A Potential Lead for Insect Growth Regulator: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity Evaluation of Novel Hexacyclic Pyrazolamide Derivatives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
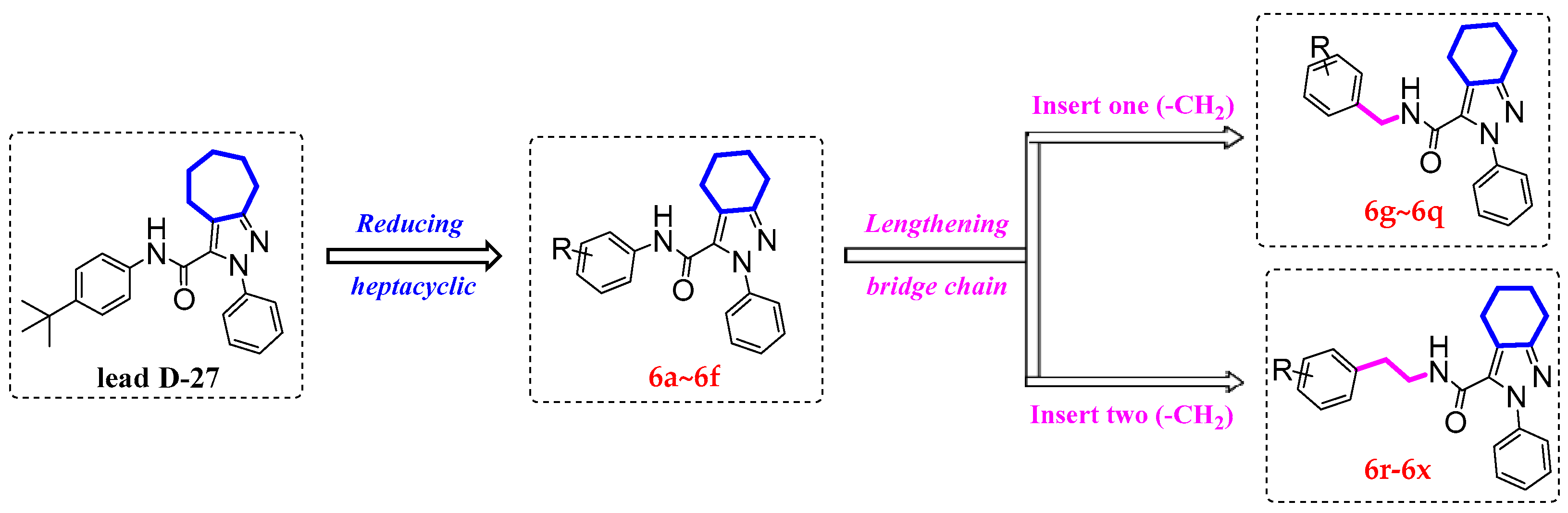
2.1. Chemical Synthesis
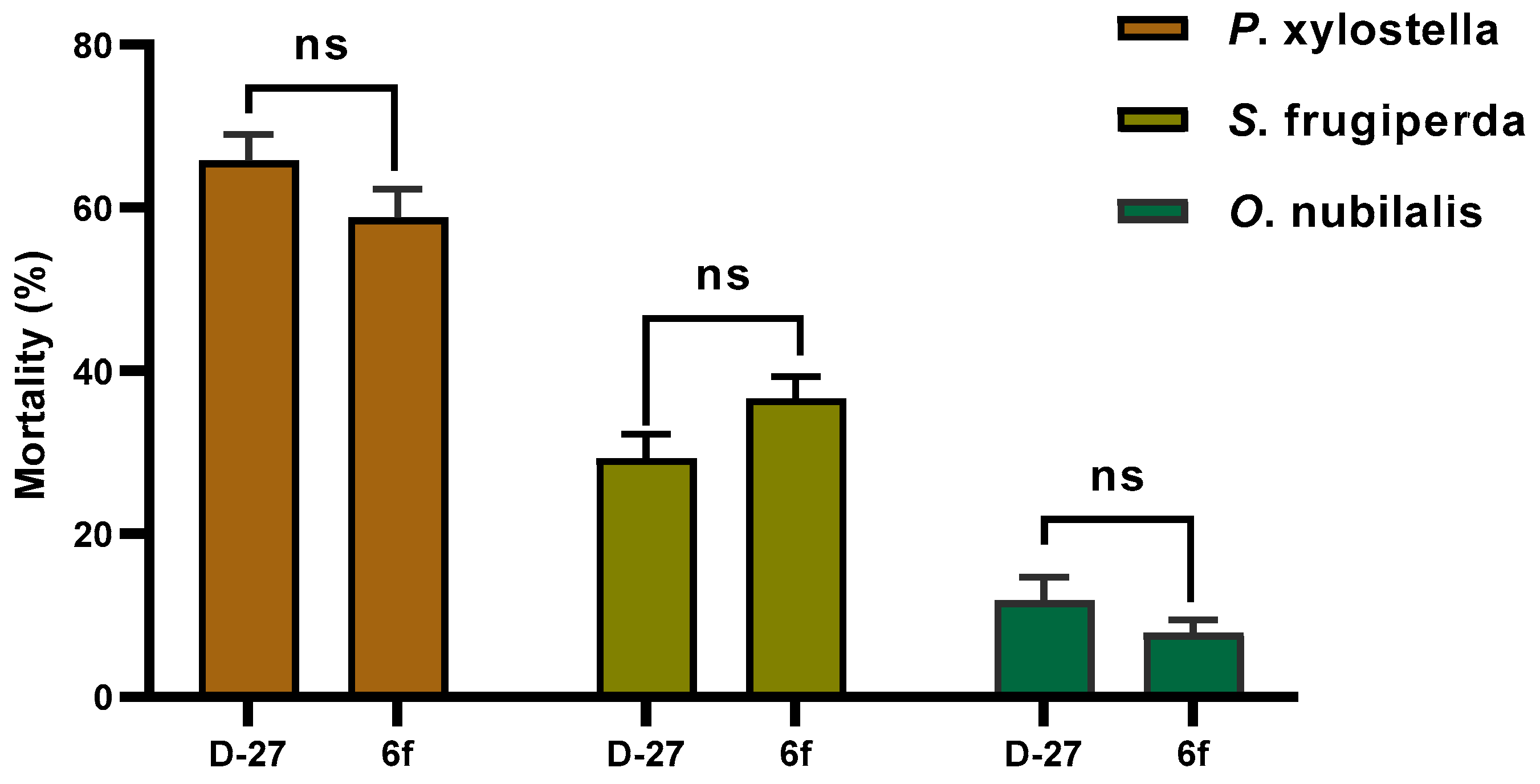
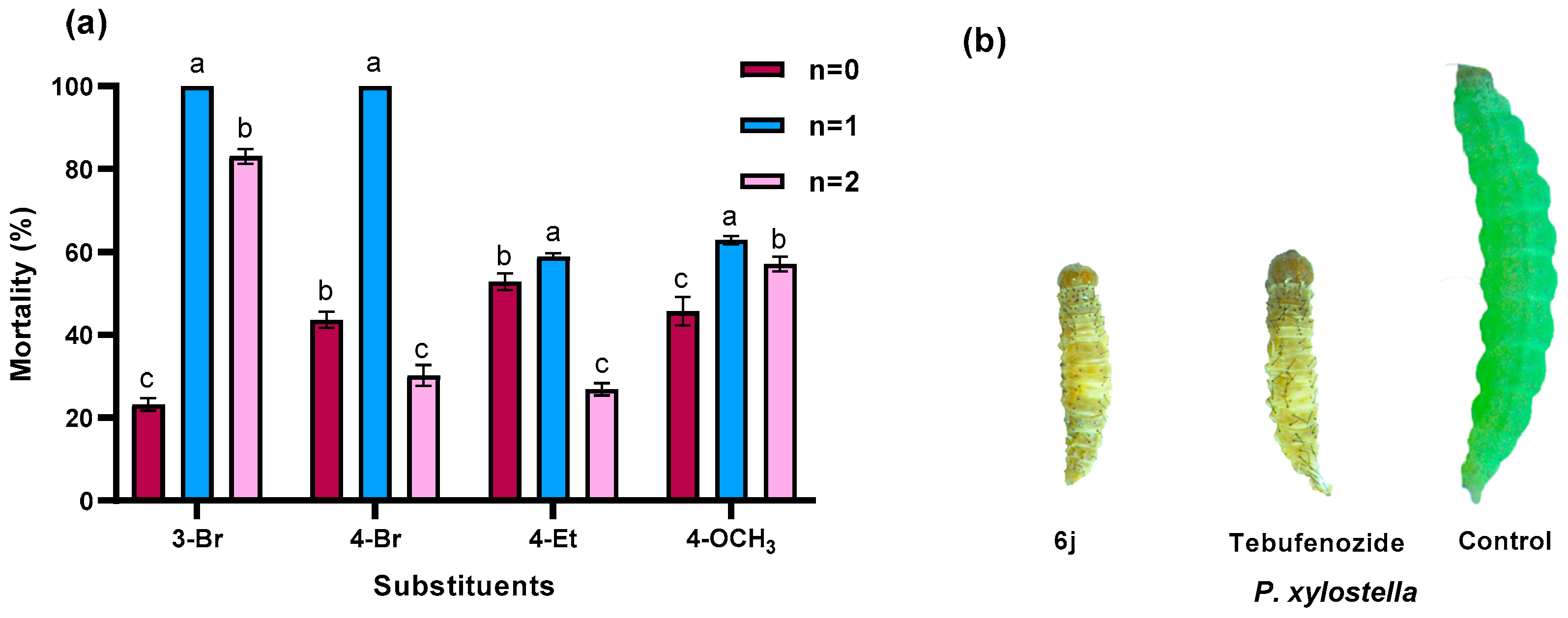
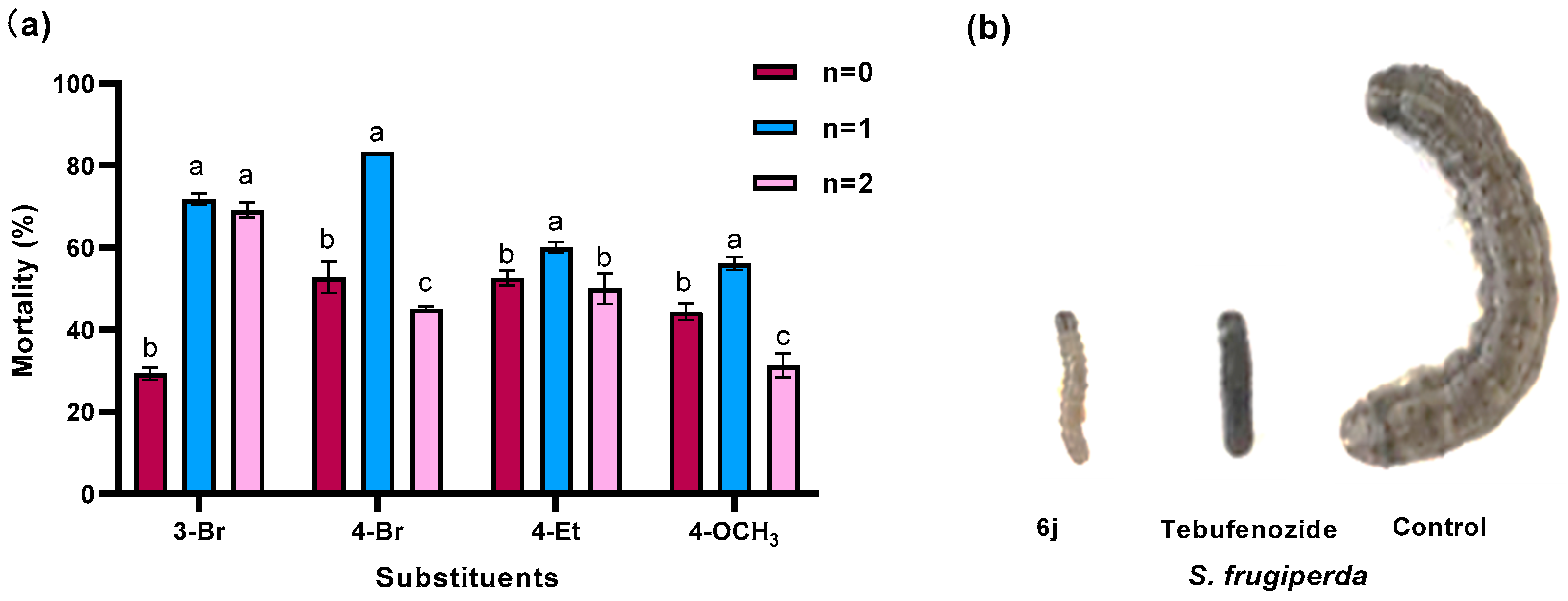
2.2. Insecticidal Biological Activity
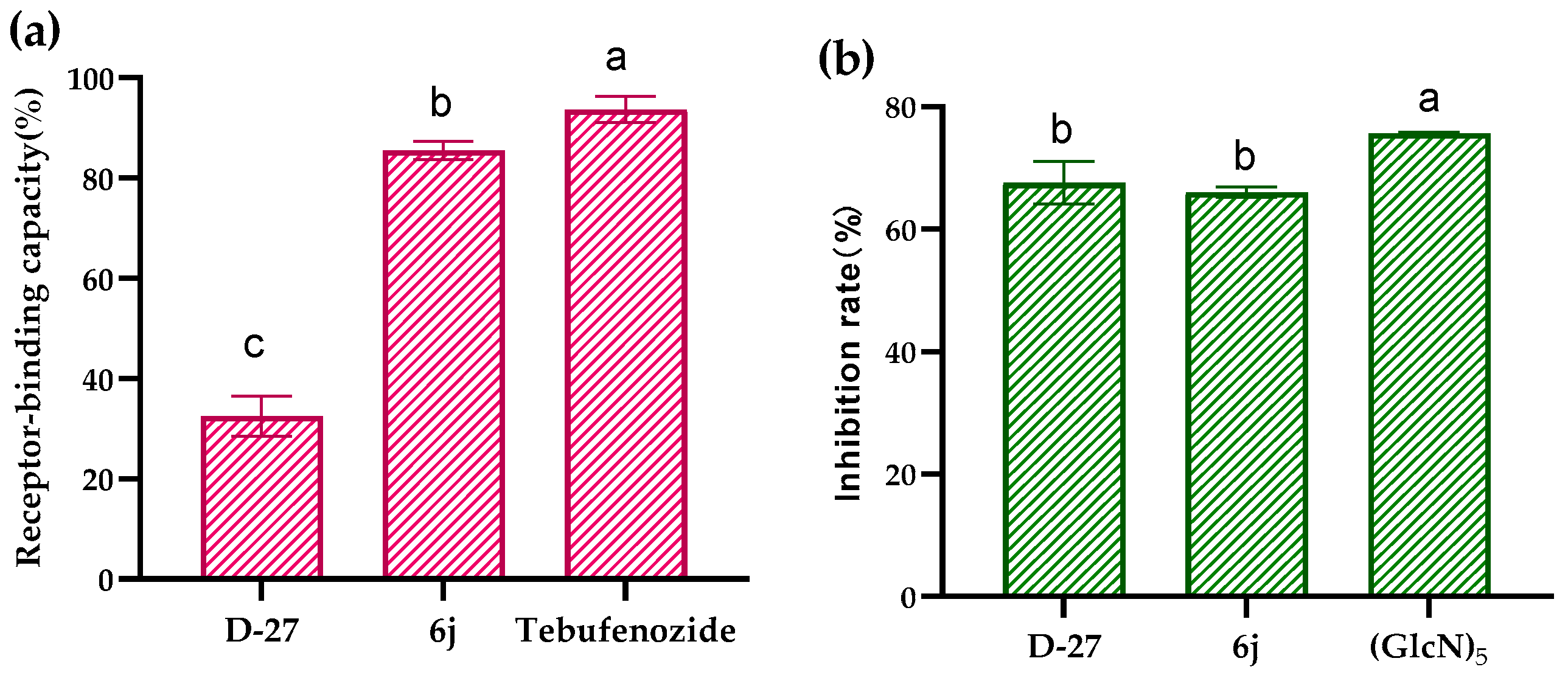
2.3. The Binding Affinity to EcR and OfChtI
2.4. Molecular Docking
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Instruments and Materials
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of the Intermediates 3~5 and 6a~6x
3.2.1. Synthetic Procedure of Intermediate 3
3.2.2. Synthetic Procedure of Intermediate 4
3.2.3. Synthetic Procedure of Intermediate 5
3.2.4. General Procedures for the Preparation of Compounds 6a~6x [6]
3.3. Biological Assay
3.3.1. Bioactivity Assay against P. xylostella and O. furnacalis
3.3.2. Bioactivity Assay against S. frugiperda
3.4. Molecular Docking
3.5. Ligand-Binding Assay on EcR/USP
3.6. Ligand-Inhibiting Assay on OfChtI
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yeeles, P.; Strain, A.; Lenancker, P.; Lach, L. Low reduction of invasive ant colony productivity with an insect growth regulator. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.V. Transovarial effects of insect growth regulators on Stephanitis pyrioides (Hemiptera: Tingidae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2182–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenson, E.A.; Arthur, F.H.; Nechols, J.R. Methoprene and synergized pyrethrins as aerosol treatments to control Plodia interpunctella (Hübner), the Indian meal moth (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2010, 46, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, L.C.; Plata-Rueda, A.; Serrão, J.E. Effects of Insect Growth Regulators on Mortality, Survival, and Feeding of Euprosterna elaeasa (Lepidoptera: Limacodidae) Larvae. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pener, M.P.; Dhadialla, T.S. Chapter One—An Overview of Insect Growth Disruptors; Applied Aspects. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Dhadialla, T.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 43, pp. 1–162. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.B.; Guo, B.B.; Cui, J.L.; Dong, Y.W.; Cui, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Q.; Yang, X.L. New lead discovery of insect growth regulators based on the scaffold hopping strategy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127500–127503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Ogura, T.; Yamada, Y.; Ohe, T.; Miyagawa, H. Virtual screening for ligands of the insect molting hormone receptor. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Wang, Q. Design and synthesis of benzoylphenylureas with fluorinated substituents on the aniline ring as insect growth regulators. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billas, I.M.L.; Iwema, T.; Garnier, J.M.; Mitschler, A.; Rochel, N.; Moras, D. Structural adaptability in the ligand-binding pocket of the ecdysone hormone receptor. Nature 2003, 426, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, C.; McEwen, A.G.; Mori, K.; Yokoi, T.; Moras, D.; Nakagawa, Y.; Billas, I.M.L. Nonsteroidal ecdysone receptor agonists use a water channel for binding to the ecdysone