Antibacterial Activity and Antibacterial Mechanism of Lemon Verbena Essential Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain Pseudosciaena D4
2.2. Materials and Reagents
2.3. Instruments and Equipment
2.4. Experimental Method
2.4.1. MIC and MBC Determination
2.4.2. Growth Curve Determination
2.4.3. Detection of Bacterial Biomembrane Structure by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM)
2.4.4. Determination of Extracellular Polysaccharide Content
2.4.5. Cell Membrane Permeability Test
2.4.6. Hemolysis Test
2.4.7. Biomembrane Formation and Metabolic Activity Experiment (XTT Experiment)
2.4.8. Biomembrane Integrity Test
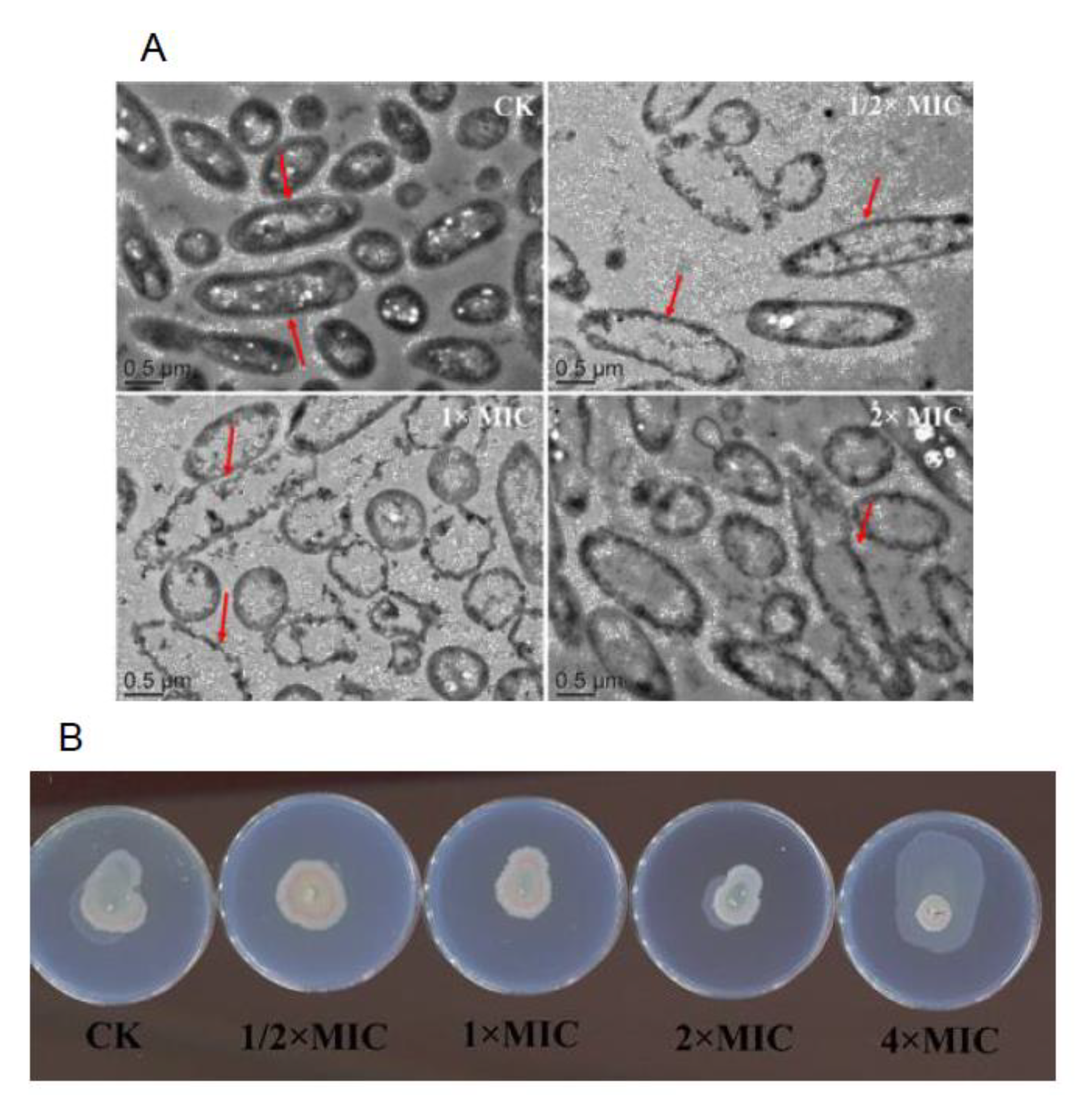
2.4.9. Observation Experiment of Bacterial Structure by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Experimental Result
3.1. MIC and MBC
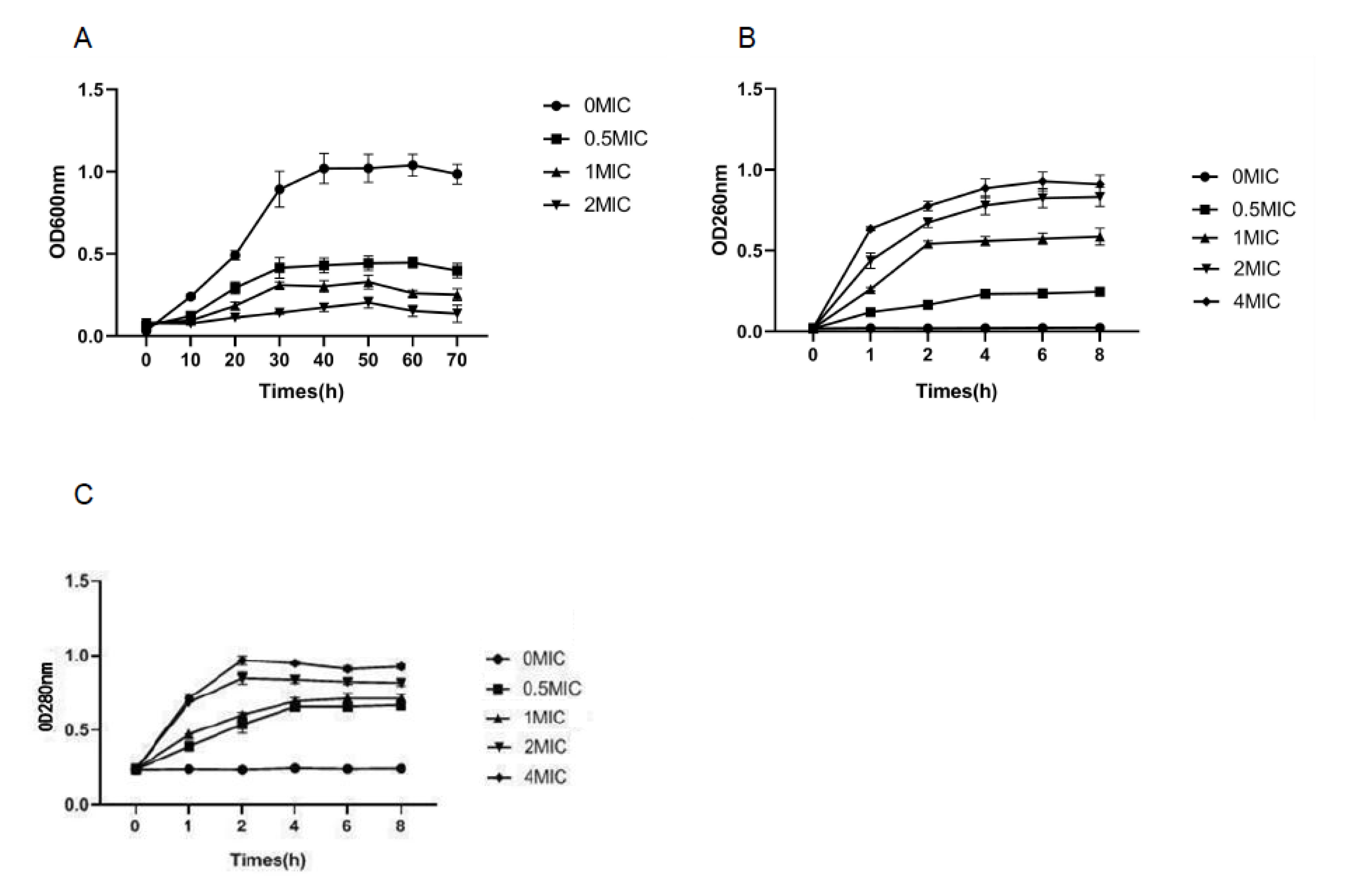
3.2. Growth Curve
3.3. Cell Membrane Integrity
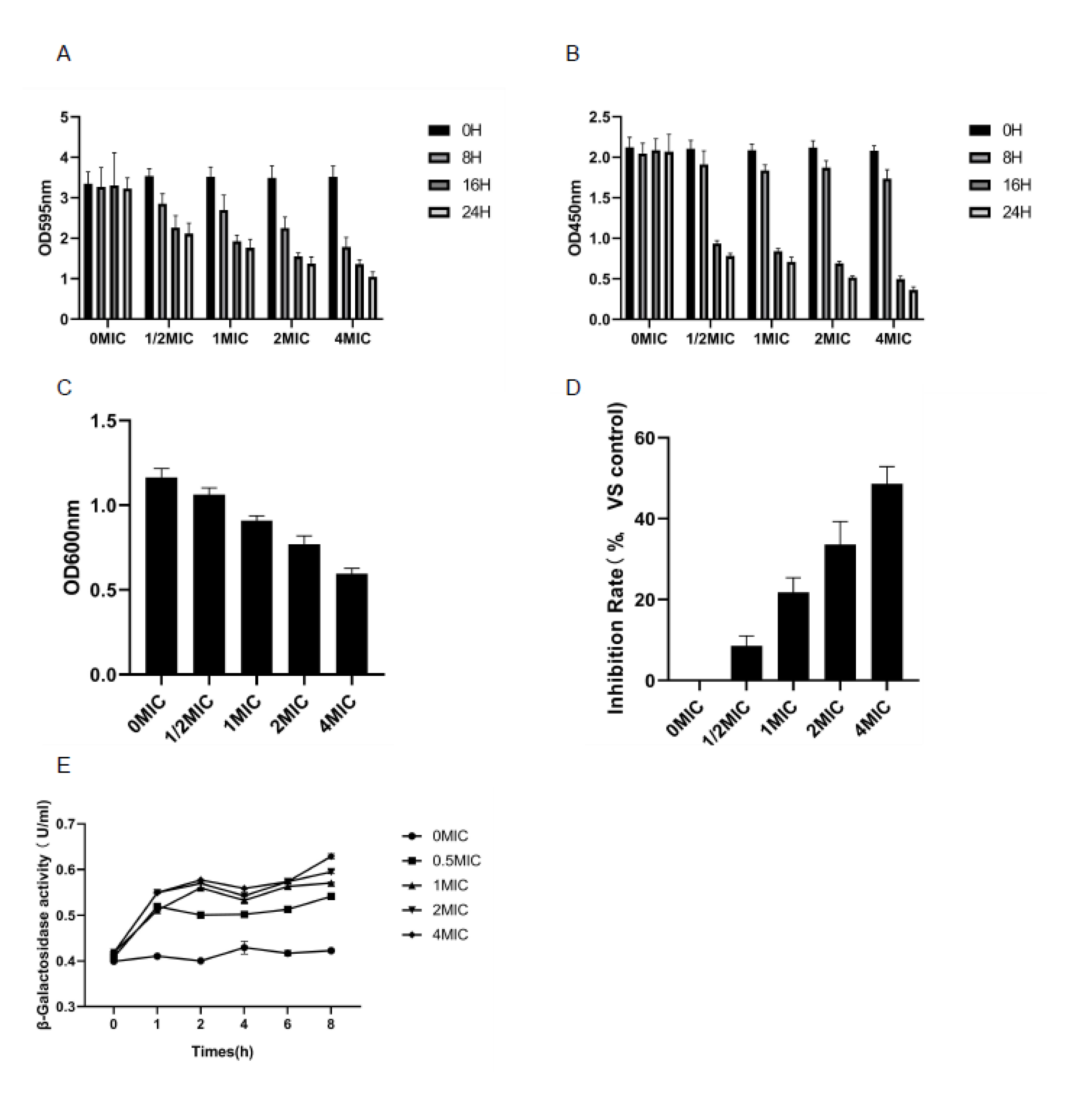
3.4. Biomembrane Biomass Determination and Biomembrane Metabolic Activity Test (XTT Reduction Test)
3.5. Determination of EPS
3.6. Cell Membrane Permeability Test
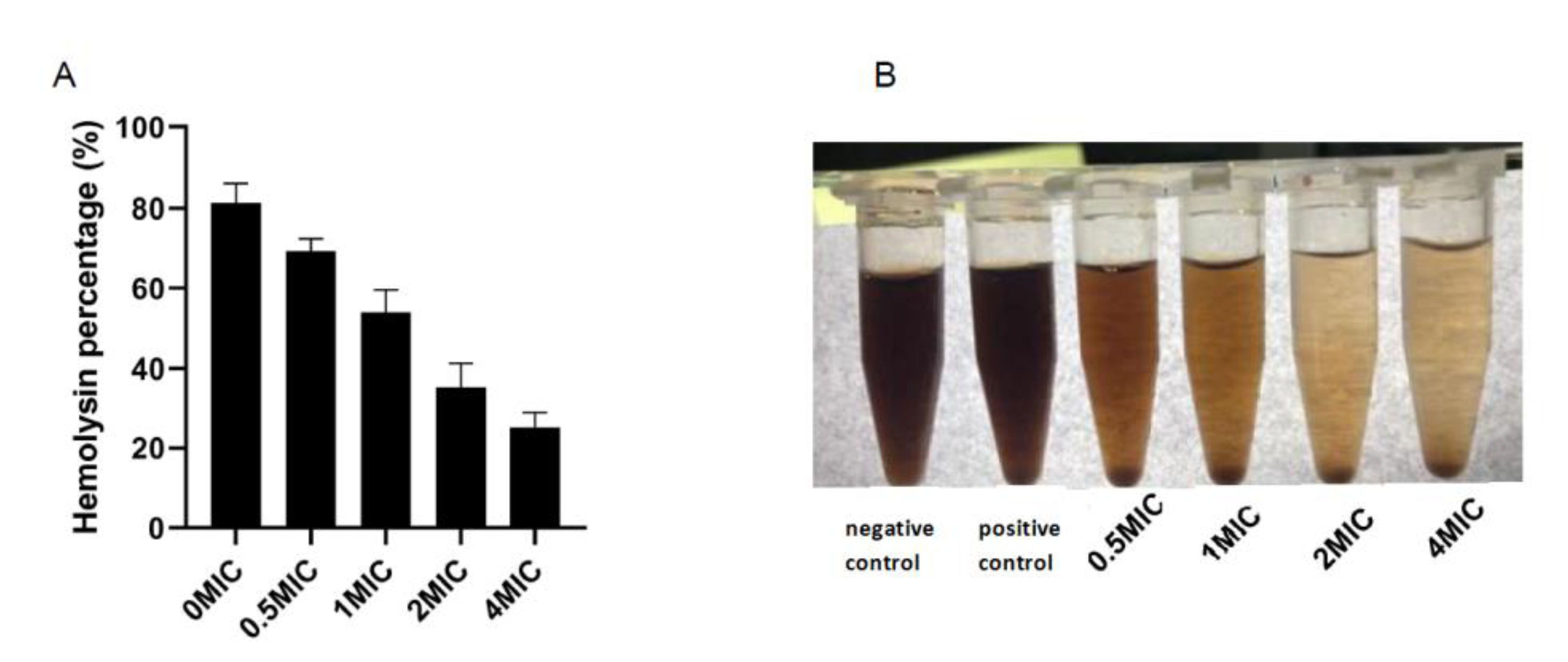
3.7. Hemolysis Test
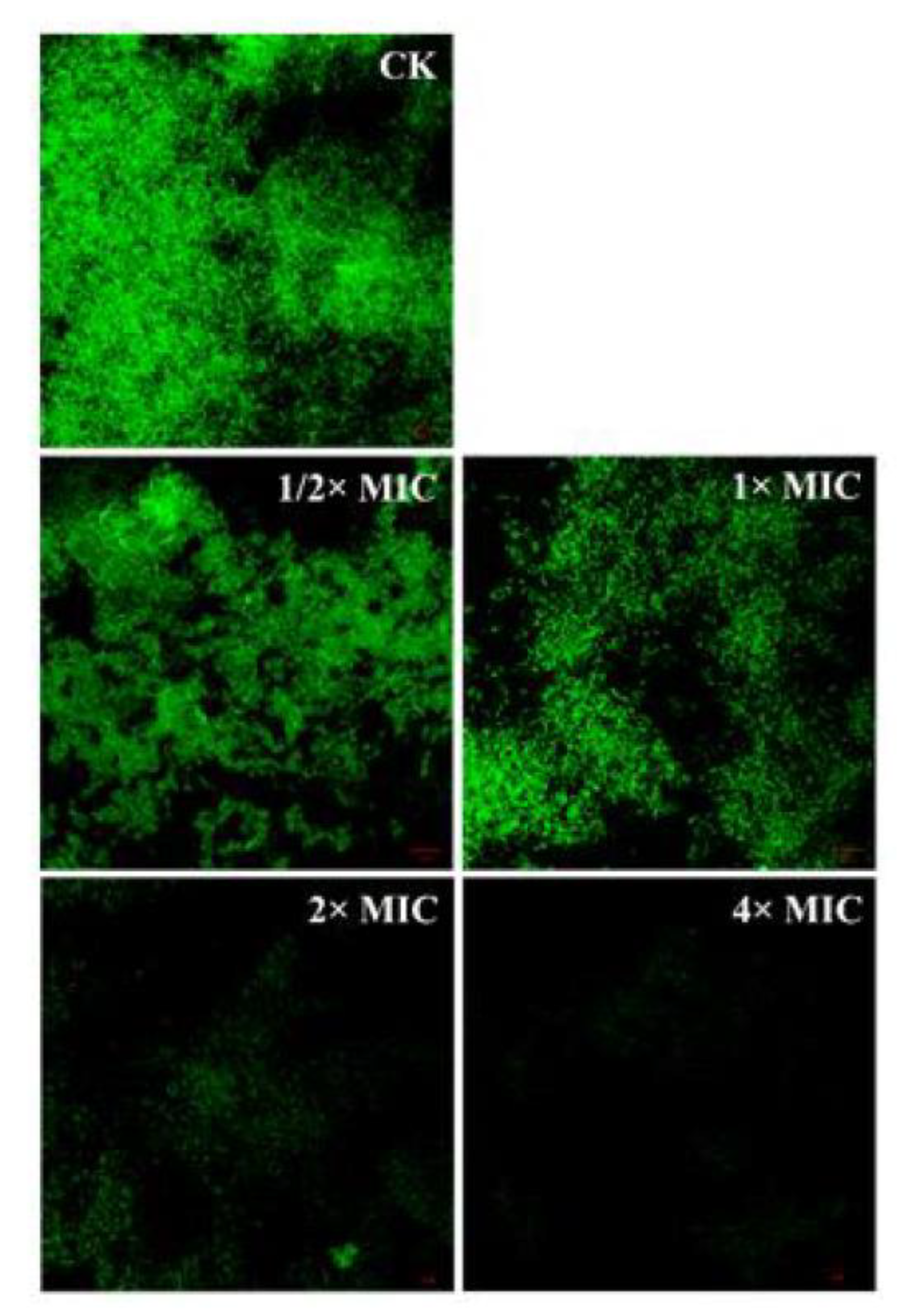
3.8. Detection of Bacterial Structure by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM)
3.9. Observation of Bacterial Structure by TEM
3.10. Anti Quorum Sensing (QS) Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, F.; Xie, J. Effects of verbena oil combined with flaxseed gum on the structure and biochemical characteristics of myo-fibrillar protein in turbot. Food Ferment. Ind. 2020, 46, 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Khalili Tilami, S.; Sampels, S.K. Nutritional Value of Fish: Lipids, Proteins, Vitamins, and Minerals. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018, 26, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.H.; Polreis, J.M.; Tintle, N.L.