A Turn-On and Colorimetric Probe Based on Isophorone Skeleton for Detecting Nerve Agent Mimic Diethyl Chlorophosphite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
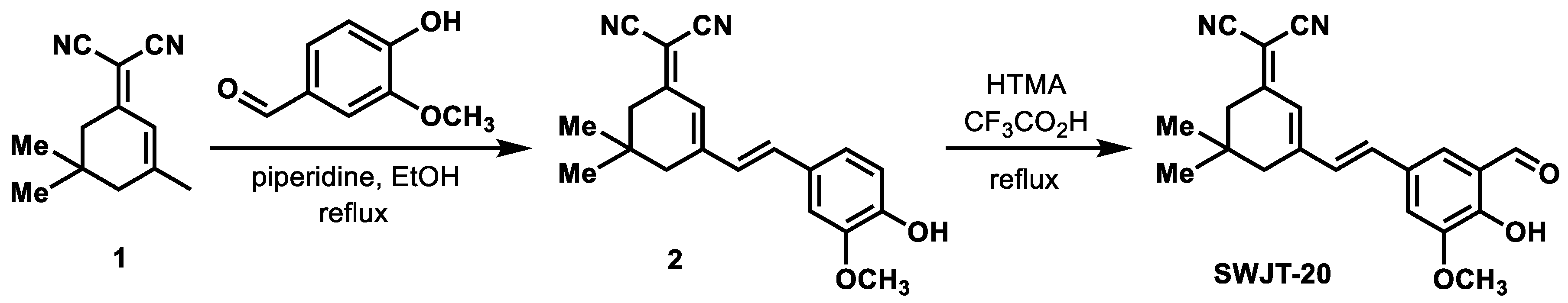
2.1. Design of SWJT-20
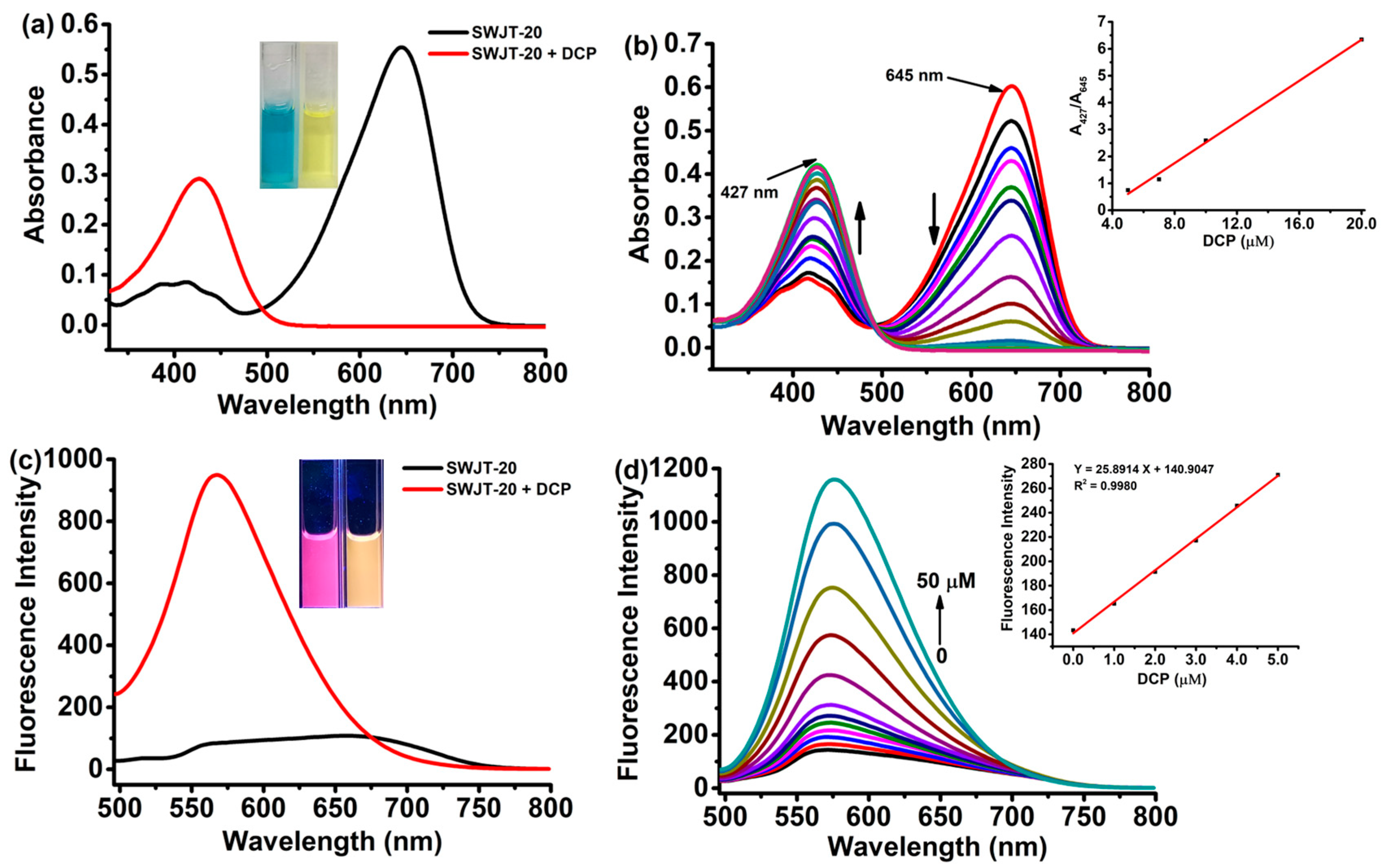
2.2. Spectral Response of SWJT-20 to DCP
2.3. Selective and Competitive Experiment
2.4. Response Mechanism
2.5. DFT Calculations
2.6. Practical Applications
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Measurements
3.3. Synthesis of Probe SWJT-20
3.4. The Preparation of the Test Stock Solution
3.5. Fluorescence Quantum Yield Calculation
3.6. Determination and Calculation of the Lowest Detection Limit
3.7. Response Time Test Method for SWJT-20 to DCP
3.8. The Fabrication of Paper Sensors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Cauwer, H.; Somville, F.J.M.P.; Joillet, M. Neurological aspects of chemical and biological terrorism: Guidelines for neurologists. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2017, 117, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, T.; Hisaoka, H.; Yamada, A.; Ishimatsu, S.; Takasu, N. The Tokyo subway sarin attack-lessons learned. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 197, 171. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, R. How to defeat a nerve agent. Science 2018, 359, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guria, U.N.; Maiti, K.; Ali, S.S.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Samanta, S.K.; Roy, K.; Mandal, D.; Mahapatra, A.K. An organic nanofibrous polymeric composite for ratiometric detection of diethyl chlorophosphate (DCP) in solution and vapor. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 3770–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Yadav, P.; Joshi, B.; Joshi, A.; Kodgire, P. A novel biosensor for the detection of organophosphorus (OP)-based pesticides using organophosphorus acid anhydrolase (OPAA)-FL variant. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, M.; Cao, J.; Yu, H.; Cao, Z.; Jin, M.; Wang, J.; She, Y. Research progress in the immobilization of key enzymes for pesticides residue detection. Biol. Bull. 2022, 38, 258–268. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hou, C.; Lei, J.; Deng, B.; Huang, J.; Yang, M. Detection of organophosphorus pesticides with colorimetry and computer image analysis. Anal. Sci. 2016, 32, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Fan, K.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, F.; Yang, D.; Lu, D.; Feng, J.; Zhao, J.J.; Yang, L.; et al. Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle peroxidase mimetic-based colorimetric assay for the rapid detection of organophosphorus pesticide and nerve agent. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, R.; Astot, C.; Juhlin, L.; Nilsson, C.; Ostin, A. Direct derivatization and rapid GC-MS screening of nerve agent markers in aqueous samples. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 7452–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhu, X.; Gao, R.; Tang, H.; Pei, C.; Wang, H.; Xiao, J. Chemometrics-assisted analysis of chemical impurity profiles of tabun nerve agent using comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1685, 463643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Lin, Y.H.; Wang, J. Microchip capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection for monitoring environmental pollutants. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2006, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Fung, Y. Capillary electrophoresis with immobilized quantum dot fluorescence detection for rapid determination of organophosphorus pesticides in vegetables. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 3107–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.D.; Lin, Y.H. Electrochemical stripping analysis of organophosphate pesticides and nerve agents. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Barry, R.; Petersen, C.; Timchalk, C.; Gassman, P.L.; Lin, Y. Nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase: An exposure biomarker of organophosphate pesticides and nerve agents. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 9951–9959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, F.; Li, Y.; Cai, W. SERS-based ultrasensitive detection of organophosphorus nerve agents via substrate’s surface modification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, J.; Feng, J.; Guo, L.; Xie, J. A simple and sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic discriminative detection of organophosphorous nerve agents. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5091–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Shi, X.; Lin, L.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, X.; Fang, C. Research progress on up-conversion fluorescence probe for detection of perfluorooctanoic acid in water treatment. Polymers 2023, 15, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, W.; Zhu, Z.; Kong, F.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, H.; Li, B. Controllable synthesis of conjugated microporous polymer films for ultrasensitive detection of chemical warfare agents. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, L.; Ghosh, P.; Das, S.; Gharami, S.; Murmu, N.; Mondal, T.K. A selective fluorogenic chemosensor for visual detection of chemical warfare reagent mimic diethylchlorophosphate. J. Photoch. A Photobio. 2020, 388, 112188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, F.; Sun, L.; Wu, S. Handy ratiometric detection of gaseous nerve agents with AIE-fluorophore-based solid test strips. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2016, 4, 10105–10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jang, S.; Ren, W.X.; Bartsch, R.A.; Sohn, H.; Kim, J.S. Imine-functionalized, turn-on fluorophore for DCP. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 153, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, M.; Ahamed, S.; Tohora, N.; Sultana, T.; Ghanta, S.; Das, S.K. A Coumarin151 derived ratiomteric and turn on chemosensor for rapid detection of sarin surrogate. Microchem. J. 2023, 185, 108240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharami, S.; Aich, K.; Das, S.; Patra, L.; Mondal, T.K. Facile detection of organophosphorus nerve agent mimic (DCP) through a new quinoline based ratiometric switch. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 8627–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radic, B.; Berend, S.; Vrdoljak, A.L.; Kukin, D.; Fuchs, N.; Kuca, K. Antidotal efficacy of bispyridinium oximes against nerve agent. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 196, S251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, B.; Rabha, M.; Sheet, S.K.; Koner, D.; Saha, N.; Khatua, S. Bis-heteroleptic Ru (II) polypyridine complex-based luminescent probes for nerve agent simulant and organophosphate pesticide. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Pramanik, A.K.; Guria, U.N.; Samanta, S.K.; Mahapatra, A.K. Ratiometric sensing of nerve agent mimic DCP through in situ benzisoxazole formation. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 170, 107585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zong, L.; Li, D.; Sui, S.; Xiao, Y.; Zhuang, B.; Shen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wu, W. A salicylaldoximate-based AIE probe for the detection of the nerve agent simulant DCP. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 4025–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Maiti, K.; Mondal, S.; Pramanik, A.K.; Guria, U.N.; Uddin, M.R.; Mandal, S.; Mandal, D.; Mahapatra, A.K. A chromogenic and ratiometric fluorogenic probe for rapid detection of a nerve agent simulant DCP based on a hybrid hydroxynaphthalene-hemicyanine dye. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 15, 5959–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.K.; Mishra, T.; Guria, S.; Das, D.; Sadhukhan, J.; Sarker, S.; Dutta, K.; Adhikary, A.