receptor complex EcR/USP. J. Pestic. Sci. 2021, 46, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Hu, S.; Jiang, X.; Liu, T.; Ling, Y.; He, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, L. Pocket-based Lead Optimization Strategy for the Design and Synthesis of Chitinase Inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3575–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.L.; Xie, J.; Li, Y.Q.; Yuan, D.K.; Hu, X.P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.M.; Chi, M.; Yang, X.L. Design, synthesis and biological activity of novel substituted pyrazole amide derivatives targeting EcR/USP receptor. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhadialla, T.S.; Jansson, R.K. Non-steroidal ecdysone agonists: New tools for IPM and insect resistance management. Pestic. Sci. 1999, 55, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, A.C.T.; Fujimoto, T.T.; Dhadialla, T.S. Structure—Activity Study and Conformational Analysis of RH—5992, the First Commercialized Nonsteroidal Ecdysone Agonist. ACS Symp. Ser. 1997, 658, 206–219. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Cui, J.; Jin, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L. In Vitro Binding Effects of the Ecdysone Receptor-Binding Domain and PonA in Plutella xylostella. Molecules 2023, 28, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, X.; Yang, Q. Glycoside hydrolase family 18 chitinases: The known and the unknown. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 43, 107553–107576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberth, C. Insertion of Small Flexible Linkers as a Useful Scaffold Hopping Tool in