Unsaturated Fatty Acids Complex Regulates Inflammatory Cytokine Production through the Hyaluronic Acid Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Endogenous Cytotoxicity of the EUFOC
2.2. Evaluation of the Antioxidant Property of the EUFOC
2.2.1. Analysis of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl-Scavenging Ability of the EUFOC
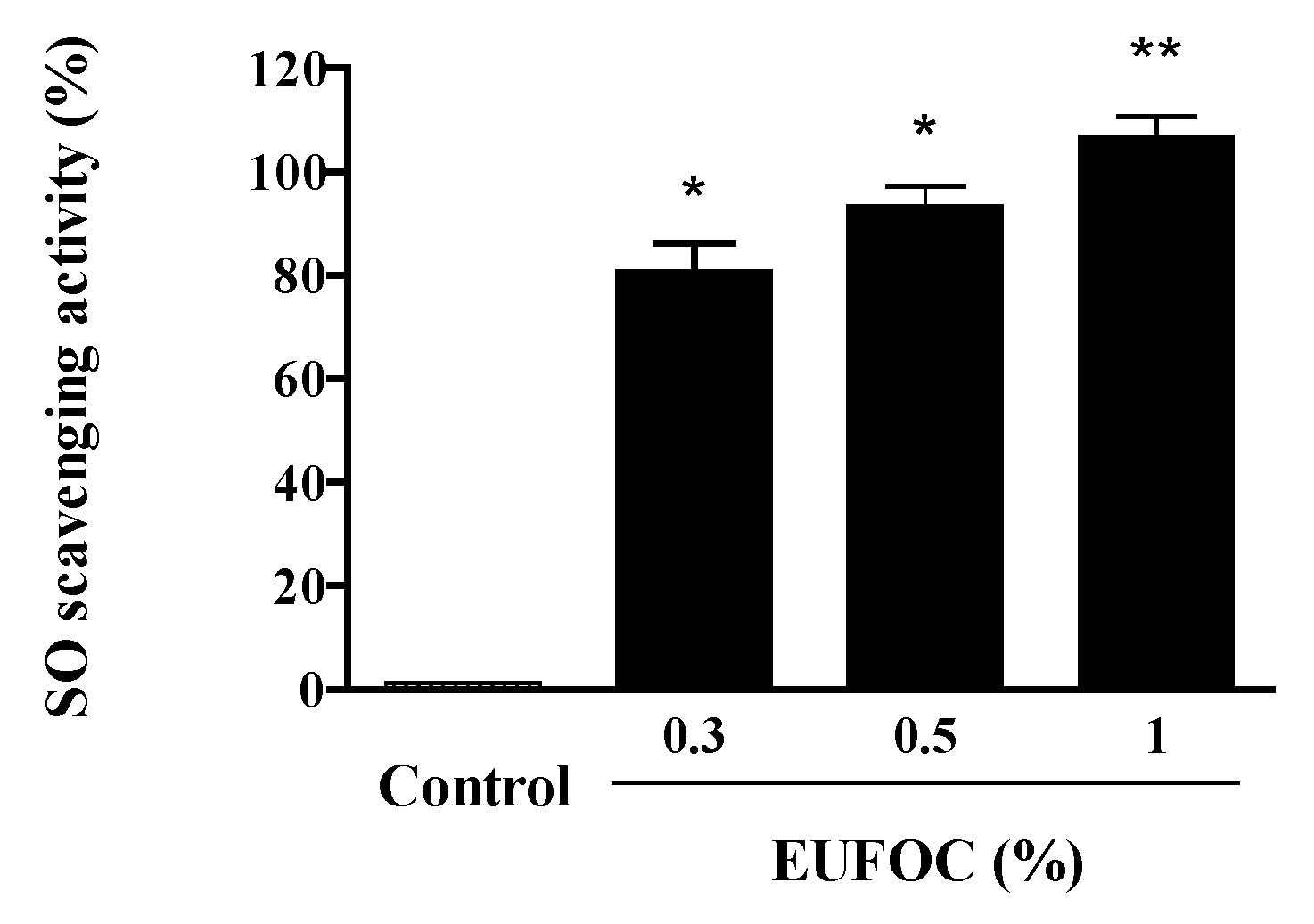
2.2.2. Analysis of Superoxide-Scavenging Ability of the EUFOC
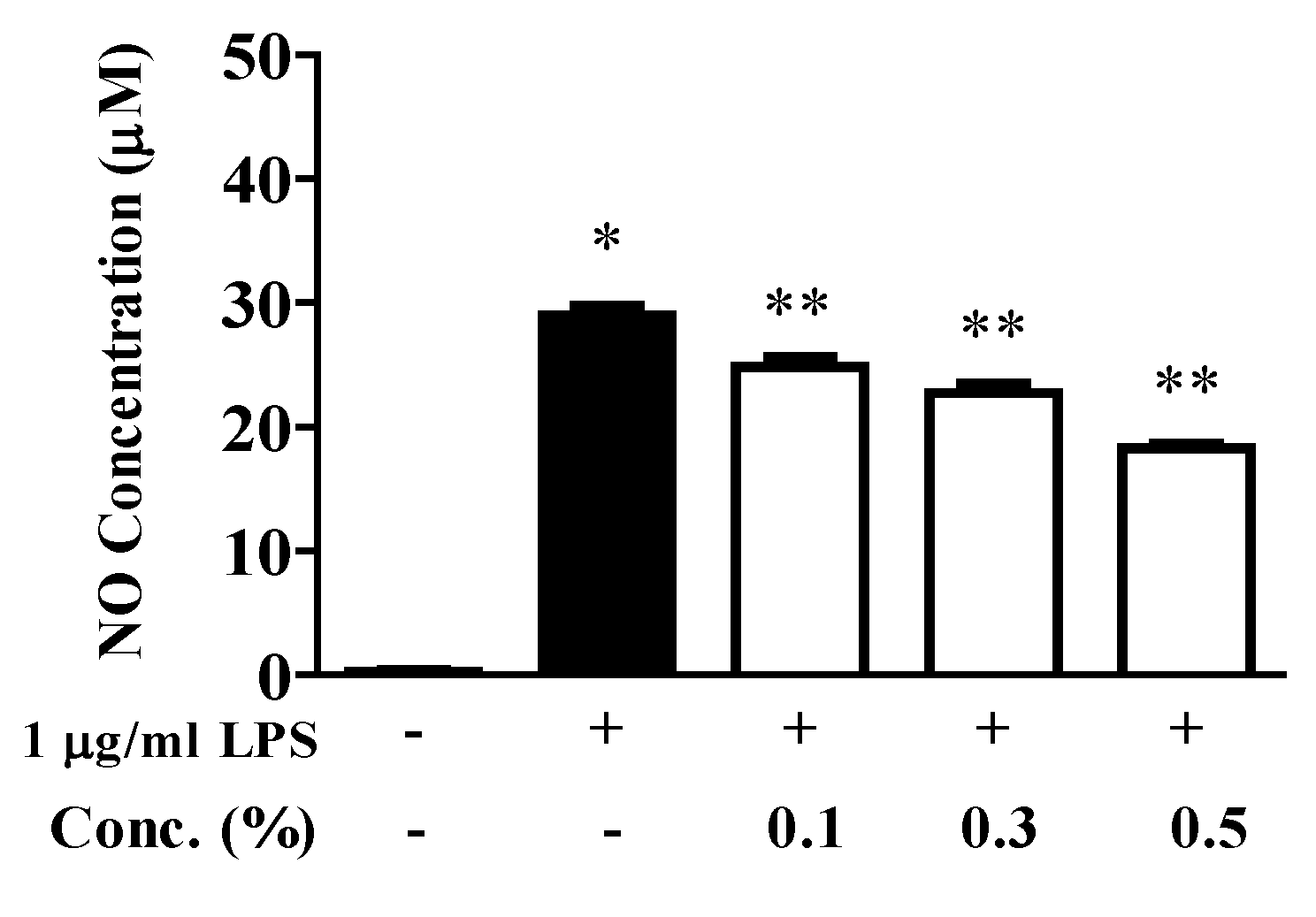
2.3. Inhibition of NO Production
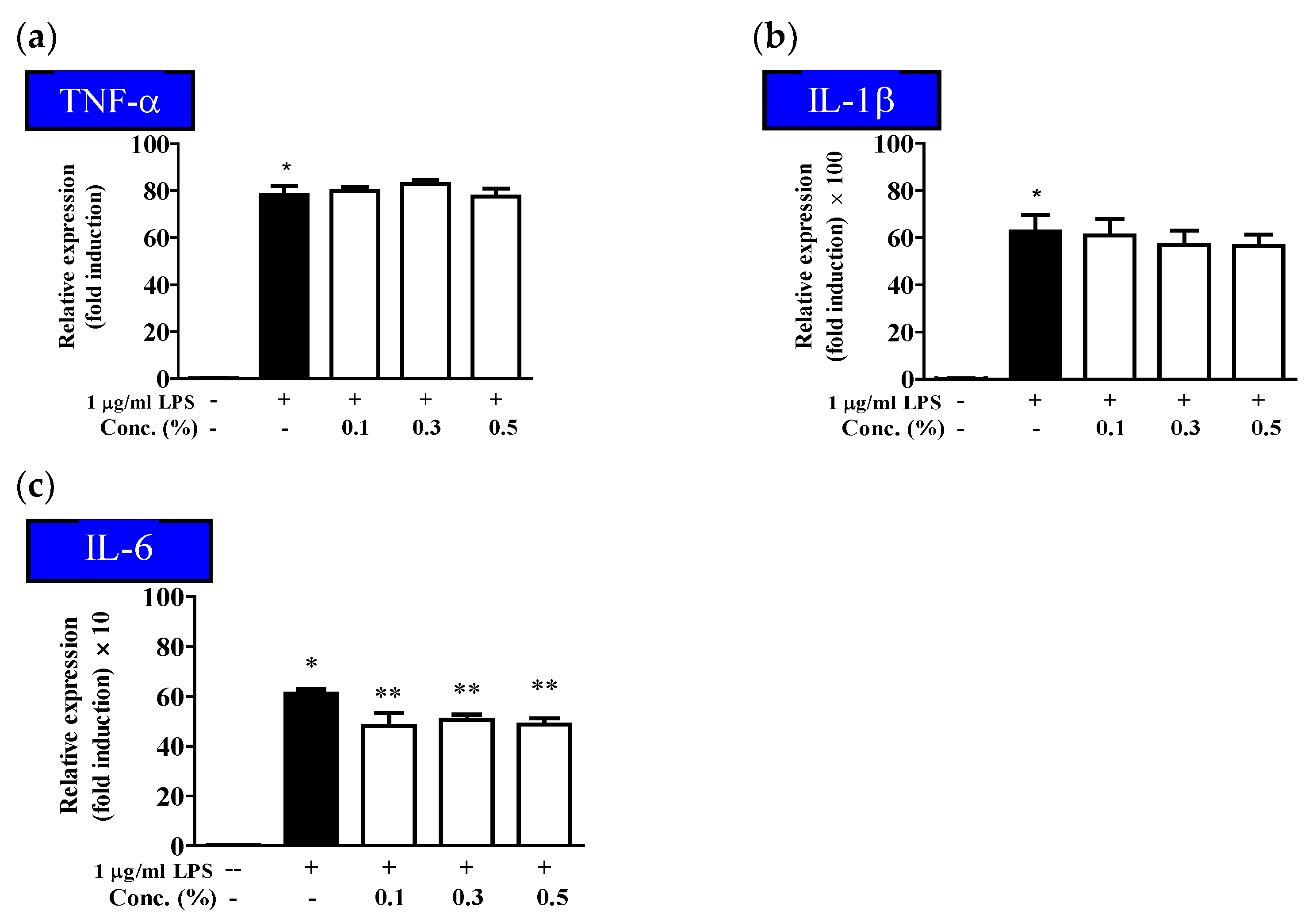
2.4. Inhibitory Effect of the EUFOC on the Production of Inflammatory Cytokines
2.5. Inhibitory Effect of the EUFOC on COX-2 and iNOS Expression
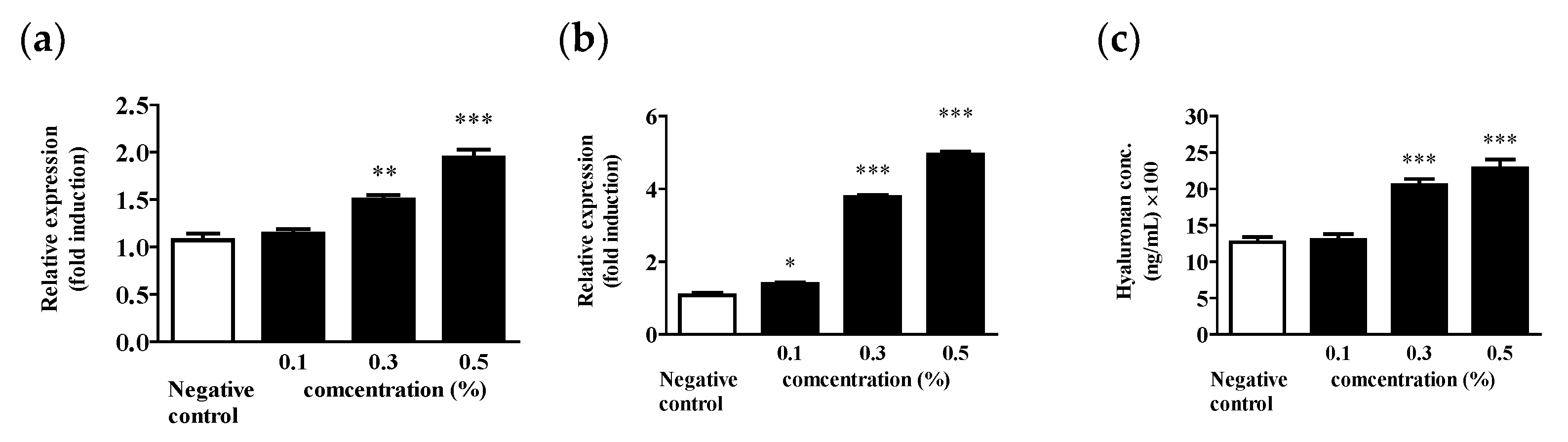
2.6. HA Promotes Intracellular Synthesis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Composition of EUFOC
3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. Antioxidant Assessment
3.4.1. Analysis of DPPH-Scavenging Ability
3.4.2. Analysis of SO-Scavenging Ability
3.5. Cell Viability Measurement Using MTT Assay
3.6. Identification of Inflammatory Genes Using RT-PCR
3.7. Inhibition of NO Production
3.8. ELISA Test
3.9. Quantative PCR
3.10. Promotion of HA Production
3.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Passeron, T.; Krutmann, J.; Andersen, M.L.; Katta, R.; Zouboulis, C.C. Clinical and biological impact of the exposome on the skin. J. Eur. Acad. Derm. Venereol. 2020, 34, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jia, Y.; Sun, Z.; Su, J.; Liu, Q.S.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, G. Environmental pollution, a hidden culprit for health issues. Eco-Environ. Health 2022, 1, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadeghrad, A.M. Factors Influencing Healthcare Service Quality. Int. J. Health Policy Manag. 2014, 3, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Supuran, C.T. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A. Natural products chemistry: The emerging trends and prospective goals. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-R.; Kim, K.-Y. Rumex crispus Ethanol Extract in Fibroblasts: Evaluation of Anti-oxidant Efficacy and Effect on Collagen Synthesis Stimulation and Degradation Inhibition. J. Invest. Cosmetol. 2017, 13, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Lou, G.-H.; Zeng, H.-R.; Hu, J.; Huang, Q.-W.; Peng, W.; Yang, X.