Phthalylglycyl Chloride as a Derivatization Agent for UHPLC-MS/MS Determination of Adrenaline, Dopamine and Octopamine in Urine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
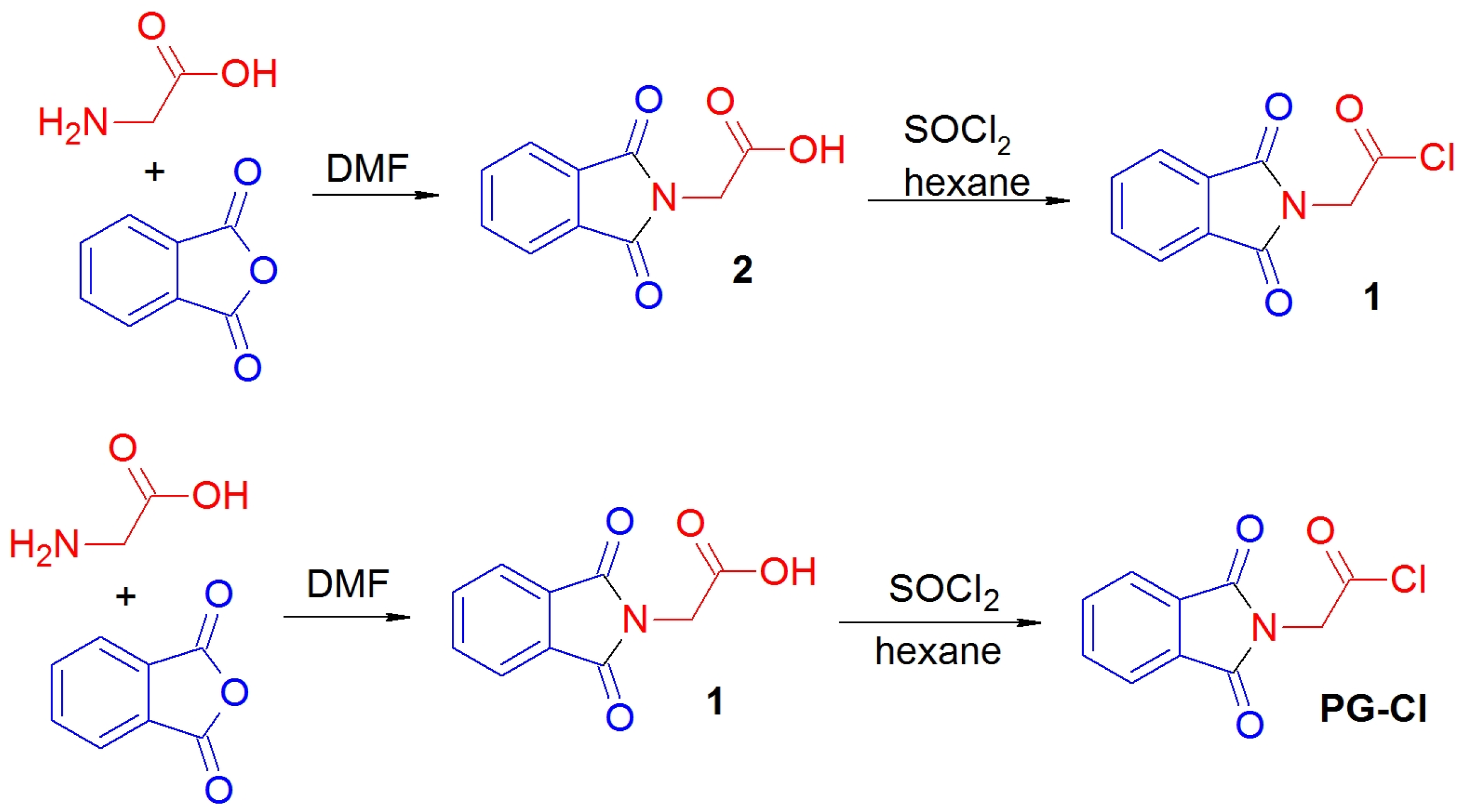
2.1. Phthalylglycyl Chloride (PG-Cl) Synthesis
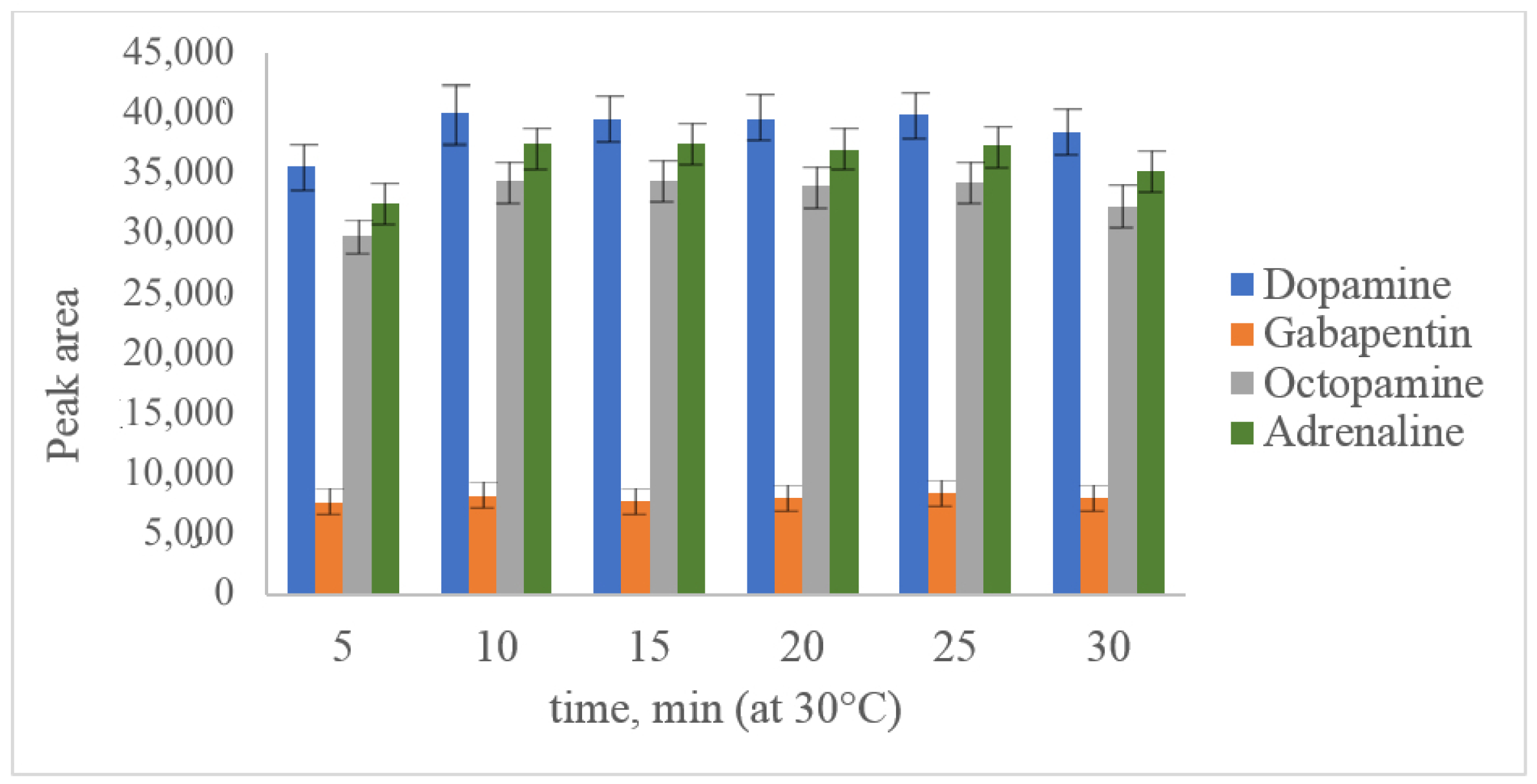
2.2. Optimization of Derivatization Conditions
2.3. MS Detection
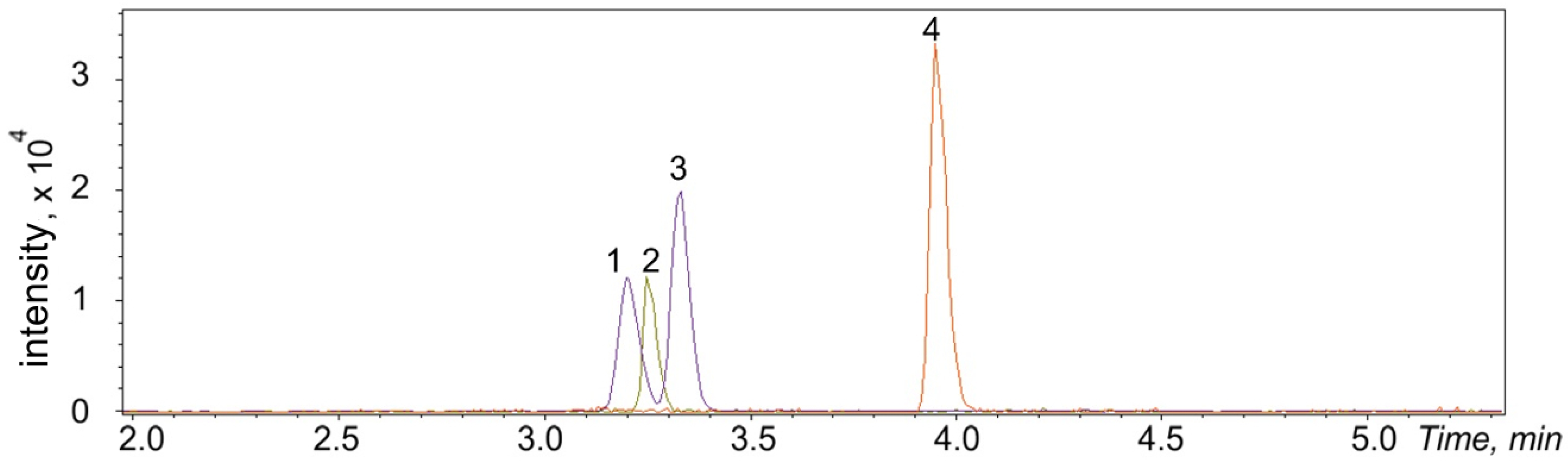
2.4. Chromatographic Conditions
3. Discussion
3.1. Comparison of PG-Cl with FMOC-Cl and DNS-Cl
3.2. Urine Samples Analysis
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Instrumentation
4.3. Urine Samples
4.4. Urine Sample Preparation
4.5. Preparation of Standard and Stock Solutions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Shi, N.; Bu, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, B.; Xu, X.; Shi, X.; Hussain, D.; Xu, X.; Chen, D. Current Sample Preparation Methodologies for Determination of Catecholamines and Their Metabolites. Molecules 2022, 27, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaway, J.E.; Peitzsch, M.; Keevil, B.G. A novel method for the measurement of plasma metanephrines using online solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 52, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhou, Z.; Dong, C.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q.; Lei, Y.; Luo, L.; Feng, Y. Facile synthesis of a boronate affinity sorbent from mesoporous nanomagnetic polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes composite and its application for enrichment of catecholamines in human urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 944, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhao, X.-E.; Zhu, S.; Tao, Y.; Ji, W.; Geng, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; You, J. A new combined method of stable isotope-labeling derivatization-ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of neurotransmitters in rat brain microdialysates by ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1054, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Stanley, R.; Paull, B.; Macka, M. Comparison of cation-exchange capillary columns used for ion chromatographic separation of biogenic amines. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1571, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilhena, R.O.; Pontes, F.L.D.; Marson, B.M.; Ribeiro, R.P.; Teixeira de Carvalho, K.A.; Cardoso, M.A.; Pontarolo, R. A new HILIC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous analysis of carbidopa, levodopa, and its metabolites in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 967, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Hart, J.P.; McCalley, D.V. Determination of catecholamines in urine using hydrophilic interaction chromatography with electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3854–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaeedi, M.; Alghamdi, H.; Hayes, P.; Hogan, A.; Glennon, J. Efficient Sub-1 Minute Analysis of Selected Biomarker Catecholamines by Core-Shell Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography (HILIC) with Nanomolar Detection at a Boron-Doped Diamond (BDD) Electrode. Separations 2021, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. KOWWIN Ver. 1.68. EPI Suite™-Estimation Program Interface. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/tsca-screening-tools/epi-suitetm-estimation-program-interface (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Kiani, F.; Abbaszadeh, M.; Pousti, M.; Koohyar, F. Ab initio and DFT studies on ionization of octopamine and 6-aminopenicillanic acid in aqueous solution. Ind. J. Chem.—Sec. A Inorg. Phys. Theor. Anal. Chem. 2015, 5, 619–626. [Google Scholar]
- Jameson, R.F.; Kiss, T. The oxovanadyl(IV) catalysed oxidation of adrenaline by molecular oxygen. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1986, 9, 1833–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.; Barlow, R.B. The ionization of phenolic amines, including apomorphine, dopamine and catecholamines and an assessment of zwitterion constants. British J. Pharm. 1976, 57, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockbrader, H.N.; Wesche, D.; Miller, R.; Chapel, S.; Janiczek, N.; Burger, P. A comparison of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of pregabalin and gabapentin. Clin. Pharm. 2010, 49, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Luo, Y.; Shang, J.; Jiang, X. Simultaneous determination of eleven compounds related to metabolism of bioamines in rat cortex and hippocampus by HPLC-ECD with boron-doped diamond working electrode. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 118, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodnik, Z.D.; Jaskiw, G.E. Effect of Mobile Phase pH on the Function of Other Optimization Parameters in an HPLC–ECD Assay of Biogenic Amines and Their Metabolites. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, X.; Shen, J.; Zhang, W. Selective solid-phase extraction of catecholamines from plasma using nanofibers doped with crown ether and their quantitation by HPLC with electrochemical detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4987–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Guo, X.-F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.-S. Analysis of catecholamines and related compounds in one whole metabolic pathway with high performance liquid chromatography based on derivatization. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wu, L.; Zhong, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Meng, J.; Li, F. Analysis of neurotransmitter catecholamines and related amines in human urine and serum by chromatography and capillary electrophoresis with 1, 3, 5, 7-tetramethyl-8-(N-hydroxysuccinimidyl propionic ester)-difluoro-boradiaza-s-indacene. AChrom 2022, 34, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Shi, X.; Yin, P.; Gao, P.; Lu, X.; Xu, G. Analysis of catecholamines and their metabolites in adrenal gland by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 609, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.; Vårdal, L.; Vidal, L.; Canals, A.; Gjelstad, A.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, S. Complexation-mediated electromembrane extraction of highly polar basic drugs—A fundamental study with catecholamines in urine as model system. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4215–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Fang, B.; Wang, S. A Fast and Validated HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine, Dobutamine, Phentolamine, Furosemide, and Aminophylline in Infusion Samples and Injection Formulations. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2021, 2021, 8821126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, W.; Xia, Z.; Jie, X.; Xia, Z.Z. Recent advances in materials for stationary phases of mixed-mode high-performance liquid chromatography. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Ma, L.; Paek, C.; Carr, P.W. Application of silica-based hyper-crosslinked sulfonate-modified reversed stationary phases for separating highly hydrophilic basic compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1202, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesoro, C.; Lelario, F.; Ciriello, R.; Bianco, G.; Di Capua, A.; Acquavia, M.A. An Overview of Methods for L-Dopa Extraction and Analytical Determination in Plant Matrices. Separations 2022, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shaw, P.N.; Barrett, D.A. Catecholamines derivatized with 4-fluoro-7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole: Characterization of chemical structure and fluorescence properties. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 478, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.M.T.; Malec, P.A.; Mabrouk, O.S.; Ro, J.; Dus, M.; Kennedy, R.T. Benzoyl chloride derivatization with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for targeted metabolomics of neurochemicals in biological samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1446, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.I.; Yang, J.S.; Oh, H.J.; Cho, Y.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.-D.; Lee, S.-Y. A simple and rapid analytical method based on solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of free catecholamines and metanephrines in urine and its application to routine clinical analysis. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 49, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roiffé, R.R.; Ribeiro, W.D.; Sardela, V.F.; de la Cruz, M.N.S.; de Souza, K.R.; Pereira, H.M.G.; Aquino Neto, F.R. Development of a sensitive and fast method for detection of catecholamines and metabolites by HRMS. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Cheng, L.; Guan, Q.; Li, H.; Lu, J.; Wang, X. Development and validation of a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the measurement of urinary catecholamines in diagnosis of pheochromocytoma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, e4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Huang, W.; Tong, Y.; Tian, M. Hollow dummy template imprinted boronate-modified polymers for extraction of norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine prior to quantitation by HPLC. Microchim. Acta. 2019, 186, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Hou, X. Tannic acid-directed synthesis of magnetic and boronic acid-functionalized metal-organic frameworks for selective extraction and quantification of catecholamines in human urine. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, J.-X.; Cui, W.-Q.; Zhang, J.-W.; Wu, D.-Q.; Yu, X.-R.; Luo, Y.-B.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Zhu, F.-P.; Hussain, D.; et al. A simultaneous extraction/derivatization strategy coupled with liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of free catecholamines in biological fluids. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1654, 462474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.H.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J. Synthesis of enhanced fluorescent graphene quantum dots for catecholamine neurotransmitter sensing. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yan, R.; Wu, X.; Jin, Y. Photoinduced Synthesis of Methylated Marine Cyclopeptide Galaxamide Analogs with Isoindolinone as Anticancer Agents. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, J.; Bao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Qu, F. The conventional turns rather than irregular γ-/β-turn secondary structures accounting for the antitumor activities of cyclic peptide Phakellistatin 6 analogs. Tetrahedron 2020, 76, 130881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.K.; Betancourt, F.; McAdorey, A.; Yalagala, R.S.; Poupon, A.; Yan, H. BODIPY quaternary ammonium salt as photosensitizers. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 434, 114213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaryan, A.; Ligor, T.; Buszewski, B.; Temerdashev, A.; Dmitrieva, E.; Gashimova, E. LC–MS/MS Determination of Catecholamines in Urine Using FMOC-Cl Derivatization on Solid-Phase Extraction Cartridge. Chromatographia 2018, 81, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubov, L.A.; Galanin, N.E.; Shaposhnikov, G.P. 5,15-diaminotetrabenzoporphyrins: Synthesis and spectral properties. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2012, 82, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaryan, A.A.; Dmitrieva, E.V.; Temerdashev, A.Z. UHPLC-HRMS determination of adrenaline and dopamine dansyl derivatives in human saliva. Analyt. Contr. 2020, 24, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarigul, N.; Korkmaz, F.; Kurultak, İ. A New Artificial Urine Protocol to Better Imitate Human Urine. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name | logPexp (X1) | pKa1 | pKa2 | pKa3 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adrenaline | −1.20 | 8.63 | 9.87 | 13.15 | [9] |
| Octopamine | −0.90 | 8.88 | 9.53 | - | [10] |
| Gabapentin | −1.10 | 3.68 | 10.70 | [11] | |
| Dopamine | −0.98 | 8.81 | 10.5 | [12] |
| Matrix | Analyte | Sample Preparation, Separation Technique | LOQ | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | Noradrenaline (NA), adrenaline (A), dopamine (D) | SPE (Strata X-CW), HILIC | NA: 7.4 ng/mL | LC-MS/MS (ESI(+)) | [26] |
| A: 3.8 ng/mL | |||||
| D: 5.4 ng/mL | |||||
| Urine | Normetanephrine (NMN), metanephrine (MN), NA, A, D | SPE (Strata X-CW), HILIC | NMN: 5.0 ng/mL | LC-MS/MS (ESI(+)) | [27] |
| MN: 5.0 ng/mL | |||||
| NA: 5.0 ng/mL | |||||
| A: 5.0 ng/mL | |||||
| D: 5.0 ng/mL | |||||
| Urine | NA, A, D | SPE (Oasis HLB), HILIC | NA: 0.4 ng/mL | LC-MS/MS (ESI(+)) | [28] |
| A: 0.2 ng/mL | |||||
| D: 0.3 ng/mL | |||||
| Urine | NA, A, D | Template imprinted polymers, RP | NA: 157 ng/mL | LC-UV | [29] |
| A: 51 ng/mL | |||||
| D: 141 ng/mL | |||||
| Urine | NA, A, D | Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles, RP | NA: 0.21 ng/mL | LC-FLD | [30] |
| A: 0.32 ng/mL | |||||
| D: 0.51 ng/mL | |||||
| Urine | NA, A, D | Derivatization with phenyl isothiocyanate, RP | NA: 0.10 ng/mL | LC-MS/MS (ESI(+)) | [31] |
| A: 0.15 ng/mL | |||||
| D: 0.10 ng/mL | |||||
| Serum | NA, A, D | Fluorescent graphene quantum dots | NA: 5 µM | Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) | [32] |
| A: 0.7 µM | |||||
| D: 0.007 µM |
| Analyte | QC, ng/mL | Inter-Day (n = 6) | Intra-day (n = 6) | Linear Range, ng/mL | R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy, % | Precision, % | Accuracy, % | Precision, % | ||||
| PG-octopamine | 250 | 1.7 | 3.7 | 1.3 | 4.1 | 5–500 | 0.993 |
| 100 | 3.6 | 5.4 | 3.2 | 6.8 | |||
| 10 | 8.2 | 13.3 | 7.4 | 12.2 | |||
| PG-dopamine | 250 | 1.9 | 4.2 | 1.5 | 4.9 | 5–500 | 0.991 |
| 100 | 4.1 | 6.3 | 3.6 | 7.5 | |||
| 10 | 8.8 | 14.1 | 8.1 | 14.7 | |||
| PG-adrenaline | 250 | 2.2 | 4.0 | 1.5 | 4.6 | 5–500 | 0.991 |
| 100 | 4.7 | 6.1 | 3.5 | 7.3 | |||
| 10 | 8.3 | 13.8 | 7.8 | 14.5 | |||