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Harris, W.S. Association of reported fish intake and supplementation status with the omega-3 index. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2019, 142, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comi, G. Spoilage of Meat and Fish. Microbiol. Qual. Food 2017, 179–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, A.; Barbieri, R.; Coppo, E.; Orhan, I.E.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.F.; Izadi, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Nabavi, S.M.; Ajami, M. Antimicrobi-al activity of eugenol and essential oils containing eugenol: A mechanistic viewpoint. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 668–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, G.; Okpala, C.O.R.; Vitale, S.; Ferrantelli, V.; Noto, A.D.; Costa, A.; Di Bella, C.; Monaco, D.L. Effects of different ozonized slurry-ice treatments and superchilling storage (−1 °C) on microbial spoilage of two important pelagic fish species. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Verdos, G.I.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Boziaris, I.S. The dynamics of Pseudomonas and volatilome during the spoilage of gut-ted sea bream stored at 2 °C. Food Control 2015, 55, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Chaves-Lopez, C.; Serio, A.; Anniballi, F.; Valbonetti, L.; Paparella, A. Effect of Origanum vulgare essential oil on biofilm for-mation and motility capacity of Pseudomonas fluorescens strains isolated from discoloured Mozzarella cheese. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippolis, R.; Rossi, C.; De Angelis, M.; Minervini, F.; Paparella, A.; Chaves-Lopez, C. Adaptive remodelling of blue pigmenting Pseudo-monas fluorescens pf59 proteome in response to different environmental conditions. Food Control 2021, 127, 108105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, B.A.; Noshad, M.; Falah, F. Cumin essential oil: Phytochemical analysis, antimicrobial activity and investigation of its mechanism of action through scanning electron microscopy. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 136, 103716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, T.; Iwano, H.; Hiyashimizu, Y.; Matsubara, K.; Higuchi, H.; Nagahata, H.; Niwa, H.; Katayama, Y.; Kinoshita, Y.; Hagiwara, K.; et al. Phage Therapy Is Effective in a Mouse Model of Bacterial Equine Keratitis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5332–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Fei, P. Multifunctional antibacterial films with silver nanoparticles reduced in situ by lemon juice. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraci, A.; Di Stefano, V.; Di Martino, E.; Schillaci, D.; Schicchi, R. Essential oil components of orange peels and antimicrobial activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosni, K.; Zahed, R.; Chrif, R.; Abid, R.; Medfei, R.; Kallel, R.; Brahim, N.B.; Sebei, R. Composition of peel essential oils from four selected Tunisian Citrus species: Evidence for the genotypic influence. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaś, N.; Myszka, K.; Wolko, L.; Nuc, K.; Szwengiel, A.; Grygier, A.; Majcher, M. Effect of black pepper essential oil on quorum sensing and efflux pump systems in the fish-borne spoiler Pseudomonas psychrophila KM02 identified by RNA-seq, RT-qPCR and molecular docking analyses. Food Control. 2021, 130, 108284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hsouna, A.; Ben Halima, N.; Smaoui, S.; Hamdi, N. Citrus lemon essential oil: Chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities with its preservative effect against Listeria monocytogenes inoculated in minced beef meat. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmandfar, R.; Asnaashari, M.; Pourshayegan, M.; Maghsoudi, S.; Moniri, H. Evaluation of antioxidant properties of lemon verbena (Lippia citriodora) essential oil and its capacity in sunflower oil stabilization during storage time. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, X.S.; Gao, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, L.L.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Shelf-Life Extension of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Using Active Coatings Containing Lemon Verbena (Lippa citriodora Kunth.) Essential Oil. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 678643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Song, X.; Yin, Z.Q.; Jia, R.Y.; Li, Z.W.; Zhou, X.; Zou, Y.F.; Li, L.X.; Yin, L.Z.; Yue, G.; et al. The antibacterial activity and action mechanism of emodin from Polygonum cuspidatum against Haemophilus parasuis in vitro. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 186–187, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Miao, X.; Lin, Z.; Xiu, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, D.; Lin, S.; He, B. Disruption of metabolic function and redox homeostasis as antibacterial mechanism of Lindera glauca fruit essential oil against Shigella flexneri. Food Control. 2021, 130, 108282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Bo, T.; Guo, F.; Cui, J.; Jia, S. Effects of epsilon-Poly-l-lysine on the cell wall of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its involved antimi-crobial mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118 Pt B, 2230–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Sun, L.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Ye, R. Inhibitory effect of glucose oxidase from Bacillus sp. CAMT22370 on the quality deterioration of Pacific white shrimp during cold storage. LWT 2018, 92, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahya, A.; Abrini, J.; Dakka, N.; Bakri, Y. Essential oils of Origanum compactum increase membrane permeability, disturb cell membrane integrity, and suppress quorum-sensing phenotype in bacteria. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Liu, D.; Ashokkumar, M.; Ye, X.; Jin, T.Z.; Guo, M. Antibacterial mechanism of ultrasound against Escherichia coli: Alterations in membrane microstructures and properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandasi, M.; Leonard, C.M.; Viljoen, A.M. The in vitro antibiofilm activity of selected culinary herbs and medicinal plants against Listeria monocytogenes. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 50, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miladi, H.; Mili, D.; Ben Slama, R.; Zouari, S.; Ammar, E.; Bakhrouf, A. Antibiofilm formation and anti-adhesive property of three mediterranean essential oils against a foodborne pathogen Salmonella strain. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 93, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, X.; Lang, Y. Research Progress of Natural Antibacterial Agents in Food Preservation. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 204–207. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Jin, P.; Gong, H.; Sun, Z.; Du, L.; Wang, D. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of thyme oil against foodborne multiple antibi-otics-resistant Enterococcus faecalis. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5127–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Du, L.; Tong, Z.; Ping, Z.; Doyle, M.P. Effects of phenyllactic acid as sanitizing agent for inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes biofilms. Food Control 2017, 78, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, R.; Tiwari, M.; Donelli, G.; Tiwari, V. Strategies for combating bacterial biofilms: A focus on anti-biofilm agents and their mechanisms of action. Virulence 2018, 9, 522–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Jin, P.; Sun, Z.; Du, L.; Wang, D.; Zhao, T.; Doyle, M.P. Carvacrol