Hydrophilic Modification of Polyester/Polyamide 6 Hollow Segmented Pie Microfiber Nonwovens by UV/TiO2/H2O2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphology Analysis
2.2. XPS Analysis
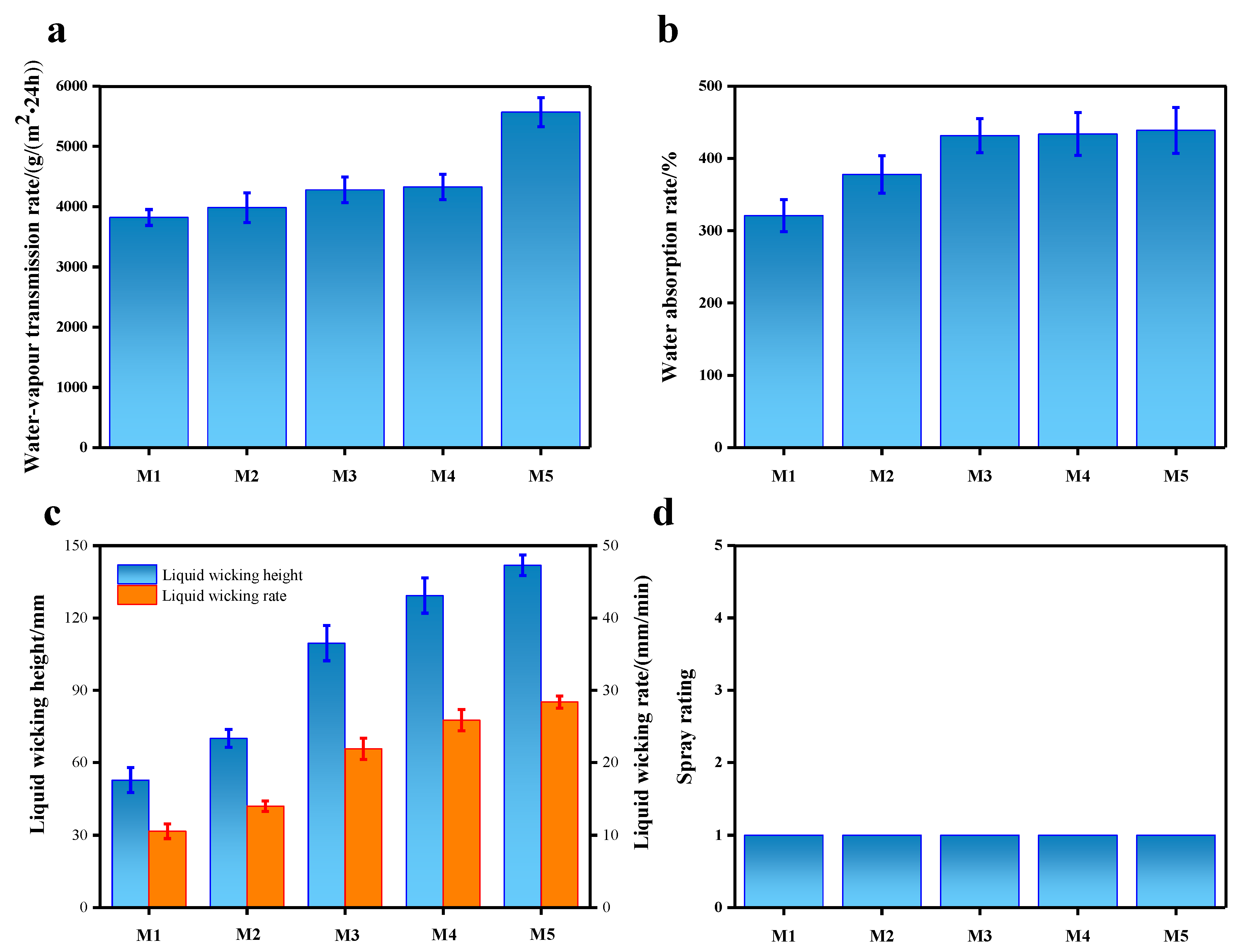
2.3. Hydrophilic Properties
2.4. Mechanical Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
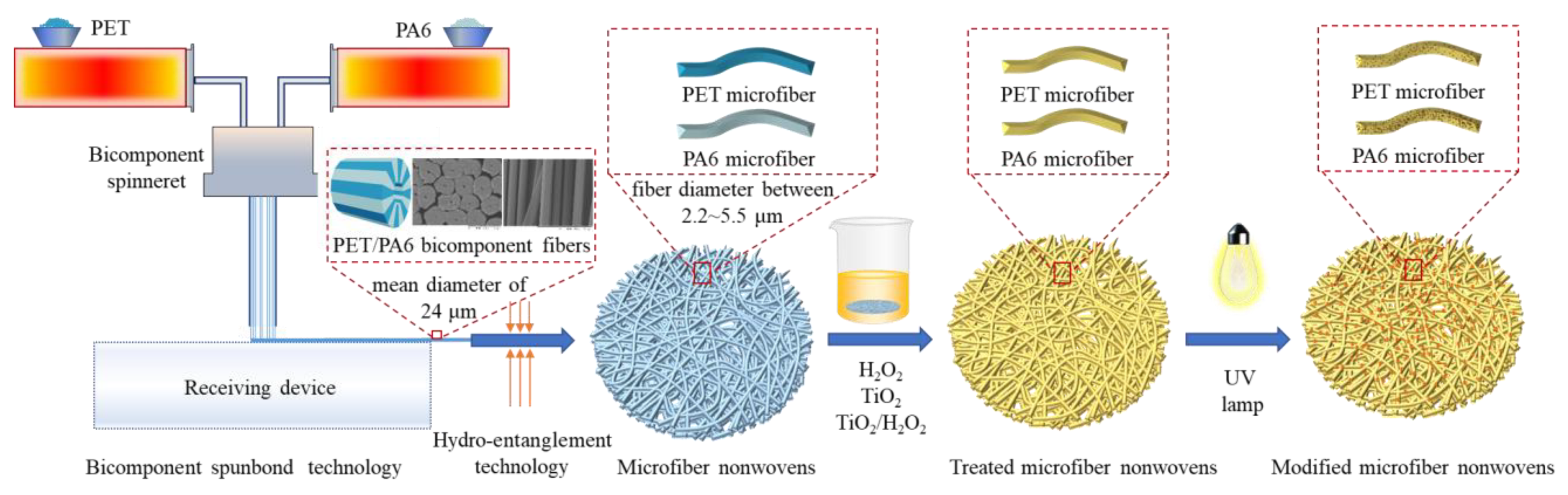
3.2. Preparation and Modification of PET/PA6
3.3. Characterization of PET/PA6
3.3.1. Morphology
3.3.2. XPS
3.3.3. Contact Angle
3.3.4. Water Vapor Transmission Rate
3.3.5. Water Absorption Rate
3.3.6. Liquid Wicking Height and Liquid Wicking Rate
3.3.7. Spray Rating
3.3.8. Tensile Strength and Elongation at Break
3.3.9. Softness
3.3.10. Crease Recovery Property
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duo, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhao, B.; Gao, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, S.; Bai, H.; Tang, L. Easily Splittable Hollow Segmented-Pie Microfiber Nonwoven Material with Excellent Filtration and Thermal-Wet Comfort for Energy Savings. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Qian, X.; Qian, Y.; Duo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Fan, J.; Chen, Y. The Application of Hollow Segmented Pie Bicomponent Spunbond Hydro-Entangled Microfiber Nonwovens for Microfiber Synthetic Leather Apparel. AATCC J. Res. 2019, 6, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhao, B.; Gao, L.; Bai, H.; Guo, X.; Song, B. Preparation and Properties of Fluffy High-Shrinkage Polyester/Polyamide 6 Hollow Segmented Pie Microfiber Nonwovens. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 3221–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahsarn, C.; Klinsukhon, W.; Padee, S.; Suwannamek, N.; Roungpaisan, N.; Srisawat, N. Hollow Segmented-Pie PLA/PBS and PLA/PP Bicomponent Fibers: An Investigation on Fiber Properties and Splittability. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 10910–10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ying, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Li, C. Unexpected Hydrophobic to Hydrophilic Transition of PET Fabric Treated in a Deep Eutectic Solvent of Choline Chloride and Oxalic Acid. Polymer 2021, 234, 124246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahsarn, C.; Matsubara, A.; Motomura, S.; Kikutani, T. Development of Bicomponent Spunbond Nonwoven Webs Consisting of Ultra-Fine Splitted Fibers. Int. Polym. Process. 2008, 23, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Li, N.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, H.; Shi, L. Development of Amino Acid-Modified PET/PA6 Segmented Pie Bicomponent Spunbonded Microfiber Nonwoven for Bilirubin Affinity Adsorption. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhao, B.; Qian, Y.; Xu, P.; Qi, J. Micro/Nano Microfiber Synthetic Leather Base with Different Nanofiber Diameters. J. Ind. Text. 2021, 50, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhao, B.; Qian, Y.; Xu, P. Improving Hygiene Performance of Microfiber Synthetic Leather Base by Mixing Polyhydroxybutyrate Nanofiber. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2019, 14, 1558925019842516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Qian, X.; Qian, Y.; Fan, J.; Feng, Y.; Duo, Y.; Zhang, H. Preparation of High-Performance Microfiber Synthetic Leather Base Using Thermoplastic Polyurethane/Sulfonated Polysulfone Electrospun Nanofibers. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, G.X.; Zhang, F.X.; Wu, D.Y. Surface Modification of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) (PET) with UV/Nano-TiO2. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 472–475, 2958–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, G.X.; Zhang, F.X.; Zheng, H.; Lu, M.; Wu, D.Y. Super Wettable Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate)(PET) Fabric Modified by UV/Nano-TiO2/H2O2. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 184–185, 1272–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Deng, T.T.; Liu, S.X.; Zhang, F.X.; Zhang, G.X. Surface Hydrophilicity Modification of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Fabric by UV/TiO2. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 781–784, 2704–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.-X.; Liang, H.; Zhang, G.-X. Colorant-Free Coloration and Superhydrophilic Modification of Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Fabric Surface by H2O2 and Nano-TiO2 Ultraviolet Photocatalysis. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; He, Y.; Cheng, B.W. A novel method for fabricating elastic conductive polyurethane filaments by in-situ reduction of polydopamine and electroless silver plating. Mater. Des. 2017, 113, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, S.; Ma, J. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticle Functionalized Polyamide Fibers with Antimicrobial Activity and Electrical Conductivity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksakal, B.; Koç, K. The Tensile Properties of Uncoated and TiO2 Coated Bombyx Mori Silk Yarns Exposed to Thermal Treatment. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 2013, 52, 1283–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksakal, B.; Koc, K.; Yargi, O.; Tsobkallo, K. Effect of UV-Light on the Uniaxial Tensile Properties and Structure of Uncoated and TiO2 Coated Bombyx Mori Silk Fibers. Spectrochim. Acta Part -Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 152, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechine, G.J.M.; Rabello, M.S.; Maior, R.M.S.; Catalani, L.H. Surface characterization of photodegraded poly (ethylene terephthalate). The effect of ultraviolet absorbers. Polymer 2004, 45, 2303–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, C.R.; Leggett, G.J. Quantitative Investigation of the Photodegradation of Polyethylene Terephthalate