| Analyte | Derivatization Reagent | tR, min | LOD, ng/mL | LOQ, ng/mL | Theoretical Mass, m/z | Observed Mass, m/z | Mass Error, ppm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adrenaline | PG-Cl | 3.25 | 1.5 | 5 | 393.1057 (+Na+) | 393.1059 (+Na+) | −0.51 |
| DNS-Cl | n.d. | ||||||
| FMOC-Cl | 4.92 | 2.5 | 5 | 428.1468 (+Na+) | 428.1455 (+Na+) | 3.04 | |
| Octopamine | PG-Cl | 3.21 | 1.5 | 5 | 363.0951 (+Na+) | 363.0943 (+Na+) | 2.20 |
| DNS-Cl | 3.83 | 3 | 10 | 387.1373 (+H+) | 387.1366 (+H+) | 1.81 | |
| FMOC-Cl | 4.81 | 5 | 10 | 398.1363 (+Na+) | 398.1353 (+Na+) | 2.51 | |
| Dopamine | PG-Cl | 3.35 | 1.5 | 5 | 363.0951 (+Na+) | 363.0941 (+Na+) | 2.75 |
| DNS-Cl | 3.93 | 3 | 10 | 387.1373 (+H+) | 387.1366 (+H+) | 1.81 | |
| FMOC-Cl | 5.22 | 25 | 50 | 398.1363 (+Na+) | 398.1352 (+Na+) | 2.76 | |
| Gabapentin | PG-Cl | 3.97 | - | - | 381.1421 (+Na+) 359.1601 (+H+) | 381.1414 (+Na+) 359.1601 (+H+) | 1.84 0.00 |
| DNS-Cl | n.d. | ||||||
| FMOC-Cl | 5.82 | - | - | 416.1832 (+Na+) | 416.1824 (+Na+) | 1.92 | |
| Sample Number | Derivatization Reagent | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMOC-Cl | PG-Cl | |||||
| Adrenaline, ng/mL | Dopamine, ng/mL | Octopamine, ng/mL | Adrenaline, ng/mL | Dopamine, ng/mL | Octopamine, ng/mL | |
| Sample 1 | 51 ± 8 | 223 ± 29 | 58 ± 9 | 57 ± 9 | 214 ± 27 | 63 ± 10 |
| Sample 2 | 62 ± 10 | 248 ± 34 | 64 ± 10 | 65 ± 10 | 255 ± 35 | 71 ± 12 |
| Sample 3 | 47 ± 7 | 212 ± 27 | 52 ± 8 | 54 ± 8 | 226 ± 29 | 58 ± 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zorina, M.; Dotsenko, V.V.; Nesterenko, P.N.; Temerdashev, A.; Dmitrieva, E.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Atapattu, S.N. Phthalylglycyl Chloride as a Derivatization Agent for UHPLC-MS/MS Determination of Adrenaline, Dopamine and Octopamine in Urine. Molecules 2023, 28, 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072900
Zorina M, Dotsenko VV, Nesterenko PN, Temerdashev A, Dmitrieva E, Feng Y-Q, Atapattu SN. Phthalylglycyl Chloride as a Derivatization Agent for UHPLC-MS/MS Determination of Adrenaline, Dopamine and Octopamine in Urine. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072900
Chicago/Turabian StyleZorina, Maria, Victor V. Dotsenko, Pavel N. Nesterenko, Azamat Temerdashev, Ekaterina Dmitrieva, Yu-Qi Feng, and Sanka N. Atapattu. 2023. "Phthalylglycyl Chloride as a Derivatization Agent for UHPLC-MS/MS Determination of Adrenaline, Dopamine and Octopamine in Urine" Molecules 28, no. 7: 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072900
APA StyleZorina, M., Dotsenko, V. V., Nesterenko, P. N., Temerdashev, A., Dmitrieva, E., Feng, Y.-Q., & Atapattu, S. N. (2023). Phthalylglycyl Chloride as a Derivatization Agent for UHPLC-MS/MS Determination of Adrenaline, Dopamine and Octopamine in Urine. Molecules, 28(7), 2900. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072900