-B. Coptidis Rhizoma: A comprehensive review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Pharm. Biol. 2019, 57, 193–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekor, M. The growing use of herbal medicines: Issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front. Pharm. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tottoli, E.M.; Dorati, R.; Genta, I.; Chiesa, E.; Pisani, S.; Conti, B. Skin Wound Healing Process and New Emerging Technologies for Skin Wound Care and Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Barbosa, A.I.; Rebelo, R.; Kwon, I.K.; Reis, R.L.; Correlo, V.M. Skin-Integrated Wearable Systems and Implantable Biosensors: A Comprehensive Review. Biosensors 2020, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, D. Cross-Cultural Perspectives on the Medicalization of Human Suffering. In Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Issues and Controversies; Rosen, G.M., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-J.; Lin, S.; Kang, H.-F.; Dai, Z.-J.; Bai, M.-H.; Ma, X.-L.; Ma, X.-B.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.-X.; Wang, B.-F. The effect of Rhizoma coptidis and Coptis chinensis aqueous extract on radiation-induced skin injury in a rat model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolarsick, P.A.J.; Kolarsick, M.A.; Goodwin, C. Anatomy and Physiology of the Skin. J. Derm. Nurses Assoc. 2011, 3, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Shalova, I.N.; Biswas, S.K. Metabolic regulation of macrophage phenotype and function. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 280, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktan, F. iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production and its regulation. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, S.R. Anti-inflammatory activities of Scolopendra subspinipes mutilans in RAW 264.7 cells. J. Nutr. Health 2018, 51, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuehr, D.J.; Cho, H.J.; Kwon, N.S.; Weise, M.F.; Nathan, C.F. Purification and characterization of the cytokine-induced macrophage nitric oxide synthase: An FAD- and FMN-containing flavoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7773–7777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouassi, M.-C.; Grisel, M.; Gore, E. Multifunctional active ingredient-based delivery systems for skincare formulations: A review. Colloids Surf. B 2022, 217, 112676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumała, P.; Jungnickel, C.; Kozłowska-Tylingo, K.; Jacyna, B.; Cal, K. Transdermal transport of collagen and hyaluronic acid using water in oil microemulsion. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 572, 118738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.; Rooney, P.; Kumar, S.; Pye, D.; West, D.C.; Scott, I.; Ledger, P. Application of Angiogenic Oligosaccharides of Hyaluronan Increases Blood Vessel Numbers in Rat Skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1994, 103, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L.; Brauner, P.; Kolar, J. Hyaluronic acid (hyaluronan): A review. Vet. Med. 2008, 53, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-S.; Ha, H.-Y.; Kim, H.-T. An Experimental Study on the Effect of Angelica acutiloba Ethanol Extract on Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis. J. Korean Med. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. Derm. 2015, 28, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Seo, J.-Y.; Shin, J.-U.; Jeong, D.-H.; Kim, J.-D.; Lee, K.-H. Efficacy of biodegradable microneedle patches on periorbital wrinkles. Korean J. Dermatol. 2014, 52, 597–607. [Google Scholar]
- Park, B.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, H.S.; Min, K.S.; Park, K.; Park, N.C.; Lee, S.W.; Chung, W.S.; et al. Evaluation of Complementary and Alternative Medicine for Treating Patients with Erectile Dysfunction. Korean J. Urol. 2006, 47, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; He, C.; Xiao, P. Genus Paeonia: A comprehensive review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, clinical application, and toxicology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 269, 113708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawid-Pać, R. Medicinal plants used in treatment of inflammatory skin diseases. Postep. Derm. Alergol. 2013, 3, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenova, N.; Tsigoriyna, L.; Arsov, A.; Petrov, K.; Petrova, P. Microbial Detoxification of Residual Pesticides in Fermented Foods: Current Status and Prospects. Foods 2023, 12, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Song, M.-J. Analysis and recordings of orally transmitted knowledge about medicinal plants in the southern mountainous region of Korea. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 676–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.-Y.; Koo, B.-S.; Kim, S.