Film by Friction Force Microscopy, Contact-Angle Goniometry, and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, M.; Wiles, D.M. The effects of light on poly (ethylene terephthalate). Can. Text J. 1972, 89, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Ye, L. Stress Photo-Oxidative Aging Behaviour of Polyamide 6. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, G.; Shen, J.; Leng, J. Fabrication of Low Dielectric Constant Polyimide/TiO2 Nanofibers with Enhanced UV-Light Shielding Properties. High Perform. Polym. 2019, 31, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, S.; Bharadwaj, A.V.S.L.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Yoo, C.G.; Kim, T.H. A Review of Biomass-Derived UV-Shielding Materials for Bio-Composites. Energies 2023, 16, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Z.; Xiaoming, Q.; Qi, Z.; Zhaohang, Y. Research on Structure Characteristics and Filtration Performances of PET-PA6 Hollow Segmented-Pie Bicomponent Spunbond Nonwovens Fibrillated by Hydro Entangle Method. J. Ind. Text. 2015, 45, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.; Su, Y.; Liu, Z.; Duan, J.; Li, Y. Analysis of Shielding Effectiveness in Different Kinds of Electromagnetic Shielding Fabrics under Different Test Conditions. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
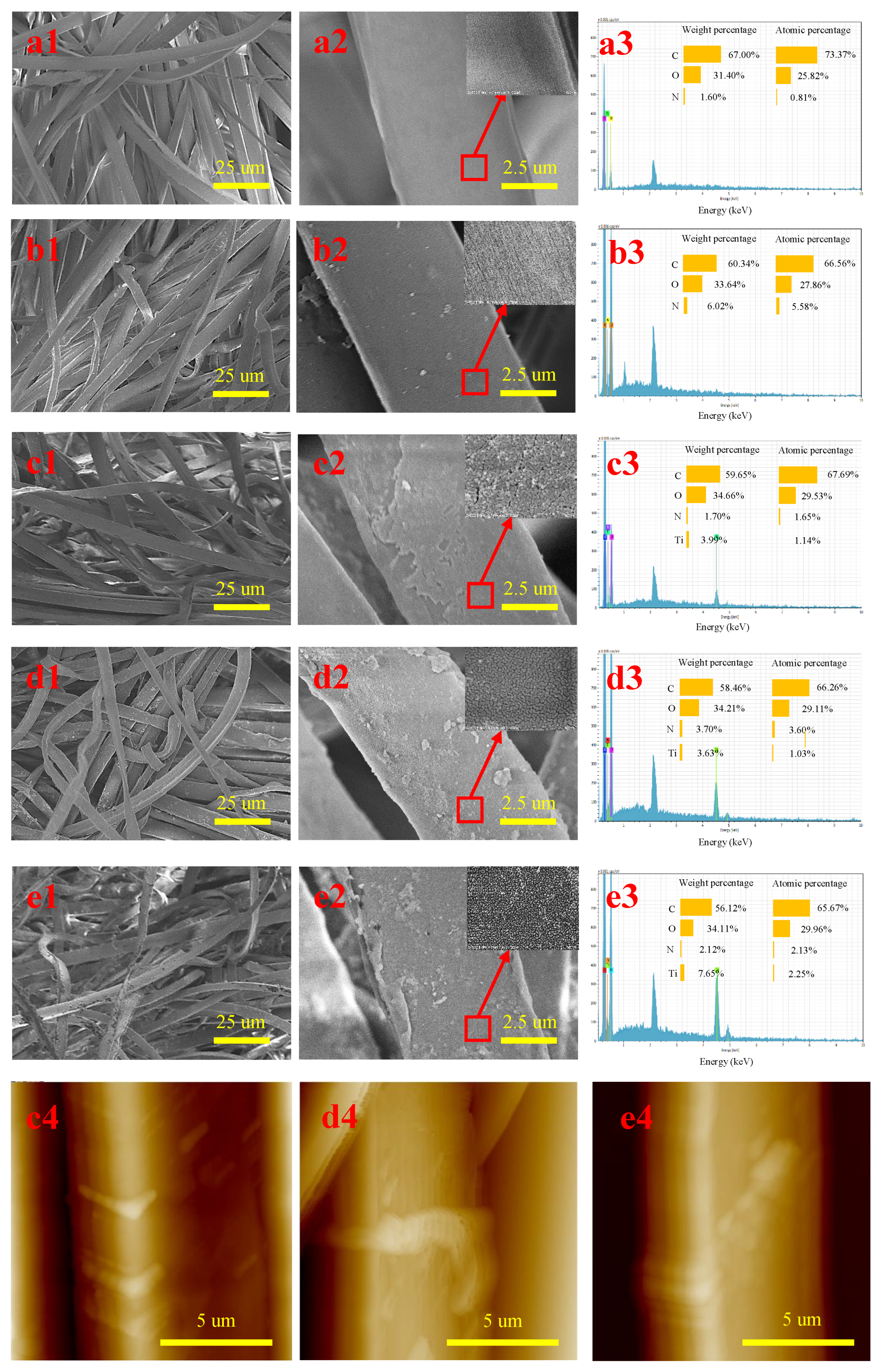



| Sample | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atomic composition (%) | C 1s | 78.80 | 75.56 | 60.00 | 59.58 | 55.50 |
| O 1s | 16.60 | 19.91 | 28.25 | 28.35 | 31.42 | |
| N 1s | 4.60 | 4.53 | 4.28 | 3.84 | 3.74 | |
| Ti 2p | 0 | 0 | 7.47 | 8.23 | 9.34 | |
| High energy resolution of C1s (%) | C–C–C ❶ | 67.56 | 67.38 | 67.27 | 62.20 | 60.50 |
| C–C–O ❷ | 4.54 | 4.56 | 4.71 | 7.87 | 8.51 | |
| O–C=O ❸ | 4.99 | 5.04 | 6.00 | 6.53 | 7.65 | |
| C–C=O ❹ | 0 | 2.81 | 3.63 | 5.71 | 6.04 | |
| N–C=O ❺ | 7.64 | 4.84 | 2.98 | 2.27 | 1.95 | |
| N–C–C ❻ | 15.28 | 15.38 | 15.40 | 15.42 | 15.36 | |
