Structure Elucidation of Two Intriguing Neo-Debromoaplysiatoxin Derivatives from Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Showing Strong Inhibition of Kv1.5 Potassium Channel and Differential Cytotoxicity. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062786
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zijun, Na Chen, Peng Fu, Weiping Wang, Shilin Bian, Huihui Zhang, Sicheng Shen, and Bingnan Han. 2023. "Structure Elucidation of Two Intriguing Neo-Debromoaplysiatoxin Derivatives from Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Showing Strong Inhibition of Kv1.5 Potassium Channel and Differential Cytotoxicity" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062786
APA StyleChen, Z., Chen, N., Fu, P., Wang, W., Bian, S., Zhang, H., Shen, S., & Han, B. (2023). Structure Elucidation of Two Intriguing Neo-Debromoaplysiatoxin Derivatives from Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp. Showing Strong Inhibition of Kv1.5 Potassium Channel and Differential Cytotoxicity. Molecules, 28(6), 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062786