-Y. Pharmacological Activities for Morus alba L., Focusing on the Immunostimulatory Property from the Fruit Aqueous Extract. Foods 2021, 10, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avula, B.; Joshi, V.; Niranjan Reddy, V.L.; Choi, Y.-W.; Khan, I. Simultaneous Determination of Eight Coumarins in Angelica gigas and in Various Other Angelica Species by High Performance Liquid Chromatography and Comparative Micro-Morphology Study of Angelica Species. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-C.; Lee, G.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Chung, W.-S.; Kim, S.-S.; Ko, S.-G.; Um, J.-Y. Immune-enhancing effect of Danggwibohyeoltang, an extract from Astragali Radix and Angelicae gigantis Radix, in vitro and in vivo. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2011, 34, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.-S.; Shaheen, H.M.; Elhawary, E.A.; Mostafa, N.M.; Eldahshan, O.A.; Sabatier, J.-M. Phytochemical Constituents, Folk Medicinal Uses, and Biological Activities of Genus Angelica: A Review. Molecules 2022, 28, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cock, I.E. The safe usage of herbal medicines: Counterindications, cross-reactivity and toxicity. Pharm. Commn. 2014, 5, 2–50. [Google Scholar]
- Miwa, T. Study on gardenia florida L. (fructus gardeniae) as a remedy for icterus. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1955, 4, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; An, C.; Hwang, S.D.; Kim, Y.S. Ceriporia lacerata Mycelium Culture Medium as a Novel Anti-Aging Microbial Material for Cosmeceutical Application. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.-S.; Lee, M.-J.; Park, C.-B.; Bang, I.S. Study on the Antioxidative and Physiological Activities of Saururus chinensis Extract. J. Life Sci. 2012, 22, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, B.; Parihar, N.; Ilaweibaphyrnai, M.; Panda, S.R.; Alexander, A.; Chella, N.; Murty, U.; Naidu, V.; Kumar, G.J.; et al. Nutraceutical prospects of Houttuynia cordata against the infectious viruses. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 101977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Cho, M.; Kim, D.-B.; Shin, G.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Park, S.-O.; Lee, S.-J.; Shin, H.; Lee, O.