oil inhibits biofilm formation and exopolysac-charide production of Enterobacter cloacae. Food Control 2021, 119, 107473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colagiorgi, A.; Di Ciccio, P.; Zanardi, E.; Ghidini, S.; Ianieri, A. A Look inside the Listeria monocytogenes Biofilms Extracellular Matrix. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Veras, B.O.; de Oliveira, J.R.S.; de Menezes Lima, V.L.; do Amaral Ferraz Navarro, D.M.; de Aguiar, J.C.R.d.O.F.; de Medeiros Moura, G.M.; da Silva, J.W.; de Assis, C.R.D.; Gorlach-Lira, K.; de Assis, P.A.C.; et al. The essential oil of the leaves of Verbesina macrophylla (Cass.) S.F.Blake has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic activities and is toxicologically safe. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 265, 113248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.F.; Cardoso, M.D.G.; Preté, P.S.C.; Teixeira, M.L.; Nelson, D.L.; Magalhães, M.L.; Ferreira, V.R.F.; Souza, R.V.; Soares, L.I.; Marcussi, S. Essential Oils from Mentha viridis (L). L. and Mentha pulegium L.: Cytogenotoxic Effects on Human Cells. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, K.A.D.F.; Amorim, L.V.; Oliveira, J.M.G.D.; Dias, C.N.; Moraes, D.F.C.; Andrade, E.H.D.A.; Maia, J.G.S.; Carneiro, S.M.P.; Carvalho, F.A.d.A. Eugenia uniflora L. Essential Oil as a Potential Anti-Leishmania Agent: Effects on Leishmania amazonensis and Possible Mechanisms of Action. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 279726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Ma, C.; Lin, L. Synergetic antibacterial efficacy of cold nitrogen plasma and clove oil against Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilms on lettuce. Food Control. 