| Sample | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contact angle (at 0 s, °) | 137.718 | 136.734 | 134.637 | 134.637 | 130.775 |
| Contact angle (at 0.015 s, °) | 137.062 | 136.389 | 133.150 | 132.769 | 0 |
| Droplet disappearance time (s) | 27.465 | 1.680 | 0.271 | 0.072 | 0.015 |
| Sample | Impregnating Solution | Composition | UV Irradiation Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | / | / | / |
| M2 | H2O2 | 2.4 mL of H2O2 solution and 180 mL of water | 45 |
| M3 | TiO2 | 20 mL of nano-TiO2 sol and 160 mL of water | 45 |
| M4 | TiO2/H2O2 | 2.4 mL of H2O2 solution, 20 mL of nano-TiO2 sol, and 160 mL of water | 45 |
| M5 | TiO2/H2O2 | 2.4 mL of H2O2 solution, 20 mL of nano-TiO2 sol and 160 mL of water | 90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, B.; Han, X.; Hu, C.; Qian, X.; Duo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Yang, Q.; Han, D. Hydrophilic Modification of Polyester/Polyamide 6 Hollow Segmented Pie Microfiber Nonwovens by UV/TiO2/H2O2. Molecules 2023, 28, 3826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093826
Zhao B, Han X, Hu C, Qian X, Duo Y, Wang Z, Feng Q, Yang Q, Han D. Hydrophilic Modification of Polyester/Polyamide 6 Hollow Segmented Pie Microfiber Nonwovens by UV/TiO2/H2O2. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093826
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Baobao, Xu Han, Chenggong Hu, Xiaoming Qian, Yongchao Duo, Zhen Wang, Quan Feng, Quan Yang, and Dongxu Han. 2023. "Hydrophilic Modification of Polyester/Polyamide 6 Hollow Segmented Pie Microfiber Nonwovens by UV/TiO2/H2O2" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093826
APA StyleZhao, B., Han, X., Hu, C., Qian, X., Duo, Y., Wang, Z., Feng, Q., Yang, Q., & Han, D. (2023). Hydrophilic Modification of Polyester/Polyamide 6 Hollow Segmented Pie Microfiber Nonwovens by UV/TiO2/H2O2. Molecules, 28(9), 3826. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093826