-H. The Antioxidant Activity and Their Major Antioxidant Compounds from Acanthopanax senticosus and A. koreanum. Molecules 2015, 20, 13281–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, C.; Windsor, R.C. An Evidence-Based Systematic Review of Black cohosh (Cimicifuga racemosa, Actaea racemosa) by the Natural Standard Research Collaboration. J. Diet. Suppl. 2014, 12, 265–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-S.; Park, K.-S.; Kim, H.-W.; Hwang, K.-E.; Song, D.-H.; Choi, M.-S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Paik, H.-D.; Kim, C.-J. Quality characteristics of reduced-fat frankfurters with pork fat replaced by sunflower seed oils and dietary fiber extracted from makgeolli lees. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhyani, A.; Chopra, R.; Garg, M. A Review on Nutritional Value, Functional Properties and Pharmacological Application of Perilla (Perilla Frutescens L.). Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2019, 12, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthäus, B.; Özcan, M.M. Fatty acids and tocopherol contents of some prunus spp. kernel oils. J. Food Lipids 2009, 16, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Lee, J.-H. Biofilm modeling systems. Korean J. Microbiol. 2016, 52, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A. Microtiter Dish Biofilm Formation Assay. J. Vis. Exp. Jove-J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 47, 2437. [Google Scholar]
- Dröge, W. Free Radicals in the Physiological Control of Cell Function. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 47–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Tak, H.M.; Kang, M.J.; Sung, N.J. Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Functional Plant Materials. J. Life Sci. 2013, 23, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodovici, M.; Guglielmi, F.; Meoni, M.; Dolara, P. Effect of natural phenolic acids on DNA oxidation in vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2001, 39, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atreya, R.; Neurath, M.F. Involvement of IL-6 in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colon Cancer. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 28, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.W.; Whisnant, R.; Nathan, C. Promoter of the mouse gene encoding calcium-independent nitric oxide synthase confers inducibility by interferon gamma and bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebovic, D.I.; Bentzien, F.; Chao, V.A.; Garrett, E.N.; Meng, Y.G.; Taylor, R.N. Induction of an angiogenic phenotype in endometriotic stromal cell cultures by interleukin-1. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2000, 6, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Yoo, H.; Yang, J.-H.; Kim, T.-Y. Homoisoflavanone inhibits UVB-induced skin inflammation through reduced cyclooxygenase-2 expression and NF-κB nuclear localization. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 59, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masferrer, J.L.; Zweifel, B.S.; Manning, P.T.; Hauser, S.D.; Leahy, K.M.; Smith, W.G.; Isakson, P.C.; Seibert, K. Selective inhibition of inducible cyclooxygenase 2 in vivo is antiinflammatory and nonulcerogenic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3228–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibert, K.; Zhang, Y.; Leahy, K.; Hauser, S.; Masferrer, J.; Perkins, W.; Lee, L.; Isakson, P. Pharmacological and biochemical demonstration of the role of cyclooxygenase 2 in inflammation and pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12013–12017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean, Y.-H.; Chen, W.-F.; Duh, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Hsu, C.-H.; Lin, C.-S.; Sung, C.-S.; Chen, I.-M.; Wen, Z.-H. Inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 participate in anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of the natural marine compound lemnalol from Formosan soft coral Lemnalia cervicorni. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 578, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xiong, H. Regulation of iNOS on Immune Cells and Its Role in Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango Duque, G.; Descoteaux, A. Macrophage Cytokines: Involvement in Immunity and Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, P.C.; Schroeder, R.A. The Emerging Multifaceted Roles of Nitric Oxide. Ann. Surg. 1995, 221, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Jang, S.; An, J.E.; Choo, B.K.; Kim, H.K.I. Inflexus (Thunb.) Kudo extract improves atopic dermatitis and depressive-like behavior in DfE-induced atopic dermatitis-like disease. Phytomedicine 2020, 67, 153137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Hanamizu, T.; Iizuka, R.; Chiba, K. Genistein and Daidzein Stimulate Hyaluronic Acid Production in Transformed Human Keratinocyte Culture and Hairless Mouse Skin. Ski. Pharm. Physiol. 