2016, 66, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Preparation of self-assembling Litsea cubeba essential oil/ diphenylalanine peptide micro/nanotubes with enhanced antibacterial properties against Staphylococcus aureus biofilm. LWT 2021, 146, 111394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, A.; Yaron, S. Pore-forming treatments induce aggregation of Salmonella Senftenberg through protein leakage. Food Microbiol. 2020, 96, 103721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inactivation of the SecA2 protein export pathway in Listeria monocytogenes promotes cell aggregation, impacts biofilm architecture and induces biofilm formation in environmental condition. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1176–1192. [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, W.; Wu, M.; Fang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Ye, C.; Xiang, F. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of essential oil from Atractylodes lancea rhizomes. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 153, 112552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.P. The influence of quorum sensing inhibitors against marine functional bacterial biofilm formation. Microbiol. China 2013, 40, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Xie, J. Antibacterial Activity and Antibacterial Mechanism of Lemon Verbena Essential Oil. Molecules 2023, 28, 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073102
Gao X, Liu J, Li B, Xie J. Antibacterial Activity and Antibacterial Mechanism of Lemon Verbena Essential Oil. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073102
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xin, Jinbao Liu, Bo Li, and Jing Xie. 2023. "Antibacterial Activity and Antibacterial Mechanism of Lemon Verbena Essential Oil" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073102
APA StyleGao, X., Liu, J., Li, B., & Xie, J. (2023). Antibacterial Activity and Antibacterial Mechanism of Lemon Verbena Essential Oil. Molecules, 28(7), 3102. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073102