Agrochemistry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11011–11018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Jin, X.; Dong, Y.; Guo, B.; Cui, L.; Deng, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity of Novel Heptacyclic Pyrazolamide Derivatives: A New Candidate of Dual-Target Insect Growth Regulators. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 6347–6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Feng, D.; Li, F.; Luo, Y.; He, S.; Dong, Y.; Hu, D. Design, Synthesis, and Insecticidal Activity of Novel Isoxazoline Compounds That Contain Meta-diamides against Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.Y.; Feng, T.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.T.; Wei, W.; Shi, R.C.; Cao, Y.M.; Liu, S.Z. Design, Synthesis, Fungicidal and Insecticidal Activities of Novel Diamide Compounds Combining Pyrazolyl and Polyfluoro-Substituted Phenyl into Alanine or 2-Aminobutyric Acid Skeletons. Molecules 2023, 28, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.P.; Yin, B.; Liang, P.; Yang, X.L. Target-based design, synthesis and biological activity of new pyrazole amide derivatives. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zheng, X.; Shao, G.; Ling, Z.; Xu, H. Discovery of a Novel Series of Phenyl Pyrazole Inner Salts Based on Fipronil as Potential Dual-Target Insecticides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3577–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeem-Ullah, U.; Ramzan, M.; Saeed, S.; Iqbal, N.; Umar, U.u.D.; Sarwar, Z.M.; Ali, M.; Saba, S.; Abid, A.D.; Khan, K.A.; et al. Toxicity of four different insecticides against Trilocha varians (Bombycidae: Lepidoptera). J. King. Saud. Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 1853–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Wu, N.