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Adhikari, S.S. Fluorometric detection of a chemical warfare agent mimic (DCP) using a simple hydroxybenzothiazole-diaminomaleonitrile based chemodosimeter. New J. Chem. 2022, 47, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Fu, Y.; Xu, W.; Fan, T.; Gao, Y.; He, Q.; Zhu, D.; Cao, H.; Cheng, J. Concise and efficient fluorescent probe via an intromolecular charge transfer for the chemical warfare agent mimic diethylchlorophosphate vapor detection. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2497–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.J.; Wang, Y.W.; Senge, M.O.; Peng, Y. Sensitive fluorescence on-off probes for the fast detection of a chemical warfare agent mimic. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.J.; Murale, D.P.; Churchill, D.G. Novel reversible and selective nerve agent simulant detection in conjunction with superoxide “turn-on” probing. Analyst 2014, 139, 1614–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Cui, Z.; Liu, H.; Cao, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, M. Ultrafast-response, highly-sensitive and recyclable colorimetric/fluorometric dual-channel chemical warfare agent probes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Liu, A.; Peng, X.; He, Q.; Cao, H.; Cheng, J. Simple and efficient chromophoric-fluorogenic probes for diethylchlorophosphate vapor. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, W.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhao, C. Chromo-fluorogenic detection of soman and its simulant by thiourea-based rhodamine probe. Molecules 2019, 24, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, B.; Du, M.; Shen, A.; Li, M.; Lai, Y.; Bai, X.; Gong, A.; Yang, Y. "Covalent-assembly"-based fluorescent probe for detection of a nerve-agent mimic (DCP) via Lossen rearrangement. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10979–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, G.; Manivannan, R.; Kim, H.; Son, Y.-A. Liquid and gaseous state visual detection of chemical warfare agent mimic DCP by optical sensor. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 171, 107712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zeng, H.; Chen, T.; Yuan, H.-Q.; Zeng, L.; Bao, G.-M. Fast and visual detection of a chemical warfare agent mimic using a simple, effective and portable chemodosimeter. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 319, 128282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, C.X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Peng, Y. A double-Site chemodosimeter for selective fluorescence detection of a nerve agent mimic. Molecules 2022, 27, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Pramanik, A.K.; Samanta, S.K.; Guria, U.N.; Manna, S.; Mahapatra, A.K. Real time detection of the nerve agent simulant diethylchlorophosphate by nonfluorophoric small molecules generating a cyclization-induced fluorogenic response. Analyst 2018, 143, 4171–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Das, S.; Aich, K. Fluorescent chemodosimeter based on spirobenzopyran for organophosphorus nerve agent mimics (DCP). RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 28996–29001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Peng, C.; Liu, G.; Cheng, T. A naphthalimide-based fluorescent probe for the highly sensitive and selective detection of nerve agent mimic DCP in solution and vapor phase. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 10713–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, T.; Mahato, M.; Tohora, N.; Ahamed, S.; Pramanik, P.; Ghanta, S.; Kumar Das, S. A phthalimide-based turn on fluorosensor for selective and rapid detection of G-series nerve agent’s mimics. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 439, 114584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; He, L.; Liu, R.; Jiang, H.; Han, X.; Zhang, K. Visual and rapid detection of nerve agent mimics in gas and solution phase by a simple fluorescent probe. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 4390–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, W.; Peng, Y. Development of BINOL-Si complexes with large stokes shifts and their application as chemodosimeters for nerve agent. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2960–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Yu, X.S.; Li, X.J.; Liu, H.B.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.W.; Peng, Y. A Rapid near-infrared fluorescent probe for cysteine based on isophorone and its application in B16 Cell imaging. J. Fluoresc. 2022, 32, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.-A.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, B.-J.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.-W.; Peng, Y. Ratiometric detection and bioimaging of endogenous alkaline phosphatase by a NIR fluorescence probe. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 358, 131505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Xue, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wen, T.B. Visual and fluorogenic detection of a nerve agent simulant via a Lossen rearrangement of rhodamine-hydroxamate. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 8413–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-I.; Maity, S.B.; Bouffard, J.; Kim, Y. Molecular rotors for the detection of chemical warfare agent simulants. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9259–9263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Xiao, S.Y.; Gong, X.L.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.W.; Peng, Y. Near-infrared fluorescent probe for recognition of hypochlorite anions based on dicyanoisophorone skeleton. Molecules 2023, 28, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimblat, N.; Sarotti, A.M.; Kaufman, T.S.; Simonetti, S.O. A theoretical study of the Duff reaction: Insights into its selectivity. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 10496–10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Suo, S.N.; Wang, Y.W.; Peng, Y.A. A red-NIR fluorescent probe for rapid and visual detection of acrolein. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 10080–10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Mu, A.U.; Lin, Y.-H.; Guo, Z.-H.; Yuan, T.; Wheeler, S.E.; Fang, L. Molecular coplanarity and self-assembly promoted by intramolecular hydrogen bonds. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 6332–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochazkova, E.; Cechova, L.; Tarabek, J.; Janeba, Z.; Dracinsky, M. Tunable push-pull interactions in 5-nitrosopyrimidines. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 3780–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Xia, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Guo, J.; Cui, H.; Kafuti, Y.S.; Wang, J.; Peng, X. Rationally modifying the dicyanoisophorone fluorophore for sensing cysteine in living cells and mice. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wu, S.A.; Lin, N.J.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.W.; Peng, Y. A NIR fluorescent probe based on C=N isomerization for fast detection of toxic acrolein. Sens. Actuators B 2022, 371, 132547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.-S.; Zhu, M.-M.; Zuo, R.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.-W. A Turn-On and Colorimetric Probe Based on Isophorone Skeleton for Detecting Nerve Agent Mimic Diethyl Chlorophosphite. Molecules 2023, 28, 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073237
Yu X-S, Zhu M-M, Zuo R, Peng Y, Wang Y-W. A Turn-On and Colorimetric Probe Based on Isophorone Skeleton for Detecting Nerve Agent Mimic Diethyl Chlorophosphite. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073237
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xue-Shuang, Mao-Mei Zhu, Rui Zuo, Yu Peng, and Ya-Wen Wang. 2023. "A Turn-On and Colorimetric Probe Based on Isophorone Skeleton for Detecting Nerve Agent Mimic Diethyl Chlorophosphite" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073237
APA StyleYu, X.-S., Zhu, M.-M., Zuo, R., Peng, Y., & Wang, Y.-W. (2023). A Turn-On and Colorimetric Probe Based on Isophorone Skeleton for Detecting Nerve Agent Mimic Diethyl Chlorophosphite. Molecules, 28(7), 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073237