2002, 15, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderegg, U.; Simon, J.C.; Averbeck, M. More than just a filler–the role of hyaluronan for skin homeostasis. Exp. Derm. 2014, 23, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.; Maibach, H.I. Hyaluronan in skin: Aspects of aging and its pharmacologic modulation. Clin. Derm. 2008, 26, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itano, N.; Kimata, K. Molecular Cloning of Human Hyaluronan Synthase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 222, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kang, B.Y.; Cho, S.Y.; Sung, D.S.; Chang, H.K.; Yeom, M.H.; Kim, D.H.; Sim, Y.C.; Lee, Y.S. Compound K induces expression of hyaluronan synthase 2 gene in transformed human keratinocytes and increases hyaluronan in hairless mouse skin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 316, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.-J.; Jin, M.-H.; Lee, S.-H. Effect of Ferulic Acid Isolated from Cnidium Officinale on the Synthesis of Hyaluronic Acid. J. Soc. Cosmet. Sci. Korea 2013, 39, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.-K.; Lee, S.-J.; Ha, H.-Y. Skin Moisturizing Effects of a Microneedle Patch Containing Hyaluronic Acid and Lonicerae flos. Processes 2021, 9, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-H.; Park, D.-R.; Kim, Y.-W.; Nam, T.-S.; Jang, K.Y.; Chung, H.T.; Kim, U.-H. The Essential Role of Ca2+ Signals in UVB–Induced IL-1β Secretion in Keratinocytes. J. Invest. Derm. 2019, 139, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, N.-Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, K.-B.-W.-R.; Park, J.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Sung, N.-Y.; Byun, E.-H.; Ahn, D.-H. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Chondrus ocellatus Holmes Ethanol Extract on Lipopolysaccharide-induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW 264.7 Cells. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 44, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.-H.; Kim, H.-O.; Jeong, J.-H.; Min, Y.; Park, K.-H.; Si, C.; Choi, S.-E. Ulmus davidiana var. japonica Extracts Suppress Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Apoptosis Through Intracellular Calcium Modulation in U937 Macrophages. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 820330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X. Effects of taraxasterol on iNOS and COX-2 expression in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisse, J.; Bourguignon, V.; De Vuyst, E.; Lambert de Rouvroit, C.; Nikkels, A.F.; Flamion, B.; Poumay, Y. Hyaluronan Metabolism in Human Keratinocytes and Atopic Dermatitis Skin Is Driven by a Balance of Hyaluronan Synthases 1 and 3. J. Invest. Derm. 2014, 134, 2174–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| NCI | CAS No | Contents (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Helianthus annuus seed oil | 8001-21-6 | Add to 100% |
| Perilla frutrscens oil | 68132-21-8 | 20% |
| Prunus armeniaca oil | 72869-69-3 | 3% |
| Paeonia lactiflora extract | 7732-18-5 | 1% |
| Cimicifuga racemosa root extract | 84776-26-1 | 1% |
| Gardenia jasminoides fruit extract | 92457-01-7 | 1% |
| Morus mongolica (Bureau) C. K. schneid extract | 94167-05-2 | 0.8% |
| Houttuynia cordata extract | 164288-50-0 | 0.8% |
| Saururus chinensis extract | 91770-72-8 | 0.8% |
| Angelica gigas root extract | 84775-41-7 | 0.8% |
| Centella Asiatica extract | 84776-24-9 | 0.5% |
| Polygala tenuifolia root extract | 94167-09-6 | 0.5% |
| Sophora flavescens extract | 519-02-8 | 0.5% |
| Acanthopanax cordata extract | 39432-56-9 | 0.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.-B.; Seo, K.; Youn, J.-U.; Kwon, I.K.; Park, J.; Park, K.-H.; Kim, J.-S. Unsaturated Fatty Acids Complex Regulates Inflammatory Cytokine Production through the Hyaluronic Acid Pathway. Molecules 2023, 28, 3554. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083554
Kim G-B, Seo K, Youn J-U, Kwon IK, Park J, Park K-H, Kim J-S. Unsaturated Fatty Acids Complex Regulates Inflammatory Cytokine Production through the Hyaluronic Acid Pathway. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3554. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083554
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Gi-Beum, Kwansung Seo, Jong-Ung Youn, Il Keun Kwon, Jinny Park, Kwang-Hyun Park, and Jong-Suk Kim. 2023. "Unsaturated Fatty Acids Complex Regulates Inflammatory Cytokine Production through the Hyaluronic Acid Pathway" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3554. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083554
APA StyleKim, G.-B., Seo, K., Youn, J.-U., Kwon, I. K., Park, J., Park, K.-H., & Kim, J.-S. (2023). Unsaturated Fatty Acids Complex Regulates Inflammatory Cytokine Production through the Hyaluronic Acid Pathway. Molecules, 28(8), 3554. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083554