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, R.L.; Li, H.L.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Huang, J.X.; Duan, H.X.; Yang, Q. Piperonyl-Tethered Rhodanine Derivatives Potently Inhibit Chitinolytic Enzymes of Ostrinia furnacalis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7387–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Xiong, L.; Yang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Synthesis and structure-insecticidal activity relationship of novel phenylpyrazole carboxylic acid derivatives containing fluorine moiety. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Jin, R.; Guo, Z.; Cai, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Huang, G.; Wan, H.; He, S.; Xie, Y.; et al. Insecticide Susceptibility and Mechanism of Spodoptera frugiperda on Different Host Plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11367–11376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.K.; Qu, C.; Pan, S.X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Luo, C.; Qin, Y.G.; Yang, X.L. Aphid-repellent, ladybug-attraction activities, and binding mechanism of methyl salicylate derivatives containing geraniol moiety. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Li, W.; Qin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Qu, C.; Luo, C.; Yang, X. Discovery of Novel Potential Aphid Repellents: Geranic Acid Esters Containing Substituted Aromatic Rings. Molecules 2022, 27, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.D.; Johnson, W.M.; Pawlak-Skrzecz, A.; Eaton, R.E.; Bliese, M.; Howell, L.; Hannan, G.N.; Hill, R.J. Ligand binding by recombinant domains from insect ecdysone receptors. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Compounds | n | R | P. xylostella a | S. frugiperda b | O. furnacalis a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg/L | 200 mg/L | 500 mg/L | 200 mg/L | |||
| 6a | 0 | 3-Br | 23.2 ± 1.5 | nt | 29.3 ± 1.5 | 4.2 ± 3.0 |
| 6b | 0 | 4-Br | 43.6 ± 1.9 | 11.6 ± 1.8 | 52.8 ± 3.9 | 6.5 ± 0.2 |
| 6c | 0 | 3-Et | 37.1 ± 1.0 | 8.4 ± 0.6 | 42.9 ± 1.8 | 24.3 ± 1.7 |
| 6d | 0 | 4-Et | 52.8 ± 2.0 | 35.0 ± 3.2 | 52.6 ± 1.8 | 2.2 ± 3.1 |
| 6e | 0 | 4-OCH3 | 45.7 ± 3.4 | 17.4 ± 1.9 | 44.4 ± 2.0 | 11.2 ± 1.7 |
| 6f | 0 | 4-tBu | 58.8 ± 3.5 | 30.3 ± 2.7 | 36.6 ± 2.7 | 7.8 ± 1.6 |
| 6g | 1 | 3-F | 14.3 ± 0.8 | nt | 50.0 ± 3.7 | 3.0 ± 4.3 |
| 6h | 1 | 4-F | 52.8 ± 2.0 | 28.4 ± 1.6 | 68.7 ± 2.9 | 4.6 ± 3.3 |
| 6i | 1 | 3-Br | 100 ± 0 | 35.0 ± 3.2 | 71.8 ± 1.3 | 12.5 ± 1.8 |
| 6j | 1 | 4-Br | 100 ± 0 | 40.3 ± 2.8 | 83.3 ± 0 | 33.5 ± 2.3 |
| 6k | 1 | 3-OCF3 | 58.9 ± 0.8 | 4.0 ± 2.9 | 55.8 ± 1.8 | 10.1 ± 0.8 |
| 6l | 1 | 4-OCF3 | 70.3 ± 3.5 | 10.8 ± 1.8 | 38.8 ± 1.7 | 0 |
| 6m | 1 | 3-CH3 | 19.4 ± 2.0 | nt | 42.4 ± 2.3 | 16.2 ± 0.6 |
| 6n | 1 | 4-CH3 | 100 ± 0 | 23.2 ± 1.5 | 44.2 ± 1.8 | 18.3 ± 2.5 |
| 6o | 1 | 4-Et | 59.4 ± 0.8 | 12.9 ± 1.3 | 60.0 ± 1.3 | 14.4 ± 1.6 |
| 6p | 1 | 4-OCH3 | 62.9 ± 1.0 | 16.4 ± 1.6 | 56.1 ± 1.6 | 16.2 ± 0.6 |
| 6q | 1 | 4-tBu | 35.8 ± 2.1 | 14.0 ± 1.0 | 43.9 ± 1.6 | 9.1 ± 0.7 |
| 6r | 2 | 3-F | 73.0 ± 3.1 | 10.8 ± 1.8 | 28.2 ± 1.3 | 0 |
| 6s | 2 | 4-F | 42.4 ± 2.3 | 8.2 ± 0.7 | 22.4 ± 2.0 | 0 |
| 6t | 2 | 3-Br | 83.1 ± 1.8 | 15.1 ± 1.4 | 69.1 ± 1.9 | 6.8 ± 0.2 |
| 6u | 2 | 4-Br | 30.2 ± 2.5 | nt | 45.1 ± 0.5 | 10.8 ± 1.8 |
| 6v | 2 | 4-CH3 | 80.1 ± 1.3 | 33.3 ± 2.0 | 17.2 ± 0.7 | 20.9 ± 2.0 |
| 6w | 2 | 4-Et | 26.9 ± 1.5 | nt | 50.0 ± 3.7 | 8.1 ± 0.3 |
| 6x | 2 | 4-OCH3 | 57.1 ± 1.8 | 36.1 ± 2.1 | 31.3 ± 2.9 | 4.9 ± 3.5 |
| D-27 | 0 | 4-tBu | 65.8 ± 3.2 | 31.6 ± 1.2 | 29.3 ± 2.9 | 11.8 ± 2.9 |
| Tebufenozide | / | / | 100 ± 2.0 | 92.3 ± 0.5 | 100 ± 0 | 100 ± 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, B.; Jiang, B.; Wang, C.; Jin, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Luo, S.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X. A Potential Lead for Insect Growth Regulator: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity Evaluation of Novel Hexacyclic Pyrazolamide Derivatives. Molecules 2023, 28, 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093741
Guo B, Jiang B, Wang C, Jin X, Wang L, Yang Z, Luo S, Yang Q, Zhang L, Yang X. A Potential Lead for Insect Growth Regulator: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity Evaluation of Novel Hexacyclic Pyrazolamide Derivatives. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093741
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Bingbo, Biaobiao Jiang, Chunying Wang, Xiaoyu Jin, Liuyang Wang, Zhaokai Yang, Shihui Luo, Qing Yang, Li Zhang, and Xinling Yang. 2023. "A Potential Lead for Insect Growth Regulator: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity Evaluation of Novel Hexacyclic Pyrazolamide Derivatives" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093741
APA StyleGuo, B., Jiang, B., Wang, C., Jin, X., Wang, L., Yang, Z., Luo, S., Yang, Q., Zhang, L., & Yang, X. (2023). A Potential Lead for Insect Growth Regulator: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity Evaluation of Novel Hexacyclic Pyrazolamide Derivatives. Molecules, 28(9), 3741. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093741





